Seasonal Variations in Invertebrates Sheltered among Corallina officinalis (Plantae, Rodophyta) Turfs along the Southern Istrian Coast (Croatia, Adriatic Sea)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
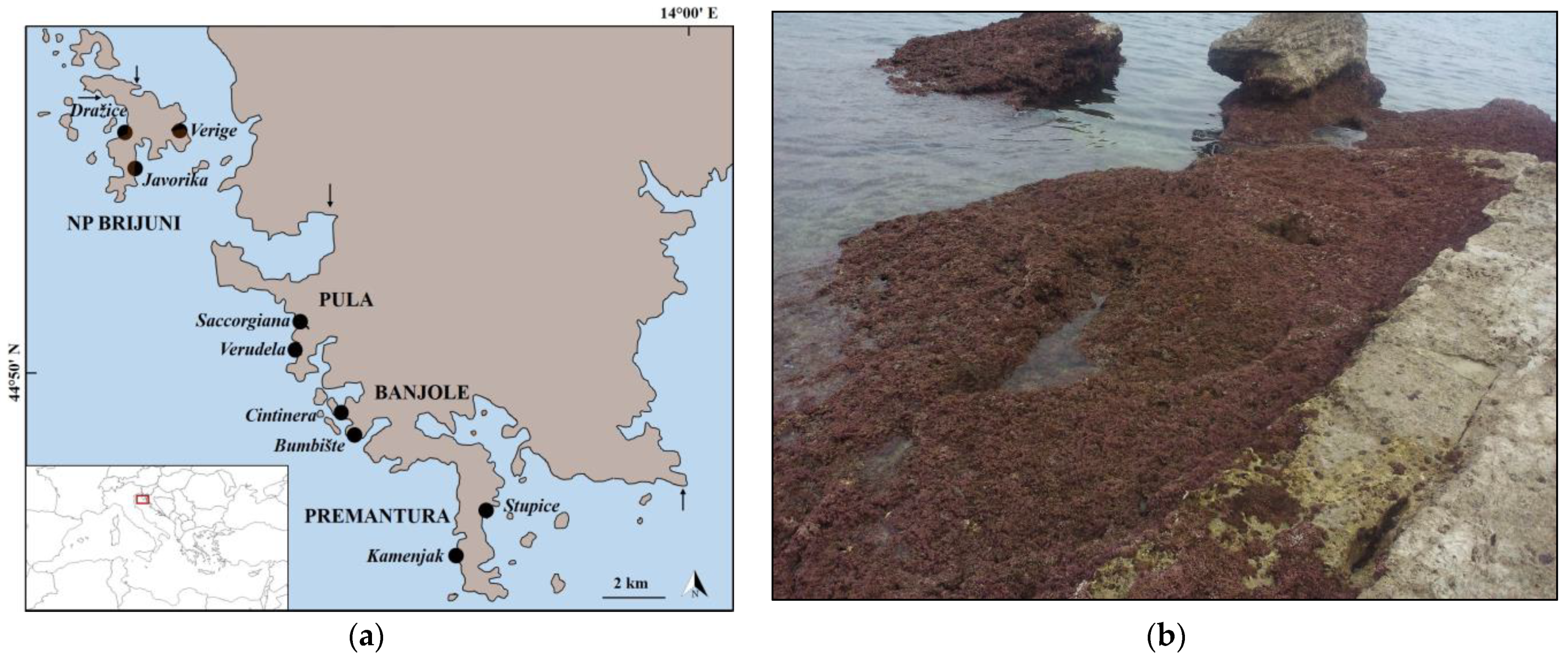
2.1. Research Area and Sampling Methods
2.2. Analysis of the Invertebrate Structure and Composition
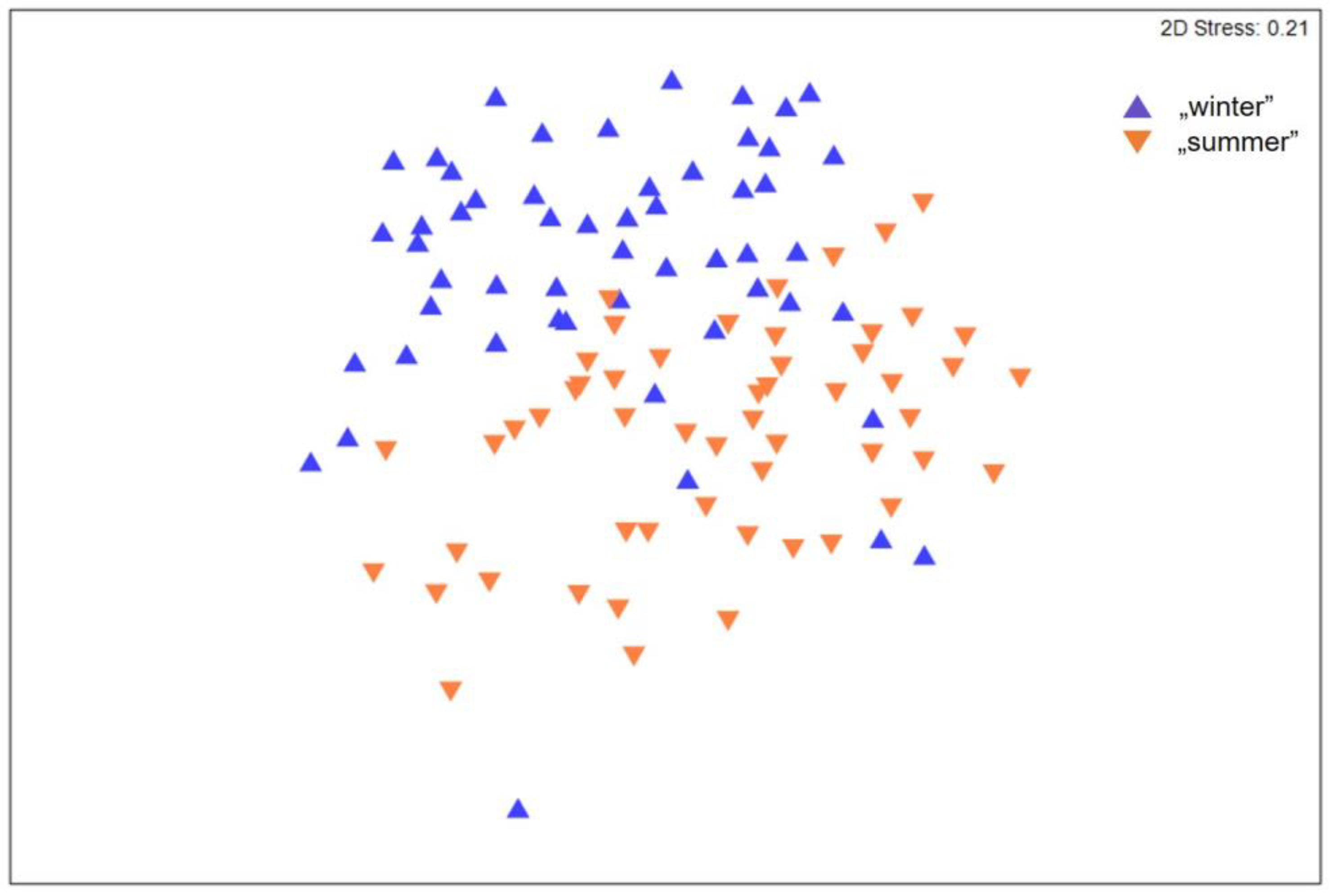
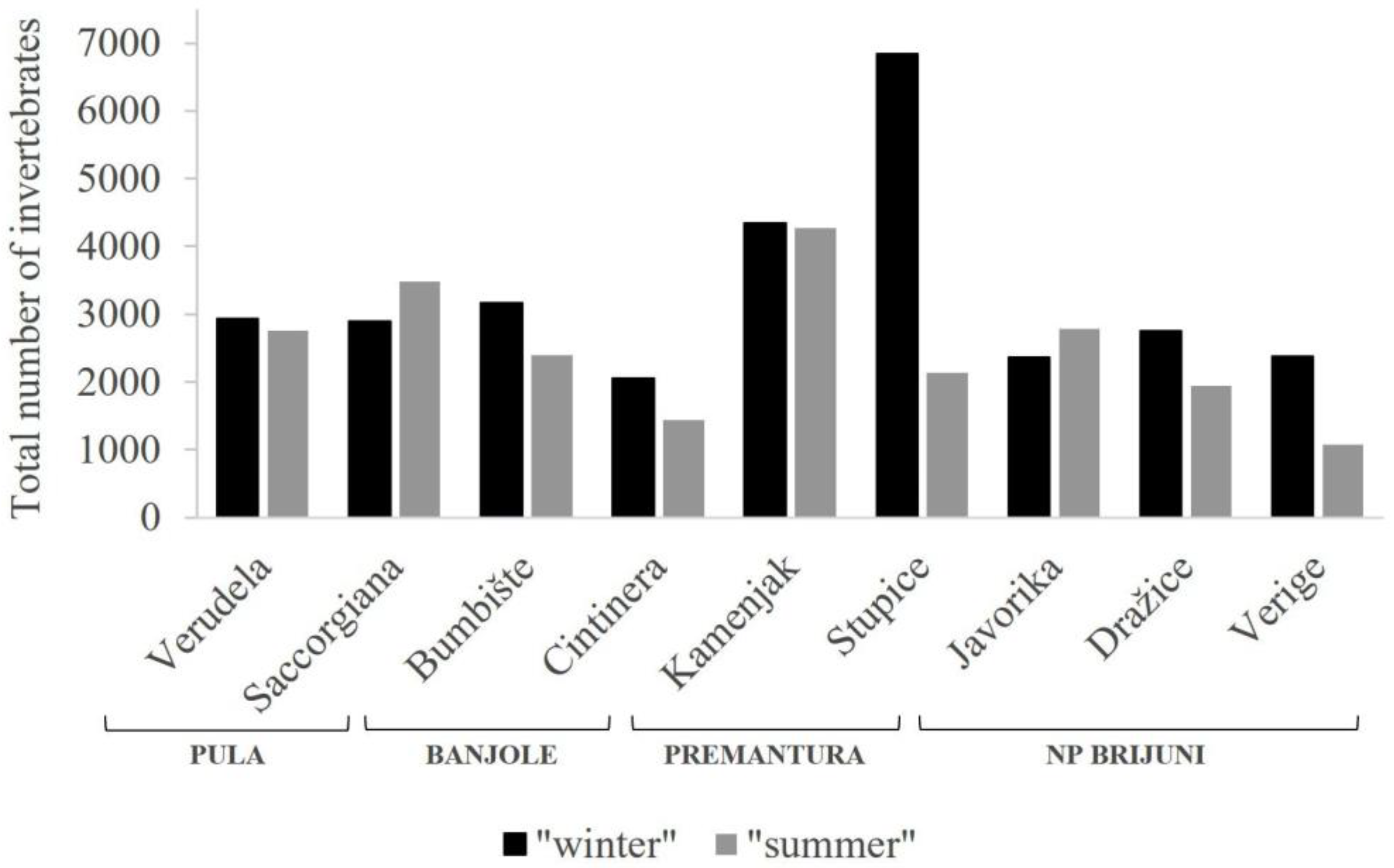
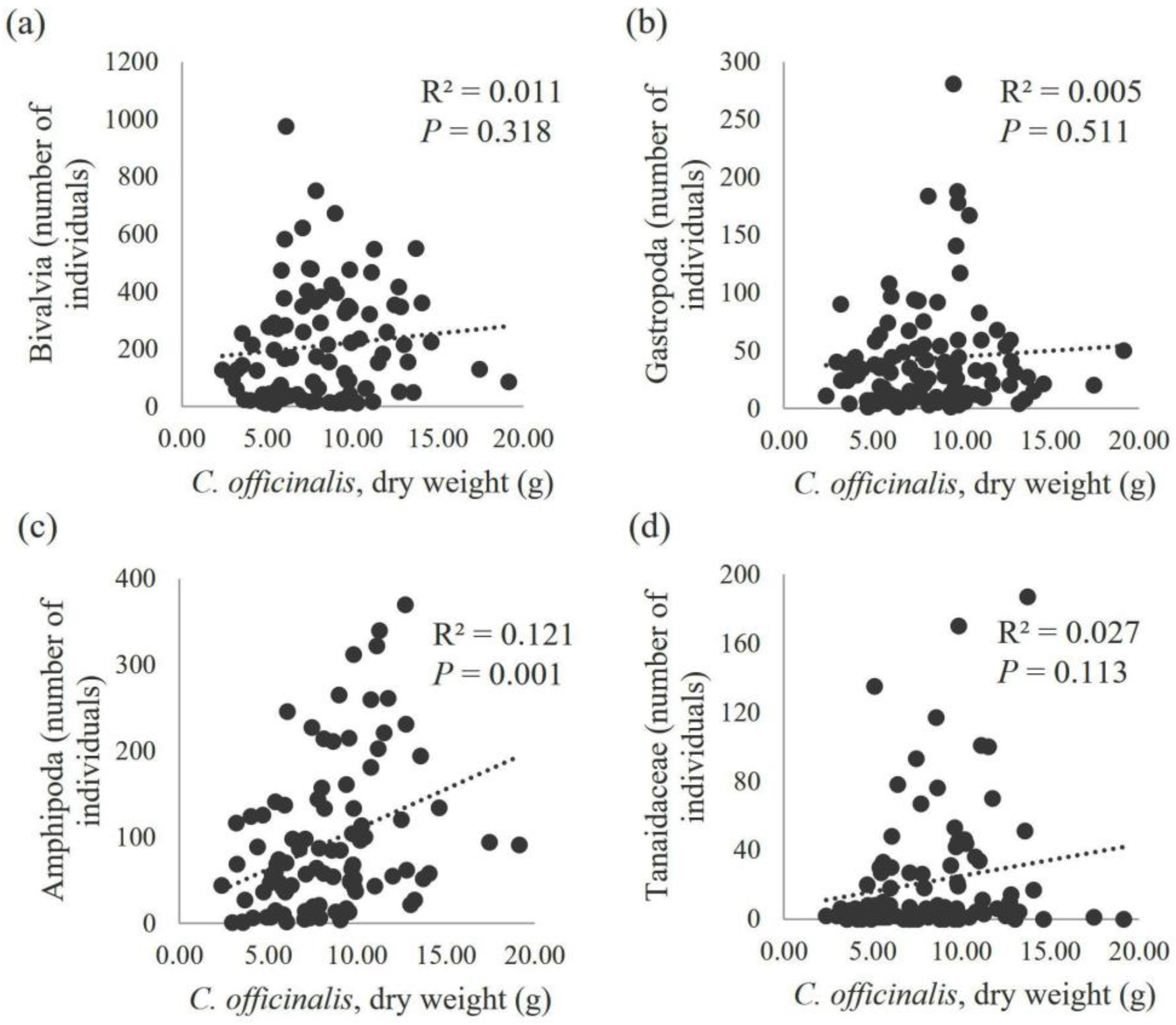
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williamson, C.J.; Perkins, R.; Voller, M.; Yallop, M.L.; Brodie, J. The regulation of coralline algal physiology, an in situ study of Corallina officinalis (Corallinales, Rhodophyta). Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 4485–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, V.; Žuljević, A.; Mangialajo, L.; Antolić, B.; Kušpilić, G.; Ballesteros, E. Cartography of littoral rocky-shore communities (CARLIT) as a tool for ecological quality assessment of coastal waters in the Eastern Adriatic Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertness, M.D.; Crain, C.M.; Silliman, B.R.; Bazterrica, M.C.; Reyna, M.V.; Hildago, F.; Farina, J.K. The community structure of western Atlantic Patagonian rocky shores. Ecol. Monogr. 2006, 76, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzi, M.; Gappa, J.L. Macrofaunal assemblages associated with coralline turf: Species turnover and changes in structure at different spatial scales. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 363, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.A. Calcified macroalgae—Critical to coastal ecosystems and vulnerable to change: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, M.E.S.; Gonzalez-Dorantes, C.A.; Stachowicz, J.J. Whole-community mutualism: Associated invertebrates facilitate a dominant habitat-forming seaweed. Ecology 2007, 88, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, K., Jr.; Crowder, L.B. habitat structure and predator—Prey interactions in vegetated aquatic systems. In Habitat Structure: The Physical Arrangement of Objects in Space; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 281–299. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, D.; Oliva, F.; Ballesteros, M. Marine invertebrate epibionts on photophilic seaweeds: Importance of algal architecture. Mar. Biodivers. 2021, 51, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Trkov, D.; Klun, K.; Pitacco, V. Diversity of Molluscan Assemblage in Relation to Biotic and Abiotic Variables in Brown Algal Forests. Plants 2022, 11, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bégin, C.; Johnson, L.; Himmelman, J. Macroalgal canopies: Distribution and diversity of associated invertebrates and effects on the recruitment and growth of mussels. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 271, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Colepicolo, P.; Pupo, M.T.; Palma, M.S. Bioprospecting macroalgae, marine and terrestrial invertebrates & their associated microbiota. Biota Neotropica 2022, 22, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Jeong, K.-S.; Joo, G.-J. Distribution pattern of epiphytic microcrustaceans in relation to different macrophyte microhabitats in a shallow wetland (Upo wetlands, South Korea). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2015, 44, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra García, J.M.; Cabezas Rodríguez, M.D.P.; Baeza-Rojano Pageo, E.; Izquierdo, D.; Corzo, J.; Ros Clemente, M.; Sánchez, J.A.; Dugo Cota, Á.; Flores León, A.M.; Soler Hurtado, M.D.M. Abundance patterns of macrofauna associated to marine macroalgae along the Iberian Peninsula. Zool. Baetica 2011, 22, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.L.; Scheibling, R.E. Effects of native and invasive macroalgal canopies on composition and abundance of mobile benthic macrofauna and turf-forming algae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 341, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehl, M.; Daniel, T.L. Hydrodynamic Interactions Between Macroalgae and Their Epibionts. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 872960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F.; Pardi, G.; Tamburello, L.; Ravaglioli, C. Nutrient enrichment stimulates herbivory and alters epibiont assemblages at the edge but not inside subtidal macroalgal forests. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, N.P.; Koehl, M.A.R. Ecological biomechanics of damage to macroalgae. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 981904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.D. The polychaetes of Lewis and Harris with notes on other marine invertebrates. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. B Biol. Sci. 1979, 77, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.B.; Attramadal, Y.G. Reproductive behaviour and larval development of Tanais cavolinii (Crustacea: Tanaidacea). Mar. Biol. 1982, 71, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, C.A.; Stotz, W.B. Description of the fauna associated with Corallina officinalis L. in the intertidal of the rocky shore of Palo Colorado (Los Vilos, IV-region, Chile). Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1998, 3, 512. [Google Scholar]
