Interaction of Serratia proteamaculans with Integrins Activates Invasion-Promoting Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
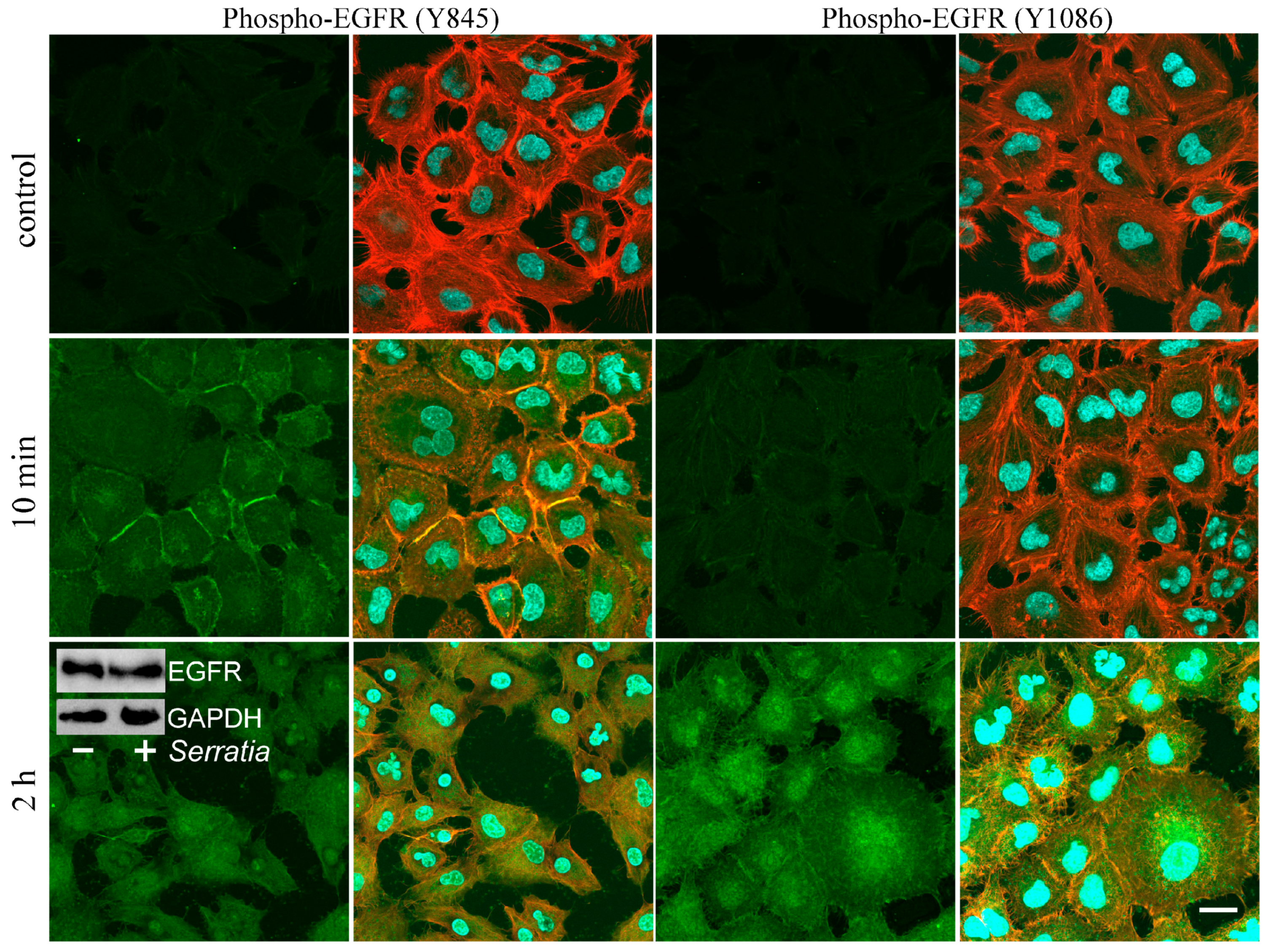
2.1. EGFR Signaling During S. proteamaculans Invasion
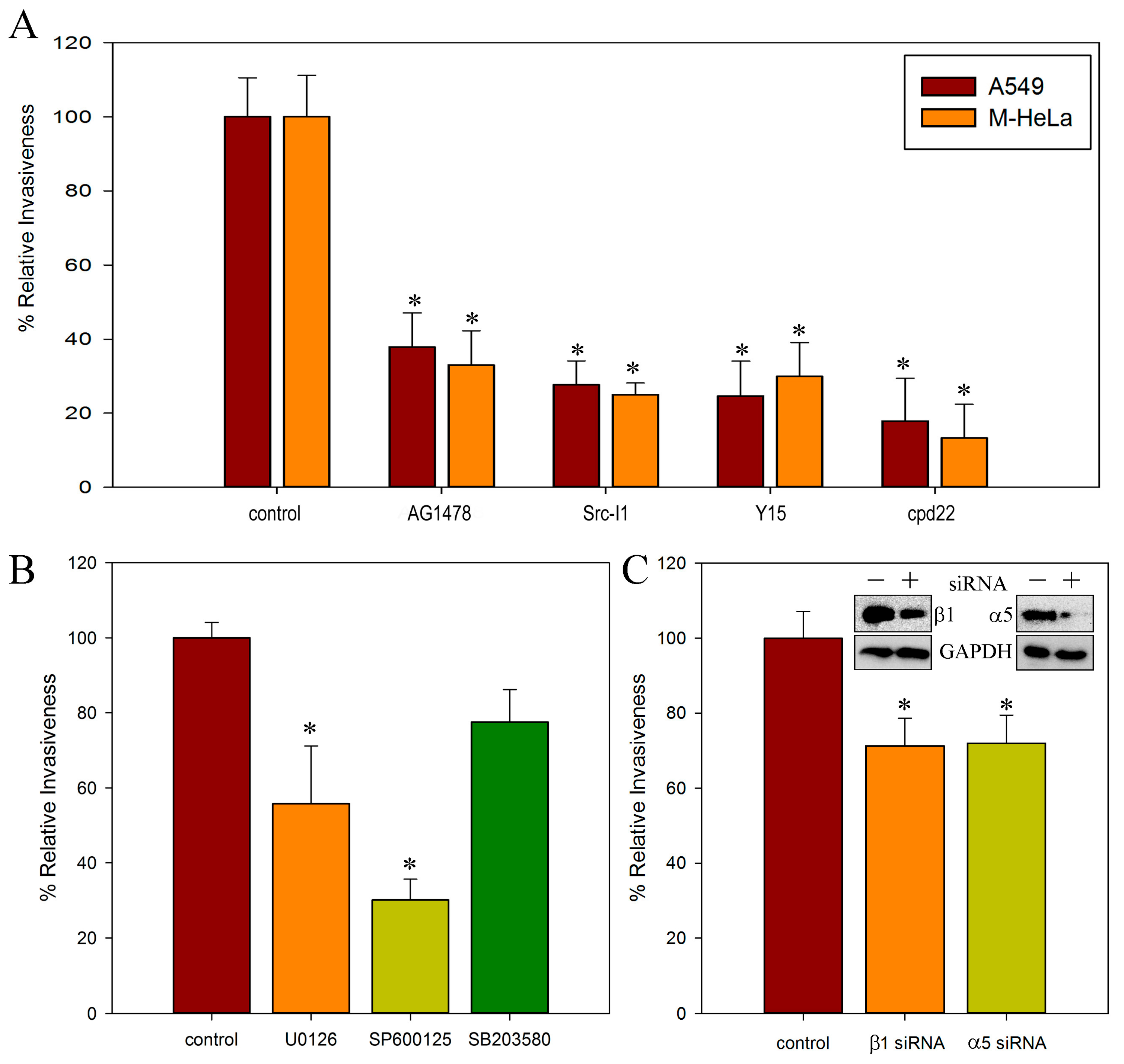
2.2. Involvement of c-Src, FAK, and ILK Kinases in S. proteamaculans Invasion
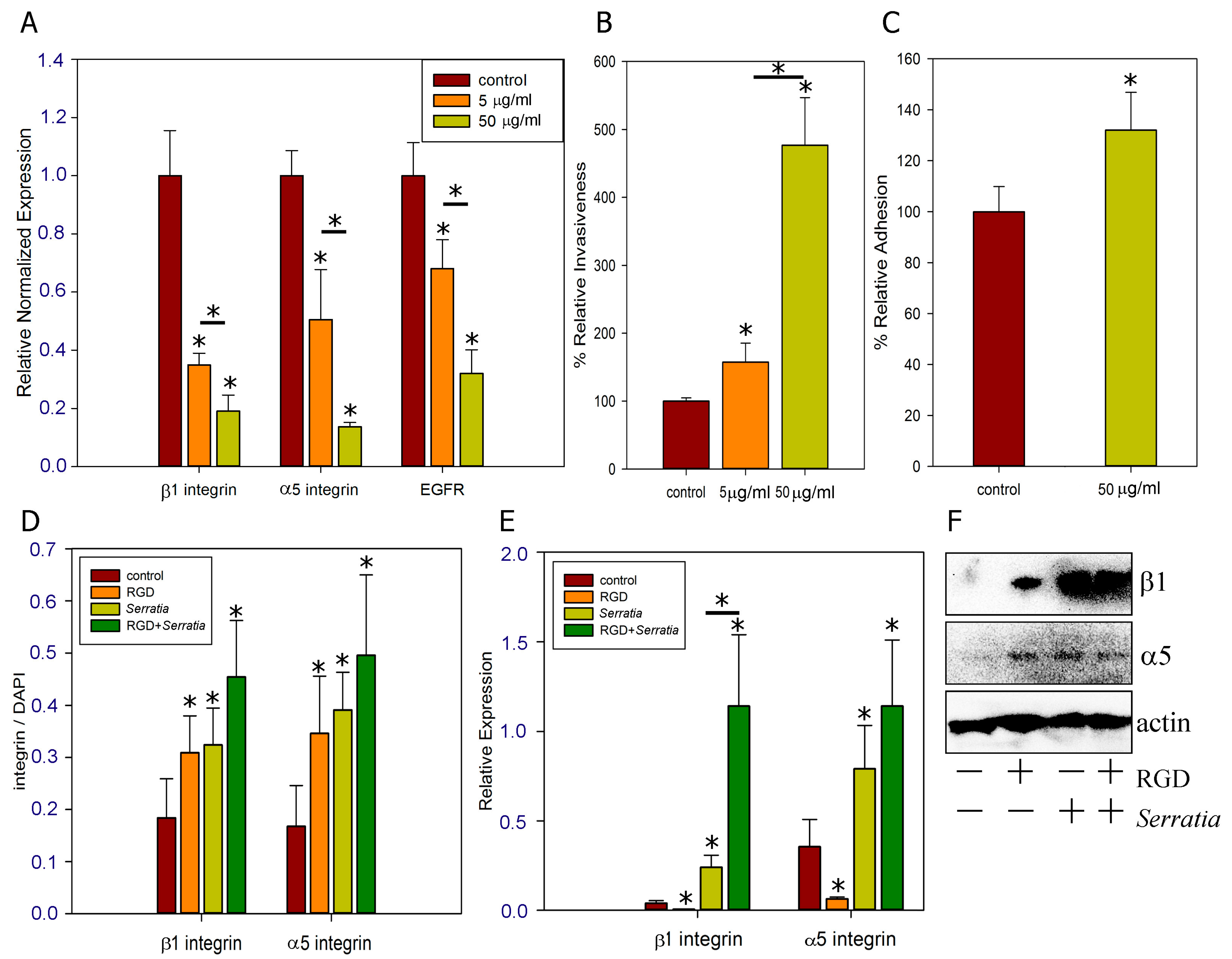
2.3. Role of α5β1 Intergin and Its RGD Binding Site in Invasion
2.4. Effect of Different Multiplicities of Infection (MOI)
3. Discussion
3.1. EGFR in Bacterial Invasion
3.2. c-Src, FAK and ILK Kinases in Bacterial Invasion
3.3. α5β1 Intergin in Bacterial Invasion
3.4. Regulation of Invasion by RGD Peptide
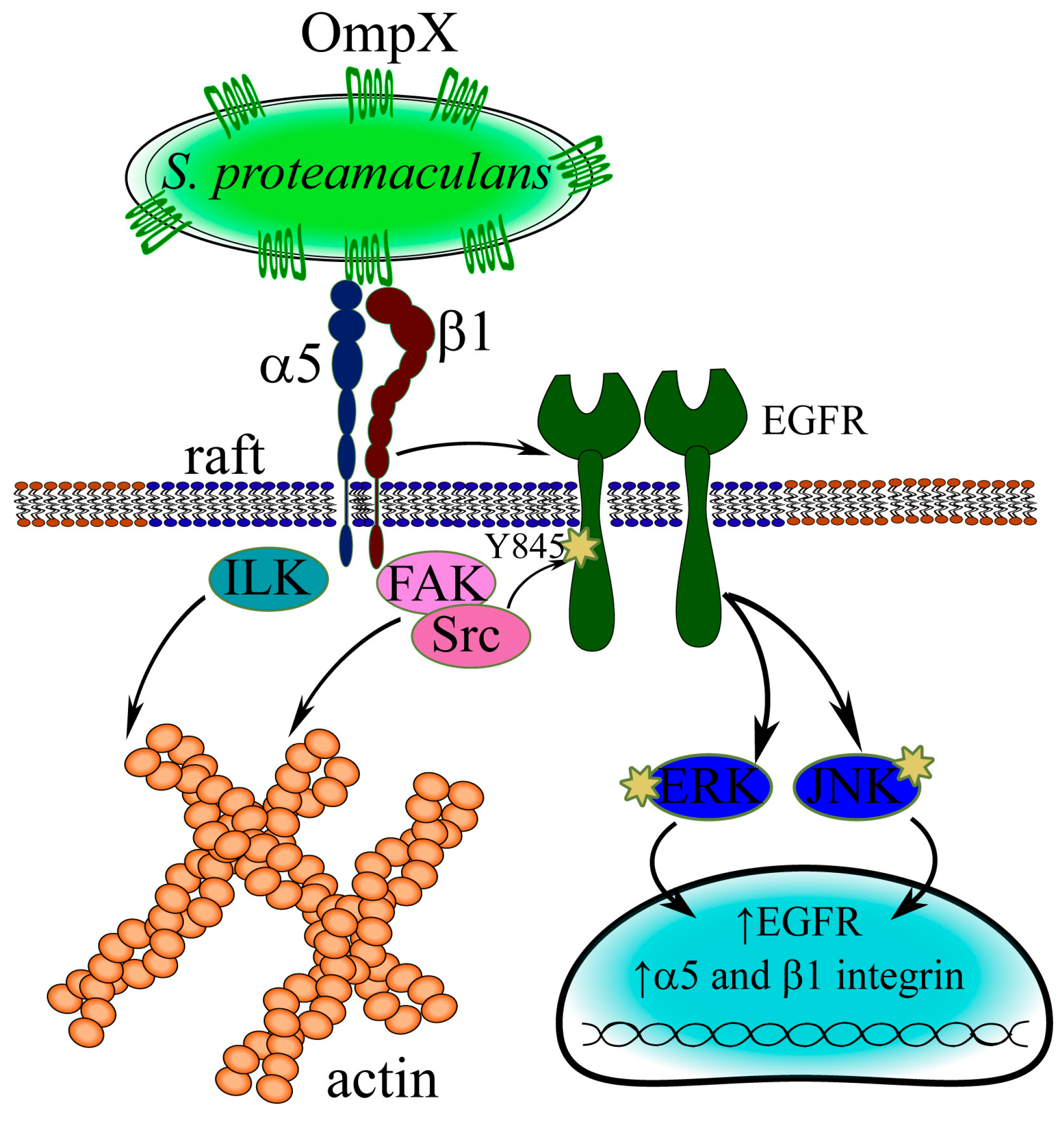
3.5. Mechanism of S. proteamaculans Invasion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures, Bacterial Strains, and Growth Conditions
4.2. siRNA Transfection
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Quantitative Invasion Assay
4.5. Fluorescence Microscopy
4.6. Real-Time RT-PCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahlen, S.D. Serratia infections: From military experiments to current practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 755–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaplina, O.A.; Efremova, T.N.; Kever, L.V.; Komissarchik, Y.Y.; Demidyuk, I.V.; Kostrov, S.V.; Khaitlina, S.Y. Probing for actinase activity of protealysin. Biochemistry 2009, 74, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaplina, O.; Demidyuk, I.; Artamonova, T.; Khodorkovsky, M.; Khaitlina, S. Cleavage of the outer membrane protein OmpX by protealysin regulates Serratia proteamaculans invasion. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedemann, A.; Mijouin, L.; Ayoub, M.A.; Barilleau, E.; Canepa, S.; Teixeira-Gomes, A.P.; Le Vern, Y.; Rosselin, M.; Reiter, E.; Velge, P. Identification of the epidermal growth factor receptor as the receptor for Salmonella Rck-dependent invasion. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4180–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, T.M.; Felek, S.; Krukonis, E.S. Ail binding to fibronectin facilitates Yersinia pestis binding to host cells and Yop delivery. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3358–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, D.; Wann, E.R.