Further Insight in the High Selectivity of Pb2+ Removal over Cd2+ in Natural and Dealuminated Rich-Clinoptilolite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Experimental Results
2.1.1. Characterization
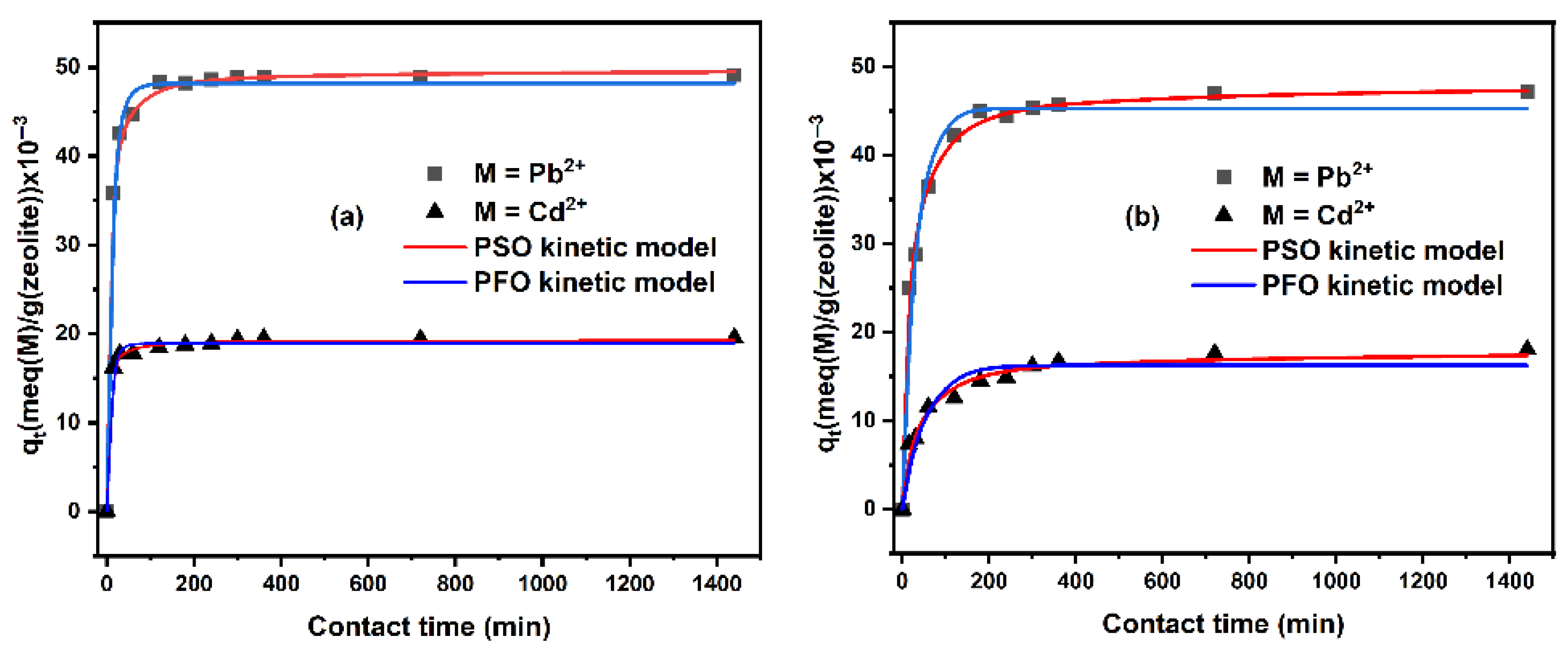
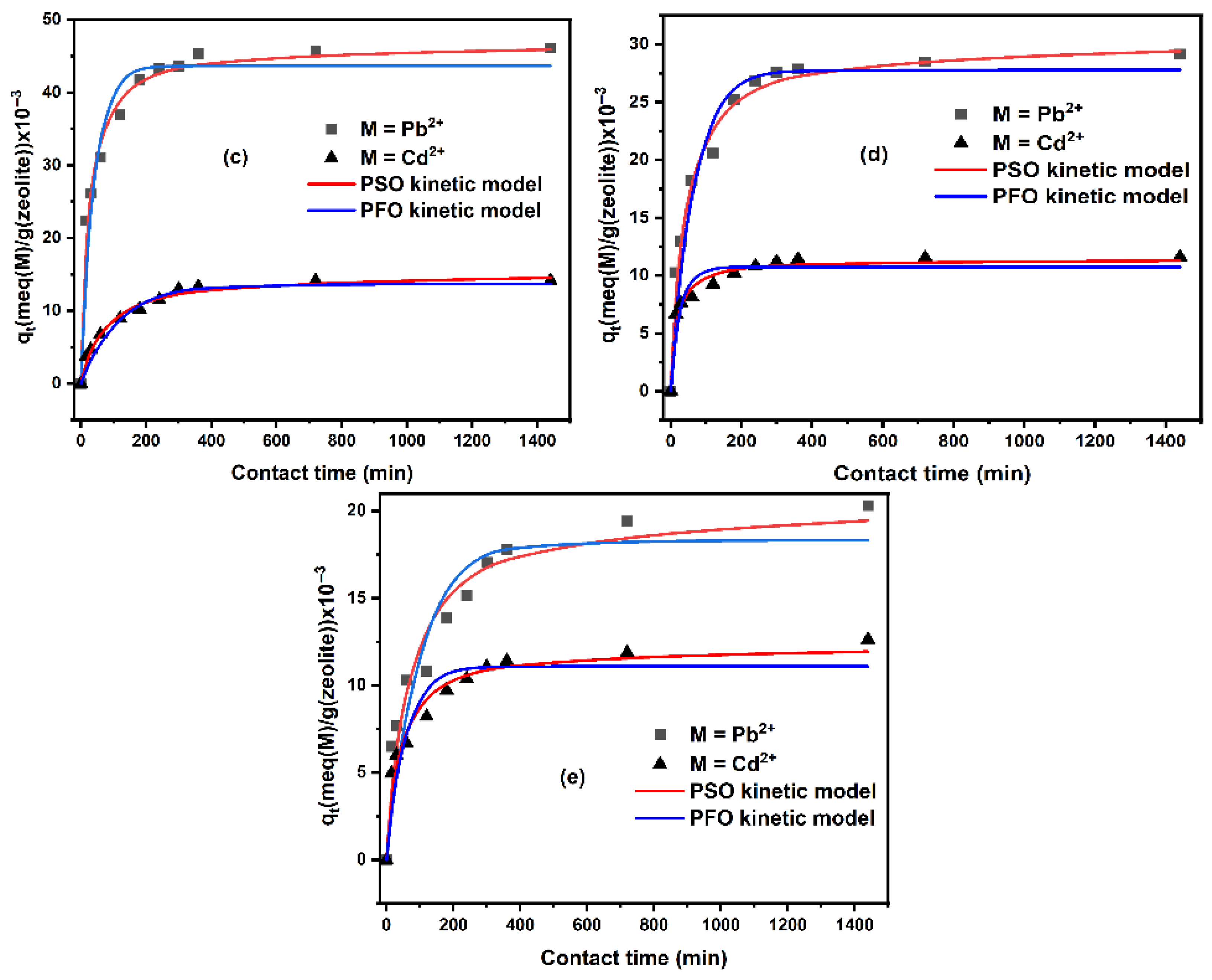
2.1.2. Kinetic Study
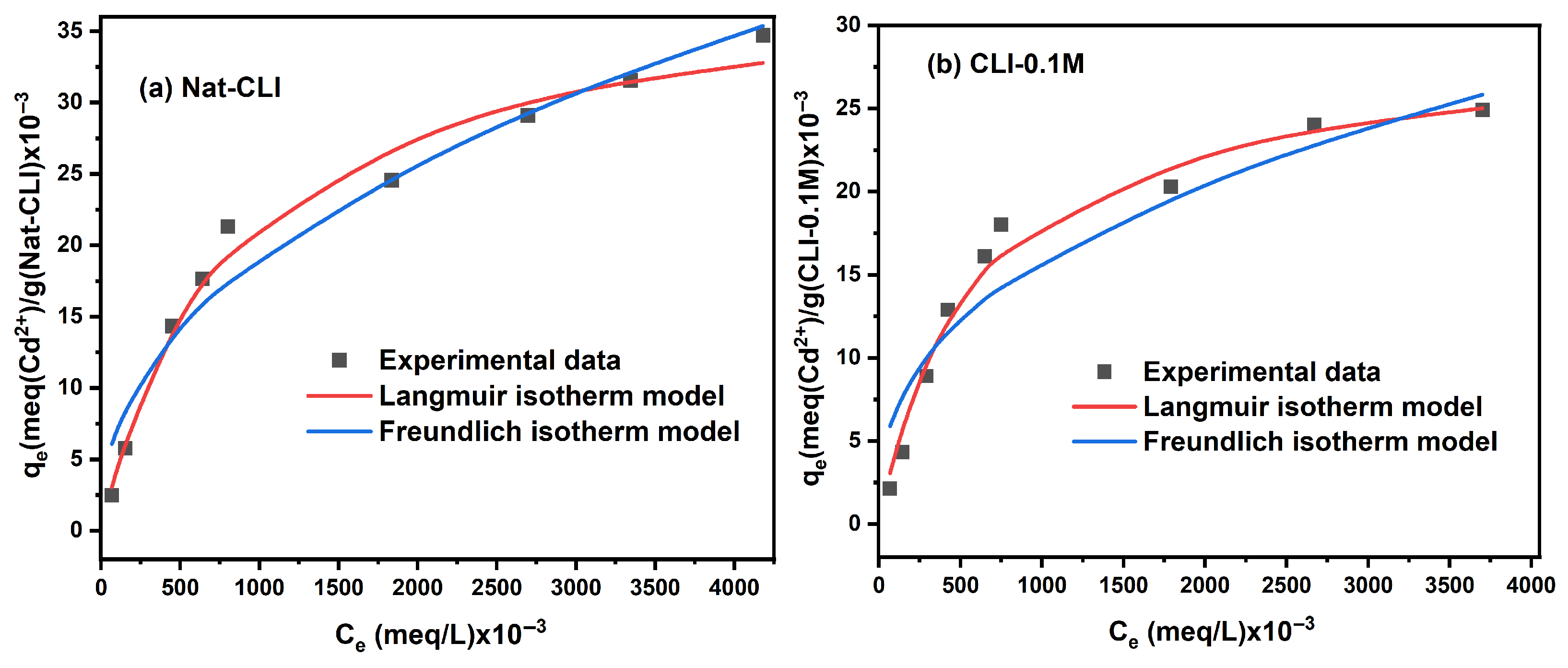
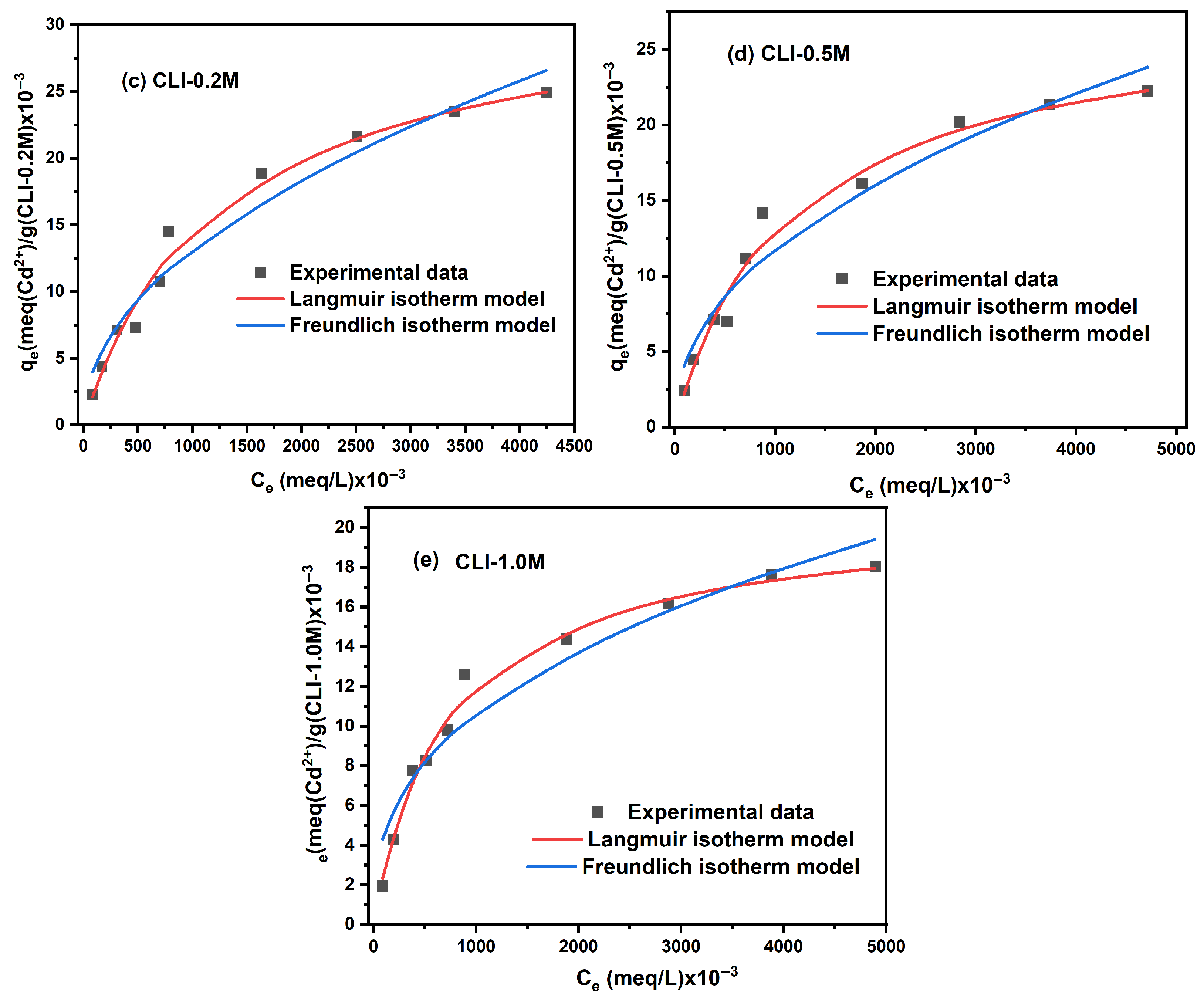
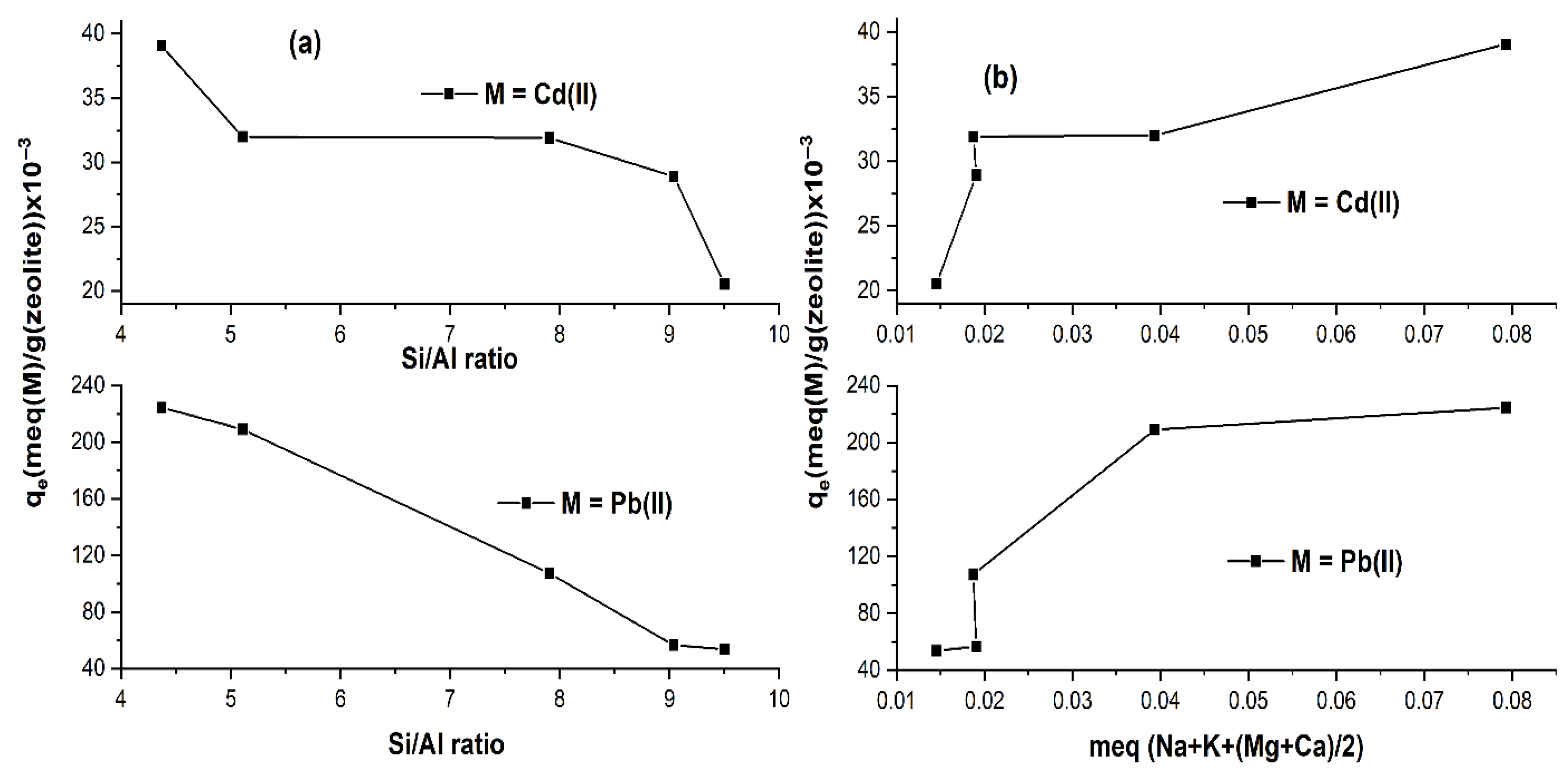
2.1.3. Isotherm Study
2.1.4. Comparation of Adsorption Capacity of Pb2+ and Cd2+ with Other Zeolitic Materials
2.2. Theoretical Study
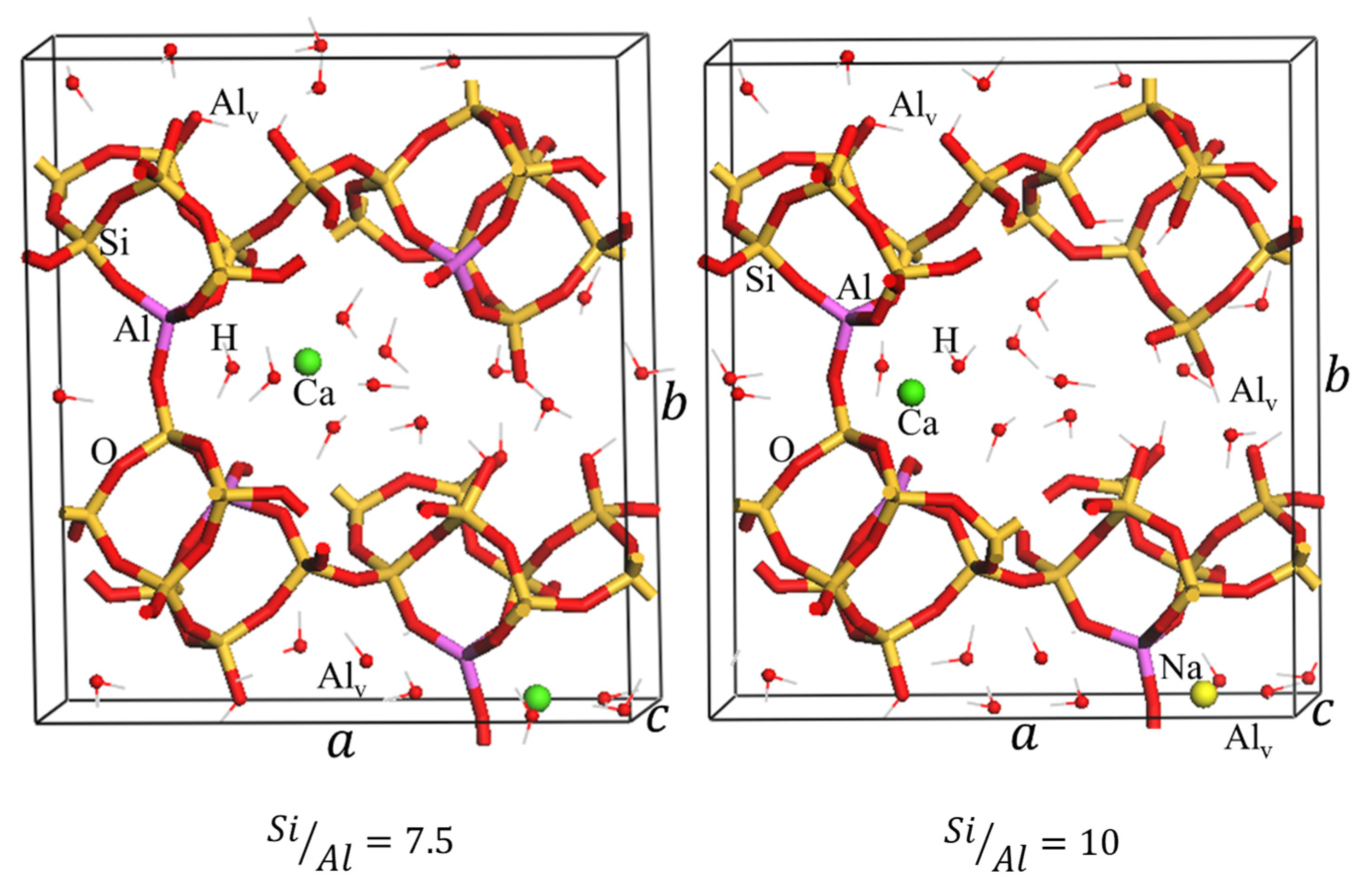
2.2.1. DFT Modeling of Natural and Dealuminated Clinoptilolite
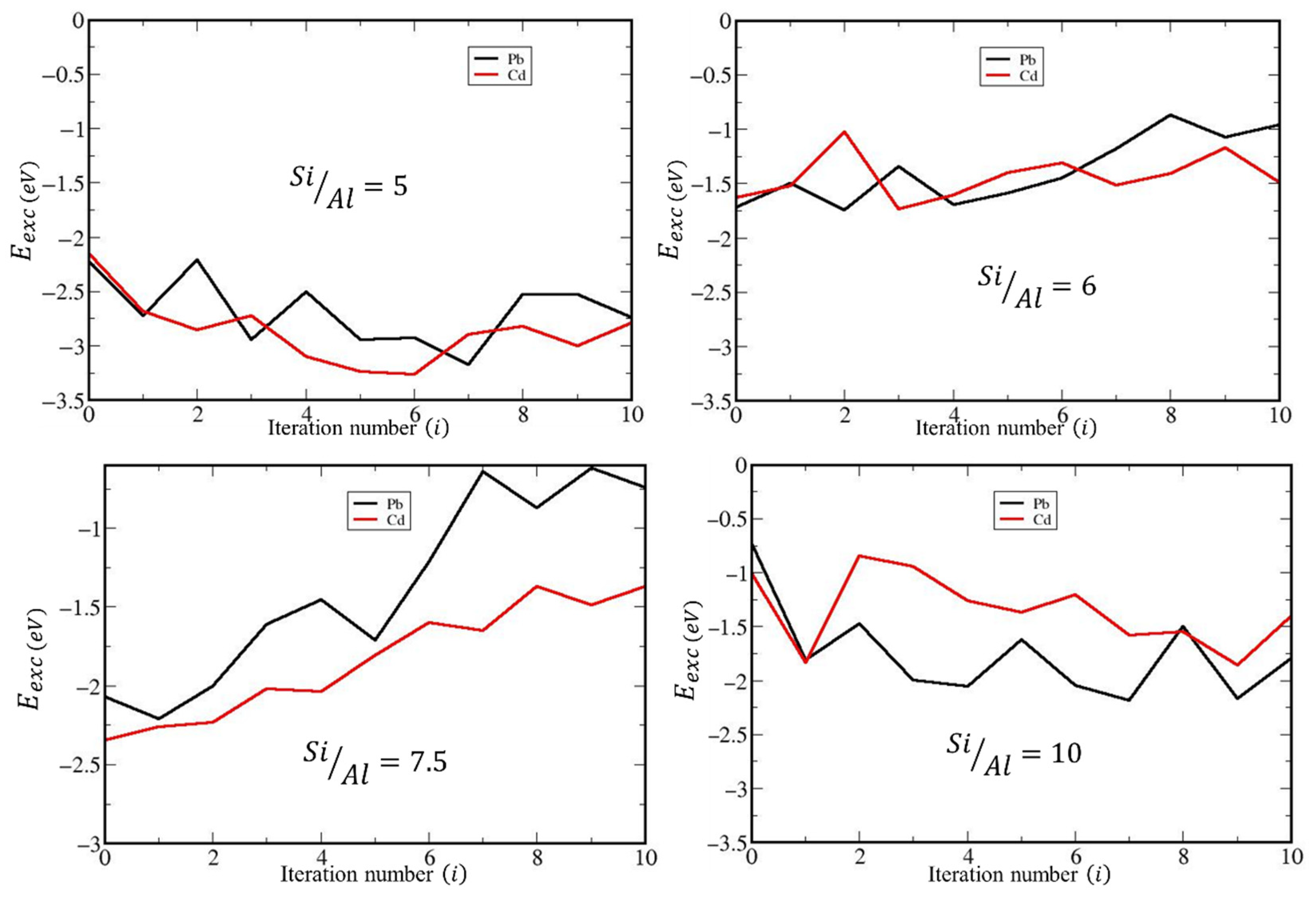
2.2.2. DFT Study of the Sorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ by Natural and Dealuminated Clinoptilolites
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experiments
3.2. DFT-Based Simulated Annealing Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. EXS 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusrini, E.; Mualim, N.M.; Rahman, A.; Usman, A. Application of Activated Na-Zeolite a as a Water Softening Agent to Remove Ca2+and Mg2+ions from Water. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Coimbatore, India, 9–10 April 2020; American Institute of Physics Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2255. [Google Scholar]
- Kusrini, E.; Mualim, N.M.; Usman, A.; Setiawan, M.D.H.; Rahman, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorption of Fe3+, Pb2+and Cu2+cations Using Na-Zeolite a Prepared from Bangka Kaolin. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Coimbatore, India, 9–10 April 2020; American Institute of Physics Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2255. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido-Ramírez, E.G.; Theng, B.K.G.; Mora, M.L. Clays and Oxide Minerals as Catalysts and Nanocatalysts in Fenton-like Reactions—A Review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reháková, M.; Čuvanová, S.; Dzivák, M.; Rimár, J.; Gaval’Ová, Z. Agricultural and Agrochemical Uses of Natural Zeolite of the Clinoptilolite Type. Curr. Opin. Solid. State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde-González, M.P.; Mattusch, J.; Einicke, W.-D.; Wennrich, R. Sorption on Natural Solids for Arsenic Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 81, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Tian, P.; Guo, X.; Song, C.; Liu, Z. Recent Advances of the Nano-Hierarchical SAPO-34 in the Methanol-to-Olefin (MTO) Reaction and Other Applications. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 4905–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, E.; Van Der Mynsbrugge, J.; Head-Gordon, M.; Bell, A.T. Impact of Long-Range Electrostatic and Dispersive Interactions on Theoretical Predictions of Adsorption and Catalysis in Zeolites. Catal. Today 2018, 312, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, C.; Wise, W.S. The IZA Handbook of Natural Zeolites: A Tool of Knowledge on the Most Important Family of Porous Minerals. