Diversity and Regional Variation of Endosymbionts in the Green Peach Aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Aphids
2.2. Clonal Assignment of M. persicae
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Metabarcoding and Quantitative PCR
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kikuchi, Y. Endosymbiotic bacteria in insects: Their diversity and culturability. Microbes Environ. 2009, 24, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P. Biology bacteriocyte-associated endosymbionts of plant sap-sucking insects. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 59, 155–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Nutritional interactions in insect-microbial symbioses: Aphids and their symbiotic bacteria Buchnera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, K.M.; Russell, J.A.; Moran, N.A.; Hunter, M.S. Facultative bacterial symbionts in aphids confer resistance to parasitic wasps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Q.; Montllor, C.B.; Purcell, A.H. Fitness effects of two facultative endosymbiotic bacteria on the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, and the blue alfalfa aphid, A. kondoi. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2003, 95, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Koga, R.; Fukatsu, T. Host plant specialization governed by facultative symbiont. Science 2004, 303, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, L.M.; Peccoud, J.; Simon, J.C.; Hadfield, J.D.; Maiden, M.J.; Ferrari, J.; Godfray, H.C.J. Horizontally transmitted symbionts and host colonization of ecological niches. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaech, H.; Vorburger, C. Horizontal transmission of the heritable protective endosymbiont Hamiltonella defensa depends on titre and haplotype. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 628755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Emden, H.F.; Harrington, R. Aphids as Crop Pests; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An Identification and Information Guide, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dedryver, C.A.; Le Ralec, A.; Fabre, F. The conflicting relationships between aphids and men: A review of aphid damage and control strategies. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2010, 333, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Puinean, A.M.; Zimmer, C.T.; Denholm, I.; Field, L.M.; Foster, S.P.; Gutbrod, O.; Nauen, R.; Slater, R.; Williamson, M.S. The evolution of insecticide resistance in the peach potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, O.R.; Franzmann, B.; Thackray, D.; Micic, S. Insecticide resistance and implications for future aphid management in Australian grains and pastures: A review. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2008, 48, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ma, K.S.; Liang, P.Z.; Yang, L.W.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.W. Combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of Myzus persicae, the green peach aphid, infected with cucumber mosaic virus. Insects 2021, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S.; Cordeiro, E.M.; Troczka, B.J.; Pym, A.; Mackisack, J.; Mathers, T.C.; Duarte, A.; Legeai, F.; Robin, S.; Bielza, P.; et al. Global patterns in genomic diversity underpinning the evolution of insecticide resistance in the aphid crop pest Myzus persicae. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saguez, J.; Giordanengo, P.; Vincent, C. Insect pests of potato: Global perspectives on biology and management. In Aphids as Major Potato Pests; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 31–63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cao, J.; Niu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Identification of the population structure of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on peach trees in China using microsatellites. J. Insect. Sci. 2015, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.C.C.; Sunnucks, P.; Blackman, R.L.; Hales, D.F. Microsatellite variation in cyclically parthenogenetic populations of Myzus persicae in south-eastern Australia. Heredity 2002, 88, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, C.L.; Ferrari, J.; Godfray, H.C.J. Aphid protected from pathogen by endosymbiont. Science 2005, 310, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.A.; Yun, Y. Experimental replacement of an obligate insect symbiont. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Koga, R.; Fujiwara, A.; Fukatsu, T. Phenotypic effect of “Candidatus Rickettsiella viridis”, a facultative symbiont of the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum), and its interaction with a coexisting symbiont. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo-Franco, J.J.; Duque-Gamboa, D.; Toro-Perea, N. Bacterial communities of Aphis gossypii and Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) from pepper crops (Capsicum sp.). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, L.M.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Ferrari, J.; Godfray, H.C.J. Insect life history and the evolution of bacterial mutualism. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Jiang, L.; Qiao, G.; Chen, J. Diversity of bacterial symbionts associated with Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Aphidinae) revealed by 16S rRNA Illumina sequencing. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 81, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, M.A.; Sunnucks, P.; Wilson, A.C.C.; Hales, D.F. Microsatellite isolation, linkage group identification and determination of recombination frequency in the peach-potato aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Genet. Res. 2001, 77, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umina, P.A.; Edwards, O.; Carson, P.; Van Rooyen, A.; Anderson, A. High levels of resistance to carbamate and pyrethroid chemicals widespread in Australian Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) populations. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2014, 107, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Author Correction: Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Koga, R.; Shibao, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Fukatsu, T. Diversity and geographic distribution of secondary endosymbiotic bacteria in natural populations of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2123–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, A.; Talebi, A.A.; Fathipour, Y.; Mehrabadi, M. Coinfection of the secondary symbionts, Hamiltonella defensa and Arsenophonus sp. contribute to