Xyloplax princealberti (Asteroidea, Echinodermata): A New Species That Is Not Always Associated with Wood Falls †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Molecular Sampling, DNA Extraction, and PCR Amplification
2.3. Mitochondrial Genome Sequencing and Assembly
2.4. Phylogenetic and Haplotype Network Analyses
2.5. Morphology
3. Results
3.1. Species Delimitation
3.2. Assembled Mitochondrial Genome
3.3. Phylogenetic Placement of Xyloplax in Asteroidea
3.4. Ecological Observations
3.5. Taxonomy
3.6. Material Examined
3.7. Diagnosis
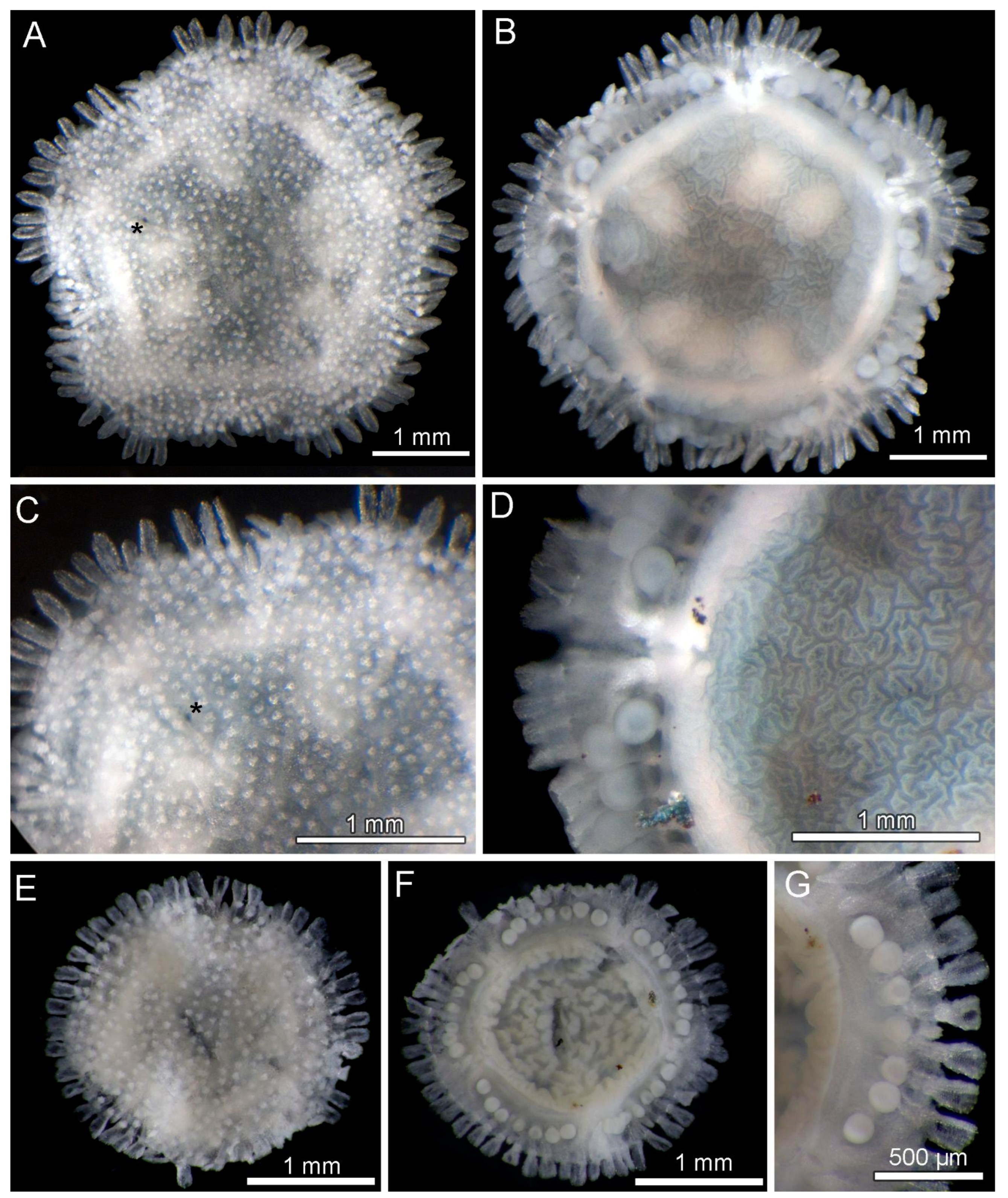
3.8. Description (Based on the Holotype Plus Paratypes, Where Relevant)
3.9. Etymology
3.10. Remarks
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, A.N.; Rowe, F.W.E.; Clark, H.E.S. A New Class of Echinodermata from New Zealand. Nature 1986, 321, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, F.W.E.; Baker, A.N.; Clark, H.E.S. The Morphology, Development and Taxonomic Status of Xyloplax Baker, Rowe and Clark (1986) (Echinodermata: Concentricycloidea), with the Description of a New Species. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1988, 233, 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, C.L. A New Species of Xyloplax (Echinodermata:Asteroidea:Concentricycloidea) from the Northeast Pacific: Comparative Morphology and a Reassessment of Phylogeny. Invertebr. Biol. 2006, 125, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voight, J.R. First Report of the Enigmatic Echinoderm Xyloplax from the North Pacific. Biol. Bull. 2005, 208, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B. To Group or Not to Group: The Taxonomic Position of Xyloplax. In Echinoderm Biology: Proceedings of the Sixth International Echinoderm Conference; Burke, R.D., Mladenov, P.V., Lambert, P., Parsley, R.L., Eds.; A. A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pearse, V.; Pearse, J. Echinoderm Phylogeny and the Place of Concentricycloids. In Echinoderms through Time (Echinoderms, Dijon); David, B., Guille, A., Feral, J.-P., Roux, M., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Janies, D.A.; Voight, J.R.; Daly, M. Echinoderm Phylogeny Including Xyloplax, a Progenetic Asteroid. Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 420–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linchangco, G.V., Jr.; Foltz, D.W.; Reid, R.; Williams, J.; Nodzak, C.; Kerr, A.M.; Miller, A.K.; Hunter, R.; Wilson, N.G.; Nielsen, W.J.; et al. The Phylogeny of Extant Starfish (Asteroidea: Echinodermata) Including Xyloplax, Based on Comparative Transcriptomics. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 115, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA Primers for Amplification of Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I from Diverse Metazoan Invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A Fast and Versatile Toolkit for Accurate de Novo Assembly of Organelle Genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Al-Arab, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Reinhardt, F.