The Soluble Cytoplasmic Tail of CD45 (ct-CD45) Regulates Dendritic Cell Activation and Function via TLR4 Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
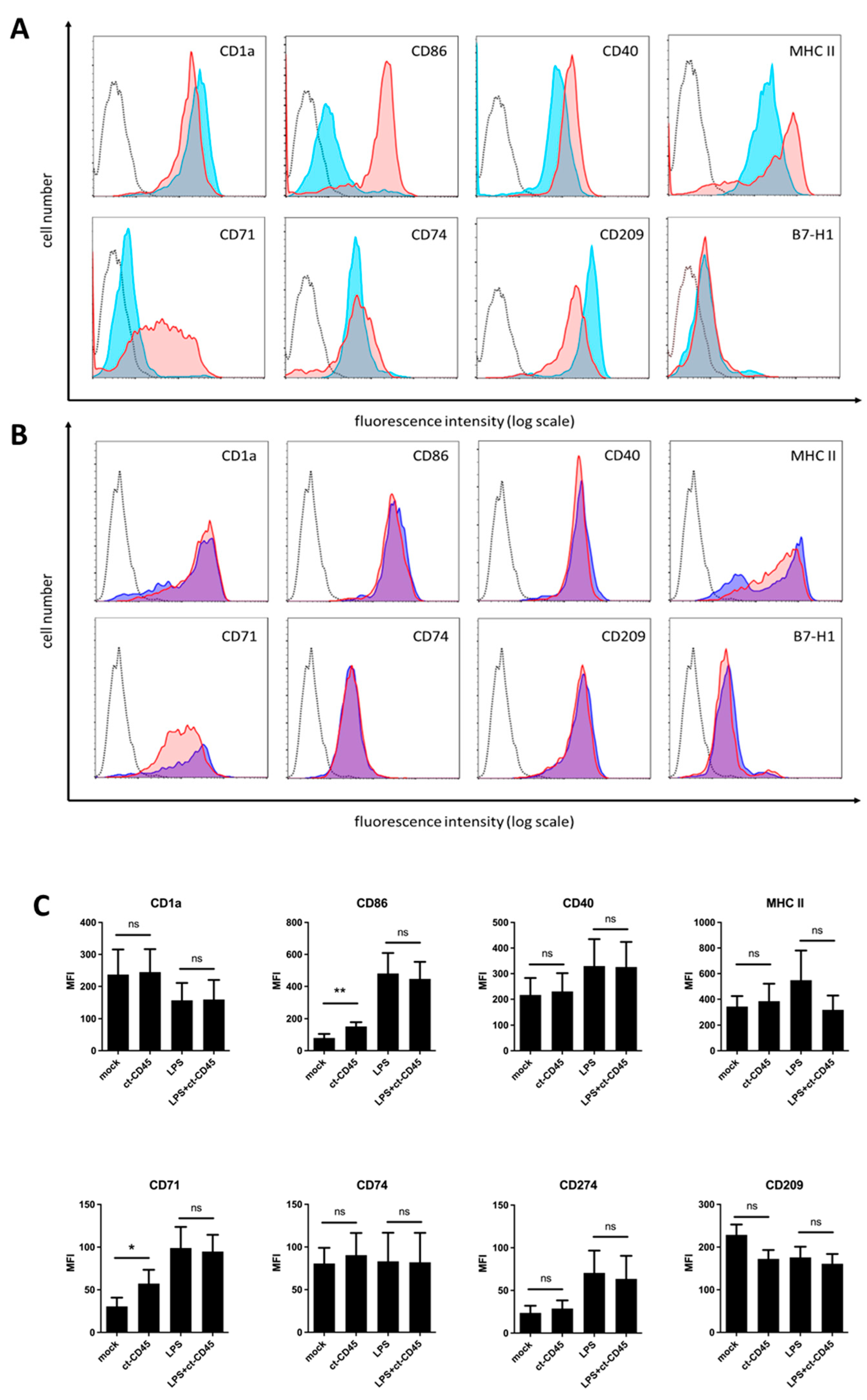
2.1. Immature DCs Upregulate CD86 and CD71 upon ct-CD45 Stimulation
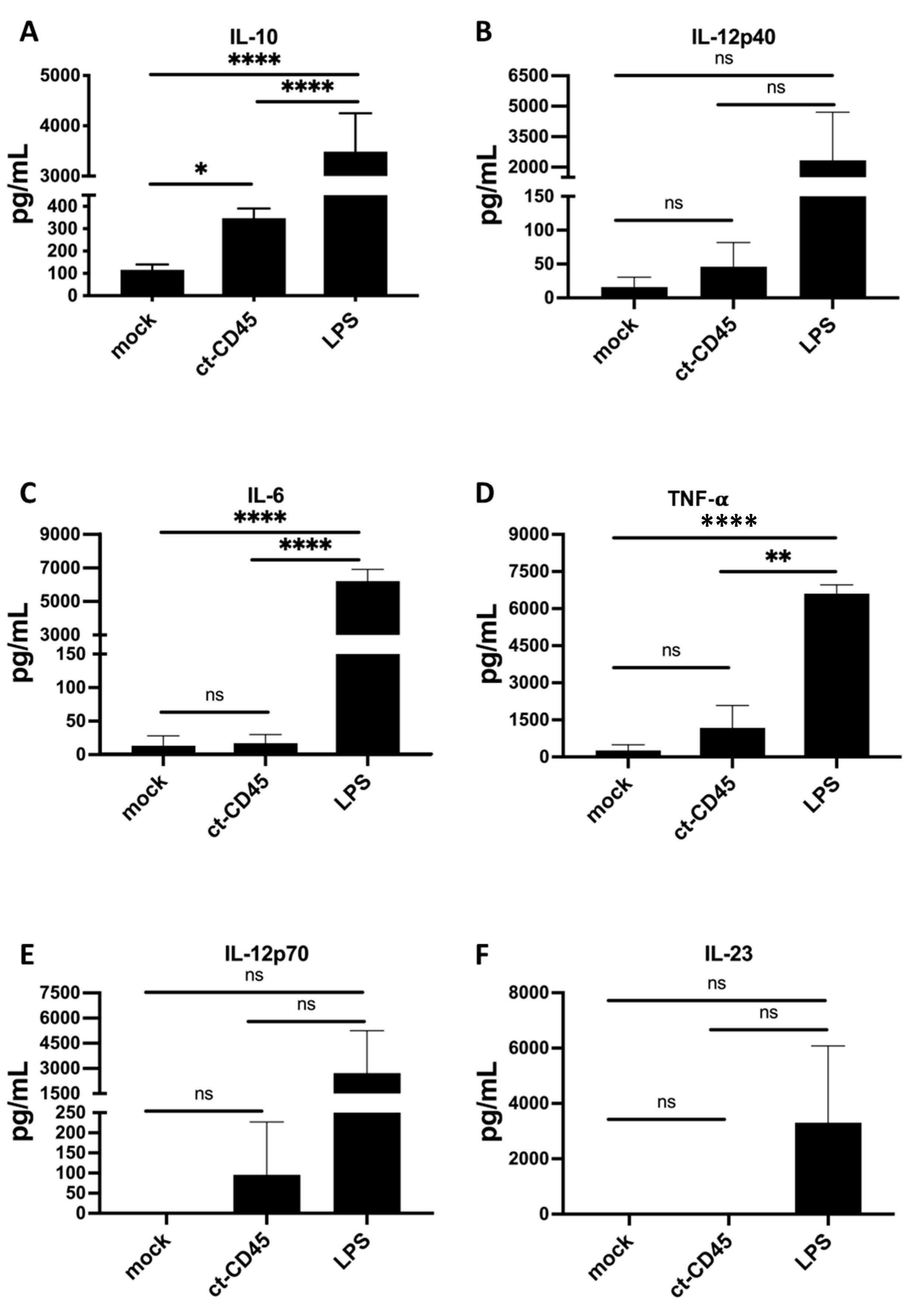
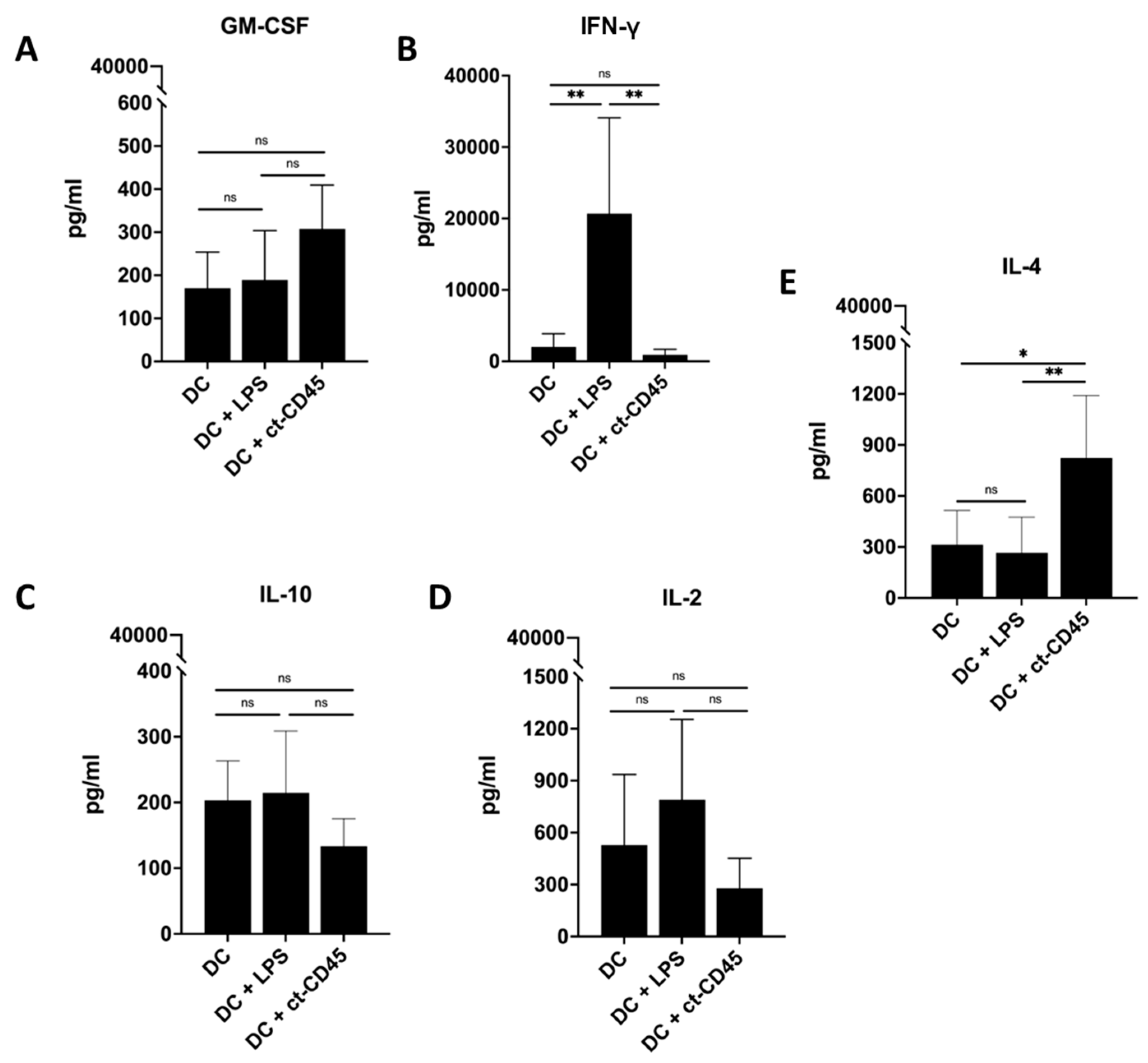
2.2. ct-CD45-Stimulated DC Release Increased Levels of IL-10
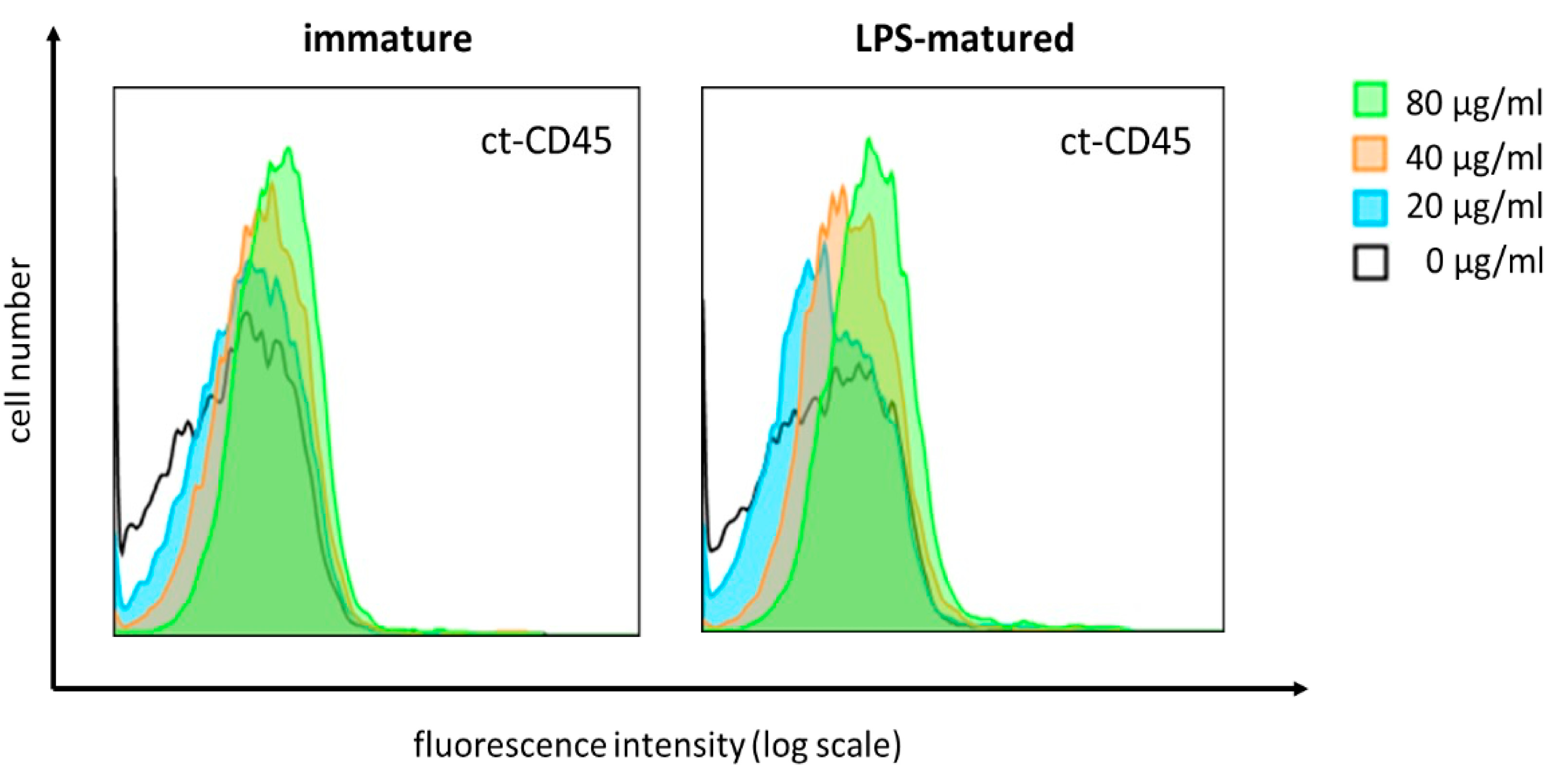
2.3. ct-CD45 Binds to Human DCs in a Dose-Dependent Manner
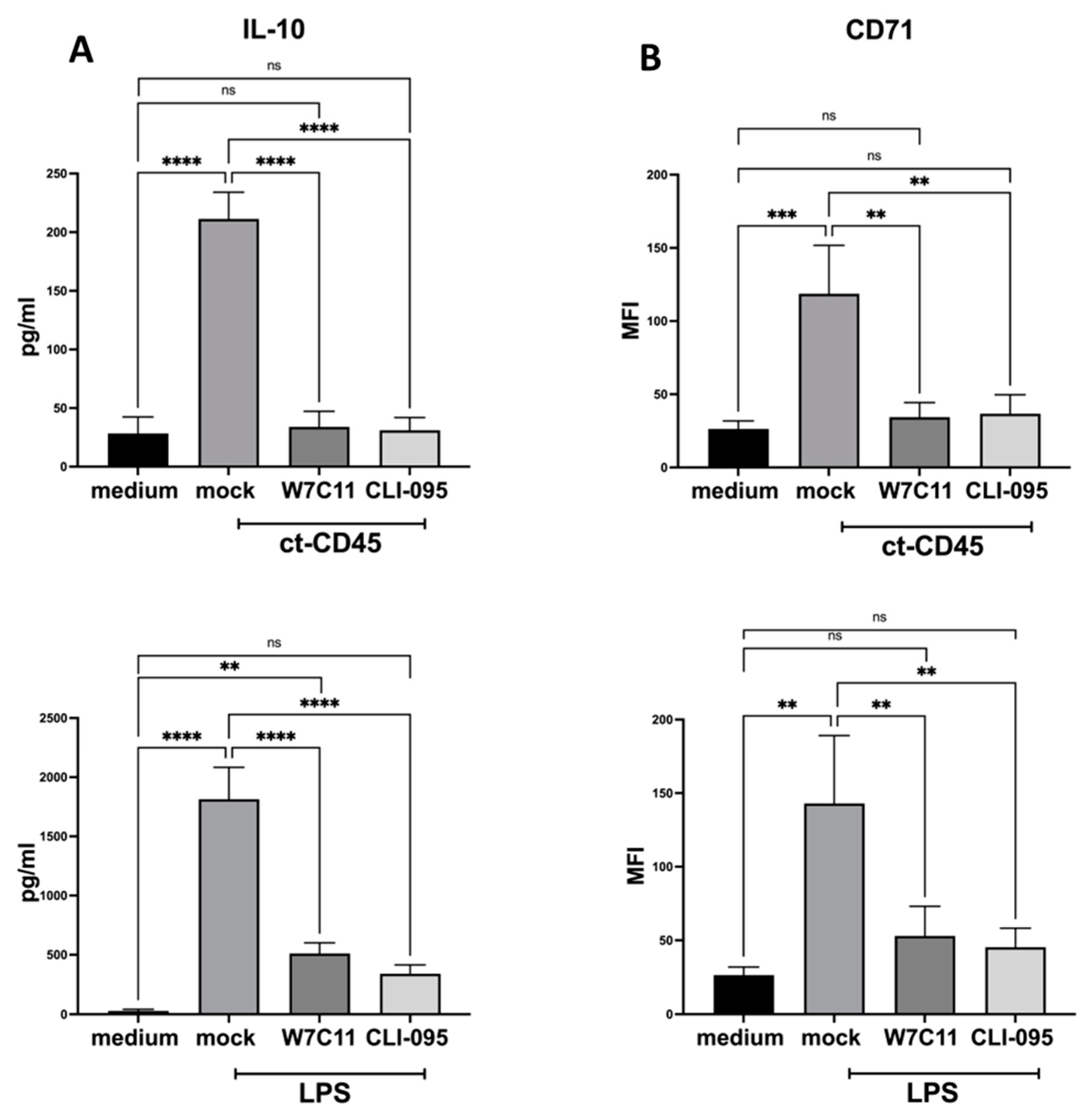
2.4. ct-CD45-Mediated the Increase in DC Surface Markers, and Cytokine Production Can Be Inhibited by a TLR4 Blockade
2.5. ct-CD45 Treatment of DCs Does Not Affect the Proliferation of Co-Cultured T Cells
2.6. Treatment of DCs with ct-CD45 Favors the Induction of Th2-Type T Cell Responses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Media, Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. Generation of Monocyte-Derived DCs
4.3. Mixed Leukocyte Reaction
4.4. Surface Marker Staining of Dendritic Cells
4.5. ct-CD45 Binding to DCs
4.6. Cytokine Measurements
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ct-CD45 | Cytoplasmic tail of CD 45 |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| DCs | Monocyte-derived dendritic cells |
