Abstract
The Humboldt Current System (HCS) off southwest America is known for its strong upwelling and the resulting high primary production and associated oxygen minimum zones (OMZs). Macrozoobenthic species represent a group of organisms that are affected by the low oxygen concentrations in the OMZ. In January 2023, benthic diversity was investigated at 8 stations on a transect off Concepción, central Chile (in the centre of the OMZ) in a water depth range from 56 to 912 m. The measured oxygen values ranged from 0 µmol/L in the OMZ to 144.64 µmol/L outside the OMZ. At each station, 3 van Veen grabs were taken, the species identified, counted and weighed. The mean abundance, biomass and diversity were calculated for each station. This analysis provided an overview of the changes in the species communities at different oxygen concentrations. The species communities at the stations with low oxygen levels differed greatly from those with higher oxygen levels. Species diversity at the stations increased during the transition from low (<2 µmol/L) to higher oxygen levels (>100 µmol/L). In contrast, species abundance and, to a lesser extent, biomass tended to be higher at low oxygen concentrations. The species composition at the various stations showed a high occurrence of polychaetes. The spionid polychaete Paraprionospio pinnata played an important role as a central key species within the OMZ. In addition to Paraprionospio, Ampelisca araucana, Magelona phyllisae, Nephtys ferruginea and Cossura chilensis were found in high abundance in the oxygen minimum zone (50–200 m water depth). At the edge and presumably below the oxygen minimum zone (300–912 m), where the oxygen concentration rises again, the dominance of individual species decreased, and the total number of species increased. In addition, the species composition changed and the abundance of other polychaete families (Cirratulidae, Amphinomidae, Oweniidae and Capitellidae) amplified. The proportion of polychaetes in the total abundance decreased from almost 100% at the low-oxygen stations to around 60% at the stations below the oxygen minimum zone. Bivalvia of the families Thyasiridae, Nuculidae and Yoldiidae were of particular importance at the deeper stations with a share of up to 20% of the total abundance. The study of benthic communities is of central importance to better understand the future changes in the structure and function of marine ecosystems in hypoxic waters.
1. Introduction
Oxygen deficiency is becoming an increasingly significant problem for benthic organisms worldwide mainly due to climate change and anthropogenic nutrient pollution [1]. Oxygen minimum zones (OMZs) are often associated with major ocean current systems and upwelling regions, where deep, nutrient-rich waters rise to the surface, fuelling high biological productivity. While upwelling supports abundant marine life at the surface, the subsequent sinking and decomposition of organic material further depletes oxygen at mid-depths [2,3,4,5]. Notable OMZs are found in the eastern tropical Pacific, the Arabian Sea and off the coasts of West Africa and South America. The OMZ of South America is part of the Humboldt Current System (HCS) and is one of the most productive marine ecosystems in the world [6]. This OMZ off the coast of Peru and Chile also surrounds the sea floor on the continental shelf and thus creates extensive habitats on the bottom that are exposed to permanent hypoxia [7].
Oxygen minimum zones are considered hotspots of microbial and biogeochemical processes [8]. In addition to the high conversion of nitrogen, the sediments in the oxygen-poor regions off the coast of Chile and Peru are rich in hydrogen sulphide. This provides ideal conditions for the occurrence of a group of sulphur-oxidising bacteria of the Beggiatoaceae family, the genus Thioploca [9]. These filamentous bacteria live in bundles surrounded by a common envelope in the form of thick mats on the sea floor. Thioploca bacteria oxidise hydrogen sulphide to sulphate and use nitrate as an electron acceptor [10,11]. By oxidising hydrogen sulphide, which is toxic to higher organisms, the Thioploca bacteria can support the occurrence of macrozoobenthic communities [12].
Despite the detoxification of the sediment by Thioploca, the macrozoobenthic species must have certain adaptations in order to survive in the low oxygen concentrations in the OMZ. Reducing metabolic costs by small body size and short life span can be seen as an initial response to a reduction in the oxygen content in the environment [13,14]. Other reactions to severe hypoxia are often behavioural changes. Mobile taxa simply move away from the low oxygen areas or swim towards the surface. Sessile animals on the seafloor can raise respiratory structures higher above the sediment-water interface by stretching, tube-building or migrating from burrows to gain access to faster-flowing water with more oxygen [15]. One of these tube-building organisms is the spionid polychaete Paraprionospio pinnata, which has developed physiological adaptations such as specialised branching structures that enhance oxygen diffusion and enzymatic adaptations for anaerobic metabolism [16]. Cossurid polychaetes in the OMZ of the Oman margin have unusually long median antennae, which presumably aid respiration [17,18]. Certain bivalves (Lucinidae, Thyasiridae, Vesicomyidae, Solemyidae) host chemosynthetic bacteria in their gills, enabling them to derive energy from sulphur oxidation instead of relying solely on oxygen [19,20,21].
In summary, the migration or mortality of large species and increased abundance of opportunistic species with special adaptations to low oxygen concentrations, such as <20 µmol/L, are the typical reactions of the benthic fauna in the OMZ. Accordingly, there is a low species diversity and a high dominance of individual species within the OMZ. The number of species increases towards the edges of the OMZ [22]. However, there are few studies that investigate and demonstrate this difference in species composition during the transition from oxygen-poor sites within to oxygen-rich stations outside the oxygen minimum zone. In our work, 8 stations along an oxygen gradient off Chile (36° S) were sampled to investigate precisely these differences in species composition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Work
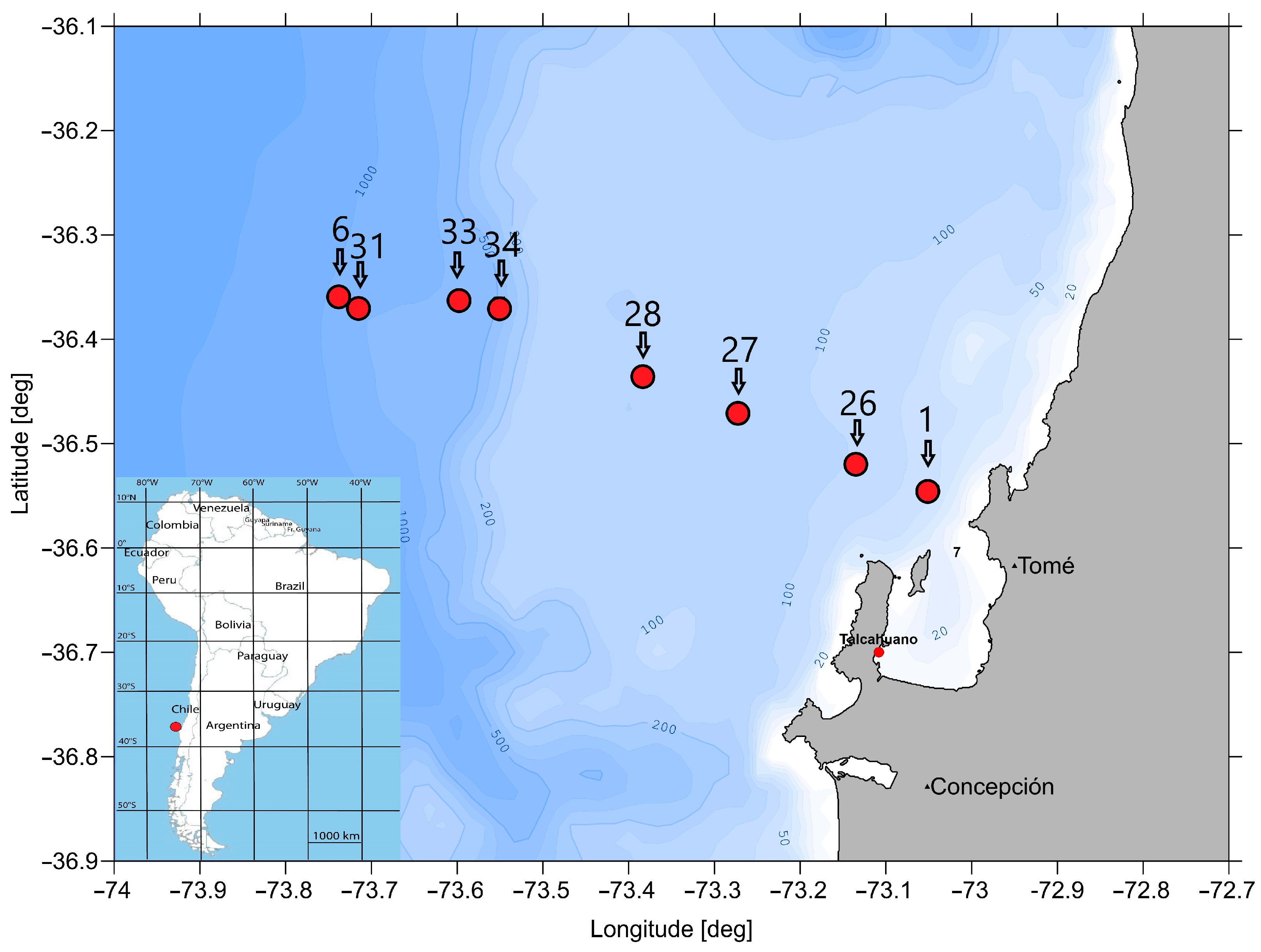
To investigate the species communities of macrozoobenthos in the centre and at the edge of the oxygen minimum zone off Chile (approx. 36° S), eight stations along a depth transect of 56 to 912 m were sampled at the beginning of 2023 during the research cruise SO296 on the R/V ‘Sonne’ (Figure 1).