the performance of the major aphid pest, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Insect Sci. 2018, 27, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Koga, R.; Meng, X.; Matsumoto, T.; Fukatsu, T. Characterization of a Facultative Endosymbiotic Bacterium of the Pea Aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.U.; Williams, S.; Susapu, M.; Weil, G.J.; Ramzy, R.; Helmy, H.; Bockarie, M.J.; Farid, H.A.; Atkinson, L.J.; Laney, S.J. A real-time PCR-based assay for detection of Wuchereria bancrofti DNA in blood and mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zytynska, S.E.; Weisser, W. The natural occurrence of secondary bacterial symbionts in aphids. Ecol. Èntomol. 2015, 41, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, H.; Guo, H. Win by quantity: A striking Rickettsia-Bias symbiont community revealed by seasonal tracking in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 81, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorburger, C.; Gehrer, L.; Rodriguez, P. A strain of the bacterial symbiont Regiella insecticola protects aphids against parasitoids. Biol. Lett. 2009, 6, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Burg, S.; Ferrari, J.; Müller, C.B.; Vorburger, C. Genetic variation and covariation of susceptibility to parasitoids in the aphid Myzus persicae: No evidence for trade-offs. Proc. Biol Sci. 2008, 275, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Chung, J.; Robinson, K.L.; Schmidt, T.L.; Ross, P.A.; Liang, J.; Hoffmann, A.A. Sex-specific distribution and classification of Wolbachia infections and mitochondrial DNA haplogroups in Aedes albopictus from the Indo-Pacific. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.-X.; Song, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Hoffmann, A.; Zhou, J.-C.; Sun, J.-T.; Hong, X.-Y. Incidence of facultative bacterial endosymbionts in spider mites associated with local environments and host plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02546-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasala, S.K.; Brown, A.M.V.; Kang, J.; Howe, D.K.; Peetz, A.B.; Zasada, I.A.; Denver, D.R. Variable abundance and distribution of Wolbachia and Cardinium endosymbionts in plant-parasitic nematode field populations. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Yu, Y.-C.; Valles, S.M.; Oi, D.H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Shoemaker, D.; Wu, W.-J.; Shih, C.-J. Loss of microbial (pathogen) infections associated with recent invasions of the red imported fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 3307–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Spooner-Hart, R.N.; Riegler, M. Loss of Wolbachia but not Cardinium in the invasive range of the Australian thrips species, Pezothrips kellyanus. Biol. Invasions 2015, 18, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.-T.; Li, Y.; Li, T.-P.; Liang, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, C.-Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zha, S.-S.; et al. Stable introduction of plant-virus-inhibiting Wolbachia into planthoppers for rice protection. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 4837–4845.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, C.H.V.; Nichols, W.L.; Chevignon, G.; Patel, V.; Allison, S.E.; Kim, K.L.; Strand, M.R.; Oliver, K.M. An aphid symbiont confers protection against a specialized RNA virus, another increases vulnerability to the same pathogen. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-K.; Cao, L.-J.; Song, W.; Shi, P.; Gao, Y.-F.; Gong, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-C.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Wei, S.-J. Chromosome-level assembly of the melon thrips genome yields insights into evolution of a sap-sucking lifestyle and pesticide resistance. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1110–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, K.M.; Moran, A.N.; Hunter, M. Costs and benefits of a superinfection of facultative symbionts in aphids. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2006, 273, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirgwin, E.; Yang, Q.; Umina, A.P.; Gill, A.; Soleimannejad, S.; Gu, X.; Ross, P.; Hoffmann, A.A. Fungicides have transgenerational effects on Rhopalosiphum padi but not their endosymbionts. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T. Molecular basis and ecological relevance of aphid body colors. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 17, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

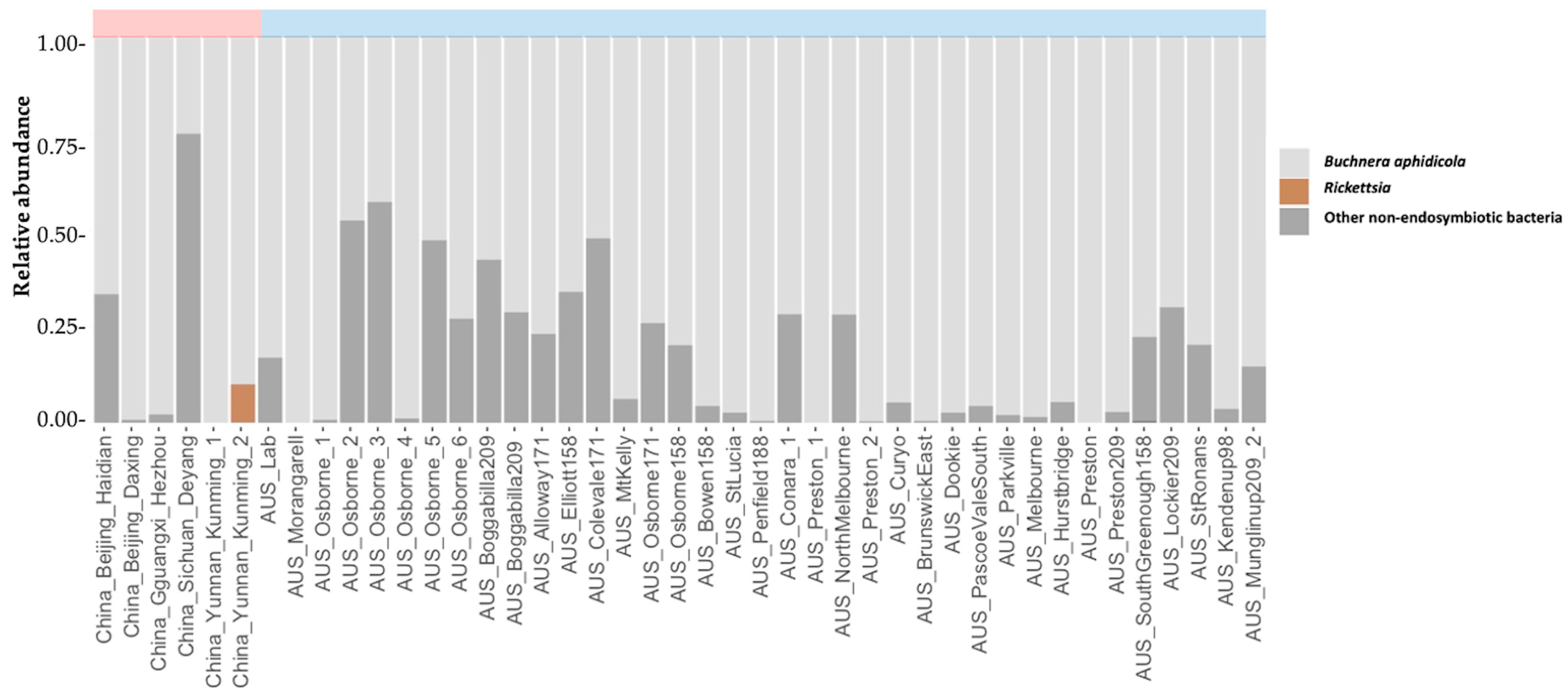
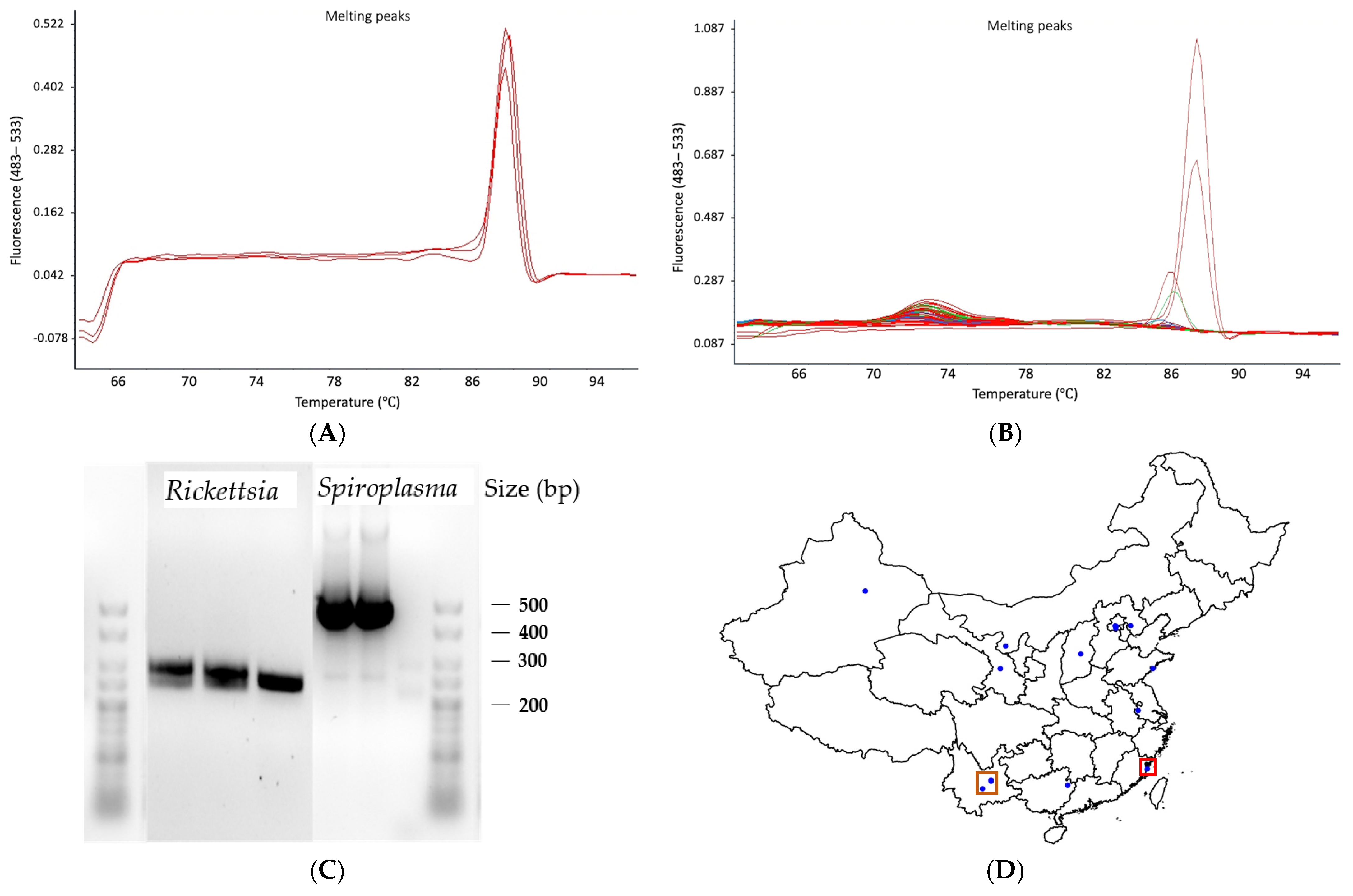
| M. persicae Sample | Latitude | Longitude | Host Plant | Date Collected | Aphids Tested | Method | Type of Sample | Microsatellite Defined Clones |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUS_Alloway171 | −24.955 | 152.394 | Celosia sp. | 5 April 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 171 |
| AUS_Boggabilla209 | −28.718 | 150.033 | Brassica napus | 16 September 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209 |
| AUS_Bowen158 | −20.010 | 148.188 | Solanum melongena | 16 August 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158 |
| AUS_BrunswickEast_1 | −37.776 | 144.975 | Capsicum sp. | 13 May 2022 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_BrunswickEast_2 | −37.776 | 144.975 | Solanum lycopersicum | 29 September 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_Colevale171 | −19.505 | 147.328 | Capsicum chinense | 27 August 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 171 |
| AUS_Conara | −41.833 | 147.464 | Brassica napus | 23 October 2019 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 4, 36, 78, 157, 209 |
| AUS_Curyo | −35.848 | 142.780 | Brassica napus | 21 September 2019 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_Dookie | −36.344 | 145.654 | Brassica napus | 23 September 2013 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209, 211 |
| AUS_Elliott158 | −24.983 | 152.304 | Capsicum annum | 4 October 2017 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158 |
| AUS_Hurstbridge | −37.642 | 145.198 | Solanum betaceum | 16 May 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_Kendenup98 | −34.480 | 117.404 | Brassica napus | 17 September 2019 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 98 |
| AUS_Lab | −36.723 | 142.175 | Trifolium sp. | 7 October 2019 | 10 | 16S | Laboratory colony | |
| AUS_Lockier209 | −29.155 | 115.360 | Brassica napus | 22 September 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209 |
