Development of Polymorphic Microsatellite Markers and Identification of Applications for Wild Walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Middle Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Excavation and Primer Design of SSRs
2.2. DNA Extraction and SSR-PCR Reaction
2.3. Data Collection and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of SSR Loci
3.2. Development and Characterization of SSR Markers
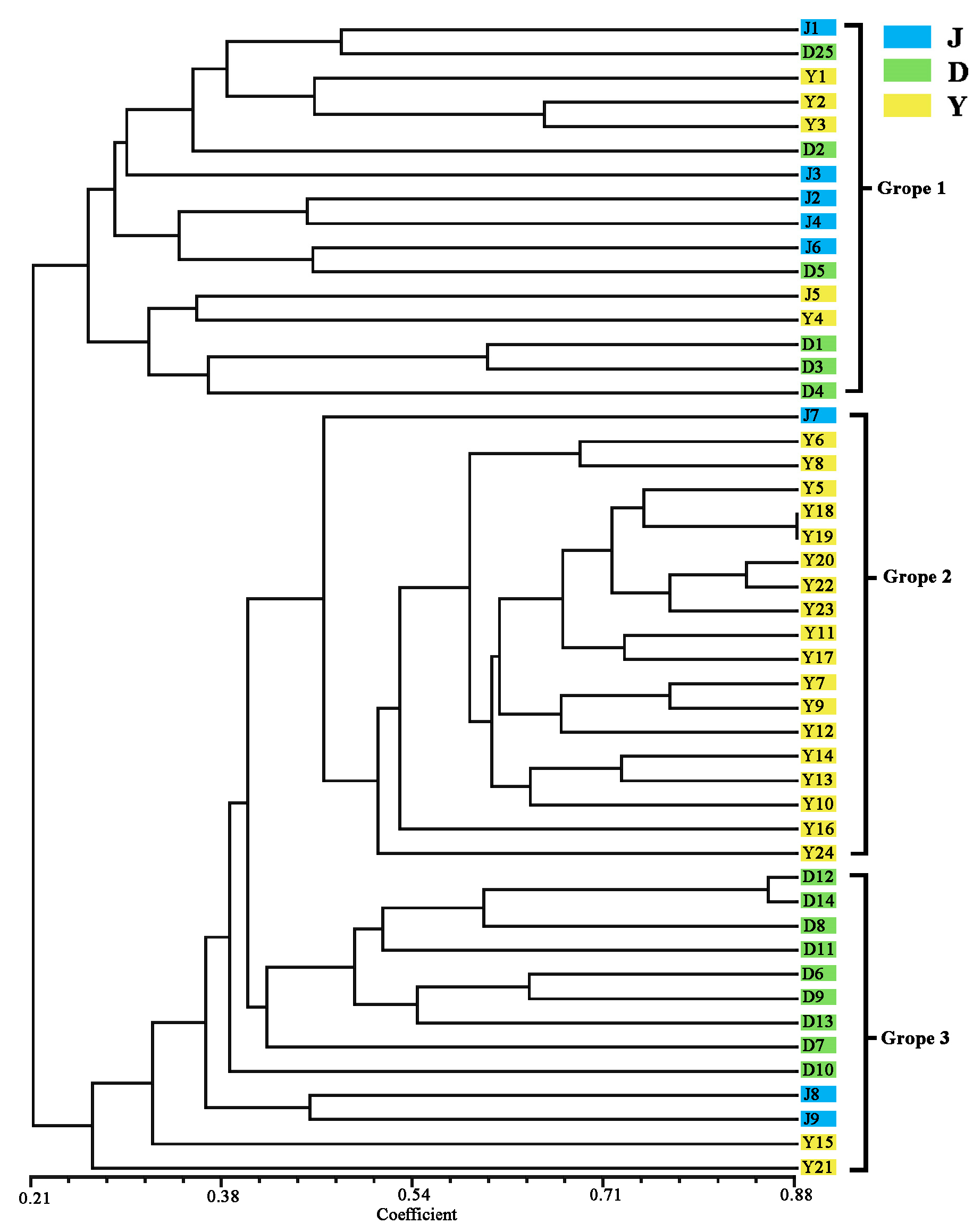
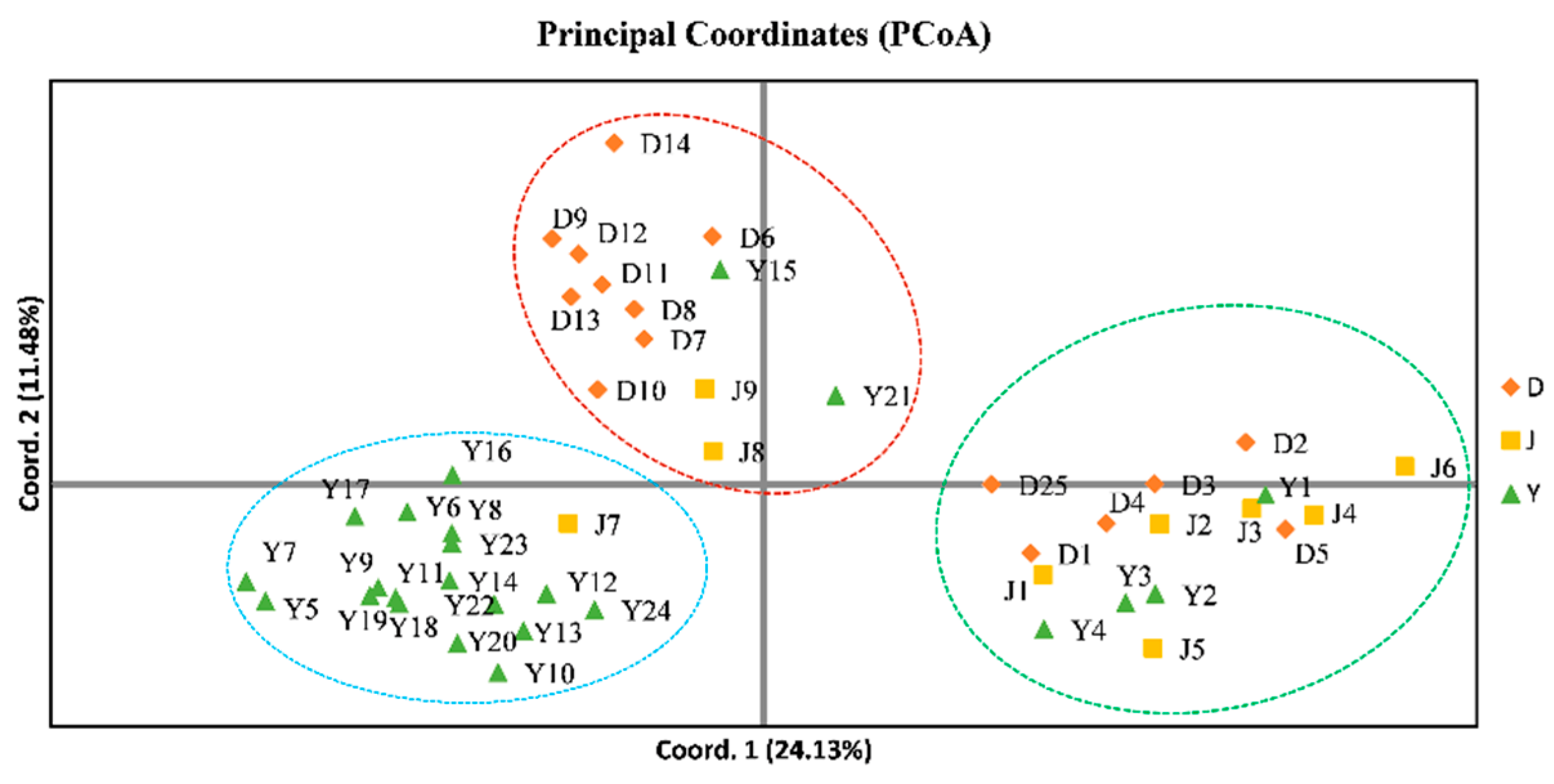
3.3. Analysis of Genetic Diversity of Walnut
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGranahan, G.; Leslie, C. Walnuts (Juglans). Acta Hortic. 1991, 290, 907–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeven, A.C.; Zhukovsky, P.M. Dictionary of Cultivated Plants and Their Centres of Diversity: Excluding Ornamentals, Forest Trees and Lower Plants; Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth, R.H. Meiosis of microsporogenesis in the Juglandaceae. Am. J. Bot. 1930, 17, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradhya, M.K.; Potter, D.; Simon, C.J. Darwin’s Harvest: New Approaches to the Origins, Evolution, and Conservation of Crops; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 143–170. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhong, L.; Yang, H.; Zhu, F.; Hou, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, Y. Comparative analysis of antioxidant activities between dried and fresh walnut kernels by metabolomic approaches. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 155, 112875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemery, G.E.; Savill, P.S.; Thakur, A. Height growth and flushing in common walnut (Juglans regia L.): 5-year results from provenance trials in Great Britain. Forestry 2005, 78, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradhya, M.; Woeste, K.; Velasco, D. Genetic Diversity, Structure and Differentiation in Cultivated Walnut (Juglans regia L.). In Proceedings of the 6th International Walnut Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 25–27 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Akça, Y.; Mehmet Sen, S. Studies on selection of walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Gürün. In Progress in Temperate Fruit Breeding; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 179–181. [Google Scholar]
- Carrion, J.S.; Sanchezgomez, P. Palynological data in support of the survival of walnut (Juglans regia L.) in the western mediterranean area during last glacial times. J. Biogeogr. 1992, 19, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, V.R. The Role of Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries in Human Nutrition-Volume III; EOLSS Publications: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, T.; Zaurov, D.; Capik, J.; Eisenman, S.; Ford, T.; Nikolyi, L.; Funk, C. Persian walnuts (Juglans regia L.) in Central Asia. Annu. Rep. North. Nut Grow. Assoc. 2011, 101, 56–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Yi, J.