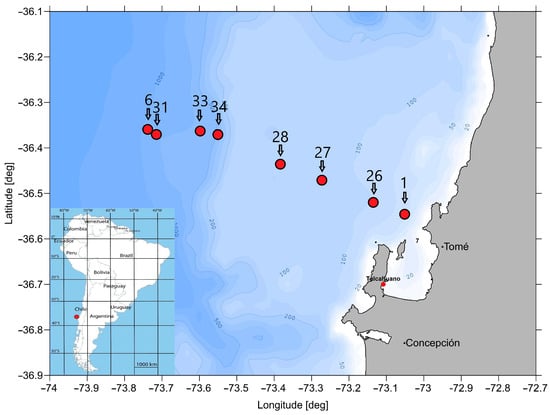
Figure 1.
Map with the eight analysed stations and the bathymetry off Concepción, Chile.
At each station, 3 samples (replicates) were taken with the van Veen grab (1000 cm2). The collected material was sieved with a mesh size of 1 mm on board and fixed with a 4% formaldehyde solution. The CTD-rosette was used to measure environmental parameters such as temperature, salinity, water depth and oxygen content. With the help of the CTD, water samples were taken from near-bottom water and used to calibrate the oxygen samples. Some accompanying environmental parameters such as water depth, salinity and oxygen are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Overview of water depth, salinity and oxygen level at the 8 stations, sorted according to water depth (ascending).
2.2. Laboratory Work
In the laboratory, the samples fixed in formol were individually washed through a 500 µm sieve. Using a stereomicroscope, the organisms were sorted and identified to species level if possible. Numerous primary literature sources were used for identification, not all of which can be listed here. A comprehensive overview of macrofauna species and identification keys of Chile can be found under the link: https://www.ifop.cl/macrofauna/ (assessed on 1 April 2025). The collected organisms were counted and weighed. Finally, the organisms were transferred to small, labelled vials, where they were preserved in ethanol for later taxonomic revision.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The samples were statistically analysed using Microsoft Excel 2010, the programming software R (Vers. 4.3.0) and the software PRIMER 6. The software licences for Microsoft, PRIMER and PERMANOVA are available at the Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research. R software is freely available (http://www.r-project.org, assessed on 11 February 2025)). To assess relationships between environmental variables and macrozoobenthic abundance, the Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) in R and the Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA) was used. To assess relationships between environmental variables and macrozoobenthic community composition, Spearman’s Rank correlation coefficient was used. Community structure was evaluated using hierarchical cluster analysis, facilitating the identification of distinct groupings based on species abundance data. The significance of these groupings was tested with PERMANOVA and the Analysis of Similarities (ANOSIM) [23].
Multidimensional scaling (MDS) ordination was applied to visualise patterns in community composition and explore spatial and environmental influences. Biodiversity was quantified using the Shannon Diversity, Margalef Richness and Hurlbert (ES50) indices, providing insights into species diversity and evenness. Rarefaction analysis was performed to standardise sampling effort, ensuring comparability among samples. To identify the contribution of individual taxa to observed differences among groups, Similarity Percentages (SIMPER) analysis was employed [23].
3. Results
3.1. Abundance, Biomass and Diversity
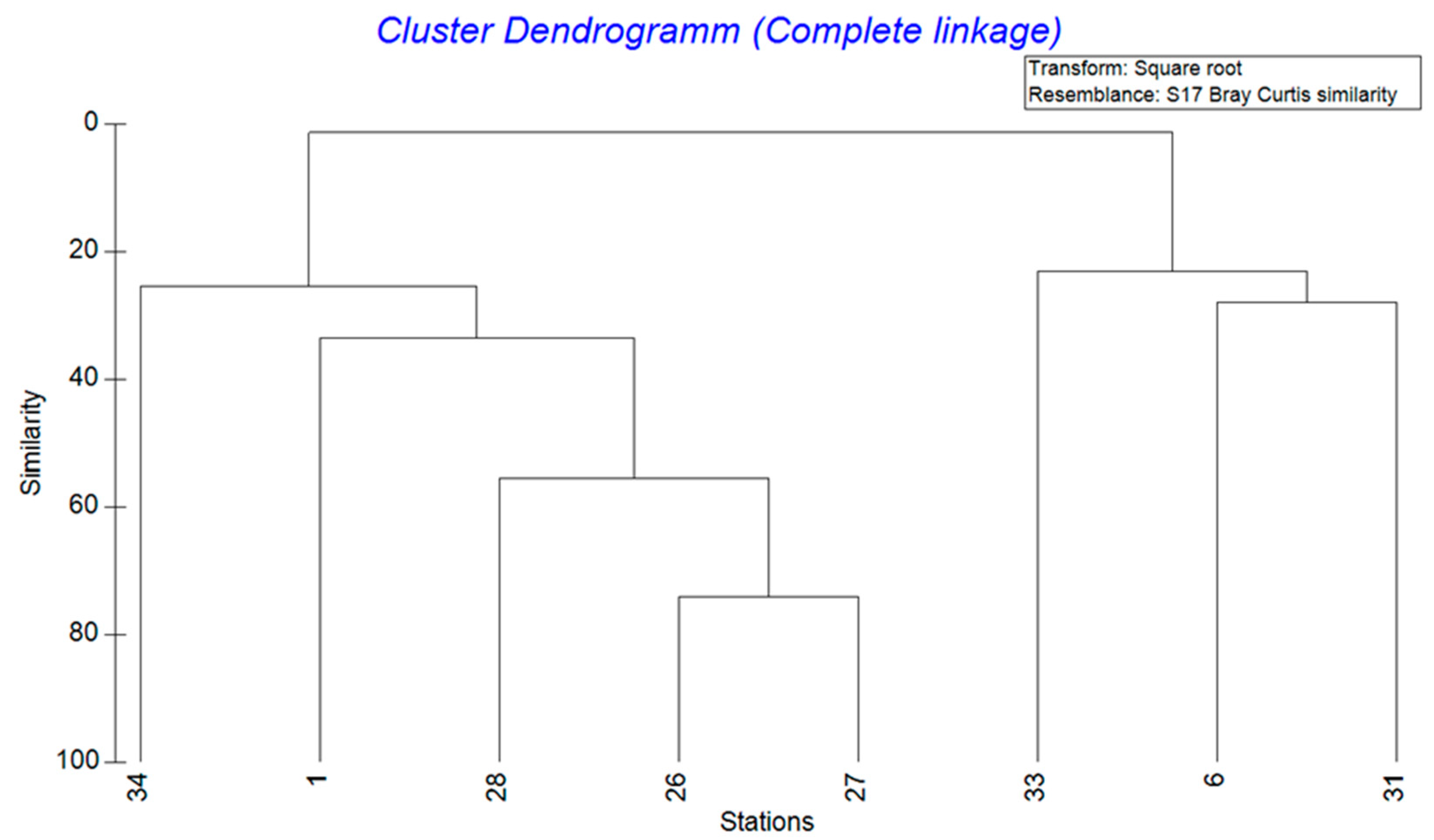
With a water depth of 56 m, station 1 was the shallowest site and station 6 the deepest at 912 m (Table 1). The salinity at all stations was similar at around 34. In contrast, the oxygen values ranged widely from a minimum of 0 at station 27 (114 m water depth) to a maximum of 144.64 µmol/L at station 33 (658 m water depth). In addition, the sampled sediment was often silty and contained the filamentous Thioploca bacteria at the oxygen-poor stations (1, 26, 27 and 28). At station 34 (350 m water depth), however, these bacteria were not found and instead many stones, carbonates and phosphorites were recovered. At Station 31 (765 m water depth), methane seepage was responsible for large amounts of carbonates covering the sea floor. In order to establish a relationship between the various abiotic factors and the calculated species abundance of the individual stations, a cluster dendrogram was created (Figure 2). Two groups with 5 and 3 stations, respectively, can be recognised, whose benthic communities were highly similar to each other.
