Geographic Patterns of Genetic Variation among Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Populations Based on Chloroplast Markers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
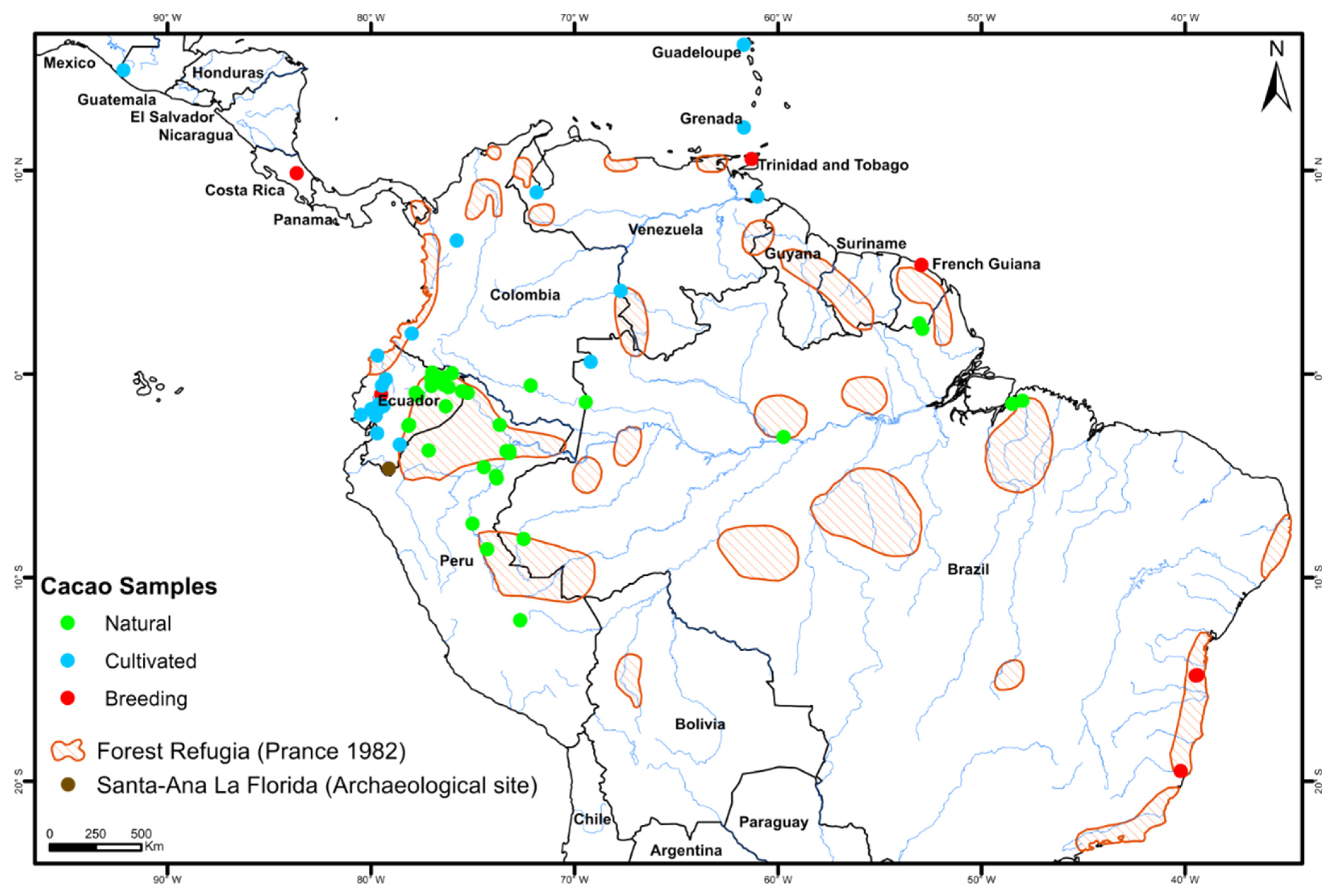
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Chloroplast DNA Markers
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Haplotypes
3.2. Western Amazonia, a Center of Haplotype Diversity
3.3. Geographically Restricted Haplotypes in Western Amazonia
3.4. Correspondence between Chloroplast and Nuclear DNA Variation
3.5. Haplotypes in Ecuadorian Plantations
3.6. Haplotypes Observed in Breeding Populations and Cultivars
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution of Haplotype Diversity
4.2. Chloroplast Haplotypes Match Genetic Groups Based on nSSRs
4.3. Chloroplast Haplotypes and Domesticated Cacao
4.4. Haplotype Diversity in Plantations and Breeding Populations
5. Conclusions
6. Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartley, B.G.D. The Genetic Diversity of Cacao and Its Utilization; CABI Pub: Cambridge MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 0851996191. [Google Scholar]
- Motamayor, J.C.; Lachenaud, P.; da Silva, E.; Mota, J.W.; Loor, R.; Kuhn, D.N.; Brown, J.S.; Schnell, R.J. Geographic and genetic population differentiation of the Amazonian chocolate tree (Theobroma cacao L). PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, R.A.; Greenberg, R. Cacao Cultivation and the Conservation of Biological Diversity. Ambio 2000, 29, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Jan, K.; Bashir, K. Status, supply chain and processing of cocoa—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.B. Out of the Amazon: Theobroma cacao enters the genomic era. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goenaga, R.; Irizarry, H.; Irish, B. TARS Series of Cacao Germplasm Selections. HortScience 2009, 44, 826–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips-Mora, W.; Arciniegas-Leal, A.; Mata-Quirós, A.; Motamayor-Arias, J.C. Catalogue of Cacao Clones: Selected by Catie for Commercial Plantings; CATIE: Turrialba, Costa Rica, 2013; ISBN 9789977575902. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Figueira, A.; Motilal, L.; Lachenaud, P.; Meinhardt, L.W. Theobroma. In Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 277–296. [Google Scholar]
- CacaoNet. A Global Strategy for the Conservation and Use of Cacao Genetic Resources, as the Foundation for a Sustainable Cocoa Economy; Bioversity International: Montpellier, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Motilal, L. Origin, Dispersal, and Current Global Distribution of Cacao Genetic Diversity. In Cacao Diseases; Bailey, B.A., Meinhardt, L.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 3–31. ISBN 978-3-319-24787-8. [Google Scholar]
- Laliberté, B.; End, M.; Cryer, N.; Daymond, A.; Engels, J.; Eskes, A.B.; Gilmour, M.; Lachenaud, P.; Phillips-Mora, W.; Turnbull, C.; et al. Conserving and exploiting cocoa genetic resources: The key challenges. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Oil Palm; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cheesman, E.E. Notes on the nomenclature, classification and possible relationships of cacao populations. Trop. Agric. 1944, 21, 144–159. [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas, J. Cacao and its allies: A taxonomic revision of the genus Theobroma. Syst. Plant Stud. 1964, 35, 379–614. [Google Scholar]