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lu, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Effects of sonication on the physicochemical and functional properties of walnut protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.N.; Ma, Q.G.; Chen, Y.K.; Wang, B.Q.; Pei, D. Identification of major walnut cultivars grown in China based on nut phenotypes and SSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 168, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicese, F.P.; Hormaza, J.I.; McGranahan, G.H. Molecular characterization and genetic relatedness among walnut (Juglans regia L.) genotypes based on RAPD markers. Euphytica 1998, 101, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.; Gao, F.Y.; Aiello, G.; Leslie, C.; McGranahan, G. Intersimple sequence repeat markers for fingerprinting and determining genetic relationships of walnut (Juglans regia) cultivars. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2002, 127, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantety, R.V.; La Rota, M.; Matthews, D.E.; Sorrells, M.E. Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.G.; Milne, R.I.; Sun, H. Morphological and molecular evidence of natural hybridization between two distantly related Rhododendron species from the Sino-Himalaya. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 156, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatahi, R.; Ebrahimi, A.; Zamani, Z. Characterization of Some Iranians and Foreign Walnut Genotypes Using Morphological Traits and RAPD Markers. Hortic. Environ. Biote. 2010, 51, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Christopoulos, M.V.; Rouskas, D.; Tsantili, E.; Bebeli, P.J. Germplasm diversity and genetic relationships among walnut (Juglans regia L.) cultivars and Greek local selections revealed by Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 125, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, S.; Kazan, K.; Gulbitti, S.; Cevik, V.; Ayanoglu, H.; Ergul, A. AFLP analysis of genetic diversity in low chill requiring walnut (Juglans regia L.) genotypes from Hatay, Turkey. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 111, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroni, I.; Rao, R.; Woeste, K. Molecular characterization of Juglans regia L. cultivars with SSR markers. In Proceedings of the 5th International Walnut Symposium, Sorrento, Italy, 9–13 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.L. Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n·(dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics 1990, 7, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, S.; Govindaraj, P.; Senthilkumar, S. Comparison of relative efficiency of genomic SSR and EST-SSR markers in estimating genetic diversity in sugarcane. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, H.; An, H.; Zhou, W. Genetic variation and population structure of rosa roxburghii by est-based and genomic SSR markers. Pak. J. Bot. 2020, 52, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard Smith, J.; Haigh, J. Hitch-hiking effect of a favorable gene. Genet. Res. 1974, 23, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, K.; Hwang, E.