Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Regulation of Immune Responses and Fibrosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
Liver’s Unique Role in Immune Regulation and the Critical Function of LSECs
2. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells: Structure and Function
2.1. Anatomy and Physiology of LSECs
2.2. Interaction of LSECs with Other Hepatic Cells: Kupffer Cells, HSCs, and Hepatocytes
3. LSECs in Immune Regulation
3.1. Antigen Presentation and Immune Tolerance
3.2. LSECs and Immune Cell Communication
3.2.1. Interaction with T Cells
3.2.2. Interaction with Kupffer Cells
3.3. Role of LSECs in Liver Diseases
3.3.1. Critical Role of LSECs in MAFLD
3.3.2. Role of LSECs in Cirrhosis
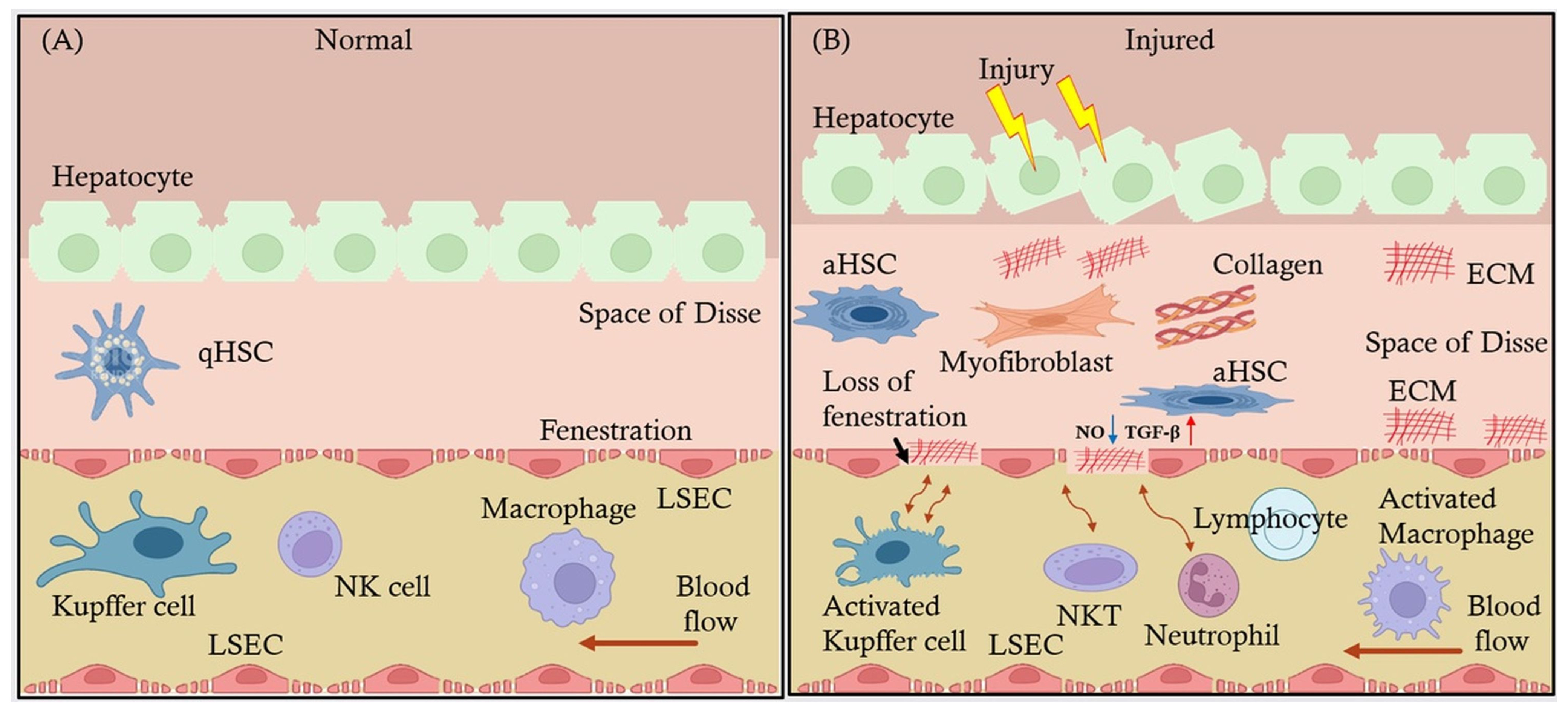
4. LSECs in Liver Fibrosis
4.1. LSECs’ Influence on Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Collagen Deposition Leading to Fibrosis
4.2. Signaling Pathways Involved in LSEC-Mediated Fibrosis and Endothelial Dysfunction
4.3. Changes in LSECs’ Phenotype Exacerbate Liver Scarring
4.4. LSECs in Liver Disease Progression
4.5. Interplay Between LSECs and Other Liver Cells During Liver Disease Progression
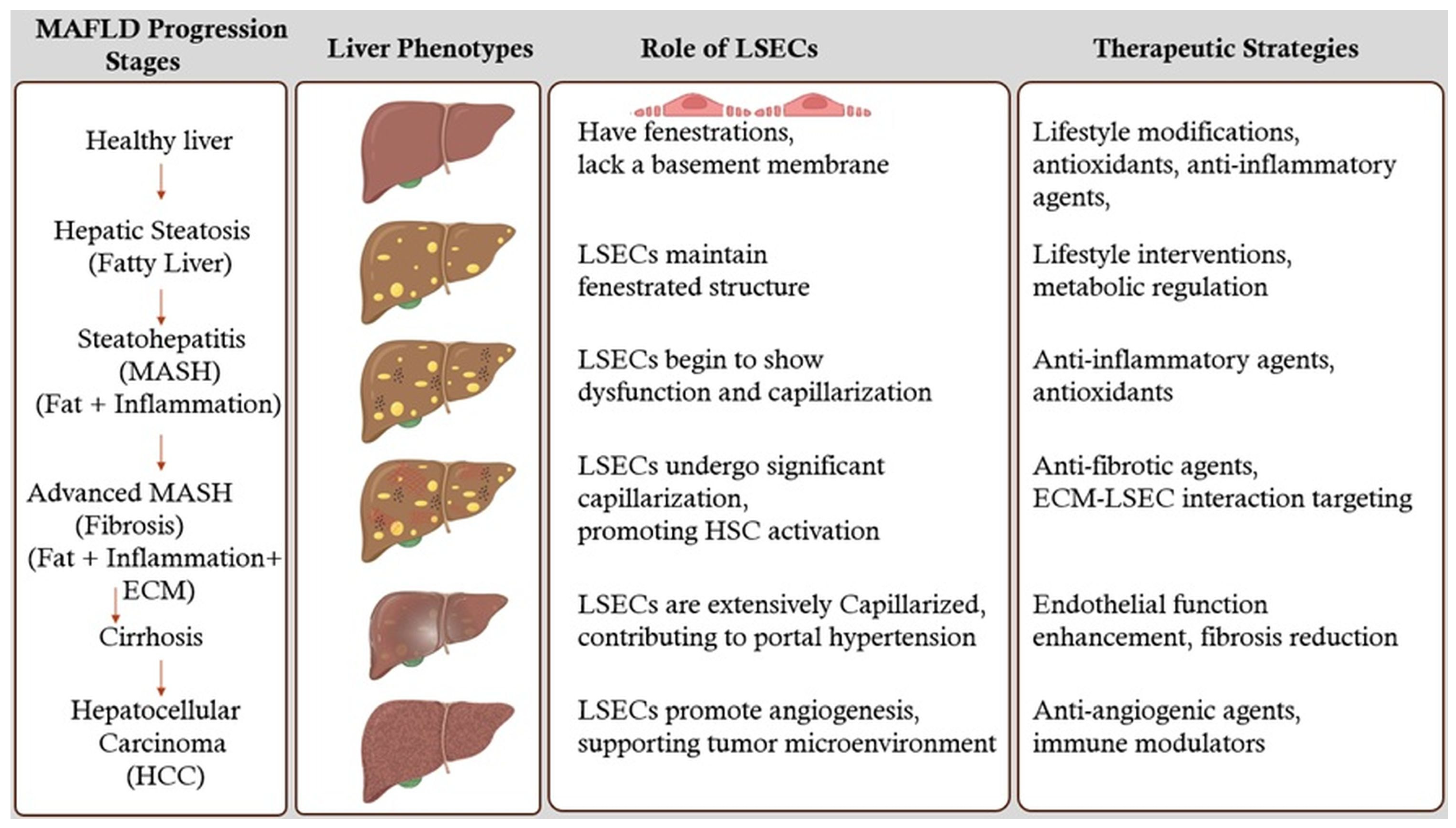
5. Stages of MAFLD Liver and Therapeutic Strategies
5.1. Healthy Liver
5.2. Hepatic Steatosis (Fatty Liver)
5.3. Steatohepatitis (MASH) (Fat + Inflammation)
5.4. Advanced MASH (Fibrosis) (Fat + Inflammation + ECM)
5.5. Cirrhosis
5.6. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
6. LSECs as Therapeutic Target
6.1. Therapeutic Approaches Targeting LSECs to Prevent or Reverse Liver Fibrosis and Modulate Immune Responses