- Sereno, M.L.; Albuquerque, P.S.B.; Vencovsky, R.; Figueira, A. Genetic Diversity and Natural Population Structure of Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) from the Brazilian Amazon Evaluated by Microsatellite Markers. Conserv. Genet. 2006, 7, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornejo, O.E.; Yee, M.-C.; Dominguez, V.; Andrews, M.; Sockell, A.; Strandberg, E.; Livingstone, D., III; Stack, C.; Romero, A.; Umaharan, P.; et al. Population genomic analyses of the chocolate tree, Theobroma cacao L., provide insights into its domestication process. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuomisto, H.; Ruokolainen, K.; Kalliola, R.; Linna, A.; Danjoy, W.; Rodriguez, Z. Dissecting Amazonian Biodiversity. Science 1995, 269, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Steege, H.; Pitman, N.; Sabatier, D.; Castellanos, H.; Van Der Hout, P.; Daly, D.C.; Silveira, M.; Phillips, O.; Vasquez, R.; Van Andel, T.; et al. A spatial model of tree α-diversity and tree density for the Amazon. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 2255–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, M.S.; Finer, M.; Jenkins, C.N.; Kreft, H.; Cisneros-Heredia, D.F.; McCracken, S.F.; Pitman, N.C.A.; English, P.H.; Swing, K.; Villa, G.; et al. Global Conservation Significance of Ecuador’s Yasuní National Park. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Davila, C.; Gomero, D.A.; Renno, J.-F.; Soria, R.D.; Pizango, G.H.; Llampazo, G.F.; Castro-Ruiz, D.; De Loayza, E.M.; Chavez, C.A.; Mader, M.; et al. Molecular evidence for three genetic species of Dipteryx in the Peruvian Amazon. Genetics 2019, 148, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prance, G. Forest refuges: Evidence from woody angiosperms. In Biological Diversification in the Tropics; Prance, G., Ed.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- van der Hammen, T.; Hooghiemstra, H. Neogene and Quaternary history of vegetation, climate, and plant diversity in Amazonia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2000, 19, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clement, C. 1492 and the loss of amazonian crop genetic resources. Crop Biogeography at contact. Econ. Bot. 1999, 53, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, C.R.; De Cristo-Araújo, M.; D’Eeckenbrugge, G.C.; Pereira, A.A.; Picanço-Rodrigues, D. Origin and Domestication of Native Amazonian Crops. Divers 2010, 2, 72–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, R.S.; DuVal, A.E.; Jensen, H.R. Patterns and processes in crop domestication: An historical review and quantitative analysis of 203 global food crops. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, C.R.; Denevan, W.M.; Heckenberger, M.J.; Junqueira, A.B.; Neves, E.G.; Teixeira, W.G.; Woods, W.I. The domestication of Amazonia before European conquest. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2015, 282, 20150813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levis, C.; Costa, F.R.C.; Bongers, F.; Peña-Claros, M.; Clement, C.R.; Junqueira, A.B.; Neves, E.G.; Tamanaha, E.K.; Figueiredo, F.O.G.; Salomão, R.P.; et al. Persistent effects of pre-Columbian plant domestication on Amazonian forest composition. Science 2017, 355, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua-Zambrana, N.; Byg, A.; Svenning, J.-C.; Moraes, M.; Grandez, C.; Balslev, H. Diversity of palm uses in the western Amazon. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 2771–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Motilal, L.A.; Dempewolf, H.; Maharaj, K.; Cronk, Q.C.B. Chloroplast microsatellite primers for cacao (Theobroma cacao) and other Malvaceae. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, e372–e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weising, K.; Nybom, H.; Wolff, K.; Kahl, G. DNA Fingerprinting in Plants: Principles, Methods, and Applications, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0849314887. [Google Scholar]
- Lemes, M.R.; Dick, C.W.; Navarro, C.; Lowe, A.J.; Cavers, S.; Gribel, R. Chloroplast DNA Microsatellites Reveal Contrasting Phylogeographic Structure in Mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King, Meliaceae) from Amazonia and Central America. Trop. Plant Biol. 2010, 3, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunders, J.A.; Mischke, S.; Leamy, E.A.; Hemeida, A.A. Selection of international molecular standards for DNA fingerprinting of Theobroma cacao. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 110, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, B.M.; Goenaga, R.; Zhang, D.; Schnell, R.; Brown, J.S.; Motamayor, J.C. Microsatellite Fingerprinting of the USDA-ARS Tropical Agriculture Research Station Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Germplasm Collection. Crop. Sci. 2010, 50, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motilal, L.A.; Zhang, D.; Umaharan, P.; Mischke, S.; Pinney, S.; Meinhardt, L.W. Microsatellite fingerprinting in the International Cocoa Genebank, Trinidad: Accession and plot homogeneity information for germplasm management. Plant Genet. Resour. 2011, 9, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemmy, T.; Ji, K.; Lyndel, M.; Sue, M.; Stephen, Y.O.; Francis, K.P.; Dapeng, Z. Verification of genetic identity of introduced cacao germplasm in Ghana using single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Susilo, A.W.; Dinarti, D.; Bailey, B.; Mischke, S.; Meinhardt, L.W. Genetic Identity, Ancestry and Parentage in Farmer Selections of Cacao from Aceh, Indonesia Revealed by Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Markers. Trop. Plant Biol. 2014, 7, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padi, F.K.; Ofori, A.; Takrama, J.; Djan, E.; Opoku, S.Y.; Dadzie, A.M.