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, Y.I.; Cregan, P.B.; Lee, S.H. Discovery of single nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean using primers designed from ESTs. Euphytica 2004, 139, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, R.; Dimmock, C.; Thomas, M.; Bower, N.; Knight, D.; Grof, C.; McIntyre, L.; Jackson, P.; Jordan, D.; Whan, V.; et al. Genetic and expression profiling in sugarcane. In Proceedings of the 24th Congress of the International Society of Sugar Cane-Technologists, Brisbane, Australia, 17–21 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hsin-shi, C. On the eco-geographical characters and the problems of classification of the wild fruit-tree forest in the Ili Valley of Sinkiang. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 1973, 2, 239–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wambulwa, M.C.; Fan, P.-Z.; Milne, R.; Wu, Z.Y.; Luo, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Gao, L.M.; Xiahou, Z.Y.; Jin, Y.C.; et al. Genetic analysis of walnut cultivars from southwest China: Implications for germplasm improvement. Plant Divers. 2022, 44, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabiri, G.; Bouda, S.; Haddioui, A. Evaluation of genetic diversity and structuration across altitude of walnut (Juglans regia L.) accessions from Morocco using SSR markers. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 28, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Cseke, K.; Bujdoso, G.; Bader, M.; Mertl, T.; Benke, A.; Kampel, J.D. Genetic Identification of Hybrid Walnuts (Juglans × intermedia Carr.) in Hungary, the Hidden Potential for Future Breeding. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhou, H.; Zulfiqar, S.; Luo, X.; Hu, Y.; Feng, L.; Malvolti, M.E.; Woeste, K.; Zhao, P. The Phytogeographic History of Common Walnut in China. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, F. Population genetic analysis of co-dominant and dominant markers and quantitative traits. Belgian J. Bot. 1997, 129, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, version 2.1; Exeter Publication Ltd. Setauket: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program Cervus accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ge, H.; Sun, X.; Yang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, M. DataFormater, a Software for SSR Data Formatting to Develop Population Genetics Analysis. Mol. Plant Breed. 2016, 14, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Dominant markers and null alleles. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 2003, 164, 1567–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A.; vonHoldt, B.M. Structure Harvester: A website and program for visualizing Structure output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software Structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waits, J.L.; Leberg, P.L. Biases associated with population estimation using molecular tagging. Anim. Conserv. 2000, 3, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Song, P.; Koo, D.H.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Weng, Y.; Yang, L. Genome wide characterization of simple sequence repeats in watermelon genome and their application in comparative mapping and genetic diversity analysis. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavagnaro, P.F.; Senalik, D.A.; Yang, L.; Simon, P.W.; Harkins, T.T.; Kodira, C.D.; Huang, S.; Weng, Y. Genome-wide characterization of simple sequence repeats in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). BMC Genomics. 