Benthic Marine Ciliate Assemblages from Southern Brazil and Their Relationship with Seasonality and Urbanization Level
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Environmental Parameters
2.3. Data Analyses
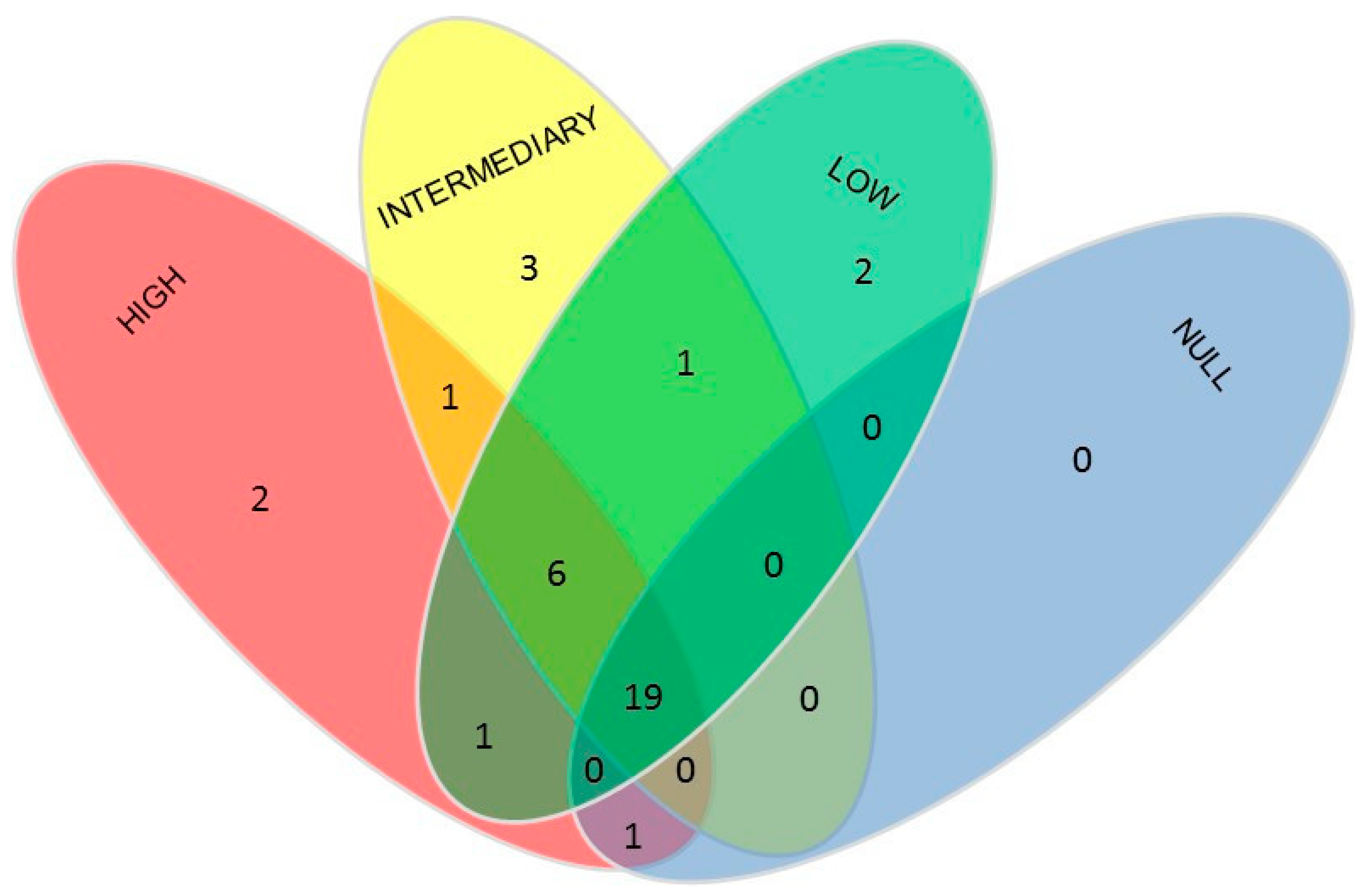
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLachlan, A.; Brown, A. The Ecology of Sandy Shores, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdan, The Netherlands, 2006; p. 392. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, D.H. The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification, and Guide to the Literature, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; p. 605. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, S.; Gieseke, A.; Beminger, U.G. Benthic ciliate identification and enumeration: An improved methodology and its application. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 22, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giere, O. Meiobenthology: The Microscopic Motile Fauna of Aquatic Sediments, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; p. 538. [Google Scholar]
- Lana Paulo, C. O valor da biodiversidade e o impasse taxonômico: A diversidade marinha como estudo de caso. Desenvol. Meio Amb. 2003, 8, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, E.F.; Pinto, A.P.B.; Perez, A.A.Q.; Veloso, V.G. Spatial and temporal changes in interstitial meiofauna on a sandy ocean beach of South America. Braz. J. Ocean. 2007, 55, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, F.; Netto, S.A. Effects of the passage of cold fronts over a coastal site: An ecosystem approach. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2004, 281, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neves, F.M.; Bemvenuti, C.E. Variabilidade diária na zonação da macrofauna bentônica em praias arenosas do litoral norte do Rio Grande do Sul. Iheringia 2009, 99, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neves, F.M.; de Sá Rodrigues da Silva, P.; Bemvenuti, C.E. Distribuição horizontal da macrofauna bentônica na Praia do Cassino, extremo sul do Brasil. Iheringia 2012, 102, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kattar, M.R. Estudo dos protozoários ciliados psamófilos do litoral brasileiro. Bol. Zool. Biol. Mar. 1970, 27, 123–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paiva, T.S.; Albuquerque, A.F.C.; Borges, B.N.; Harada, M.L. Description and phylogeny of Tetrakeronopsis silvanetoi gen. nov., sp. nov. (Hypotrichia, Pseudokeronopsidae), a new benthic marine ciliate from Brazil. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanick, R.C.; Silva-Neto, I.D. Benthic ciliates from Sepetiba Bay (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) with description of Pseudokeronopsis sepetibensis n. sp. (Spirotrichea: Urostylida). Zootaxa 2004, 587, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Lubchenco, J.; Melillo, J.M. Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, S.M. Assessing cause and effect of multiple stressors on marine systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyce, D.G.; Lewis, M.R.; Worm, B. Global phytoplankton decline over the past century. Nature 2010, 466, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, C.D.L.; Arantes, N.; Faveri, C.; Batista, M.B.; Oliveira, E.C.; Pagliosa, P.R.; Fonseca, A.L.; Nunes, J.M.C.; Chow, F.; Pereira, S.B.; et al. The impact of coastal urbanization on the structure of phytobenthic communities in southern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, N.S.V.; Moran, E.F.; Strohaecker, T.M.; Kunst, A.V. A urbanização na zona costeira: Processos locais e regionais e as transformações ambientais—O caso do Litoral Norte do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Ciência Natura 2015, 37, 594–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gheskiere, T.; Vincx, M.; Weslawski, J.M.; Scapini, F.; Degraer, S. Meiofauna as descriptor of tourism-induced