Barcoding Mullets (Mugilidae): Genetic Characterization of Exploited Species in Southern Peninsular India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- Crenimugil Schultz, 1946—Type species: Crenimugil crenilabis (Forsskål 1775) (JQ060435) (“A” in Supplementary Figure S1)
- 2.
- Plicomugil Schultz, 1953—Type species: Plicomugil labiosus (Valenciennes 1836) (topotype: MN728289) (“G” in Supplementary Figure S1)
- 3.
- Ellochelon Whitley, 1930—Type species: Ellochelon vaigiensis (Quoy & Gaimard 1825) (topotype: JQ060444) (“F” in Supplementary Figure S1)
- 4.
- Osteomugil Schultz, 1946—Type species: Osteomugil cunnesius (Valenciennes 1836) (topotype: JQ045777) (“E” in Supplementary Figure S1)
- 5.
- Planiliza Whitley, 1945—Type species: Planiliza ordensis (Whitley 1945) (topotype: JQ060449–50) (“H” in Supplementary Figure S1)
- 6.
- Mugil Linnaeus, 1758—Type species: Mugil cephalus Linnaeus 1758 (topotypes: KY683176, JQ060529, JQ060532–34) (“C” in Supplementary Figure S1)
- 7.
- Rhinomugil Gill, 1863—Type species: Rhinomugil corsula (topotype: JX105471) (“A” in Supplementary Figure S1)
- 8.
- Minimugil Durand, Chen, Shen, Fu, and Borsa, 2012—Type species: Minimugil cascasia (Hamilton 1822) (topotypes: JQ060624 and MK572330) (“B” in Supplementary Figure S1)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-Castro, M.; Ghasemzadeh, J. Morphology and morphometry-based taxonomy of Mugilidae. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetti, D. Current state of grey mullet fisheries and culture. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 398–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefeuvre, J.C.; Laffaille, P.; Feunteun, E. Do fish communities function as biotic vectors of organic matter between salt marshes and marine coastal waters? Aquat. Ecol. 1999, 33, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Yearbook. Fish. Aquacult. Stat. 2019/FAO Annuaire. Statistiques des Pêches et de L’aquaculture 2019/FAO Anuario. Estadísticas de Pesca y Acuicultura 2019; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; 82p. [Google Scholar]
- Linnaeus, C.V. Systems Naturae per Regna Tria Naturae, Secundum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, cum Characteribus, Differentiis, Synonymis, Locis. Editio Decima, Reformata. Laurentii Salvii: Stockholm, Sweden, 1758; Volume 1, 824p. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, I.J.; Nirchio, M.; Oliveira, C.; Ron, E.; Gaviria, J. A new species of mullet (Teleostei: Mugilidae) from Venezuela, with a discussion on the taxonomy of Mugil gaimardianus. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.D.; Shen, K.N.; Chen, W.J.; Jamandre, B.W.; Blel, H.; Diop, K.; Nirchio, M.; Garcia de León, F.J.; Whitfield, A.K.; Chang, C.W.; et al. Systematics of the grey mullets (Teleostei: Mugiliformes: Mugilidae): Molecular phylogenetic evidence challenges two centuries of morphology-based taxonomy. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 64, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delrieu-Trottin, E.; Durand, J.D.; Limmon, G.; Sukmono, T.; Kadarusman; Sugeha, H.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Busson, F.; Borsa, P.; Dahruddin, H.; et al. Biodiversity inventory of the grey mullets (Actinopterygii: Mugilidae) of the Indo-Australian Archipelago through the iterative use of DNA-based species delimitation and specimen assignment methods. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, J.D.; Hubert, N.; Shen, K.N.; Borsa, P. DNA barcoding grey mullets. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2017, 27, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; van der Laan, R. Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species, References. 2023. Available online: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Durand, J.D.; Borsa, P. Mitochondrial phylogeny of grey mullets (Acanthopterygii: Mugilidae) suggests high pro-portion of cryptic species. CR Biol. 2015, 338, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.D. Implications of molecular phylogeny for the taxonomy of Mugilidae. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Durand, J.D.; Fu, C. Multilocus resolution of Mugilidae phylogeny (Teleostei: Mugiliformes): Implications for the family’s taxonomy. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 96, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.B.; Kim, J.K.; Li, C. A new perspective on biogeographic barrier in the flathead grey mullet (Pisces: Mugilidae) from the northwest Pacific. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.M.M.; Almeida, J.P.F.A.; Sturaro, M.J.; Fabré, N.N.; Pereira, R.J.; Mott, T. Deep genetic divergence and paraphyly in cryptic species of Mugil fishes (Actinopterygii: Mugilidae). Syst. Biodivers. 2020, 18, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, T.V.R. On the culture of grey mullets in association with commercial carps in freshwater tanks in Bengal. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1949, 48, 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Mugil cephalus; Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006–2021; Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/culturedspecies/Mugil_cephalus/en (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Panda, D.; Mohanty, S.K.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Das, S.; Karna, S.K. Growth, mortality and stock status of mullets (Mugilidae) in Chilika Lake, India. Lakes Reserv. Sci. Policy Manag. Sustain. Use 2018, 23, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, F. An Account of the Fishes Found in the River Ganges and Its Branches; Archibald Constable and Company: Edinburgh, UK; London, UK, 1822; 405p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvier, G.; Valenciennes, A. Histoire Naturelle des Poisons; Chez, F.G., Ed.; Levrault: Paris, France, 1836; Volume 11, 506p. [Google Scholar]
- Day, F. The Fishes of India; Being a Natural History of the Fishes Known to Inhabit the Seas and Fresh Waters of India Burma, and Ceylon; Bernard Quaritch: London, UK, 1878; Volume 1, 778p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, R.H. The grey mullets of Tuticorin. Madras Fish Bull. 1922, 15, 71–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kutty, M.N.; Sukumaran, N.; Kasim, H.M. Influence of temperature and salinity on survival of the freshwater mullet, Rhinomugil corsula (Hamilton). Aquaculture 1980, 20, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.S.B.R.; Rengaswamy, V.S.; Raju, A.; Mohanraj, G. Studies on diurnal variations in the occurrence of grey mullet seed at Mandapam. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal Aquaculture, Marine Biological Association of India; Silas, E.G., Rao, P.V., Nakayana Rao, K.V., George, K.C., Rengarajan, K., Pillai, P.P., Krishnan, L., Eds.; The Diocesan Press: Madras, India, 1984; pp. 765–775. [Google Scholar]
- Rekharani, Z.; Madhavi, R. Digenetic trematodes from mullets of Visakhapatnam (India). J. Nat. Hist. 1985, 19, 929–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, S.; Nandakumaran, K. The intensive farming of striped Mullet, Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus 1758), in the polyethylene film-lined ponds developed on the sea shore at Calicut, Kerala. In Aquaculture Productivity; Sinha, V.R.P., Srivastava, H.C., Eds.; OXFORD and IBH Publishing CO. PVT. LTD: New Delhi, India, 1991; pp. 521–531. [Google Scholar]
