Determining the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes for rs1801133 Genotypes in Multiethnic Populations: A Global Meta-Epidemiological Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
2.1. Study Selection and Identification
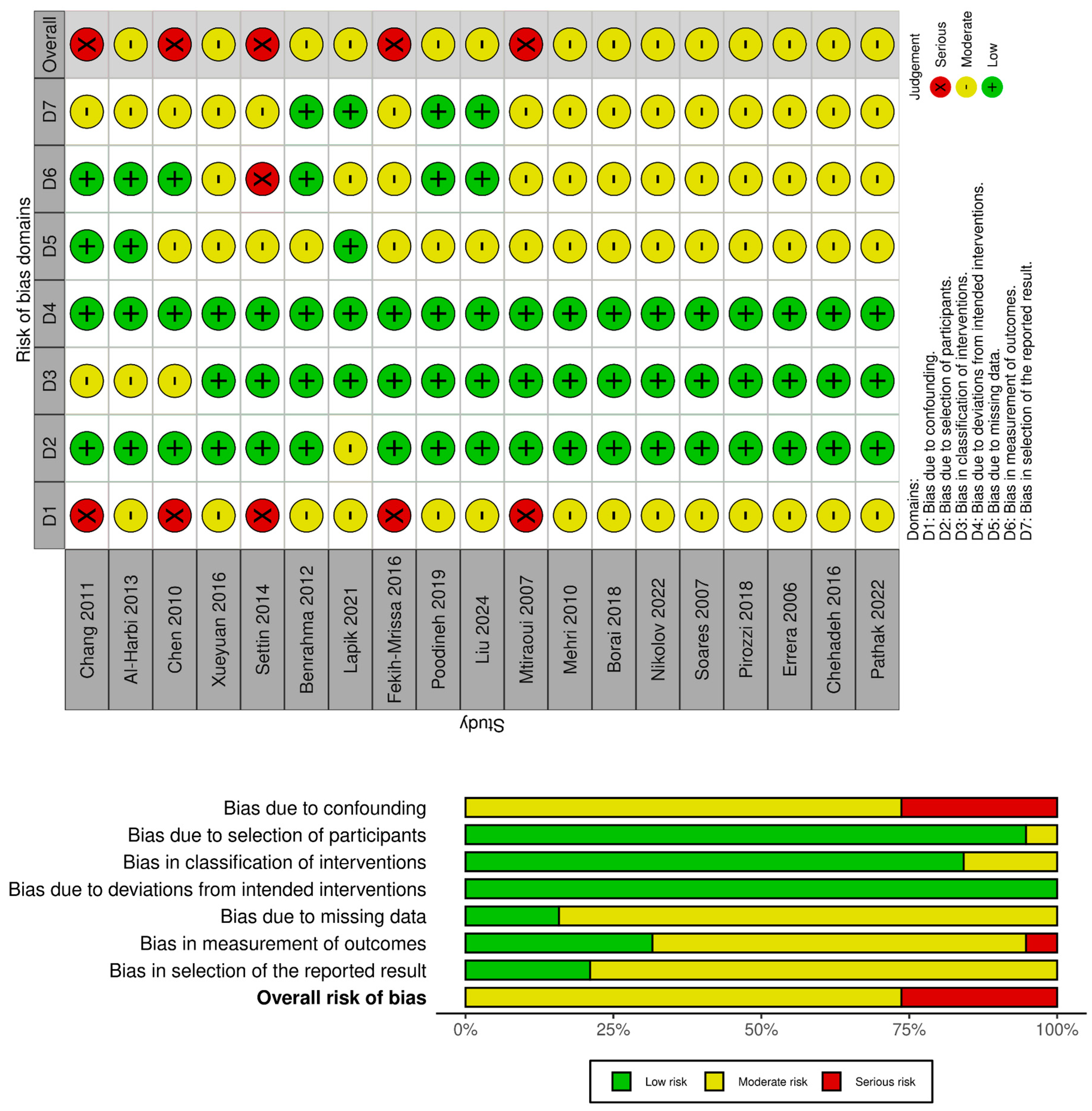
