Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Hepatotoxicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Black-Spotted Frogs (Rana nigromaculata)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals Treatments
2.3. Liver Transcriptome Analysis
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and Assembly of Transcriptome
3.2. Functional Annotation of Unigenes
3.3. Differentially Expressed Gene Analysis
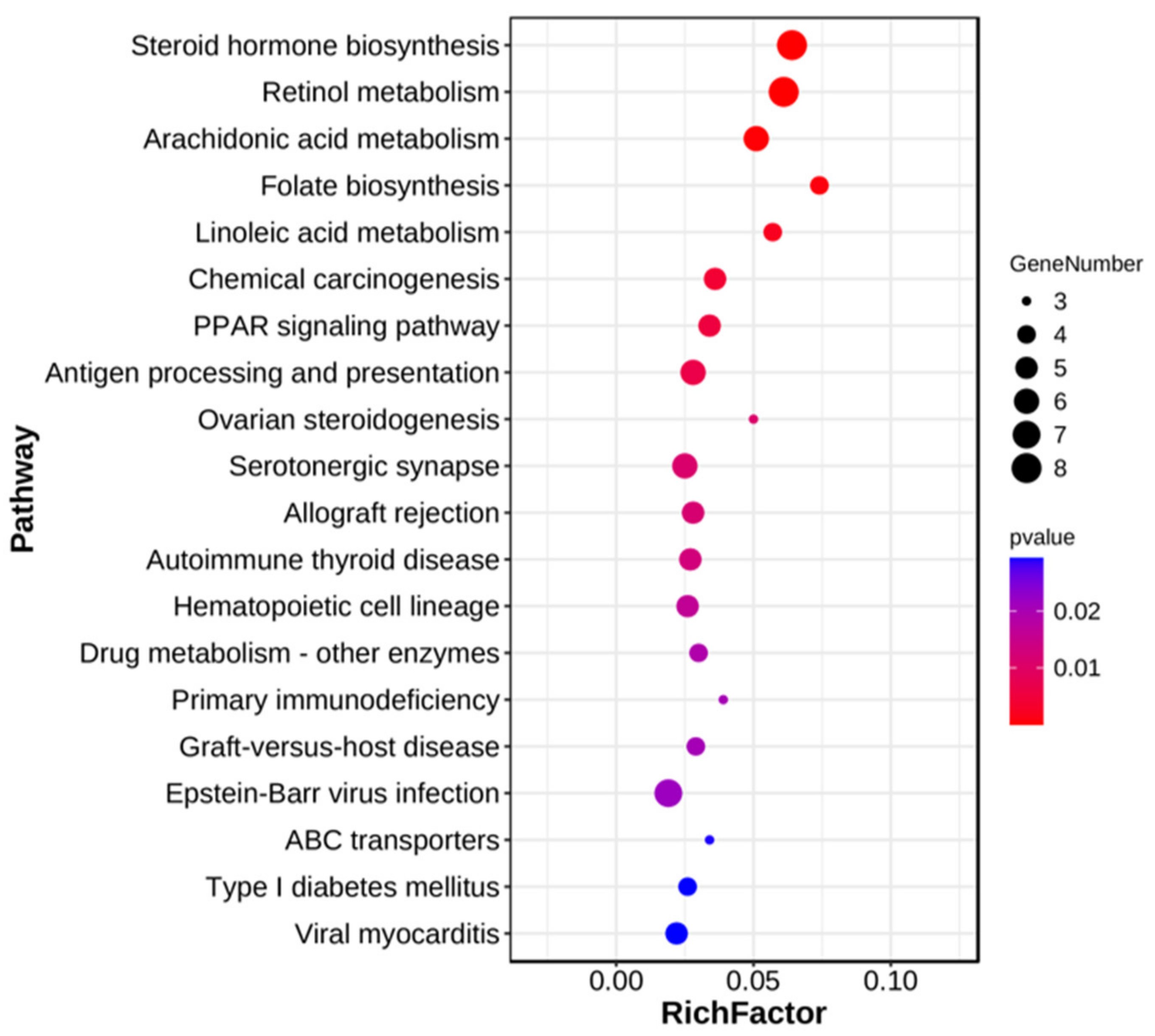
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
3.5. GO Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.6. Gene Expression Verification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Jin, L.; Lin, H.; Yan, M.; Gu, J.; Yuen, C.N.T.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lam, P.K.S. Tissue-specific uptake, depuration kinetics, and suspected metabolites of three emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in marine Medaka. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6182–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotthoff, M.; Müller, J.; Jürling, H.; Schlummer, M.; Fiedler, D. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in consumer products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 14546–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitehead, H.D.; Venier, M.; Wu, Y.; Eastman, E.; Urbanik, S.; Diamond, M.L.; Shalin, A.; Schwartz-Narbonne, H.; Bruton, T.A.; Blum, A.; et al. Fluorinated compounds in North American cosmetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. Let. 2021, 8, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suja, F.; Pramanik, B.K.; Zain, S.M. Contamination, bioaccumulation and toxic effects of perfluorinated chemicals (PFCs) in the water environment: A review paper. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, B.C.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Blair, J.D.; Morin, A.E.; Gobas, F.A.P.C. Food web-specific biomagnification of persistent Organic Pollutants. Science 2007, 317, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Polprasert, C.; Tanaka, S.; Hong Lien, N.P.; Qiu, Y. New POPs in the water environment: Distribution, bioaccumulation and treatment of perfluorinated compounds—A review paper. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2007, 56, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, A.; Masetti, R.; Gazzotti, T.; Zama, D.; Astolfi, A.; Veyrand, B.; Pession, A.; Pagliuca, G. Perfluoroalkyl substances in human milk: A first survey in Italy. Environ. Int. 2013, 51, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Q.; Sheng, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. Worldwide distribution of novel perfluoroether carboxylic and sulfonic acids in surface water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7621–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, temporal variation (2010–2018), distribution, and source appointment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in mollusks from the Bohai Sea, China. ACS EST Water 2021, 2, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seals, R.; Bartell, S.M.; Steenland, K. Accumulation and clearance of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in current and former residents of an exposed community. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillouzo, A. Liver cell models in in vitro toxicology. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudo, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Sunaga, K.; Tsuda, T.; Mitsumoto, A.; Kawashima, Y. Effects of perfluorinated fatty acids with different carbon chain length on fatty acid profiles of hepatic lipids in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bao, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Perfluorooctanoic acid exposure in early pregnancy induces oxidative stress in mice uterus and liver. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 66355–66365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.F.; Liao, C.Y.; Fu, J.J.; Jiang, G.B. Studies on the toxicological effects of PFOA and PFOS on rats using histological observation and chemical analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 56, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, J.P.; Soto, J.O. Modern approaches into biochemical and molecular biomarkers: Key roles in environmental biotechnology. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2016, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Q.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Di, Y.; Ding, J.; Yu, D.; Yan, L.; Shen, L.; Yan, D.; et al. Identification of novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma using transcriptome analysis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 4851–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, P.; Sree, K.S.; Appenroth, K.J. Duckweed biomarkers for identifying toxic water contaminants? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 14797–14822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Union for Conservation of Nature. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Version 2020-1; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Lu, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, H. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) impair lipid metabolism in Rana nigromaculata: A field investigation and laboratory study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13222–13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, H.; Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Assessing the hepatotoxicity of PFOA, PFOS, and 6:2 Cl-PFESA in black-spotted frogs (Rana nigromaculata) and elucidating potential association with gut microbiota. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion-Letellier, R.; Savoye, G.; Ghosh, S. Fatty acids, eicosanoids and PPAR gamma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, X.M.; Guo, L.H. Structure-based investigation on the interaction of perfluorinated compounds with human liver fatty acid binding protein. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11293–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yu, Y.; Guo, M.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, M.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Tan, Z. Integrated analysis of physiological, transcriptomics and metabolomics provides insights into detoxication disruption of PFOA exposure in Mytilus edulis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Guo, H.; Dai, J. Transcriptome analysis of 3D primary mouse liver spheroids shows that long-term exposure to hexafluoropropylene oxide trimer acid disrupts hepatic bile acid metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Liu, M.; Wan, T.; Tang, L.; Sun, B.; Zhou, B.; Lam, J.C.W.; Lam, P.K.S.; Chen, L. Disturbances in microbial and metabolic communication across the gut-liver axis induced by a dioxin-like pollutant: An integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, R.; Luan, F.; Li, N.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, W.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, X. Identification of molecular initiating events and key events leading to endocrine disrupting effects of PFOA: Integrated molecular dynamic, transcriptomic, and proteomic analyses. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Guo, C.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Su, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, K.P. Integrative omics analysis reveals the protective role of vitamin C on perfluorooctanoic acid-induced hepatoxicity. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 35, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.T.; Lai, K.P.; Wong, C.K.C. Comparative Analysis of PFOS and PFOA Toxicity on Sertoli Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3465–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gong, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Chai, Y.; Liu, J. The responses of the growth, cytochrome P450 isoenzymes activities and the metabolomics in earthworms to sublethal doses of dichlorvos in soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Klaassen, C.D. Perfluorocarboxylic acids induce cytochrome P450 enzymes in mouse liver through activation of PPAR-alpha and CAR transcription factors. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 106, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Qu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Wu, P.; Xue, J.; Hangbiao, J. Per-/polyfluoroalkyl substance concentrations in human serum and their associations with immune markers of rheumatoid arthritis. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, U.; Seliger, B. The transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP): Structural integrity, expression, function, and its clinical relevance. Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Shen, L.; Ye, X.; Zhou, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, H. Mechanism of immunosuppression in zebrafish (Danio rerio) spleen induced by environmentally relevant concentrations of perfluorooctanoic acid. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Category | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total reads | 48,625,956 | 36,803,570 | 45,578,514 | 48,676,036 | 38,909,934 | 41,953,882 | 40,187,302 | 38,610,866 | 38,980,172 | 51,300,610 |
| Clean reads | 44,947,858 | 33,650,206 | 40,731,048 | 44,445,616 | 35,623,160 | 38,395,600 | 36,810,398 | 35,239,340 | 35,923,774 | 46,437,278 |
| Clean read proportion (%) | 92.43 | 91.43 | 89.36 | 91.3 | 91.55 | 91.55 | 91.59 | 91.26 | 92.15 | 90.51 |
| Q20 (%) | 97.43 | 97.15 | 97.43 | 97.27 | 97.29 | 97.4 | 97.17 | 97.17 | 97.17 | 96.28 |
| Q30 (%) | 93.12 | 92.51 | 93.2 | 92.86 | 92.89 | 93.06 | 92.61 | 92.65 | 92.64 | 90.76 |
| GC (%) | 44.39 | 44.39 | 44.6 | 44.43 | 44.43 | 44.37 | 44.17 | 44.75 | 44.33 | 44.39 |
| Unigene number | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 | 104,143 |
| Unigene average length (bp) | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 | 979.22 |
| Unigene N50 (bp) | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 | 1480 |
| Database | Number of Annotated Unigenes | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| NR | 28,828 | 27.68 |
| GO | 19,480 | 18.71 |
| KEGG | 15,815 | 15.19 |
| eggNOG | 18,816 | 18.07 |
| Swiss-Prot | 26,839 | 25.77 |
| Pfam | 22,204 | 21.32 |
| In all databases | 10,661 | 10.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Han, Y.; Yuan, X.; Gao, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, Z. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Hepatotoxicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Black-Spotted Frogs (Rana nigromaculata). Diversity 2022, 14, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110971
Lin H, Feng Y, Zheng Y, Han Y, Yuan X, Gao P, Zhang H, Zhong Y, Liu Z. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Hepatotoxicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Black-Spotted Frogs (Rana nigromaculata). Diversity. 2022; 14(11):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110971
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Huikang, Yixuan Feng, Yueyue Zheng, Yu Han, Xia Yuan, Panpan Gao, Hangjun Zhang, Yuchi Zhong, and Zhiquan Liu. 2022. "Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Hepatotoxicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Black-Spotted Frogs (Rana nigromaculata)" Diversity 14, no. 11: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110971
APA StyleLin, H., Feng, Y., Zheng, Y., Han, Y., Yuan, X., Gao, P., Zhang, H., Zhong, Y., & Liu, Z. (2022). Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Hepatotoxicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Black-Spotted Frogs (Rana nigromaculata). Diversity, 14(11), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110971