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 189, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural Zeolites as Effective Adsorbents in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, B.B.; Walspurger, S.; Sommer, J. Quantitative Determination of Bro¨nstedBro¨nsted Acid Sites on Zeolites: A New Approach towards the Chemical Composition of Zeolites. Catal. Lett. 2004, 93, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca-Buentello, F.; Daar, A. Harnessing Nanotechnology to Improve Global Equity. Issues Sci. Technol. 2005, 21, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, N.; Rikhtegar, N.; Ahmad Panahi, H.; Atabi, F.; Shahraki, B.K. Porosity, Characterization and Structural Properties of Natural Zeolite—Clinoptilolite—As a Sorbent. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2013, 39, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Cobzaru, C.; Inglezakis, V. Mathematical Modeling of Sorption Process of Cu2+ Ions on Analcime and Clinoptilolite. Env. Eng. Manag. J. 2012, 11, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, T. Clinoptilolite-Heulandite: Applications and Basic Research. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 7–35. [Google Scholar]
- Irannajad, M.; Kamran Haghighi, H. Removal of Heavy Metals from Polluted Solutions by Zeolitic Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Buszewski, B.; Terzyk, A.P.; Namieśnik, J. Study of the Selection Mechanism of Heavy Metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+) Adsorption on Clinoptilolite. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of Heavy Metals from Waters by Means of Natural Zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malliou, E.; Loizidou, M.; Spyrellis, N. Uptake of Lead and Cadmium by Clinoptilolite. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 149, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müjgan, Ç.; Yaǧiz, M. Ion Exchange Properties of Natural Clinoptilolite: Lead-Sodium and Cadmium-Sodium Equilibria. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 37, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvidović, N.V.; Perić, J.; Trgo, M. Column Performance in Lead Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Fixed Bed of Natural Zeolite-Clinoptilolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Moon, H. Adsorption Equilibrium of Heavy Metals on Natural Zeolites. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2001, 18, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, P.; Santona, L.; Enzo, S.; Melis, P. Sorption Processes and XRD Analysis of a Natural Zeolite Exchanged with Pb2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+ Cations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berber-Mendoza, M.S.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Alonso-Davila, P.; Mendoza-Barron, J.; Diaz-Flores, P.E. Effect of PH and Temperature on the Ion-Exchange Isotherm of Cd(II) and Pb(II) on Clinoptilolite. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J. Solubility-Normalized Dubinin-Astakhov Adsorption Isotherm for Ion-Exchange Systems. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 103, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curkovi, L.; Cerjan-Stefanovi, S.; Filipan, T. Metal Ion Exchange by Natural and Modified Zeolites. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzow, M.J.; Eichbaum, B.R.; Sandgren, K.R.; Shanks, D.E. Removal of Heavy Metals and Other Cations from Wastewater Using Zeolites. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1990, 25, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorimbo, J.; Taenzana, B.; Muleja, A.A.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Jewell, L.L. Adsorption of Cadmium, Nickel and Lead Ions: Equilibrium, Kinetic and Selectivity Studies on Modified Clinoptilolites from the USA and RSA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30962–30978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylechko, V.O.; Gryshchouk, G.V.; Kuz’ma, Y.B.; Zakordonskiy, V.P.; Vasylechko, L.O.; Lebedynets, L.O.; Kalytovs’ka, M.B. Adsorption of Cadmium on Acid-Modified Transcarpathian Clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 60, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrikhpour, H.; Jalali, M. Comparative and Competitive Adsorption of Cadmium, Copper, Nickel, and Lead Ions by Iranian Natural Zeolite. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, C. Environmental Applications of Natural Zeolitic Materials Based on Their Ion-Exchange Properties. Nat. Microporous Mater. Environ. Technol. 1999, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouki, S.K.; Kavannagh, M. Treatment of Metals-Contaminated Wastewaters by Use of Natural Zeolites. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, M.; Santos, M.J.; Abrão, T.; Rodríguez, J.; Rigol, A. Modeling Competitive Metal Sorption in a Mineral Soil. Geoderma 2009, 149, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penilla, R.P.; Guerrero Bustos, A.; Goñi Elizalde, S. Immobilization of Cs, Cd, Pb and Cr by Synthetic Zeolites from Spanish Low-Calcium Coal Fly Ash. Fuel 2006, 85, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, H.; Bayati, B.; Rahbar Shahrouzi, J.; Babaluo, A.A.; Ghorbani, A. Molecular Simulation of the Ion Exchange Behavior of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ Ions on Different Zeolites Exchanged with Sodium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Immobilization of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) Ions on Kaolinite and Montmorillonite Surfaces from Aqueous Medium. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J. The Concept of “Capacity” in Zeolite Ion-Exchange Systems. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2005, 281, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, D.; Pepe, F. Experiments and Data Processing of Ion Exchange Equilibria Involving Italian Natural Zeolites: A Review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 105, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, A.; Akgül, G. Modification of Natural Zeolite with NaOH for Removal of Manganese in Drinking Water. Powder Technol. 2016, 287, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M.; Maicici, M. 13 Molecuar Sieve Sorbents from Clinoptilolite. Can. J. Chem. 1964, 17, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rožić, M.; Cerjan-Stefanović, Š.; Kurajica, S.; Maěefat, M.R.; Margeta, K.; Farkaš, A. Decationization and Dealumination of Clinoptilolite Tuff and Ammonium Exchange on Acid-Modified Tuff. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Basabe, Y.; Rodriguez-Iznaga, I.; De Menorval, L.C.; Llewellyn, P.; Maurin, G.; Lewis, D.W.; Binions, R.; Autie, M.; Ruiz-Salvador, A.R. Step-Wise Dealumination of Natural Clinoptilolite: Structural and Physicochemical Characterization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 135, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zou, Q.; Fu, L. Zeolite Modification for Adsorptive Removal of Nitrite from Aqueous Solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 252, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobzaru, C.; Oprea, S.; Dumitriu, E.; Hulea, V. Gas Phase Aldol Condensation of Lower Aldehydes over Clinoptilolite Rich Natural Zeolites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 351, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, H.L.; Yin, H.; Waller, A.; Khosravi, A.; Lind, M.L.; Patel, M. Impact of Acids on the Structure and Composition of Linde Type A Zeolites for Use in Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Recovery of Urine-Containing Wastewaters. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 201, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Hessou, E.P.; Badawi, M.; Netto, M.S.; Dotto, G.L.; Silva, L.F.O.; Tielens, F.; Ifthikar, J.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Chen, Z. Trapping of Ag+, Cu2+, and Co2+ by Faujasite Zeolite Y: New Interpretations of the Adsorption Mechanism via DFT and Statistical Modeling Investigation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuah, J.B.; Dzade, N.Y.; Tia, R.; Adei, E.; Kwakye-Awuah, B.; Catlow, R.A.; De Leeuw, N.H. A Density Functional Theory Study of Arsenic Immobilization by the Al(Iii)-Modified Zeolite Clinoptilolite. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 11297–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abatal, M.; Olguin, M.T. Comparative Adsorption Behavior between Phenol and P-Nitrophenol by Na- and HDTMA-Clinoptilolite-Rich Tuff. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Lecus, A.; Lin, Y.; Corrao, J. Tailoring Natural Zeolites by Acid Treatments. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Macedo, J.L.; Dias, S.C.L.; Dias, J.A. Multiple Adsorption Process Description of Zeolite Mordenite Acidity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 72, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borissenko, E.; Porcher, F.; Bouché, A.; Lecomte, C.; Souhassou, M. Single Crystal Structure of Fully Dehydrated Partially Co2+-Exchanged Zeolite X: Comparison with Partially Dehydrated Partially Co2+—Exchanged Zeolites X. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 114, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Nascimento, L.; Brito, M.; da Silva, K.; Paschoal, W.; Fujiyama, R. Biosorption of Methylene Blue Dye Using Natural Biosorbents Made from Weeds. Materials 2019, 12, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baimenov, A.; Montagnaro, F.