2010, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Gu, Y.Q.; Hu, Y.; You, F.M.; Dandekar, A.M.; Leslie, C.A.; Aradhya, M.; Dvorak, J.; Luo, M.C. Characterizing the walnut genome through analyses of BAC end sequences. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 78, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, H.; Ikhsan, A.S.; Sutyemez, M.; Coban, N.; Guney, M.; Kafkas, S. Development of 185 polymorphic simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from walnut (Juglans regia L.). Sci. Hortic. 2015, 194, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Sun, K.; Huang, C.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Development of a core SNP arrays based on the KASP method for molecular breeding of rice. Rice 2019, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, M.; Liu, Z.X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.J.; Hu, Y.H.; Zhao, P. Identification, development, and application of 12 polymorphic EST-SSR markers for an endemic Chinese walnut (Juglans cathayensis L.) using next-generation sequencing technology. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 60, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, V.; Kobayashi, M.C.; De La Cruz, M.; Clegg, M.T. Microsatellite markers in avocado (Persea americana Mill.): Development of dinucleotide and trinucleotide markers. Sci. Hortic. 2004, 101, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portis, E.; Lanteri, S.; Barchi, L.; Portis, F.; Valente, L.; Toppino, L.; Rotino, G.L.; Acquadro, A. Comprehensive Characterization of Simple Sequence Repeats in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Genome and Construction of a Web Resource. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, S.; Ben Hamida, W.; Rebai, A.; Harrabi, M. SSR-based genetic diversity assessment among Tunisian winter barley and relationship with morphological traits. Euphytica 2004, 135, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic-linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, U.N.; Mir, J.; Ahmed, N.; Fazili, K.M. Assessment of germplasm diversity and genetic relationships among walnut (Juglans regia L.) genotypes through microsatellite markers. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Magige, E.A.; Fan, P.Z.; Wambulwa, M.C.; Milne, R.; Wu, Z.Y.; Luo, Y.H.; Khan, R.; Wu, H.Y.; Qi, H.L.; Zhu, G.F.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Structure of Persian Walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Pakistan: Implications for Conservation. Plants 2022, 11, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y.; Tashiro, H.; Nishi, S.; Hiehata, N.; Nagano, A.J.; Fukuda, S. Genetic diversity of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) revealed using RAD-Seq SNP markers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.; Barreneche, T.; Lheureux, F.; Dirlewanger, E. Analysis of genetic diversity and structure in a worldwide walnut (Juglans regia L.) germplasm using SSR markers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Han, W.; Wu, S. Plant genetic diversity and its influencing factors. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2010, 30, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin, M.; Barton, N.H. A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating average levels of gene flow. Evolution 1989, 43, 1349–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torokeldiev, N.; Ziehe, M.; Gailing, O.; Finkeldey, R. Genetic diversity and structure of natural Juglans regia L. populations in the southern Kyrgyz Republic revealed by nuclear SSR and EST-SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genom. 2019, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pan, G.; Ma, Q.G.; Zhang, J.P.; Pei, D. The genetic diversity and introgression of Juglans regia and Juglans sigillata in Tibet as revealed by SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genom. 2015, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, C.V.; Aguirre, N.; Rivas, J.G.; Zubrzycki, J.; Puebla, A.; Cordes, D.; Moreno, M.V.; Fusari, C.M.; Alvarez, D.; Heinz, R.A.; et al. Population structure and genetic diversity characterization of a sunflower association mapping population using SSR and SNP markers. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, H.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Shao, G.; Chen, H.; Han, R.; Xu, Z. SSR marker based analysis for identification and of genetic diversity of non-heading Chinese cabbage varieties. Front. Plant. Sci. 2023, 14, 1112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, J.L.; Godt, M.J.W.; Shermanbroyles, S.L. Factors influencing levels of genetic diversity in woody plant-species. In Proceedings of the International Symp on Population Genetics of Forest Trees, Corvallis, OR, USA, 31 July–2 August 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, A.S. SSR genotyping. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1245, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro Vieira, M.L.; Santini, L.; Diniz, A.L.; Munhoz, C.d.F. Microsatellite markers: What they mean and why they are so useful. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollegioni, P.; Woeste, K.; Mugnozza, G.S.; Malvolti, M.E. Retrospective identification of hybridogenic walnut plants by SSR fingerprinting and parentage analysis. Mol. Breed. 2009, 24, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, B.F.; Aradhya, M.; Salick, J.M.; Miller, A.J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Hai, X. Gentic variation in walnuts (Juglans regia and J. sigillata; Juglandaceae): Species distinctions, human impacts, and the conservation of agrobiodiversity in Yunnan, China. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victory, E.R.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Rhodes, O.E.; Woeste, K.E. Genetic homogeneity in Juglans nigra (Juglandaceae) at nuclear microsatellites. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdati, K. Traditions and Folks for Walnut Growing around the Silk Road. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Fruit Culture and Its Traditional Knowledge along Silk Road Countries, Yerevan, Armenia, 4–8 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- French, D. Pre and early Roman roads of Asia Minor: The Persian royal road. Iran 1998, 36, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanazarov, A.A.; Chernova, G.M.; Venglovskiy, B.I.; Ashimov, K.S.; Kenjabaev, S.K. Man-made green monuments of Central Asia: Some examples of Uzbekistan. Schweizerische Zeitschrift fur Forstwesen 2003, 154, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubaile, F. Pathways of diffusion of some plants and animals between Asia and the Mediterranean region. Rev. d’Ethnoécologie 2012, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, B.; Vahdati, K.; Rezaee, R.; Hassani, D. Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.) grafting as influenced by different bench grafting methods and scion cultivars. J. Appl. Hortic. 2009, 11, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollegioni, P.; Woeste, K.E.; Chiocchini, F.; Del Lungo, S.; Olimpieri, I.; Tortolano, V.; Clark, J.; Hemery, G.E.; Mapelli, S.; Malvolti, M.E. Ancient Humans Influenced the Current Spatial Genetic Structure of Common Walnut Populations in Asia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J.; Gross, B.L. From forest to field: Perennial fruit crop domestication. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 1389–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.R. Domestication of plants in the old world: The origin and spread of cultivated plants in west Asia, Europe and the Nile valley. Agr. Hist. Rev. 2001, 49, 226–227. [Google Scholar]
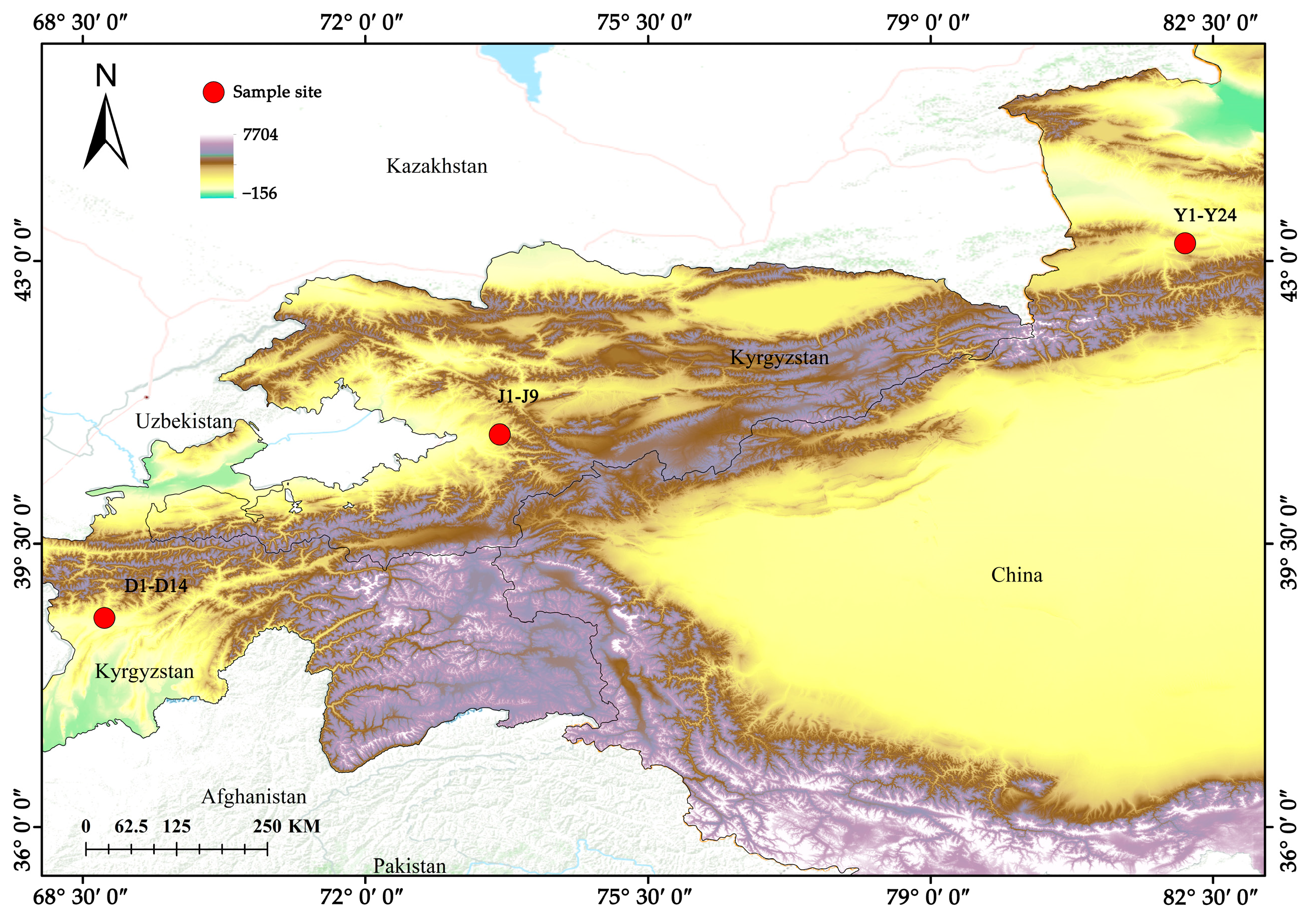


| Serial Number | ID | Location | Number | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J1-J9 | Kyrgyzstan | 8 | 40.853421 | 73.66128 |
| 2 | D1-D14 | Tajikistan | 14 | 38.584371 | 68.768641 |
| 3 | Y1-Y24 | China | 23 | 43.217701 | 82.152833 |
| Name | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Repeat Motif | Ta (°C) | Fluorescent Dye | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WJR001 | WJR001F: GGTGTAGGTTTGGAAGGCCA WJR001R: ATTGAGGCAACGGGAAGAGG | CT (8) | 60 | 5′-FAM | 139 |
| WJR029 | WJR029F: TTCTTGGCCGCAGAGCATTA WJR029R: TGTGCGTGCTAGATGGATGT | TC (7) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 148 |
| WJR105 | WJR105F: CACACACACACACACACACA WJR105R: CGTCTCACTCTCACTTCCAGG | GA (7) | 60 | 5′-FAM | 114 |
| WJR157 | WJR157F: GGTCGAGATCACCAAATGGC WJR157R: GCCGGCAGCTTTACTACTCA | AG (9) | 60 | 5′-FAM | 150 |
| WJR621 | WJR621F: TGCATGCTGTCAAAGGTGTC WJR621R: CGAGCTAGTGAACATTTGCAGT | AT (15) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 155 |
| WJR679 | WJR679F: TTTTCTCGCAAAGCAGCTGG WJR679R: TGGTCATCGTCTGGTTGCAA | AT (9) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 81 |
| WJR1022 | WJR1022F: AACTGGACAACCTTGCCCAA WJR1022R: CAGCTCAATGGCTTCTTGGC | AT (16) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 166 |
| WJR1193 | WJR1193F: GGGCGCCGTTGAACAAATAT WJR1193R: CGGCCATCAGAGAGGGATTC | TC (12) | 60 | 5′-FAM | 134 |
| WJR19057 | WJR19057F: CCGTGGCACCTAATCCTTGT WJR19057R: AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGA | AC (10) | 61 | 5′-FAM | 129 |
| WJR18870 | WJR18870F: TCACCTCTCTCTCACTCTCTCA WJR18870R: GCGCGCAACAGAAAGAGAAA | CT (6) | 59 | 5′-FAM | 151 |
| WJR18123 | WJR18123F: GCATTTTTGCCACCCACCTT WJR18123R: TGCCAAGTGGTACAAGTGGA | AC (8) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 129 |
| WJR27081 | WJR27081F: ACAAACAACACCGACGAGGA WJR27081R: TTGACGTTGTTAGTGTGCCC | GA (9) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 112 |
| WJR20785 | WJR20785F: TCAGGACGGTATGCTTGACT WJR20785R: TGTGTGTTGGTGTGTGTGGA | TC (14) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 182 |
