Diversity of Parasitic Animals in Hypersaline Waters: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Group I: Ectoparasites with a direct life cycle; all their life stages are directly affected by the hypersaline environment;
- -
- Group II: Endoparasitic developmental stages not directly affected by the environment but having younger free-living development stages in the lifeir cycle;
- -
- Group III: Endoparasitic adults and pre-adults (in definitive hosts) under nondirect abiotic environmental impact (maritae of Trematoda and adults and pre-adults of Cestoda, Nematoda, and Acanthocephala), that have more endoparasitic younger stages than the intermediate host, and were transmitted to definitive hosts via food chains. A definitive host eats an intermediate one.
3. Results and Discussion
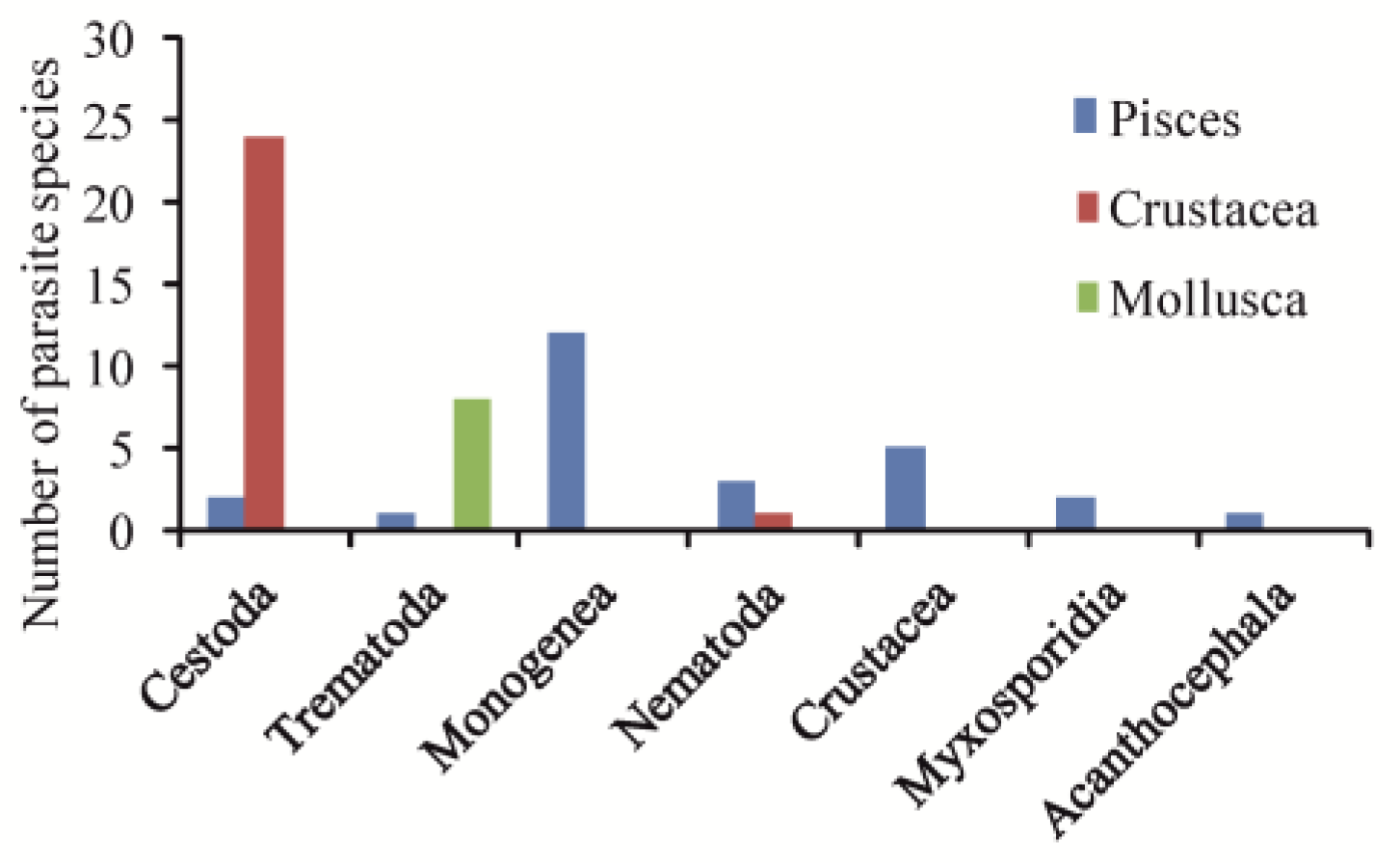
3.1. Diversity of Parasites Occurring in Hypersaline Waters
3.2. Hosts of Parasites
3.3. Host–Parasite Interactions in Hypersaline Waters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anufriieva, E.V. Do copepods inhabit hypersaline waters worldwide? A short review and discussion. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignatti, A.M.; Capecce, C.; Cabrera, G.C.; Echaniz, S.A. Biology of Artemia persimilis Piccinelli and Prosdocimi, 1968 in a hypersaline lake in a semiarid protected area (Parque Luro Reserve, La Pampa, Argentina). Limnetica 2020, 39, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, M.; White, N.E.; Harrod, C.; Salazar, G.; Aguilar, P.; Cubillos, C.F.; Meredith, K.; Baxter, B.K.; Oren, A.; Anufriieva, E.; et al. Salt to conserve: A review on the ecology and preservation of hypersaline ecosystems. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 2828–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebovich, V.V.; Aladin, N.V. The salinity factor in animal life. Her. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2010, 80, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrin, N.; Anufriieva, E. Ecosystems of hypersaline waters: Structure and trophic relations. Zh. Obshch. Biol. 2018, 79, 418–427. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Getz, E.; Eckert, C. Effects of salinity on species richness and community composition in a hypersaline estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beklemishev, V.N. Biocenotic Foundations of Comparative Parasitology; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1970; 502p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shigin, A.A. Role of free-living stages of trematode development in biocenoses. Parazitologiya 1978, 12, 193–200. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shigin, A.A. On the place and role of trematodes in the biosphere. Proc. Inst. Parasitol. RAS 1997, 41, 192–208. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hatcher, M.J.; Dick, J.T.A.; Dunn, A.M. How parasites affect interactions between competitors and predators. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, K.D.; Allesina, S.; Arim, M.; Briggs, C.J.; De Leo, G.; Dobson, A.P.; Dunne, J.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kuris, A.M.; Marcogliese, D.J.; et al. Parasites in food webs: The ultimate missing links. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.M. Parasites and biological invasions. Adv. Parasit. 2009, 68, 161–184. [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins, D.M.; Dunn, A.M.; Smith, M.J.; Telfer, S. Wildlife diseases: From individuals to ecosystems. J. Anim. Ecol. 2010, 80, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, C.L.; Johnson, P.T. A world without parasites: Exploring the hidden ecology of infection. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcogliese, D.J. Parasites of the superorganism: Are they indicators of ecosystem health? Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.C.; Chabaud, A.G.; Willmott, S. Keys to the Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates: Archival Volume; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2009; 463p. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, L.F.; Jones, A.; Bray, R.A. Keys to the Cestode Parasites of Vertebrates; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1994; 768p. [Google Scholar]
- Mariaux, J.; Tkach, V.V.; Vasileva, G.P.; Waeschenbach, A.; Beveridge, I.; Dimitrova, Y.D.; Haukisalmi, V.; Greiman, S.E.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Makarikov, A.A.; et al. Cyclophyllidea van Beneden in Braun, 1900. In Planetary Biodiversity Inventory (2008–2017): Tapeworms from Vertebrate Bowels of the Earth; Caira, J.N., Jensen, K., Eds.; University of Kansas, Natural History Museum: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2017; Special Publication No. 25; pp. 77–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, D.I.; Jones, A.; Bray, R.A. Keys to the Trematoda, vol. 1; CABI and The Natural History Museum: Wallingford, UK, 2002; 521p. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, O.M. Classification of the acanthocephala. Folia Parasitol. 2013, 60, 273–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Descriptive Statistics. In Biometry, the Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 4th ed.; Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; 937p. [Google Scholar]