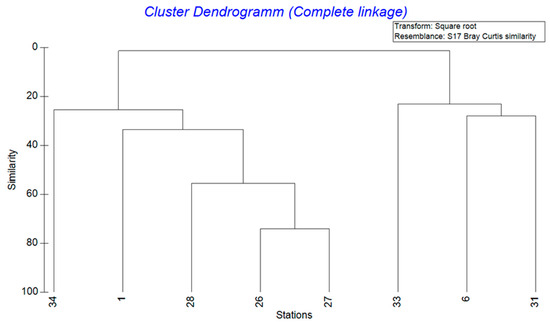
Figure 2.
Cluster dendrogram of the stations with a square root transformation based on the species abundances with calculation of the distance using the Bray–Curtis similarity measure.
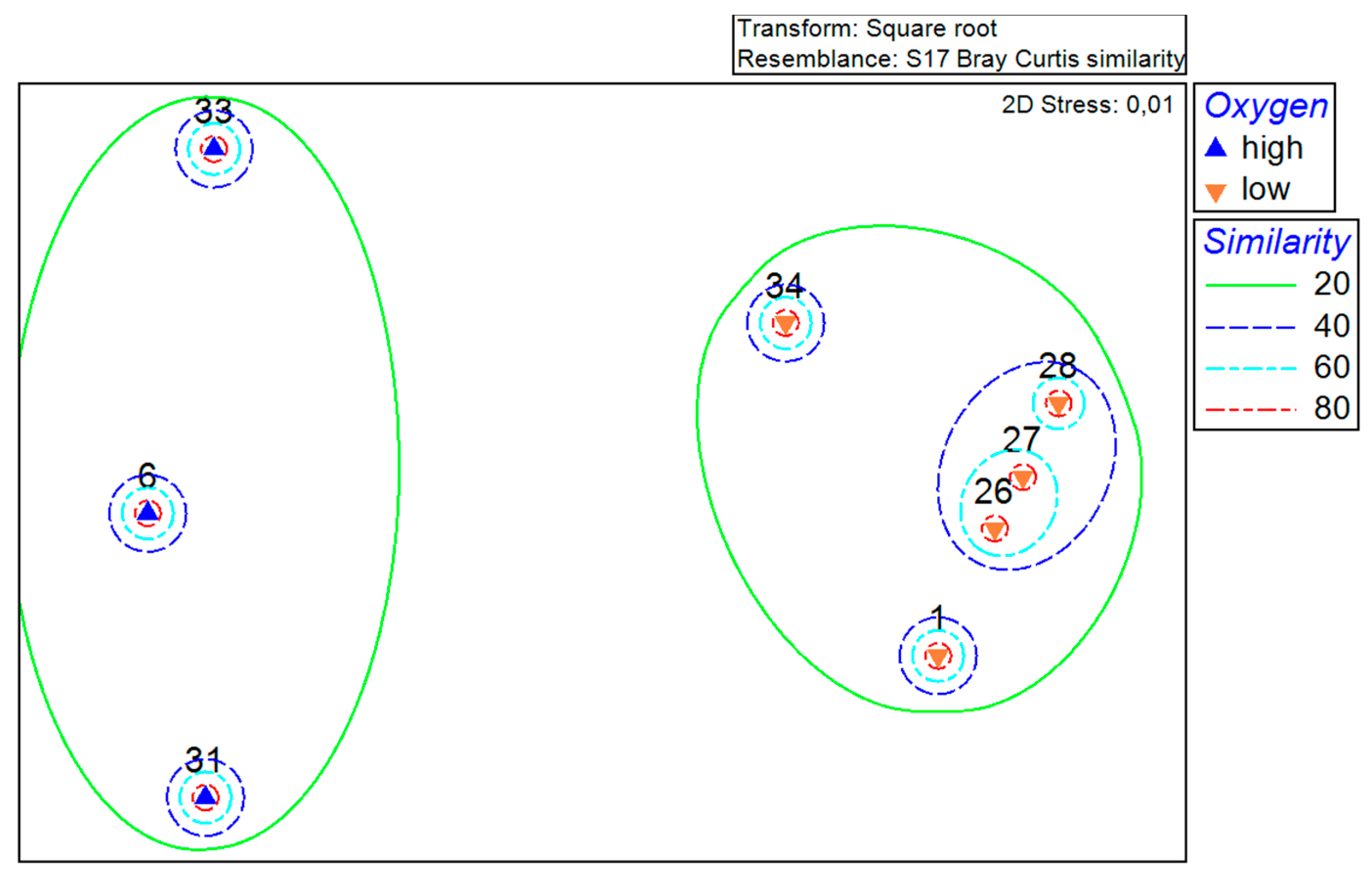
The established grouping of the stations has been further clarified with the help of the MDS plot (Figure 3). The distances between the points on the plot represent the similarities and, as in the previous figure, are based on Bray–Curtis similarity. The stations are again divided into the same two different groups, with 3 and 5 stations. In addition to the similarity levels in the MDS plot, the oxygen content is shown as ‘high’ (>100 µmol/L) and ‘low’ (<2 µmol/L) for each station.

Figure 3.
MDS plot of the total abundance at the stations with a square root transformation based on the Bray–Curtis similarity measure and a display of the oxygen content (up arrow (high) for oxygen content > 100 µmol/L and down arrow (low) for oxygen content < 2 µmol/L).
The species richness varied between 7 and 104 per station (Table 2, Table S1). The highest species diversity was recorded at station 31 (765 m water depth), while the highest total abundance was calculated at the shallow station 1 (56 m water depth).

Table 2.
Overview of diversity parameters of the stations: S = number of species, N = total abundance (individual per square meter), ES (50) = Hurlbert index with estimated species at 50 individuals, H’(log2) = Shannon index and DMg(log) = Margalef index.
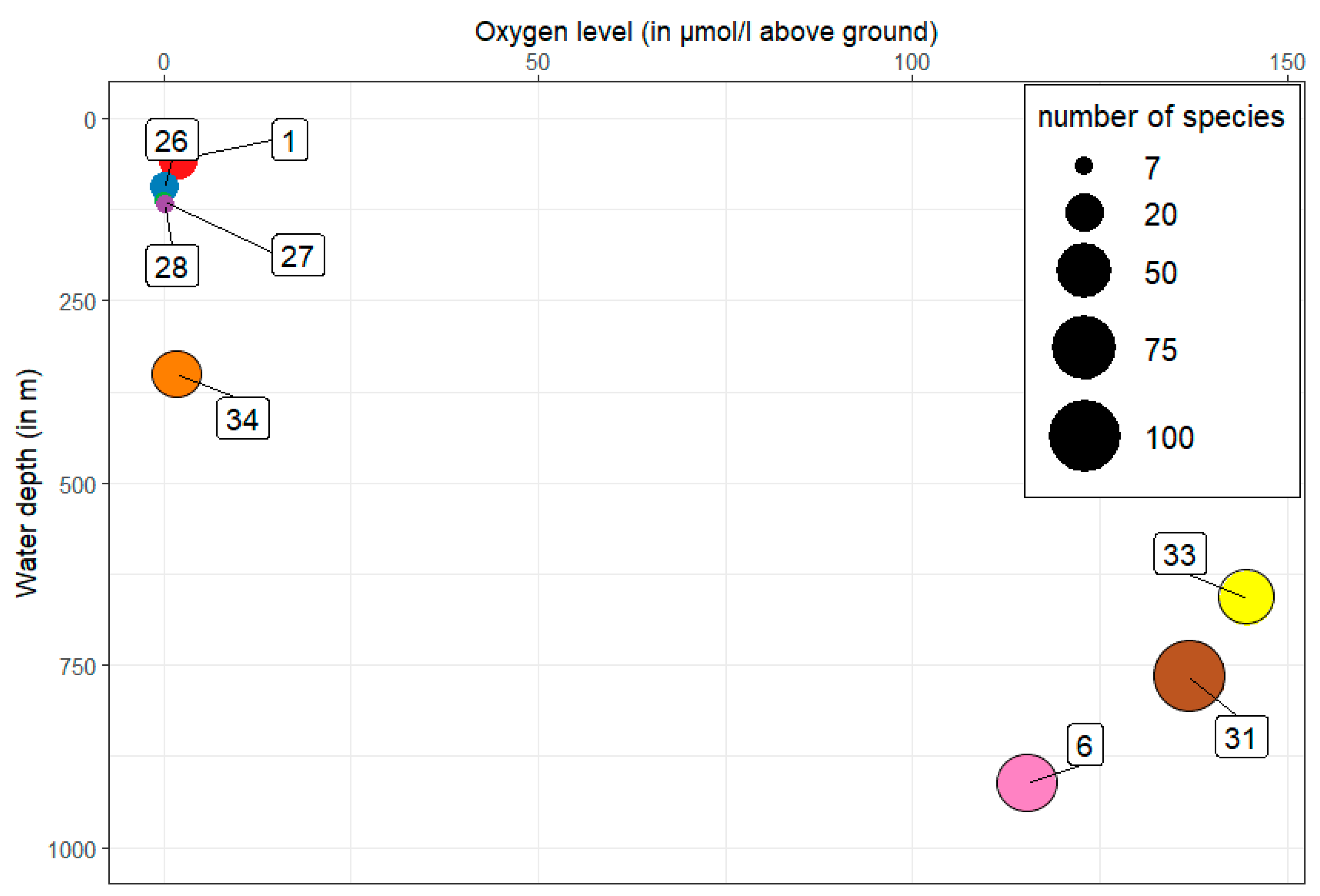
A clear picture emerges with regard to the number of species as a function of the oxygen content in the near-bottom water (Figure 4). The five stations (1, 26, 27, 28 and 34) with low oxygen content and low water depth show a low number of species of only 7 species in some cases. From a water depth of 658 m and a higher oxygen content, the number of species increases more than fourfold with up to 104 species at station 31.