References
- McCarthy, A.J.; Coleman-Vaughan, C.; McCarthy, J.V. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: Emergent role in cell signalling pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penninger, J.M.; Irie-Sasaki, J.; Sasaki, T.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J. CD45: New jobs for an old acquaintance. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchberger, S.; Majdic, O.; Blüml, S.; Schrauf, C.; Leitner, J.; Gerner, C.; Paster, W.; Gundacker, N.; Sibilia, M.; Stöckl, J. The cytoplasmic tail of CD45 is released from activated phagocytes and can act as an inhibitory messenger for T cells. Blood 2008, 112, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puck, A.; Hopf, S.; Modak, M.; Majdic, O.; Cejka, P.; Blüml, S.; Schmetterer, K.; Arnold-Schrauf, C.; Gerwien, J.G.; Frederiksen, K.S.; et al. The soluble cytoplasmic tail of CD45 (ct-CD45) in human plasma contributes to keep T cells in a quiescent state. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puck, A.; Künig, S.; Modak, M.; May, L.; Fritz, P.; Battin, C.; Radakovics, K.; Steinberger, P.; Reipert, B.M.; Crowe, B.A.; et al. The soluble cytoplasmic tail of CD45 regulates T-cell activation via TLR4 signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 3176–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.E. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: All we need to know about danger. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, V.N.; Oskolkova, O.V.; Birukov, K.G.; Levonen, A.L.; Binder, C.J.; Stöckl, J. Generation and biological activities of oxidized phospholipids. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2010, 12, 1009–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midwood, K.; Sacre, S.; Piccinini, A.M.; Inglis, J.; Trebaul, A.; Chan, E.; Drexler, S.; Sofat, N.; Kashiwagi, M.; Orend, G.; et al. Tenascin-C is an endogenous activator of Toll-like receptor 4 that is essential for maintaining inflammation in arthritic joint disease. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Varga, J. Endogenous ligands of TLR4 promote unresolving tissue fibrosis: Implications for systemic sclerosis and its targeted therapy. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 195, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kagan, J.C. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown-Longo, P.J.; Higgins, P.J. Integration of Canonical and Noncanonical Pathways in TLR4 Signaling: Complex Regulation of the Wound Repair Program. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grześk, G.; Szadujkis-Szadurski, L. Physiological antagonism of angiotensin II and lipopolysaccharides in early endotoxemia: Pharmacometric analysis. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kajita, M.; Murata, T.; Horiguchi, K.; Iizuka, M.; Hori, M.; Ozaki, H. iNOS expression in vascular resident macrophages contributes to circulatory dysfunction of splanchnic vascular smooth muscle contractions in portal hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1021–H1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebe, K.; Janssen, E.; Beutler, B. The interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L.; Ancuta, P.; Crowe, S.; Dalod, M.; Grau, V.; Hart, D.N.; Leenen, P.J.M.; Liu, Y.-J.; MacPherson, G.; Randolph, G.J.; et al. Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood 2010, 116, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, M.; Ginhoux, F. Human dendritic cells. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 86, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.N.; Birkinshaw, C. Hyaluronic acid based scaffolds for tissue engineering—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R.M. Decisions about dendritic cells: Past, present, and future. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A. Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.J.; Symmons, M.F.; Gangloff, M.; Bryant, C.E. Assembly and localization of Toll-like receptor signalling complexes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nardo, D. Toll-like receptors: Activation, signalling and transcriptional modulation. Cytokine 2015, 74, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, D.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Ma, W.; Tan, Y.; Gygi, S.P.; Higgins, D.E.; Kagan, J.C. Molecular definition of the endogenous Toll-like receptor signalling pathways. Nature 2024, 631, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płóciennikowska, A.; Hromada-Judycka, A.; Borzęcka, K.; Kwiatkowska, K. Co-operation of TLR4 and raft proteins in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2015, 72, 557–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatinovich, J.M.; Grogan, E.W.; Norris, M.; Steinkasserer, A.; Lemos, H.; Mellor, A.L.; Tcherepanova, I.Y.; Nicolette, C.A.; DeBenedette, M.A. Soluble CD83 Inhibits T Cell Activation by Binding to the TLR4/MD-2 Complex on CD14+ Monocytes. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950. 2017, 198, 2286–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüml, S.; Kirchberger, S.; Bochkov, V.N.; Krönke, G.; Stuhlmeier, K.; Majdic, O.; Zlabinger, G.J.; Knapp, W.; Binder, B.R.; Stöckl, J.; et al. Oxidized phospholipids negatively regulate dendritic cell maturation induced by TLRs and CD40. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950. 2005, 175, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, L.; Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Asa’ad, F.; Castilho, R.M. Understanding the role of endotoxin tolerance in chronic inflammatory conditions and periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, A.M.; Zuliani-Alvarez, L.; Lim, J.M.P.; Midwood, K.S. Distinct microenvironmental cues stimulate divergent TLR4-mediated signaling pathways in macrophages. Sci. Signal 2016, 9, ra86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickl, W.F.; Majdic, O.; Kohl, P.; Stöckl, J.; Riedl, E.; Scheinecker, C.; Bello-Fernandez, C.; Knapp, W. Molecular and functional characteristics of dendritic cells generated from highly purified CD14+ peripheral blood monocytes. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 1996, 157, 3850–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil-Cantero, S.; Puck, A.; Künig, S.; Pinnarò, V.; Waidhofer-Söllner, P.; Stöckl, J. The Soluble Cytoplasmic Tail of CD45 (ct-CD45) Regulates Dendritic Cell Activation and Function via TLR4 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083888
Gil-Cantero S, Puck A, Künig S, Pinnarò V, Waidhofer-Söllner P, Stöckl J. The Soluble Cytoplasmic Tail of CD45 (ct-CD45) Regulates Dendritic Cell Activation and Function via TLR4 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083888
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil-Cantero, Sara, Alexander Puck, Sarojinidevi Künig, Veronica Pinnarò, Petra Waidhofer-Söllner, and Johannes Stöckl. 2025. "The Soluble Cytoplasmic Tail of CD45 (ct-CD45) Regulates Dendritic Cell Activation and Function via TLR4 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083888
APA StyleGil-Cantero, S., Puck, A., Künig, S., Pinnarò, V., Waidhofer-Söllner, P., & Stöckl, J. (2025). The Soluble Cytoplasmic Tail of CD45 (ct-CD45) Regulates Dendritic Cell Activation and Function via TLR4 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083888





