Functions of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) in Seed Germination and Low-Temperature Stress Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
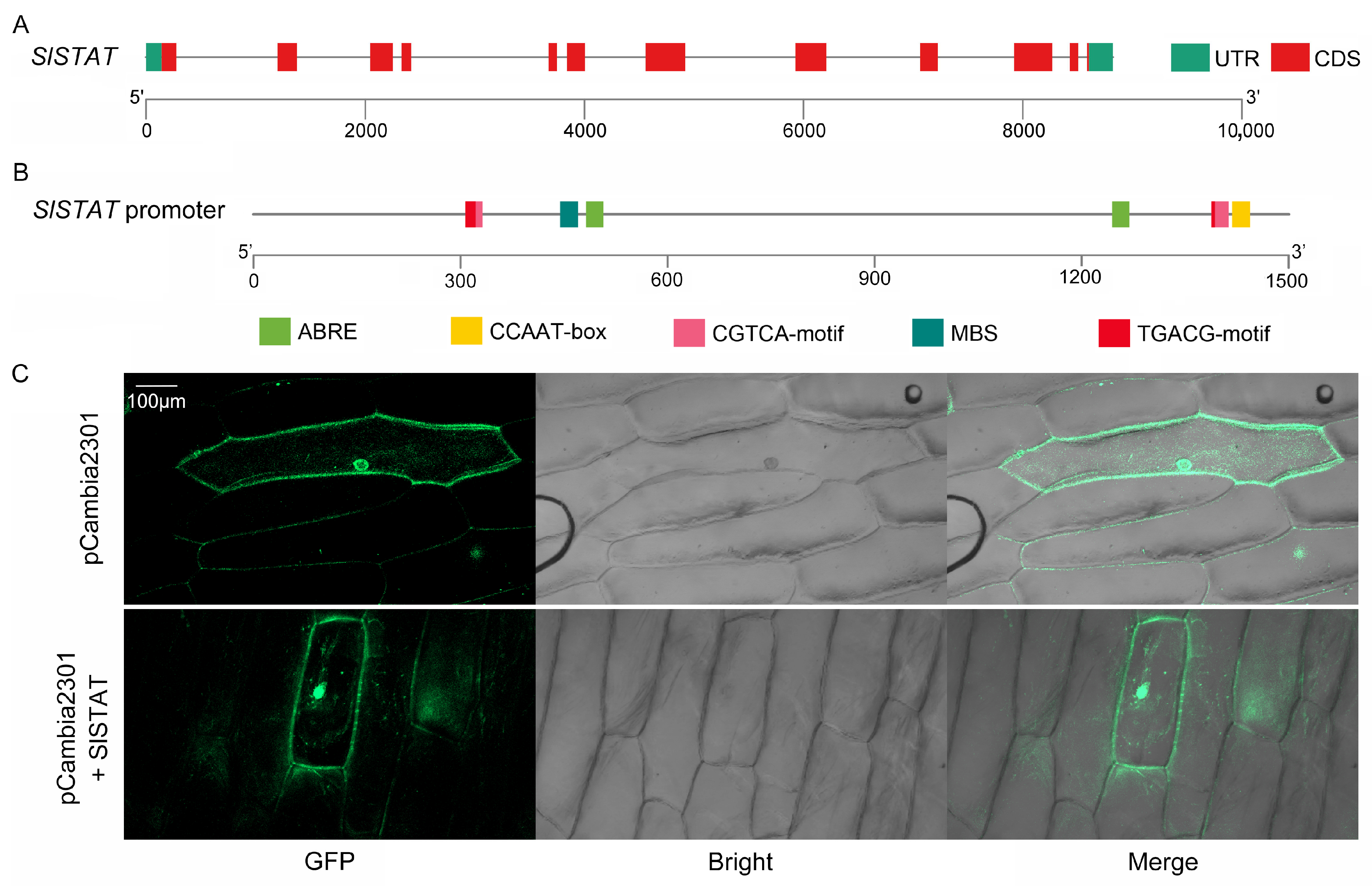
2.1. SlSTAT Family Member Identification and Analysis
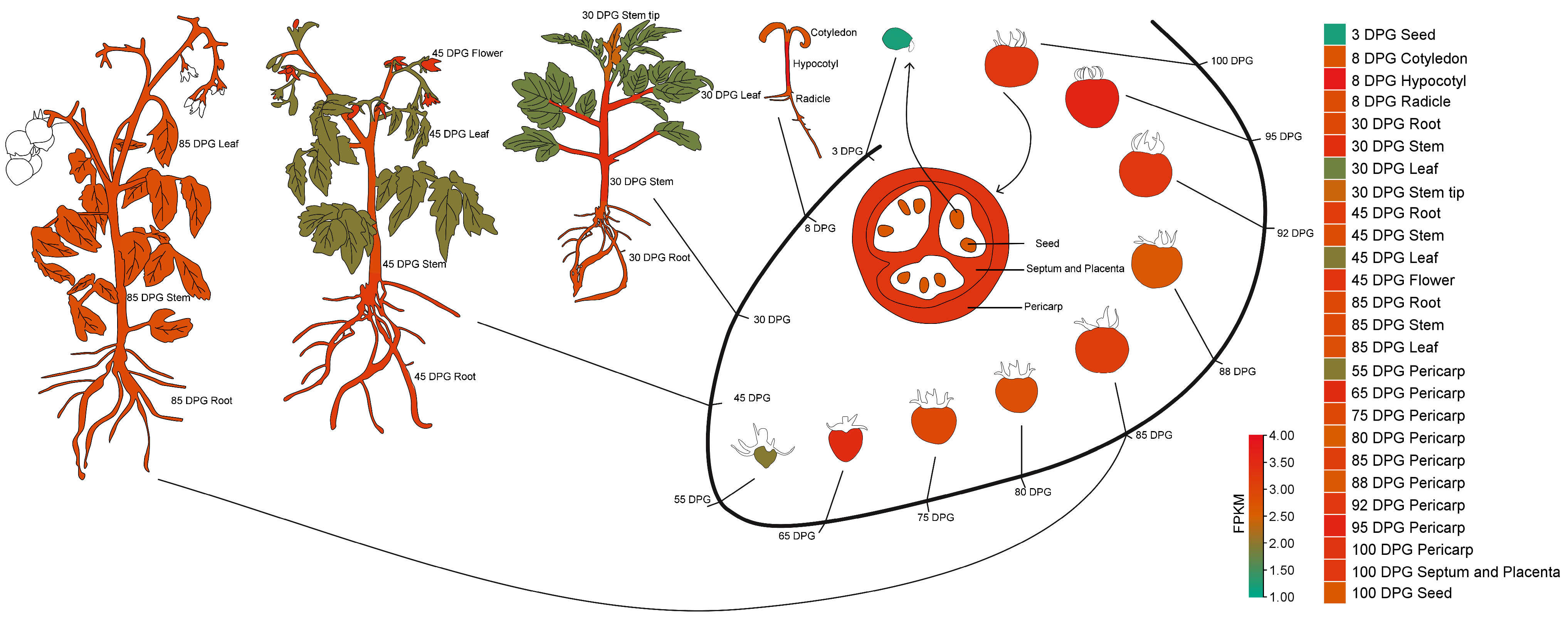
2.2. Expression Levels of SlSTAT in Different Tomato Tissue/Organs
2.3. Function of SlSTAT During Seed Germination Processes
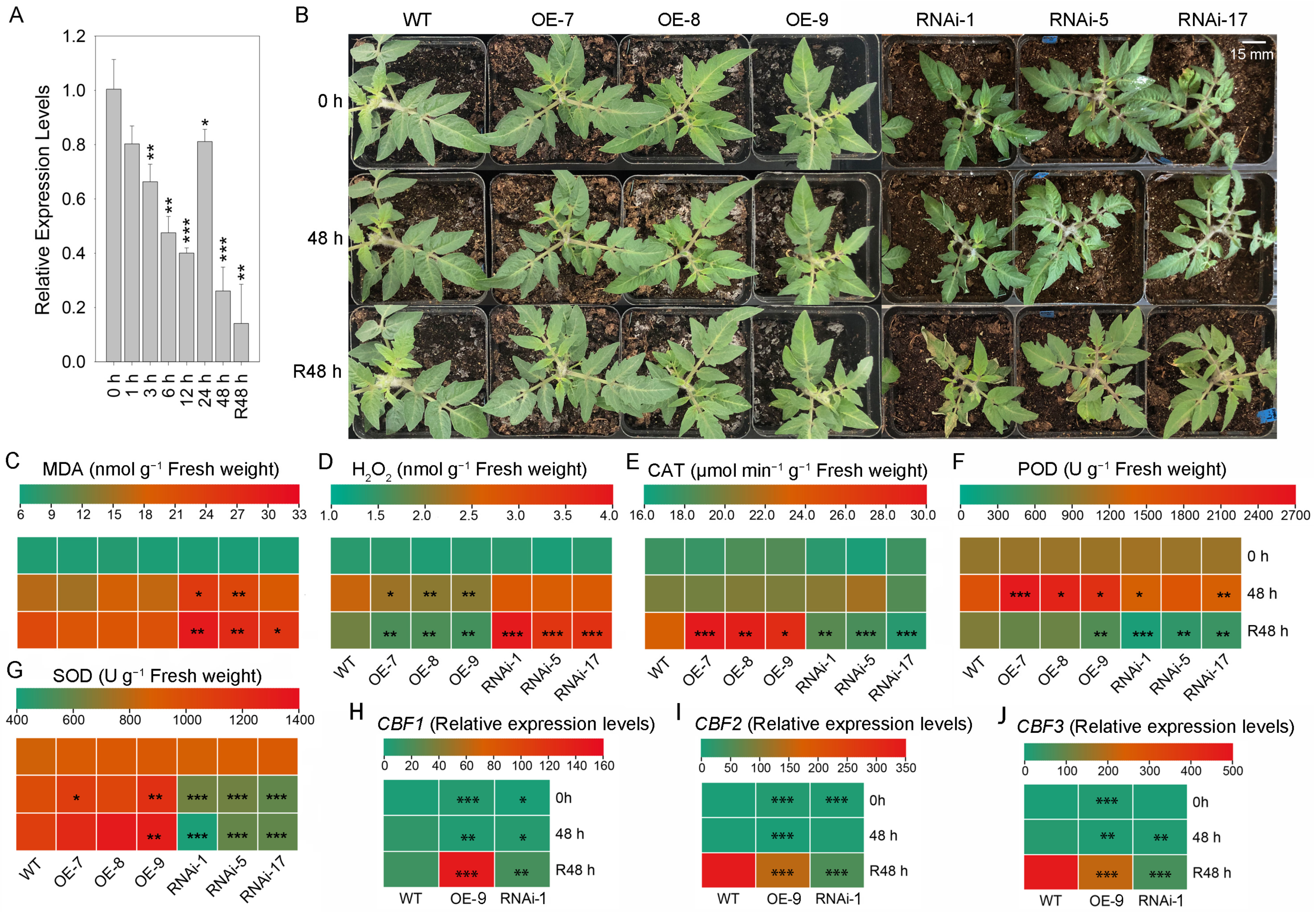
2.4. Expression of SlSTAT Change the Chilling Resistance of Tomato
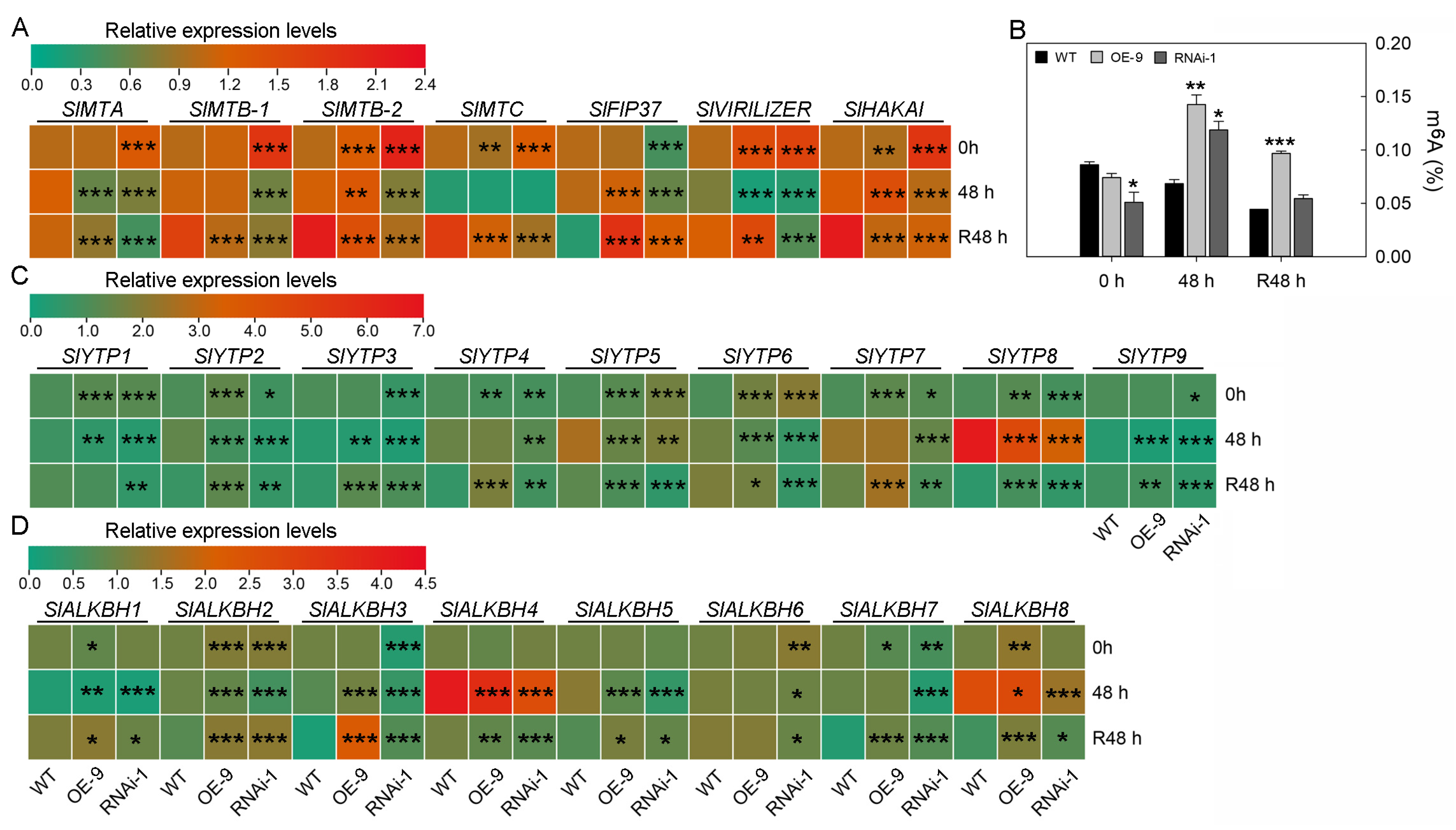
2.5. The Effect of STAT on RNA m6A Modification in Tomato Leaves and Its Relationship with Chilling Resistance
3. Discussion
3.1. SlSTAT Family Member Identification and Analysis
3.2. Expression Levels of SlSTAT in Different Tomato Tissues and Its Function in Seed Germination
3.3. Expression of SlSTAT Changes the Chilling Resistance of Tomato
3.4. The Effect of SlSTAT on RNA m6A Modification in Tomato Low-Temperature Stress Response
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Analysis of the SlSTAT Gene Family
4.2. Gene Clone and Gene Structure Analysis
4.3. Promoter Clone and Cis-Acting Element Analysis
4.4. Sub-Cellular Localization
4.5. Plot Cartoon Heatmap
4.6. Plant Growth and Treatments
4.7. qRT-PCR
4.8. Tomato Transformation and Identification
4.9. Measurement of Stress-Related Physiological Indexes
4.10. RNA m6A Modification Level Identification
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Isaacs, A.; Lindenmann, J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1957, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar]
- Philips, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Cheon, H.; Kanno, Y.; Gadina, M.; Sartorelli, V.; Horvath, C.M.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Stark, G.R.; O’Shea, J.J. The JAK-STAT pathway at 30: Much learned, much more to do. Cell 2022, 185, 3857–3876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1984–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Qi, J.; Babon, J.J.; Cao, L.; Fan, G.; Lang, J.; Zhang, J.; Mi, P.; Kobe, B.; Wang, F. The JAK-STAT pathway: From structural biology to cytokine engineering. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Song, C.; Yan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. JAK/STAT in leukemia: A clinical update. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Niu, F.; Pu, M.; Wang, J.; Hung, L.W.; Shao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structural basis for DNA recognition by STAT6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13015–13020. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, A.; Tang, T.H.; Ng, S.K. Interferon regulatory factor 9 structure and regulation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1831. [Google Scholar]
- Rengachari, S.; Groiss, S.; Devos, J.M.; Caron, E.; Grandvaux, N.; Panne, D. Structural basis of STAT2 recognition by IRF9 reveals molecular insights into ISGF3 function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E601–E609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, P.Y.; Kim, G.; Lim, S.C.; Choi, H.S. METTL3-STAT5B interaction facilitates the co-transcriptional m6A modification of mRNA to promote breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2024, 603, 217215. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, D.; Schwartz, S. The epitranscriptome beyond m6A. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Jia, G. Principles, functions, and biological implications of m6A in plants. RNA 2024, 30, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Sun, X.; Qin, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, X. FTO promotes proliferation and migration of bladder cancer via enhancing stability of STAT3 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. Epigenetics 2023, 18, 2242688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lai, W.; Zheng, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, X.; Gao, J.; Lou, Z. Linderae Radix extract attenuates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazmi, R.H.; Willems, L.A.J.; Joosen, R.V.L.; Khan, N.; Ligterink, W.; Hilhorst, H.W.M. Metabolomic analysis of tomato seed germination. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Shang, L.; Wang, X.; Xing, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Z. MAPK11 regulates seed germination and ABA signaling in tomato by phosphorylating SnRKs. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 1677–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohat, H.; Cheriker, H.; Cohen, A.; Weiss, D. Tomato ABA-IMPORTING TRANSPORTER 1.1 inhibits seed germination under high salinity conditions. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 1404–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, S. Advances and challenges in uncovering cold tolerance regulatory mechanisms in plants. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 1690–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Song, J.; Tang, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y. CALMODULIN6 negatively regulates cold tolerance by attenuating ICE1-dependent stress responses in tomato. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 2105–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, G.; Luo, G.; Shen, X.; Ouyang, B.; Bie, Z. Transcription factor SlWRKY50 enhances cold tolerance in tomato by activating the jasmonic acid signaling. Plant Physiol. 2024, 194, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Qi, Z.; Fotopoulos, V.; Yu, J.; Zhou, J. Loss of cold tolerance is conferred by absence of the WRKY34 promoter fragment during tomato evolution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, B.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wang, N. Transcriptome-level analysis of gene expressions in different tissues of tomato and key gene identifications during seed germination. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 337, 113565. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Luo, H.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Dearolf, C.R. A JAK-STAT pathway regulates wing vein formation in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5842–5847. [Google Scholar]