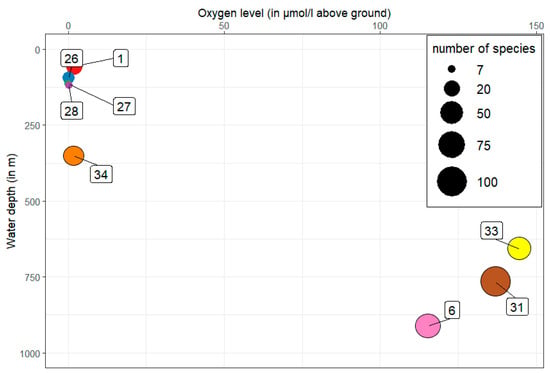
Figure 4.
Number of species (circle diameter) in relation to the oxygen content and the water depth of the individual stations (numbers in frame).
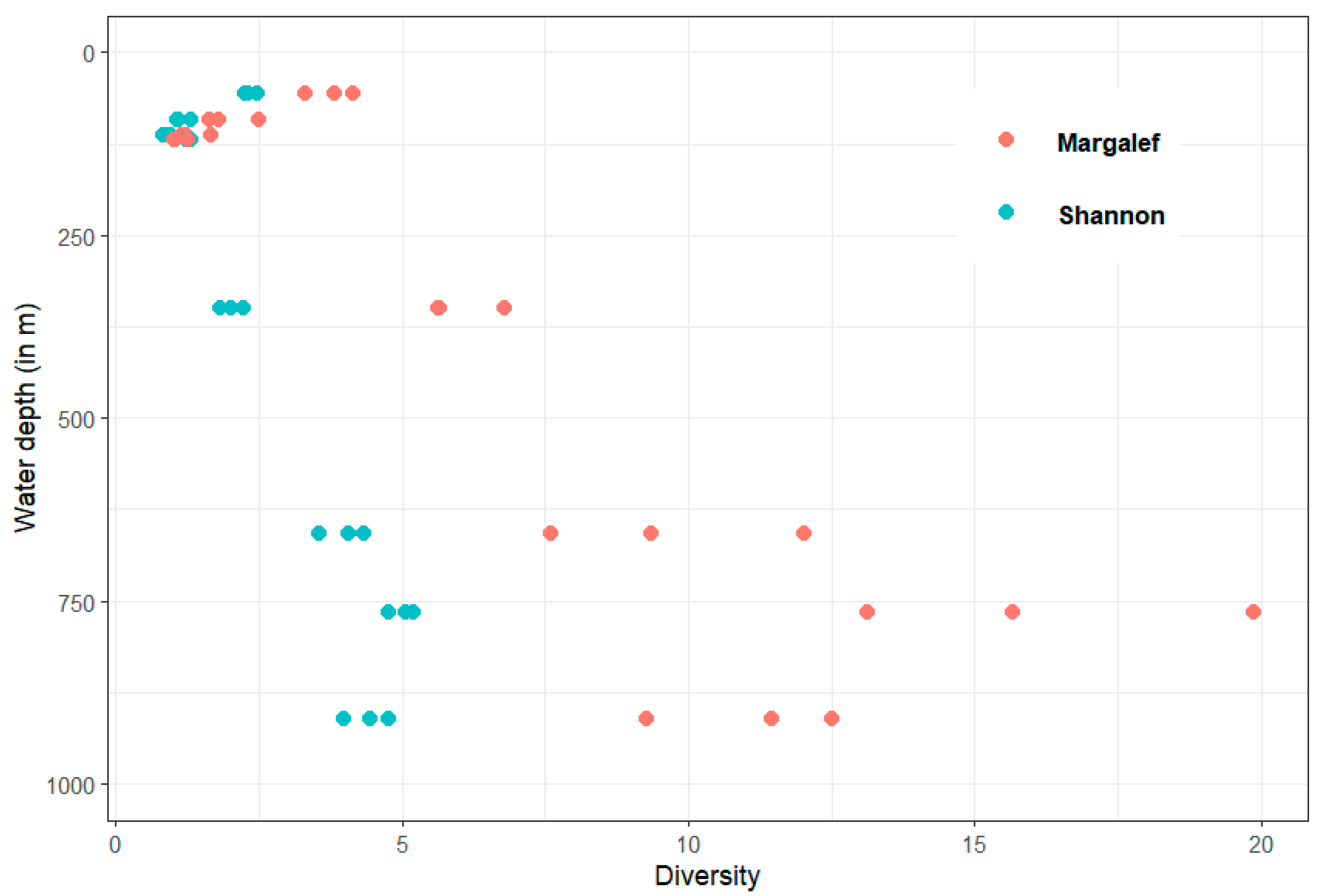
The Shannon and Margalef indices also show an increase with increasing water depth and oxygen content (Figure 5). However, it is noticeable that the diversity indices of the replicates of the deeper stations are more different from each other than those of the stations at shallower water depths. Therefore, the variability within the stations seems to increase with increasing water depth.
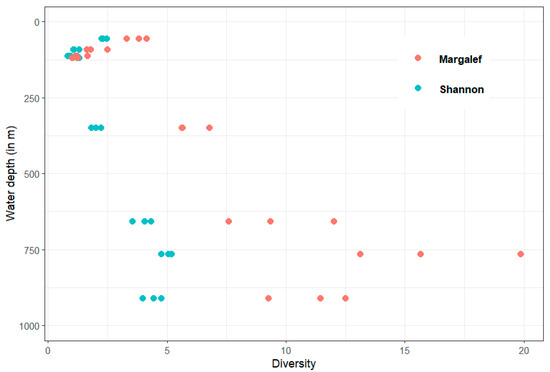
Figure 5.
Shannon and Margalef indexes in relation to water depth with three replicates for each station.
