Mitochondrial Genetic Mutations in the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly: Possible DNA Damage via the Fukushima Nuclear Accident and Real-Time Molecular Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Butterfly Species and Subspecies
2.2. Butterfly Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR
2.4. DNA Sequencing and Sequence Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Seven Localites in 2011–2013
3.2. Offspring F1 Generation
3.3. Northeastern Japan and Okinawa
3.4. Additional Individuals from Fukushima and Hirono
3.5. Zizeeria maha maha and Zizeeria karsandra
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of Homoplasmic and Heteroplasmic Nonsynonymous Substitutions
4.2. Real-Time Molecular Evolution of COI
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| COI | Cytochrome oxidase subunit I |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EMS | Ethyl methane sulfonate |
| FDNPP | Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant |
| ICRP | International Commission on Radiological Protection |
| Myr | Million years ago |
| ND5 | NADH dehydrogenase 5 |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
References
- D’Mello, J.P.F. (Ed.) Preface. In A Handbook of Environmental Toxicology: Human Disorders and Ecotoxicology; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2020; pp. xxv–xxxvi. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, S.; Ugawa, S.; Nanko, K.; Shichi, K. The total amounts of radioactively contaminated materials in forests in Fukushima, Japan. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, K. Atmospheric effects of Fukushima nuclear accident: A review from a sight of atmospheric monitoring. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 218, 106240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onda, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Kato, H.; Takahashi, J.; Wakiyama, Y.; Coppin, F.; Smith, H. Radionuclides from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in terrestrial systems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Environmental protection–The concept and use of reference animals and plants. ICRP Publication 108. Ann. ICRP 2008, 38, 1–242. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, A.P.; Mousseau, T.A. Low-dose radiation, scientific scrutiny, and requirements for demonstrating effects. BMC Biol. 2013, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, T.Y.; Mousseau, T. Outcomes of Fukushima: Biological effects of radiation on nonhuman species. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mousseau, T.A.; Møller, A.P. Genetic and ecological studies of animals in Chernobyl and Fukushima. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.S.; Ramli, A.T.; Garba, N.N.; Saleh, M.A.; Gabdo, H.T.; Liman, M.S. Fukushima nuclear accident: Preliminary assessment of the risks to non-human biota. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 163, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.S.; Evangeliou, N.; Mousseau, T.A.; Wu, J.; Ramli, A.T. An overview of current knowledge concerning the health and environmental consequences of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaoki, M. Studies on radiation effects from the Fukushima nuclear accident on wild organisms and ecosystems. Glob. Environ. Res. 2016, 20, 073–082. [Google Scholar]
- Bréchignac, F.; Oughton, D.; Mays, C.; Barnthouse, L.; Beasley, J.C.; Bonisoli-Alquati, A.; Bradshaw, C.; Brown, J.; Dray, S.; Geras’kin, S.; et al. Addressing ecological effects of radiation on populations and ecosystems to improve protection of the environment against radiation: Agreed statements from a Consensus Symposium. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 158–159, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vives i Batlle, J.; Aono, T.; Brown, J.E.; Hosseini, A.; Garnier-Laplace, J.; Sazykina, T.; Steenhuisen, F.; Strand, P. The impact of the Fukushima nuclear accident on marine biota: Retrospective assessment of the first year and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, P.; Sundell-Bergman, S.; Brown, J.E.; Dowdall, M. On the divergences in assessment of environmental impacts from ionising radiation following the Fukushima accident. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 169–170, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, G.; Kiang, J.G. A review of the impact on the ecosystem after ionizing irradiation: Wildlife population. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiniwa, H.; Okano, T.; Endoh, D.; Hirayama, H.; Yoshioka, A.; Yokohata, Y.; Shindo, J.; Koshimoto, C.; Shinohara, A.; Sakamoto, S.H.; et al. Oxidative stress on the male reproductive organs of wild mice collected from an area contaminated by radioactive materials in Fukushima. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyoshi, K.; Miura, T.; Kasai, K.; Goh, V.S.T.; Fujishima, Y.; Nakata, A.; Takahashi, A.; Shimizu, Y.; Shinoda, H.; Yamashiro, H.; et al. Environmental radiation on large Japanese field mice in Fukushima reduced colony forming potential in hematopoietic progenitor cells without inducing genomic instability. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, Y.; Nakata, A.; Ujiie, R.; Kasai, K.; Ariyoshi, K.; Goh, V.S.T.; Suzuki, K.; Tazoe, H.; Yamada, M.; Yoshida, M.A.; et al. Assessment of chromosome aberrations in large Japanese field mice (Apodemus speciosus) in Namie Town, Fukushima. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagoshi, T.; Shiomi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Fuma, S.; Doi, K.; Kawaguchi, I.; Aoki, M.; Kubota, M.; Furuhata, Y.; et al. Chromosomal aberrations in large Japanese field mice (Apodemus speciosus) captured near Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4632–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, Y.; Tsuji, H.; Kawagoshi, T.; Shiomi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Fuma, S.; Doi, K.; Kawaguchi, I.; Aoki, M.; et al. Chromosomal aberrations in wild mice captured in areas differentially contaminated by the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10074–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Belli, M.; De Rubeis, M.; Tokita, S.; Ikema, H.; Yamashiro, H.; Fujishima, Y.; Anderson, D.; Goh, V.S.T.; Shinoda, H.; et al. Ultrastructural analysis of large Japanese field mouse (Apodemus speciosus) testes exposed to low-dose-rate (LDR) radiation after the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accident. Biology 2024, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproull, M.; Hayes, J.; Ishiniwa, H.; Nanba, K.; Shankavaram, U.; Camphausen, K.; Johnson, T.E. Proteomic biomarker analysis of serum from Japanese field mice (Apodemus Speciosus) collected within the Fukushima difficult-to-return zone. Health Phys. 2021, 121, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, T.; Ishiniwa, H.; Onuma, M.; Shindo, J.; Yokohata, Y.; Tamaoki, M. Effects of environmental radiation on testes and spermatogenesis in wild large Japanese field mice (Apodemus speciosus) from Fukushima. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, H.; Abe, Y.; Hayashi, G.; Urushihara, Y.; Kuwahara, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kobayashi, J.; Kino, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Tong, B.; et al. Electron probe X-ray microanalysis of boar and inobuta testes after the Fukushima accident. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56 (Suppl. S1), i42–i47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, K.; Hinton, T.G.; Luxton, J.J.; Bordman, A.; Okuda, K.; Taylor, L.E.; Hayes, J.; Gerke, H.C.; Chinn, S.M.; Anderson, D.; et al. Evaluation of DNA damage and stress in wildlife chronically exposed to low-dose, low-dose rate radiation from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Murata, K.; Yamashiro, H.; Goh, V.S.T.; Nakayama, R.; Fujishima, Y.; Ono, T.; Kino, Y.; Simizu, Y.; et al. Morphological reproductive characteristics of testes and fertilization capacity of cryopreserved sperm after the Fukushima accident in raccoon (Procyon lotor). Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2021, 56, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.J.; Suzuki, M.; Redon, C.E.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashiro, H.; Abe, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Fukuda, T.; Isogai, E.; Bonner, W.M.; et al. The causal relationship between DNA damage induction in bovine lymphocytes and the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accident. Radiat. Res. 2017, 187, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, I.; Sasaki, J.; Satoh, H.; Natsuhori, M.; Murata, T.; Okada, K. Assessments of DNA damage and radiation exposure dose in cattle living in the contaminated area caused by the Fukushima Nuclear Accident. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikami, D.; Sayama, N.; Sasaki, J.; Kusuno, H.; Matsuzaki, H.; Hayashi, A.; Nakamura, T.; Satoh, H.; Natsuhori, M.; Okada, K.; et al. The effect of exposure on cattle thyroid after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, J.; Uehara, M.; Sato, I.; Satoh, H.; Deguchi, Y.; Chida, H.; Natsuhori, M.; Murata, T.; Ochiai, K.; Otani, K.; et al. Pathological characteristics of thyroid glands from Japanese Black Cattle living in the restricted area of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonisoli-Alquati, A.; Koyama, K.; Tedeschi, D.J.; Kitamura, W.; Sukuzi, H.; Ostermiller, S.; Arai, E.; Møller, A.P.; Mousseau, T.A. Abundance and genetic damage of barn swallows from Fukushima. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, A.P.; Hagiwara, A.; Matsui, S.; Kasahara, S.; Kawatsu, K.; Nishiumi, I.; Suzuki, H.; Ueda, K.; Mousseau, T.A. Abundance of birds in Fukushima as judged from Chernobyl. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 164, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Murase, J.; Horie, R.; Endo, K. Effects of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident on goshawk reproduction. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier-Laplace, J.; Beaugelin-Seiller, K.; Della-Vedova, C.; Métivier, J.M.; Ritz, C.; Mousseau, T.A.; Møller, A.P. Radiological dose reconstruction for birds reconciles outcomes of Fukushima with knowledge of dose-effect relationships. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, Y.; Shirai, K.; Kubota, K.; Togashi, H.; Morita, T. Relationship between stable cesium concentration and body size of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus and the effect of a size-dependent shift in diet. J. Fish Biol. 2024, 104, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerebours, A.; Regini, J.; Quinlan, R.A.; Wada, T.; Pierscionek, B.; Devonshire, M.; Kalligeraki, A.A.; Uwineza, A.; Young, L.; Girkin, J.M.; et al. Evaluation of cataract formation in fish exposed to environmental radiation at Chernobyl and Fukushima. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 165957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, T.; Yoshii, H.; Mizuno, S.; Shiraishi, H. Decline in intertidal biota after the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami and the Fukushima nuclear disaster: Field observations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, S. Morphological abnormalities in gall-forming aphids in a radiation-contaminated area near Fukushima Daiichi: Selective impact of fallout? Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, S.I.; Li, Y.; Imanaka, T.; Sato, H.; Ishida, K. Effects of Radiation From Contaminated Soil and Moss in Fukushima on Embryogenesis and Egg Hatching of the Aphid Prociphilus oriens. J. Hered. 2018, 109, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M.; Kajihara, R.; Kato, Y.; Takano-Shimizu, T.; Inoue, Y. Frequencies of chromosomal inversions in Drosophila melanogaster in Fukushima after the nuclear power plant accident. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, A.; Mishima, Y.; Fukasawa, K. Pollinators and other flying insects inside and outside the Fukushima evacuation zone. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.; Smith, J.T.; Takase, T.; Ford, A.T.; Wada, T. Radiocaesium accumulation and fluctuating asymmetry in the Japanese mitten crab, Eriocheir japonica, along a gradient of radionuclide contamination at Fukushima. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292 Pt B, 118479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousseau, T.A.; Møller, A.P. Plants in the light of ionizing radiation: What have we learned from Chernobyl, Fukushima, and other “hot” places? Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludovici, G.M.; Chierici, A.; de Souza, S.O.; d’Errico, F.; Iannotti, A.; Malizia, A. Effects of ionizing radiation on flora ten years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi disaster. Plants 2022, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Ichikawa, S.; Kubota, M.; Hoshino, J.; Kubota, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Fuma, S.; Kawaguchi, I.; Yoschenko, V.I.; Yoshida, S. Morphological defects in native Japanese fir trees around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoschenko, V.; Nanba, K.; Yoshida, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Takase, T.; Sato, N.; Keitoku, K. Morphological abnormalities in Japanese red pine (Pinus densiflora) at the territories contaminated as a result of the accident at Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Plant. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 165, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, V.; Geras’kin, S.; Bondarenko, E.; Yoschenko, V.; Bondarenko, S.; Khanova, A.; Garbaruk, D.; Nanba, K. Comparative analysis of epigenetic variability in two pine species exposed to chronic radiation in the Chernobyl and Fukushima affected zones. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, G.; Shibato, J.; Imanaka, T.; Cho, K.; Kubo, A.; Kikuchi, S.; Satoh, K.; Kimura, S.; Ozawa, S.; Fukutani, S.; et al. Unraveling low-level gamma radiation–Responsive changes in expression of early and late genes in leaves of rice seedlings at Iitate Village, Fukushima. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakwal, R.; Hayashi, G.; Shibato, J.; Deepak, S.A.; Gundimeda, S.; Simha, U.; Padmanaban, A.; Gupta, R.; Han, S.I.; Kim, S.T.; et al. Progress toward rice seed OMICS in low-level gamma radiation environment in Iitate Village, Fukushima. J. Hered. 2018, 109, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakauchi, K.; Otaki, J.M. Soil microbes and plant-associated microbes in response to radioactive pollution may indirectly affect plants and insect herbivores: Evidence for indirect field effects from Chernobyl and Fukushima. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushihara, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Ohtaki, M.; Kuwahara, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Uno, T.; Fujita, S.; Saito, A.; Yamashiro, H.; et al. Haematological analysis of Japanese macaques (Macaca fuscata) in the area affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, K.; Hayama, S.; Nakiri, S.; Nakanishi, S.; Ishii, N.; Uno, T.; Kato, T.; Konno, F.; Kawamoto, Y.; Tsuchida, S.; et al. Low blood cell counts in wild Japanese monkeys after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayama, S.I.; Tsuchiya, M.; Ochiai, K.; Nakiri, S.; Nakanishi, S.; Ishii, N.; Kato, T.; Tanaka, A.; Konno, F.; Kawamoto, Y.; et al. Small head size and delayed body weight growth in wild Japanese monkey fetuses after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayama, S.I.; Nakanishi, S.; Tanaka, A.; Konno, F.; Kawamoto, Y.; Omi, T. Influence of radiation exposure to delayed fetal growth in wild Japanese monkeys after the Fukushima accident. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1151361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, S.I.; Nakanishi, S.; Tanaka, A.; Kato, T.; Watanabe, C.; Kikuchi, N.; Danjo, R.; Matsuda, A.; Mori, W.; Kawabata, Y.; et al. Decline in the conception rate of wild Japanese monkeys after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 86, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherb, H.; Hayashi, K. Spatiotemporal association of low birth weight with Cs-137 deposition at the prefecture level in Japan after the Fukushima nuclear power plant accidents: An analytical-ecologic epidemiological study. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körblein, A. Perinatal mortality after the Fukushima nuclear accident: An ecological study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körblein, A.; Küchenhoff, H. Perinatal mortality after the Fukushima accident: A spatiotemporal analysis. J. Radiol. Prot. 2019, 39, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherb, H.H.; Mori, K.; Hayashi, K. Increases in perinatal mortality in prefectures contaminated by the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident in Japan: A spatially stratified longitudinal study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Murase, J.; Machidori, K.; Mizuno, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Kohri, K. Nationwide increase in cryptorchidism after the Fukushima nuclear accident. Urology 2018, 118, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Murase, J.; Mishima, A. Nationwide increase in complex congenital heart diseases after the Fukushima nuclear accident. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e009486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, J.M. Fukushima nuclear accident: Potential health effects inferred from butterfly and human cases. In A Handbook of Environmental Toxicology: Human Disorders and Ecotoxicology; D’Mello, J.P.F., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2020; pp. 497–514. [Google Scholar]
- Hiyama, A.; Nohara, C.; Kinjo, S.; Taira, W.; Gima, S.; Tanahara, A.; Otaki, J.M. The biological impacts of the Fukushima nuclear accident on the pale grass blue butterfly. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiyama, A.; Nohara, C.; Taira, W.; Kinjo, S.; Iwata, M.; Otaki, J.M. The Fukushima nuclear accident and the pale grass blue butterfly: Evaluating biological effects of long-term low-dose exposures. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, C.; Hiyama, A.; Taira, W.; Tanahara, A.; Otaki, J.M. The biological impacts of ingested radioactive materials on the pale grass blue butterfly. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohara, C.; Taira, W.; Hiyama, A.; Tanahara, A.; Takatsuji, T.; Otaki, J.M. Ingestion of radioactively contaminated diets for two generations in the pale grass blue butterfly. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiyama, A.; Taira, W.; Nohara, C.; Iwasaki, M.; Kinjo, S.; Iwata, M.; Otaki, J.M. Spatiotemporal abnormality dynamics of the pale grass blue butterfly: Three years of monitoring (2011–2013) after the Fukushima nuclear accident. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, W.; Nohara, C.; Hiyama, A.; Otaki, J.M. Fukushima’s biological impacts: The case of the pale grass blue butterfly. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taira, W.; Hiyama, A.; Nohara, C.; Sakauchi, K.; Otaki, J.M. Ingestional and transgenerational effects of the Fukushima nuclear accident on the pale grass blue butterfly. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56 (Suppl. S1), i2–i18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, J.M.; Taira, W. Current Status of the Blue Butterfly in Fukushima Research. J. Hered. 2018, 109, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, J.M. Fukushima’s lessons from the blue butterfly: A risk assessment of the human living environment in the post-Fukushima era. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2016, 12, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, J.M.; Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W. The second decade of the blue butterfly in Fukushima: Untangling the ecological field effects after the Fukushima nuclear accident. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, W.; Toki, M.; Kakinohana, K.; Sakauchi, K.; Otaki, J.M. Developmental and hemocytological effects of ingesting Fukushima’s radiocesium on the cabbage white butterfly Pieris rapae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, R.D.; Taira, W.; Sakauchi, K.; Iwata, M.; Hiyama, A.; Otaki, J.M. Tolerance of high oral doses of nonradioactive and radioactive caesium chloride in the pale grass blue butterfly Zizeeria maha. Insects 2019, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaki, J.M. Understanding low-dose exposure and field effects to resolve the field-laboratory paradox: Multifaceted biological effects from the Fukushima nuclear accident. In New Trends in Nuclear Science; Awwad, N.S., AlFaify, S.A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Metabolomic profiles of the creeping wood sorrel Oxalis corniculata in radioactively contaminated fields in Fukushima: Dose-dependent changes in key metabolites. Life 2022, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Metabolomic response of the creeping wood sorrel Oxalis corniculata to low-dose radiation exposure from Fukushima’s contaminated soil. Life 2021, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Toki, M.; Tsuhako, M.; Umetsu, K.; Otaki, J.M. Nutrient