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Motamayor, J.C.; Zhang, D. The impact of SNP fingerprinting and parentage analysis on the effectiveness of variety recommendations in cacao. Tree Genet. Genomes 2015, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Zhang, D.; Motilal, L.A.; Boccara, M.; Lachenaud, P.; Meinhardt, L.W. Genetic diversity and parentage in farmer varieties of cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) from Honduras and Nicaragua as revealed by single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2013, 60, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.B. Tropical tree gene flow and seed dispersal. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 401, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, H.; Dumas, S.; Marque, G.; Messier, C.; Bandou, E.; Petit, R.J.; Kremer, A. Spatial and temporal distribution of chloroplast DNA polymorphism in a tropical tree species. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavers, S.; Navarro, C.; Lowe, A.J. Chloroplast DNA phylogeography reveals colonization history of a Neotropical tree, Cedrela odorata L., in Mesoamerica. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, C.W. Phylogeography and Population Structure of Tropical Trees. Trop. Plant Biol. 2010, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, M.; Gailing, O.; Leinemann, L.; Finkeldey, R. Molecular markers provide evidence for long-distance planting material transfer during plantation establishment of Dalbergia sissoo Roxb. in Nepal. Ann. For. Sci. 2004, 61, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Milne, R.I.; Zhu, J.; Gao, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Evolutionary legacy of a forest plantation tree species (Pinus armandii): Implications for widespread afforestation. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 2646–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Scascitelli, M.; Motilal, L.A.; Sveinsson, S.; Engels, J.M.M.; Kane, N.C.; Dempewolf, H.; Zhang, D.; Maharaj, K.; Cronk, Q.C.B. Complex origin of Trinitario-type Theobroma cacao (Malvaceae) from Trinidad and Tobago revealed using plastid genomics. Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-López, N.; Ovando-Medina, I.; Salvador-Figueroa, M.; Molina-Freaner, F.; Arrazate, C.H.A.; Vázquez-Ovando, A. Unique haplotypes of cacao trees as revealed bytrnH-psbAchloroplast DNA. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coe, S.D.; Coe, M.D. The True History of Chocolate, 3rd ed.; Thames & Hudson: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780500290682. [Google Scholar]
- Pound, F.J. Cacao and witches’ broom disease (Marasmius perniciosus) of South America with notes on other species of Theobroma. Arch. Cocoa Res. 1938, 1, 26–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vello, F.; Madeiros, A. Expedicao botanica a Amazonica brasileira. Cacau Atualidades (Brasil). Cacau Atual. 1965, 2, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sallée, B. Compte-Rendu de Prospection Dans les POPULATIONS Naturelles de Theobroma Cacao L. du Haut Camopi (Guyane Française), 14/4 au 12/5/1987; Camopi: Haut Camopi, French Guiana, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.B. Geographical Variation and Population Biology in Wild Theobroma Cacao. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull, C.; Hadley, P. International Cocoa Germplasm Database (ICGD). Available online: http://www.icgd.reading.ac.uk (accessed on 24 November 2019).
