Multiple LPA3 Receptor Agonist Binding Sites Evidenced Under Docking and Functional Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LPA3 Receptor Model Without Refinement
2.2. LPA3 Refined Model
2.3. Trp102-Focused Model
2.4. Tyr293-Focused Model
2.5. Membrane-Inserted LPA3 Receptor Structural Model
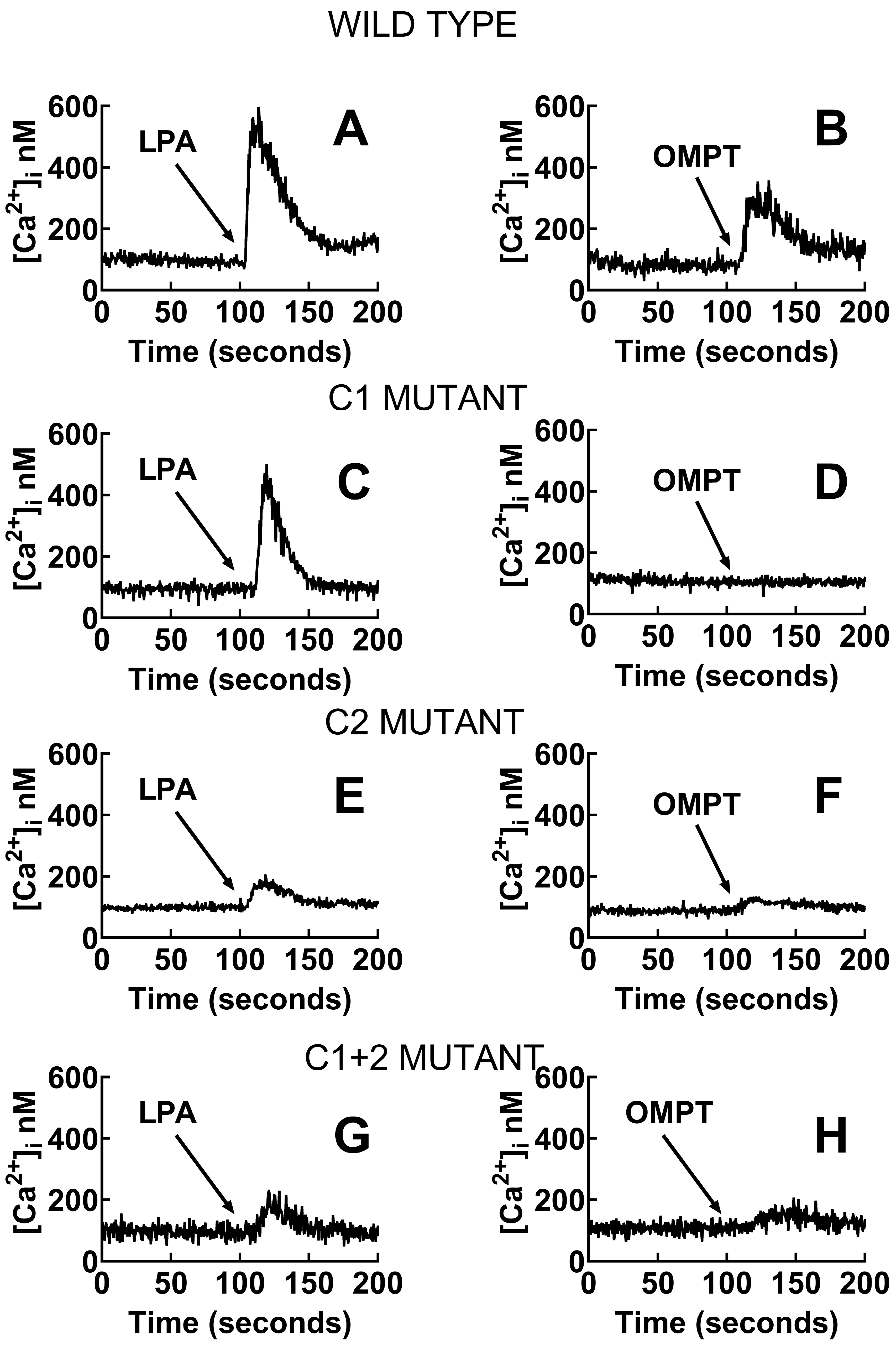
2.6. In Cellulo Signaling Experiments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Modeling of LPA3 Receptor Structure, Gene ID:23566
4.2. Refinement and Validation of the LPA3 Receptor 3D Structure
4.3. Search for Ligand-Binding Cavities on the LPA3 Receptor
4.4. LPA and OMPT Docking at the LPA3 Receptor Binding Sites
4.5. Structural Model of the LPA3 Receptor Inserted in the Membrane and Binding Site Detection
4.6. Reagents, Plasmids, and Cells
4.7. Intracellular Calcium Concentration
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.W.; Herr, D.R.; Noguchi, K.; Yung, Y.C.; Lee, C.W.; Mutoh, T.; Lin, M.E.; Teo, S.T.; Park, K.E.; Mosley, A.N.; et al. LPA receptors: Subtypes and biological actions. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, Y.C.; Stoddard, N.C.; Chun, J. LPA receptor signaling: Pharmacology, physiology, and pathophysiology. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1192–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, N.; Chun, J. The LPA receptors. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2001, 64, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama, K.; Aoki, J. LPA(3), a unique G protein-coupled receptor for lysophosphatidic acid. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, K.H.; Romero-Ávila, M.T.; Guzmá-Silva, A.; García-Sáinz, J.A. The LPA(3) Receptor: Regulation and Activation of Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contos, J.J.; Chun, J. The mouse lp(A3)/Edg7 lysophosphatidic acid receptor gene: Genomic structure, chromosomal localization, and expression pattern. Gene 2001, 267, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fells, J.I.; Tsukahara, R.; Liu, J.; Tigyi, G.; Parrill, A.L. Structure-based drug design identifies novel LPA3 antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7457–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandoh, K.; Aoki, J.; Taira, A.; Tsujimoto, M.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors of the EDG family are differentially activated by LPA species. Structure-activity relationship of cloned LPA receptors. FEBS Lett. 2000, 478, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urs, N.M.; Kowalczyk, A.P.; Radhakrishna, H. Different mechanisms regulate lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-dependent versus phorbol ester-dependent internalization of the LPA1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 5249–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonegge, A.M.; Gallion, J.; Picard, L.P.; Wilkins, A.D.; Le Gouill, C.; Audet, M.; Stallaert, W.; Lohse, M.J.; Kimmel, M.; Lichtarge, O.; et al. Evolutionary action and structural basis of the allosteric switch controlling beta (2)AR functional selectivity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.S.; Kooistra, A.J.; Munk, C.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Bouvier, M.; Babu, M.M.; Gloriam, D.E. GPCR activation mechanisms across classes and macro/microscales. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, A.; Coin, I. Capturing Peptide-GPCR Interactions and Their Dynamics. Molecules 2020, 25, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flock, T.; Hauser, A.S.; Lund, N.; Gloriam, D.E.; Balaji, S.; Babu, M.M. Selectivity determinants of GPCR-G-protein binding. Nature 2017, 545, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, D.; Masureel, M.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, D.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhong, L.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Jang, W.; Shakhnovich, E.I.; et al. Common activation mechanism of class A GPCRs. Elife 2019, 8, e50279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, M.R.; Randal, M.; DeLano, W.L.; Hyde, J.; Luong, T.N.; Oslob, J.D.; Raphael, D.R.; Taylor, L.; Wang, J.; McDowell, R.S.; et al. Binding of small molecules to an adaptive protein-protein interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stank, A.; Kokh, D.B.; Fuller, J.C.; Wade, R.C. Protein Binding Pocket Dynamics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Morales, J.C.; Romero-Ávila, M.T.; Reyes-Cruz, G.; García-Sáinz, J.A. Roles of Receptor Phosphorylation and Rab Proteins in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Function and Trafficking. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 101, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, M.; Fernandez-Recio, J. Docking-based identification of small-molecule binding sites at protein-protein interfaces. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 3750–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fells, J.I.; Tsukahara, R.; Fujiwara, Y.; Liu, J.; Perygin, D.H.; Osborne, D.A.; Tigyi, G.; Parrill, A.L. Identification of non-lipid LPA3 antagonists by virtual screening. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6207–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Sardar, V.; Tokumura, A.; Baker, D.; Murakami-Murofushi, K.; Parrill, A.; Tigyi, G. Identification of residues responsible for ligand recognition and regioisomeric selectivity of lysophosphatidic acid receptors expressed in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35038–35050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, W.J.; Fells, J.I.; Perygin, D.H.; Mujahid, S.; Yokoyama, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tsukahara, R.; Van Brocklyn, J.R.; Parrill, A.L.; Tigyi, G. Subtype-specific residues involved in ligand activation of the endothelial differentiation gene family lysophosphatidic acid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12175–12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, B.; Pazmany, T.; Matyus, P. Analysis of Edg-Like LPA Receptor-Ligand Interactions. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 3533–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995, 25, 366–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandy-Szekeres, G.; Munk, C.; Tsonkov, T.M.; Mordalski, S.; Harpsoe, K.; Hauser, A.S.; Bojarski, A.J.; Gloriam, D.E. GPCRdb in 2018: Adding GPCR structure models and ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D440–D446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Erickson, J.R.; Goddard, G.J.; Yu, S.; Liu, S.; Cheng, K.W.; Eder, A.; Bandoh, K.; Aoki, J.; Jarosz, R.; et