6.2. Potential Therapeutic Approaches Targeting LSECs
6.2.1. Restoration of LSECs’ Phenotype and Function
- Vasoactive Agents: Agents such as VEGF and NO donors can promote the maintenance of LSECs’ fenestrations and prevent capillarization. Enhancing VEGF signaling has been shown to sustain LSECs’ differentiation and function [17].
- Shear Stress Modulators: LSECs respond to shear stress induced by blood flow. Modulating shear stress through mechanical or pharmacological means can influence LSECs’ phenotype and prevent fibrosis progression [53].
6.2.2. Inhibition of Pro-Fibrotic Signaling Pathways
- TGF-β Signaling Inhibitors: TGF-β is a key cytokine involved in HSCs activation. Inhibiting TGF-β signaling in LSECs can reduce their pro-fibrotic influence on HSCs. TGF-β serves a dual role in the immune system and liver pathology. As an anti-inflammatory cytokine, it promotes immune tolerance by supporting regulatory T cell differentiation and suppressing pro-inflammatory responses. This mechanism is critical for maintaining immune homeostasis in normal LSECs and limiting inflammation-driven tissue damage during early stages of liver disease [54].
- Notch Pathway Modulators: The Notch signaling pathway in LSECs influences vascular remodeling and fibrogenesis. Modulating Notch signaling may attenuate fibrotic responses [55].
6.2.3. Modulation of Immune Responses
- Immune Checkpoint Modulators: targeting immune checkpoints such as PD-L1 on LSECs can regulate T cell responses, reducing chronic inflammation and fibrogenesis [56].
- Cytokine Therapy: administering anti-inflammatory cytokines or inhibitors of pro-inflammatory cytokines can rebalance the immune milieu toward fibrosis resolution [57].