2.2. Risk of Bias Analysis
2.3. Summary of Included Studies
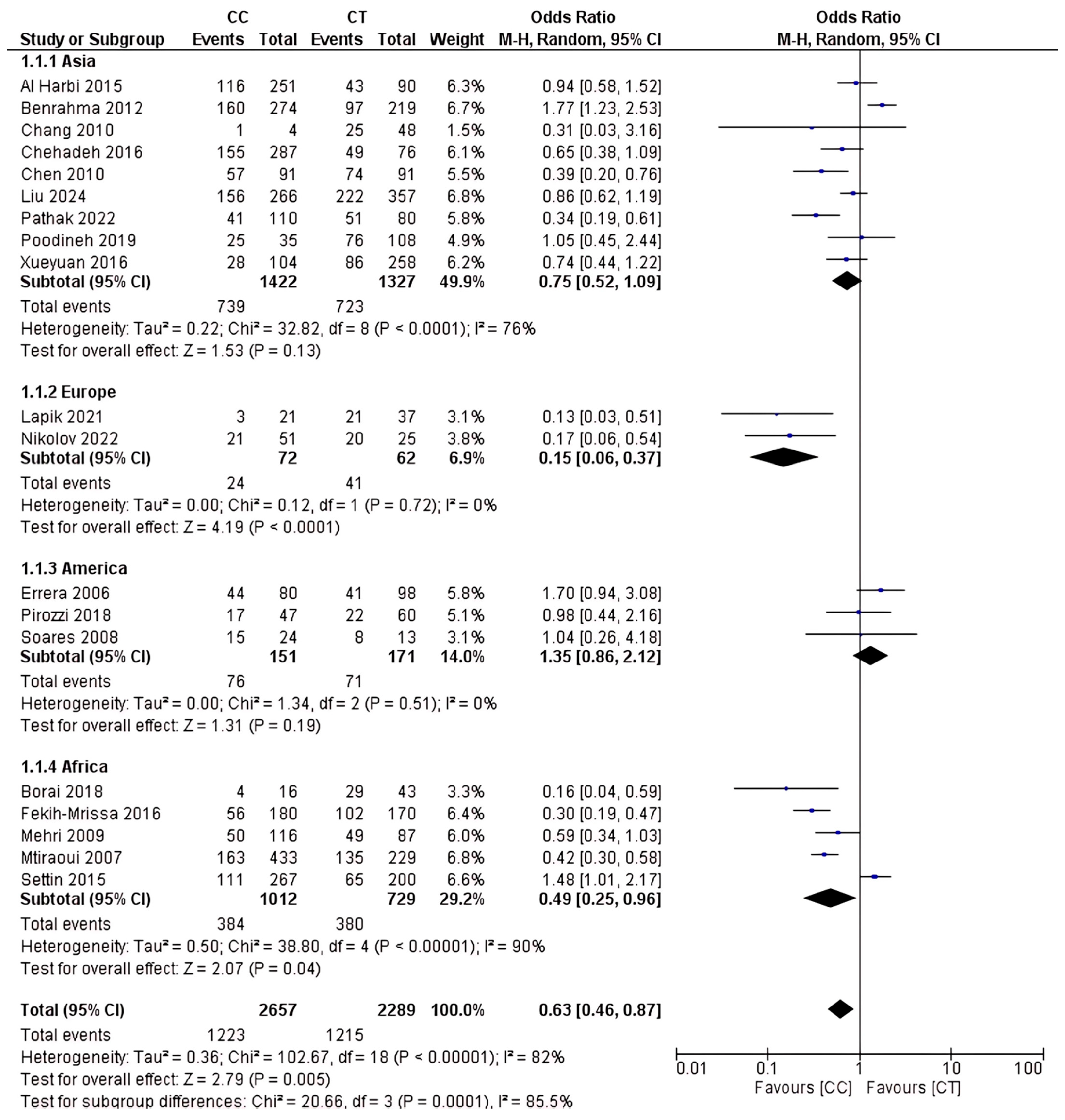
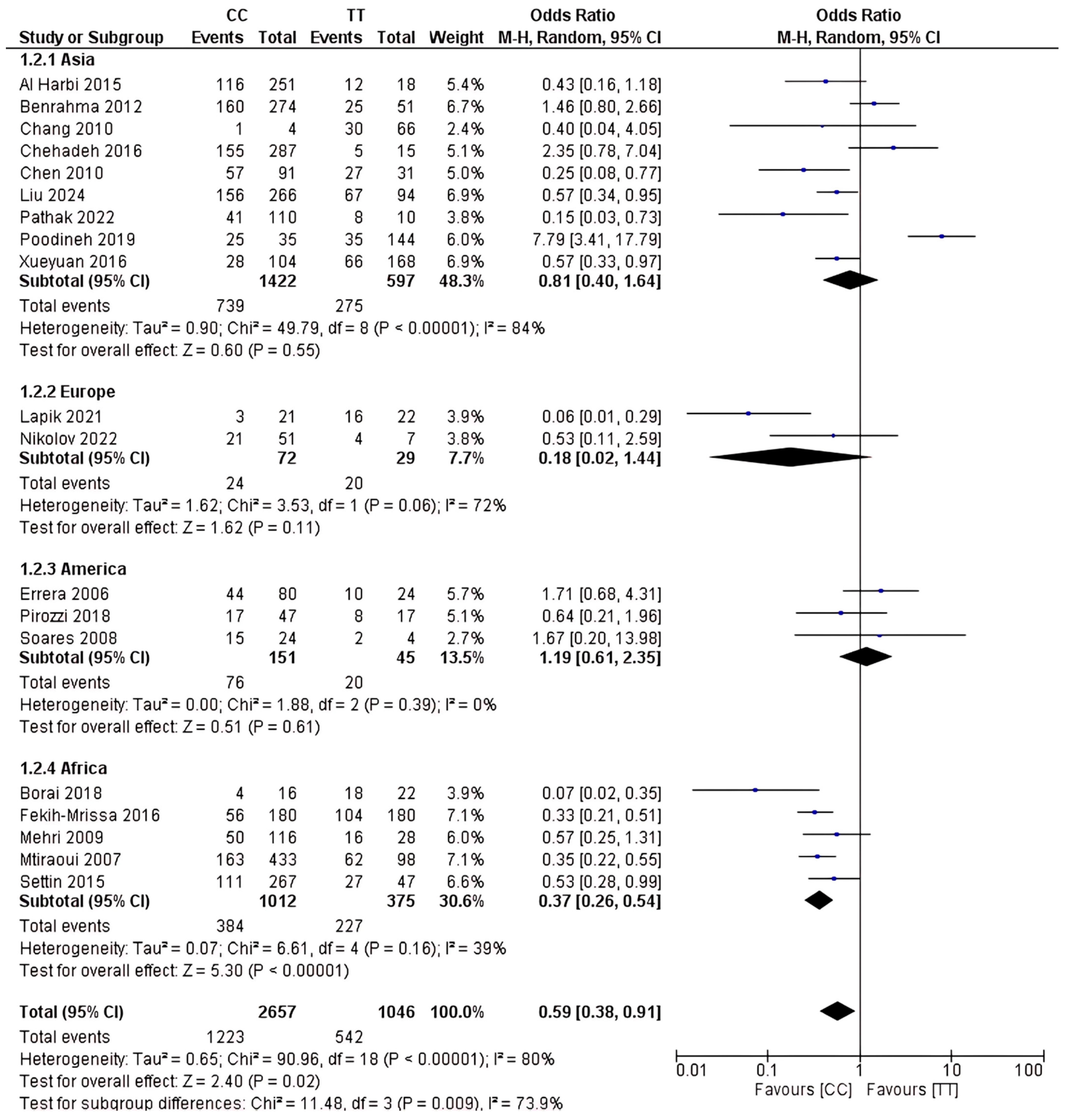
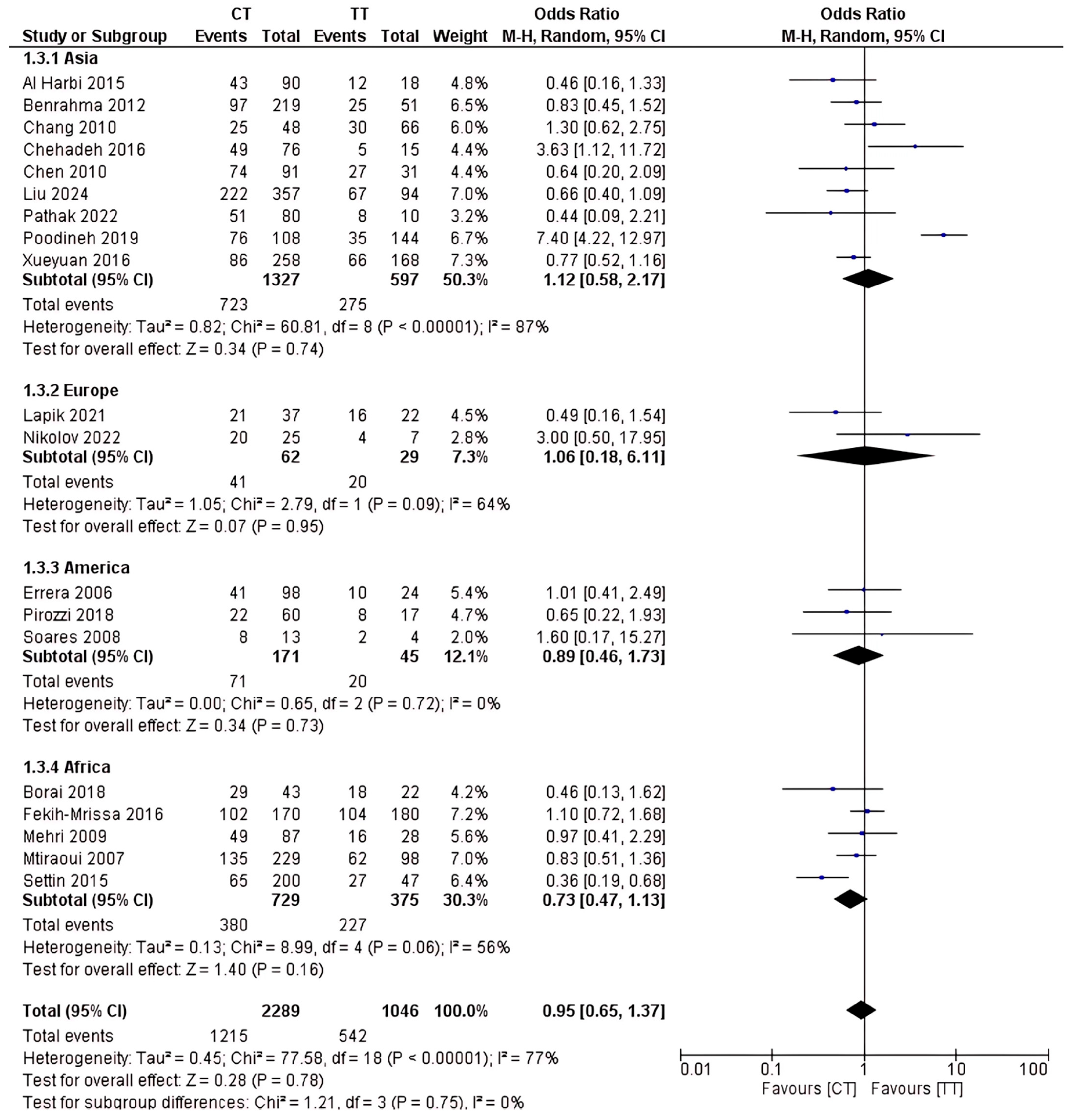
2.4. Analysis of rs1801133 Polymorphism
3. Discussion
3.1. SNP Correlation with Type 2 Diabetes
3.2. Dominant Genotype
3.3. Other Contributing Factors
3.4. Limitation
4. Method
4.1. Aims and Research Questions
- What is the overall association between the rs1801133 polymorphism and the risk of T2D in the global population?
- Does the contribution to T2D risk differ between the CC, CT, and TT genotypes?
- How does the strength of association vary across different continents (Asia, Africa, Europe, and America)?
- What are the potential implications of these genetic findings for population-specific screening and lifestyle-based prevention strategies?