imbalance of the host plant for larvae of the pale grass blue butterfly may mediate the field effect of low-dose radiation exposure in Fukushima: Dose-dependent changes in the sodium content. Insects 2021, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A.; Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Ingestional Toxicity of radiation-dependent metabolites of the host plant for the pale grass blue butterfly: A mechanism of field effects of radioactive pollution in Fukushima. Life 2022, 12, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.; Vo, N.T.K.; Omar-Nazir, L.; Batlle, J.V.I.; Otaki, J.M.; Hiyama, A.; Byun, S.H.; Seymour, C.B.; Mothersill, C. Transgenerational effects of historic radiation dose in pale grass blue butterflies around Fukushima following the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant meltdown accident. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Hiyama, A.; Imanaka, T.; Otaki, J.M. The pale grass blue butterfly in ex-evacuation zones 5.5 years after the Fukushima nuclear accident: Contributions of initial high-dose exposure to transgenerational effects. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakauchi, K.; Otaki, J.M. Imaging plate autoradiography for ingested anthropogenic cesium-137 in butterfly bodies: Implications for the biological impacts of the Fukushima nuclear accident. Life 2023, 13, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Toki, M.; Iraha, Y.; Otaki, J.M. Overwintering States of the pale grass blue butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) at the time of the Fukushima nuclear accident in March 2011. Insects 2019, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombeau, K.; Bonzom, J.M.; Cavalié, I.; Camilleri, V.; Orjollet, D.; Dubourg, N.; Beaugelin-Seiller, K.; Bourdineaud, J.P.; Lengagne, T.; Armant, O.; et al. Dose-dependent genomic DNA hypermethylation and mitochondrial DNA damage in Japanese tree frogs sampled in the Fukushima Daiichi area. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 225, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, M.F.B.; Kwada, G.; Enomoto, M.; Tomiya, A.; Watanabe, M.; Morishita, D.; Izumi, S.; Nakajima, M. Mutations observed in mitochondrial DNA of salmon collected in Mano river, Fukushima prefecture, Japan. In Low-Dose Radiation Effects on Animals and Ecosystems: Long-Term Study on the Fukushima Nuclear Accident; Fukumoto, M., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, M.F.B.; Kawada, G.; Enomoto, M.; Tomiya, A.; Watanabe, M.; Morishita, D.; Izumi, S.; Nakajima, M. Effect of radiocesium on mitochondrial DNA sequence in Masu salmon. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 2017, 83, 814. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Kaneko, S.; Harshman, A.; Okuda, K.; Takagi, T.; Chinn, S.; Beasley, J.C.; Nanba, K.; Ishiniwa, H.; Hinton, T.G. Radiocesium accumulation and germline mutations in chronically exposed wild boar from Fukushima, with radiation doses to human consumers of contaminated meat. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Negishi, Y.; Ishiniwa, H.; Okuda, K.; Hinton, T.G.; Toma, R.; Nagata, J.; Tamate, H.B.; Kaneko, S. Introgression dynamics from invasive pigs into wild boar following the March 2011 natural and anthropogenic disasters at Fukushima. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20210874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, K.; Niwamoto, R.; Horie, J.; Murase, J.; Saito, M.; Kodera, Y.; Okuda, K.; Koganezawa, M.; Sato, T. Large microsatellite shifts in wild boar after the Fukushima accident. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 35, e02059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.T.; Willey, N.J.; Hancock, J.T. Low dose ionizing radiation produces too few reactive oxygen species to directly affect antioxidant concentrations in cells. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivo, P.D.; Van de Walle, M.J.; Laipis, P.J.; Hauswirth, W.W. Nucleotide sequence evidence for rapid genotypic shifts in the bovine mitochondrial DNA D-loop. Nature 1983, 306, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Shitara, H.; Horii, T.; Nagao, Y.; Imai, H.; Abe, K.; Hara, T.; Hayashi, J.; Yonekawa, H. The mitochondrial bottleneck occurs without reduction of mtDNA content in female mouse germ cells. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, L.M.; Samuels, D.C.; de Sousa Lopes, S.C.; Rajasimha, H.K.; Wonnapinij, P.; Mann, J.R.; Dahl, H.H.; Chinnery, P.F. A reduction of mitochondrial DNA molecules during embryogenesis explains the rapid segregation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, T.; Teoli, D.; Shoubridge, E.A. The mitochondrial DNA genetic bottleneck results from replication of a subpopulation of genomes. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuppen, H.A.; Blakely, E.L.; Turnbull, D.M.; Taylor, R.W. Mitochondrial DNA mutations and human disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1797, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahier, A.; Dai, C.Y.; Tweedie, A.; Bezawork-Geleta, A.; Kirmes, I.; Zuryn, S. Affinity purification of cell-specific mitochondria from whole animals resolves patterns of genetic mosaicism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Duanmu, X.; Zeng, L.; Liu, B.; Song, Z. Mitochondrial DNA: Distribution, mutations, and elimination. Cells 2019, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.C.; Chalkia, D. Mitochondrial DNA genetics and the heteroplasmy conundrum in evolution and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a021220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Als, T.D.; Vila, R.; Kandul, N.P.; Nash, D.R.; Yen, S.H.; Hsu, Y.F.; Mignault, A.A.; Boomsma, J.J.; Pierce, N.E. The evolution of alternative parasitic life histories in large blue butterflies. Nature 2004, 432, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandul, N.P.; Lukhtanov, V.A.; Dantchenko, A.V.; Coleman, J.W.S.; Sekercioglu, C.H.; Haig, D.; Pierce, N.E. Phylogeny of Agrodiaetus Hübner 1822 (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) inferred from mtDNA sequences of COI and COII and nuclear sequences of EF1-α: Karyotype diversification and species radiation. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 278–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megens, H.-J.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; Piel, W.H.; Pierce, N.E.; de Jong, R. Tempo of speciation in a butterfly genus from the Southeast Asian tropics, inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequence data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 31, 1181–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; de Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270 (Suppl. S1), S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuret, V.H. Zizeeria karsandra Moore in Europa und die systematische Stellung der Zizeerinae (Lepidoptera, Lycaenidae). Mitt. Ent. Ges. Basel (n.f.) 1955, 5, 123–130. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Shirôzu, T. Butterflies in Formosa in Colour; Hoikusha: Osaka, Japan, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Shirôzu, T. The Standard of Butterflies in Japan; Gakken: Tokyo, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yago, M.; Odagiri, K. Lycaenidae. In Iconographia Insectorum Japonicorum Colore Naturali, Vol I (Lepidoptera); Yata, O., Ed.; Hokuryukan: Tokyo, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yago, M.; Hirai, N.; Kondo, M.; Tanikawa, T.; Ishii, M.; Wang, M.; Williams, M.; Ueshima, R. Molecular systematics and biogeography of the genus Zizina (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Zootaxa 2008, 1746, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, S.; Nagahara, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Yago, M. Filed Guide to the Butterflies of Japan; Expanded and Revised Edition; Japan Butterfly Conservation Society, Ed.; Seibundo Shinkosha: Tokyo, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hiyama, A.; Otaki, J.M. Dispersibility of the pale grass blue butterfly Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) revealed by one-individual tracking in the field: Quantitative comparisons between subspecies and between sexes. Insects 2020, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakauchi, K.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Instruction, table, picture sheet, and original pictures: Morphological abnormalities in the field samples of the pale grass blue butterfly for three years after the Fukushima nuclear accident. In Figshare Collection; Figshare: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyama, A.; Taira, W.; Iwasaki, M.; Sakauchi, K.; Gurung, R.; Otaki, J.M. Geographical distribution of morphological abnormalities and wing color pattern modifications of the pale grass blue butterfly in northeastern Japan. Entomol. Sci. 2017, 20, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzanowski, A.; Ostell, J. The Genetic Codes. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), Bethesda, Maryland, USA. Updated on 23 September 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Utils/wprintgc.cgi#SG5 (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Otaki, J.M.; Hiyama, A.; Iwata, M.; Kudo, T. Phenotypic plasticity in the range-margin population of the lycaenid butterfly Zizeeria maha. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Yamada, A.; Kawanishi, Y.; Gurung, R.D.; Sasaki, T.; Tokuda, G.; Maekawa, H. Widespread distribution and evolutionary patterns of mariner-like elements among various spiders and insects. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericol. 2015, 84, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, A.Y.; Storer, C.; Carvalho, A.P.S.; Plotkin, D.M.; Condamine, F.L.; Braga, M.P.; Ellis, E.A.; St Laurent, R.A.; Li, X.; Barve, V.; et al. A global phylogeny of butterflies reveals their evolutionary history, ancestral hosts and biogeographic origins. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.W.; Ji, Y.; Emerson, B.C.; Wang, X.; Ye, C.; Yang, C.; Ding, Z. Biodiversity soup: Metabarcoding of arthropods for rapid biodiversity assessment and biomonitoring. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Akhtar, S.; Khan, A.M.; Adamowicz, S.J.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcode analysis of butterfly species from Pakistan points towards regional endemism. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, T.; Miura, K.; Miyatake, T. Wolbachia density changes seasonally amongst populations of the pale grass blue butterfly, Zizeeria maha (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Sabir, J.S.M.; El-Ansary, H.O.; Perez, K.; Levesque-Beaudin, V.; Khan, A.M.; Rasool, A.; Gallant, C.; Addesi, J.; Hebert, P.D.N. Insect diversity in the Saharo-Arabian region: Revealing a little-studied fauna by DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, M.V.; Laipis, P.J.; Hauswirth, W.W. Rapid segregation of heteroplasmic bovine mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 7325–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solignac, M.; Monnerot, M.; Mounolou, J.C. Mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in Drosophila mauritiana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 6942–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, L.R.; Singh, R.S. Extensive variation and heteroplasmy in size of mitochondrial DNA among geographic populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8813–8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.G.; Rand, D.M.; Wheeler, W.C. Mitochondrial DNA size variation within individual crickets. Science 1985, 228, 1446–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D.M.; Harrison, R.G. Mitochondrial DNA transmission genetics in crickets. Genetics 1986, 114, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.; Posada, D.; Zardoya, R. MtArt: A new model of amino acid replacement for Arthropoda. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and the Secretariat of the Nuclear Regulation Authority. Radioactivity Concentration Analysis of Iodine in the Distribution Survey of Radioactive Substances. Japan Atomic Energy Agency. 2014. Available online: https://emdb.jaea.go.jp/emdb_old/en/portals/b1020311/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- St Johnston, D. The art and design of genetic screens: Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bökel, C. EMS screens: From mutagenesis to screening and mapping. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 420, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Hiyama, A.; Otaki, J.M. System-dependent regulations of colour-pattern development: A mutagenesis study of the pale grass blue butterfly. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemers, M.; Fiedler, K. Does the DNA barcoding gap exist?—A case study in blue butterflies (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Front. Zool. 2007, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckerkandl, E.; Pauling, L. Molecular disease, evolution, and genetic heterogeneity. In Horizons in Biochemistry; Kasha, M., Pullman, B., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1962; pp. 189–225. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Ho, S.Y. Molecular clocks. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R399–R402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohara, C.; Hiyama, A.; Taira, W.; Otaki, J.M. Robustness and radiation resistance of the pale grass blue butterfly from radioactively contaminated areas: A possible case of adaptive evolution. J. Hered. 2018, 109, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



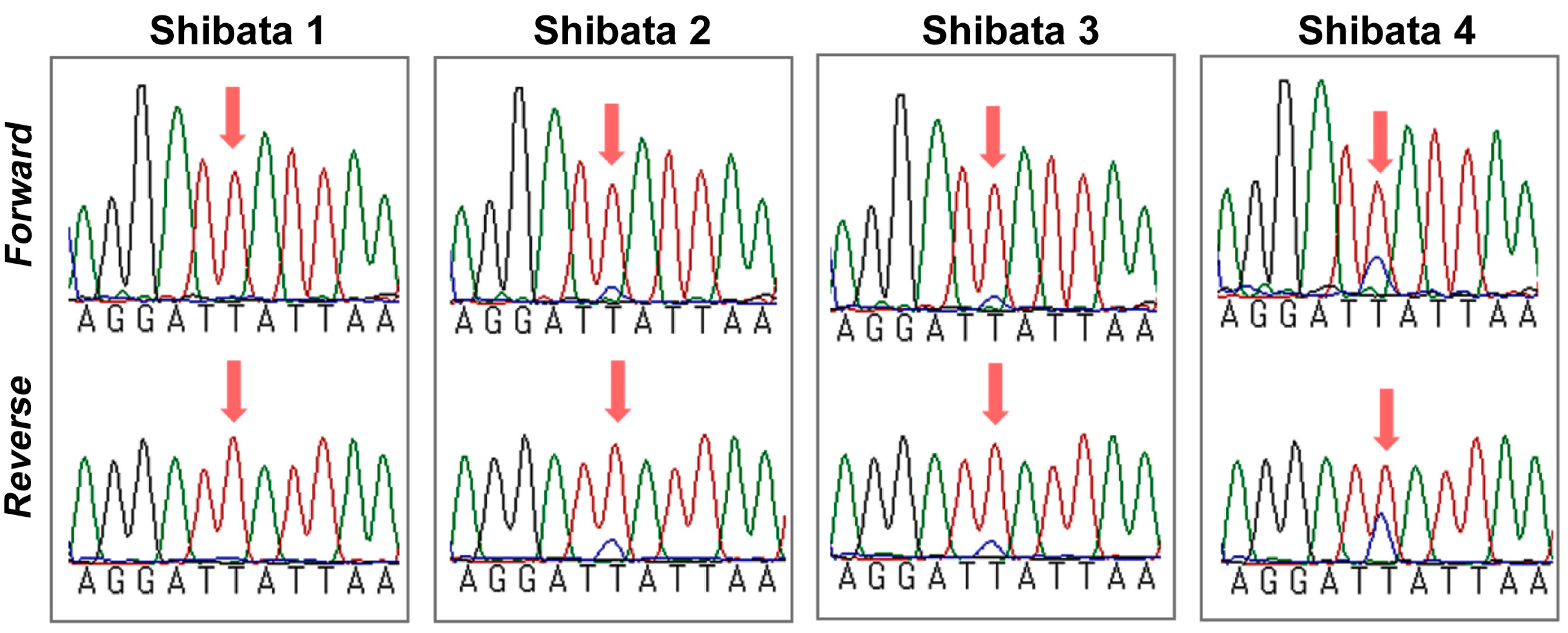
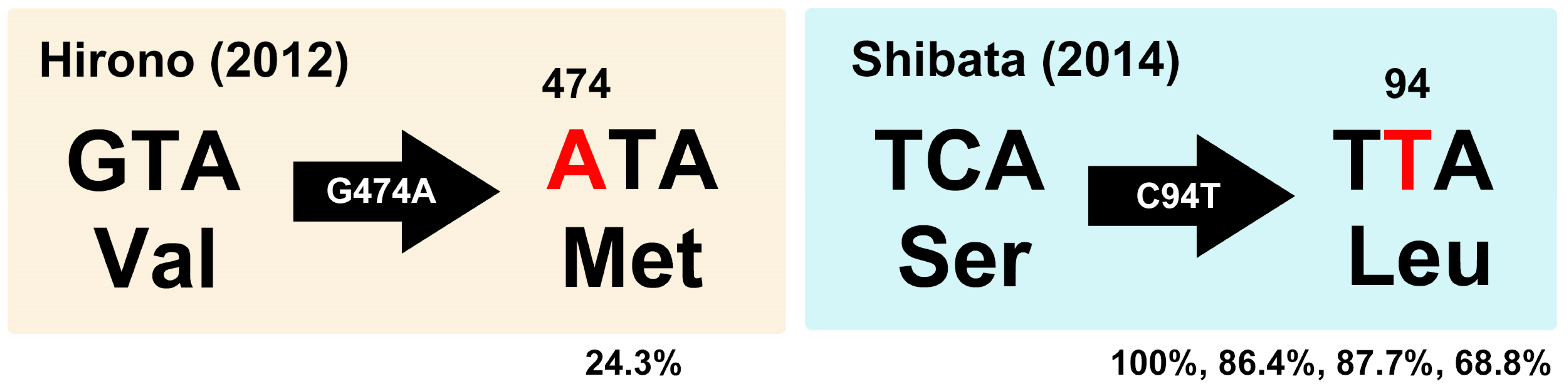
| Year | Tsukuba | Mito | Takahagi | Iwaki | Hirono | Motomiya | Fukushima | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring 2011 | 5 + 1 | 5 + 2 | 5 + 0 | 5 + 0 | 5 + 0 | 4 + 0 | 8 + 1 | 37 + 4 |
| Fall 2011 | 2 + 0 | 1 + 0 | 2 + 0 | 1 + 0 | 1 + 0 | 1 + 1 | 3 + 0 | 11 + 1 |
| Spring 2012 | 5 + 2 | 5 + 2 | 5 + 7 | 7 + 10 | 3 + 1 | 2 + 1 | 8 + 3 | 35 + 26 |
| Fall 2012 | 5 + 5 | 5 + 3 | 5 + 5 | 4 + 9 | 5 + 2 | 6 + 4 | 8 + 1 | 38 + 29 |
| Spring 2013 | 5 + 1 | 5 + 1 | 5 + 1 | 5 + 2 | 5 + 2 | 5 + 1 | 8 + 2 | 38 + 10 |
| Fall 2013 | 5 + 2 | 5 + 4 | 5 + 1 | 5 + 5 | 5 + 2 | 5 + 4 | 8 + 5 | 38 + 23 |
| Total | 27 + 11 | 26 + 12 | 27 + 14 | 27 + 26 | 24 + 7 | 23 + 11 | 43 + 12 | 197 + 93 |
| Year | Tsukuba | Mito | Takahagi | Iwaki | Hirono | Motomiya | Fukushima | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring 2011 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 15 |
| Fall 2011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| Spring 2012 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| Total | 5 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 27 |
| Miyagi Pref. | Fukushima Pref. | Yamagata Pref. | Niigata Pref. | Toyama Pref. | Ishikawa Pref. | Tochigi Pref. | Ibaraki Pref. | Saitama Pref. | Okinawa Pref. | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of localities | 5 | 14 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 44 |
| Number of samples (Fall 2014) | 23 | 70 | 5 | 35 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 34 | 5 | 9 | 216 |
| Year | Sex | Omori, Fukushima | Terasho, Hirono | Futatsunuma, Hirono | Elementary School, Hirono | Ohira, Hirono | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 2021 | Male | 26 | 27 | 32 | 5 | 9 | 99 |
| October 2021 | Female | 2 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| Total | Total | 28 | 27 | 39 | 5 | 9 | 108 |
| GenBank Accession Number | Species (Subspecies) | Collection Locality | Identities | Gaps | Substitutions (Nucleotides and Amino Acids) | Remarks [Ref] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DQ837206.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha argia | Tsubakiyama, Fukaura, Aomori, Japan | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | na | RefSeq [115] |
