A Novel Rexinoid Agonist, UAB116, Decreases Metastatic Phenotype in Hepatoblastoma by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway via Upregulation of TRIM29
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LXR/RXR Pathway Is Downregulated in HLM_2 Cells
2.2. Effects of UAB116 on Differential Gene Expression in HLM_2 Cells
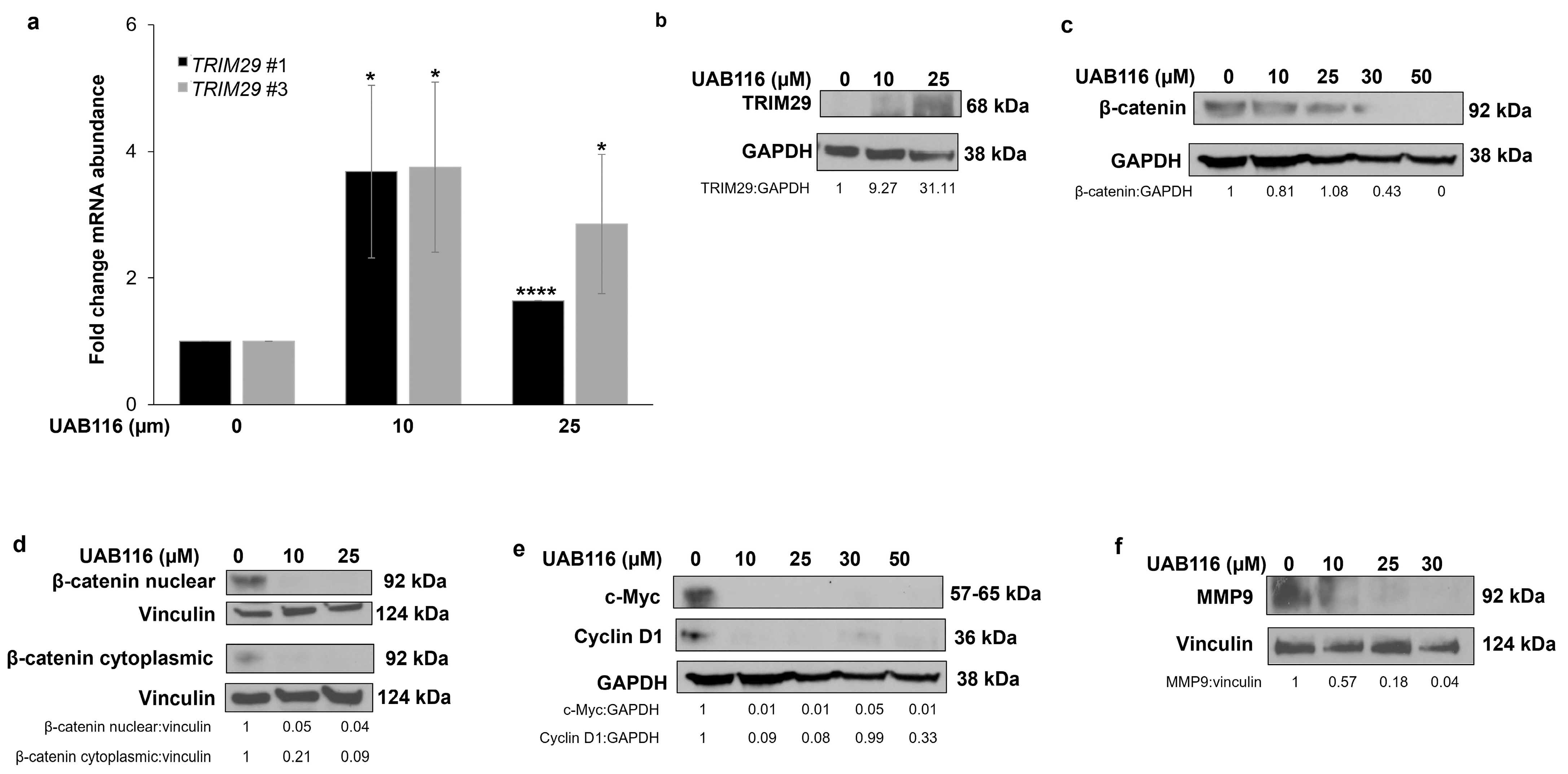
2.3. UAB116 Upregulates TRIM29 in HLM_2 Cells
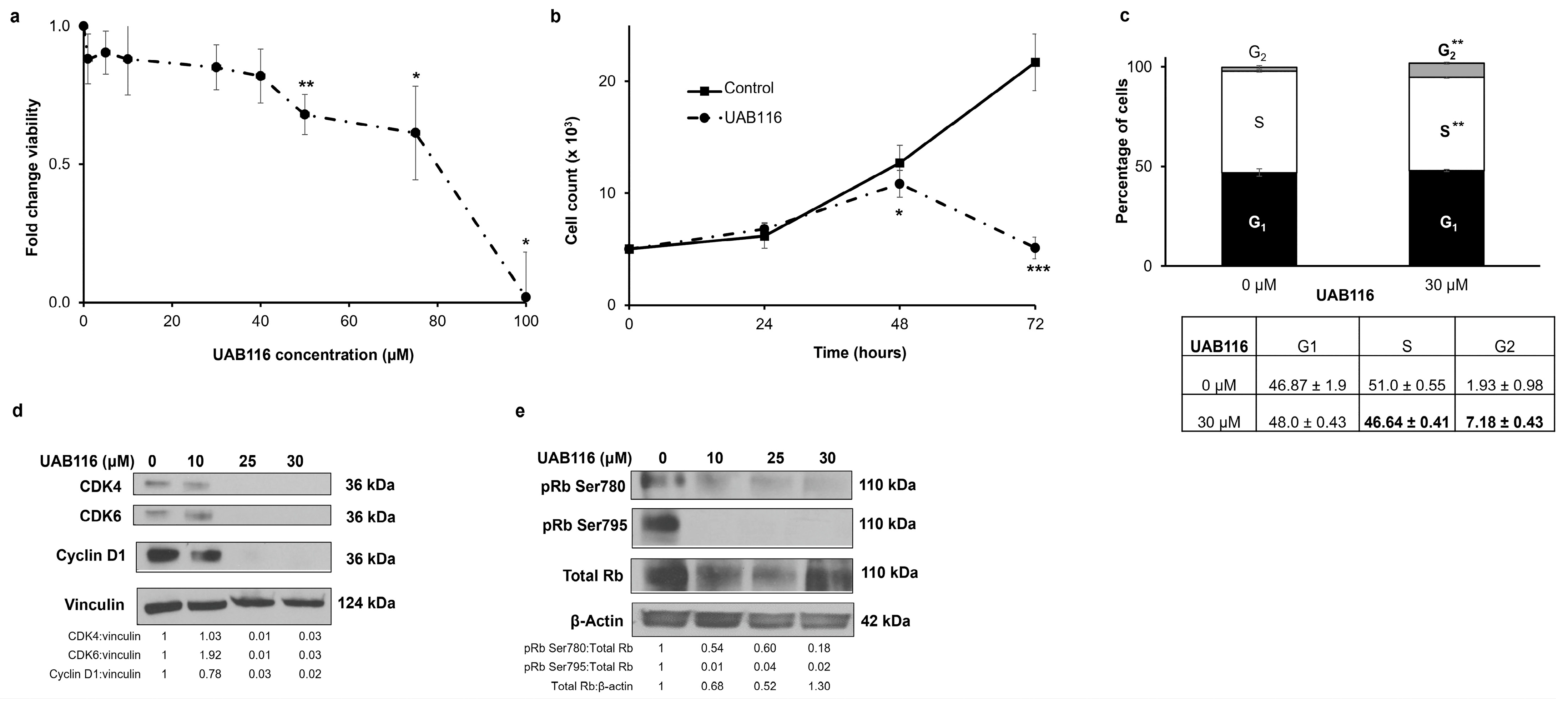
2.4. UAB116 Decreases HLM_2 Proliferation and Affects the Cell Cycle
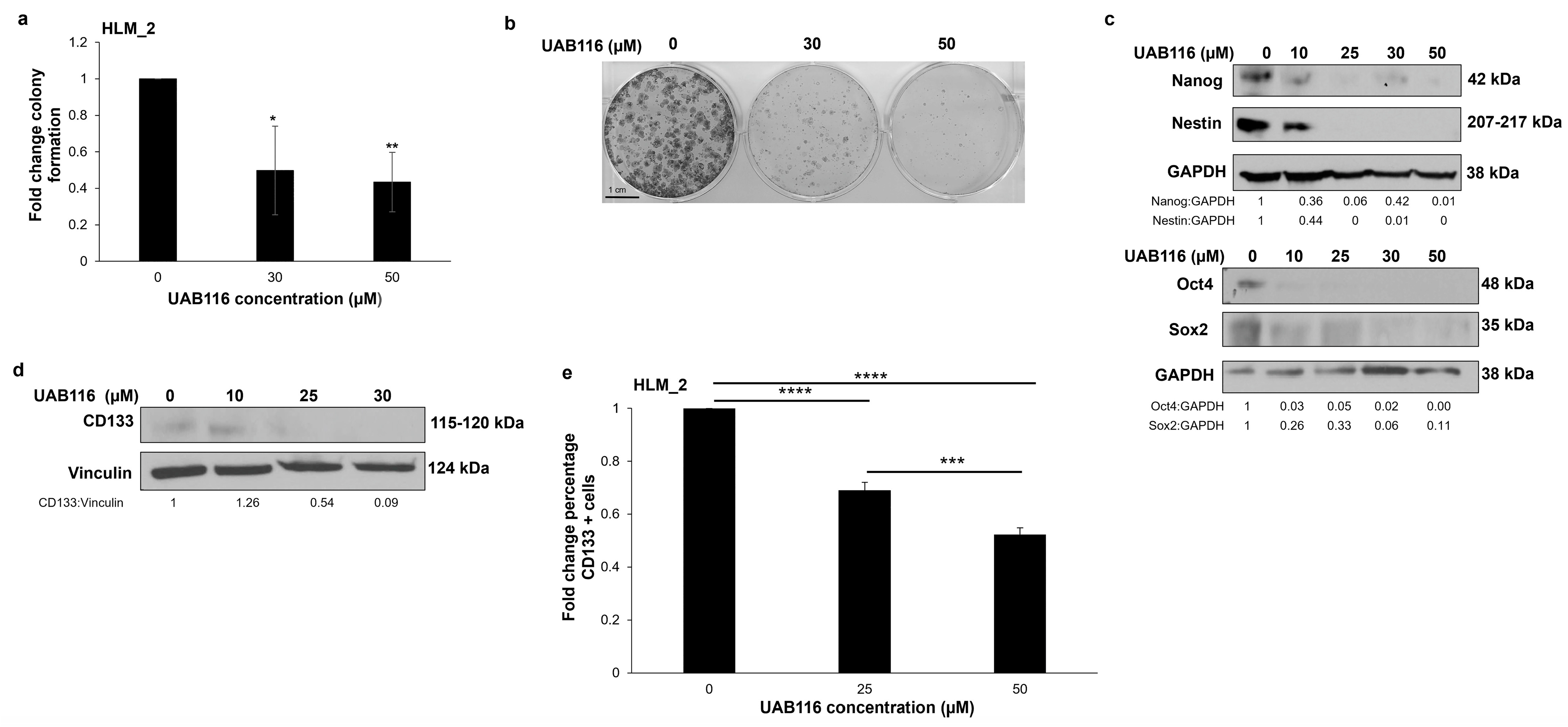
2.5. UAB116 Decreases HLM_2 Invasion
2.6. UAB116 Decreases HLM_2 Stemness
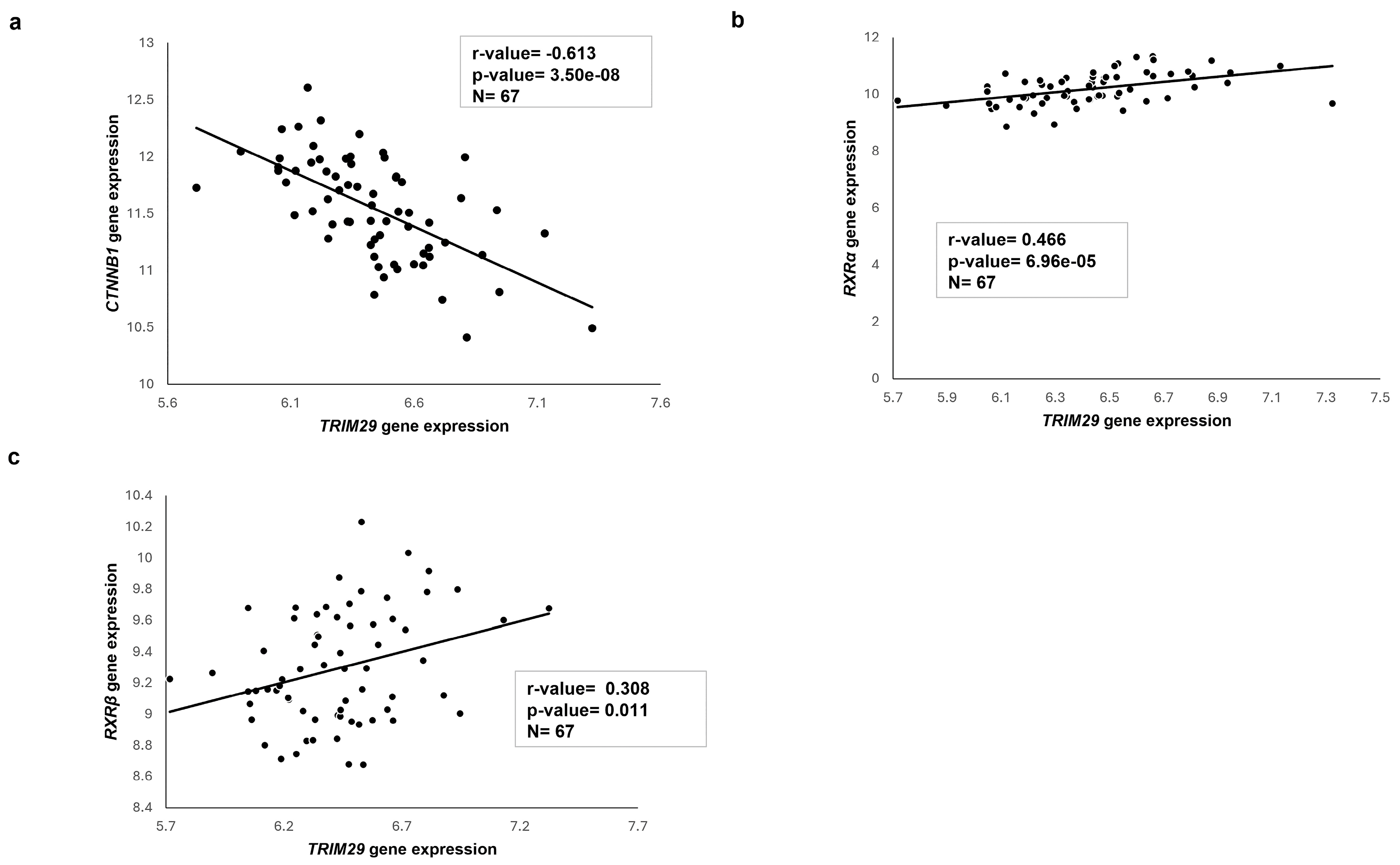
2.7. Transcriptome Analysis of Published HB Patient Cohorts
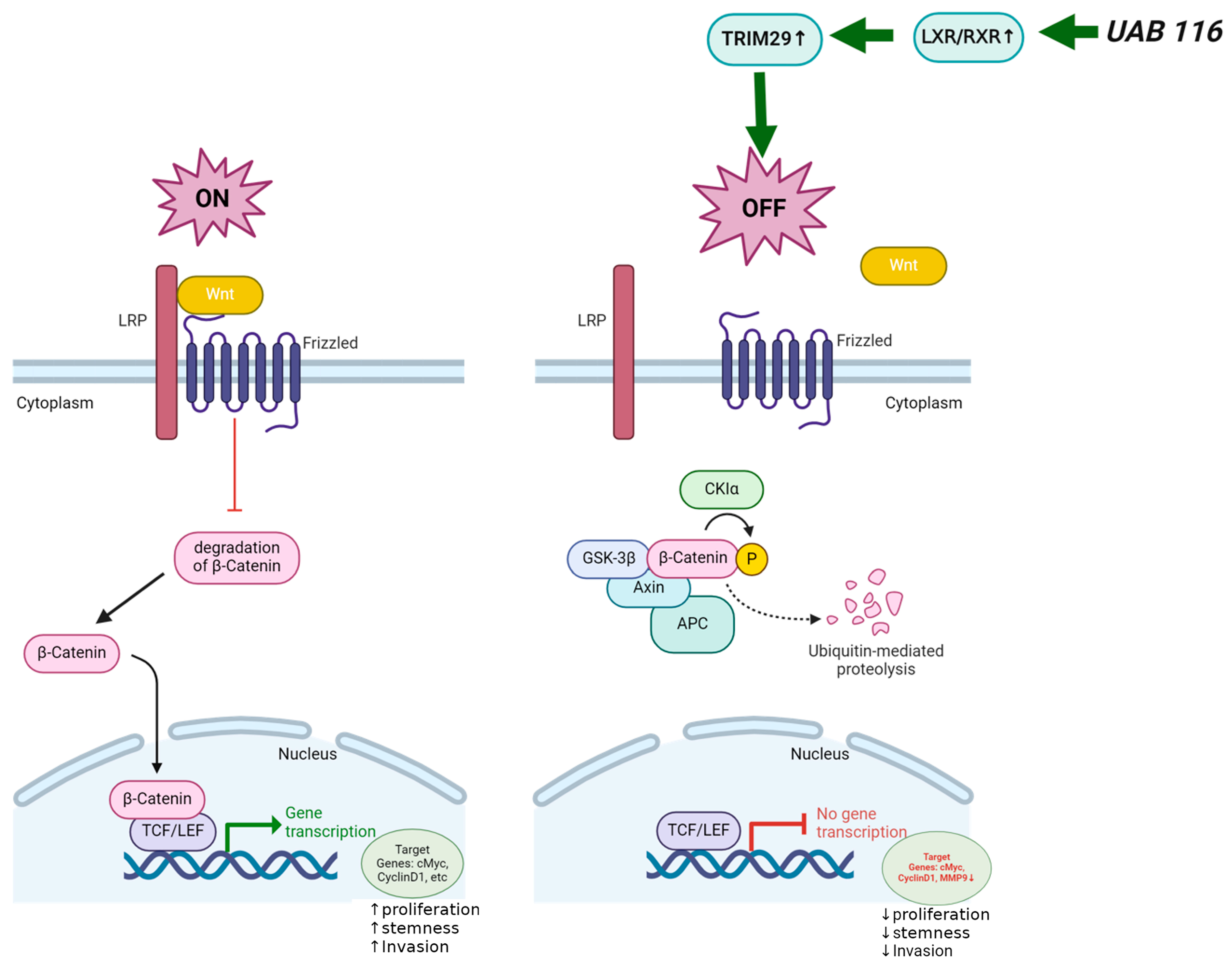
2.8. Proposed Mechanism of UAB116 Effect on HLM_2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Cell Culture
4.2. Antibodies and Reagents
4.3. Viability
4.4. Proliferation
4.5. Cell Cycle
4.6. Colony Forming Assays
4.7. Immunoblotting
4.8. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
4.9. RNA Sequencing Analysis
4.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.11. Invasion
4.12. CD133 Expression
4.13. UAB116
4.14. Data Analysis
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HB | Hepatoblastoma |
| LXR | Liver X Receptor |
| RXR | Retinoid X Receptor |
| TRIM29 | Tripartite motif containing 29 |
| CTNNB1 | CATENIN β1 |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| FXR | Farnesoid X Receptor |
| LBD | Ligand binding domain |
| ATDC | Ataxia-telangiectasia group D-associated protein |
| Dvl2 | Disheveled 2 |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3β |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| LD50 | Lethal dose 50% |