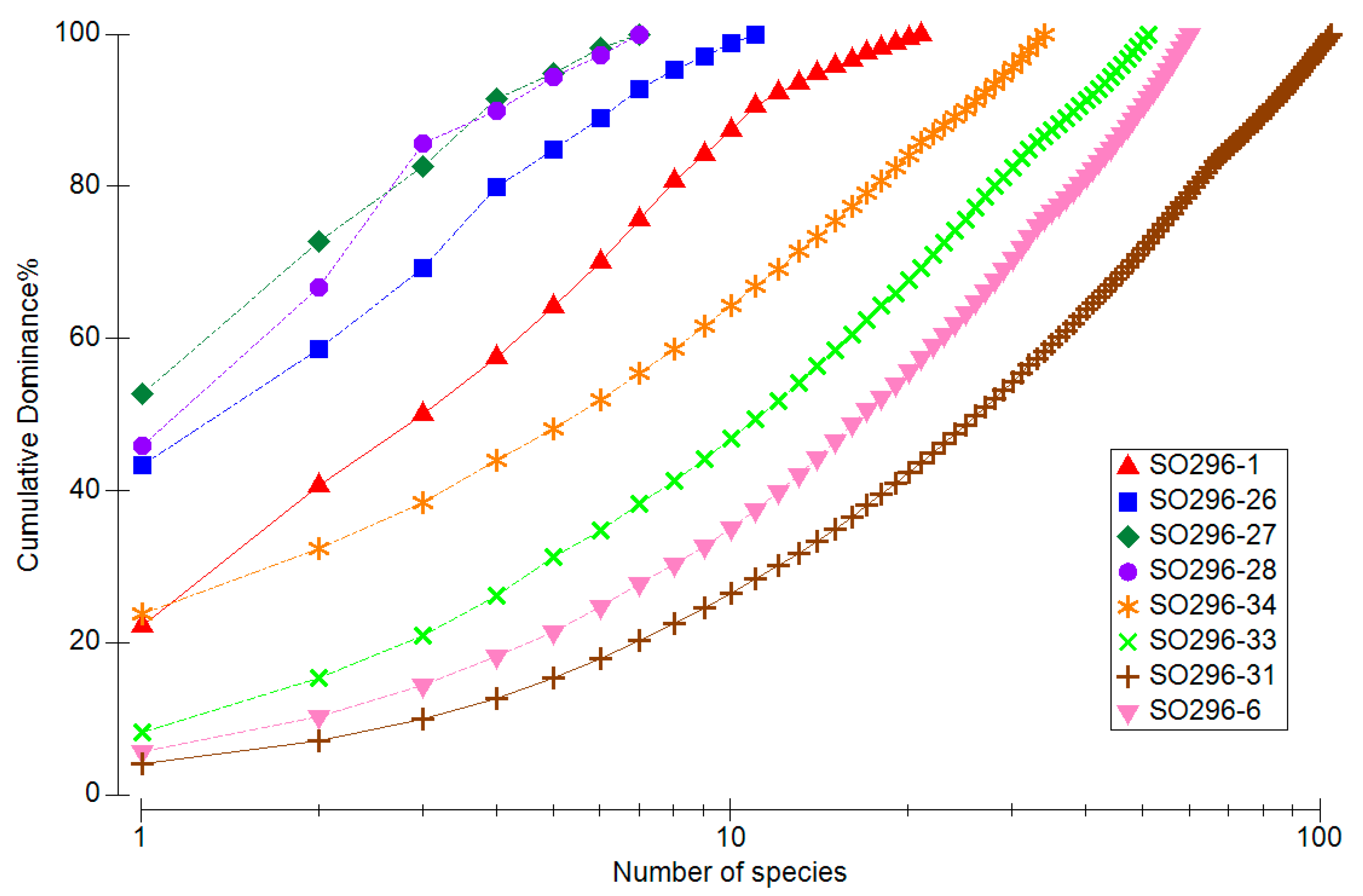
The low species diversity of the oxygen-poor stations (26, 27 and 28) in low water depths therefore shows a high dominance of individual species (Figure 6). The most common species at station 27 alone accounts for over 50% of the species composition. It can also be seen how few species were collected at stations 26, 27 and 28 in comparison with the other 5 stations. The species-rich stations show a rather concave curve with a relative dominance of the most common species far below 10%.
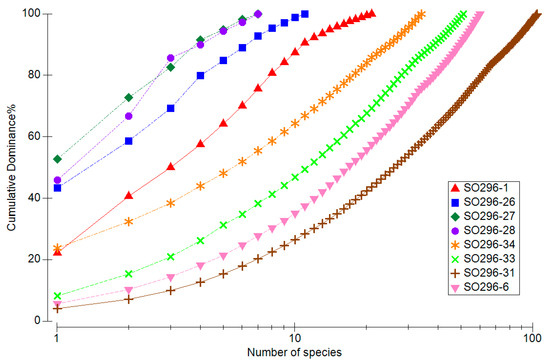
Figure 6.
Species sum curve with the cumulative abundance of species per station.
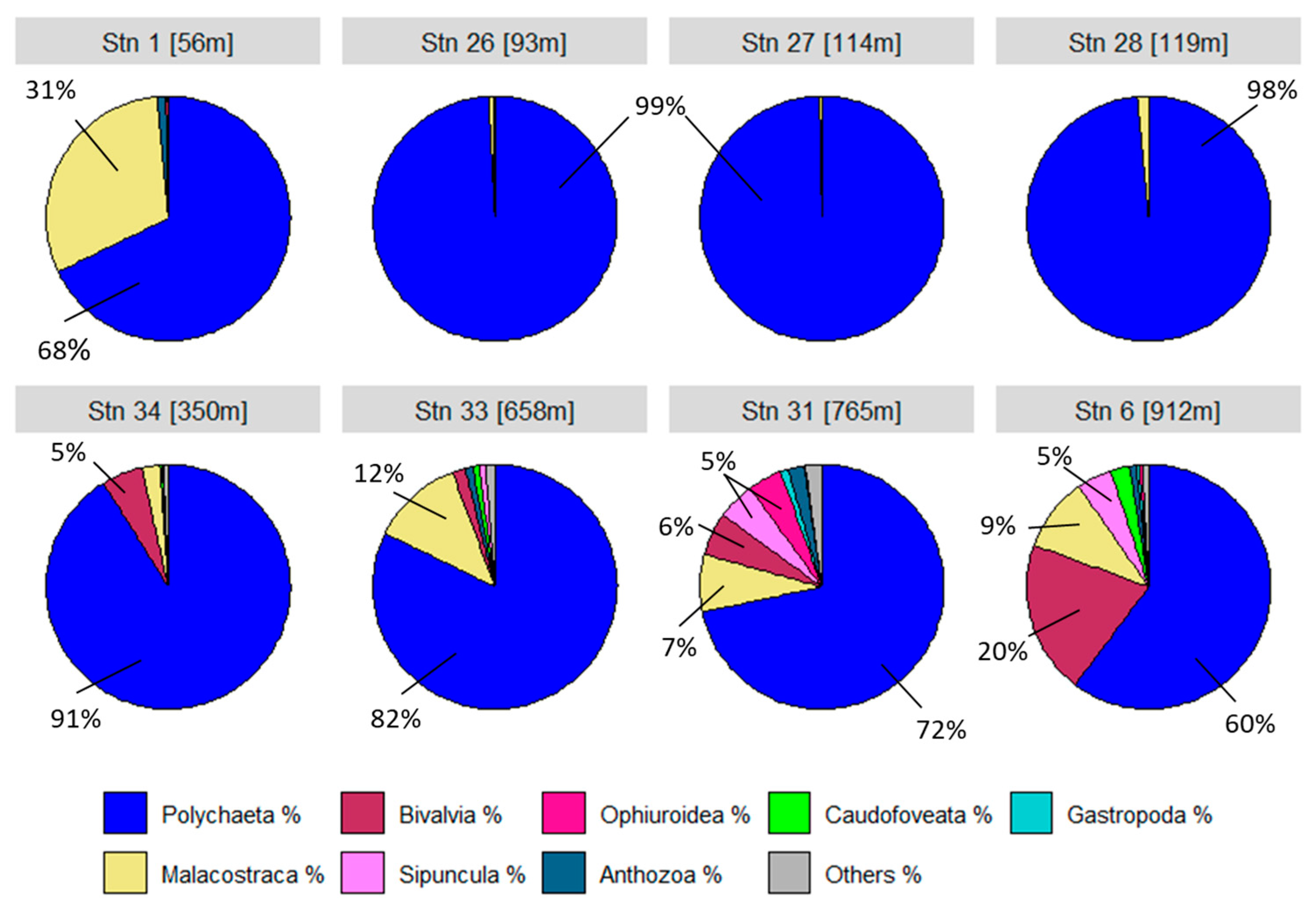
The species communities at the stations are largely made up of the polychaete class (Figure 7). At station 1, the higher crustaceans (Malacostraca) account for just over a quarter. Bivalves appear from station 34 onwards and account for around 20% at the deepest station 6. The grey area in the pie charts represents all other classes that make up no more than 1%. These include the classes Priapulida, Scaphopoda, Solenogastres, Nemertea, Brachiopoda, Polyplacophora and Clitellata. This diversity of the community is particularly evident at stations 33, 31 and 6 with the highest oxygen levels.
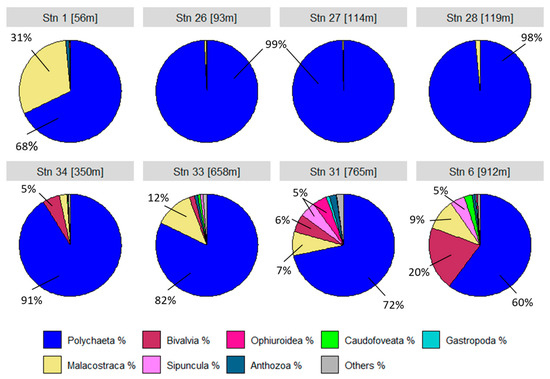
Figure 7.
Classes/groups as percentage distribution for each individual station.