changes at sandy beaches. Mar. Environ. Res. 2005, 60, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harguinteguy, C.A.; Cofré, M.N.; Pastor de Ward, C.T. Change in the meiofauna community structure of sandy beaches of the Nuevo Gulf (Chubut, Argentina). Papéis Avulsos Zoologia 2012, 52, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomazelli, L.J.; Villwock, J.A. Mapeamento geológico de planícies costeiras: O exemplo da costa do Rio Grande do Sul. Gravel 2005, 3, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Toldo, E.E., Jr.; Almeida, L.E.S.B.; Nicoldi, J.L.; Absalonsen, L.; Gruber, N.L.S. O controle da deriva litorânea no desenvolvimento do campo de dunas e da antepraia no Litoral Médio do Rio Grande do Sul. Pesqu. Geociências 2006, 3, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calliari, L.J.; Toldo, E.E.; Nicolodi, J.L. Rio Grande do Sul: Classificação geomorfológica. In Erosão e Progradação no Litoral Brasileiro, 1st ed.; Muehe, D., Ed.; Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasília, Brazil, 2006; pp. 438–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro, L.W.; Hasenack, H. Clima. In Ecossistemas e Biodiversidade do Litoral Norte do Rio Grande do Sul, 1st ed.; Würdig, N.L., Freitas, S.M.F., Eds.; Nova Prova: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2009; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sherr, E.B.; Sherr, B.F. Preservation and Storage of Samples for Enumeration of Heterotrophic Protists. In Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 1st ed.; Kemp, P.F., Sherr, B.F., Sherr, E.B., Cole, J.J., Eds.; Lewis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, R.M.P. Métodos de coleta, preservação, contagem e determinação de biomassa em zooplâncton de águas epicontinentais. In Amostragem em Limnologia, 1st ed.; Bicudo, C.D.M., Bicudo, D.D.C., Eds.; RiMA: São Carlos, Brazil, 2004; pp. 149–165. [Google Scholar]
- Small, E.B. A simple method for obtaining concentrated populations of protists from sediments. In Protocols in Protozoology, 1st ed.; Lee, J.J., Soldo, A.T., Eds.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1992; p. A25. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, P.G. Marine Interstitial Ciliates. An Illustrated Key, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1992; p. 351. [Google Scholar]
- Dragesco, J.; Dragesco-Kernéis, A. Cilie’s libres de l’Afrique intertropicale. Introduction a‘la connaissanceet a‘l’e´tude des Cilie´s. Faune Tropicale 1986, 26, 1–559. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, F.; Hu, X.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S. Apotrachelocerca arenicola (Kahl, 1933) n. g., comb. n. (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Trachelocercidae): Morphology and Phylogeny. J. Euk. Mic. 2011, 58, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Miao, M.; Warren, A.; Song, W. Diversity of the karyorelictid ciliates: Remanella (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Karyorelictida) inhabiting intertidal areas of Qingdao, China, with descriptions of three species. Syst. Biodiv. 2012, 10, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Song, W. Morphology and phylogeny of three trachelocercids (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Karyorelictea), with description of two new species and insight into the evolution of the family Trachelocercidae: Two New Ciliates and Evolution of Trachelocercids. Zool. J. Linnean Soc. 2016, 177, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golterman, H.L.; Clymo, R.S.; Ohnstad, M.A.M. Methods for Physical and Chemical Analysis of Freshwater; Oxford Blackwell Scientific Publications IBP Handbook; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1978; p. 213. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, S.E. Chemical Analysis of Ecological Materials, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science Inc.: Oxford, UK, 1989; p. 565. [Google Scholar]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring Biological Diversity, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; 264p. [Google Scholar]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R Package Version 1.0.12. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 9 December 2019).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-5. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 9 December 2019).