- Paperna, I.; Lahav, M. Parasites of fish of the hypersaline Bardawil Lagoon, North Sinai. A preliminary communication. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Mediterr. 1975, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kuperman, B.I.; Matey, V.E.; Hurlbert, S.H. Parasites of fish from the Salton Sea, California, USA. In Saline Lakes: Publications from the 7th International Conference on Salt Lakes, held in Death Valley National Park, California, USA, September 1999; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Paladini, G.; Huyse, T.; Shinn, A.P. Gyrodactylus salinae n. sp. (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea) infecting the south European toothcarp Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes) (Teleostei, Cyprinodontidae) from a hypersaline environment in Italy. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paperna, I. Study of Caligus minimus (Otto, 1821) (Caligidae Copepoda) infections of the sea Bass Dicentrarcbus labrax (L.) in, Bardawil lagoon. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1980, 55, 687–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, O.H. Aquaculture of Grey Mullets; International Biological Programme No. 26; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981; p. 507. [Google Scholar]
- Louizi, H.; Hill-Spanik, K.M.; Qninba, A.; Connors, V.A.; Belafhaili, A.; Agnèse, J.-F.; Pariselle, A.; de Buron, I. Parasites of Moroccan desert Coptodon guineensis (Pisces, Cichlidae): Transition and resilience in a simplified hypersaline ecosystem. Parasite 2022, 29, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huspeni, T.C.; Lafferty, K.D. Using larval trematodes that parasitize snails to evaluate a salt–marsh restoration project. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, W.P. Host life history and the effect of parasitic castration growth: A field study of Cerithidea californica Haldeman (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) and its trematode parasites. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1983, 73, 273–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, W.P.; Gleason, M. Does parasitic infection compromise host survival under extreme environmental conditions? The case for Cerithidea californica (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia). Oecologia 1989, 80, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redón, S.; Berthelemy, N.J.; Mutafchiev, Y.; Amat, F.; Georgiev, B.B.; Vasileva, G.P. Helminth parasites of Artemia franciscana (Crustacea: Branchiopoda) in the Great Salt Lake, Utah: First data from the native range of this invader of European wetlands. Folia Parasitol. 2015, 62, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redón, S.; Vasileva, G.P.; Georgiev, B.B.; Gajardo, G. Exploring parasites in extreme environments of high conservational importance: Artemia franciscana (Crustacea: Branchiopoda) as intermediate host of avian cestodes in Andean hypersaline lagoons from Salar de Atacama, Chile. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimova, A.P. Branchiopods–intermediate hosts of cestodes of Anomolepis averini (Spassky et Yurpalova, 1967) (Cestoda: Dilepididae). Parazitologiya 1977, 11, 77–79. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, M.I.; Paredes, I.; Lebouvier, M.; Green, A.J. Functional role of native and invasive filter-feeders, and the effect of parasites: Learning from hypersaline ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, M.I.; Pons, I.; Martínez-Haro, M.; Taggart, M.A.; Lenormand, T.; Green, A.J. When parasites are good for health: Cestode parasitism increases resistance to arsenic in brine shrimps. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgiev, B.B.; Sánchez, M.I.; Green, A.J.; Nikolov, P.N.; Vasileva, G.P. Cestodes from Artemia parthenogenetica (Crustacea, Branchiopoda) in the Odiel Marshes, Spain: A systematic survey of cysticercoids. Acta Parasitol. 2005, 50, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, B.B.; Sánchez, M.I.; Vasileva, G.P.; Nikolov, P.N.; Green, A.J. Cestode parasitism in invasive and native brine shrimps (Artemia spp.) as a possible factor promoting the rapid invasion of A. franciscana in the Mediterranean region. Parasitol Res. 2007, 101, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redón, S.; Green, A.J.; Georgiev, B.B.; Vasileva, G.P.; Amat, F. Influence of developmental stage and sex on infection of the American brine shrimp Artemia franciscana Kellogg, 1906 by avian cestodes in Ebro Delta salterns, Spain. Aquat. Inv. 2015, 10, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, S.; Hyland, K.; Schuster, R. Tapeworm larvae in Artemia franciscana (Crustacea: Anostraca) in the Godolphin lakes of Dubai (United Arab Emirates) throughout an annual cycle. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.I.; Rode, N.O.; Flaven, E.; Redón, S.; Amat, F.; Vasileva, G.P.; Lenormand, T. Differential susceptibility to parasites of invasive and native species of Artemia living in sympatry: Consequences for the invasion of A. franciscana in the Mediterranean region. Biol. Inv. 2012, 14, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimova, A.P. On ecology and biology of Eurycestus avoceti (Cestoda: Dilepididae). Parazitologiya 1991, 25, 73–76. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, R.K. On two morphologically different cysticercoids of the genus Eurycestus (Cestoda: Dilepididae) in Artemia franciscana (Arthropoda: Artemiidae) in a hypersaline pond in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Helminthologia 2019, 56, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maksimova, A.P. Branchinella spinosa (Anostraca), an intermediate host of cestodes of the genus Wardium (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae). Parazitologiya 1990, 24, 89–92. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vasileva, G.P.; Redón, S.; Amat, F.; Nikolov, P.N.; Sánchez, M.I.; Lenormand, T.; Georgiev, B.B. Records of cysticercoids of Fimbriarioides tadornae Maksimova, 1976 and Branchiopodataenia gvozdevi (Maksimova, 1988) (Cyclophyllidea: Hymenolepididae) from brine shrimps at the Mediterranean coasts of Spain and France, with a key to cestodes from Artemia spp. from the Western Mediterranean. Acta Parasitol. 