3.2. Species-Specific Differences
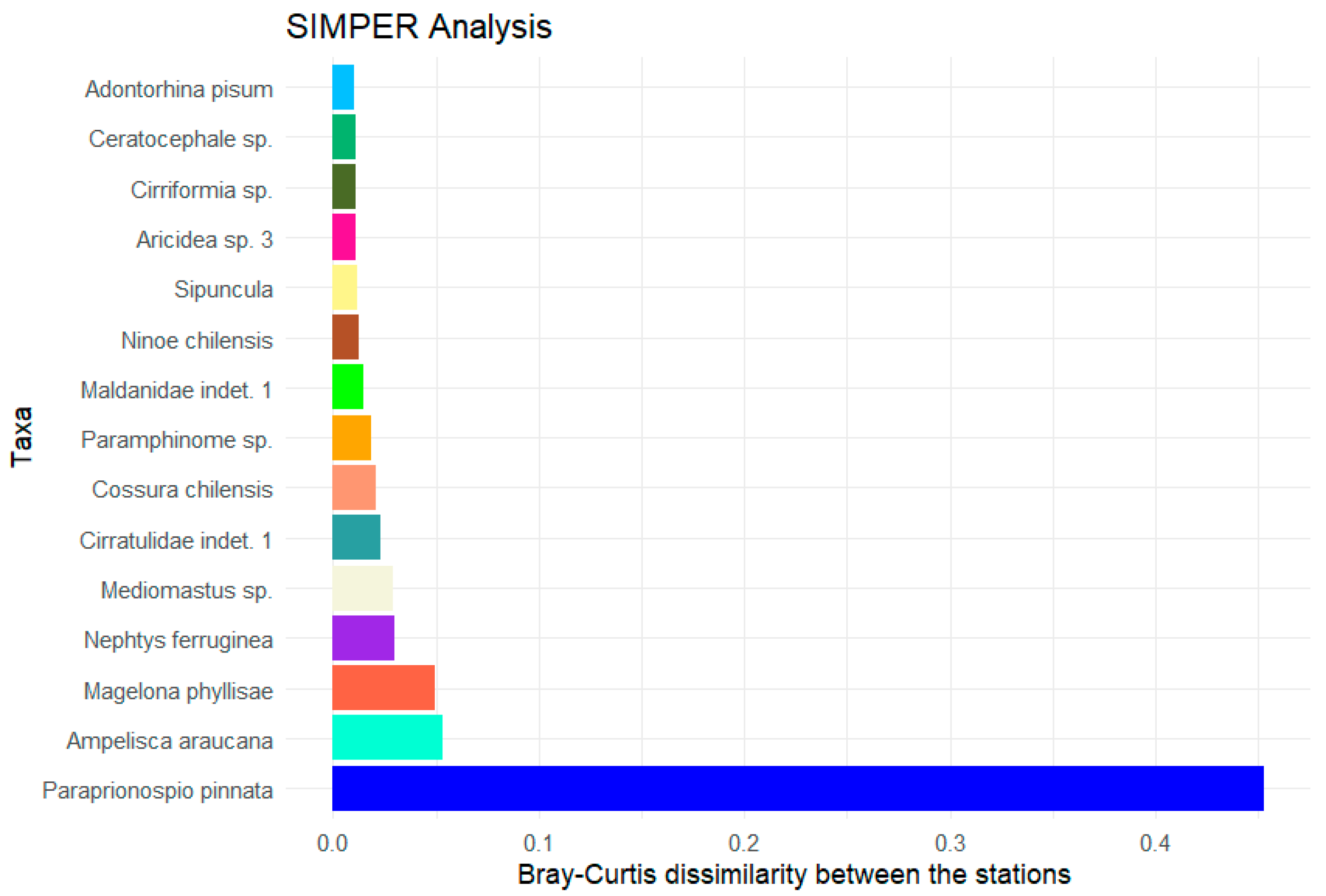
The polychaetes are clearly the predominant class at the stations. Some of them stand out due to their high abundance and their contribution to the observed differences between the high- and low-oxygen stations (Figure 8). The polychaete Paraprionospio pinnata shows the highest value at around 0.45. For all other shown species, the calculated Bray–Curtis value is below 0.1. Added together, the average contributions of all species sum up to 1.
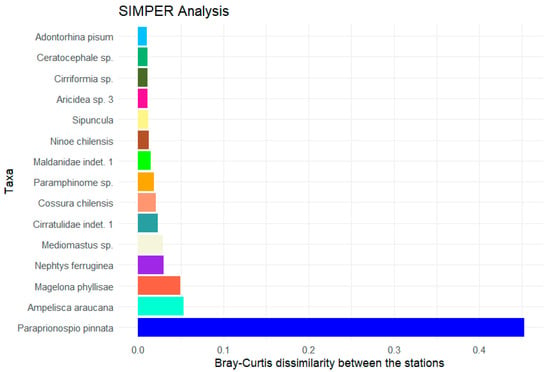
Figure 8.
Result of the SIMPER analysis based on the total abundance with the 15 taxa with the highest contributions to the average Bray–Curtis dissimilarity between the stations with high oxygen content (>100 µmol/L) and the stations with low oxygen concentrations (<2 µmol/L).
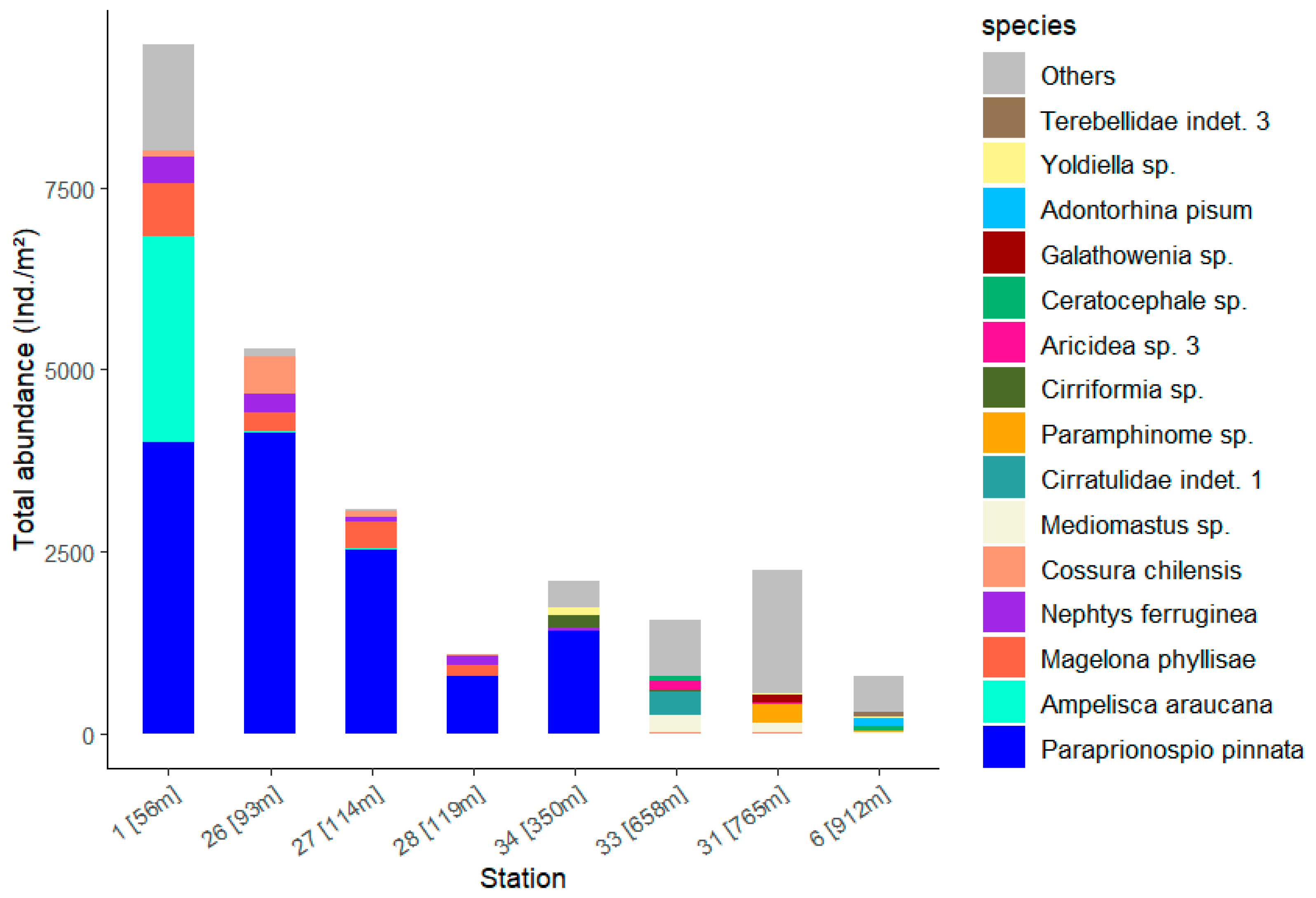
The species with high SIMPER contributions to the difference between the stations show high abundances at the stations in low water depths (Figure 9, Table S5). In addition to the numerous polychaetes, the amphipod Ampelisca araucana at Station 1 accounts for around a quarter of the total abundance and is thus in second place after Paraprionospio pinnata. P. pinnata occurs only at the stations at a water depth of 56 to 350 metres with very high abundance. It makes a significant contribution to the total abundance at Station 1, which shows the highest total abundance with 9473 Ind./m2 (Table 2). At the deeper stations 33, 31 and 6 with water depths greater than 600 m, the abundance is made up of many different species; at station 31 in particular, the column is mainly filled by the summarised ‘Other’ species. This collective term ‘Others’ summarises all species that contribute less than 5% to the total abundance at the stations.