| AB969805.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha okinawana | Nishihara, Okinawa, Japan | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Different subspecies [116] |
| KT236360.1 | Zizeeria karsandra karsandra | Wuhu, Anhui, China | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Different species in the genus Zizeeria |
| KT236339.1 | Orthomiella sinensis | Wuhu, Anhui, China | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Different genus in the family Lycaenidae |
| KF492057.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha argia | Fujinomiya, Shizuoka, Japan | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Same subspecies as RefSeq |
| ON436063.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha argia | Shimobe, Minobu, Yamanashi, Japan | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Same subspecies as RefSeq [117] |
| KT236376.1 | Tongeia filicaudis | Wuhu, Anhui, China | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Different genus in the family Lycaenidae |
| KT236363.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Wuhu, Anhui, China | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Different subspecies |
| JQ344731.1 | Lepidoptara sp. | China | 564/564 (100%) | 0/564 (0%) | none | Species identity unknown [118] |
| HQ990365.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Sargodha, Punjab, Pakistan | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution [119] |
| LC125180.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha argia | Miyagi, Sendai, Japan (collected in 2014) | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | G170A (M→M) | Synonymous substitution [120] |
| PQ327494.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Dharamshala, Pradesh, Himachal, India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| KY839357.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Islamabad, Pakistan | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution [121] |
| KJ402272.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| KY832499.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Islamabad, Pakistan | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution [121] |
| KU973819.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| OR477325.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| KJ402269.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| KJ402162.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| KU973820.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| OQ147023.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Punjab, India | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| MK719689.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Bangladesh | 563/564 (99.8%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution |
| KY843820.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Islamabad, Pakistan | 560/561 (99.8%) | 0/561 (0%) | T416G (A→A) | Synonymous substitution [121] |
| KY845460.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Islamabad, Pakistan | 562/564 (99.6%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) C161T (F→F) | Two synonymous substitutions [121] |
| KY839619.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Islamabad, Pakistan | 562/564 (99.6%) | 0/564 (0%) | T416G (A→A) G170A (M→M) | Two synonymous substitutions [121] |
| KC158459.1 | Pseudozizeeria maha maha | Kalam, Upper Sawat, KPK, Pakistan | 510/513 (99.4%) | 0/513 (0%) | T416G (A→A) A530N (T→T) A552N (S→S) | Three synonymous substitutions [121] |
| KY834653.1 | Zizeeria karsandra karsandra | Islamabad, Pakistan | 543/564 (96.3%) | 0/564 (0%) | A89T (P→P) C161T (F→F) G170A (M→M) C206T (V→V) C224A (A→A) T239C (F→F) T353A (L→L) A386C (V→V) C389T (D→D) T419A (G→G) A473T (R→R) G478A (S→N) T504C (L→L) A524T (G→G) T543C (L→L) A545T (L→L) A551T (S→S) G566A (A→A) C600T (L→L) T602A (L→L) C608T (T→T) | 20 synonymous substitutions and one nonsynonymous substitution [121] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toki, M.; Taira, W.; Sakauchi, K.; Otaki, J.M. Mitochondrial Genetic Mutations in the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly: Possible DNA Damage via the Fukushima Nuclear Accident and Real-Time Molecular Evolution. Diversity 2025, 17, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040275
Toki M, Taira W, Sakauchi K, Otaki JM. Mitochondrial Genetic Mutations in the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly: Possible DNA Damage via the Fukushima Nuclear Accident and Real-Time Molecular Evolution. Diversity. 2025; 17(4):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040275
Chicago/Turabian StyleToki, Mariko, Wataru Taira, Ko Sakauchi, and Joji M. Otaki. 2025. "Mitochondrial Genetic Mutations in the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly: Possible DNA Damage via the Fukushima Nuclear Accident and Real-Time Molecular Evolution" Diversity 17, no. 4: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040275
APA StyleToki, M., Taira, W., Sakauchi, K., & Otaki, J. M. (2025). Mitochondrial Genetic Mutations in the Pale Grass Blue Butterfly: Possible DNA Damage via the Fukushima Nuclear Accident and Real-Time Molecular Evolution. Diversity, 17(4), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040275