2009, 54, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, B.B.; Angelov, A.; Vasileva, G.P.; Sánchez, M.I.; Hortas, F.; Mutafchiev, Y.; Pankov, P.; Green, A.J. Larval helminths in the invasive American brine shrimp Artemia franciscana throughout its annual cycle. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gvosdev, E.V.; Maksimova, A.P. Eucypris inflata, an intermediate host of avian cestodes in the biocoenosis of the lake Tengiz. Parazitologiya 1978, 7, 339–344. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Redón, S.; Vasileva, G.P.; Georgiev, B.B.; Gajardo, G. First report of cestode infection in the crustacean Artemia persimilis from Southern Chilean Patagonia and its relation with the Neotropical aquatic birds. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guagliardo, S.E.; Graff, M.E.; Gigola, G.; Tanzola, R.D. Biological aspects of the life history of Confluaria podicipina (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae) from a hypersaline pampasic lagoon. Pan-Am. J. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 15, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimova, A.P. Branchiopods (Branchiopoda: Anostraca), intermediate hosts of cestodes fam. Hymenolepididae. Parazitologiya 1973, 7, 349–352. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Maksimova, A.P. Morphology and developmental cycle of the cestode Confluaria podicipina Szymanski (Cestoda: Hymenolepididae). Parazitologiya 1981, 15, 325–331. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Robert, F.; Gabrion, C. Cestodoses de l’avifaune Camarguaise. Rôle d’Artemia (Crustacea, Anostraca) et stratégies de rencontre hôte-parasite. Ann. De Parasitol. Hum. Et Comparée 1991, 66, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabrion, C.; MacDonald, G. Artemia sp. (Crustacé, Anostracé), hôte intermédiaire d’Eurycestus avoceti Clark, 1954 (Cestode Cyclophyllide). Ann. Parasit. Hum. Comp. 1980, 55, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiéry, A.; Robert, F.; Gabrion, C. Distribution des populations d’Artemia et de leur parasite Flamingolepis liguloïdes (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea), dans les salins du littoral méditerranéen français. Can. J. Zool. 1990, 68, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat, F.; Illescas, M.P.; Fernandez, J. Brine shrimp Artemia parasitized by Flamingolepis liguloides (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae) cysticercoids in Spanish Mediterranean salterns. Quantitative aspects. Vie Et Milieu 1991, 41, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Mura, G. Cestode parasitism (Flamingolepis liguloides Gervais, 1847 Spassky & Spasskaja 1954) in an Artemia population from south-western Sardinia. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1994, 3, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Amarouayache, M.; Derbal, F.; Kara, M. The parasitism of Flamingolepis liguloides (Gervais, 1847) (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae) in Artemia salina (Crustacea, Branchiopoda) in two saline lakes in Algeria. Acta Parasitol. 2009, 54, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimova, A.P. A new cestode, Fimbriarioides tadornae sp. n., from Tadorna tadorna and its development in the intermediate host. Parazitologiya 1976, 10, 17–24. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.T. The larva of Hymenolepis californicus in the brine shrimp (Artemia salina). J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 1952, 42, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimova, A.P. On morphology and developmental cycle of the cestode Wardium fusa (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae). Parazitologiya 1987, 21, 157–158. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gvosdev, E.V.; Maksimova, A.P. Morphology and developmental cycle of the cestode Gynandrotaenia stammeri (Cestoidea: Cyclophyllidea), a parasite of Phoenicopterus roseus. Parazitologiya 1979, 13, 56–60. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Koru, E. Cestode Infection of the Native Brine Shrimp (Artemia parthenogenetica) in Çamaltı Saltpan (İzmir/Türkiye). COMU J. Mar. Sci. Fish. 2022, 5, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mayo-Hernández, E.; Peñalver, J.; García-Ayala, A.; Serrano, E.; Muñoz, P.; deYbáñez, R.R. Richness and diversity of helminth species in eels from a hypersaline coastal lagoon, Mar Menor, south-east Spain. J. Helminthol. 2015, 89, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anufriieva, E.V.; El-Shabrawy, G.M.; Shadrin, N.V. Copepoda in the shallow hypersaline Bardawil coastal lake (Egypt): Are there long-term changes in composition and abundance? Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2018, 47, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, G.; Anufriieva, E.; Shadrin, N. Tintinnina (Ciliophora) and Foraminifera in plankton of hypersaline Lagoon Bardawil (Egypt): Spatial and temporal variability. Turk. J. Zool. 2018, 42, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redón, S.; Gajardo, G.; Vasileva, G.P.; Sánchez, M.I.; Green, A.J. Explaining variation in abundance and species diversity of avian cestodes in brine shrimps in the Salar de Atacama and other Chilean wetlands. Water 2021, 13, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, N.G.; Shadrin, N.V.; Anufriieva, E.V. Long-term changes (1979–2015) in the nematode fauna in Sivash Bay (Sea of Azov), Russia, worldwide the largest hypersaline lagoon, during salinity transformations. Nematology 2019, 21, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrin, N.; Kolesnikova, E.; Revkova, T.; Latushkin, A.; Chepyzhenko, A.; Drapun, I.; Dyakov, N.; Anufriieva, E. Do separated taxa react differently to a long-term salinity increase? The meiobenthos changes in Bay Sivash, largest hypersaline lagoon worldwide. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2019, 420, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozer, A.; Yılmaz Kırca, D. Parasite fauna of the grey mullet Mugil cephalus L. 1758, and its relationship with some ecological factors in Lower Kızılırmak Delta located by the Black Sea, Turkey. J. Nat. Hist. 2015, 49, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anufriieva, E.V. Diversity and the Role of Animals in the Structure, Functioning and Dynamics of Hypersaline Water Ecosystems. Ph.D. Thesis, Papanin Institute for Biology of Inland Waters Russian Academy of Sciences, Borok, Russia, 18 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Balushkina, E.V.; Golubkov, S.M.; Golubkov, M.S.; Litvinchuk, L.F.; Shadrin, N.V. Effect of abiotic and biotic factors on the structural and functional organization of the saline lake ecosystems in Crimea. Zh. Obshch. Biol. 2009, 70, 504–514. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Golubkov, S.M.; Shadrin, N.V.; Golubkov, M.S.; Balushkina, E.V.; Litvinchuk, L.F. Food chains and their dynamics in ecosystems of shallow lakes with different water salinities. Russ. J. Ecol. 2018, 49, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anufriieva, E.V.; Shadrin, N.V. General patterns of salinity influence on the energy balance of aquatic animals in hypersaline environment. Zh. Obshch. Biol. 2022, 83, 369–379. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Galaktionov, K.V.; Dobrovolskij, A.A. The Biology and Evolution of Trematodes: An Essay Onthe Biology, Morphology, Life Cycles, Transmission, and Evolution of Digenetic Trematodes; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2003; 592p. [Google Scholar]
- Rhode, K. Marine Parasitology; CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne and CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2005; 565p. [Google Scholar]
- Koprivnikar, J.; Lim, D.; Fu, C.; Brack, S.H.M. Effects of temperature, salinity, and pH on the survival and activity of marine cercariae. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 106, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokofiev, V.V. Influence of temperature and salinity on a life span of cercariae of marine littoral trematodes Cryptocotyle sp. (Heterophyidae), Levinseniella brachysoma and Maritrema subdolum (Microphallidae). Parasitolgiya 1999, 33, 520–526. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Studer, A.; Poulin, R. Effects of salinity on an intertidal host-parasite system: Is the parasite more sensitive than its host? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 412, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajardo, G.M.; Beardmore, J.A. The Brine Shrimp Artemia: Adapted to Critical Life Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shadrin, N.V.; Anufriieva, E.V. Size polymorphism and fluctuating asymmetry of Artemia (Branchiopoda: Anostraca) populations from the Crimea. J. Sib. Fed. Univ. Biol. 2017, 10, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, J.; Healy, A. Relationship between medium salinity, body density, buoyancy and swimming in Artemia franciscana larvae: Constraints on water column use? Hydrobiologia 2006, 556, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoyeva, N.Y.; Anufriieva, E.V.; Shadrin, N.V. The Effect of Gamma Radiation on Parthenogenetic Artemia (Branchiopoda, Anostraca) Cysts: Nauplius Hatching and Postnauplial Survival under Varying Salinity. Biol. Bull. 2019, 46, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Food-web modification by an invertebrate predator in the Great Salt Lake (USA). Oecologia 1992, 89, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Anufriieva, E.; Liu, X.; Kong, F.; Shadrin, N. Intentional introduction of Artemia sinica (Anostraca) in the high-altitude Tibetan Lake Dangxiong Co: The new population and consequences for the environment and for humans. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anufriieva, E.; Kolesnikova, E.; Revkova, T.; Latushkin, A.; Shadrin, N. Human-induced sharp salinity changes in the world’s largest hypersaline lagoon Bay Sivash (Crimea) and their effects on the ecosystem. Water 2022, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.I.; Green, A.J.; Castellanos, E.M. Temporal and spatial variation of an aquatic invertebrate community subjected to avian predation at the Odiel salt pans (SW Spain). Arch. Hydrobiol. 2006, 166, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coop, R.L.; Holmes, P.H. Nutrition and parasite interaction. Int. J. Parasitol. 1996, 26, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R. The evolution of parasite manipulation of host behaviour: A theoretical analysis. Parasitology 1994, 109, S109–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Poulin, R.; Brodeur, J. Host manipulation by parasites: A multidimensional phenomenon. Oikos 2010, 119, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, K.D. Effect of parasitic castration on growth, reproduction and population dynamics of the marine snail Cerithidea californica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 96, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Sánchez, A.; Valencia, J.M.; Box, A.; Solomando, A.; Tejada, S.; Pinya, S.; Catanese, G.; Sureda, A. Black spot disease related to a trematode ectoparasite causes oxidative stress in Xyrichtys novacula. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2023, 560, 151854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y. Intestinal flucks. In Food Born Parasytic Zoonoses, Fish and Plant-Borne Parasites; Murrel, K.D., Fried, B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 53–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cezilly, F.; Gregoire, A.; Bertin, A. Conflict between co-occurring manipulative parasites? An experimental study of the joint influence of two acanthocephalan parasites on the behaviour of Gammarus pulex. Parasitology 2000, 120, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.I.; Georgiev, B.B.; Nikolov, P.N.; Vasileva, G.P.; Green, A.J. Red and transparent brine shrimps (Artemia parthenogenetica): Comparative study of their cestode infections. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 100, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.I.; Thomas, F.; Perrot-Minnot, M.J.; Biron, D.G.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Missé, D. Neurological and physiological disorders in Artemia harboring manipulative cestodes. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat, F.; Gozalbo, A.; Navarro, J.C.; Hontoria, F.; Varó, I. Some aspects of Artemia biology affected by cestode parasitism. Hydrobiologia 1991, 212, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cespedes, V.; Sanchez, M.I.; Green, A.J. Predator–prey interactions between native brine shrimp Artemia parthenogenetica and the alien boatman Trichocorixa verticalis: Influence of salinity, predator sex, and size, abundance and parasitic status of prey. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varo, I.; Taylor, A.C.; Navarro, J.C.; Amat, F. Effect of parasytizm on respiration rates of different Artemia strains from Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2000, 86, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.I.; Georgiev, B.B.; Green, A.J. Avian cestodes affect the behaviour of their intermediate host Artemia parthenogenetica: An experimental study. Behav. Proc. 2007, 74, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redón, S.; Amat, F.; Sanchez, M.I.; Green, A.J. Comparing cestode infections and their consequences for host fitness in two sexual branchiopods: Alien Artemia franciscana and native A. salina from syntopic populations. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuris, A.M.; Hechinger, R.F.; Shaw, J.C.; Whitney, K.L.; Aguirre-Macedo, L.; Boch, C.A.; Dobson, A.P.; Dunham, E.J.; Fredensborg, B.L.; Huspeni, T.C.; et al. Ecosystem energetic implications of parasite and free-living biomass in three estuaries. Nature 2008, 454, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.T.; Dobson, A.; Lafferty, K.D.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Memmott, J.; Orlofske, S.A.; Poulin, R.; Thieltges, D.W. When parasites become prey: Ecological and epidemiological significance of eating parasites. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, K.T.; Larsen, M.H.; Iversen, N.K.; Mouritsen, K.N. The influence of trematodes on the macroalgae consumption by the common periwinkle Littorina littorea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2008, 88, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buschbaum, C.; Buschbaum, G.; Schrey, I.; Thieltges, D.W. Shell-boring polychaetes affect gastropod shell strength and crab predation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrin, N.; Stetsiuk, A.; Anufriieva, E. Differences in Mercury Concentrations in Water and Hydrobionts of the Crimean Saline Lakes: Does Only Salinity Matter? Water 2022, 14, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielma, S.; Lagrue, C.; Poulin, R.; Selbach, C. Non-host organisms impact transmission at two different life stages in a marine parasite. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parasite/Life Stage | Host | S, g·L−1 | Locality | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I * | ||||
| Phylum PLATHELMINTHES Class Monogenea | ||||
| Fam. Calceostomatidae Parona & Perugia, 1890 Calceostoma calceostoma (Wagener, 1857) | Pisces: Argyrosomus regius (Asso, 1801) | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [22] |
| Fam. Diplectanidae Montichelli, 1903 Diplectanum aculeatum Parona & Perugia, 1889 | Umbrina cirrosa (Linnaeus, 1758) | |||
| Diplectanum simile Bychowsky, 1957 | A. regius, U. cirrosa | |||
| Diplectanum aequans (Wagener, 1857) | Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758), D. punctatus (Bloch, 1792) | |||
| Lamellodiscus echeneis (Wagener, 1857) | Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758 | |||
| Pseudorhabdosynochus cf. epinepheli (Yamaguti, 1938) Kritsky & Beverley-Burton, 1986 | Epinephelus aeneus (Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817) | |||
| Fam. Ancyrocephalidae Bychowsky, 1937 Ligophorus vanbenedenii (Parona & Perugia, 1890) Euzet & Suriano, 1977 | Mugilidae | |||
| Fam. Gyrodactylidae Cobbold, 1864 Gyrodactylus imperialis Mizelle & Kritsky, 1967 | Gillichthys mirabilis Cooper, 1864, Oreochromis mossambicus (Peters, 1852) | 41–45 | Lake in Salton Sea, California, USA (North America) | [23] |
| Gyrodactylus olsoni Mizelle & Kritsky, 1967 | G. mirabilis | |||
| Gyrodactylus salinae Paladini, Huyse & Shinn, 2011 | Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes, 1821) | 65 | Isolated pools in Cervia Saline, the Emilia Romagna region of northern Italy (Europe) | [24] |
| Gyrodactylus n. sp. A. | Mugilidae, Aphanius dispar (Rüppell, 1829) | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [22] |
| Fam. Lernaeopodidae Milne-Edwards, 1840 Naobranchia sp. (as Axine sp.) | Hemiramphus far (Forsskål, 1775) | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [22] |
| Fam. Microcotylidae Taschenberg, 1879 Microcotyle sp. | Mugilidae | |||
| Phylum ARTHROPODA Class Copepoda | ||||
| Fam. Caligidae Burmeister, 1835 Caligus apodus (Brian, 1924) | Mugilidae | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [22] |
| Caligus minimus Otto, 1821 | D. labrax, D. punctatus | [22,25] | ||
| Caligus tenuis (Beneden, 1852) (as Sciaenophilus tenuis Beneden, 1852) | A. regius | [22] | ||
| Fam. Lernanthropidae Kabata, 1979 Lernanthropus kroyeri Beneden, 1851 | D. labrax, D. punctatus | [22,25] | ||
| Lernanthropus sp. | ||||
