Occurrence of Gastrointestinal Parasites in Synanthropic Neozoan Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca, Linnaeus 1766) in Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca) in Europe
1.2. Antropozoonotic Investiagations
2. Materials and Methods
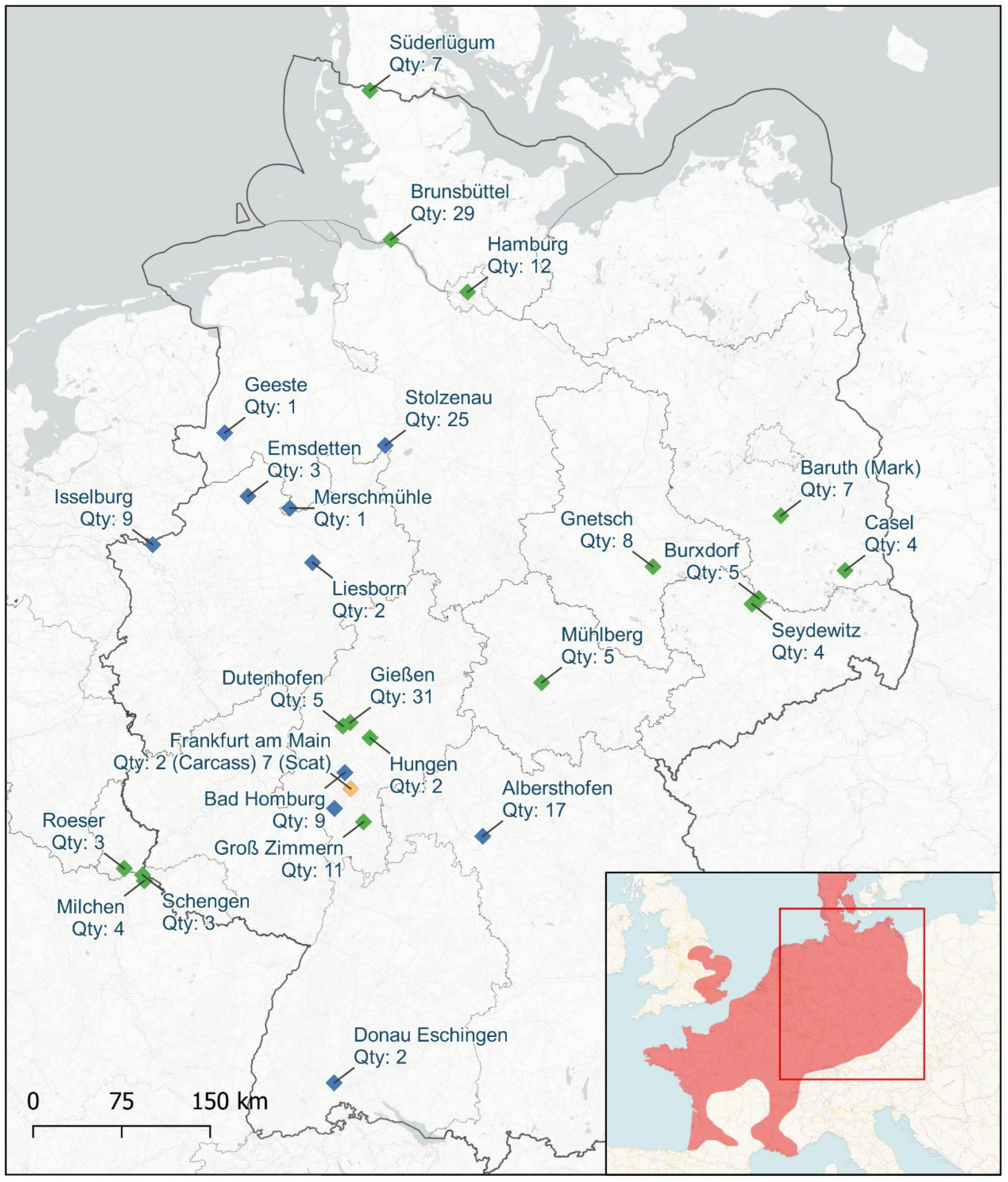
2.1. Sample Collection and Habitat Research
2.2. Macroscopic Analyses
Pathological Analyses
2.3. Microscopic Analyses
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.4. Molecular Analyses
2.4.1. Quantitative PCR on Cryptosporidium spp.
2.4.2. Coproantigen Analyses
2.4.3. PCR and Sequencing of Echinostoma spp.
2.4.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Observation of the Egyptian Geese in Germany