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M.; Bernt, M. Improved Annotation of Protein-Coding Genes Boundaries in Metazoan Mitochondrial Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10543–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-Length Transcriptome Assembly from RNA-Seq Data without a Reference Genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddison, W.P.; Maddison, D.R. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. Version 3.5. 2018. Available online: http://www.mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edler, D.; Klein, J.; Antonelli, A.; Silvestro, D. RaxmlGUI 2.0: A Graphical Interface and Toolkit for Phylogenetic Analyses Using RAxML. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A Fast, Scalable and User-Friendly Tool for Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4453–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Posada, D.; Kozlov, A.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Morel, B.; Flouri, T. ModelTest-NG: A New and Scalable Tool for the Selection of DNA and Protein Evolutionary Models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods); Version 4; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, M.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. TCS: A Computer Program to Estimate Gene Genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-Feature Software for Haplotype Network Construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, Z.B.R.; Chang, J.J.M.; Ip, Y.C.A.; Chan, Y.K.S.; Huang, D. Mitogenomes Reveal Alternative Initiation Codons and Lineage-Specific Gene Order Conservation in Echinoderms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Xiao, N.; Sha, Z. Mitogenomics Provides New Insights into the Phylogenetic Relationships and Evolutionary History of Deep-Sea Sea Stars (Asteroidea). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, H. An Approximately Unbiased Test of Phylogenetic Tree Selection. Syst. Biol. 2002, 51, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limaye, A. Drishti: A Volume Exploration and Presentation Tool. In Proceedings of the Developments in X-ray Tomography VIII, SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 17 October 2012; Volume 8506, pp. 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, A. The Phylogeny of Post-Palaeozoic Asteroidea (Echinodermata, Neoasteroidea). Spec. Pap. Palaeontol. 2011, 85, 1–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological Identifications through DNA Barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.D.; Holmes, B.H.; O’Hara, T.D. DNA Barcoding Discriminates Echinoderm Species. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, E.L.; Wilson, N.G.; Rouse, G.W. Resolving the Taxonomy of the Antarctic Feather Star Species Complex Promachocrinus ‘Kerguelensis’ (Echinodermata: Crinoidea). Invertebr. Syst. 2023, 37, 498–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, R.; Macfarlane, J.L.; Wolstenholme, D.R. Evidence for the Frequent Use of TTG as the Translation Initiation Codon of Mitochondrial Protein Genes in the Nematodes, Ascaris Suum and Caenorhabditis Elegans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6113–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelièvre, Y.; Sarrazin, J.; Marticorena, J.; Schaal, G.; Day, T.; Legendre, P.; Hourdez, S.; Matabos, M. Biodiversity and Trophic Ecology of Hydrothermal Vent Fauna Associated with Tubeworm Assemblages on the Juan de Fuca Ridge. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, D. A New Class of Echinoderms. Nature 1986, 321, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| X. princealberti n. sp. | X. janetae | X. medusiformis | X. turnerae | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abactinal spine base | Round | Rounded to polygonal | Stellate/jagged edges | Stellate/jagged edges |
| Abactinal spine size range | Uniform, short | Uniform, long | Uniform, long | Bimodal |
| Adambulacral spines per plate | 2–3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Total adambulacral spines | >100 | 70 | 50 | 80–100 |
| Tube feet per segment | 10 | 7 | 9 | 11–13 |
| Tube foot shape | Round-bulbous | Round-bulbous | Papillate | Round-bulbous |
| Terminal plate shape | Badge-shape | Rounded | Square | Badge-shape |
| Gut expression | Gut absent | Gut absent | Gut absent | Residual gut present |
| Sexual mode | Hermaphrodite | Gonochoric | Gonochoric | Gonochoric |
| Developmental mode | “Viviparous” | “Viviparous” | “Viviparous” | Oviparous? |
| Occurrence | Eastern Pacific (Canada–Costa Rica) | Northeastern Pacific (Oregon) | South Pacific (New Zealand) | Atlantic (Bahamas) |
| Depth (m) | 1845–2421 | 2675 | 1057–1208 | 2066 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Payne, C.Y.; Tilic, E.; Boschen-Rose, R.E.; Gannon, A.; Stiller, J.; Hiley, A.S.; Grupe, B.M.; Mah, C.L.; Rouse, G.W. Xyloplax princealberti (Asteroidea, Echinodermata): A New Species That Is Not Always Associated with Wood Falls. Diversity 2023, 15, 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121212
Payne CY, Tilic E, Boschen-Rose RE, Gannon A, Stiller J, Hiley AS, Grupe BM, Mah CL, Rouse GW. Xyloplax princealberti (Asteroidea, Echinodermata): A New Species That Is Not Always Associated with Wood Falls. Diversity. 2023; 15(12):1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121212
Chicago/Turabian StylePayne, Cheyenne Y., Ekin Tilic, Rachel E. Boschen-Rose, Amanda Gannon, Josefin Stiller, Avery S. Hiley, Benjamin M. Grupe, Christopher L. Mah, and Greg W. Rouse. 2023. "Xyloplax princealberti (Asteroidea, Echinodermata): A New Species That Is Not Always Associated with Wood Falls" Diversity 15, no. 12: 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121212
APA StylePayne, C. Y., Tilic, E., Boschen-Rose, R. E., Gannon, A., Stiller, J., Hiley, A. S., Grupe, B. M., Mah, C. L., & Rouse, G. W. (2023). Xyloplax princealberti (Asteroidea, Echinodermata): A New Species That Is Not Always Associated with Wood Falls. Diversity, 15(12), 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15121212