4.2. Eligibility Criteria
4.3. Search Strategy and Screening
4.4. Data Extraction and Analysis
4.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
4.6. Quantitative Analysis
4.7. Intervention of Interest
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| T2D | Type 2 Diabetes |
| MTHFR | Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase |
| SAM | S-adenosylmethionine |
| SNP | Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| lncRNA | Long Non-Coding RNA |
| UTR | Untranslated Region |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| NETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| IR | Insulin Receptor |
| C-Hcy | Cysteine-homocysteinylation |
| UCS | Unpredictable Chronic Stressor |
| IL | Interleukin |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| ADRB | Beta-Adrenergic Receptor |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| ROBINS-I | Risk Of Bias In Non-randomised Studies–of Interventions |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
References
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinajero, M.G.; Malik, V.S. An Update on the Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes: A Global Perspective. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, D.; Shrivastav, D.; Verma, A.K.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Yadav, P.; Khan, N.H.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; Khan, M.I.; Bihade, K.; Singh, D.D.; et al. Role of Metabolizing MTHFR Gene Polymorphism (Rs1801133) and Its MRNA Expression among Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, K.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M.; Zhao, M.; Guan, M.-X.; Qin, G. Association of MTHFR C677T Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Susceptibility. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, G.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, K.; Wang, S.; Liang, X.; Hu, S.; Sun, S.; Lai, M. Association Analysis of MTHFR (Rs1801133 and Rs1801131) Gene Polymorphism towards the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Dali Area Population from Yunnan Province, China. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangelosi, G.; Grappasonni, I.; Nguyen, C.T.T.; Acito, M.; Pantanetti, P.; Benni, A.; Petrelli, F. Mediterranean Diet (MedDiet) and Lifestyle Medicine (LM) for Support and Care of Patients with Type II Diabetes in the COVID-19 Era: A Cross-Observational Study. Acta Biomed. 2023, 94, e2023189. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela, P.L.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Saco-Ledo, G.; Castillo-García, A.; Lucia, A. Obesity, Cardiovascular Risk, and Lifestyle: Cross-Sectional and Prospective Analyses in a Nationwide Spanish Cohort. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azrak, M.Á.; Fasano, M.V.; Avico, A.J.; Sala, M.; Casado, C.; Padula, M.; Kruger, A.L.; Malpeli, A.; Andreoli, M.F. Prolonged Body Weight Gain, Lifestyle Changes and Health-Related Quality of Life in Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown: A Follow-up Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 77, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, E.M.; Farid, E.M.; Gumaa, K.A.; Darwish, A.H.; Alenizi, M.; Singh, J. Genetic Combination of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme with Methylene Tetrahydrofolate Reductase Polymorphisms and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Bahrain. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015, 16, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benrahma, H.; Abidi, O.; Melouk, L.; Ajjemami, M.; Rouba, H.; Chadli, A.; Oudghiri, M.; Farouqui, A.; Barakat, A. Association of the C677T Polymorphism in the Human Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Gene with the Genetic Predisposition for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Moroccan Population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2012, 16, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Fu, W.-M.; Wu, Y.-H.; Yeh, C.-J.; Huang, C.-N.; Shiau, M.-Y. Prevalence of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase C677T and A1298C Polymorphisms in Taiwanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajj Chehadeh, S.W.; Jelinek, H.F.; Al Mahmeed, W.A.; Tay, G.K.; Odama, U.O.; Elghazali, G.E.B.; Al Safar, H.S. Relationship between MTHFR C677T and A1298C Gene Polymorphisms and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in an Emirati Population. Meta Gene 2016, 9, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.