3.2. Body Weights
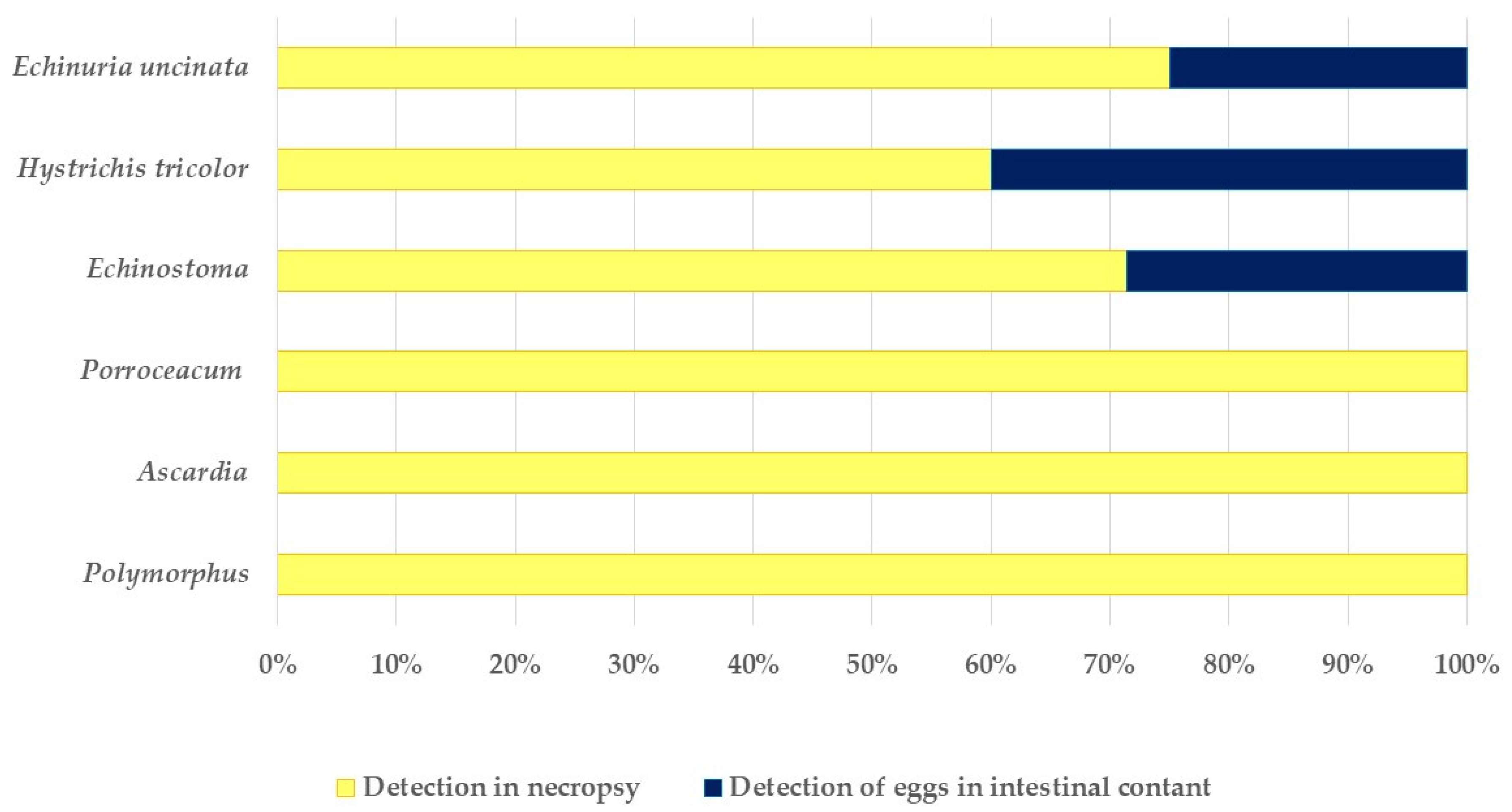
3.3. Macroscopic Findings
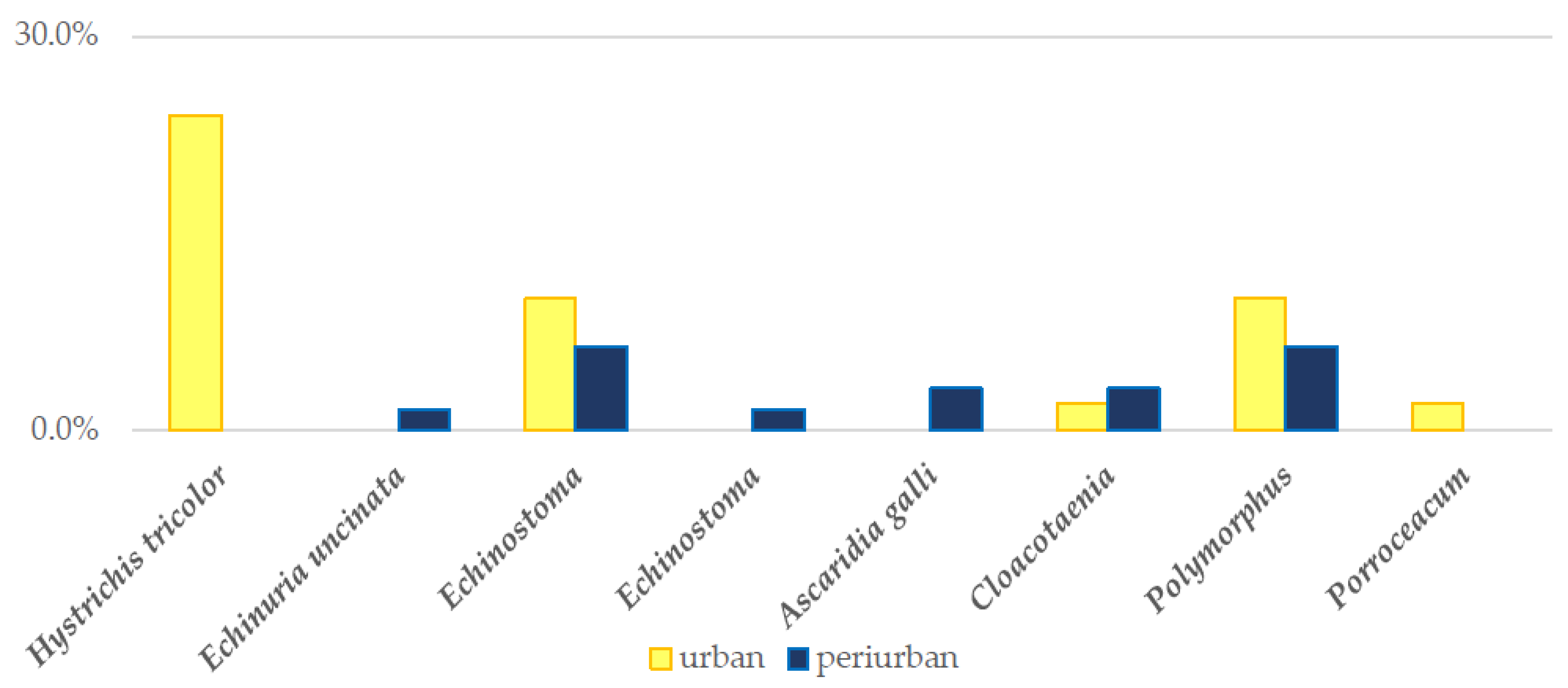
3.4. Microscopic Findings
3.4.1. Coprological Findings in Ingesta
3.4.2. Coprological Findings in Scat Samples
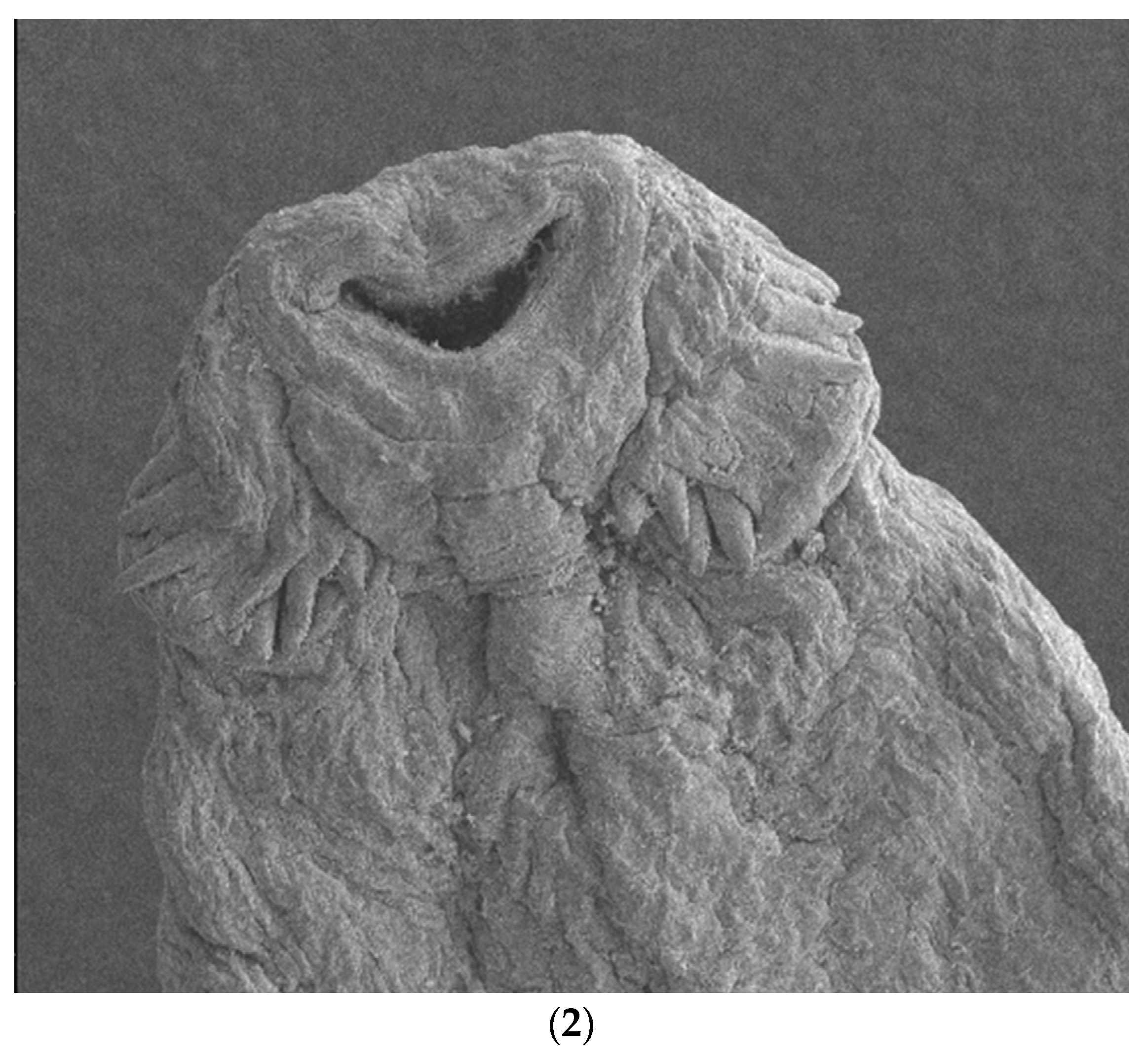
3.4.3. SEM Findings
3.5. Molecular Findings
3.5.1. Cryptosporidium spp.
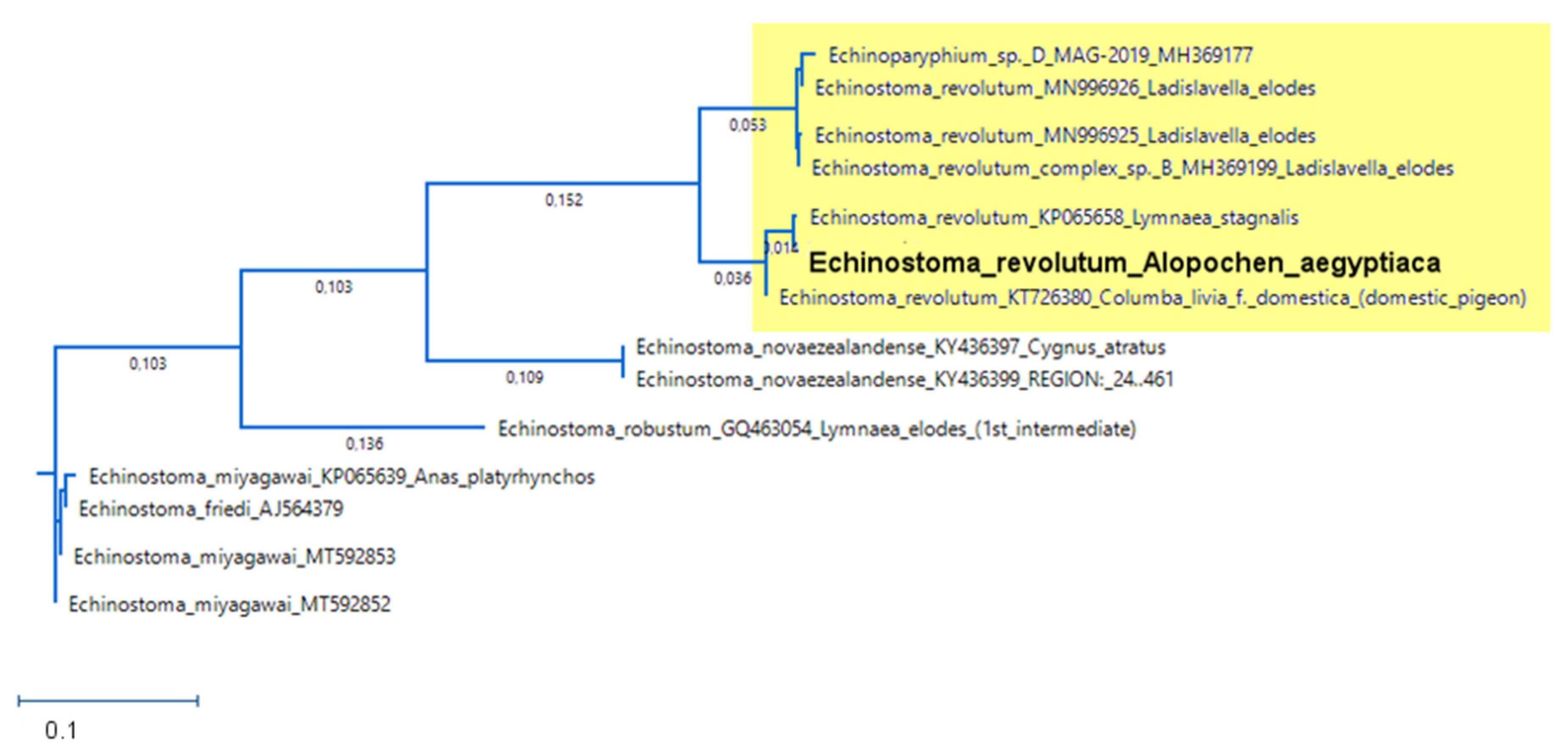
3.5.2. Sequencing of E. revolutum
4. Discussion
Anthropozoonotic Parasites in Egyptian Geese
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nentwig, W. Invasive Arten; Haupt: Bern, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-3825233839. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, T.M.; Lockwood, J.L.; Cassey, P. Avian Invasions: The ecology and Evolution of Exotic Birds; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; ISBN 9780191552588. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.L. Introduced Birds of the World: The Worldwide History Distribution and Influence of Birds Introduced to New Environments; Long, J.L., Ed.; David & Charles: London, UK, 1981; ISBN 0715381806. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, A.N.; Wright, L.J.; Maclean, I.M.D.; Hann, C.; Rehfisch, M.M. Review of the Status of Introduced Non-Native Waterbird Species in the Area of the African-Eurasian Waterbird Agreement: 2007 Update; British Trust for Ornithology: Thretford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huysentruyt, F.; van Moer, K.; Adriaens, T. Testing the efficacy of different Larson trap designs for trapping Egyptian geese (Alopochen aegyptiacus L.) in Flanders (northern Belgium). MBI 2022, 13, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, L. Der Kosmos Vogelführer: Alle Arten Europas, Nordafrikas und Vorderasiens; Neue Einbandgestaltung 2017, 2. Auflage; Kosmos: Stuttgart, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-440-15635-3. [Google Scholar]
- Madge, S.; Burn, H. Wildfowl: An Identification Guide to the Ducks, Geese and Swans of the World; Christopher Helm: London, UK, 1988; ISBN 9780747022015. [Google Scholar]
- Dachverband Deutscher Avifaunisten Database. Deutschlandweite Nilgansbeobachtungen. Available online: https://www.ornitho.de/index.php?m_id=81&sp_tg=1&speciesFilter=&frmSpecies=81&frmDisplay=Auflisten (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Bauer, H.G.; Bezzel, E.; Fiedler, W. Das Kompendium der Vögel Mitteleuropas, 2nd ed.; Aula: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-3-89104-758-3. [Google Scholar]
- Huysentruyt, F.; Callaghan, C.T.; Strubbe, D.; Winston, K.; Adriaens, T.; Brooks, D.M. Egyptian Goose (Alopochen aegyptiaca Linnaeus, 1766). In Invasive Birds: Global Trends and Impacts; Downs, C.T., Hart, L.A., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781789242065. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, A.M.; Kark, S. Competition an Invasive Specie: Impacts on Native Communities. In Invasive Birds: Global Trends and Impacts; Downs, C.T., Hart, L.A., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781789242065. [Google Scholar]