| Rb | Retinoblastoma |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| CSC | Cancer stem cell |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| RIPA | Radio-immunoprecipitation assay |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NP40 | Nonidet P-40 |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
References
- Kahla, J.A.; Siegel, D.A.; Dai, S.; Lupo, P.J.; Foster, J.H.; Scheurer, M.E.; Heczey, A.A. Incidence and 5-Year Survival of Children and Adolescents with Hepatoblastoma in the United States. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, 29763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maibach, R.; Roebuck, D.; Brugieres, L.; Capra, M.; Brock, P.; Dall’igna, P.; Otte, J.B.; De Camargo, B.; Zsiros, J.; Zimmermann, A.; et al. Prognostic Stratification for Children with Hepatoblastoma: The SIOPEL Experience. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikhi, R.R.; Spady, K.K.; Hoffman, R.I.; Bateman, M.S.; Bateman, M.; Howard, L.E. Hepatoblastoma: A Need for Cell Lines and Tissue Banks to Develop Targeted Drug Therapies. Front. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marayati, R.; Julson, J.R.; Bownes, L.V.; Quinn, C.H.; Hutchins, S.C.; Williams, A.P.; Markert, H.R.; Beierle, A.M.; Stewart, J.E.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; et al. Metastatic Human Hepatoblastoma Cells Exhibit Enhanced Tumorigenicity, Invasiveness and a Stem Cell-like Phenotype. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2022, 57, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavudi, K.; Madhav Nuguri, S.; Olverson, Z.; Krishna Dhanabalan, A.; Patnaik, S.; Rani Kokkanti, R. Targeting the Retinoic Acid Signaling Pathway as a Modern Precision Therapy against Cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1254612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, D.J.; Dedhar, S.; Coetzee, G.A.; Nelson, C.C. Interaction of Nuclear Receptors with the Wnt/β-Catenin/Tcf Signaling Axis: Wnt You Like to Know? Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 898–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Meyfeldt, J.; Wang, H.; Kulkarni, S.; Lu, J.; Mandel, J.A.; Marburger, B.; Liu, Y.; Gorka, J.E.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. β-Catenin Mutations as Determinants of Hepatoblastoma Phenotypes in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 17524–17542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengol, C.; Cairo, S.; Fabre, M.; Buendia, M.A. Wnt Signaling and Hepatocarcinogenesis: The Hepatoblastoma Model. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atigadda, V.R.; Kashyap, M.P.; Yang, Z.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Melo, N.; Sinha, R.; Belyaeva, O.V.; Chou, C.-F.; Chang, P.-L.; Kedishvili, N.Y.; et al. Conformationally Defined Rexinoids for the Prevention of Inflammation and Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 14409–14423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Ni, J.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Cao, X. RXR Signaling Targeted Cancer Therapy. Innov. Life 2023, 1, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, S. Early Evidence for the Role of TRIM29 in Multiple Cancer Models. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ross, A.C. Retinoic Acid Regulates Cell Cycle Progression and Cell Differentiation in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 297, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Y.L.; Liu, S.; Yan, W.W.; Dong, B. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling as a Useful Therapeutic Target in Hepatoblastoma. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20192466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, S.; Armengol, C.; lien De Reyniè, A.; Wei, Y.; Thomas, E.; lique Renard, C.