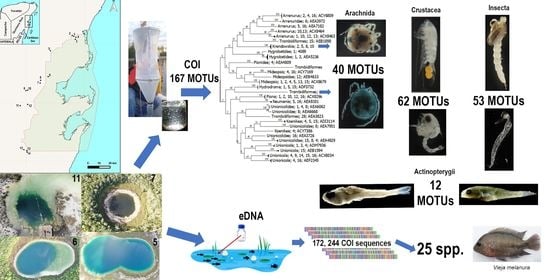
DNA Barcodes Applied to a Rapid Baseline Construction in Biodiversity Monitoring for the Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems in the Sian Ka’an Reserve (Mexico) and Adjacent Areas
Abstract
Share and Cite
Valdez-Moreno, M.; Mendoza-Carranza, M.; Rendón-Hernández, E.; Alarcón-Chavira, E.; Elías-Gutiérrez, M. DNA Barcodes Applied to a Rapid Baseline Construction in Biodiversity Monitoring for the Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems in the Sian Ka’an Reserve (Mexico) and Adjacent Areas. Diversity 2021, 13, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070292
Valdez-Moreno M, Mendoza-Carranza M, Rendón-Hernández E, Alarcón-Chavira E, Elías-Gutiérrez M. DNA Barcodes Applied to a Rapid Baseline Construction in Biodiversity Monitoring for the Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems in the Sian Ka’an Reserve (Mexico) and Adjacent Areas. Diversity. 2021; 13(7):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070292
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdez-Moreno, Martha, Manuel Mendoza-Carranza, Eduardo Rendón-Hernández, Erika Alarcón-Chavira, and Manuel Elías-Gutiérrez. 2021. "DNA Barcodes Applied to a Rapid Baseline Construction in Biodiversity Monitoring for the Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems in the Sian Ka’an Reserve (Mexico) and Adjacent Areas" Diversity 13, no. 7: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070292
APA StyleValdez-Moreno, M., Mendoza-Carranza, M., Rendón-Hernández, E., Alarcón-Chavira, E., & Elías-Gutiérrez, M. (2021). DNA Barcodes Applied to a Rapid Baseline Construction in Biodiversity Monitoring for the Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems in the Sian Ka’an Reserve (Mexico) and Adjacent Areas. Diversity, 13(7), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070292