6.3. Current and Emerging Treatments Targeting LSECs
6.3.1. Pharmacological Agents Enhancing LSECs’ Function
- Statins: Beyond their lipid-lowering effects, statins have been shown to improve endothelial function. In LSECs, statins can enhance nitric oxide production, maintain fenestrations, and inhibit HSC activation. Clinical studies have suggested that statin therapy may slow fibrosis progression in chronic liver diseases [58].
- Angiogenesis Inhibitors: While angiogenesis is often associated with pathological conditions, controlled inhibition can prevent aberrant vascular remodeling in fibrosis. Agents targeting VEGF receptors may help maintain LSECs structure and function [59].
- FXR Agonists: Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists, such as obeticholic acid, have hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic effects. They modulate bile acid metabolism and exhibit anti-inflammatory properties that indirectly benefit LSECs’ function [60].
6.3.2. Antifibrotic Therapies Targeting the Fibrotic Cascade
- Pirfenidone and Nintedanib: approved for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, these agents have shown potential in liver fibrosis by inhibiting fibrogenic pathways, including those mediated by LSECs [61].
- Galectin-3 Inhibitors: Galectin-3 is involved in fibrogenesis and inflammation. Inhibiting galectin-3 can reduce HSCs activation and ECM production, with beneficial effects on LSECs’ function [62]. More potent and specific inhibitors are currently being developed to enhance therapeutic outcomes [63].