-A.; Goga, A.; Balakrishnan, A.; Semeraro, M.; Gresh, L.; et al. Hepatic Stem-like Phenotype and Interplay of Wnt/b-Catenin and Myc Signaling in Aggressive Childhood Liver Cancer. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafman, L.L.; Mruthyunjayappa, S.; Waters, A.M.; Garner, E.F.; Aye, J.M.; Stewart, J.E.; Yoon, K.J.; Whelan, K.; Mroczek-Musulman, E.; Beierle, E.A. Targeting PIM Kinase as a Therapeutic Strategy in Human Hepatoblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22665–22679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanawa, M.; Hiyama, E.; Kawashima, K.; Hiyama, K.; Ikeda, K.; Morihara, N.; Kurihara, S.; Fukazawa, T.; Ueda, Y. Gene Expression Profiling in Hepatoblastoma Cases of the Japanese Study Group for Pediatric Liver Tumors-2 (JPLT-2) Trial. Eur. J. Mol. Cancer 2019, 1, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Yuan, M.; Yan, L.; Tang, H. Emerging Insights into Liver X Receptor α in the Tumorigenesis and Therapeutics of Human Cancers. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Molecular Mechanism of Liver X Receptors in Cancer Therapeutics. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan Ramalingam, P.; Elangovan, S.; Ramaiah Mekala, J.; Arumugam, S.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Sridaran, D. Liver X Receptors (LXRs) in Cancer-an Eagle’s View on Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1386102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.H.; Ghosn, C.; Hinchman, C.; Forbes, C.; Wang, J.; Snider, N.; Cordrey, A.; Zhao, Y.; Chandraratna, R.A.S. Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC)-Independent Regulation of Beta-Catenin Degradation via a Retinoid X Receptor-Mediated Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29954–29962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, S.; Endo, K.; Jeong, Y.; Kawana, K.; Miyachi, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Makishima, M. Suppression of β-Catenin Signaling by Liver X Receptor Ligands. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.W. The Regulation of β-Catenin Activity and Function in Cancer: Therapeutic Opportunities. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33972–33989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Hu, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhong, Y.; Lin, N.; Xu, R. TRIM29 Prevents Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys Sin 2019, 51, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Kimura, T.; Nonomura, K.; Tanaka, S.; Hatakeyama, S. TRIM29 as a Novel Prostate Basal Cell Marker for Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Kim, W.J.; Alpay, M.; Tang, M.; Pardo, C.; Hatakeyama, S.; May, W.S.; Kladde, M.; Heldermon, C.; Siegel, E.; et al. TRIM29 Suppresses TWIST1 and Invasive Breast Cancer Behavior. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4875–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Nandi, D.; Sharma, D. TRIM-Endous Functional Network of Tripartite Motif 29 (TRIM29) in Cancer Progression and Beyond. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025, 44, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, H.K.; Bertoli, C.; de Bruin, R.A.M. Cell Cycle Control in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.; La Monica, S.; Fumarola, C.; Alfieri, R. Multiple Effects of CDK4/6 Inhibition in Cancer: From Cell Cycle Arrest to Immunomodulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 170, 113676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marayati, R.; Bownes, L.V.; Stafman, L.L.; Williams, A.P.; Quinn, C.H.; Atigadda, V.; Aye, J.M.; Stewart, J.E.; Yoon, K.J.; Beierle, E.A. 9-Cis-UAB30, a Novel Rexinoid Agonist, Decreases Tumorigenicity and Cancer Cell Stemness of Human Neuroblastoma Patient-Derived Xenografts. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Solinas, A.; Cairo, S.; Evert, M.; Chen, X.; Calvisi, D.F. Molecular Mechanisms of Hepatoblastoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingraham, C.A.; Park, G.C.; Makarenkova, H.P.; Crossin, K.L. Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 Induced by Wnt Signaling Increases the Proliferation and Migration of Embryonic Neural Stem Cells at Low O2 Levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17649–17657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgwick, A.E.; D’souza-Schorey, C. Wnt Signaling in Cell Motility and Invasion: Drawing Parallels between Development and Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Mckee, C.; Cao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Kessler, B.M.; Muschel, R.J. Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Regulates Tumor Cell Invasion via Cleavage of Protease Nexin-1. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6988–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Liu, H. Overview of Cancer Stem Cells and Stemness for Community Oncologists. Target Oncol. 2017, 12, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.S.; Wang, A.X.; Dong, B.; Pu, K.F.; Yuan, L.H.; Zhu, Y.-M. A New Prospect in Cancer Therapy: Targeting Cancer Stem Cells to Eradicate Cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2012, 12, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, B.; Wan, F.; Farhadi, M.; Ernst, A.; Zeppernick, F.; Tagscherer, K.E.; Ahmadi, R.; Lohr, J.; Dictus, C.; Gdynia, G.; et al. Human Cancer Biology Differentiation Therapy Exerts Antitumor Effects on Stem-like