- Peters, C. PreColumbian silviculture and indigenous management of neotropical forests. In Imperfect Balance: Landscape Transformations in the Precolumbian Americas; Lentz, D., Ed.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 203–224. ISBN 0-231-11157-6. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, J.; Gardner, T.A.; Lees, A.; Parry, L.; Peres, C.A. How pristine are tropical forests? An ecological perspective on the pre-Columbian human footprint in Amazonia and implications for contemporary conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 151, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, F.J. First Report on the Selection of Cacao Trees for Resistance to Witches’ Broom Disease (Marasmius perniciosa): Report on a Recent Visit to the Amazon Territory of Peru, September 1942–February 1943; International Cocoa Genebank: Centeno, Trinidad and Tobago, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Boccara, M.; Motilal, L.; Butler, D.R.; Umaharan, P.; Mischke, S.; Meinhardt, L. Microsatellite variation and population structure in the “Refractario” cacao of Ecuador. Conserv. Genet. 2007, 9, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weising, K.; Gardner, R.C. A set of conserved PCR primers for the analysis of simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in chloroplast genomes of dicotyledonous angiosperms. Genome 1999, 42, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubisiak, T.L.; Nelson, C.D.; Staton, M.E.; Zhebentyayeva, T.; Smith, C.; Olukolu, B.A.; Fang, G.-C.; Hebard, F.V.; Anagnostakis, S.; Wheeler, N.; et al. A transcriptome-based genetic map of Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima) and identification of regions of segmental homology with peach (Prunus persica). Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliades, N.; Eliades, D. Haplotype Analysis; Forest Genetics and Forest Tree Breeding, Georg-August; University Goettingen: Goettingen, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bekele, F.; Phillips-Mora, W. Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Breeding. In Advances in Plant Breeding Strategies: Industrial and Food Crops; Al-Khayri, J.M., Jain, S.M., Johnson, D.V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 409–487. ISBN 978-3-030-23264-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, U.V.; Monteiro, W.R.; Pires, J.L.; Clement, D.; Yamada, M.M.; Gramacho, K.P. Cacao breeding in Bahia, Brazil: Strategies and results. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 11, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.A.D.S. The contributions of breeding. In Genetic Improvement of Cacao; Dias, L.A.D.S., Ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.; Van Zonneveld, M.; Loo, J.; Hodgkin, T.; Galluzzi, G.; Van Etten, J. Present Spatial Diversity Patterns of Theobroma cacao L. in the Neotropics Reflect Genetic Differentiation in Pleistocene Refugia Followed by Human-Influenced Dispersal. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haffer, J.; Prance, G. Climatic forcing of evolution in Amazonia during the Cenozoic: On the refuge theory of biotic differ-entiation. Limnol. Oecologia Reg. Syst. Fluminis Amazon. 2001, 16, 579–607. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, C.R. A Center of Crop Genetic Diversity in Western Amazonia. Biosciences 1989, 39, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, A.H. Neotropical Floristic Diversity: Phytogeographical Connections Between Central and South America, Pleistocene Climatic Fluctuations, or an Accident of the Andean Orogeny? Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1982, 69, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, A.H. Speciation in tropical forests. In Tropical Forests: Botanical Dynamics, Speciation and Diversity: Symposium: Papers; Holm-Nielsen, L.B., Nielsen, I.C., Balslev, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 113–134. ISBN 9780123535504. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Steege, H.; Pitman, N.C.A.; Sabatier, D.; Baraloto, C.; Salomão, R.P.; Guevara, J.E.; Phillips, O.L.; Castilho, C.V.; Magnusson, W.E.; Molino, J.-F.; et al. Hyperdominance in the Amazonian Tree Flora. Science 2013, 342, 1243092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levis, C.; Flores, B.M.; Moreira, P.A.; Luize, B.G.; Alves, R.; Franco-Moraes, J.; Lins, J.; Konings, E.; Peña-Claros, M.; Bongers, F.; et al. How People Domesticated Amazonian Forests. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caetano-Andrade, V.L.; Clement, C.; Weigel, D.; Trumbore, S.; Boivin, N.; Schöngart, J.; Roberts, P. Tropical Trees as Time Capsules of Anthropogenic Activity. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lachenaud, P.; Zhang, D. Genetic diversity and population structure in wild stands of cacao trees (Theobroma cacaoL.) in French Guiana. Ann. For. Sci. 2008, 65, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solórzano, R.G.L.; Fouet, O.; Lemainque, A.; Pavek, S.; Boccara, M.; Argout, X.; Amores, F.; Courtois, B.; Risterucci, A.M.; Lanaud, C. Insight into the Wild Origin, Migration and Domestication History of the Fine Flavour Nacional Theobroma cacao L. Variety from Ecuador. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eskes, A.; Rodriguez, C.; Cruz-Condori, D.; Seguine, E.; Garcia-Carrion, L.; Lachenaud, P. Large genetic diversity for fi-ne-flavor traits unveiled in cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) with special attention to the native Chuncho variety in Cusco, Peru. Agrotrópica 2018, 30, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrillo, S.; Gaikwad, N.; Lanaud, C.; Powis, T.; Viot, C.; Lesur, I.; Fouet, O.; Argout, X.; Guichoux, E.; Salin, F.; et al. The use and domestication of Theobroma cacao during the mid-Holocene in the upper Amazon. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, R. Dynamics and patterns of deforestation in the western Amazon: The Napo deforestation front, 1986–1996. Appl. Geogr. 2000, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, V.M. Plantas Cultivadas y Animales Domésticos en América Equinoccial, 1st ed.; Imprenta Departamental: Prado, Colombia, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo-Gardini, E.; Meinhardt, L.W.; Zuñiga, L.C.; Arévalo-Gardni, J.; Motilal, L.; Zhang, D. Genetic identity and origin of “Piura Porcelana”—A fine-flavored traditional variety of cacao (Theoborma cacao) from the Peruvian Amazon. Tree Genet. Genomes 2019, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Martínez, W.J.; Johnson, E.S.; Somarriba, E.; Phillips-Mora, W.; Astorga, C.; Mischke, S.; Meinhardt, L.W. Genetic diversity and spatial structure in a new distinct Theobroma cacao L. population in Bolivia. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2012, 59, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, L.A.D.S.; Barriga, J.P.; Kageyama, P.Y.; De Almeida, C.M.V.C. Variation and its distribution in wild cacao populations from the Brazilian Amazon. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2003, 46, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Neto, F.; Silva, P.; Medeiros, J.; Lima, A. Genetic resources of cacao in Rondônia: Historical overview, origin and inventory (in Portuguese). Agrotrópica 2015, 27, 93–124. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, F.; Schongart, J.; Montero, J.C.; Motzer, T.; Junk, W.J.; Piedade, M.T.F.; Queiroz, H.L.; Worbes, M. Tree species composition and diversity gradients in white-water forests across the Amazon Basin. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 1334–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Chloroplast Haplotype | CaCr1 | CaCr2 | CaCr4 | CaCr5 | CaCr8 | CaCr9 | Western Amazonia | Other Locations * | Plantations | Breeding Populations | N | Frequency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 361 | 243 | 177 | 207 | 309 | 345 | 2 | 2 | 0.9 | |||
| 2 | 366 | 243 | 177 | 206 | 309 | 345 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 12 | 5.3 |
| 3 | 366 | 243 | 177 | 207 | 309 | 345 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 4 | 366 | 244 | 177 | 206 | 309 | 345 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 5 | 371 | 242 | 178 | 206 | 308 | 345 | 12 | 1 | 13 | 5.7 | ||
| 6 | 371 | 243 | 177 | 206 | 309 | 345 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.9 | ||
| 7 | 376 | 241 | 177 | 206 | 308 | 345 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 8 | 376 | 241 | 178 | 211 | 309 | 345 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 9 | 376 | 242 | 178 | 206 | 308 | 345 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 3.9 | |
| 10 | 376 | 242 | 178 | 211 | 309 | 345 | 4 | 24 | 9 | 37 | 16.2 | |
| 11 | 376 | 242 | 178 | 219 | 309 | 345 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 12 | 376 | 244 | 179 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 2 | 2 | 0.9 | |||
| 13 | 376 | 245 | 179 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 2 | 2 | 0.9 | |||