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Balsamo, M. Experimental and Modeling Studies of Sr2+and Cs+ Sorption on Cryogels and Comparison to Commercial Adsorbents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 8204–8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Bai, H.; Gao, S.; Li, K. Characterization of Modified Sawdust, Kinetic and Equilibrium Study about Methylene Blue Adsorption in Batch Mode. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrrpn, M.E.; AnunnusrE, L.; KoHLER, T.; Kxowrns, C.R. Crystal Structure and Optical Properties of Na-and Pb-Exchanged Heulandite-Group Zeolites. Am. Mineral. 1994, 79, 675–682. [Google Scholar]
- Stolz, J.; Yang, P.; Armbruster, T. Cd-Exchanged Heulandite: Symmetry Lowering and Site Preference. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 37, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Arish, N.A.S.; Zaki, R.S.R.M.; Miskan, S.N.; Setiabudi, H.D.; Jaafar, N.F. Adsorption of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Alkaline-Treated Natural Zeolite: Process Optimization Analysis. Total Environ. Res. Themes 2022, 3–4, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragović, M.; Daković, A.; Marković, M.; Krstić, J.; Gatta, G.D.; Rotiroti, N. Characterization of Lead Sorption by the Natural and Fe(III)-Modified Zeolite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, A.; Arslankaya, E.; Tosun, I. Lead Removal from Aqueous Solution by Natural and Pretreated Clinoptilolite: Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosso, S.T.; Enzweiler, J. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solution onto Scolecite. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4795–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi, H.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A. An Efficient Modified Zeolite for Simultaneous Removal of Pb(II) and Hg(II) from Aqueous Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhym, A.B.; Seilkhanova, G.A.; Kurmanbayeva, T.S. Adsorption of Lead (II) Ions from Water Solutions with Natural Zeolite and Chamotte Clay. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanes-Monter, M.M.; Olguín, M.T.; Solache-Ríos, M.J. Lead Sorption by a Mexican, Clinoptilolite-Rich Tuff. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Xie, T.; Yan, G.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L. Effective Removal of Pb2+ from Aqueous Solutions by Magnetically Modified Zeolite. Powder Technol. 2018, 332, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, S.M.; Jimenez, R.S.; Carvalho, W.A. Removal of Toxic Metals from Wastewater by Brazilian Natural Scolecite. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2005, 281, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ayuso, E.; García-Sánchez, A.; Querol, X. Purification of Metal Electroplating Waste Waters Using Zeolites. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4855–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.C.; Chen, S.S.; Hsu, H.T.; Li, C.W. Separation of Three Divalent Cations (Cu2+, Co2+ and Ni2+) by NF Membranes from PHs3 to 5. Desalination 2013, 328, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Martínez, R.