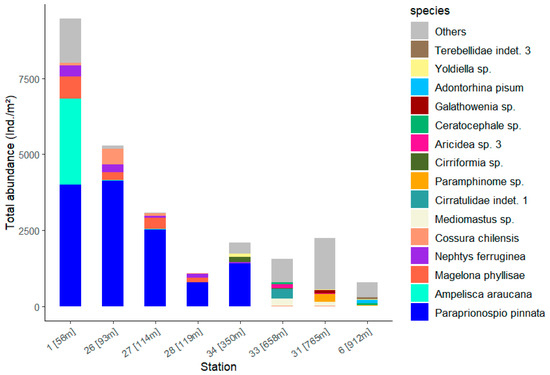
Figure 9.
Total abundance of the 15 dominant taxa (see Figure 8) for each station with the corresponding water depth.
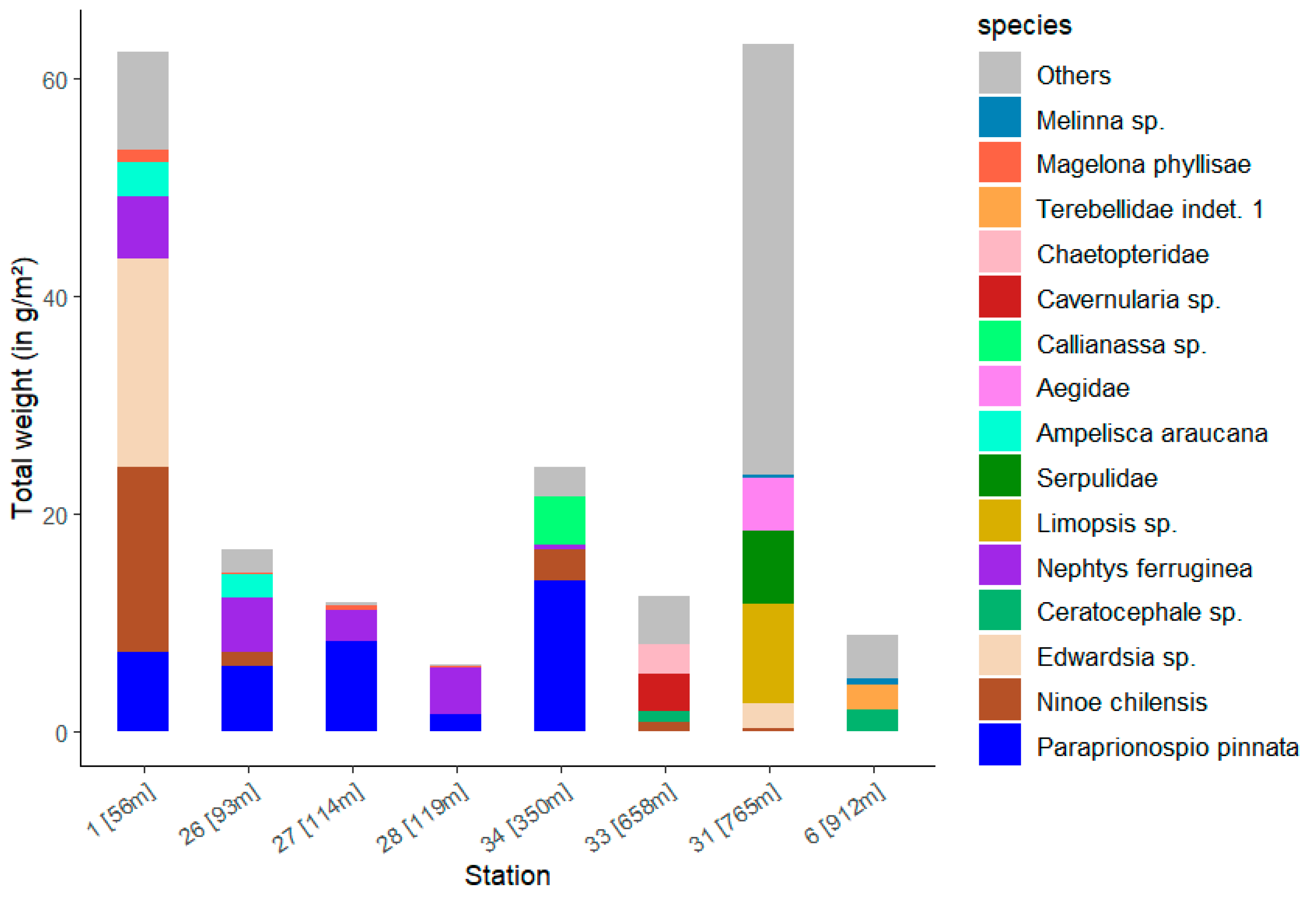
Station 31 shows the highest total weight with 63.2 g/m2, just ahead of Station 1 with 62.4 g/m2 (Figure 10). The lowest total biomass was calculated for station 28 with 6.1 g/m2. At this station, the polychaete Nephtys ferruginea accounts for the majority of its weight. The largest contribution to the total weight of the stations is made by the polychaete Paraprionospio pinnata, as was previously the case with abundance. This polychaete occurs at stations 1, 26, 27 and 28 with a medium weight (Table S2). At station 34, on the other hand, it visibly takes up the largest biomass proportion. Ninoe chilensis is also represented there, occurring mainly at station 1 with a wet weight of 16.9 g/m2.
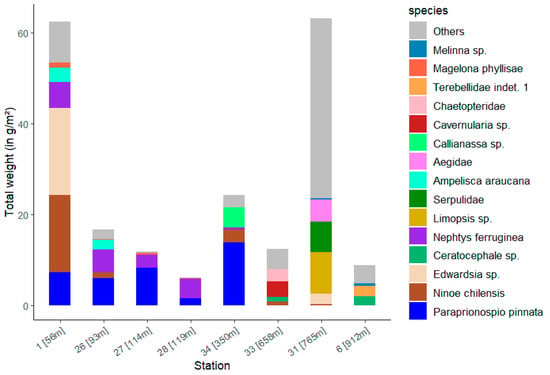
Figure 10.
Total wet weight of the 15 dominant taxa (see Figure 8) for each station with the corresponding water depth.