| Group II. Endopasrasitic nonadult stages | ||||
| Phylum PLATHELMINTHES Class Trematoda | ||||
| Fam. Heterophyidae Leiper, 1909 Heteropyes heterophyes (von Siebold, 1852) Stiles & Hassall, 1900/metacercariae | Pisces: Chelon ramada (Risso, 1827), Mugil cephalus Linnaeus, 1758, Chelon auratus (Risso, 1810, Chelon saliens (Risso, 1810), Chelon labrosus (Risso, 1827) | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [25] |
| Chelon ramada, M. cephalus, Chelon auratus, Mugil sp. | [26] | |||
| Heteropyes aequalis Loos, 1902/metacercariae | Chelon ramada (as Mugil capito) | |||
| Stictodora sawakinensis Looss, 1899/metacercariae | ||||
| Heterophyidae gen. sp./metacercariae | Mugilidae, D. labrax, D. punctatus | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [22] |
| Pygidiopsis genata Looss, 1907/metacercariae | Coptodon guineensis (Günther, 1862) | 50–60 | Sebkha Imlili salt flat, Atlantic Sahara (Africa) | [27] |
| unidentified digenean metacercariae | ||||
| Euhaplorchis californiensis Martin, 1950/rediae | Mollusca: Cerithideopsis californica (Haldeman, 1840) | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] |
| 60 | Bolinas Lagoon, California, USA (North America) | [29,30] | ||
| Phocitremoides ovale Martin, 1950/rediae | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] | |
| Pygidiopsoides spindalis Martin, 1951/rediae | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [29] | |
| Fam. Himasthlidae Odhner, 1910 Acanthoparyphium spinulosum Johnston, 1917/rediae | C. californica | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] |
| 60 | Bolinas Lagoon, California, USA (North America) | [29] | ||
| Fam. Cyathocotylidae Mühling, 1898 Mesostephanus appendiculatoides (Price, 1934) Lutz, 1935/rediae | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] | |
| Fam. Echinostomatidae Looss, 1988 Himasthla rhigedana Dietz, 1909/rediae | C. californica | 60 | California, USA (North America) | [29] |
| Himasthla sp B./rediae | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] | |
| Echinoparyphium sp./rediae | C. californica | 60 | Bolinas Lagoon, California, USA (North America) | [29] |
| Fam. Renicolidae Dollfus, 1939 Renicola buchanani (Martin & Gregory, 1951) | C. californica | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] |
| Renicola cerithidicola Martin, 1971 | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] | |
| Renicolidae fam. gen. sp./rediae | 60 | California, USA (North America) | [29] | |
| Fam. Philophthalmidae Looss, 1899 Cloacitrema michiganensis McIntosh, 1938 | C. californica | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] |
| Parorchis acanthus (Nicoll, 1906) Nicoll, 1907/rediae | 60 | Bolinas Lagoon, California, USA (North America) | [29] | |
| Fam. Notocotylidae Lühe, 1909 Catatropis johnstoni Martin, 1956 | C. californica | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] |
| 60 | California, USA (North America) | [29] | ||
| Fam. Microphallidae Ward, 1901 Probolocoryphe uca (Sarkisian, 1957) Heard & Sikora, 1969 | C. californica | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] |
| Sporosysts with unidentified xiphidiocercaria | 35 | Carpinteria Salt Marsh, USA (North America) | [28] | |
| 60 | Bolinas Lagoon, California, USA (North America) | [29] | ||
| Class Cestoda | ||||
| Fam. Dilepididae Fuhrmann, 1907 Fuhrmannolepis averini Spasskii & Yurpalova, 1967/cysticercoids | Crustacea: Artemia franciscana Kellog, 1906 | 105–150 | Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA (North America) | [31] |
| Tebenquiche Lagoon (Salar de Atacama), Chile (South America) | [32] | |||
| Artemia salina (Linnaeus, 1758), Phallocryptus spinosa (Milne-Edwards, 1840) | 65–70 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [33] | |
| Anomotaenia tringae (Burt, 1940)/cysticercoids | A. franciscana, Artemia parthenogenetica Bowen & Sterling, 1978 | 110–170 | Salt marshes Odiel and La Tapa, Spain (Europe) | [34,35] |
| A. parthenogenetica | 110–200 | Odiel salt marshes, Spain (Europe) | [36] | |
| Salterns Nuestra Señora del Rocío, Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| A. franciscana | Salterns Castro Marim, Las Ánimas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | ||
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| 70–160 | Godolphin lakes, Unated Arab Emirates (Asia) | [39] | ||
| Anomotaenia microphallos (Krabbe, 1869)/cysticercoids | A. parthenogenetica | 110 | Odiel and Tinto estuary, Spain (Europe) | [36] |
| Saltern Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| A. franciscana | Saltern Castro Marim, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | ||
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| Anomotaenia sp., probably A. microphallos/cysticercoids | A. parthenogenetica | 110–200 | Odiel salt marshes, Spain (Europe) | [36] |
| Eurycestus avoceti Clark, 1954)/cysticercoids | A. franciscana | 70–160 | Godolphin lakes (Dubai) | [39] |
| 80 | Barros Negros Lagoon (Salar de Atacama), Chile (South America) | [32] | ||
| Salterns Castro Marim, Las Ánimas, Santa Barbara, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| Aigues-Mortes saltern, France (Europe) | [40] | |||
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| Artemia sp. | 133–210 | salt marshes of Camargue, France (Europe) | [32] | |
| A. salina | 65–80 | Tengiz lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [41] | |
| Saltern de Cerrillos, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| A. parthenogenetica | 110 | Odiel and La Tapa salterns, Spain (Europe) | [35] | |
| 110–200 | Odiel Marshes, Huelva Province, SW Spain | [36] | ||
| Salterns Odiel, Nuestra Señora del Rocío, Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| Aigues-Mortes saltern, France (Europe) | [40] | |||
| 86–209 | Saltern La Tapa, Spain (Europe) | [41] | ||