-R.; Zhang, H.-G.; Wang, Z.-P.; Fu, S.-J.; Yang, P.-Q.; Ren, J.-G.; Ning, Y.-Y.; Hu, X.-J.; Tian, L.-H. C-Reactive Protein, Vitamin B12 and C677T Polymorphism of N-5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Are Related to Insulin Resistance and Risk Factors for Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Population. Clin. Investig. Med. 2010, 33, E290–E297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poodineh, M.; Saravani, R.; Mirhosseini, M.; Sargazi, S. Association of Two Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Polymorphisms (Rs1801133, Rs1801131) with the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in South-East of Iran. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 8, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, X.; Yang, B.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; He, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, G. Additive Interaction of MTHFR C677T and MTRR A66G Polymorphisms with Being Overweight/Obesity on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapik, I.A.; Ranjit, R.; Galchenko, A.V. Impact of KCNJ11 Rs5219, UCP2 Rs659366, and MTHFR Rs1801133 Polymorphisms on Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2021, 17, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolov, D.; Stoyanova, V.K.; Vladimirova-Kitova, L.; Linev, A.; Nikolov, G.; Kitov, S. Analysis and Evaluation of Correlation between DNA Polymorphism in the Genes MTHFR, PAI-1 and Serum Creatinine, Creatinine Clearance and Albumin/Creatinine Ratio in Morning Urine of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Nephropathy. Folia Med. 2022, 64, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errera, F.I.V.; Silva, M.E.R.; Yeh, E.; Maranduba, C.M.C.; Folco, B.; Takahashi, W.; Pereira, A.C.; Krieger, J.E.; Passos-Bueno, M.R. Effect of Polymorphisms of the MTHFR and APOE Genes on Susceptibility to Diabetes and Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy in Brazilian Patients. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, F.F.; Belini Junior, E.; Okumura, J.V.; Salvarani, M.; Bonini-Domingos, C.R.; Ruiz, M.A. The Relationship between of ACE I/D and the MTHFR C677T Polymorphisms in the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Population of Brazilian Obese Patients. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 62, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.L.; Fernandes, A.P.; Cardoso, J.E.; Sousa, M.O.; Lasmar, M.C.; Novelli, B.A.; Lages, G.F.; Dusse, L.M.; Vieira, L.M.; Lwaleed, B.A.; et al. Plasma Total Homocysteine Levels and Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2008, 36, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borai, I.H.; Soliman, A.F.; Ahmed, H.M.; Ahmed, G.F.; Kassim, S.K. Association of MTHFR C677T and ABCA1 G656A Polymorphisms with Obesity among Egyptian Children. Gene Rep. 2018, 11, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekih-Mrissa, N.; Mrad, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Akremi, I.; Sayeh, A.; Jaidane, A.; Ouertani, H.; Zidi, B.; Gritli, N. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) (C677T and A1298C) Polymorphisms and Vascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehri, S.; Koubaa, N.; Nakbi, A.; Hammami, S.; Chaaba, R.; Mahjoub, S.; Zouari, B.; Abid, M.; Ben Arab, S.; Baudin, B.; et al. Relationship between Genetic Polymorphisms of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase as Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes in Tunisian Patients. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mtiraoui, N.; Ezzidi, I.; Chaieb, M.; Marmouche, H.; Aouni, Z.; Chaieb, A.; Mahjoub, T.; Vaxillaire, M.; Almawi, W.Y. MTHFR C677T and A1298C Gene Polymorphisms and Hyperhomocysteinemia as Risk Factors of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 75, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settin, A.; El-Baz, R.; Ismaeel, A.; Tolba, W.; Allah, W.A. Association of ACE and MTHFR Genetic Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Susceptibility and Complications. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015, 16, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogozheva, A.V.; Sorokina, E.Y.; Aristarkhova, T.V. Evaluation of an Association of the Rs1801133 MTHFR Gene Polymorphism with Folic Acid Deficiency in Obese Patients. Alm. Clin. Med. 2018, 46, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luo, Z.; Lu, Z.; Muhammad, I.