- Bussell, J.A.; Lucas, I.A.; Seed, R. Patterns in the invertebrate assemblage associated with Corallina officinalis in tide pools. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2007, 87, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelaher, B.P.; Castilla, J.C.; Prado, L.; York, P.; Schwindt, E.; Bortolus, A. Spatial variation in molluscan assemblages from coralline turfs of Argentinean Patagonia. J. Molluscan Stud. 2007, 73, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, C.L.; Maggs, C.A.; Johnson, M.P.; O’connor, N. Sustainable Harvesting of the Ecosystem Engineer Corallina officinalis for Biomaterials. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buršić, M.; Iveša, L.; Jaklin, A.; Pijevac, M.A. A preliminary study on the diversity of invertebrates associated with Corallina officinalis Linnaeus in southern Istrian peninsula. Acta Adriat. 2019, 60, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buršić, M.; Iveša, L.; Jaklin, A.; Pijevac, M.A.; Kučinić, M.; Štifanić, M.; Neal, L.; Mađarić, B.B. DNA Barcoding of Marine Mollusks Associated with Corallina officinalis Turfs in Southern Istria (Adriatic Sea). Diversity 2021, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buršić, M.; Iveša, L.; Jaklin, A.; Pijevac, M.A.; Mađarić, B.B.; Neal, L.; Pustijanac, E.; Burić, P.; Iveša, N.; Paliaga, P. Changes in Composition of Mollusks within Corallina officinalis Turfs in South Istria, Adriatic Sea, as a Response to Anthropogenic Impact. Diversity 2023, 15, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, A.; Scuderi, D.; Fraschetti, S.; Guidetti, P.; Boero, F. Molluscs on subtidal cliffs: Patterns of spatial distribution. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2003, 83, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarore, A.; Fioretti, S.; Meccariello, A.; Saccone, G.; Patti, F.P. Molluscs community associated with the brown algae of the genus Cystoseira in the Gulf of Naples (South Tyrrhenian Sea). BioRxiv 2017, 160200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakkonen, H.M.; Strelkov, P.; Väinölä, R. Molecular lineage diversity and inter-oceanic biogeographical history in Hiatella (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Zool. Scr. 2015, 44, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Moyano, J.; Estacio, F.; García-Adiego, E.; García-Gómez, J. The molluscan epifauna of the alga halopteris scoparia in southern Spain as a bioindicator of coastal environmental conditions. J. Molluscan Stud. 2000, 66, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, D.; Guerra-García, J.M. Distribution patterns of the peracarid crustaceans associated with the alga Corallina elongata along the intertidal rocky shores of the Iberian Peninsula. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2011, 65, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-García, J.M.; de Figueroa, J.M.T.; Barranco, C.N.; Ros, M.; Sanchez-Moyano, J.E.; Moreira, J. Dietary analysis of the marine Amphipoda (Crustacea: Peracarida) from the Iberian Peninsula. J. Sea Res. 2014, 85, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Spelda, J.; Melzer, R.; Buršić, M. Pycnogonida (Arthropoda) from Northern Adriatic Corallina officinalis Linnaeus, 1758 belts. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2020, 22, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquete, P.; Rubal, M.; Veiga, P.; Troncoso, J. New records of Sea Spiders (Arthropoda: Pycnogonida) for continental Portugal and notes on species distribution. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2016, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, S.; Davenport, J. Oxygen microenvironment of coralline algal tufts and their associated epiphytic animals. In Biology and Environment: Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy; Royal Irish Academy: Dublin, Ireland, 2010; pp. 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Matias, M.G.; Arenas, F.; Rubal, M.; Pinto, I.S. Macroalgal Composition Determines the Structure of Benthic Assemblages Colonizing Fragmented Habitats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Airoldi, L.; Cinelli, F. Effects of sedimentation on subtidal macroalgal assemblages: An experimental study from a mediterranean rocky shore. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 215, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordsieck, F. Die Europäischen Meeres-Gehäuseschnecken (Prosobranchia); Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1968; pp. 1–273. [Google Scholar]
- Nordsieck, F. Die Europäischen Meeresmuscheln (Bivalvia); Gustav Fisher Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1969; pp. 1–256. [Google Scholar]
- Parenzan, P. Gasteropodi. In Carta d’Identità delle Conchiglie del Mediterraneo; Bios Taras: Taranto, Italy, 1970; Volume 1, pp. 1–283. [Google Scholar]
- Parenzan, P. Bivalves. In Carta d’Identità delle Conchiglie del Mediterraneo; Bios Taras: Taranto, Italy, 1974; Volume 2, pp. 1–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sabelli, B.; Gianuzzi-Savelli, R.; Bedulli, D. Catalogo Annotato dei Molluschi Marini del Mediterraneo; Libreria Naturalistica Bolognese: Bologna, Italy, 1990; Volume 1, pp. 1–348. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, G.T.; Goto, Y. Scaphopoda, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda. In European Seashells; Verlag Christa Hemmen: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 1–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gianuzzi-Savelli, R.; Pusateri, F.; Palmeri, A.; Ebreo, C. Atlante delle Conchiglie Marine del Mediterraneo; La Conchiglia: Roma, Italy, 1996; pp. 1–258. [Google Scholar]