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Solache-Ríos, M.; García-Sosa, I. Evaluation of Natural and Surfactant-Modified Zeolites in the Removal of Cadmium from Aqaeous Solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 2711–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatal, M.; Ruiz-Salvador, A.R.; Hernández, N.C. A DFT-Based Simulated Annealing Method for the Optimization of Global Energy in Zeolite Framework Systems: Application to Natrolite, Chabazite and Clinoptilolite. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2020, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Salvador, A.R.; Lewis, D.W.; Rubayo-Soneira, J.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, G.; Sierra, L.R.; Catlow, C.R.A. Aluminum Distribution in Low Si/Al Zeolites: Dehydrated Na-Clinoptilolite. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 8417–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Salvador, A.R.; Almora-Barrios, N.; Gómez, A.; Lewis, D.W. Interplay of Water, Extra-Framework Cations and Framework Atoms in the Structure of Low-Silica Zeolites: The Case of the Natural Zeolite Goosecreekite as Studied by Computer Simulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmiiller, B.J. Efficiency of Ab-Initio Total Energy Calculations for Metals and Semiconductors Using a Plane-Wave Basis Set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient Iterative Schemes for Ab Initio Total-Energy Calculations Using a Plane-Wave Basis Set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From Ultrasoft Pseudopotentials to the Projector Augmented-Wave Method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blochl, P.E. Blöchl Projector Augmented-Wave Method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A Consistent and Accurate Ab Initio Parametrization of Density Functional Dispersion Correction (DFT-D) for the 94 Elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104–154119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
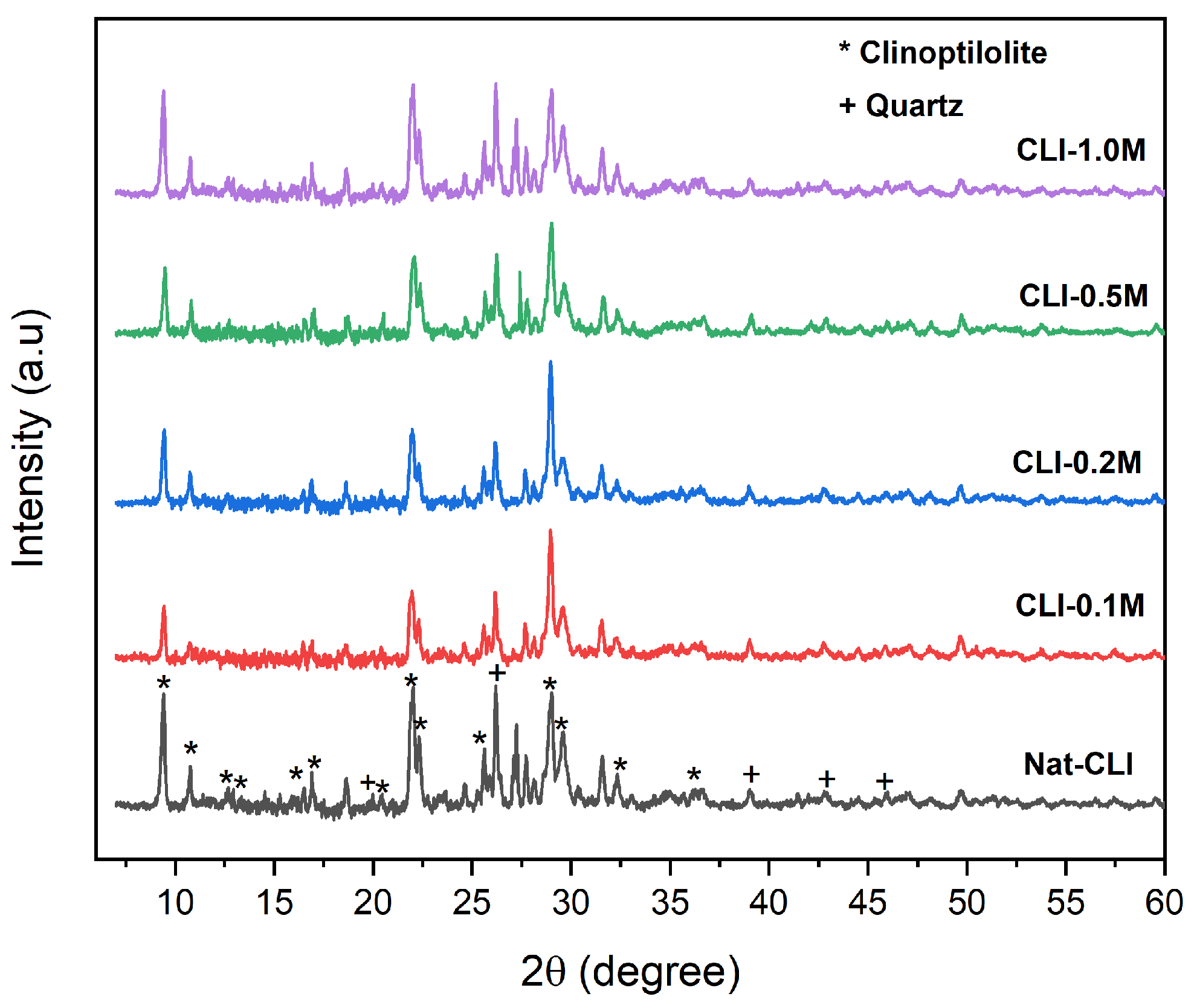
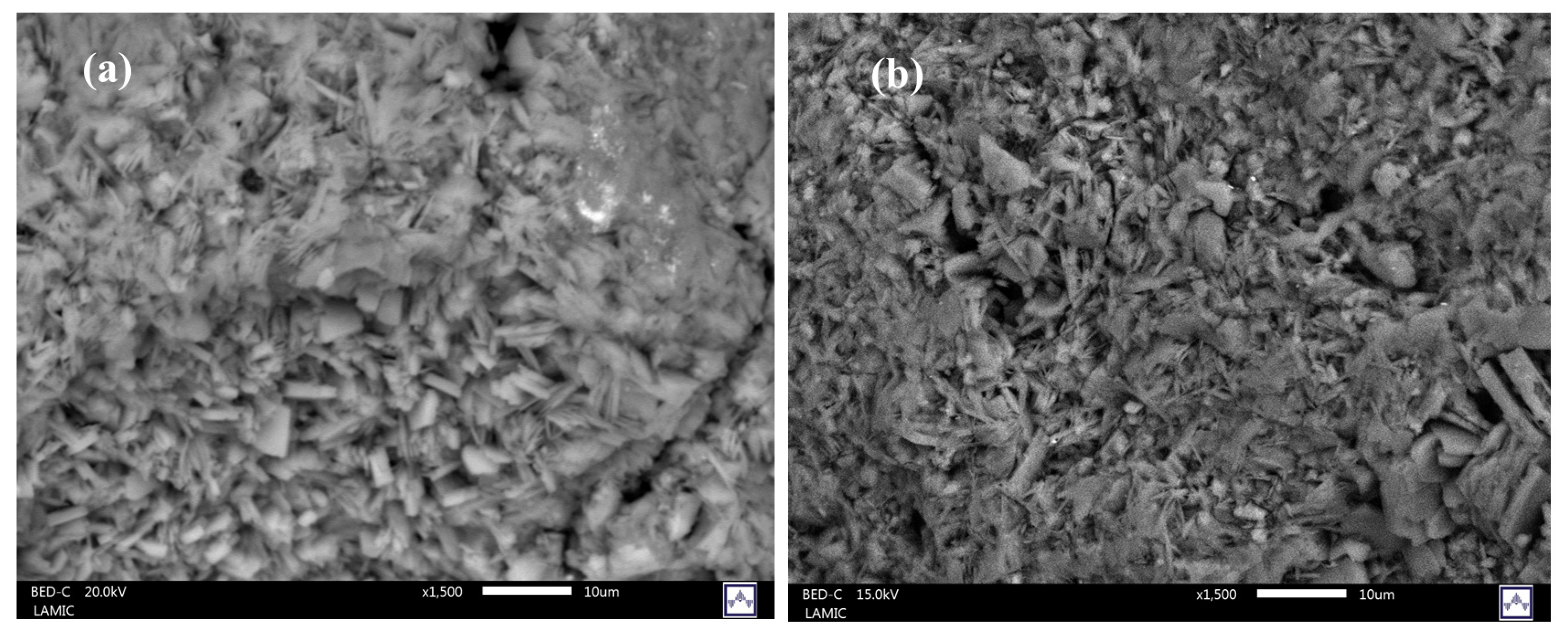
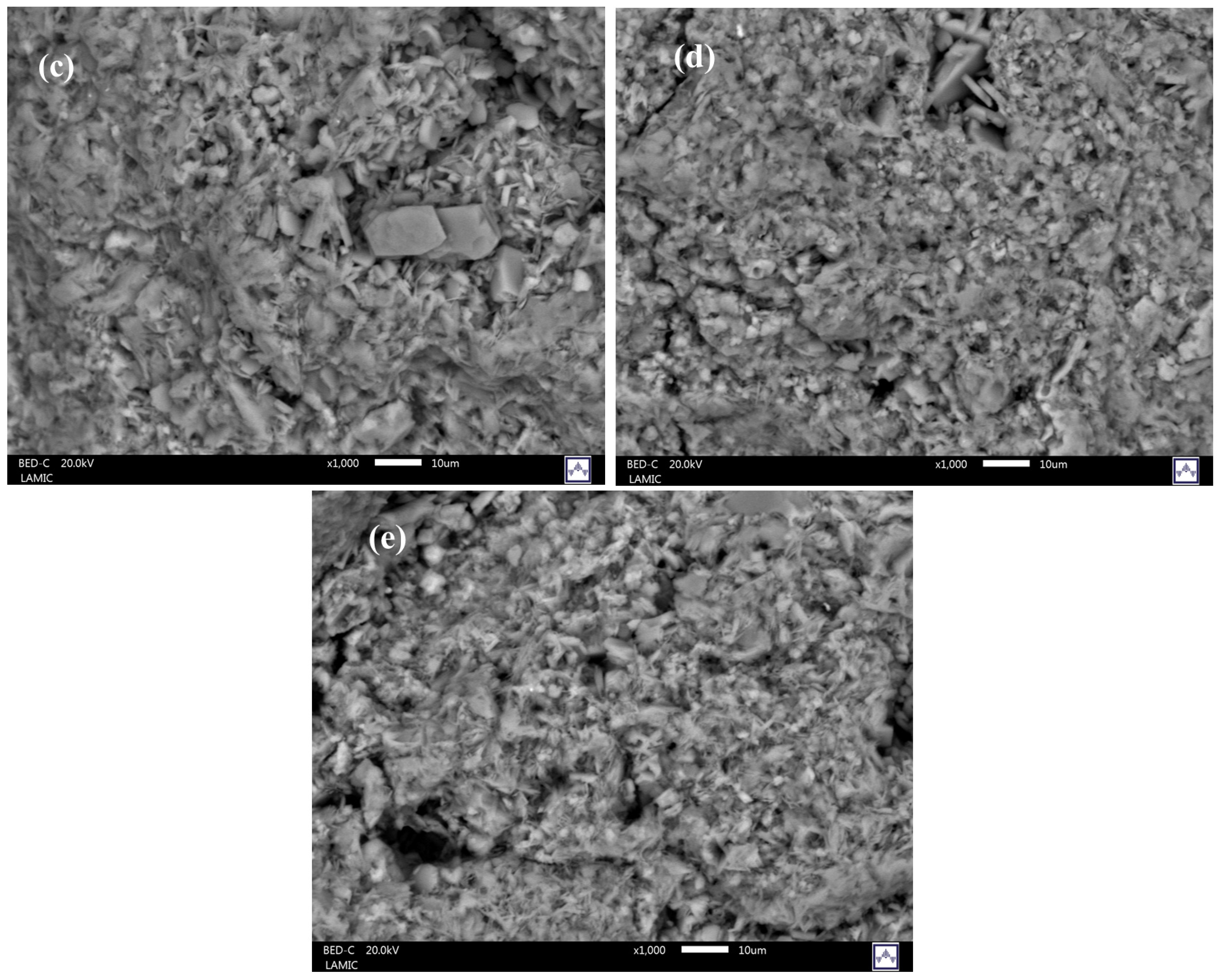





| Weight % of Elements | Zeolites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nat-CLI | CLI-0.1 M | CLI-0.2 M | CLI-0.5 M | CLI-1.0 M | |
| Na | 0.56 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| K | 1.17 | 0.97 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.46 |
| Ca | 1.65 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 0.50 | 0.22 |
| Mg | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Fe | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.07 |
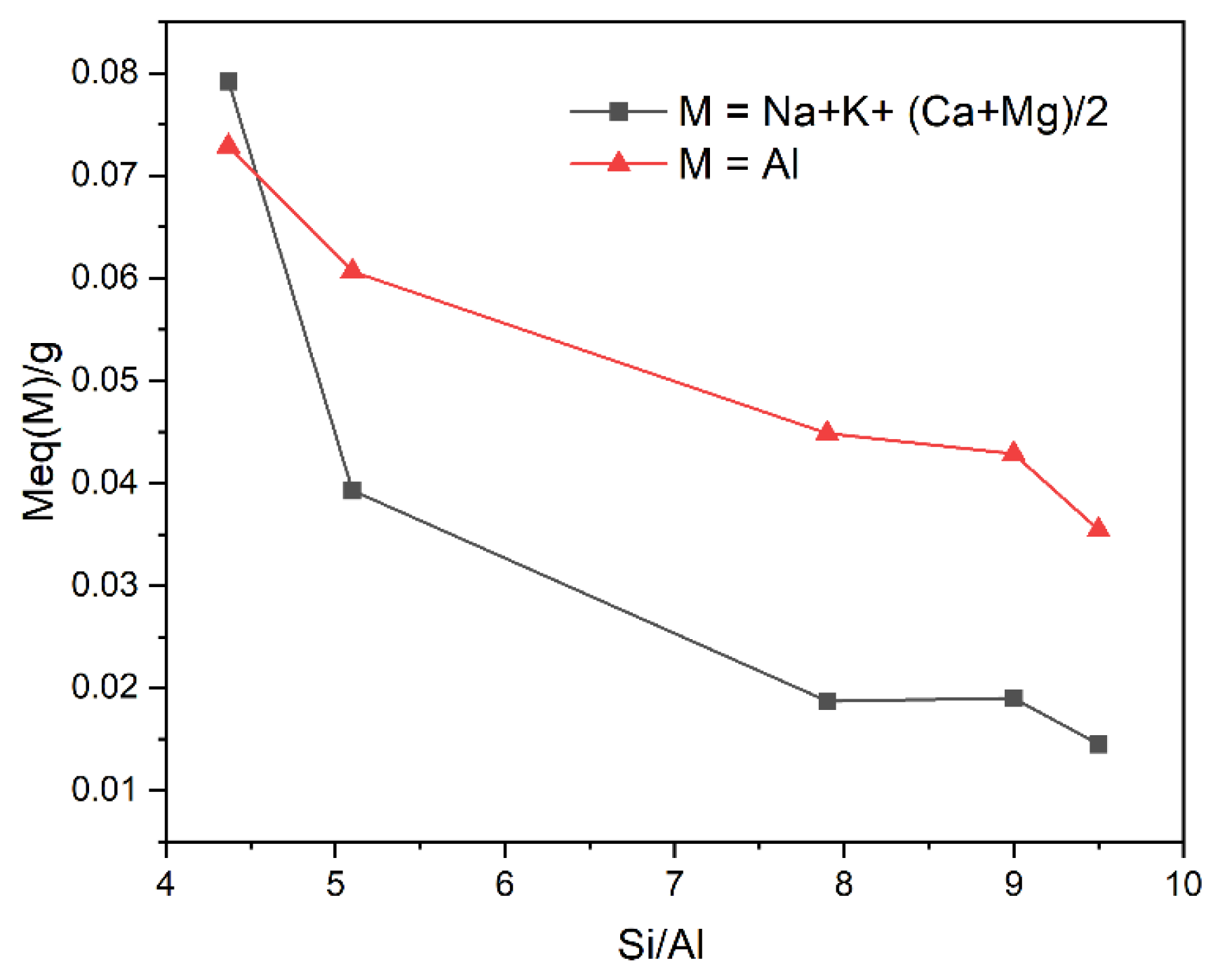
| Si | 25.77 | 26.44 | 27.78 | 28.85 | 27.71 |
| Al | 5.90 | 4.98 | 3.51 | 3.19 | 2.91 |
| O | 64.37 | 66.34 | 67.24 | 66.84 | 68.63 |
| Si/Al | 4.37 | 5.31 | 7.91 | 9.04 | 9.52 |
| Non-Linear Pseudo First Order Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite | qe,exp (×10−3) (meq/g) | qe,cal (×10−3) (meq/g) | k1 (1/min) | R2 | ||||
| Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | |
| Nat-CLI | 49.118 | 19.536 | 48.168 | 18.915 | 0.084 | 0.120 | 0.899 | 0.686 |
| CLI-0.1 M | 47.181 | 18.015 | 44.995 | 16.272 | 0.038 | 0.021 | 0.890 | 0.822 |