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y. Associations of the MTHFR Rs1801133 Polymorphism with Coronary Artery Disease and Lipid Levels: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesnina, A.; Prosekov, A.; Kozlova, O.; Atuchin, V. Genes and Eating Preferences, Their Roles in Personalized Nutrition. Genes 2020, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Bordoni, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S.; Obesity Programs of Nutrition, Education, Research and Assessment (OPERA) Group. Nutrigenetics-Personalized Nutrition in Obesity and Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Obes. Suppl. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinadane, A.V.; Ramasamy, R.; Lenin, M.; Velu, K.; Hussain, S.A. Association of MTHFR (Rs 1801133) Gene Polymorphism with Biochemical Markers of B12 Deficiency in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients on Metformin Therapy. Meta Gene 2021, 29, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, Y.-Y.; Liu, L.; Qiao, Y.-N.; Geng, H.-R.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W.; Cao, J.; Zhao, J.-Y. Homocysteine Inhibits Pro-Insulin Receptor Cleavage and Causes Insulin Resistance via Protein Cysteine-Homocysteinylation. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.B.; Baipadithaya, G.; Balakrishnan, A.; Hegde, M.; Vohra, M.; Ahamed, R.; Nagri, S.K.; Ramachandra, L.; Satyamoorthy, K. Elevated Homocysteine Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Induce Constitutive Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaché, A.D.; Oaks, J.R. The Utility of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Data in Phylogenetics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 48, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Zhou, H.; Fan, H.; Yuan, Y. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Cancer Susceptibility. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110635–110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghvirdizadeh, P.; Mohamed, Z.; Abdullah, N.A.; Haghvirdizadeh, P.; Haerian, M.S.; Haerian, B.S. KCNJ11: Genetic Polymorphisms and Risk of Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 908152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, M.; Sultana, M.I.; Akter, F.; Hossain, M.M. Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms Associated with Diabetes Mellitus: A Descriptive Review. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, R.; Pradeepa, R.; Joshi, S.R.; Mohan, V. Type 2 Diabetes: Demystifying the Global Epidemic. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzago, M.; Santurbano, D.; Vitacolonna, E.; Stuppia, L. Genes and Diet in the Prevention of Chronic Diseases in Future Generations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadayifci, F.Z.; Zheng, S.; Pan, Y.-X. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Link between Diet and DNA Methylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boqué, N.; de la Iglesia, R.; de la Garza, A.L.; Milagro, F.I.; Olivares, M.; Bañuelos, O.; Soria, A.C.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, S.; Martínez, J.A.; Campión, J. Prevention of Diet-Induced Obesity by Apple Polyphenols in Wistar Rats through Regulation of Adipocyte Gene Expression and DNA Methylation Patterns. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryndyak, V.P.; Marrone, A.K.; Latendresse, J.R.; Muskhelishvili, L.; Beland, F.A.; Pogribny, I.P. MicroRNA Changes, Activation of Progenitor Cells and Severity of Liver Injury in Mice Induced by Choline and Folate Deficiency. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 28, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia, A.; Elcoroaristizabal, X.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Miranda, J.; Bediaga, N.G.; M de Pancorbo, M.; Rimando, A.M.; Portillo, M.P. Fatty Acid Synthase Methylation Levels in Adipose Tissue: Effects of an Obesogenic Diet and Phenol Compounds. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsten, K.; Pompermaier, A.; Koakoski, G.; Mendonça-Soares, S.; da Costa, R.A.; Maffi, V.C.; Kreutz, L.C.; Barcellos, L.J.G. Acute and Chronic Stress Differently Alter the Expression of Cytokine and Neuronal Markers Genes in Zebrafish Brain. Stress 2021, 24, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Yin, K.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. Chronic Stress Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression and Metastasis: An Essential Role for ADRB2. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, N.F.P.; de Souza, B.F.; de Castro Coêlho, M. UV Radiation and Its Relation to DNA Methylation in Epidermal Cells: A Review. Epigenomes 2020, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.M.; Woo, H.W.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Shin, D.H.; Shin, M.-H.; Chun, B.-Y.; Choi, B.Y. A Prospective Association between Dietary Folate Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Risk among Korean Adults Aged 40 Years or Older: The Korean Multi-Rural Communities Cohort (MRCohort) Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, T.B. Dietary Behaviour and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Sub-Saharan African Populations Under Transition. Ph.D. Thesis, Heidelberg University, Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hills, A.P.; Arena, R.; Khunti, K.; Yajnik, C.S.; Jayawardena, R.; Henry, C.J.; Street, S.J.; Soares, M.J.; Misra, A. Epidemiology and Determinants of Type 2 Diabetes in South Asia. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Author | Country | Samples | Genotypes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2D | Non-T2D | CC | CT | TT | ||||||
| Diabetes | Non-Diabetes | Diabetes | Non-Diabetes | Diabetes | Non-Diabetes | |||||
| Asia | ||||||||||
| 1 | Al-Harbi 2015 [9] | Bahrain | 171 | 188 | 116 | 135 | 43 | 47 | 12 | 6 |
| 2 | Benrahma 2012 [10] | Morocco | 282 | 262 | 160 | 114 | 97 | 122 | 25 | 26 |
| 3 | Chang 2010 [11] | China | 56 | 62 | 1 | 3 | 25 | 23 | 30 | 36 |
| 4 | Chehadeh 2016 [12] | United Arab Emirates | 209 | 169 | 155 | 132 | 49 | 27 | 5 | 10 |
| 5 | Chen 2010 [13] | China | 158 | 55 | 57 | 34 | 74 | 17 | 27 | 4 |
| 6 | Liu 2024 [5] | China | 445 | 272 | 156 | 110 | 222 | 135 | 67 | 27 |
| 7 | Pathak 2022 [3] | India | 100 | 100 | 41 | 69 | 51 | 29 | 8 | 2 |
| 8 | Poodineh 2019 [14] | Iran | 136 | 151 | 25 | 10 | 76 | 32 | 35 | 109 |
| 9 | Xueyuan 2016 [15] | China | 180 | 350 | 28 | 76 | 86 | 172 | 66 | 102 |
| Europe | ||||||||||
| 10 | Lapik 2021 [16] | Russia | 40 | 40 | 3 | 18 | 21 | 16 | 16 | 6 |
| 11 | Nikolov 2022 [17] | Bulgaria | 45 | 38 | 21 | 30 | 20 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| America | ||||||||||
| 12 | Errera 2006 [18] | Brazil | 95 | 107 | 44 | 36 | 41 | 57 | 10 | 14 |
| 13 | Pirozzi 2018 [19] | Brazil | 25 | 16 | 15 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 |
| 14 | Soares 2008 [20] | Brazil | 47 | 77 | 17 | 30 | 22 | 38 | 8 | 9 |
| Africa | ||||||||||
| 15 | Borai 2018 [21] | Egypt | 51 | 30 | 4 | 12 | 29 | 14 | 18 | 4 |
| 16 | Fekih-Mrissa 2016 [22] | Tunisia | 160 | 200 | 56 | 124 | 102 | 68 | 104 | 76 |
| 17 | Mehri 2009 [23] | Tunisia | 115 | 116 | 50 | 66 | 49 | 38 | 16 | 12 |
| 18 | Mtiraoui 2007 [24] | Tunisia | 267 | 400 | 163 | 270 | 135 | 94 | 62 | 36 |
| 19 | Settin 2015 [25] | Egypt | 203 | 311 | 111 | 156 | 65 | 135 | 27 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nurkolis, F.; Amalia, N.; Tandi, Y.Y.P.; Athallah, A.F.; Aditya, M.R.; Nojaid, A.; Humardani, F.M.; Prapriatna, A.F.; Taslim, N.A.; Harbuwono, D.S.; et al. Determining the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes for rs1801133 Genotypes in Multiethnic Populations: A Global Meta-Epidemiological Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093987
Nurkolis F, Amalia N, Tandi YYP, Athallah AF, Aditya MR, Nojaid A, Humardani FM, Prapriatna AF, Taslim NA, Harbuwono DS, et al. Determining the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes for rs1801133 Genotypes in Multiethnic Populations: A Global Meta-Epidemiological Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093987
Chicago/Turabian StyleNurkolis, Fahrul, Nurlinah Amalia, Yosi Yohanes Putra Tandi, Ariq Fadhil Athallah, Muhammad Reva Aditya, Ammar Nojaid, Farizky Martriano Humardani, Achmad Fabiansyah Prapriatna, Nurpudji Astuti Taslim, Dante Saksono Harbuwono, and et al. 2025. "Determining the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes for rs1801133 Genotypes in Multiethnic Populations: A Global Meta-Epidemiological Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093987
APA StyleNurkolis, F., Amalia, N., Tandi, Y. Y. P., Athallah, A. F., Aditya, M. R., Nojaid, A., Humardani, F. M., Prapriatna, A. F., Taslim, N. A., Harbuwono, D. S., & Tjandrawinata, R. R. (2025). Determining the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes for rs1801133 Genotypes in Multiethnic Populations: A Global Meta-Epidemiological Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093987