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Speziale, P.; Hook, M. Role of fibronectin-binding MSCRAMMs in bacterial adherence and entry into mammalian cells. Matrix Biol. 1999, 18, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaplina, O.; Bozhokina, E. Bacterial Outer Membrane Protein OmpX Regulates β1 Integrin and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Involved in Invasion of M-HeLa Cells by Serratia proteamaculans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Akiyama, S.K.; Yamada, K.M. Synergistic roles for receptor occupancy and aggregation in integrin transmembrane function. Science 1995, 267, 883–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 1992, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legate, K.R.; Wickstrom, S.A.; Fassler, R. Genetic and cell biological analysis of integrin outside-in signaling. Genes. Dev. 2009, 23, 397–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, L.; Venturino, M.; Bozzo, C.; Silengo, L.; Altruda, F.; Beguinot, L.; Tarone, G.; Defilippi, P. Integrins induce activation of EGF receptor: Role in MAP kinase induction and adhesion-dependent cell survival. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6622–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabodi, S.; Moro, L.; Bergatto, E.; Boeri Erba, E.; Di Stefano, P.; Turco, E.; Tarone, G.; Defilippi, P. Integrin regulation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and of EGF-dependent responses. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biscardi, J.S.; Maa, M.C.; Tice, D.A.; Cox, M.E.; Leu, T.H.; Parsons, S.J. c-Src-mediated phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor on Tyr845 and Tyr1101 is associated with modulation of receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8335–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Teramoto, H.; Gutkind, J.S.; Yamada, K.M. Integrins can collaborate with growth factors for phosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases and MAP kinase activation: Roles of integrin aggregation and occupancy of receptors. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, N.; Abreu, S.; Carvalho, F.A.; Fernandes, F.; Santos, N.C.; Fialho, A.M. Modulation of membrane properties of lung cancer cells by azurin enhances the sensitivity to EGFR-targeted therapy and decreased β1 integrin-mediated adhesion. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, Y.; Khaitlina, S.; Tsaplina, O. Involvement of Lipid Rafts in the Invasion of Opportunistic Bacteria Serratia into Eukaryotic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkel, M.E.; Samuelson, D.R.; Eucker, T.P.; Shelden, E.A.; O’Loughlin, J.L. Invasion of epithelial cells by Campylobacter jejuni is independent of caveolae. Cell Commun. Signal 2013, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eucker, T.P.; Konkel, M.E. The cooperative action of bacterial fibronectin-binding proteins and secreted proteins promote maximal Campylobacter jejuni invasion of host cells by stimulating membrane ruffling. Cell Microbiol. 2012, 14, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause-Gruszczynska, M.; Boehm, M.; Rohde, M.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Takahashi, S.; Buday, L.; Oyarzabal, O.A.; Backert, S. The signaling pathway of Campylobacter jejuni-induced Cdc42 activation: Role of fibronectin, integrin β1, tyrosine kinases and guanine exchange factor Vav2. Cell Commun. Signal 2011, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slanina, H.; Mundlein, S.; Hebling, S.; Schubert-Unkmeir, A. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in the interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with endothelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaplina, O.A. Redistribution of EGF receptor and α5, β1 integrins in response to infection of epithelial cells by Serratia proteamaculans. Cell Tissue Biol. 2020, 14, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J.; Zalyte, E.; Rimkus, A.; Dapkus, D.; Noreika, R.; Urbonavicius, S. JNK, p38, ERK, and SGK1 Inhibitors in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K. Cellular functions regulated by phosphorylation of EGFR on Tyr845. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10761–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, K.L.; Powell, K.; Madden, J.M.; Eblen, S.T.; Boerner, J.L. EGFR Tyrosine 845 Phosphorylation-Dependent Proliferation and Transformation of Breast Cancer Cells Require Activation of p38 MAPK. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Carr, B.I. Integrin α5-induced EGFR activation by prothrombin triggers hepatocyte apoptosis via the JNK signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 216, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, M.; Yasui, H.; Ohnishi, Y. Ligand-Independent EGFR Activation by Anchorage-Stimulated Src Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation and Cetuximab Resistance via ErbB3 Phosphorylation. Cancers 2019, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.J.; Schwarzbauer, J.E.; Boettiger, D. Distinct activation states of α5β1 integrin show differential binding to RGD and synergy domains of fibronectin. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 9063–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Relman, D.A.; Nishikawa, A. Invasion of human respiratory epithelial cells by Bordetella pertussis: Possible role for a filamentous hemagglutinin Arg-Gly-Asp sequence and α5β1 integrin. Microb. Pathog. 2001, 30, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Kim, B.J.; Paco, C.; Del Rosario, Y.; Courtney, H.S.; Doran, K.S. Identification of a group B streptococcal fibronectin binding protein, SfbA, that contributes to invasion of brain endothelium and development of meningitis. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2276–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaplina, O.; Lomert, E.; Berson, Y. Host-Cell-Dependent Roles of E-Cadherin in Serratia Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linggi, B.; Carpenter, G. ErbB receptors: New insights on mechanisms and biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikami, F.; Gu, H.; Jono, H.; Andalibi, A.; Kai, H.; Li, J.D. Epidermal growth factor receptor acts as a negative regulator for bacterium nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced Toll-like receptor 2 expression via an Src-dependent p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36185–36194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Cao, H.; Chaturvedi, R.; Krishna, U.; Hobbs, S.S.; Dempsey, P.J.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Cover, T.L.; Washington, M.K.; Wilson, K.T.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation protects gastric epithelial cells from Helicobacter pylori-induced apoptosis. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.V.; Griffiss, J.M.; Edwards, V.L.; Stein, D.C.; Song, W. Neisseria gonorrhoeae-induced transactivation of EGFR enhances gonococcal invasion. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, C.A.; Mezouar, S.; Mege, J.L. The E-Cadherin Cleavage Associated to Pathogenic Bacteria Infections Can Favor Bacterial Invasion and Transmigration, Dysregulation of the Immune Response and Cancer Induction in Humans. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancotti, F.G.; Ruoslahti, E. Integrin signaling. Science 1999, 285, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeri Erba, E.; Bergatto, E.; Cabodi, S.; Silengo, L.; Tarone, G.; Defilippi, P.; Jensen, O.N. Systematic analysis of the epidermal growth factor receptor by mass spectrometry reveals stimulation-dependent multisite phosphorylation. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2005, 4, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Mitra, S.K.; Ilic, D. Control of motile and invasive cell phenotypes by focal adhesion kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1692, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrutz, M.A.; Isberg, R.R. Involvement of focal adhesion kinase in invasin-mediated uptake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13658–13663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegtmeyer, N.; Hartig, R.; Delahay, R.M.; Rohde, M.; Brandt, S.; Conradi, J.; Takahashi, S.; Smolka, A.J.; Sewald, N.; Backert, S. A small fibronectin-mimicking protein from bacteria induces cell spreading and focal adhesion formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23515–23526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, S.; Dedhar, S.; Cleary, P.P. Paxillin phosphorylation: Bifurcation point downstream of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in streptococcal invasion. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legate, K.R.; Montanez, E.; Kudlacek, O.; Fassler, R. ILK, PINCH and parvin: The tIPP of integrin signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickstrom, S.A.; Lange, A.; Hess, M.W.; Polleux, J.; Spatz, J.P.; Kruger, M.; Pfaller, K.; Lambacher, A.; Bloch, W.; Mann, M.; et al. Integrin-linked kinase controls microtubule dynamics required for plasma membrane targeting of caveolae. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Streuli, C.H. An integrin-ILK-microtubule network orients cell polarity and lumen formation in glandular epithelium. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, Y.M.; Bozhokina, E.S.; Tsaplina, O.A. The role of microtubules and microfilaments in the invasion of eukaryotic cells by bacteria Serratia grimesii and Serratia proteamaculans. Cell Tissue Biol. 2025, 19, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yurecko, R.S.; Dedhar, S.; Cleary, P.P. Integrin-linked kinase is an essential link between integrins and uptake of bacterial pathogens by epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeri, V.; Rosenshine, I.; Ben-Ze’Ev, A.; Bokoch, G.M.; Jou, T.S.; Hanski, E. De novo formation of focal complex-like structures in host cells by invading Streptococci. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watarai, M.; Funato, S.; Sasakawa, C. Interaction of Ipa proteins of Shigella flexneri with α5β1 integrin promotes entry of the bacteria into mammalian cells. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isberg, R.R.; Hamburger, Z.; Dersch, P. Signaling and invasin-promoted uptake via integrin receptors. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.J.; Takagi, J.; Boettiger, D. Two-stage activation for α5β1 integrin binding to surface-adsorbed fibronectin. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34710–34715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneres, J.L.; Roquet, F.; Martin, A.; Parello, J. A minimized human integrin α5β1 that retains ligand recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5888–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttobene, M.R.; Schachter, J.; Alvarez, C.L.; Saffioti, N.A.; Leal Denis, M.F.; Kessler, H.; Garcia Vescovi, E.; Schwarzbaum, P.J. ShlA toxin of Serratia induces P2Y2- and α5β1-dependent autophagy and bacterial clearance from host cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFlamme, S.E.; Akiyama, S.K.; Yamada, K.M. Regulation of fibronectin receptor distribution. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 117, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plopper, G.E.; McNamee, H.P.; Dike, L.E.; Bojanowski, K.; Ingber, D.E. Convergence of integrin and growth factor receptor signaling pathways within the focal adhesion complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 1995, 6, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, L.; Dolce, L.; Cabodi, S.; Bergatto, E.; Boeri Erba, E.; Smeriglio, M.; Turco, E.; Retta, S.F.