- Creed, R.P.; Brown, B.L.; Skelton, J. The potential impacts of invasions on native symbionts. Ecology 2022, 103, e3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchin, M.E.; Lafferty, K.D.; Dobson, A.P.; McKenzie, V.J.; Kuris, A.M. Introduced species and their missing parasites. Nature 2003, 421, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchin, M.E.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M. Release from Parasites as Natural Enemies: Increased Performance of a Globally Introduced Marine Crab. Biol. Invasions 2001, 3, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.W.; Paterson, R.A.; Townsend, C.R.; Poulin, R.; Tompkins, D.M. Parasite spillback: A neglected concept in invasion ecology? Ecology 2009, 90, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.S.; Mohamed, F.A.M.M.; Nachev, M.; Méabed, E.M.H.; Sabry, A.H.A.; Sures, B. Invasion biology meets parasitology: A case study of parasite spill-back with Egyptian Fasciola gigantica in the invasive snail Pseudosuccinea columella. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, W.J.; Allport, G. The distribution and ecology of naturalized Egyptian Geese Alopochen aegyptiacus in Britain. Bird Study 1991, 38, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, C.T.; Major, R.E.; Wilshire, J.H.; Martin, J.M.; Kingsford, R.T.; Cornwell, W.K. Generalists are the most urban-tolerant of birds: A phylogenetically controlled analysis of ecological and life history traits using a novel continuous measure of bird responses to urbanization. Oikos 2019, 128, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.L.; Allen, C.R. Continental Analysis of Invasive Bids: North America. In Invasive Birds: Global Trends and Impacts; Downs, C.T., Hart, L.A., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781789242065. [Google Scholar]
- Callaghan, C.T.; Brooks, D.M. Ecology, Behavior, and Reproduction of Invasive Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca) in Texas. Bull. Tex. Ornithol. Soc. 2016, 49, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mooij, J.H. Die Nilgans- ein etablierter Neubürger in Westeuropa. Der Falke 1998, 45, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Sedinger, J.S. Adaptations to and Consequences of an Herbivorous Diet in Grouse and Waterfowl. Condor 1997, 99, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anseriformes; Ritchie, B.W.; Harrison, G.J.; Harrison, L.R. (Eds.) Avian Medicine: Principles and Application; Wingers Pub: Lake Worth, FL, USA, 1994; ISBN 0963699601. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, S.M.; Barron, H.W.; Miller, E.A.; Aguilar, R.F.; Yabsley, M.J. (Eds.) Medical Management of Wildlife Species: A Guide for Practitioners; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781119036586. [Google Scholar]
- Kowarik, I.; Boye, P. Biologische Invasionen: Neophyten und Neozoen in Mitteleuropa; 76 Tabellen; Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germeny, 2003; ISBN 978-3800139248. [Google Scholar]
- Prüter, H.; Czirják, G.Á.; Twietmeyer, S.; Harder, T.; Grund, C.; Mühldorfer, K.; Lüschow, D. Sane and sound: A serologic and molecular survey for selected infectious agents in neozootic Egyptian geese (Alopochen aegyptiacus) in Germany. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2018, 64, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.S.; Shepard, E.; Okanga, S.; Caron, A.; Ndlovu, M.; Peters, J.L. Host associations, biogeography, and phylogenetics of avian malaria in southern African waterfowl. Parasitology 2013, 140, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, A. Nasal trichobilharziasis: A new avian schistosomiasis. Nature 1956, 177, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.E. Catalogue of Helminths of Waterfowl (Anatidae); Special Scientific Report Wildlife No 126; Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife: Washington, WA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Avery, R.A. Helminth parasites of wildfowl from Slimbridge, Gloucestershire. I. Parasites of captive Anatidae. J. Helminthol. 1966, 40, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, N.A. Waterfowl and Acuaria. Aviculatural Mag. 1974, 80, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lapage, G. A list of the parasitic protozoa, Helminths and Arthropoda recorded from species of the Family Anatidae (Ducks, Geese and Swans) species of the Family Anatidae (Ducks, Geese and Swans). Parasitology 1960, 51, 1–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, M.; Krauss, H.; Weber, A.; Enders, B.; von Graevenitz, A.; Schiefer, H.G.; Isenberg, H.; Slenczka, W.; Zahner, H. Zoonosen: Von Tier zu Mensch Übertragene Infektionskrankheiten; Leitfaden für die Praxis; Dt. Ärzte-Verl.: Köln, Germeny, 1986; ISBN 978-3769100990. [Google Scholar]
- RKI—RKI-Ratgeber—Kryptosporidiose. Available online: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/EpidBull/Merkblaetter/Ratgeber_Kryptosporidiose.html (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Atkinson, C.T.; Thomas, N.J.; Hunter, D.B. (Eds.) Parasitic Diseases of Wild Birds; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2008; ISBN 0813804574. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Speer, C.A.; Fayer, R. Cryptosporidiosis of Man and Animals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781351071260. [Google Scholar]
- Elmberg, J.; Berg, C.; Lerner, H.; Waldenström, J.; Hessel, R. Potential disease transmission from wild geese and swans to livestock, poultry and humans: A review of the scientific literature from a One Health perspective. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2017, 7, 1300450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, L.; Winn, T.; Rusli, B.N. Practical Issues in Calculating the Sample Size for Prevalence Studies. Orofac. Sci. 2006, 1, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, M. Field Manual of Wildlife Diseases: General Field Procedures and Diseases of Birds; U.S. Dept. of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, WA, USA, 1999; ISBN 0-607-88096-1.
- Wobeser, G.A. Diseases of Wild Waterfowl, 2nd ed.; Springer US; Imprint; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-1-4615-5951-1. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, M.E. Key to Nematodes Reported in Waterfowl; Department of the Interior, Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife: Washington, WA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, M.E. Key to Trematodes Reported in Waterfowl; Resource Publication: Searcy, AR, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, M.E. Key to Acanthocephala Reported in Waterfowl; Resource Publication: Searcy, AR, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, W.C. Host-Parasite Catalogue of the Helminths of Ducks. Am. Midl. Nat. 1939, 22, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwich, G. Revision der vogelparasitischen Nematoden Mitteleuropas I. Die Gattung Porrocaecum Railliet & Henry, 1912 (Ascaridoidea). Mitt Zool Mus Berl 1958, 40, 15–53. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, L.F. (Ed.) Keys to the cestode parasites of vertebrates; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1994; ISBN 0851988792. [Google Scholar]
