Resurrection of Diplostomum numericum Niewiadomska, 1988 (Digenea, Diplostomatoidea: Diplostomidae) Based on Novel Molecular Data from the Type-Host
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Morphological Study
2.2. Molecular Data and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
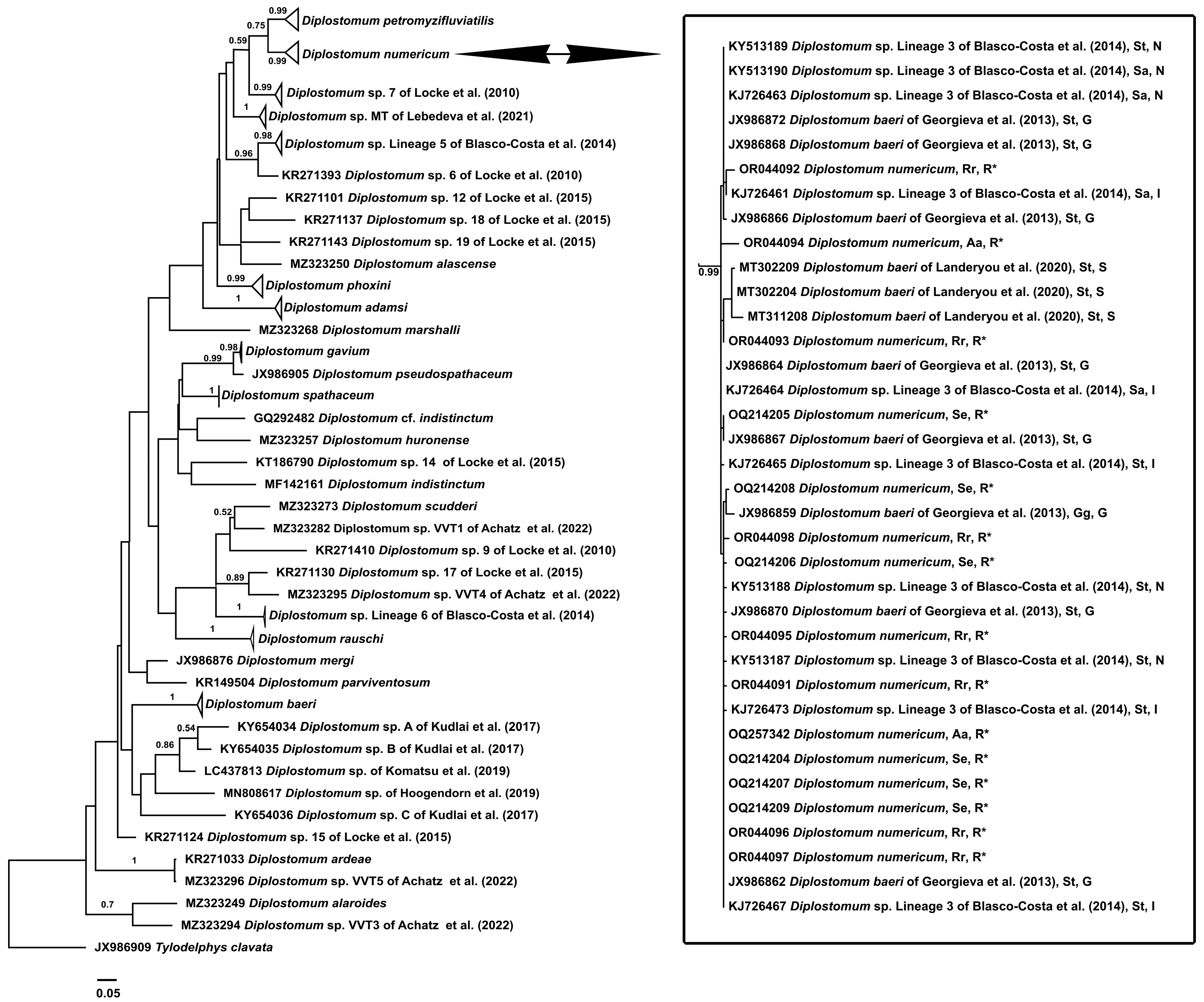
Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nordmann, A.v. Mikrographische Beiträge zur Naturgeschichte der Wirbellosen Thiere; Zweites Heft. Mit zehn Kupfertafeln, G. Reimer: Berlin, Germany, 1832; pp. 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, G. Synopsis des Strigeidae et des Diplostomatidae (Trematoda). Douxième Partie. Mem. Soc. Neuchl. Sci. Nat. 1970, 10, 259–727. [Google Scholar]
- Shigin, A.A. Trematodes of the genus Diplostomum in the biocenosis of the trout farm “Skhodnia”. Trudy Gel'mintologicheskoi Lab. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1980, 30, 140–202. [Google Scholar]
- Shigin, A.A. Trematodes in the Fauna of the USSR: The Genus Diplostomum. Metacercariae; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1986; p. 252. [Google Scholar]
- Shigin, A.A. Trematodes of the Fauna of Russia and Neighbouring Regions. Genus Diplostomum. Adults; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1993; p. 207. [Google Scholar]
- Mikheev, V.N.; Pasternak, A.F.; Taskinen, J.; Valtonen, E.T. Parasite-induced aggression and impaired contest ability in a fish host. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvonen, A.; Marcogliese, D.J. Diplostomiasis (Diplostomum spathaceum and related species). In Climate Change and Infectious Fish Diseases; Woo, P.T.K., Leong, J.-A., Buchmann, K., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2020; pp. 434–456. [Google Scholar]
- Stables, J.N.; Chappell, L.H. The epidemiology of diplostomiasis in farmed rainbow trout from north-east Scotland. Parasitology 1986, 92, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avsever, M.L.; Selver, M.M.; Yazicioğlu, Ö.; Tokşen, E.; Tay, S.; Erdal, G.; Günen, M.Z. The first report of diplostomiasis from cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in Turkey. Ank. Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2016, 63, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Locke, S.A.; McLaughlin, J.D.; Dayanandan, S.; Marcogliese, D.J. Diversity and specificity in Diplostomum spp. metacercariae in freshwater fishes revealed by cytochrome c oxidase I and internal transcribed spacer sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, S.A.; McLaughlin, J.D.; Marcogliese, D.J. DNA barcodes show cryptic diversity and a potential physiological basis for host specificity among Diplostomoidea (Platyhelminthes: Digenea) parasitizing freshwater fishes in the St. Lawrence River, Canada. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 2813–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, S.A.; Al-Nasiri, F.S.; Caffara, M.; Drago, F.; Kalbe, M.; Lapierre, A.R.; McLaughlin, J.D.; Nie, P.; Overstreet, R.M.; Souza, G.T.R.; et al. Diversity, specificity and speciation in larval Diplostomidae (Platyhelminthes: Digenea) in the eyes of freshwater fish, as revealed by DNA barcodes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, S.A.; Van Dam, A.; Caffara, M.; Pinto, H.A.; Blanard, C.A. Validity of the Diplostomoidea and Diplostomida (Digenea, Platyhelminthes) upheld in phylogenomic analysis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, S.A.; Drago, F.B.; Núñez, V.; Souza, G.T.R.E.; Takemoto, R.M. Phylogenetic position of Diplostomum spp. from New World herons based on complete mitogenomes, rDNA operons, and DNA barcodes, including a new species with partially elucidated life cycle. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, S.; Soldánová, M.; Pérez-del-Olmo, A.; Dangel, R.D.; Sitko, J.; Sures, B.; Kostadinova, A. Molecular prospecting for European Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) reveals cryptic diversity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibwana, F.D.; Blasco-Costa, I.; Georgieva, S.; Hosea, K.M.; Nkwengulila, G.; Scholz, T.; Kostadinova, A. A first insight into the barcodes for African diplostomids (Digenea: Diplostomidae): Brain parasites in Clarias gariepinus (Siluriformes: Clariidae). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 17, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco-Costa, I.; Faltýnková, A.; Georgieva, S.; Skírnisson, K.; Scholz, T.; Kostadinova, A. Fish pathogens near the Arctic Circle: Molecular, morphological and ecological evidence for unexpected diversity of Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) in Iceland. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-del-Olmo, A.; Georgieva, S.; Pula, H.J.; Kostadinova, A. Molecular and morphological evidence for three species of Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae), parasites of fishes and fish-eating birds in Spain. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldánová, M.; Georgieva, S.; Rohacova, J.; Knudsen, R.; Kuhn, J.A.; Henriksen, E.H.; Siwertsson, A.; Shaw, J.C.; Kuris, A.M.; Amundsen, P.A.; et al. Molecular analyses reveal high species diversity of trematodes in a sub-Arctic lake. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendoorn, C.; Smit, N.J.; Kudlai, O. Resolution of the identity of three species of Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) parasitising freshwater fishes in South Africa, combining molecular and morphological evidence. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, D.I.; Chrisanfova, G.G.; Ieshko, E.P.; Guliaev, A.S.; Yakovleva, G.A.; Mendsaikhan, B.; Semyenova, S.K. Morphological and molecular differentiation of Diplostomum spp. metacercariae from brain of minnows (Phoxinus phoxinus L.) in four populations of northern Europe and East Asia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 92, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, D.I.; Popov, I.Y.; Yakovleva, G.A.; Zaicev, D.O.; Bugmyrin, S.V.; Makhrov, A.A. No strict host specificity: Brain metacercariae Diplostomum petromyzifluviatilis Müller (Diesing, 1850) are conspecific with Diplostomum sp. Lineage 4 of Blasco-Costa et al. (2014). Parasitol. Int. 2022, 91, 102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwelm, J.; Georgieva, S.; Grabner, D.; Kostadinova, A.; Sures, B. Molecular and morphological characterisation of Diplostomum phoxini (Faust, 1918) with a revised classification and an updated nomenclature of the species-level lineages of Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) sequenced worldwide. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1648–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achatz, T.J.; Martens, J.R.; Kostadinova, A.; Pulis, E.E.; Orlofske, S.A.; Bell, J.A.; Fecchio, A.; Oyarzún-Ruiz, P.; Syrota, Y.Y.; Tkach, V.V. Molecular phylogeny of Diplostomum, Tylodelphys, Austrodiplostomum and Paralaria (Digenea: Diplostomidae) necessitates systematic changes and reveals a history of evolutionary host switching events. Int. J. Parasitol. 2022, 52, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltýnková, A.; Georgieva, S.; Kostadinova, A.; Blasco-Costa, I.; Scholz, T.; Skírnisson, K. Diplostomum von Nordmann, 1832 (Digenea: Diplostomidae) in the sub-Arctic: Descriptions of the larval stages of six species discovered recently in Iceland. Syst. Parasitol. 2014, 89, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiadomska, K. The genus Diplostomum—Taxonomy, morphology and biology. Acta Parasitol. 