6.3.3. Regenerative and Cell-Based Therapies
- Stem Cell Therapy: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) can differentiate into functional LSECs, promoting vascular repair and reducing fibrosis [64].
- Gene Therapy: delivery of genes encoding protective factors such as VEGF or antifibrotic proteins to LSECs can enhance their regenerative capacity and inhibit fibrogenic signaling [65].
6.3.4. Nanotechnology and Targeted Drug Delivery
- LSEC-Targeted Nanoparticles: utilizing ligands that bind to receptors uniquely expressed on LSECs, such as mannose receptors, allows for precise delivery of antifibrotic drugs or siRNA molecules to these cells [66].
- Controlled Release Systems: nanotechnology-enabled systems can provide sustained release of therapeutic agents, ensuring prolonged LSECs modulation and fibrosis inhibition.
6.3.5. Biomolecular Inhibitors and Small Molecules
- MicroRNA Modulators: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression in LSECs. Therapeutics that mimic or inhibit specific miRNAs can alter LSECs’ behavior to favor antifibrotic outcomes [67].
- Small Molecule Inhibitors: Identifying small molecules that inhibit profibrotic enzymes or signaling molecules. LSECs can provide targeted antifibrotic effects [68].
6.4. Clinical Implications
- Biomarker Development: identifying reliable biomarkers for LSECs dysfunction can aid in patient stratification and monitoring therapeutic responses [69].
- Combination Therapies: combining LSEC-targeted therapies with other antifibrotic agents may produce synergistic effects, enhancing overall treatment efficacy [70].
- Personalized Medicine: tailoring therapies based on individual patient profiles and specific LSECs pathophysiology could optimize treatment outcomes.
- Clinical Trials: rigorous clinical testing of emerging therapies is essential to establish safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing strategies for patients with liver fibrosis [71].
7. Current Challenges and Future Directions
7.1. Gaps in the Current Understanding of LSECs in Liver Disease
7.2. LSECs Dysfunction in Liver Disease
7.3. Unifying Hypothesis of LSECs-Mediated Pathology in MAFLD
7.4. Emerging Research Areas
7.5. Future Research Directions: Role of LSECs in Liver Regeneration and Transplantation
8. Limitations
8.1. Hurdles in Studying LSECs
8.2. Translational Obstacles
9. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shetty, S.; Lalor, P.F.; Adams, D.H. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells—Gatekeepers of Hepatic Immunity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.-E. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells: Physiology and Role in Liver Diseases. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A.; Wohlleber, D. Immunological Functions of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Immunology in the Liver—from Homeostasis to Disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the Epidemic of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Demonstrates an Exponential Increase in Burden of Disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-K.; Chuah, K.-H.; Rajaram, R.B.; Lim, L.-L.; Ratnasingam, J.; Vethakkan, S.R. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskridge, W.; Cryer, D.R.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Malhi, H.; Allen, A.M.; Noureddin, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: The Patient and Physician Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Larsen, A.K.; McCourt, P.; Smedsrød, B.; Sørensen, K.K. The Scavenger Function of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 757469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Brenner, D.A. Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogliati, B.; Yashaswini, C.N.; Wang, S.; Sia, D.; Friedman, S.L. Friend or Foe? The Elusive Role of Hepatic Stellate Cells in Liver Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyao, M.; Kotani, H.; Ishida, T.; Kawai, C.; Manabe, S.; Abiru, H.; Tamaki, K. Pivotal Role of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in NAFLD/NASH Progression. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeve, L.D. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells and Liver Regeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, L.; Esser, H.; Huch, M.; Forbes, S. Liver Regeneration and Inflammation: From Fundamental Science to Clinical Applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-K.; Peng, Z.-G. Targeting Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells: An Attractive Therapeutic Strategy to Control Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 655557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, L. The Crosstalk Between Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells and Hepatic Microenvironment in NASH Related Liver Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 936196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, K.; Guo, Q.; Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H. Emerging Roles of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Biology 2020, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, M.J.; Kostallari, E.