- George, K.C.; Pandey, A.K.; Peer Mohamed, M. Mercury chloride induced renal lesions in the mullet Liza parsia (Hamilton-Buchanan). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. India 1995, 37, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, J.; Viswanathan Nair, P.G.; Ammu, K.; Mathew, S. Lipase activity in different tissues of four species of fish: Rohu (Labeo rohita Hamilton), oil sardine (Sardinella longiceps Linnaeus), mullet (Liza subviridis Valenciennes) and Indian mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta Cuvier). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmi Priya, S.; Senthilkumar, B.; Hariharan, G.; Paneer Selvam, A.; Purvaja, R.; Ramesh, R. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in mullet (Mugil cephalus) and oyster (Crassostrea madrasensis) from Pulicat lake, south east coast of India. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2011, 27, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariharan, G.; Purvaja, R.; Ramesh, R. Environmental safety level of lead (Pb) pertaining to toxic effects on grey mullet (Mugil cephalus) and Tiger perch (Terapon jarbua). Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 31, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ranjan, R.; Megarajan, S.; Pattnaik, P.; Dash, B.; Edward, L. Mixed culture of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) and flathead grey mullet Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) in floating cages. Indian J. Fish. 2016, 61, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Swain, S.; Chadha, N.K.; Sundaray, J.K.; Sawant, P.B.; Chhandaprajnadarsini, E.M. Effect of vitamin C dietary supplementation on growth and survival of grey mullet, Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) fry. Asian J. Microbiol. Bio Technol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 18, 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- John, C.M. The grey mullets of Kayamkulam Lake, India and their fishery. Copeia 1955, 1955, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarojini, R.P. A revision of Indian Mugilidae. Part I and II. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1962, 59, 254–270. [Google Scholar]
- Luther, G. The grey mullet fishery resources of India. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Living Resources of the Seas around India; Special Publication. Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute: Cochin, India, 1973; pp. 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Luther, G. New characters for consideration in the taxonomic appraisal of grey mullets. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. India 1977, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzes, M.R.; Martins, M.; Naik, S. Interspecific genetic divergence in grey mullets from the Goa region. Aquaculture 1992, 105, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.U.; Khan, S.A.; Lyla, P.; Kumar, C.P. DNA barcoding resolves taxonomic ambiguity in mugilidae of Parangipettai waters (southeast coast of India). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 13, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.N.; Durand, J.D. The biogeography of Mugilidae in India South-East and East Asia. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, D.M.; Mankodi, P.C. An annotated checklist of family Mugilidae Jarocki, 1822 (Actinopterygii: Mugiliformes) from India. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2022, 16, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.D.; Whitfield, A.K. Biogeography and distribution of Mugilidae in the western, central and southern regions of Africa. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 102–115. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.E.; Hasan, A.; Béarez, P.; Shen, K.N.; Chang, C.W.; Tran, T.T.V.; Golani, D.; Al-Saboonchi, A.; Siddiqui, P.J.A.; Durand, J.D. Planiliza lauvergnii (Eydoux and Souleyet, 1850), a senior synonym of Planiliza affinis (Günther, 1861) with a re-evaluation of keeled back mullets (Mugiliformes: Mugilidae). Zootaxa 2022, 5194, 497–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D. DNA barcode divergence among species and genera of birds and fishes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial, J.M.; Miralles, A.; De la Riva, I.; Vences, M. The integrative future of taxonomy. Front. Zool. 2010, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, I.J.; Senou, H. Mugilidae. Bony Fishes Part 2 (Mugilidae to Carangidae). In FAO Species Identification Guide for Fishery Purposes. The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Pacific; Carpenter, K.E., Niem, V.H., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1999; Volume 4, pp. 2069–2108. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahanukar, N.; Philip, S.; Krishnakumar, K.; Ali, A.; Raghavan, R. The phylogenetic position of Lepidopygopsis typus (Teleostei: Cyprinidae), a monotypic freshwater fish endemic to the Western Ghats of India. Zootaxa 2013, 3700, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Haeseler, A.V.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. Terrace aware data structure for phylogenomic inference from super matrices. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Haeseler, A.V.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree; Version 1.4.2; Inst. Evol. Biol.; University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2014; Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. A DNA-based registry for all animal species: The barcode index number (BIN) system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottelat, M. The fishes of the inland waters of Southeast Asia: A catalogue and core bibliography of the fishes known to occur in freshwaters, mangroves and estuaries. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2013, 27, 1–663. [Google Scholar]
- Kurup, B.M. Studies on the Systematics and Biology of the Fisheries of the Vembanad Lake. Ph.D. Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kochi, India, 1982; 683p. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, W.; Bianchi, G. Species Identification Sheets for Fishery Purposes; Western Indian Ocean (Fishing Area 51); FAO: Rome, Italy, 1984; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.T.V.; Ke Phan, L.; Durand, J.D. Diversity and distribution of cryptic species within the Mugil cephalus species complex in Vietnam. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 28, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syama Dayal, J.; Ambasankar, K.; Jannathulla, R.; Kumaraguruvasagam, K.P.; Kailasam, M.; Vijayan, K.K. Poly-culture of mullets in brackishwater using compounded feed: Proximate and mineral profiles in comparision with wild mullets. Indian J. Fish. 2017, 64, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, K.; Thomas, D.; Rekha, M.U.; Angel, J.R.J.; Bera, A.; Mandal, B.; Subburaj, R.; Thiagarajan, G.; Makesh, M.; Ambasankar, K.; et al. Reproductive maturation and induced breeding of two geographical groups of grey mullet, Mugil cephalus Linnaeus, 1758. Aquaculture 2021, 536, 736423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, F. The Fishes of Malabar; Bernard Quaritch: London, UK, 1865; 293p. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, B.L. Fauna of the Chilka Lake Fish Part III. Mem. Indian Mus. 1917, 5, 491–508. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, M.S.; Natarajan, M. PCR-RFLP and sequence analysis of 12S and 16S rRNA mitochontrial genes of grey mullets from East coast of India. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2011, 40, 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, C.P.; John, B.A.; Khan, S.A.; Lyla, P.S.; Murugan, S.; Rozihan, M.; Jalal, K.C.A. Efficiency of universal barcode gene (Coxi) on morphologically cryptic Mugilidae fishes delineation. Trends Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 6, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Karna, S.K.; Mukherjee, M.; Suresh, V.R. Length–weight relationships for four mullets from the Chilika lagoon, East coast of India. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2018, 34, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Kumaran, M. Fishes of the Laccadive Archipelago; The Nature Conservation and Aquatic Sciences Service: Trivandrum, India, 1980; 760p. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, A.; Siddiqui, P.J.A.; Amir, S.A.; Durand, J.