- Ballweber, L.R. Waterfowl parasites. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 2004, 13, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Scholten, T. A fixative for intestinal parasites permitting the use of concentration and permanent staining procedures. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1977, 67, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommel, M.; Eckert, J.; Kutzer, E.; Körting, W.; Schnieder, T.; Boch, J. Veterinärmedizinische Parasitologie: 100 Tabellen; Parey: Berlin, Germany, 2000; ISBN 3-8263-3178-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schmäschke, R. Die koproskopische Diagnostik von Endoparasiten in der Veterinärmedizin; Schlütersche: Hannover, Germany, 2014; ISBN 3899936760. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, J. Lehrbuch der Parasitologie für die Tiermedizin: 112 Tabellen; Enke: Stuttgart, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9783830410720. [Google Scholar]
- Deplazes, P.; Joachim, A.; Mathis, A.; Strube, C.; Taubert, A.; Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Zahner, H. Parasitologie für die Tiermedizin; 4. Überarbeitete Auflage; Georg Thieme Verlag: Stuttgart, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 9783132421387. [Google Scholar]
- Zajac, A.M.; Conboy, G.A. Veterinary Clinical Parasitology, 8th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2012; ISBN 0813820537. [Google Scholar]
- Heine, J. Eine einfache Nachweismethode für Kryptosporidien im Kot. Zent. Für Veterinärmedizin Reihe B 1982, 29, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.A.B.; Smith, H.V. Optimization of DNA extraction and molecular detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts in natural mineral water sources. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwin, K.; Robinson, G.; Hadfield, S.J.; Fairclough, H.V.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Chalmers, R.M. A comparison of two approaches to extracting Cryptosporidium DNA from human stools as measured by a real-time PCR assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 89, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.A.B.; Moore, J.E.; Smith, H.V. A rapid method for extracting oocyst DNA from Cryptosporidium-positive human faeces for outbreak investigations. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 65, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Gawlowska, S.; Daugschies, A.; Bangoura, B. Quantitative comparison of different purification and detection methods for Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 177, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.A.; Blair, D. Relative merits of nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacers and mitochondrial CO1 and ND1 genes for distinguishing among Echinostoma species (Trematoda). Parasitology 1998, 116 Pt 3, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNASTAR. Lasergene Genomics|NGS Analysis Software DNASTAR. Available online: https://www.dnastar.com/software/lasergene/genomics/ (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Gajadhar, A.A.; Wobeser, G.; Stockdale, P.H.G. Coccidia of domestic and wild waterfowl (Anseriformes). Can. J. Zool. 1983, 61, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berto, B.P.; Brice, B.; Thomas, G.; Elloit, A.; Zahedi, A.; Yang, R. Eimeria spp. and Tyzzeria perniciosa Allen, 1936 (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from a Pacific black duck, Anas superciliosa Gmelin (Aves: Anseriformes), in western Australia. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector-Borne Dis. 2022, 2, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, U.M.; Pallant, L.; Dwyer, B.W.; Forbes, D.A.; Rich, G.; Thompson, R.C.A. Comparison of PCR and Microscopy for Detection of Cryptosporidium parvum in Human Fecal Specimens: Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, J.E.; Fried, B. Echinostoma and Echinostomiasis. In Advances in Parasitology Volume 29; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 215–269. ISBN 9780120317295. [Google Scholar]
- Graczyk, T.K.; Fried, B. Echinostomiasis: A common but forgotten food-borne disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1998, 58, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, S.; Faltýnková, A.; Brown, R.; Blasco-Costa, I.; Soldánová, M.; Sitko, J.; Scholz, T.; Kostadinova, A. Echinostoma ‘revolutum’ (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) species complex revisited: Species delimitation based on novel molecular and morphological data gathered in Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, P.J. Red Grouse: The Biology and Management of a Wild Gamebird; The Game Conservancy Trust: Fordingbridge, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Toft, C.A. Current theory of host-parasite interactions. In Bird-Parasite Interactions: Ecology, Evolution and Behaviour; Loye, J.E., Zuk, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; ISBN 0-19-857738-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.; Hamilton, W.D. Sex against virulence: The coevolution of parasitic diseases. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sraml, M.; Christidis, L.; Easteal, S.; Horn, P.; Collet, C. Molecular Relationships Within Australasian Waterfowl (Anseriformes). Aust. J. Zool. 1996, 44, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirsa, F.; Reier, S.; Smales, L. Helminths of the mallard Anas platyrhynchos Linnaeus, 1758 from Austria, with emphasis on the morphological variability of Polymorphus minutus Goeze, 1782. J. Helminthol. 2021, 95, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüter, H.; Franz, M.; Auls, S.; Czirják, G.Á.; Greben, O.; Greenwood, A.D.; Lisitsyna, O.; Syrota, Y.; Sitko, J.; Krone, O. Chronic lead intoxication decreases intestinal helminth species richness and infection intensity in mallards (Anas platyrhynchos). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetska, K.M.; Rzad, I.; Kornyushin, V.V.; Korol, E.N.; Sitko, J.; Szałańska, K. Helmintofauna przewodu pokarmowego krzyzówki Anas platyrhynchos L., 1758 północno-zachodniej Polski. Wiad. Parazytol. 2008, 54, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bolte, A.L.; Lutz, W.; Kaleta, E.F. Investigation of the occurence of infective agents among free living gray geese (Anser anser Linne, 1758). Z. Für Jagdwiss. 2000, 46, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Guillemain, M.; Söderquist, P.; Champagnon, J.; Elmberg, J. Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos Linnaeus, 1758). In Invasive Birds: Global Trends and Impacts; Downs, C.T., Hart, L.A., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781789242065. [Google Scholar]