| Eurycestus sp./cysticercoids | A. franciscana | 70 | Asia (Dubai) | [42] |
| Fam. Hymenolepididae Perrier, 1897 Branchiopodataenia gvozdevi (Maksimova, 1988) Bondarenko & Kontrimavichus, 2004/cysticercoids | A. salina | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [43] |
| San Pedro del Pinatar, Spain (Europe) | [44] | |||
| A. franciscana | River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [45] | ||
| [38] | ||||
| A. parthenogenetica | Bras del Port, Spain (Europe) | [44] | ||
| Cloacotaenia megalops (Nitzsch in Creplin, 1829)/cysticercoids | Eucypris mareotica (Fischer, 1855) | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [46] |
| Diorchis elisae (Skrjabin, 1914) Spassky et Frese, 1961/cysticercoids | E. mareotica | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [46] |
| Confluaria podicipina (Szymanski, 1905)/cysticercoids | A. parthenogenetica | 110–170 | Odiel and La Tapa salt marshes, Spain (Europe) | [34,35] |
| 110–200 | Odiel salt marsh, Spain (Europe) | [36] | ||
| Saltern Odiel, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| A. franciscana | 70–160 | Godolphin lakes (Dubai) | [39] | |
| 105–150 | Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA (North America) | [31] | ||
| Artemia persimilis Piccinelli & Prosdocimi, 1968 | 55–86 | Los Cisnes and Amarga lagoons, Chile (South America) | [47] | |
| 320 | Epecuén lagoon, Lagunas Encadenadas del Oeste, Argentina (South America) | [48] | ||
| A. salina | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [49] | |
| Saltern de Cerrillos, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| Fimbriarioides tadornae Maksimova, 1976/cysticercoids | A. salina | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [50] |
| A. parthenogenetica | 110 | Odiel and Tinto estuary, Spain (Europe) | [35] | |
| Saltern Odiel, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| Bras del Port, Spain and Aigues-Mortes, France (Europe) | [44] | |||
| Aigues-Mortes saltern, France (Europe) | [40] | |||
| A. franciscana | River Ebro Delta, Spain (Europe) | [44] | ||
| Aigues-Mortes saltern, France (Europe) | [40] | |||
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| Fimbriarioides ? sp./cysticercoids | A. persimilis | 55–86 | Los Cisnes and Amarga lagoons (South America, Chile) | [47] |
| Flamingolepis caroli (Parona, 1887)/cysticercoids | A. salina | 133–210 | Salt marshes of Camargue, France (Europe) | [51] |
| Artemia sp. | 133–210 | Salt marshes of Camargue, France (Europe) | [52] | |
| Flamingolepis dolguschini Gvozdev & Maksimova, 1968/cysticercoids | A. salina | 65–70 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [40] |
| Flamingolepis flamingo (Skrjabin, 1914)/cysticercoid | A. franciscana | 70–160 | Godolphin lakes (Dubai) | [39] |
| Saltern Castro Marim, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| A. parthenogenetica | 110 | Odiel and Tinto estuary, SW Spain (Europe) | [35] | |
| 110–200 | Odiel Marshes, Spain (Europe) | [36] | ||
| Salterns Odiel, Nuestra Señora del Rocío, Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| Aigues-Mortes saltern, France (Europe) | [40] | |||
| 86–209 | Saltern La Tapa, Spain (Europe) | [45] | ||
| A. salina | Saltern de Cerrillos, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | ||
| Artemia sp. | 133–210 | Salt marshes of Camargue, France (Europe) | [51,52] | |
| Flamingolepis liguloides (Gervais, 1847)/cysticercoids | A. franciscana, A. parthenogenetica | 110–130 | Odiel and La Tapa salt marshes, Spain (Europe) | [34,35] |
| A. parthenogenetica | 110–200 | Odiel Marshes, Spain (Europe) | [36] | |
| 40–320 | Çamaltı salt pans, İzmir, Turkey (Asia) | [52] | ||
| Salterns Odiel, Nuestra Señora del Rocío, Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| Aigues-Mortes saltern, France (Europe) | [40] | |||
| Salt marshes Aigues Mortes, Fangassier, Fos-sur-Mer, Lavalduc, Berre, Hybes-Pesquier, France (Europe) | [53] | |||
| 86–209 | Saltern La Tapa, Spain (Europe) | [47] | ||
| Flamingolepis liguloides (Gervais, 1847)/cysticercoids | A. franciscana | Saltern Castro Marim, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| 70–160 | Godolphin lakes, Dubai (Asia) | [39] | ||
| Artemia sp. | 35 | La Mata lagoon, Bonmati salterns, Spain (Europe) | [54] | |
| 65–110 | Su Pallosu pond (south-western Sardinia), Italy (Europe) | [55] | ||
| 133–210 | Salt marshes of Camargue, France (Europe) | [51] | ||
| A. salina | 233–287 | Chott Marouane and Sebkha Ez-Zemoul lakes, Algeria (North Africa) | [56] | |
| Saltern de Cerrillos, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| A. salina, Phallocryptus spinosa (Milne-Edwards, 1840) | 65–70 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [43,57] | |
| Flamingolepis megalorchis (Luhe, 1898)/cysticercoids | E. mareotica | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [46] |
| Flamingolepis tengizi Gvozdev et Maksimova, 1968/cysticercoids | E. mareotica | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [46] |
| A. salina | 65–70 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [49] | |
| Flamingolepis sp. 1/cysticercoids | A. persimilis | 55–86 | Los Cisnes lagoon, Chile (South America) | [47] |
| A. franciscana | Barros Negros Lagoon (Salar de Atacama), Chile (South America) | [32] | ||
| Flamingolepis sp. 2/cysticercoids | A. franciscana | Chaxas, Tebenquiche and Barros Negros Lagoons (Salar de Atacama), Chile (South America) | [32] | |
| Microsomacanthus paramicrosoma (Gasowska, 1931)/cysticercoids | E. mareotica | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [46] |
| Parabiglandatrium phoenicopteri Gvosdev et Maksimova, 1968/cysticercoids | E. mareotica | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [46] |
| Hymenolepis californicus Young, 1950/cysticercoids | A. franciscana | 105–150 | Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA (North America) | [31] |