-D. DNA Barcoding of Mullets (Family Mugilidae) from Pakistan Reveals Surprisingly High Number of Unknown Candidate Species. Diversity 2021, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi-Yeganeh, M.S.; Ghasemzadeh, J.; Kouhi, S.; Durand, J.-D. The squaretail mullet Ellochelon vaigiensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1825) a complex of cryptic species? Contrib. Zool. 2023, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tridge. Import Value Trend of HS Code 030389 (Grey Mullet) from All Countries to India. Available online: https://www.tridge.com/trades/data?code=030389&flow=i&reporter=IN (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Smith, A. Illustrations of the Zoology of South Africa; Consisting Chiefly of Figures and Descriptions of the Objects of Nat. Hist. Collected during an Expedition into the Interior of South Africa, in the Years 1834, 1835, and 1836; Fitted out by "The Cape of Good Hope Association for Exploring Central Africa"; Smith, Elder and Co.: London, UK, 1838–1847; Volume 4, 31p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Panfili, J.; Durand, J.D. A global review of the cosmopolitan flathead mullet Mugil cephalus Linnaeus 1758 (Teleostei: Mugilidae), with emphasis on the biology, genetics, ecology and fisheries aspects of this apparent species complex. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2012, 22, 641–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.N.; Jamandre, B.W.; Hsu, C.C.; Tzeng, W.N.; Durand, J.D. Plio-Pleistocene Sea level and temperature fluctuations in the northwestern Pacific promoted speciation in the globally-distributed flathead mullet Mugil cephalus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.N.; Chang, C.W.; Durand, J.D. Spawning segregation and philopatry are major prezygotic barriers in sympatric cryptic Mugil cephalus species. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2015, 338, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, B.; Ghosh, S.K. Genetic assessment of ornamental fish species from North East India. Gene 2015, 555, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dor, L.; Shirak, A.; Rosenfeld, H.; Meiri-Ashkenazi, I.; Rubinstein, G.; Seroussi, E.; Weller, J.I.; Ron, M. Genetic Stock Identification of the Flathead Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus) in Lake Tiberias Based on Parent Offspring Relationship. Isr. J. Aquac. 2018, 70, 2-11. IJA_70.2018.1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.D.; Chen, W.J.; Shen, K.N.; Fu, C.; Borsa, P. Genus-level taxonomic changes implied by the mitochondrial phylogeny of grey mullets (Teleostei: Mugilidae). Comptes Rendus Biol. 2012, 335, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedkar, G.D.; Jamdade, R.; Naik, S.; David, L.; Haymer, D. DNA barcodes for the fishes of the Narmada, one of India’s longest rivers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.R. Biosystematic Studies in Mullets (Family: Mugilidae) of Porto Novo, Tamil Nadu, South India. Ph.D. Thesis, Annamalai University, Chidambaram, India, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, M.; de Beaufort, L.F. The Fishes of the Indo-Australian Archipelago, Heteromi, Solenichthyes, Synentognathi, Percesoces, Labyrinthici, Microcyprini; EJ Brill Ltd.: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1922; Volume 4, 409p. [Google Scholar]
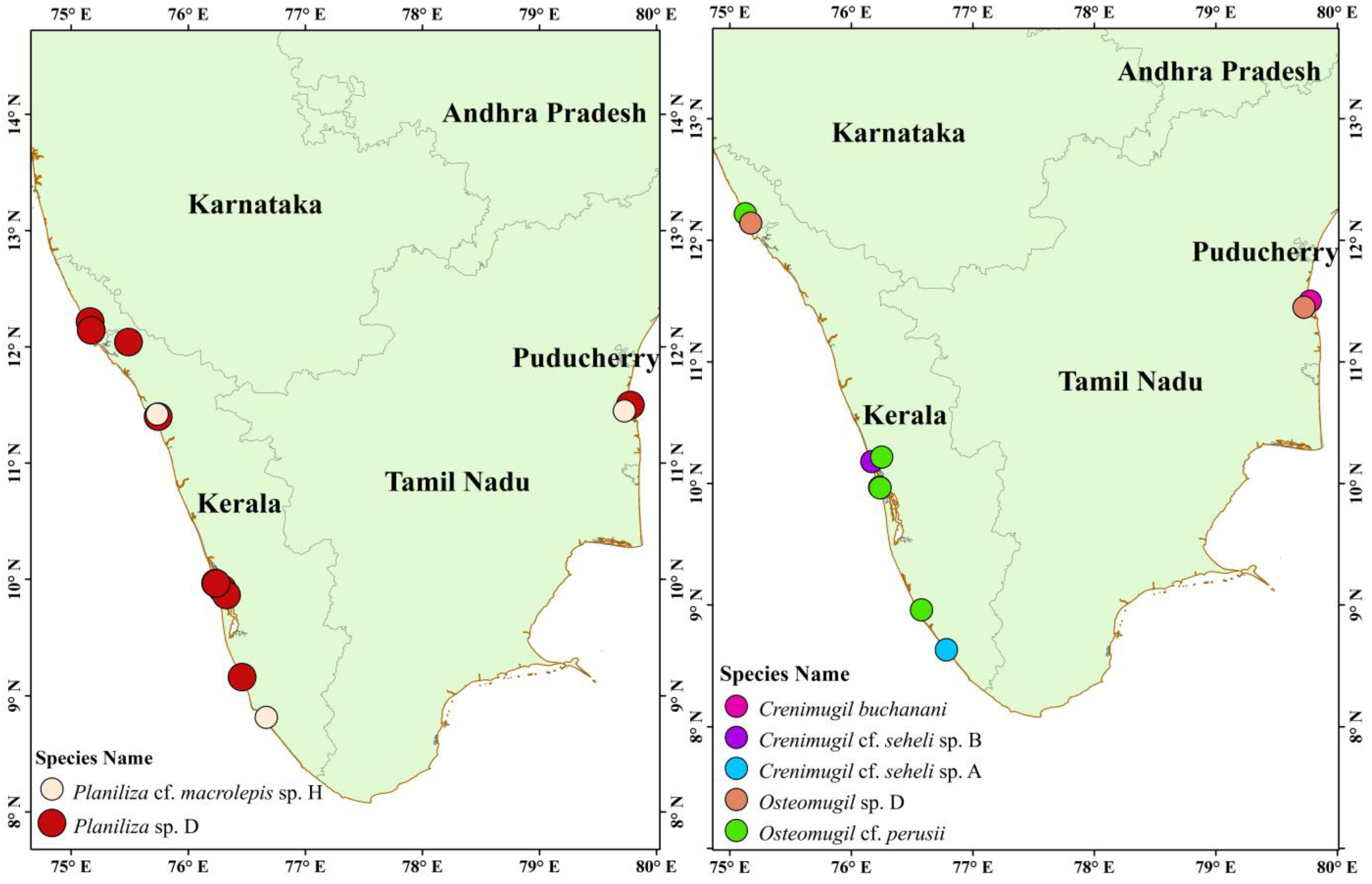




| Species Name | Fishing Locations | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | COI Sequence Length (bp) | GenBank Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crenimugil buchanani (Bleeker 1853) | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 645 | MW137482 |
| Crenimugil buchanani | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137480 |
| Crenimugil buchanani | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137481 |
| Crenimugil cf. seheli sp. A | Muthalapozhi, Kerala | 8.631 | 76.783 | 582 | MN728321 |