- Dragičević, P.; Grbin, D.; Maguire, I.; Blažević, S.A.; Abramović, L.; Tarandek, A.; Hudina, S. Immune Response in Crayfish Is Species-Specific and Exhibits Changes along Invasion Range of a Successful Invader. Biology 2021, 10, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.A.; Klasing, K.C. A role for immunology in invasion biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, S.; Sorci, G.; Moret, Y. Biological invasion and parasitism: Invaders do not suffer from physiological alterations of the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis. Parasitology 2010, 137, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchin, M.E.; Mitchell, C.E. Parasites, Pathogens, and Invasions by Plants and Animals. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.H.; Urban, E.K.; Newman, K. The Birds of Africa: Volume 1; Academic Press Inc. (London) Ltd.: London, UK, 1982; ISBN 0-12-137301-0. [Google Scholar]
- Halse, S.A. Diet, Body Condition, and Gut Size of Egyptian Geese. J. Wildl. Manag. 1984, 48, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R. Evolutionary Ecology of Parasites, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA; Woodstock, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-691-12085-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.R. Ecology of the Acanthocephala; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-521-85008-7. [Google Scholar]
- Romeo, C.; Wauters, L.A.; Ferrari, N.; Lanfranchi, P.; Martinoli, A.; Pisanu, B.; Preatoni, D.G.; Saino, N. Macroparasite fauna of alien grey squirrels (Sciurus carolinensis): Composition, variability and implications for native species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetska, K.M.; Pilarczyk, B.; Królaczyk, K. Stomach Nematodes of Wild Ducks (Subfamily Anatinae) Wintering in the North-Western Poland. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2012, 56, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, C.T.; Hart, L.A. (Eds.) Invasive Birds: Global Trends and Impacts; CABI: Wallingford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781789242065. [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler, W.; Geiter, O.; Köppen, U. Ringfunde—Herausgepickt: Meldungen aus den Beringungszentralen. Vogelwart 2013, 51, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, T.; Kruckenberg, H. Ergebnisse der Synchronzählung von Gänsen und Schwänen am 12./13. Januar 2008. Rundbrief 2008, 2008, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- DeutscherWetterdienst. Clima Data Center. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/klimaumwelt/cdc/cdc_node.html;jsessionid=3BDBBEEB1D56FF9C2400DDA9E8AC97D4.live11054 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Vale, P.F.; Choisy, M.; Little, T.J. Host nutrition alters the variance in parasite transmission potential. Biol. Lett. 2013, 9, 20121145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, S.; Bichet, C.; Larcombe, S.; Faivre, B.; Sorci, G. Impact of host nutritional status on infection dynamics and parasite virulence in a bird-malaria system. J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 83, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehring, S.; Essl, F.; Rabitsch, W. Methodik der Naturschutzfachlichen Invasivitätsbewertung Für Gebietsfremde Arten: Version 1.3; unter Verwendung von Ergebnissen aus den F+E-Vorhaben FKZ 806 82 330, FKZ 3510 86 0500 und FKZ 3511 86 0300 und FKZ 3514 86 0200; Bundesamt für Naturschutz: Bonn, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-89624-136-8. [Google Scholar]



| Parasite Species | Family | Described by | Country Where Detected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmodium spp. | Plasmodiidae | Cumming et al. [27] | South Africa, Zimbabwe |
| Haemoproteus spp. | Plasmodiidae | Cumming et al. [27] | South Africa |
| Trichobilharzia spinulata | Schistosomatidae | Fain [28] | Ruanda |
| Hymenolepsis biaculeata | Hymenolepididae | McDonald [29] | Sudan/South Africa |
| Hystrichis tricolor | Dioctophymatoidae | Avery [30] | Great Britain |
| Echinuria uncinata | Acuariidae | Wood [31] | Great Britain |
| Species | Prevalence of Adult Parasites in Necropsy (n = 114) | Prevalence of Eggs in Collected Faeces (n = 148) |
|---|---|---|
| Nematodes | ||
| Hystrichis tricolor | 10.5% | 1.4% |
| Echinuria uncinata | 2.6% | 0.7% |
| Porrocaecum spp. | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| Ascardia galli | 1.8% | 0.7% |
| Capillaria spp. | 2.0% | |
| Hetrakis dispar | 1.4% | |
| Syngamus trachae | 0.7% | |
| Amidostomum anseris | 0.7% | |
| unknown nematodes | 1.4% | |
| Tapeworms | ||
| Cloacoteania spp. | 2.6% | - |
| Acantocephalans | ||
| Polymorphus minutus | 7.9% | - |
| Trematodes | ||
| Echinostoma spp. | 6.8% | |
| Echinostoma revolutum | 7.9% | |
| Echinostoma grandis | 0.9% | |
| Notocotylidae | 0.7% | |
| unknown trematodes | 1.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, E.F.; Recht, S.; Vélez, J.; Rogge, L.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.R. Occurrence of Gastrointestinal Parasites in Synanthropic Neozoan Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca, Linnaeus 1766) in Germany. Diversity 2023, 15, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030388
Fischer EF, Recht S, Vélez J, Rogge L, Taubert A, Hermosilla CR. Occurrence of Gastrointestinal Parasites in Synanthropic Neozoan Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca, Linnaeus 1766) in Germany. Diversity. 2023; 15(3):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030388
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, Ella F., Sabine Recht, Juan Vélez, Linda Rogge, Anja Taubert, and Carlos R. Hermosilla. 2023. "Occurrence of Gastrointestinal Parasites in Synanthropic Neozoan Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca, Linnaeus 1766) in Germany" Diversity 15, no. 3: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030388
APA StyleFischer, E. F., Recht, S., Vélez, J., Rogge, L., Taubert, A., & Hermosilla, C. R. (2023). Occurrence of Gastrointestinal Parasites in Synanthropic Neozoan Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca, Linnaeus 1766) in Germany. Diversity, 15(3), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030388