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Venturino, M.; et al. Integrin-induced epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor activation requires c-Src and p130Cas and leads to phosphorylation of specific EGF receptor tyrosines. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9405–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidyuk, I.V.; Kalashnikov, A.E.; Gromova, T.Y.; Gasanov, E.V.; Safina, D.R.; Zabolotskaya, M.V.; Rudenskaya, G.N.; Kostrov, S.V. Cloning, sequencing, expression, and characterization of protealysin, a novel neutral proteinase from Serratia proteamaculans representing a new group of thermolysin-like proteases with short N-terminal region of precursor. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 47, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouty, A.M.; Gunn, J.S. Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium invasion is repressed in the presence of bile. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6763–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target Gene | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|
| α5 integrin | Forward 5′-GGCTTCAACTTAGACGCGGA-3′ |
| Reverse 5′-AAGCCTCCTTGGCAGTAACC-3′ | |
| β1 integrin | Forward 5′-GACGCCGCGCGGAAAAG-3′ |
| Reverse 5′-ATCTGGAGGGCAACCCTTCT-3′ | |
| EGFR | Forward 5′-GTGCAGCTTCAGGACCACAA-3′ |
| Reverse 5′-AAATGCATGTGTCGAATATCTTGAG-3′ | |
| β-actin | Forward 5′-AATCTGGCACCACACCTTCTACA-3′ |
| Reverse 5′-GACGTAGCACAGCTTCTCGTTA-3′ | |
| GADPH | Forward 5′-GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG-3′ |
| Reverse 5′-TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsaplina, O. Interaction of Serratia proteamaculans with Integrins Activates Invasion-Promoting Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093955
Tsaplina O. Interaction of Serratia proteamaculans with Integrins Activates Invasion-Promoting Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093955
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsaplina, Olga. 2025. "Interaction of Serratia proteamaculans with Integrins Activates Invasion-Promoting Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093955
APA StyleTsaplina, O. (2025). Interaction of Serratia proteamaculans with Integrins Activates Invasion-Promoting Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093955