| Crenimugil cf. seheli sp. A | Muthalapozhi, Kerala | 8.631 | 76.783 | 582 | MN728322 |
| Crenimugil cf. seheli sp. B | Cochin, Kerala | 9.9667 | 76.2333 | 676 | MW137486 |
| Crenimugil cf. seheli sp. B | Munambam, Kerala | 10.178 | 76.169 | 582 | MN728320 |
| Ellochelon sp. B | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 645 | MW137487 |
| Ellochelon sp. B | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137488 |
| Ellochelon sp. B | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 643 | MW137489 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 627 | MW137496 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 645 | MW137497 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137498 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 645 | MW137499 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 646 | MW137500 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Cochin, Kerala | 9.9667 | 76.2333 | 676 | MW137495 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Cochin, Kerala | 9.9667 | 76.2333 | 644 | MW137494 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Poyya, Kerala | 10.221 | 76.234 | 582 | MN728324 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728325 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Poyya, Kerala | 10.221 | 76.234 | 582 | MN728326 |
| Mugil cf. cephalus | Kattampally, Kerala | 11.937 | 75.376 | 582 | MN728327 |
| Osteomugil cf. perusii | Ashtamudi, Kerala | 8.959 | 76.577 | 582 | MN728329 |
| Osteomugil cf. perusii | Poyya, Kerala | 10.221 | 76.234 | 582 | MN728330 |
| Osteomugil cf. perusii | Fort Kochi, Kerala | 9.963 | 76.237 | 582 | MN728331 |
| Osteomugil cf. perusii | Madakkara, Kerala, | 12.21672 | 75.130238 | 582 | MN728332 |
| Osteomugil sp. D | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 676 | MW137515 |
| Osteomugil sp. D | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 653 | MW137514 |
| Osteomugil sp. D | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 655 | MW137516 |
| Osteomugil sp. D | Thrikkaripur, Kerala | 12.138 | 75.16 | 582 | MN728328 |
| Planiliza cf. macrolepis sp. H | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 679 | MW137525 |
| Planiliza cf. macrolepis sp. H | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 658 | MW137524 |
| Planiliza cf. macrolepis sp. H | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 658 | MW137523 |
| Planiliza cf. macrolepis sp. H | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 658 | MW137522 |
| Planiliza cf. macrolepis sp. H | Paravoor, Kerala | 8.835 | 76.667 | 582 | MN728317 |
| Planiliza cf. macrolepis sp. H | Paravoor, Kerala | 8.835 | 76.667 | 582 | MN728318 |
| Planiliza cf. macrolepis sp. H | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.418 | 75.734 | 582 | MN728319 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 652 | MW137518 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Cochin, Kerala | 9.9667 | 76.2333 | 678 | MW137535 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Cochin, Kerala | 9.9667 | 76.2333 | 644 | MW137544 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Cochin, Kerala | 9.9667 | 76.2333 | 644 | MW137540 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Cheruvathur, Kerala | 12.203 | 75.129 | 582 | MN728302 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Valapattanam, Kerala | 12.04 | 75.49 | 582 | MN728303 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Kayamkulam, Kerala | 9.161 | 76.46 | 582 | MN728304 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728305 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Thrikkaripur, Kerala | 12.141 | 75.172 | 582 | MN728306 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728307 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728308 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Edakochi, Kerala | 9.916 | 76.291 | 582 | MN728309 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728310 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728311 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728312 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Kayamkulam, Kerala | 9.161 | 76.46 | 582 | MN728313 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Cochin, Kerala | 9.863 | 76.32 | 582 | MN728314 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Cochin, Kerala | 9.863 | 76.32 | 582 | MN728315 |