| WJR19806 | WJR19806F: AGAGTGGTGTGTGTGAGTGC WJR19806R: TCCCACCCTTCTCCTTCCTT | AG (6) | 60 | 5′-FAM | 138 |
| WJR28944 | WJR28944F: AAAAGACCTTCGATCGAGCC WJR28944R: AAAAGACCTTCGATCGAGCC | TA (7) | 60 | 5′-FAM | 161 |
| WJR30675 | WJR30675F: CGCTGGTTTCTGGCATGAAA WJR30675R: GAAGAGATCAGAACCGGCCA | AT (8) | 59 | 5′-FAM | 183 |
| WJR32508 | WJR32508F: AGCAGAGCGAAAGAGAGCAG WJR32508R: AGACGCAACCCTCAAACCAT | GA (21) | 59 | 5′-FAM | 183 |
| WJR37937 | WJR37937F: TGCATTCAGAACACGGGTGA WJR37937R: AAAGCATGAGTTATCCTTGCAAAA | TCT (7) | 56 | 5′-FAM | 150 |
| WJR41945 | WJR41945F: TGGTTAATCAGGCCATGGCT WJR41945R: GCAGTTGCCGCAAACTTGTA | AT (15) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 178 |
| WJR17197 | WJR17197F: TGCCATCACCATGTTCACCA WJR17197R: TTGCGGCAACCCTAGTTCTT | AT (9) | 58 | 5′-FAM | 165 |
| WJR20924 | WJR20924F: AGAGATGTGCGTGTGTGTGT WJR20924R: AAGTGACGGTGTCCCACAAG | TA (9) | 59 | 5′-FAM | 116 |
| WJR19609 | WJR19609F: GAAGCATGTGTGTGTGTGTGT WJR19609R: AGGCTCGTTCGTTTATGCCC | TA (10) | 59 | 5′-FAM | 141 |
| Items | Numbers |
|---|---|
| Total size of genome (Mb) | 540 |
| Total number of identified SSRs | 357,629 |
| Total length of SSRs (bp) | 7,641,320 |
| Frequency (SSRs/Mb) | 662.28 |
| Density (bp/Mb) | 14,150.59 |
| Total content of genome SSRs (%) | 1.41 |
| Locus | Na | Ne | Ho | He | uHe | I | Nm | PIC | Fis | Fst | F (Null) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WJR001 | 7 | 2.23 | 0.11 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 1.08 | 5.23 | 0.52 | 0.81 | 0.05 | 0.68 |
| WJR029 | 11 | 2.16 | 0.17 | 0.49 | 0.54 | 1.27 | 3.05 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 0.54 |
| WJR105 | 27 | 19.51 | 0.55 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 3.12 | 3.70 | 0.93 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.26 |
| WJR157 | 10 | 3.04 | 0.49 | 0.64 | 0.67 | 1.48 | 3.76 | 0.65 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.17 |
| WJR621 | 23 | 11.05 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 2.67 | 2.91 | 0.90 | −0.12 | 0.08 | −0.003 |
| WJR679 | 19 | 5.66 | 0.53 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 2.22 | 4.27 | 0.82 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 0.23 |
| WJR1022 | 23 | 8.23 | 0.62 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 2.54 | 2.30 | 0.87 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.18 |
| WJR1193 | 12 | 3.16 | 0.48 | 0.65 | 0.68 | 1.62 | 1.62 | 0.66 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.21 |
| WJR19057 | 15 | 5.10 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 1.99 | 2.30 | 0.82 | 0.45 | 0.10 | 0.38 |
| WJR18870 | 15 | 5.20 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 2.01 | 1.63 | 0.79 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| WJR18123 | 15 | 3.99 | 0.40 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 1.90 | 1.9 | 0.73 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.31 |
| WJR17197 | 17 | 4.46 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 1.95 | 8.35 | 0.75 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.13 |
| WJR27081 | 7 | 2.62 | 0.29 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 1.33 | 7.53 | 0.59 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.37 |