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 3.1-139. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 9 December 2019).
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 1006. [Google Scholar]
- De Caceres, M.; Legendre, P. Associations between species and groups of sites: Indices and statistical inference. Ecology 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrêne, M.; Legendre, P. Species assemblages and indicator species: The need for a flexible asymetrical approach. Ecol. Monog. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar]
- Azovsky, A.; Mazei, Y. Do microbes have macroecology? Large-scale patterns in the diversity and distribution of marine benthic ciliates. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenchel, T. The ecology of marine microbenthos. IV. Structure and function of the benthic ecosystem. Ophelia 1969, 6, 1–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, G.; Lucchesi, P. The ciliated protozoa of an interstitial Mediterranean microcommunity. Hydrobiologia 1992, 230, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y. 21-Year dynamics of marine benthic ciliate community in the White Seaintertidal flat: Gradual or discrete? Russian J. Ecosyst. Ecol. 2017, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Sleigh, M.A. Distribution and Abundance of Interstitial Ciliates in Southampton Water in Relation to Physicochemical Conditions, Metal Pollution and the Availability of Food Organisms. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 41, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rasheid, K.A.S. New records of interstitial ciliates (Protozoa Ciliophora) from the Saudi coasts of the Red Sea. Trop. Zool. 2001, 14, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A.; Saburova, M.; Tikhonenkov, D.; Khazanova, K.; Esaulov, A.; Mazei, Y. Composition, diversity and distribution of microbenthos across the intertidal zones of Ryazhkov Island (the White Sea). Eur. J. Protist. 2013, 49, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, G.; Lucchesi, P. Spatial distribution pattern of ciliated protozoa in a Mediterranean interstitial environment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1995, 9, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, X.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Song, W. Phylogeny and systematic revision of the karyorelictid genus Remanella (Ciliophora, Karyorelictea) with descriptions of two new species. Eur. J. Protistol. 2013, 49, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Shen, P.; Huang, H.; Dai, M.; Qi, Z. A first description of ciliate assemblages in a subtropical eutrophic bay, South China Sea: Species assemblage and environmental correlates. Aquat. Living Resour. 2016, 29, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A.I.; Mazei, Y.A. Diversity and distribution of free-living ciliates from High-Artic Kara sea sediments. Protist 2018, 169, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Soininem, J. Spatial patterns of functional diversity and composition in marine benthic ciliates along the coast of China. MEPS 2019, 627, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazei, Y.A.; Burkovsky, I.V. Species composition of benthic ciliate community in the Chernaya River estuary (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea) with a total checklist of the White Sea benthic ciliate fauna. Protistology 2015, 4, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, S.S.; Gallagher, E.D. Evidence for facilitation and inhibition of ciliate population growth by meiofauna and macrofauna on a temperate zone sandflat. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 155, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Stoeck, T.; Forster, D.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X. Environmental status assessment using biological traits analyses and functional diversity indices of benthic ciliate communities. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2018, 131, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.M. The Disturbing History of Intermediate Disturbance. Oikos 1999, 84, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Patel, S.N. Community assembly in the presence of disturbance: A microcosm experiment. Ecology 2008, 89, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| Class | Urbanization Degree | Beaches | Density of Residences Close to the Collection Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban with permanent population | High | Torres | High |
| Urban with permanent population | High | Tramandaí | High |
| Urban base for second residence | Intermediary | Arroio do Sal | Low |
| Urban base for second residence | Intermediary | Bal. Pinhal | Low |
| Pristine beaches | Low | Magistério | Very Low |
| Pristine beaches | Low | Sta Rita | Very Low |
| Dune Field | Almost null | Cidreira | Null |
| Areas | Shared Taxa |
|---|---|
| High × Intermediary | Uroleptus |
| High × Low | Strongylidium |
| High × Null | Lacrymaria |
| Intermediary × Low | Geleia |
| High × Intermediary × Low | Apotrachelocerca, Holosthica, Nassula, Pseudoprorodon, Spirostomum, Stichotricha |
| High × Intermediary × Low × Null | Amphisiella, Aspidisca, Chaenea, Chilodonella Coleps, Condylostoma Dysteria, Euplotes,Frontonia, Loxophyllum, Mesodinium, Pleuronema, Prorodon, Remanella, Sathrophilus, Strombidium, Trachelocerca, Trachelonema, Tracheloraphis, Uronema |
| Degree of Urbanization | Exclusive Taxa |
| High | Keronopsis, Metopus |
| Intermediary | Aristerostoma, Stylonchia, Blepharisma |
| Low | Tinntinopsis, Gruberia |
| Descriptors | Urbanization | Season | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Temperature | 0.2180 | 0.6603 | 290.1780 | 0.0001 |
| Chlorophyll a | 0.0355 | 0.8580 | 5.0841 | 0.0101 |
| Organic matter | 0.6369 | 0.4610 | 0.9918 | 0.4190 |
| Species richness | 0.6377 | 0.4608 | 3.0878 | 0.0434 |
| Species diversity | 0.0022 | 0.9647 | 2.9976 | 0.0480 |
| Conductivity | 0.0600 | 0.8122 | 180.2800 | 0.0001 |
| Tukey’s Post-Hoc | ||||
| Temperature | All contrasts significant (p < 0.0001) | |||
| Chlorophyll a | W-Sp (p = 0.0026), W-Su (p = 0.0104), W-A (p = 0.001) | |||
| Species richness | W-Su (p = 0.0262), W-A (p = 0.016) | |||
| Species diversity | A-Su (p = 0.0088) | |||
| Conductivity | All contrasts significant (p < 0.0001), except A-Sp | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarragô, L.D.; Ferreira, P.M.A.; Utz, L.R.P. Benthic Marine Ciliate Assemblages from Southern Brazil and Their Relationship with Seasonality and Urbanization Level. Diversity 2020, 12, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12010016
Tarragô LD, Ferreira PMA, Utz LRP. Benthic Marine Ciliate Assemblages from Southern Brazil and Their Relationship with Seasonality and Urbanization Level. Diversity. 2020; 12(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarragô, Luana D., Pedro M. A. Ferreira, and Laura R. P. Utz. 2020. "Benthic Marine Ciliate Assemblages from Southern Brazil and Their Relationship with Seasonality and Urbanization Level" Diversity 12, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12010016
APA StyleTarragô, L. D., Ferreira, P. M. A., & Utz, L. R. P. (2020). Benthic Marine Ciliate Assemblages from Southern Brazil and Their Relationship with Seasonality and Urbanization Level. Diversity, 12(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12010016