1996, 41, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Niewiadomska, K. Diplostomum metacercariae (Digenea) in fish of the Dgal Wielki and Warniak lakes: D. numericum sp. n. and D. baeri Dubois, 1937, with comments on the synonymy of this species. Acta Parasitol. 1988, 33, 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Niewiadomska, K. Fauna słodkowodna Polski. 34A. In Przywry (Trematoda).Część ogólna; Część systematyczna—Aspidogastrea, Digenea: Strigeida; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego: Łódź, Poland, 2010; p. 388. [Google Scholar]
- Shigin, A.A.; Stanislavetz, A.N. On the species validity of metacercariae of the genus Diplostomum from the vitreous body of the eyes of freshwater fish. Mater. Nauchnoi Conf. Vsesoyuznogo Obschestva Gel'mintolgov 1989, 38, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Guberlet, J.E. Three new species of Holostomidae. J. Parasitol. 1922, 9, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, A. Studies on the taxonomy and biology of Diplostomum species (Digenea). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stirling, Stirling, UK, 1989; p. 277. [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen, E.T.; Gibson, D.I. Aspects of the Biology of Diplostomid Metacercarial (Digenea) Populations Occurring in Fishes in Different Localities of Northern Finland. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1997, 34, 47–59. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/23735430 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Behrmann-Godel, J. Parasite identification, succession and infection pathways in perch fry (Perca fluviatilis): New insights through a combined morphological and genetic approach. Parasitology 2013, 140, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeryou, T.; Kett, S.M.; Ropiquet, A.; Wildeboer, D.; Lawton, S.P. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Diplostomum baeri. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 79, 102166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltýnková, A.; Kudlai, O.; Pantoja, C.; Yakovleva, G.; Lebedeva, D. Another plea for ‘best practice’ in molecular approaches to trematode systematics: Diplostomum sp. clade Q identified as Diplostomum baeri Dubois, 1937 in Europe. Parasitology 2022, 149, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarikov, V.E.; Shigin, A.A. On the methods for working with metacercariae of the Strigeidida. Trudy Gel'mintologicheskoi Lab. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1965, 15, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lockyer, A.E.; Olson, P.D.; Stergaard, P.; Rollinson, D.; Johnston, D.A.; Attwood, S.W.; Southgate, V.R.; Horak, P.; Snyder, S.D.; Le, T.H.; et al. The phylogeny of the Schistosomatidae based on three genes with emphasis on the interrelationships of Schistosoma Weinland, 1858. Parasitology 2003, 126, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubels, J.L.; DeJong, R.J.; Hoolsema, B.; Wurzberger, A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Blankespoor, H.D.; Blankespoor, C.L. Impairment of retinal function in yellow perch (Perca flavescens) by Diplostomum baeri metacercariae. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 7, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordy, M.A.; Kish, L.; Tarrabain, M.; Hanington, P.C. A comprehensive survey of larval digenean trematodes and their snail hosts in central Alberta, Canada. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3867–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordy, M.A.; Hanington, P.C. A fine-scale phylogenetic assessment of digenean trematodes in central Alberta reveals we have yet to uncover their total diversity. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3153–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcogliese, D.J.; Locke, S.A. Infection of Diplostomum spp. in invasive round gobies in the St Lawrence River, Canada. J. Helminthol. 2021, 95, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selbach, C.; Soldánová, M.; Georgieva, S.; Kostadinova, A.; Sures, B. Integrative taxonomic approach to the cryptic diversity of Diplostomum spp. in lymnaeid snails from Europe with a focus on the ‘Diplostomum mergi’ species complex. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, A.K.; Krassmann, J.; Tsobanidis, K.; MacColl, A.D.C.; Bakker, T.C.M. Strong neutral genetic differentiation in a host, but not in its parasite. Infect. Gen. Evol. 2016, 44, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.A.; Kristoffersen, R.; Knudsen, R.; Jakobsen, J.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Locke, S.A.; Primicerio, R.; Amundsen, P.-A. Parasite communities of two three-spined stickleback populations in subarctic Norway—Effects of a small spatial-scale host introduction. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, J.; Kostadinova, A.; Scholz, T.D.; Littlewood, T.J. Complete mitochondrial genomes and nuclear ribosomal RNA operons of two species of Diplostomum (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda): A molecular resource for taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of important fish pathogens. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, N.; Itoh, N.; Ogawa, K. Worm Cataract of Hatchery-Reared Japanese Dace Tribolodon hakonensis Caused by Diplostomum sp. (Digenea: Diplostomidae). Fish Pathol. 2019, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudlai, O.; Oros, M.; Kostadinova, A.; Georgieva, S. Exploring the diversity of Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) in fishes from the river Danube using DNA mitochondrial barcodes. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1. 4. Molecular Evolution, Phylogenetics and Epidemiology. 2012. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Moszczynska, A.; Locke, S.A.; McLaughlin, J.D.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Crease, T.J. Development of primers for the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I gene in digenetic trematodes (Platyhelminthes) illustrates the challenge of barcoding parasitic helminths. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, G.; Raush, R. Les Strigeata (Trematoda) des Gaviides nord-americans. Rev. Suisse Zool. 1967, 74, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
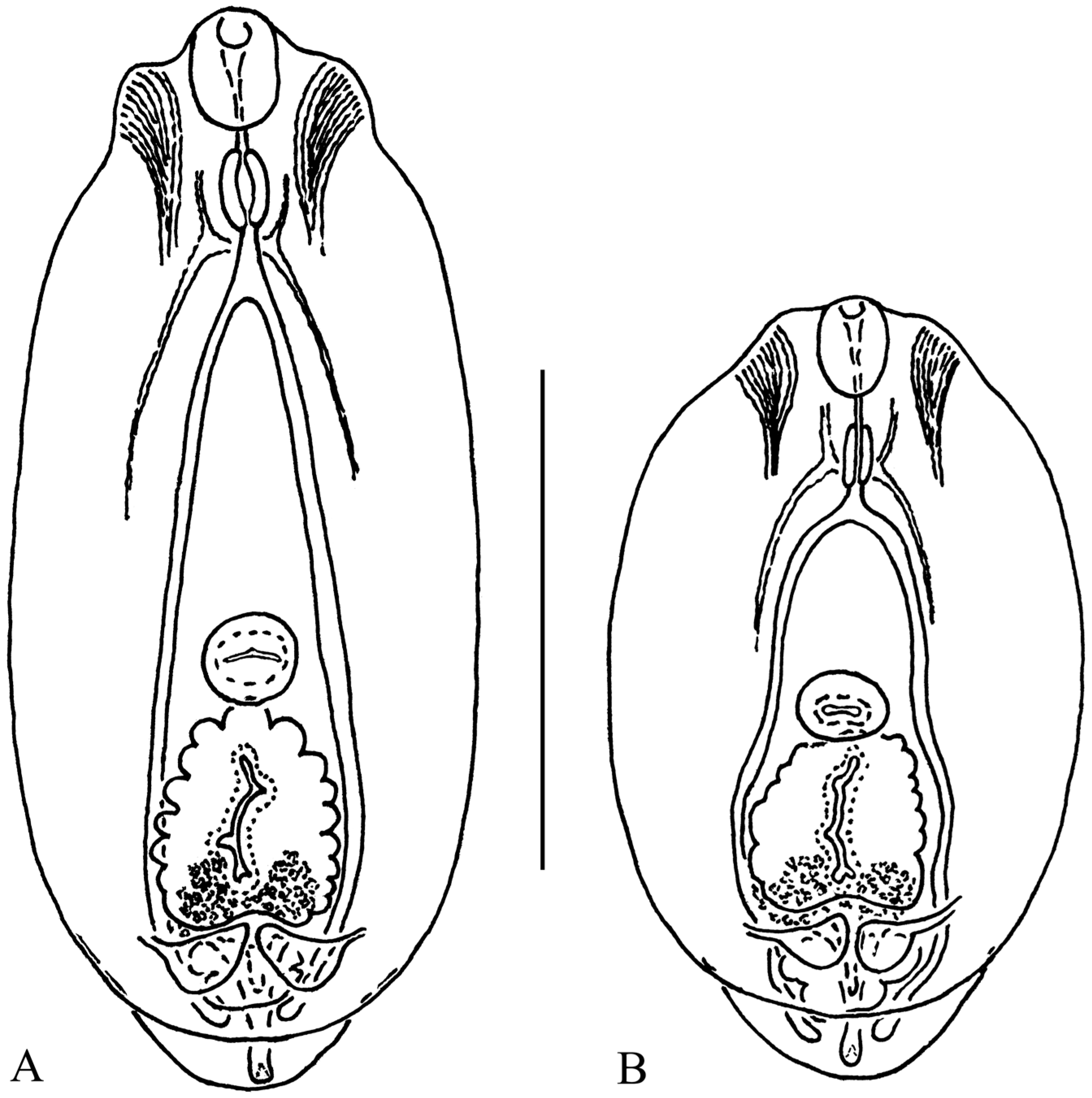
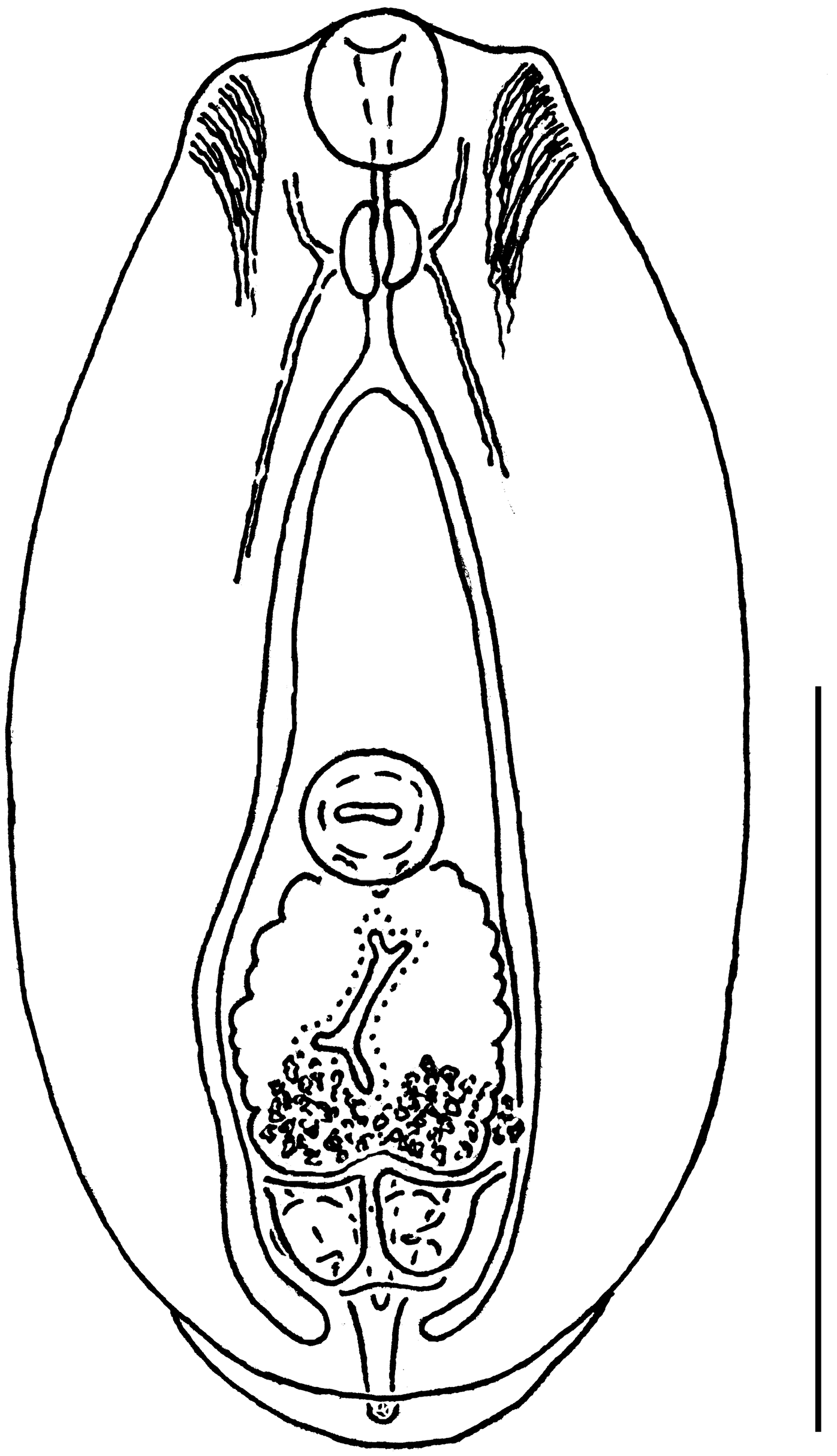
| Characters | Our Material; Range (Mean) | Niewiadomska [27]; Range (Mean) | Shigin and Stanislavetz [29] [as D. vitreophilum]; Range (Mean) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host | Scardinius erythrophthalmus | Rutilus rutilus | Scardinius erythrophthalmus | Rutilus rutilus, *Coregonus albula, *Alburnus alburnus * |
| Total body length (BL), μm | 440–651 (545) | 543–644 (578) | 451–547 (512) | 465–587 (526) |
| Maximum body width (BW), μm | 242–336 (289) | 256–298 (280) | 244–288 (270) | 210–265 (239) |
| Oral sucker length (OL), μm | 52–69 (64) | 58–72 (64) | 51–68 (62) | 48–62 (56) |
| Oral sucker width (OW), μm | 45–55 (50) | 48–58 (52) | 40–54 (47) | 45–58 (51) |
| Pharynx length (PL), μm | 31–48 (40) | 34–52 (42) | 30–42 (37) | 28–40 (33) |
| Pharynx width (PB), μm | 22–31 (27) | 26–34 (32) | 17–30 (24) | 25–35 (29) |
| Ventral sucker length (VL), μm | 41–58 (49) | 50–58 (53) | 40–57 (47) | 43–51 (47) |
| Ventral sucker width (VW), μm | 52–62 (56) | 52–58 (56) | 40–64 (51) | 46–55 (51) |