al. Identification of a phosphothionate analogue of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) as a selective agonist of the LPA3 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11962–11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Xu, Y.; Simper, T.; Jiang, G.; Aoki, J.; Umezu-Goto, M.; Arai, H.; Yu, S.; Mills, G.B.; Tsukahara, R.; et al. Phosphorothioate analogues of alkyl lysophosphatidic acid as LPA3 receptor-selective agonists. ChemMedChem 2006, 1, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajitani, N.; Okada-Tsuchioka, M.; Inoue, A.; Miyano, K.; Masuda, T.; Boku, S.; Iwamoto, K.; Ohtsuki, S.; Uezono, Y.; Aoki, J.; et al. G protein-biased LPAR1 agonism of prototypic antidepressants: Implication in the identification of novel therapeutic target for depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 49, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Inoue, A.; Aoki, J.; Prestwich, G.D. Phosphorothioate analogs of sn-2 radyl lysophosphatidic acid (LPA): Metabolically stabilized LPA receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, K.H.; Romero-Ávila, M.T.; Rincón-Heredia, R.; Martínez-Morales, J.C.; García-Sáinz, J.A. LPA3: Pharmacodynamic Differences Between Lysophosphatidic Acid and Oleoyl-Methoxy Glycerophosphothionate: Biased Agonism, Two Sites. Receptors 2024, 3, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malar, D.S.; Verma, K.; Prasanth, M.I.; Tencomnao, T.; Brimson, J.M. Network analysis-guided drug repurposing strategies targeting LPAR receptor in the interplay of COVID, Alzheimer’s, and diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solís, K.H.; Romero-Ávila, M.T.; Rincón-Heredia, R.; García-Sáinz, J.A. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 3 (LPA3): Signaling and Phosphorylation Sites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, H.; Sato, K.; Murata, N.; Damirin, A.; Malchinkhuu, E.; Kon, J.; Kimura, T.; Tobo, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Watanabe, T.; et al. Ki16425, a subtype-selective antagonist for EDG-family lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghersi, D.; Sanchez, R. Improving accuracy and efficiency of blind protein-ligand docking by focusing on predicted binding sites. Proteins 2009, 74, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Paknejad, N.; Zhu, L.; Kihara, Y.; Ray, M.; Chun, J.; Liu, W.; Hite, R.K.; Huang, X.-Y. Differential activation mechanisms of lipid GPCRs by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Doerr, S.; Martinez-Rosell, G.; Rose, A.S.; De Fabritiis, G. DeepSite: Protein-binding site predictor using 3D-convolutional neural networks. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3036–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, K.H.; Romero-Ávila, M.T.; Rincón-Heredia, R.; García-Sáinz, J.A. LPA(3) Receptor Phosphorylation Sites: Roles in Signaling and Internalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynkiewicz, G.; Poenie, M.; Tsien, R.Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
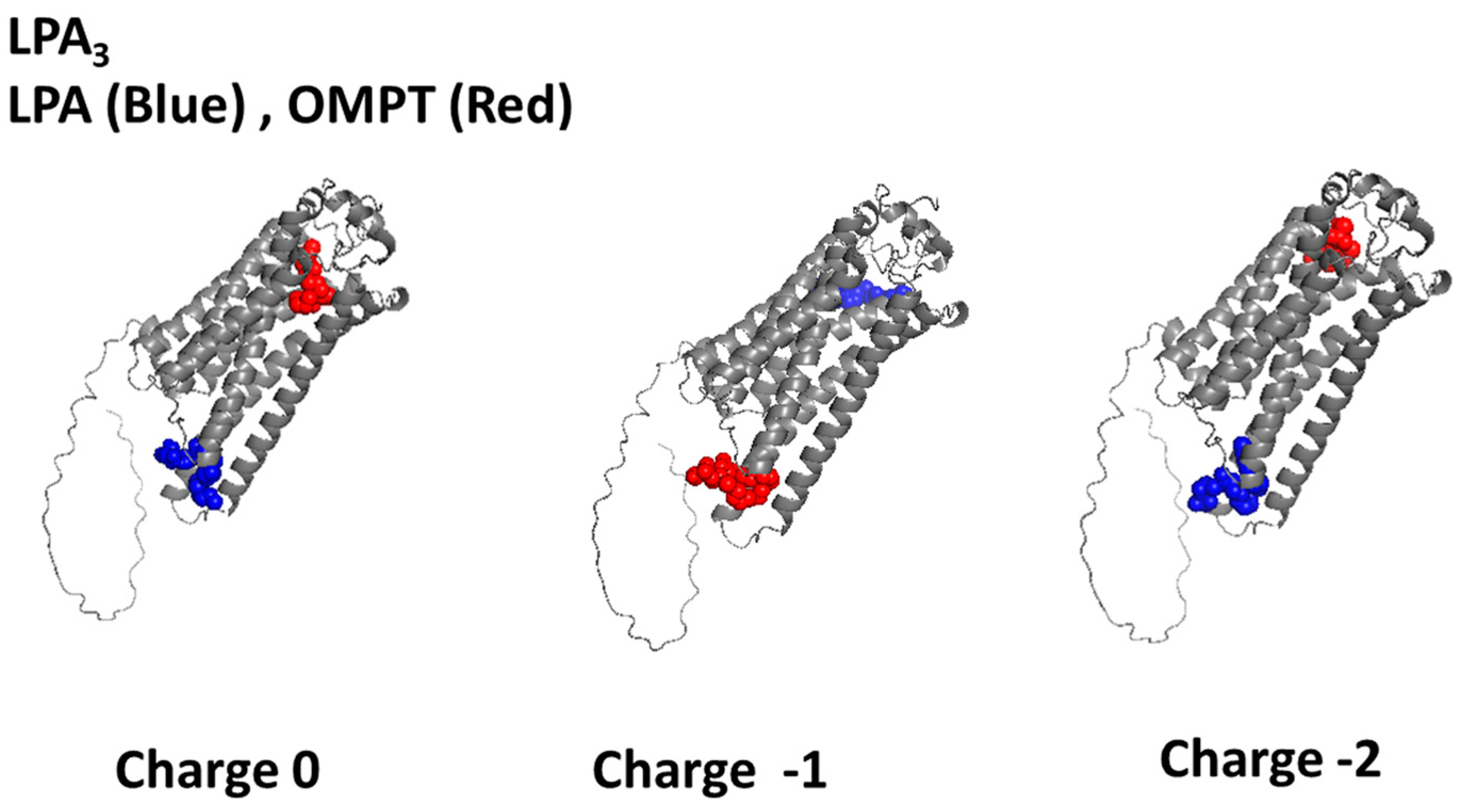
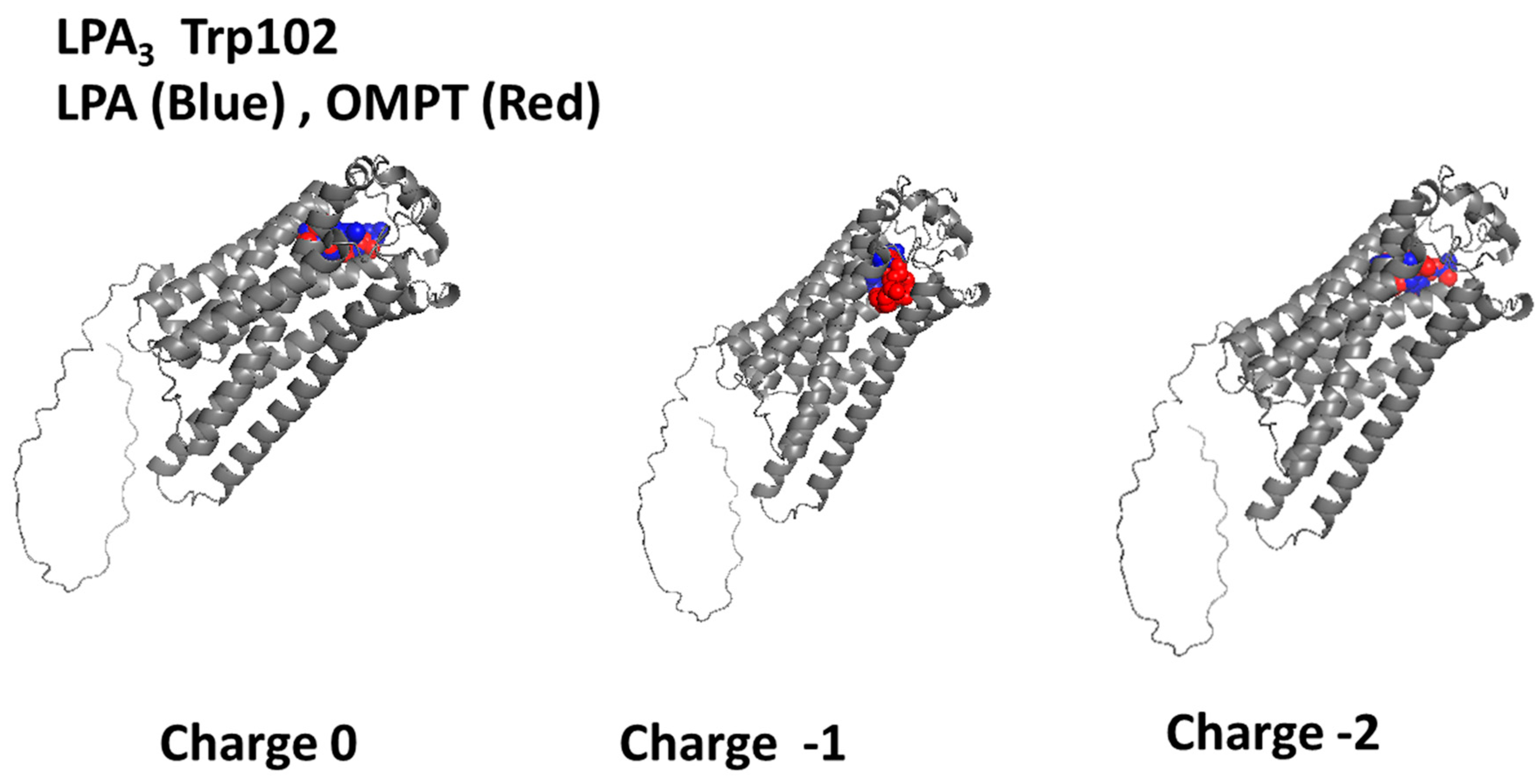

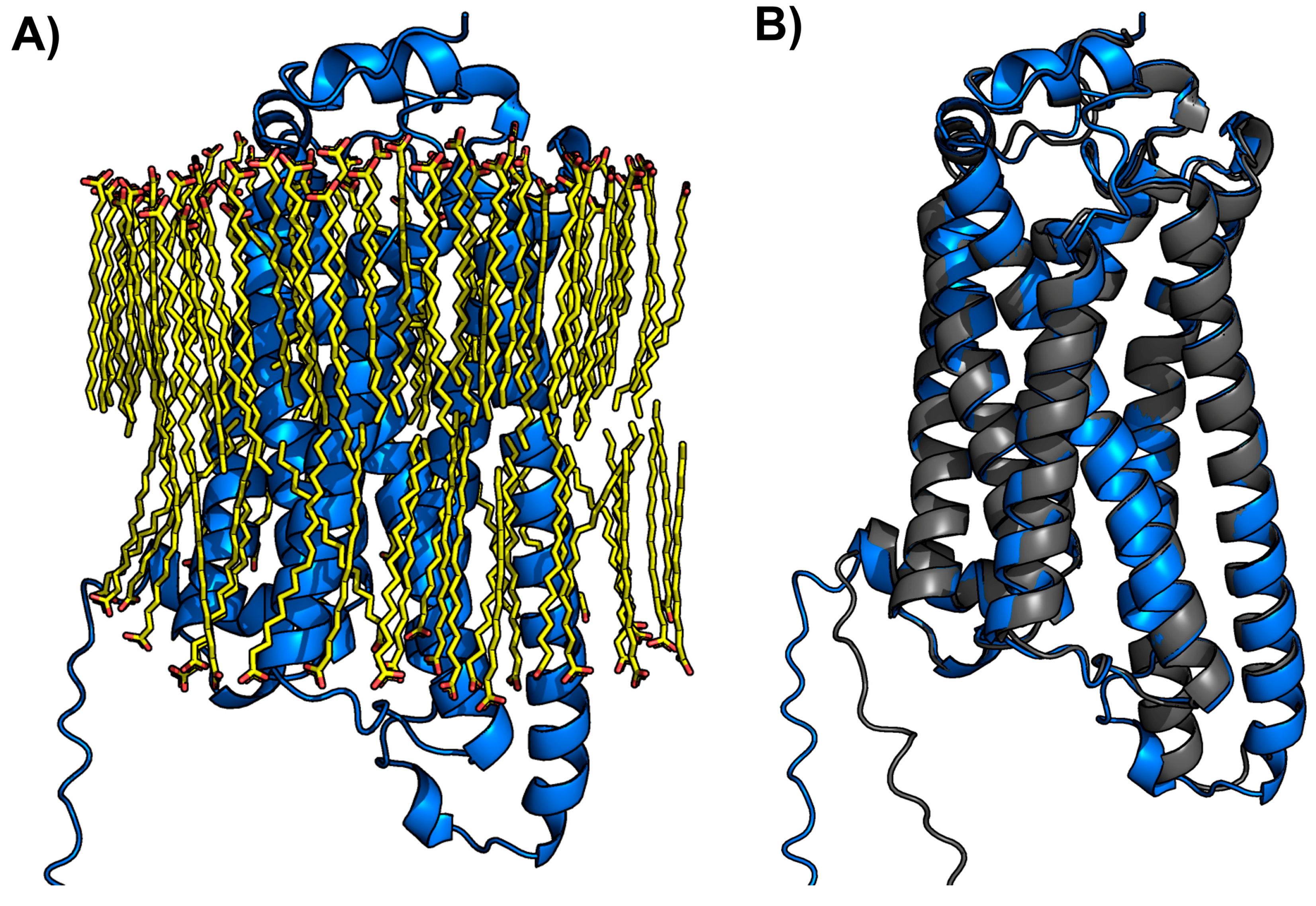
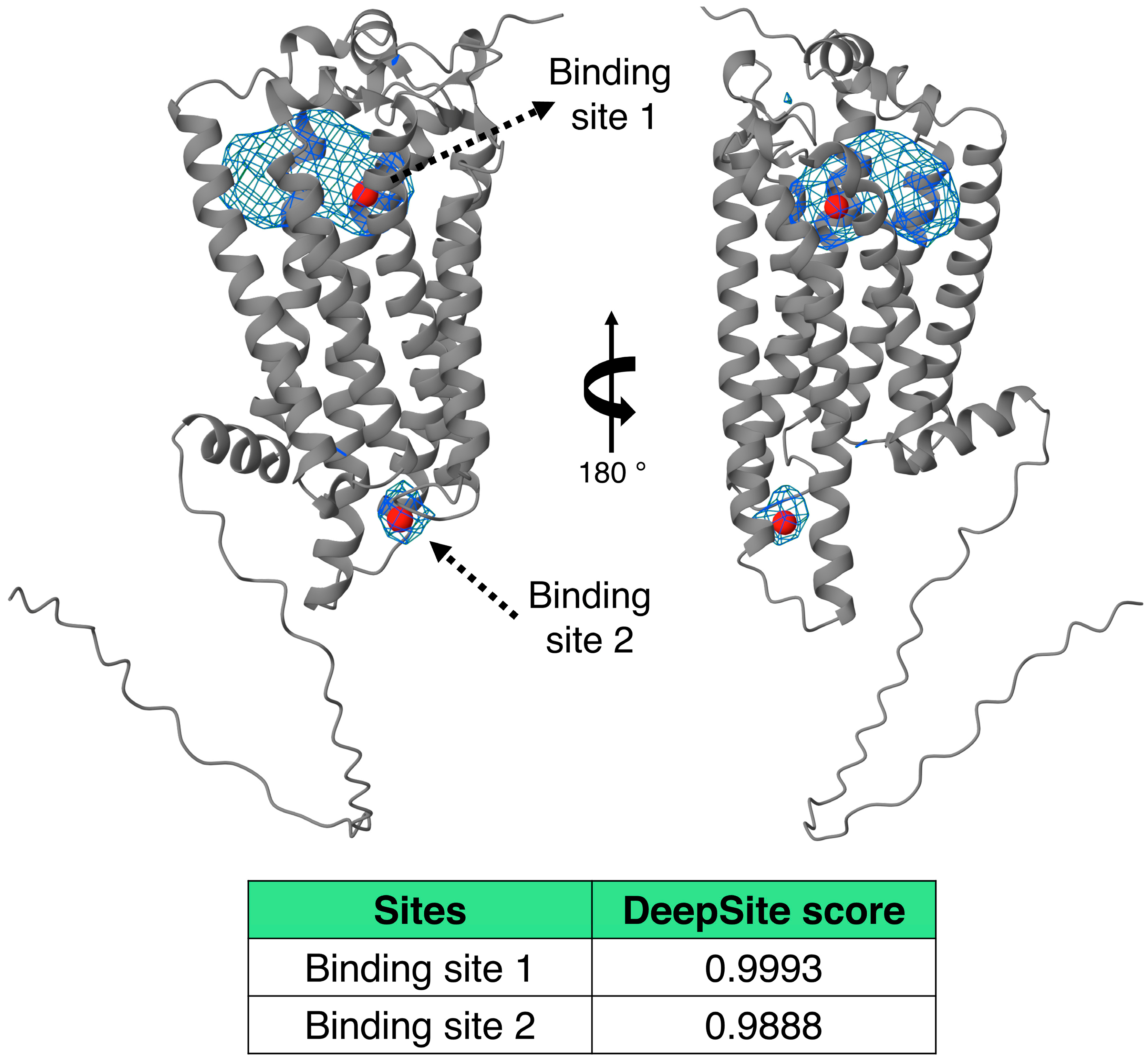


| Focus (Charge) | ∆G (Kcal/mol) | Interacting Amino Acids |