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Iwakiri, Y. The Evolving Role of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Liver Health and Disease. Hepatology 2023, 78, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.-S.; Lee, K.H.; Goerdt, S.; Augustin, H.G. Angiodiversity and Organotypic Functions of Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Angiogenesis 2021, 24, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrfeld, C.; Zenner, S.; Kornek, M.; Lukacs-Kornek, V. The Contribution of Non-Professional Antigen-Presenting Cells to Immunity and Tolerance in the Liver. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-García, C.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Arráez-Aybar, L.A.; Nevzorova, Y.A.; Cubero, F.J. The Space of Disse: The Liver Hub in Health and Disease. Livers 2021, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, A.L.; Qurashi, M.; Shetty, S. The Role of Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Axis of Inflammation and Cancer Within the Liver. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, O.; Phillips, A.; Ruggiero, K.; Bartlett, A.; Dunbar, P.R. Immunofluorescence Identifies Distinct Subsets of Endothelial Cells in the Human Liver. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacke, F.; Zimmermann, H.W. Macrophage Heterogeneity in Liver Injury and Fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Malhi, H. Macrophage Heterogeneity in NASH: More Than Just Nomenclature. Hepatology 2021, 74, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeve, L.D. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Hepatic Fibrosis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Intercellular Crosstalk of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafranska, K.; Kruse, L.D.; Holte, C.F.; McCourt, P.; Zapotoczny, B. The wHole Story About Fenestrations in LSEC. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 735573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; He, W.; Dong, H.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, G.; Shi, X.; Wang, D.; Lu, F. Role of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasa, E.; Hartmann, P.; Schnabl, B. Liver Cirrhosis and Immune Dysfunction. Int. Immunol. 2022, 34, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Niu, J. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells Are Implicated in Multiple Fibrotic Mechanisms. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 2803–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.-P.; Ge, J.-Y.; Song, Y.-M.; Yu, X.-Q.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Ye, D.; Zheng, Y.-W. A Novel Efficient Strategy to Generate Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, A.K.; Neumann, K.; Diehl, L.; Tiegs, G. Modulation of Liver Tolerance by Conventional and Nonconventional Antigen-Presenting Cells and Regulatory Immune Cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limmer, A.; Ohl, J.; Kurts, C.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Reiss, Y.; Groettrup, M.; Momburg, F.; Arnold, B.; Knolle, P.A. Efficient Presentation of Exogenous Antigen by Liver Endothelial Cells to CD8+ T Cells Results in Antigen-Specific T-Cell Tolerance. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Y.; Flavell, R.A. TGF-β and Regulatory T Cell in Immunity and Autoimmunity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Immune Surveillance by the Liver. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; Schwabe, R.F. Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis: Functional Links and Key Pathways. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Li, J.-M.; Liu, M.-K.; Zhang, T.-T.; Wang, D.-P.; Zhou, W.-H.; Hu, L.-Z.; Lv, W.-L. Pathological Process of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Liver Diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7666–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell: An Important yet Often Overlooked Player in the Liver Fibrosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zuo, B.; He, Y. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells as Potential Drivers of Liver Fibrosis (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Seki, E. The Liver Fibrosis Niche: Novel Insights into the Interplay between Fibrosis-Composing Mesenchymal Cells, Immune Cells, Endothelial Cells, and Extracellular Matrix. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Duan, J.-L.; Xu, H.; Tao, K.-S.; Han, H.; Dou, G.-R.; Wang, L. Capillarized Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells Undergo Partial Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition to Actively Deposit Sinusoidal ECM in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 671081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkız, H.; Gieseler, R.K.; Canbay, A. Liver Fibrosis: From Basic Science towards Clinical Progress, Focusing on the Central Role of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elpek, G.Ö. Angiogenesis and Liver Fibrosis. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allameh, A.; Niayesh-Mehr, R.; Aliarab, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; Yi, Q.; Tang, L. Liver Fibrosis Resolution: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeve, L.D.; Maretti-Mira, A.C. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell: An Update. Semin. Liver Dis. 2017, 37, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Li, X.; Slevin, E.; Harrison, K.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Klaunig, J.E.; Wu, C.; Shetty, A.K.; Dong, X.C.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Pathological Processes of Chronic Liver Disease during Aging. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Y.; Yuan, W.-G.; He, P.; Lei, J.-H.; Wang, C.-X. Liver Fibrosis and Hepatic Stellate Cells: Etiology, Pathological Hallmarks and Therapeutic Targets. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10512–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, Y. Unlocking the Role of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells: Key Players in Liver Fibrosis: Editorial on “Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell: An Important yet Often Overlooked Player in the Liver Fibrosis”. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, M. Spatial Computational Hepatic Molecular Biomarker Reveals LSEC Role in Midlobular Liver Zonation Fibrosis in DILI and NASH Liver Injury. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 4, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyzynska-Cichon, I.; Kotlinowski, J.; Blacharczyk, O.; Giergiel, M.; Szymanowski, K.; Metwally, S.; Wojnar-Lason, K.; Dobosz, E.; Koziel, J.; Lekka, M.; et al. Early and Late Phases of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell (LSEC) Defenestration in Mouse Model of Systemic Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, D.; Maude, H.; Birdsey, G.M.; Randi, A.M.; Cebola, I. RISING STARS: Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Transcription Factors in Metabolic Homeostasis and Disease. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2023, 71, e230026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soydemir, S.; Comella, O.; Abdelmottaleb, D.; Pritchett, J. Does Mechanocrine Signaling by Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells Offer New Opportunities for the Development of Anti-Fibrotics? Front. Med. 2020, 6, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schon, H.-T.; Weiskirchen, R. Immunomodulatory Effects of Transforming Growth Factor-β in the Liver. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, F.; Strazzabosco, M. Emerging Roles of Notch Signaling in Liver Disease. Hepatology 2015, 61, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurje, I.; Hammerich, L.; Tacke, F. Dendritic Cell and T Cell Crosstalk in Liver Fibrogenesis and Hepatocarcinogenesis: Implications for Prevention and Therapy of Liver Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignold, R.; Johnson, J.R. Effects of Cytokine Signaling Inhibition on Inflammation-Driven Tissue Remodeling. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2021, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.; Raurell, I.; Hide, D.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Gil, M.; Barberá, A.; Salcedo, M.T.; Augustin, S.; Genescà, J.; Martell, M. Restoration of Liver Sinusoidal Cell Phenotypes by Statins Improves Portal Hypertension and Histology in Rats with NASH. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Bokov, D.; Markov, A.; Jalil, A.T.; Shalaby, M.N.; Suksatan, W.; Chupradit, S.; AL-Ghamdi, H.S.; Shomali, N.; Zamani, A.; et al. Cancer Combination Therapies by Angiogenesis Inhibitors; a Comprehensive Review. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Li, X.; Fan, G.; Liu, R. Targeting Bile Acid Signaling for the Treatment of Liver Diseases: From Bench to Bed. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bayliss, G.; Zhuang, S. Application of Nintedanib and Other Potential Anti-Fibrotic Agents in Fibrotic Diseases. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, N.C.; Mackinnon, A.C.; Farnworth, S.L.; Poirier, F.; Russo, F.P.; Iredale, J.P.; Haslett, C.; Simpson, K.J.; Sethi, T. Galectin-3 Regulates Myofibroblast Activation and Hepatic Fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5060–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, A.; Magnani, J.L. Clinical Trials and Applications of Galectin Antagonists. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 2018, 30, SE211–SE220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Mao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wei, J.; Yao, J. Stem Cells for Treatment of Liver Fibrosis/Cirrhosis: Clinical Progress and Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-L.; Zheng, X.-L.; Li, Q.-S.; Liu, W.-Y.; Hu, L.-S.; Sha, H.