Glioma Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2715–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudas, L.J.; Wagner, J.A. Retinoids Regulate Stem Cell Differentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 226, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, G.; Dawson, M.I.; Zhang, X.K.; Thiele, C.J. Activation of Three Distinct RXR/RAR Heterodimers Induces Growth Arrest and Differentiation of Neuroblastoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26693–26701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uray, I.P.; Dmitrovsky, E.; Brown, P.H. Retinoids and Rexinoids in Cancer Prevention: From Laboratory to Clinic. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, M.; Liu, S.J.; Zou, L.N.; Smith, Z.; Meissner, A.; Ramanathan, S. Pluripotency Circuit Members Mediate Germ Layer Fate Choice of Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell 2011, 145, 875–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerland, J.A.; Zhang, D.; Reich, L.A.; Carapellucci, S.; Lockwood, B.; Leal, A.S.; Krieger-Burke, T.; Aleiwi, B.; Ellsworth, E.; Liby, K.T. The Novel Rexinoid MSU-42011 Is Effective for the Treatment of Preclinical Kras-Driven Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, K.; Li, Q.; Jiang, N.; Chen, Q. Role of TRIM29 in Disease: What Is and Is Not Known. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 147, 113983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marayati, R.; Stafman, L.L.; Williams, A.P.; Bownes, L.V.; Quinn, C.H.; Markert, H.R.; Easlick, J.L.; Stewart, J.E.; Crossman, D.K.; Mroczek-Musulman, E.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout of PIM3 Suppresses Tumorigenesis and Cancer Cell Stemness in Human Hepatoblastoma Cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschup, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, J.; Jung, C.K.; Shackel, I.; Williams, P.M. Development and Validation of Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction for Monitoring Gene Expression in Cardiac Myocytes in Vitro. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 270, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butey, S.; Brown, M.L.; Julson, J.R.; Marayati, R.; Atigadda, V.R.; Shaikh, M.G.; Nazam, N.; Quinn, C.H.; Shirley, S.; Stafman, L.L.; et al. A Novel Rexinoid Agonist, UAB116, Decreases Metastatic Phenotype in Hepatoblastoma by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway via Upregulation of TRIM29. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093933
Butey S, Brown ML, Julson JR, Marayati R, Atigadda VR, Shaikh MG, Nazam N, Quinn CH, Shirley S, Stafman LL, et al. A Novel Rexinoid Agonist, UAB116, Decreases Metastatic Phenotype in Hepatoblastoma by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway via Upregulation of TRIM29. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093933
Chicago/Turabian StyleButey, Swatika, Morgan L. Brown, Janet R. Julson, Raoud Marayati, Venkatram R. Atigadda, Maryam G. Shaikh, Nazia Nazam, Colin H. Quinn, Sorina Shirley, Laura L. Stafman, and et al. 2025. "A Novel Rexinoid Agonist, UAB116, Decreases Metastatic Phenotype in Hepatoblastoma by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway via Upregulation of TRIM29" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093933
APA StyleButey, S., Brown, M. L., Julson, J. R., Marayati, R., Atigadda, V. R., Shaikh, M. G., Nazam, N., Quinn, C. H., Shirley, S., Stafman, L. L., & Beierle, E. A. (2025). A Novel Rexinoid Agonist, UAB116, Decreases Metastatic Phenotype in Hepatoblastoma by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway via Upregulation of TRIM29. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093933