|---|---|---|
| NONE (0) | −5.01 | Val219, Leu220, Ser221, Lys216, Arg230, Pro234, Val136 |
| NONE (−1) | −4.10 | Arg276, Trp277, Val22, His273, Val274, Lys 29, Trp25, Ile 32, Leu 280, Val33, Val 36, Tyr83, Gly 37, Leu283, Met 87, Leu86, Cys41 |
| NONE (−2) | −7.18 | Lys216, Thr217, Ile131, Met134, Arg230, Pro234, Leu237, Arg127, Val136 |
| Trp102 (0) | −5.99 | Leu283, Leu280, Leu279, Met87, Val33, Thr90, Trp25, Arg276, Lys29 |
| Trp102 (−1) | −4.10 | Gln106, Arg105, Lys275, Leu86, Tyr14, Leu109, Trp102, Ala180, Leu279, Thr90, Asp23, Gly91, Arg276, Val36, Val33, Leu280, Trp277, Trp225, Lys29, Ile32 |
| Trp102 (−2) | −8.93 | Trp277, Leu279, Arg276, Gly37, Val33, Trp25, Lys29, Thr90, Leu86, Met87 |
| Tyr293 (0) | −5.79 | Leu220, Lys216, Thr217, Ile131, Val213, Pro234, Arg135, Met134, Val136, Asn139, His137, Phe63 |
| Tyr293 (−1) | −2.88 | Thr146, Lys142, Val145, Trp153, Ile149, Leu150, Tyr67, Val55, Ile56, His62, Ala70, Asn71 |
| Tyr293 (−2) | −7.62 | Trp277, Leu280, Leu279, Leu283, Tyr83, Arg276, Gly37, Val33, Trp25, Leu86, Met87 |
| Focus (Charge) | ∆G (Kcal/mol) | Interacting Amino Acids |
|---|---|---|
| ONE (0) | −5.67 | Trp277, Leu279, Leu280, Leu283, Arg276, Tyr14, Asp23, Trp25, Ser94, Thr90, Arg105, Leu86, Val33 |
| NONE (−1) | −5.36 | Lys216, Val213, Ile131, Met134, Arg230, Val136, Arg135 |
| NONE (−2) | −5.85 | Ser94, Arg105, Leu86, Asp23, Lys275, Arg276, Leu279, Val36, Trp277, Val33, Ile32 |
| Trp102 (0) | −5.15 | Leu283, Leu280, Leu279, Tyr83. Val36, Met87, Val33, Thr90, Trp25, Arg276, Trp277, Leu86 |
| Trp102 (−1) | −7.75 | Leu256, Leu159, Leu188, Phe278, Lys275, Trp191, Leu179, Ala180, Tyr183, Tyr187, Gln106, Arg105, asp110, Ala282, Leu279, Trp252 |