| CLI-0.2 M | 46.103 | 14.154 | 43.231 | 13.693 | 0.030 | 0.009 | 0.828 | 0.938 |
| CLI-0.5 M | 29.140 | 11.590 | 27.396 | 10.735 | 0.018 | 0.042 | 0.916 | 0.662 |
| CLI-1.0 M | 20.309 | 12.623 | 18.317 | 11.097 | 0.011 | 0.019 | 0.806 | 0.775 |
| Non-linear pseudo second order model | ||||||||
| qe,exp (×10−3) (meq/g) | qe,cal (×10−3) (meq/g) | k2 (g/(meq min)) | R2 | |||||
| Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | |
| Nat-CLI | 49.118 | 19.536 | 49.663 | 19.296 | 3.614 | 17.144 | 0.993 | 0.976 |
| CLI-0.1 M | 47.181 | 18.015 | 47.846 | 17.772 | 1.261 | 1.702 | 0.983 | 0.952 |
| CLI-0.2 M | 46.103 | 14.154 | 46.607 | 15.255 | 0.966 | 0.914 | 0.962 | 0.981 |
| CLI-0.5 M | 29.140 | 11.590 | 30.189 | 11.401 | 0.876 | 5.907 | 0.978 | 0.912 |
| CLI-1.0 M | 20.309 | 12.623 | 20.303 | 12.258 | 0.783 | 2.184 | 0.921 | 0.926 |
| Nonlinear Langmuir Isotherm Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite | q,max, (×10−3) (meq/g) | KL (×10−2) (L/meq) | R2 | |||
| Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | |
| Nat-CLI | 224.554 | 39.044 | 8.429 | 0.125 | 0.964 | 0.985 |
| CLI-0.1 M | 209.044 | 28.596 | 4.666 | 0.184 | 0.977 | 0.988 |
| CLI-0.2 M | 107.284 | 31.995 | 5.127 | 0.084 | 0.979 | 0.986 |
| CLI-0.5 M | 56.541 | 27.403 | 0.197 | 0.092 | 0.920 | 0.980 |
| CLI-1.0 M | 53.802 | 20.529 | 0.103 | 0.142 | 0.948 | 0.990 |
| Nonlinear Freundlich isotherm model | ||||||
| n | KF (L/g) | R2 | ||||
| Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cd2+ | |
| Nat-CLI | 2.653 | 2.344 | 35.204 | 1.008 | 0.918 | 0.960 |
| CLI-0.1 M | 3.112 | 2.701 | 31.578 | 1.233 | 0.836 | 0.914 |
| CLI-0.2 M | 3.908 | 2.059 | 19.974 | 0.460 | 0.953 | 0.960 |
| CLI-0.5 M | 2.150 | 2.216 | 1.429 | 0.524 | 0.980 | 0.953 |
| CLI-1.0 M | 1.766 | 2.653 | 0.515 | 0.789 | 0.977 | 0.941 |
| Type of Zeolite | Qmax (meq/g) | Experimental Conditions | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural zeolite | Kazakhstanil zeolite | 0.068 | pH = 6 Contact time = 4 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 1 | [62] |
| Ukraine clinoptilolite | 0.067 | pH = 6.2 Contact time = 48 h T(°C) = 20 Dose (g/L) = 0.5 | [17] | |
| Clinoptilolite | 0.931 | pH = 4.5 Contact time = 4 h T (°C) = 22 Dose (g/L) = 0.5 | [59] | |
| Scolecite | 0.028 | pH = 6.0 Contact time = 24 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 5 | [60] | |
| Mexican clinoptilolite | 0.701 | pH = 5.0 Contact time = 48 h T (°C) = 30 Dose (g/L) = 0.1 | [63] | |
| Clinoptilolite | 0.035 | pH = 5.0 Contact time = 8 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 5 | [61] | |
| Clinoptilolite | 0.319 | pH = 4.24 Contact time = 24 h T (°C) = 60 Dose (g/L) = 20 | [58] | |
| Clinoptilolite | 0.224 | pH = 5.6 Contact time = 12 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 10 | In this study | |
| Chemically modified zeolite | NaCl treated | 0.591 | pH = 4.5 Contact time = 4 h T (°C) = 22 Dose (g/L) = 20 | [59] |
| Fe(III)-modified zeolite | 0.642 | pH = 4.24 Contact time = 24 h T (°C) = 60 Dose (g/L) = 20 | [58] | |
| Magnetically Modified Zeolite | 0.406 | pH = 4 T (°C) = 20 Dose (g/L) = 2 | [64] | |
| NaOH treated zeolite | 0.929 | pH = 6 Contact time = 2 h T (°C) = 20 Dose (g/L) = 1 | [57] | |