| Distance from anterior margin of body to center of ventral sucker (O), μm | 242–402 (304) | 298–367 (322) | 234–306 (275) | – |
| Holdfast organ length (HL), μm | 107–144 (124) | 110–138 (120) | 81–119 (98) | 100–130 (112) |
| Holdfast organ width (HW), μm | 103–120 (112) | 103–120 (113) | 74–108 (87) | 92–135 (107) |
| Proteolytic gland length, μm | 28–55 (44) | 41–69 (54) | 23–40 (30) | – |
| Proteolytic gland width, μm | 76–110 (94) | 79–110 (97) | 68–102 (81) | – |
| Number of excretory bodies | 638, 659, 813 | 957, 1088 | ~ 700 | 760–1150 (965) |
| BW/BL, % | 42.62–61.54 (53.32) | 43.09–53.75 (48.52) | 40.67–58.42 (52.39) | 41.70–50.50 (45.50) |
| O/BL, % | 50.63–61.70 (55.61) | 52.49–58.33 (55.62) | 50.38–55.94 (53.74) | 51.30–56.60 (54.50) |
| [BL × BW]/[VL × VW] | 43.43–77.17 (57.69) | 45.05–63.27 (54.52) | 41.89–78.64 (58.40) | 43.20–58.90 (53.10) |
| [BL × BW]/[HL × HW] | 9.87–14.22 (11.38) | 10.54–13.21 (11.99) | 11.35–20.46 (16.51) | 8.37–12.89 (10.58) |
| [OL × OW]/[VL × VW] | 0.94–1.34 (1.15) | 0.96–1.31 (1.13) | 0.94–1.84 (1.22) | 1.06–1.39 (1.21) |
| [HL × HW]/[VL × VW] | 4.13–6.25 (5.10) | 3.76–5.47 (4.56) | 2.63–5.04 (3.63) | 3.89–7.02 (5.02) |
| [OL × OW]/[PL × PW] | 2.08–3.72 (2.94) | 1.90–3.36 (2.57) | 2.13–4.21 (3.22) | 2.29–3.79 (3.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokolov, S.G.; Ieshko, E.P.; Lebedeva, D.I. Resurrection of Diplostomum numericum Niewiadomska, 1988 (Digenea, Diplostomatoidea: Diplostomidae) Based on Novel Molecular Data from the Type-Host. Diversity 2023, 15, 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070840
Sokolov SG, Ieshko EP, Lebedeva DI. Resurrection of Diplostomum numericum Niewiadomska, 1988 (Digenea, Diplostomatoidea: Diplostomidae) Based on Novel Molecular Data from the Type-Host. Diversity. 2023; 15(7):840. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070840
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokolov, Sergey G., Evgeny P. Ieshko, and Daria I. Lebedeva. 2023. "Resurrection of Diplostomum numericum Niewiadomska, 1988 (Digenea, Diplostomatoidea: Diplostomidae) Based on Novel Molecular Data from the Type-Host" Diversity 15, no. 7: 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070840
APA StyleSokolov, S. G., Ieshko, E. P., & Lebedeva, D. I. (2023). Resurrection of Diplostomum numericum Niewiadomska, 1988 (Digenea, Diplostomatoidea: Diplostomidae) Based on Novel Molecular Data from the Type-Host. Diversity, 15(7), 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070840