| WJR20924 | 21 | 7.68 | 0.46 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 2.54 | 1.6 | 0.87 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.32 |
| WJR20785 | 25 | 7.53 | 0.96 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 2.55 | 2.80 | 0.86 | −0.13 | 0.08 | −0.06 |
| WJR19806 | 9 | 2.75 | 0.20 | 0.58 | 0.64 | 1.29 | 1.96 | 0.61 | 0.51 | 0.11 | 0.55 |
| WJR28944 | 12 | 1.88 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 1.16 | 2.70 | 0.45 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0.32 |
| WJR29601 | 7 | 2.81 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 1.37 | 1.77 | 0.64 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.26 |
| WJR32508 | 12 | 6.27 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 2.10 | 1.92 | 0.83 | −0.12 | 0.12 | 0.008 |
| WJR37937 | 9 | 3.44 | 1.00 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 1.52 | 6.82 | 0.66 | −0.40 | 0.04 | −0.19 |
| WJR41945 | 13 | 1.47 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.89 | 2.75 | 0.39 | −0.04 | 0.08 | 0.03 |
| WJR19609 | 7 | 3.56 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 1.41 | 3.84 | 0.70 | −0.08 | 0.06 | −0.06 |
| Total | 316 | ||||||||||
| Mean | 14.36 | 5.17 | 0.52 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 1.82 | 2.68 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.22 |
| Pop | N | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | uHe | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | Mean | 8.27 | 7.64 | 5.06 | 1.69 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.14 |
| SE | 0.19 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.06 | |
| D | Mean | 14.68 | 7.86 | 4.29 | 1.59 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.18 |
| SE | 0.17 | 0.63 | 0.43 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| Y | Mean | 23.18 | 7.73 | 3.32 | 1.33 | 0.43 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.31 |
| SE | 0.31 | 0.75 | 0.54 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z.; Shi, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, J. Development of Polymorphic Microsatellite Markers and Identification of Applications for Wild Walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Middle Asia. Diversity 2023, 15, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101073
Li X, Wang X, Cui Z, Shi W, Huang J, Wang J. Development of Polymorphic Microsatellite Markers and Identification of Applications for Wild Walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Middle Asia. Diversity. 2023; 15(10):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101073
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuerong, Xiyong Wang, Zhijun Cui, Wei Shi, Junhua Huang, and Jiancheng Wang. 2023. "Development of Polymorphic Microsatellite Markers and Identification of Applications for Wild Walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Middle Asia" Diversity 15, no. 10: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101073
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, X., Cui, Z., Shi, W., Huang, J., & Wang, J. (2023). Development of Polymorphic Microsatellite Markers and Identification of Applications for Wild Walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Middle Asia. Diversity, 15(10), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101073