-C.; Guo, K.; Lv, Y.; Wang, B. The Effect of Aging on VEGF/VEGFR2 Signal Pathway Genes Expression in Rat Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carambia, A.; Gottwick, C.; Schwinge, D.; Stein, S.; Digigow, R.; Şeleci, M.; Mungalpara, D.; Heine, M.; Schuran, F.A.; Corban, C.; et al. Nanoparticle-Mediated Targeting of Autoantigen Peptide to Cross-Presenting Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells Protects from CD8 T-Cell-Driven Autoimmune Cholangitis. Immunology 2021, 162, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouve, M.; Carpentier, R.; Kraiem, S.; Legrand, N.; Sobolewski, C. MiRNAs in Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward New Therapeutic Approaches? Cancers 2023, 15, 5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, A.; Kothari, A.; Sarma, P.; Medhi, B.; Omar, B.J.; Kaushal, K. Recent Advancements in Antifibrotic Therapies for Regression of Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2022, 11, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Ribera, M.; Gibert-Ramos, A.; Abad-Jordà, L.; Magaz, M.; Téllez, L.; Paule, L.; Castillo, E.; Pastó, R.; de Souza Basso, B.; Olivas, P.; et al. Increased Sinusoidal Pressure Impairs Liver Endothelial Mechanosensing, Uncovering Novel Biomarkers of Portal Hypertension. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Racanelli, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; Ding, B.; et al. Targeting Fibrosis: Mechanisms and Clinical Trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautwein, C.; Friedman, S.L.; Schuppan, D.; Pinzani, M. Hepatic Fibrosis: Concept to Treatment. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S15–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, M. Automated Machine Learning Diagnostic Support System as a Computational Biomarker for Detecting Drug-Induced Liver Injury Patterns in Whole Slide Liver Pathology Images. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2020, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwokoye, P.N.; Abilez, O.J. Bioengineering Methods for Vascularizing Organoids. Cell Rep. Methods 2024, 4, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathiri, E.; Prakash, P.; Kumaravel, P.; Jayaprakash, J.; Ragunathan, M.G.; Sankar, S.; Pandiaraj, S.; Thirumalaivasan, N.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Govindasamy, R. Computational Approaches for Modeling and Structural Design of Biological Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Prog Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2023, 185, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kidambi, S.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Thuy, L.T.T.; Nieto, N.; Cogger, V.C.; Xie, W.-F.; Tacke, F.; Gracia-Sancho, J. In Vitro Models for the Study of Liver Biology and Diseases: Advances and Limitations. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 15, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, N.; Kundu, B.; Kundu, S.C.; Reis, R.L.; Correlo, V. In Vitro Cancer Models: A Closer Look at Limitations on Translation. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic Approaches | Emerging Treatments | Drug Examples and Roles | Future Directions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vasoactive Agents | Statins, Angiogenesis Inhibitors, FXR Agonists | Promote vascular stability and reduce fibrosis (e.g., Simvastatin). | Investigate how these treatments can restore LSEC function to improve overall hepatic microcirculation. |
| Shear Stress Modulators | Pirfenidone, Nintedanib, Galectin-3 Inhibitors | Modulate fibrosis progression (e.g., Nintedanib for antifibrotic effects). | Examine their ability to alleviate shear stress-induced damage to LSECs and enhance endothelial integrity. |
| TGF-β Signaling Inhibitors | Stem Cell Therapy, Gene Therapy | SB431542, LY2109761 to enhance stem cell engraftment and gene delivery. | Explore their role in creating an LSEC-supportive microenvironment for regenerative therapies. |
| Notch Pathway Modulators | LSEC-Targeted Nanoparticles, Controlled Release Systems | γ-secretase inhibitors (DAPT, MK-0752), Monoclonal Antibodies (OMP-59R5) to modulate LSEC dysfunction. | Investigate how targeting Notch signaling can reverse LSEC capillarization and promote vascular repair. |
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors | MicroRNA Modulators, Small Molecule Inhibitors | Nivolumab (anti-PD-1), Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) to modulate immune responses and reduce liver inflammation. | Study their effects on reducing chronic inflammation and improving LSEC-mediated immune tolerance. |
| Cytokine Therapy | Combination Therapies (with emerging treatments like stem cell therapy) | Leverage cytokines to improve immune regulation in combination with other therapeutic approaches. | Investigate their potential in modulating LSEC-related inflammatory responses for better therapeutic outcomes. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puri, M.; Sonawane, S. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Regulation of Immune Responses and Fibrosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093988
Puri M, Sonawane S. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Regulation of Immune Responses and Fibrosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093988
Chicago/Turabian StylePuri, Munish, and Snehal Sonawane. 2025. "Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Regulation of Immune Responses and Fibrosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093988
APA StylePuri, M., & Sonawane, S. (2025). Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Regulation of Immune Responses and Fibrosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093988