| 14 | 381 | 243 | 177 | 206 | 309 | 345 | 2 | 2 | 0.9 | |||
| 15 | 381 | 243 | 178 | 214 | 308 | 353 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 16 | 381 | 243 | 178 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 24 | 34 | 2 | 2 | 62 | 27.2 |
| 17 | 381 | 244 | 178 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 5.7 |
| 18 | 386 | 244 | 178 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 19 | 391 | 244 | 178 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 19 | 8.3 | |
| 20 | 406 | 244 | 177 | 207 | 309 | 345 | 6 | 7 | 13 | 5.7 | ||
| 21 | 416 | 243 | 178 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| 22 | 416 | 244 | 178 | 216 | 308 | 353 | 26 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 31 | 13.6 |
| 23 | 416 | 244 | 178 | 216 | 309 | 353 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 |
| Amazonia | N | NLoc | Nh | HS | HT | FST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western | 115 | 28 | 19 | 0.676 | 0.725 | 0.068 |
| Eastern | 32 | 3 | 2 | 0.037 | 0.087 | 0.572 |
| Genetic Group | Chloroplast Haplotype Frequency | Number of Samples | |
|---|---|---|---|
| This Study | Motamayor et al. [2] | ||
| Nanay | 19 (0.91) | 12 | 121 |
| 3 (0.08) | |||
| Iquitos | 22 (0.86) | 22 | 75 |
| 23 (0.04) | |||
| 20 (0.04) | |||
| 16 (0.04) | |||
| Marañon | 16 (0.78) | 23 | 130 |
| 14 (0.08) | |||
| 17 (0.04) | |||
| 15 (0.04) | |||
| 14 (0.04) | |||
| Guiana | 16 (1.0) | 2 | 51 |
| Amelonado | 17 (0.62) | 8 | 63 |
| 22 (0.12) | |||
| 16 (0.12) | |||
| 5 (0.12) | |||
| Contamana | 20 (0.51) | 6 | 59 |
| 1 (0.33) | |||
| 19 (0.16) | |||
| Curaray | 9 (0.33) 2 (0.33) 13 (0.16) 20 (0.16) | 6 | 87 |
| Nacional | 10 (0.50) | 2 | 36 |
| 6 (0.50) | |||
| Accession | Source | Haplotype | Tentative Geographic Origin | Breeding Program Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC 137 | Cacao Center | 2 | Morona River, Peru | CATIE |
| * UF 168 | United Fruit selections | UF Company, Costa Rica | ||
| NA 399 | Nanay | 3 | Nanay River, Peru | ICG,T |
| ICS 68 | Imperial Collection Selection | 5 | Western Amazonia | ICG,T |
| POUND 18 | Pound Collections | Iquitos, Peru | ICG,T | |
| CC 252 | Cacao Center | 9 | The northeast of Ecuador (Coca and San Miguel rivers) | CATIE |
| PMCT 93 | Programa Mejoramiento de Cultivos Tropicales | CATIE | ||
| * UF 712 | United Fruit selections | UF Company, Costa Rica | ||
| * UF 273 | United Fruit selections | 10 | The northeast of Ecuador (Coca River) and north of Peru (Morona and Marañon rivers) | UF Company, Costa Rica |
| * ICS 5, 15, 42, 46, 48, 63 | Imperial Collection Selection | ICG,T | ||
| EET 19, 95 | Estación Experimental Tropical | EET, Pichilingue, Ecuador | ||
| PA 150, 169 | Parinari | 16 | Marañon River, Peru | ICG,T |
| SCA 9,10 | Scavina | 19 | Ucayali River, Peru | ICG,T |
| NA 33, | Nanay | Nanay River, Peru | ICG,T | |
| * CRU 100 | Cocoa Research Unit | Nanay River, Peru | ICG,T | |
| * ICS 35, 41 | Imperial Collection Selection | 20 | Western Amazonia | ICG,T |
| * TSA 654, 656,792 | Trinidad Selected Amazons | ICG,T | ||
| SCA 11, 12, 6 | Scavina | Ucayali River, Peru | ICG,T | |
| * ICS 10 | Imperial Collection Selection | 22 | Western Amazonia | ICG,T |
| IMC 47, 60, 67 | Iquitos Mixed Calabacillo | Iquitos, Peru | ICG,T |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nieves-Orduña, H.E.; Müller, M.; Krutovsky, K.V.; Gailing, O. Geographic Patterns of Genetic Variation among Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Populations Based on Chloroplast Markers. Diversity 2021, 13, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060249
Nieves-Orduña HE, Müller M, Krutovsky KV, Gailing O. Geographic Patterns of Genetic Variation among Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Populations Based on Chloroplast Markers. Diversity. 2021; 13(6):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060249
Chicago/Turabian StyleNieves-Orduña, Helmuth Edisson, Markus Müller, Konstantin V. Krutovsky, and Oliver Gailing. 2021. "Geographic Patterns of Genetic Variation among Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Populations Based on Chloroplast Markers" Diversity 13, no. 6: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060249
APA StyleNieves-Orduña, H. E., Müller, M., Krutovsky, K. V., & Gailing, O. (2021). Geographic Patterns of Genetic Variation among Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Populations Based on Chloroplast Markers. Diversity, 13(6), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060249