| AUS_Melbourne | −37.817 | 144.965 | Helianthus annuus | 26 March 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_Morangarell209 | −34.220 | 147.714 | Brassica napus | 9 September 2019 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209 |
| AUS_MtKelly171 | −19.696 | 147.319 | Cucurbita sp. | 10 August 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 171 |
| AUS_Munglinup209_2 | −33.681 | 120.820 | Brassica napus | 29 August 2018 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209 |
| AUS_NorthMelbourne 1 | −37.795 | 144.949 | Plantago sp. | 15 April 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_Osborne_1 2 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158, 171 |
| AUS_Osborne_2 2 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Laboratory colony | 158 |
| AUS_Osborne_3 2 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Laboratory colony | 171 |
| AUS_Osborne_4 3 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158, 171 |
| AUS_Osborne_5 3 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Laboratory colony | 158 |
| AUS_Osborne_6 3 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Laboratory colony | 171 |
| AUS_Osborne171 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 171 |
| AUS_Osborne158 | −19.706 | 147.361 | Capsicum frutescens | 26 August 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158 |
| AUS_SouthGreenough158 | −29.028 | 114.832 | Capsicum sp. | 30 October 2019 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158 |
| AUS_StLucia209 | −27.496 | 153.009 | Brassica oleracea | 16 November 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209 |
| AUS_StRonans209 | −31.909 | 116.703 | Brassica napus | 28 September 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209 |
| AUS_Parkville | −37.780 | 144.940 | Brassica oleracea | 12 March 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_PascoeValeSouth | −37.738 | 144.935 | Capsicum sp. | 11 March 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_Penfield188 | −34.687 | 138.633 | Solanum melongena | 10 October 2014 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 188 |
| AUS_Preston | −37.742 | 145.000 | Prunus persica | 10 October 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| AUS_Preston158_1 4 | −37.733 | 145.009 | Brassica oleracea | 22 April 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158 |
| AUS_Preston158_2 5 | −37.733 | 145.009 | Brassica oleracea | 22 April 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 158 |
| AUS_Preston209 | −37.742 | 145.000 | Solanum betaceum | 23 November 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | 209 |
| China_Beijing_Haidian | 39.944 | 116.288 | Capsicum sp. | 22 October 2021 | 25 | 16S | Field sample | |
| China_Beijing_Daxing | 39.733 | 116.349 | Capsicum sp. | 21 March 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| China_Beijing_1 | 39.903 | 116.401 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 2016 | 10 | qPCR | Field sample | 253, 254, 256, 257, 258, 259 |
| China_Beijing_2 | 39.903 | 116.401 | Amygdalus persica | 2016 | 5 | qPCR | Field sample | 103, 244, 307, 315 |
| China_Beijing_3 | 39.903 | 116.401 | Amygdalus persica | 2016 | 5 | qPCR | Field sample | 237, 244, 304, 313 |
| China_Fujian_Ningde | 26.160 | 119.767 | Brassica napus | 2005 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| China_Gansu_Lanzhou_1 | 36.062 | 103.832 | Nicotiana tabacum | 2016 | 6 | qPCR | Field sample | 110, 260 |