- Gofas, S.; Moreno, D.; Salas, C. (Eds.) Moluscos marinos de Andalucía; Universidad de Málaga: Málaga, Spain, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 1–342. [Google Scholar]
- Gofas, S.; Moreno, D.; Salas, C. (Eds.) Moluscos marinos de Andalucía; Universidad de Málaga: Málaga, Spain, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 343–798. [Google Scholar]
- Tischler, W. Grundzüge der Terrestrischen Tierökologie; Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn: Braunschweig, Germany, 1949; 219p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travizi, A. The nematode fauna of the northern Adriatic offshore sediments: Community structure and biodiversity. Acta Adriat. 2010, 51, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Năstase, A.; Honț, S.; Iani, M.; Paraschiv, M.; Cernișencu, I.; Năvodaru, I. Ecological status of fish fauna from Razim Lake and the adjacent area, the Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve, Romania. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2022, 52, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelaher, B.P. Changes in habitat complexity negatively affect diverse gastropod assemblages in coralline algal turf. Oecologia 2003, 135, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, M.; Underwood, T.; Hochuli, D.; Coleman, R. Habitat identity influences species—Area relationships in heterogeneous habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 437, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelaher, B. Influence of physical characteristics of coralline turf on associated macrofaunal assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 232, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavender, J.T.; Dafforn, K.A.; Bishop, M.J.; Johnston, E.L. Small-scale habitat complexity of artificial turf influences the development of associated invertebrate assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 492, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urra, J.; Rueda, J.; Ramírez, M.; Marina, P.; Tirado, C.; Salas, C.; Gofas, S. Seasonal variation of molluscan assemblages in different strata of photophilous algae in the Alboran Sea (western Mediterranean). J. Sea Res. 2013, 83, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K.H. Production and use of detritus in various freshwater, estuarine, and coastal marine ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 910–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarria, C.; Chapman, M. Comparison of patterns of spatial variation of microgastropods between 2 contrasting intertidal habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 220, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarria, C.; Chapman, M. Habitat-associated variability in survival and growth of three species of microgastropods. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2001, 81, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, G.R.F. Meiofauna associated with rocky shore algae. In The Ecology of Rocky Coasts; Moore, P.G., Seed, R., Eds.; Hodder and Stoughton: London, UK, 1985; pp. 36–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bussell, J.A. Biodiversity of the Invertebrate Community Associated with the Turf-Forming Red Alga Corallina officinalis in Tide Pools; Bangor University: London, UK, 2003; pp. 1–248. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, A. Molluscs: Prosobranch and Pyramidellid Gastropods: Keys and Notes for the Identification of the Species; E.J. Brill/Dr. W. BackhuYs: Leiden, Germany, 1988; pp. 1–662. [Google Scholar]
- Hayward, P.J.; Ryland, J.S. Handbook of the Marine Fauna of North-West Europe; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995; pp. 1–799. [Google Scholar]




| Taxonomic Group | “Winter” | “Summer” | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A% | F% | A% | F% | |
| Platyhelminthes | 0.01 | 7.41 | 0.01 | 1.85 |
| Nemertea | 0.12 | 31.48 | 0.13 | 18.52 |
| Nematoda | 3.08 | 98.15 | 2.17 | 81.48 |
| Sipuncula | 0.24 | 38.89 | 0.20 | 37.04 |
| Gastropoda | 7.69 | 100.00 | 10.21 | 100.00 |
| Bivalvia | 31.72 | 100.00 | 55.24 | 100.00 |
| Polyplacophora | 0.31 | 62.96 | 0.75 | 77.78 |
| Polychaeta | 13.62 | 100.00 | 9.27 | 100.00 |
| Decapoda | 0.08 | 33.33 | 0.01 | 1.85 |
| Cumacea | 0.11 | 22.22 | 0.02 | 7.41 |
| Tanaidacea | 5.67 | 87.04 | 6.02 | 79.63 |
| Isopoda | 3.66 | 87.04 | 1.44 | 75.93 |
| Amphipoda | 26.95 | 100.00 | 9.71 | 100.00 |
| Caprellidae | 0.80 | 51.85 | 0.06 | 14.81 |
| Copepoda | 1.96 | 90.74 | 0.87 | 75.93 |
| Pantopoda | 0.78 | 79.63 | 0.15 | 33.33 |
| Acari | 2.02 | 94.44 | 1.92 | 85.19 |
| Diptera | 0.43 | 50.00 | 0.73 | 50.00 |
| Echinoidea | 0.02 | 7.41 | 0.22 | 51.85 |
| Ophiuroidea | 0.72 | 64.81 | 0.89 | 62.96 |
| Relative Abundance | “Winter” | “Summer” | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Taxonomic Groups | % | No. of Taxonomic Groups | % | |
| eudominant (>10%) | 3 | 15.00 | 2 | 10.00 |
| dominant (5–10%) | 2 | 10.00 | 3 | 15.00 |
| subdominant (2–5%) | 3 | 15.00 | 1 | 5.00 |
| recedent (1–2%) | 1 | 5.00 | 2 | 10.00 |
| subrecedent (<1%) | 11 | 55.00 | 12 | 60.00 |
| TOTAL | 20 | 100.00 | 20 | 100.00 |
| Frequency of Occurrence | “Winter” | “Summer” | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Taxonomic Groups | % | No. of Taxonomic Groups | % | |