- Kawata, T.; Shevchenko, A.; Fukuzawa, M.; Jermyn, K.A.; Totty, N.F.; Zhukovskaya, N.V.; Sterling, A.E.; Mann, M.; Williams, J.G. SH2 signaling in a lower eukaryote: A STAT protein that regulates stalk cell differentiation in dictyostelium. Cell 1997, 89, 909–916. [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson, D.S.; Horvath, C.M. A road map for those who don’t know JAK-STAT. Science 2002, 296, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development 2018, 145, dev149344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fleishon, S.; Shani, E.; Ori, N.; Weiss, D. Negative reciprocal interactions between gibberellin and cytokinin in tomato. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 609–617. [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt, H.C.; Metge, B.J.; Weeks, S.E.; Chen, D.; Wei, S.; Kesterson, R.A.; Shevde, L.A.; Samant, R.S. Conditional knockout of N-Myc and STAT interactor disrupts normal mammary development and enhances metastatic ability of mammary tumors. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1610–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Lang, Z.; Zhu, J.K. Cold responsive gene transcription becomes more complex. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 781–803. [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow, M.F. Molecular basis of plant cold acclimation: Insights gained from studying the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Lin, R.; Tang, M.; Wang, L.; Fan, P.; Xia, X.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y. SlMPK1- and SlMPK2-mediated SlBBX17 phosphorylation positively regulates CBF-dependent cold tolerance in tomato. New Phytol. 2023, 239, 1887–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Tong, J.; Zhu, S.; Batista, P.J.; Duffy, E.E.; Zhao, J.; Bailis, W.; Cao, G.; Kroehling, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways. Nature 2017, 548, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fang, X.; Zhong, P.; Song, Z.; Hu, X. N6-methyladenosine modifications: Interactions with novel RNA-binding proteins and roles in signal transduction. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Ali, M.; Xu, X.; Lu, G. RNA N6-methyladenosine responds to low-temperature stress in tomato anthers. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 687826. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Bi, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. METTL3 inhibits BMSC adipogenic differentiation by targeting the JAK1/STAT5/C/EBPβ pathway via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 7529–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; He, J.; Zhu, J.; Pan, J.; Liao, W.; Ye, H.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Du, Y.; Cui, B.; et al. Lactylation-driven METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification promotes immunosuppression of tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 1660–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, N. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein (YTP) family members participate in low-temperature treatment and waterlogging stress responses. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Luo, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wu, T.; Chen, G. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of m6A gene family in Solanum lycopersicum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, N.; Zheng, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; et al. RBM4 regulates M1 macrophages polarization through targeting STAT1-mediated glycolysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastan, J.P.; Tremblay, M.W.; Brown, M.C.; Trimarco, J.D.; Dobrikova, E.Y.; Dobrikov, M.I.; Gromeier, M. Enterovirus 2Apro cleavage of the YTHDF m6A readers implicates YTHDF3 as a mediator of type I interferon-driven JAK/STAT signaling. mBio 2021, 12, e00116-21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Oh, S.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Kong, L.Z.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.D. FTO negatively regulates the cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e55681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Guo, T.; Jiang, L. Multi-omics analysis reveals the epitranscriptomic and proteomic regulation network of tomato in low-temperature stress response. Hortic. Plant J. 2025, 11, 758–773. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Huang, H.; Kanwar, M.K.; Yang, P.; Zhou, J. BAG8 positively regulates cold stress tolerance by modulating photosystem, antioxidant system and protein protection in Solanum lycopersicum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 206, 108267. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Cai, J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yun, J.Y.; Xu, T.; Kang, H. N6-Methyladenosine mRNA methylation is important for salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2021, 106, 1759–1775. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, N. Functions of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) in Seed Germination and Low-Temperature Stress Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073338
Zhang Y, Zhao J, Li J, Li Y, Jiang L, Wang N. Functions of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) in Seed Germination and Low-Temperature Stress Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073338
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yidan, Jiahui Zhao, Jingyuan Li, Yanting Li, Libo Jiang, and Na Wang. 2025. "Functions of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) in Seed Germination and Low-Temperature Stress Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073338
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhao, J., Li, J., Li, Y., Jiang, L., & Wang, N. (2025). Functions of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) in Seed Germination and Low-Temperature Stress Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073338