| Planiliza sp. D | Fort Kochi, Kerala | 9.963 | 76.237 | 582 | MN728316 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Vellar, Kerala | 11.498 | 79.776 | 652 | MW137547 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Cochin, Kerala | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137546 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Cochin, Kerala | 11.498 | 79.776 | 665 | MW137545 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Cochin, Kerala | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137548 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 643 | MW137551 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137550 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 644 | MW137566 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Vellar, Tamil Nadu | 11.498 | 79.776 | 652 | MW137549 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Cochin, Kerala | 9.863 | 76.32 | 646 | MW137552 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Kattampally, Kerala | 11.937 | 75.376 | 582 | MN728289 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Varapuzha, Kerala | 10.074 | 76.239 | 582 | MN728290 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Cheliya, Kerala | 12.04 | 75.49 | 582 | MN728291 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Thrikkaripur, Kerala | 12.138 | 75.16 | 582 | MN728292 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Kayamkulam, Kerala | 9.161 | 76.46 | 582 | MN728293 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728294 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Paravoor, Kerala | 8.835 | 76.667 | 582 | MN728295 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Thrikkaripur, Kerala | 12.138 | 75.16 | 582 | MN728296 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Fort Kochi, Kerala | 9.963 | 76.237 | 582 | MN728297 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Poyya, Kerala | 10.221 | 76.234 | 582 | MN728298 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Kattampally, Kerala | 11.937 | 75.376 | 582 | MN728299 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Korapuzha, Kerala | 11.396 | 75.745 | 582 | MN728300 |
| Planiliza subviridis | Kayamkulam, Kerala | 9.161 | 76.46 | 582 | MN728301 |
| Plicomugil labiosus | Agatti, Lakshadweep | 10.857 | 72.1959 | 582 | MN728323 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajan, R.; Durand, J.-D.; Thomas, L.; Sidharthan, A.; Rahman, M.A.U.; Xavier, B.; Raghavan, R. Barcoding Mullets (Mugilidae): Genetic Characterization of Exploited Species in Southern Peninsular India. Diversity 2023, 15, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121193
Rajan R, Durand J-D, Thomas L, Sidharthan A, Rahman MAU, Xavier B, Raghavan R. Barcoding Mullets (Mugilidae): Genetic Characterization of Exploited Species in Southern Peninsular India. Diversity. 2023; 15(12):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121193
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajan, Rahul, Jean-Dominique Durand, Liju Thomas, Arya Sidharthan, M. Ashiq Ur Rahman, Bibin Xavier, and Rajeev Raghavan. 2023. "Barcoding Mullets (Mugilidae): Genetic Characterization of Exploited Species in Southern Peninsular India" Diversity 15, no. 12: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121193
APA StyleRajan, R., Durand, J.-D., Thomas, L., Sidharthan, A., Rahman, M. A. U., Xavier, B., & Raghavan, R. (2023). Barcoding Mullets (Mugilidae): Genetic Characterization of Exploited Species in Southern Peninsular India. Diversity, 15(12), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121193