| very frequent (75–100%) | 10 | 50.00 | 10 | 50.00 |
| frequent (50–75%) | 4 | 20.00 | 3 | 15.00 |
| widespread (25–50%) | 3 | 15.00 | 2 | 10.00 |
| rare (0–25%) | 3 | 15.00 | 5 | 25.00 |
| TOTAL | 20 | 100.00 | 20 | 100.00 |
| (a) | ||||||||||
| Taxonomic Group | Pula | Banjole | Premantura | Brijuni National Park | Total | |||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | ||
| Platyhelminthes | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Nemertea | 2 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 37 |
| Nematoda | 89 | 125 | 151 | 148 | 78 | 134 | 57 | 71 | 61 | 914 |
| Sipuncula | 3 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 29 | 18 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 70 |
| Gastropoda | 294 | 194 | 408 | 129 | 789 | 187 | 86 | 117 | 82 | 2286 |
| Bivalvia | 1158 | 1367 | 468 | 862 | 1298 | 3269 | 422 | 450 | 131 | 9425 |
| Polyplacophora | 14 | 20 | 12 | 2 | 19 | 17 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 92 |
| Polychaeta | 332 | 289 | 612 | 390 | 306 | 1044 | 343 | 378 | 353 | 4047 |
| Decapoda | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 23 |
| Cumacea | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 22 | 33 |
| Tanaidacea | 96 | 10 | 64 | 6 | 42 | 258 | 387 | 669 | 154 | 1686 |
| Isopoda | 4 | 135 | 293 | 39 | 207 | 32 | 29 | 55 | 293 | 1087 |
| Amphipoda | 587 | 585 | 821 | 216 | 1315 | 1638 | 939 | 871 | 1035 | 8007 |
| Caprellidae | 20 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 8 | 87 | 4 | 3 | 103 | 239 |
| Copepoda | 62 | 58 | 65 | 230 | 11 | 63 | 5 | 38 | 50 | 582 |
| Pantopoda | 47 | 24 | 84 | 2 | 10 | 21 | 30 | 3 | 12 | 233 |
| Acari | 185 | 59 | 104 | 15 | 94 | 44 | 30 | 46 | 22 | 599 |
| Diptera | 4 | 14 | 15 | 3 | 50 | 13 | 0 | 5 | 23 | 127 |
| Echinoidea | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Ophiuroidea | 31 | 1 | 33 | 3 | 62 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 29 | 215 |
| Total | 2929 | 2887 | 3170 | 2058 | 4338 | 6836 | 2366 | 2749 | 2378 | 29,711 |
| (b) | ||||||||||
| Taxonomic Group | Pula | Banjole | Premantura | Brijuni National Park | Total | |||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | ||
| Platyhelminthes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Nemertea | 1 | 17 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 29 |
| Nematoda | 23 | 125 | 30 | 12 | 110 | 88 | 34 | 17 | 44 | 483 |
| Sipuncula | 0 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 10 | 9 | 13 | 3 | 1 | 45 |
| Gastropoda | 132 | 358 | 339 | 117 | 269 | 28 | 568 | 279 | 186 | 2276 |
| Bivalvia | 1773 | 2459 | 1430 | 649 | 2613 | 1103 | 1122 | 796 | 368 | 12,313 |