| Trp 102 (−2) | −7.11 | Leu280, Leu279, Leu283, Ile32, Gly37, Val36, Val33, Arg276, Trp25, Met87 |
| Tyr293 (0) | −4.64 | Arg230, Leu220, Lys216, Thr217, Arg231, Ile131, His137, Val136, Thr233, Pro234 |
| Tyr293 (−1) | −5.76 | Arg232, Met235, Lys239, Lys236, Thr240, Tyr295, Glu298, Ser294, Tyr301, Ile291 |
| Tyr293 (−2) | −5.64 | Lys296, Lys236, Thr240, Lys305, Ile308, Tyr295, Glu298, Tyr301, Ser294, Met304,Ile291 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solís, K.H.; Romero-Ávila, M.T.; Rincón-Heredia, R.; Romero-Romero, S.; Correa-Basurto, J.; García-Sáinz, J.A. Multiple LPA3 Receptor Agonist Binding Sites Evidenced Under Docking and Functional Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094123
Solís KH, Romero-Ávila MT, Rincón-Heredia R, Romero-Romero S, Correa-Basurto J, García-Sáinz JA. Multiple LPA3 Receptor Agonist Binding Sites Evidenced Under Docking and Functional Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094123
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolís, K. Helivier, M. Teresa Romero-Ávila, Ruth Rincón-Heredia, Sergio Romero-Romero, José Correa-Basurto, and J. Adolfo García-Sáinz. 2025. "Multiple LPA3 Receptor Agonist Binding Sites Evidenced Under Docking and Functional Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094123
APA StyleSolís, K. H., Romero-Ávila, M. T., Rincón-Heredia, R., Romero-Romero, S., Correa-Basurto, J., & García-Sáinz, J. A. (2025). Multiple LPA3 Receptor Agonist Binding Sites Evidenced Under Docking and Functional Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094123