| China_Gansu_Lanzhou_2 | 36.061 | 103.832 | Nicotiana tabacum | 2016 | 6 | qPCR | Field sample | 223, 249, 291, 309 |
| China_Guangxi_Hezhou | 24.468 | 111.130 | Solanum melongena | 21 June 2018 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| China_Hebei_Tangshan | 39.958 | 117.967 | Prunus persica | 2016 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| China_Jiangsu_Nanjing | 32.060 | 118.791 | Raphanus sativus | 2016 | 12 | qPCR | Field sample | 241, 245, 247, 256, 302, 303, 310, 316 |
| China_Shanxi_Jinzhong | 37.421 | 112.545 | Brassica oleracea | 2016 | 12 | qPCR | Field sample | 231, 255, 256 |
| China_Shandong_Qindao | 36.066 | 120.378 | Amygdalus persica | 2016 | 4 | qPCR | Field sample | 105, 140, 266, 314 |
| China_Sichuan_Deyang | 38.142 | 104.417 | Brassica napus | 12 March 2021 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| China_Xinjiang_Tulufan_1 | 42.941 | 89.183 | Prunus persica | 2016 | 4 | qPCR | Field sample | 6, 59, 121, 292 |
| China_Xinjiang_Tulufan_2 | 42.941 | 89.183 | Prunus persica | 2016 | 8 | qPCR | Field sample | 10, 86, 120, 141, 143, 228, 308, 317 |
| China_Yunnan_Kunming_1 | 25.009 | 102.825 | Brassica oleracea | 19 July 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| China_Yunnan_Yuxi | 24.094 | 101.910 | Nicotiana tabacum | 20 July 2020 | 10 | 16S | Field sample | |
| China_Yunnan_Kunming_2 | 24.883 | 102.832 | Nicotiana tabacum | 2016 | 5 | qPCR | Field sample | 117, 290 |
| China_YunnanKunming_3 | 24.883 | 102.832 | Nicotiana tabacum | 2016 | 5 | qPCR | Field sample | 117, 261, 290 |
| China_Y_Kunming_4 | 24.883 | 102.832 | Nicotiana tabacum | 2016 | 2 | qPCR | Field sample | 117 |
| Chile_Duao | 35.558 | 71.588 | Prunus persica | 2018 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| France | Unknown | Unknown | Prunus persica | 2009 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| Greece_ Tyrnavos | 39.759 | 22.286 | Prunus persica | 2018 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| Greece_ Neo Keramidi | 40.286 | 22.463 | Nicotiana tabacum | 2018 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| Italy_Salvo | 42.048 | 14.734 | Prunus persica | 2012 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| Italy_Benevento | 41.130 | 14.783 | Nicotiana tabacum | 1999 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| Japan | Unknown | Unknown | Solanum melongena | 1983 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| South Korea_ North Gyeongsang | 35.848 | 129.202 | Brassica oleracea | Unknown | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| Spain | 37.755 | 1.103 | Capsicum sp. | Unknown | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| UK_ Worcestershire | 52.255 | 2.267 | Chrysanthemum | 1982 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| UK_1 | Unknown | Unknown | Brassica oleracea | 2004 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| UK_2 | Unknown | Unknown | Beta vulgaris | 1974 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| UK_3 | Unknown | Unknown | Solanum tuberosum | 2007 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| USA_ North Carolina | 35.883 | 77.665 | Nicotiana tabacum | 2015 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory | |
| Zimbabwe | Unknown | Unknown | Nicotiana tabacum | 2010 | 5 | qPCR | Clone_laboratory |
| Target Endosymbiont | Primer Name | Primer Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arsenophonus | Arsen_yaeT_F | AATATGCCTGTTCGGGTAGG | [30] |
| Arsen_yaeT_R | GTTGGCCGCTCTTTTACTTG | ||
| Hamiltonella defensa | Ham_16Sl_F1 | AGGAGGAAGCGATAAATGC | This study |
| Ham_16Sl_R1 | CCCTCTAGAAAACTCTAGCGAC | ||
| Regiella insecticola | U99F | ATCGGGGAGTAGCTTGCTAC | [31] |
| 16SB4 | CTAGAGATCGTCGCCTAGGTA | ||
| Rickettsia | Rickettsia_16S_F1 | GTGCGTAGGCGGTTTAGTA | This study |
| Rickettsia_16S_R1 | TTGTAGCCCAGATGACCG | ||
| Rickettsiella viridis | RCL16S-211F | GGGCCTTGCGCTCTAGGT | [31] |
| RCL16S-470R | TGGGTACCGTCACAGTAATCGA | ||
| Serratia symbiotica | Serr_16S_F1 | TTGTTGCCAGCGATAAAG | This study |
| Serr_16S_R1 | CCATTGTAGCACGTGTGT | ||
| Wolbachia | Wol_16S_F | CCAGCAGCCGCGGTAAT | [32] |
| Wol_16S_R | CGCCCTTTACGCCCAAT | ||
| Wol_probe | CGGAGAGGGCTAGCGTTATTCGGAATT | ||
| Reference gene | actin_aphid_F1 | GTGATGGTGTATCTCACACTGTC | This study |
| actin_aphid_R1 | AGCAGTGGTGGTGAAACTG |
| Endosymbiont | No. Aphids Infected/Sample Size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Study | Xu et al. (2019) [24] | |||
| China | Australia | Other Countries | China | |
| Buchnera aphidicola | 21/21 | 37/37 | 15/15 | 92/92 |
| Serratia symbiotica | 0/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | 15/92 |
| Rickettsiella viridis | 0/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | NA |
| Hamiltonella defensa | 0/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | 4/92 |
| Rickettsia | 4/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | 15/92 |
| Regiella insecticola | 0/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | 12/92 |
| Wolbachia | 0/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | 53/92 |
| Arsenophonus | 0/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | 15/92 |
| Spiroplasma | 1/21 | 0/37 | 0/15 | 3/92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Umina, P.A.; Wei, S.; Bass, C.; Yu, W.; Robinson, K.L.; Gill, A.; Zhan, D.; Ward, S.E.; van Rooyen, A.; et al. Diversity and Regional Variation of Endosymbionts in the Green Peach Aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Diversity 2023, 15, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020206
Yang Q, Umina PA, Wei S, Bass C, Yu W, Robinson KL, Gill A, Zhan D, Ward SE, van Rooyen A, et al. Diversity and Regional Variation of Endosymbionts in the Green Peach Aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Diversity. 2023; 15(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qiong, Paul A. Umina, Shujun Wei, Chris Bass, Wenjuan Yu, Katie L. Robinson, Alex Gill, Dongwu Zhan, Samantha E. Ward, Anthony van Rooyen, and et al. 2023. "Diversity and Regional Variation of Endosymbionts in the Green Peach Aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer)" Diversity 15, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020206
APA StyleYang, Q., Umina, P. A., Wei, S., Bass, C., Yu, W., Robinson, K. L., Gill, A., Zhan, D., Ward, S. E., van Rooyen, A., & Hoffmann, A. A. (2023). Diversity and Regional Variation of Endosymbionts in the Green Peach Aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Diversity, 15(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020206