| Polyplacophora | 19 | 22 | 13 | 14 | 24 | 5 | 42 | 18 | 11 | 168 |
| Polychaeta | 84 | 196 | 226 | 229 | 261 | 318 | 344 | 144 | 264 | 2066 |
| Decapoda | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Cumacea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Tanaidacea | 180 | 2 | 8 | 15 | 383 | 202 | 280 | 246 | 25 | 1341 |
| Isopoda | 23 | 19 | 57 | 23 | 125 | 20 | 5 | 31 | 19 | 322 |
| Amphipoda | 327 | 90 | 167 | 326 | 329 | 286 | 267 | 304 | 68 | 2164 |
| Caprellidae | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 13 |
| Copepoda | 22 | 20 | 9 | 15 | 11 | 14 | 20 | 29 | 55 | 195 |
| Pantopoda | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 33 |
| Acari | 94 | 115 | 37 | 17 | 32 | 12 | 55 | 38 | 27 | 427 |
| Diptera | 62 | 39 | 31 | 0 | 18 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 162 |
| Echinoidea | 0 | 3 | 9 | 13 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 48 |
| Ophiuroidea | 8 | 16 | 28 | 9 | 72 | 30 | 22 | 12 | 1 | 198 |
| Total | 2752 | 3488 | 2390 | 1443 | 4275 | 2141 | 2787 | 1939 | 1077 | 22,292 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buršić, M.; Jaklin, A.; Arko Pijevac, M.; Bruvo Mađarić, B.; Neal, L.; Pustijanac, E.; Burić, P.; Iveša, N.; Paliaga, P.; Iveša, L. Seasonal Variations in Invertebrates Sheltered among Corallina officinalis (Plantae, Rodophyta) Turfs along the Southern Istrian Coast (Croatia, Adriatic Sea). Diversity 2023, 15, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101099
Buršić M, Jaklin A, Arko Pijevac M, Bruvo Mađarić B, Neal L, Pustijanac E, Burić P, Iveša N, Paliaga P, Iveša L. Seasonal Variations in Invertebrates Sheltered among Corallina officinalis (Plantae, Rodophyta) Turfs along the Southern Istrian Coast (Croatia, Adriatic Sea). Diversity. 2023; 15(10):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101099
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuršić, Moira, Andrej Jaklin, Milvana Arko Pijevac, Branka Bruvo Mađarić, Lucija Neal, Emina Pustijanac, Petra Burić, Neven Iveša, Paolo Paliaga, and Ljiljana Iveša. 2023. "Seasonal Variations in Invertebrates Sheltered among Corallina officinalis (Plantae, Rodophyta) Turfs along the Southern Istrian Coast (Croatia, Adriatic Sea)" Diversity 15, no. 10: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101099
APA StyleBuršić, M., Jaklin, A., Arko Pijevac, M., Bruvo Mađarić, B., Neal, L., Pustijanac, E., Burić, P., Iveša, N., Paliaga, P., & Iveša, L. (2023). Seasonal Variations in Invertebrates Sheltered among Corallina officinalis (Plantae, Rodophyta) Turfs along the Southern Istrian Coast (Croatia, Adriatic Sea). Diversity, 15(10), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101099