| Acidified clinoptilolites (Si/Al =4.5 –9.5) | 0.054–0.209 | pH = 5.6 Contact time = 12 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 10 | In this study | |
| Type of Zeolite | Qmax (meq/g) | Experimental Conditions | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural zeolite | Ukraine clinoptilolite | 0.020 | pH = 6.2 Contact time = 48 h T(°C) = 20 Dose (g/L) = 2.5 | [17] |
| Scolecite | 0.002 | pH = 6.0 Contact time = 24 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 5 | [60] | |
| Brazilian scolecite | 0.893 | pH = 6.0 Contact time = 24 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 16 | [65] | |
| Clinoptilolite | 0.041 | pH = 6.0 Contact time = 6 h T (°C) = 22 Dose (g/L) = 10 | [66] | |
| Clinoptilolite | 0.039 | pH = 5.6 Contact time = 12 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 10 | In this study | |
| Chemically modified zeolite | Iron-coated zeolite | 0.065 | pH = 6.5 Contact time = 24 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 1 | [67] |
| NaCl modified zeolite | 0.112 | pH = 6.0 Contact time = 48 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 10 | [68] | |
| Surfactant-modified zeolite | 0.090 | pH = 6.0 Contact time = 48 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 10 | [68] | |
| Acidified clinoptilolites (Si/Al =4.5–9.5) | 0.021–0.028 | pH = 5.6 Contact time = 12 h T (°C) = 25 Dose (g/L) = 10 | In this study | |
| 5 | 17.545 | 18.214 | 7.427 | 2121.2 | 89.13 | 116.60 |
| 6 | 17.512 | 18.349 | 7.421 | 2128.3 | 90.48 | 116.69 |
| 7.5 | 17.631 | 18.514 | 7.434 | 2169.4 | 90.67 | 116.47 |
| 10 | 17.683 | 18.577 | 7.410 | 2166.6 | 90.48 | 117.04 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | −3.17 | −3.26 |
| 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | −1.60 | −1.64 |
| 7.5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | −2.21 | −2.34 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | −2.18 | −1.85 |
| Ions | (eV) | (eV) |
|---|---|---|
| Pb2+ | 0.88 | 1.13 |
| Cd2+ | 1.05 | 1.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durán-Avendaño, Y.S.; Hernández, N.C.; Ruiz-Salvador, A.R.; Abatal, M. Further Insight in the High Selectivity of Pb2+ Removal over Cd2+ in Natural and Dealuminated Rich-Clinoptilolite. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094154
Durán-Avendaño YS, Hernández NC, Ruiz-Salvador AR, Abatal M. Further Insight in the High Selectivity of Pb2+ Removal over Cd2+ in Natural and Dealuminated Rich-Clinoptilolite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094154
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurán-Avendaño, Yaneth Stephanie, Norge Cruz Hernández, A. Rabdel Ruiz-Salvador, and Mohamed Abatal. 2025. "Further Insight in the High Selectivity of Pb2+ Removal over Cd2+ in Natural and Dealuminated Rich-Clinoptilolite" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094154
APA StyleDurán-Avendaño, Y. S., Hernández, N. C., Ruiz-Salvador, A. R., & Abatal, M. (2025). Further Insight in the High Selectivity of Pb2+ Removal over Cd2+ in Natural and Dealuminated Rich-Clinoptilolite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094154