| A. salina | Mono lake and salt pools, California, USA (North America) | [58] | ||
| Wardium fusa (Krabbe, 1869)/cysticercoids | A. salina | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [43] |
| Wardium manubriatum Spassky et Dao, 1963/cysticercoids | Phallocryptus spinosa | [49] | ||
| Wardium stellorae (Deblock, Biguet & Capron, 1960)/cysticercoids | A. franciscana | 70–160 | Godolphin lakes, Dubai (Asia) | [39] |
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| A. parthenogenetica | 110 | Odiel and Tinto estuary, SW Spain (Europe) | [35] | |
| Salterns Nuestra Señora del Rocío, Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| Aigues-Mortes saltern, France (Europe) | [40] | |||
| A. salina | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [49] | |
| Saltern de Cerrillos, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| 65–70 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [40] | ||
| Artemia sp. | 133–210 | Salt marshes of Camargue, France (Europe) | [32] | |
| Wardium sp./cysticercoids | A. franciscana | 105–150 | Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA (North America) | [31] |
| A. persimilis | 55 | Los Cisnes and Amarga lagoons, Chile (South America) | [47] | |
| Hymenolepididae gen. sp/cysticercoids | A. parthenogenetica | Saltern Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |
| Fam. Progynotaeniidae Fuhrmann, 1936 Gynandrotaenia stammeri Fuhrmann, 1936/cysticercoids | A. franciscana | 70–160 | Godolphin lakes, Dubai (South-Western Asia) | [39] |
| 80 | Barros Negros Lagoon (Salar de Atacama), Chile (South America) | [32] | ||
| Saltern Castro Marim, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | |||
| River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [38] | |||
| A. parthenogenetica | Salterns Nuestra Señora del Rocío, Portuguesas, Portugal (Europe) | [37] | ||
| 110 | Odiel and Tinto estuary, SW Spain (Europe) | [35] | ||
| 110–200 | Odiel Marshes, Huelva Province, Spain (Europe) | [36] | ||
| 86–209 | Saltern La Tapa, Spain (Europe) | [45] | ||
| Fam. ProgynotaeniidaeFuhrmann, 1936 Gynandrotaenia stammeri Fuhrmann, 1936/cysticercoids | A. salina | 65–80 | Tengiz Lake, Kazakhstan (Middle Asia) | [50,59,60] |
| Saltern de Cerrillos, Portugal (Europe) | [45,61] | |||
| Artemia sp. | 133–210 | salt marshes of Camargue, France (Europe) | [51,52] | |
| Gynandrotaenia sp./cysticercoids | A. franciscana | River Ebro Delta, La Trinitat coastal saltern complex, Spain (Europe) | [40] | |
| Scolex pleuronectis larvae | Fishes | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [26] |
| Phylum NEMATODA Class Nematoda insertae sedis | ||||
| Fam. Acuariidae Railliet, Henry & Sisoff, 1912 Acuariidae fam. gen. sp./larvae | Crustacea: A. franciscana | 105–150 | Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA (North America) | [31] |
| Acuariinae fam. gen. sp./larvae | Saltern La Tapan, Spain (Europe) | [45] | ||
| Fam. Anisakidae Railliet & Henry, 1912 Contracaecum sp./larvae in muscules | Pisces: Anguilla anguilla (Linnaeus, 1758) | 43–47 | coastal lagoon Mar Menor (Iberian Peninsula), Spain (Europe) | [62] |
| Phylum CNIDARIA Class Myxozoa | ||||
| Fam. Myxobolidae Thélohan, 1892 Myxobolus parvus | grey mullets, Dicentrarchus spp. | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [22] |
| Fam. Myxidiidae Thélohan, 1892 Myxidium sp. | grey mullets | |||
| Group III. Endoparasitic adults | ||||
| Phylum PLATHELMINTHES Class Trematoda | ||||
| Fam. Bucephalidae Poche, 1907 Bucephalus anguillae Spakulova, Macko, Berrilli & Dezfuli, 2002/adults | Pisces: Anguilla anguilla (Linnaeus, 1758) | 43–47 | Mar Menor lagoon, Spain (Europe) | [62] |
| Fam. Deropristidae Cable & Hunninen, 1942 Deropristis inflata (Molin, 1859) Odhner, 1902/adults | ||||
| Class Cestoda | ||||
| Fam. Proteocephalidae La Rue, 1911 Proteocephalidae/larvae | Anguilla anguilla | 43–46.5 | Mar Menor lagoon, Spain (Europe) | [62] |
| Phylum NEMATODA Class Nematoda insertae sedis | ||||
| Fam. Anguillicolidae Yamaguti, 1935 Anguillicoloides crassus (Kuwahara, Niimi & Itagaki, 1974) Moravec & Taraschewski, 1988/pre-adults and adults | Anguilla anguilla | 43–47 | Mar Menor lagoon, Spain (Europe) | [62] |
| Contracaecum sp. | ||||
| Phylum ACANTHOCEPHALA Class Eoacanthocephala | ||||
| Fam. Neoechinorhynchidae Ward, 1917 Neoechinorhynchus agilis (Rudolphi, 1819)/adults | Pisces: Mugil cephalus | 50–75 | Bardawil lagoon (Sinai Peninsula), Egypt (Western Asia) | [22] |
| N. agilis/cystacanths and juvenile adults | Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758, Dicentrarchus punctatus (Bloch, 1792), Atherina boyeri Risso, 1810, Hemiramphus far (Forsskål, 1775), Argyrosomus regius (Asso, 1801) | |||
| Fam. Quadrigyridae Van Cleave, 1920 Acanthogyrus (Acanthosentis) tilapiae (Baylis, 1948) Amin, 1985 | Coptodon guineensis (Günther, 1862) | 50–60 | Sebkha Imlili salt flat, Atlantic Sahara (Africa) | [27] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kornyychuk, Y.; Anufriieva, E.; Shadrin, N. Diversity of Parasitic Animals in Hypersaline Waters: A Review. Diversity 2023, 15, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030409
Kornyychuk Y, Anufriieva E, Shadrin N. Diversity of Parasitic Animals in Hypersaline Waters: A Review. Diversity. 2023; 15(3):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030409
Chicago/Turabian StyleKornyychuk, Yuliya, Elena Anufriieva, and Nickolai Shadrin. 2023. "Diversity of Parasitic Animals in Hypersaline Waters: A Review" Diversity 15, no. 3: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030409
APA StyleKornyychuk, Y., Anufriieva, E., & Shadrin, N. (2023). Diversity of Parasitic Animals in Hypersaline Waters: A Review. Diversity, 15(3), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030409