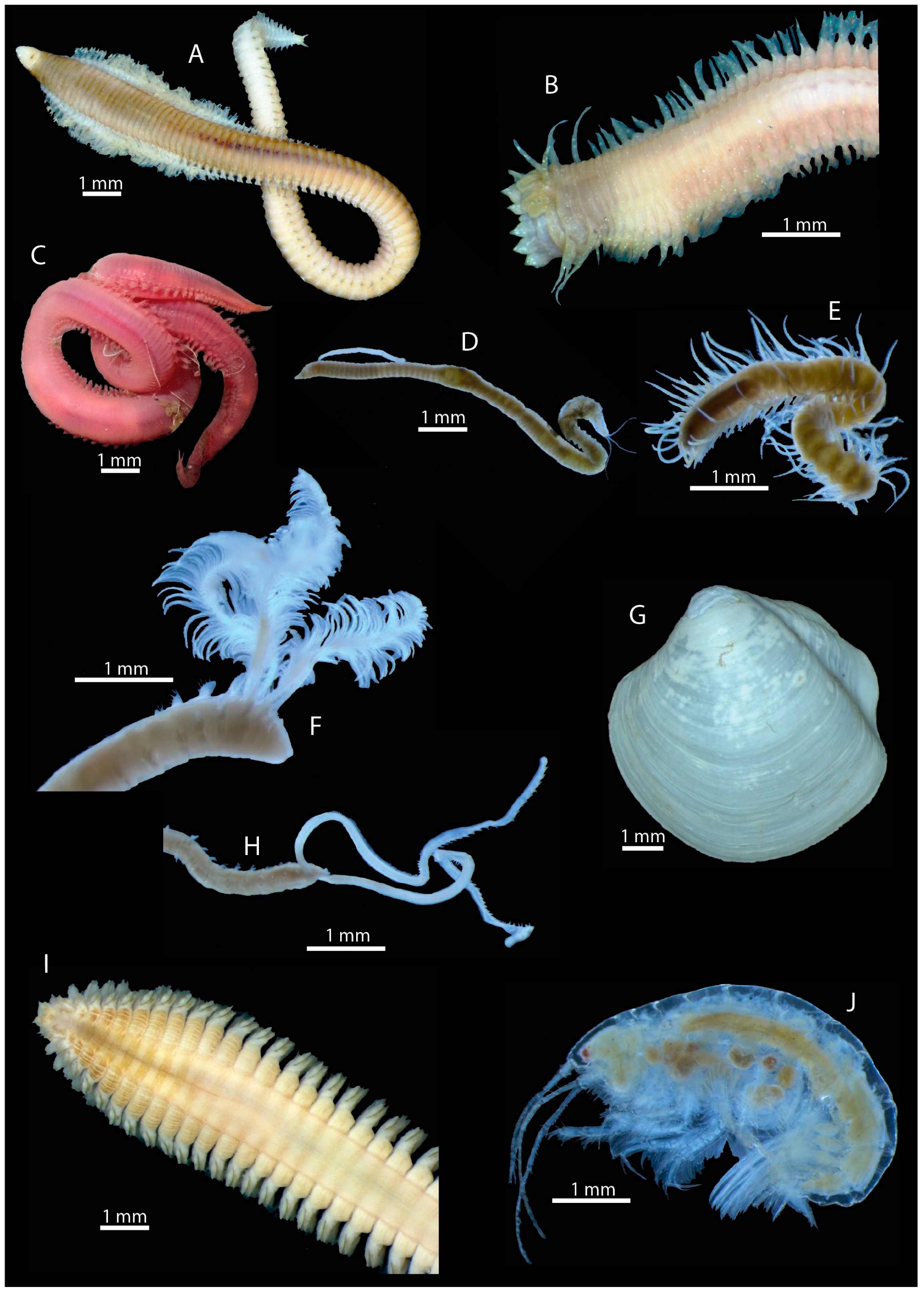
Ninoe chilensis Kinberg, 1865 (Figure 11A) is a polychaete that occurs regularly in the OMZ off Chile. The average density there was between 10 and 70 ind./m2. At the shallowest station, as many as 500 ind./m2 were observed. The polychaete Sigambra bassi (Hartman, 1945) (Figure 11B) also inhabits the OMZ off Chile and was discovered with an abundance of 280 ind./m2 at the shallowest station with low oxygen content. The polychaete Glycera sp. (Figure 11C) was also found at these low-oxygen sites with an abundance of up to 13 ind./m2. In addition, the polychaete Cossura chilensis Hartmann-Schröder, 1965 (Figure 11D) appeared at almost all stations. This polychaete seems to inhabit stations with both low and high oxygen content. The abundance was highest at the stations with low oxygen content at shallow water depths with up to 510 ind./m2. A representative of the family Syllidae (Figure 11E) showed an abundance of up to 83 ind./m2 at the stations at higher water depths with a higher oxygen content.
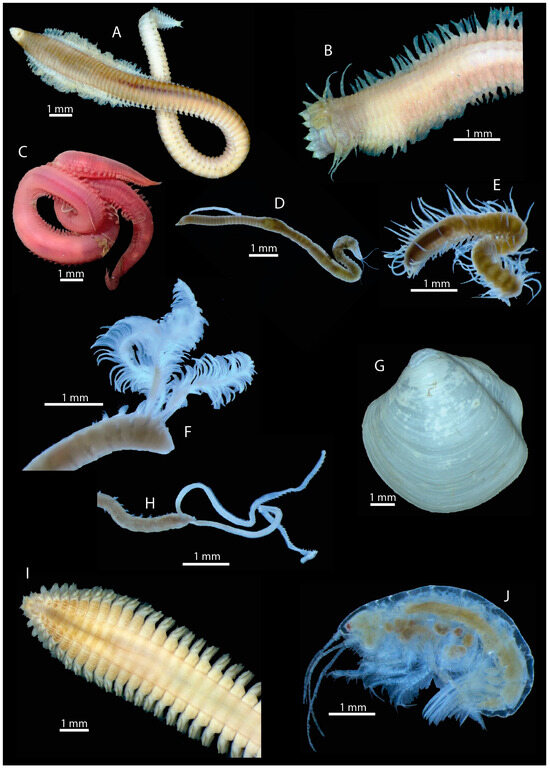

Figure 11.
Key species of the oxygen minimum zone: Ninoe chilensis (A), Sigambra bassi (B), Glycera sp. (C), Cossura chilensis (D), Syllidae (E), Paraprionospio pinnata (F), Thyasira tomeana (G), Magelona phyllisae (H), Nephtys ferruginea (I) and Ampelisca araucana (J).
The small bodied spionid polychaete Paraprionospio pinnata (Ehlers, 1901) (Figure 11F) has a high proportion of the total weight due to its very high abundance at the stations with low oxygen content. The abundance of P. pinnata there varied between 780 and 4127 ind./m2. During sample analysis in the laboratory, it was often found embedded in the filamentous structure of the sulphur bacterium Thioploca under the microscope. The marine bivalve mollusc Thyasira tomeana Dall, 1901 (Figure 11G) could only be found at the shallowest station with low oxygen content with an abundance of 23 ind./m2. The polychaetes Magelona phyllisae Jones, 1963 (Figure 11H) and Nephtys ferruginea Hartman, 1940 (Figure 11I) appeared exclusively in the samples with low oxygen content. M. phyllisae showed abundances between 160 and 723 ind./m2 while N. ferruginea could be identified with an abundance of up to 377 ind./m2. The amphipod Ampelisca araucana Gallardo, 1963 (Figure 11J) could almost only be identified in the samples with an oxygen content of <2 µmol/L above ground. The abundance of the amphipod amounted to 2823 ind./m2 and decreased sharply with increasing depth.
4. Discussion
The main objective of this study is to analyse the macrozoobenthic communities within and at the edge of the oxygen minimum zone off Chile (ca. 36° S). The occurrence and the duration of the oxygen minimum zone plays an important role for the species abundance, biomass and biodiversity of macrozoobenthic communities. Distinct groupings of species communities were observed: within the OMZ and below it. Opportunistic species like Paraprionospio pinnata dominated hypoxic zones, while higher species diversity characterised areas with increased oxygen levels. Oxygen values that are as extremely low as in the present study suggest that higher life should hardly be possible, or only to a very limited extent [15]. Oxygen values of less than 2 µmol/L were measured in the core zone of the OMZ. Nevertheless, a relatively high diversity of macrozoobenthos was found at the same time. Simultaneously, there was no hydrogen sulphide, a metabolic poison that makes higher life impossible. This is probably due to the high occurrence of Thioploca mats, which detoxify the seabed by oxidising hydrogen sulphide. Thereby, they significantly influence the composition and distribution of macrozoobenthic communities in these hypoxic regions [24,25]. In other oxygen minimum zones such as off the coast of Namibia and in the Arabian Sea, where Thioploca bacteria do not occur (or at least not in such mats), significantly lower macrozoobenthic abundances were determined [26,27,28].
Total macrofaunal abundance at our stations off Concepción varied between 788 and 9473 ind./m2 with a significant influence of water depth and oxygen content shown by CCA analysis (Tables S3 and S4). These findings can be aligned with studies from Palma et al. [29], who investigated the effect of low oxygen levels on the distribution and composition of macrozoobenthic species communities off Concepción. They determined similar abundance values, with the highest value at 13,808 ind./m2 in 124 metres water depth. Despite the low oxygen concentrations, certain species appear to have adapted to these hypoxic conditions, with the Thioploca bacteria certainly providing an important basis for life there. Polychaetes were identified as the dominant group in all transects and water depths [29]. The same applies to our results (Figure 7), whereby the polychaetes accounted for almost 100% in the OMZ between 56 and 350 m water depth in particular. With increasing water depth and rising oxygen content, the proportions of other species groups increased. At the stations outside the OMZ, Malacostraca even accounted for around 30%. This result can be confirmed by the study from Gallardo et al. [30], according to which the relative abundance of crustaceans increased with increasing depth off central Chile. The increase in the proportion of other species groups is accompanied by an increase in species diversity as the oxygen concentration rises. The calculated diversity parameters (Shannon, Margalef, ES50) showed a significant increase in species diversity with increasing oxygen content. The cumulative dominance plot (Figure 6) illustrated above all the dominance of a few individual species within the OMZ. These include the relatively small polychaetes Cossura chilensis and Paraprionospio pinnata [29]. P. pinnata was dominant at all 5 stations with low oxygen content. Numerous studies have already shown its adaptations to low oxygen levels and therefore key role in oxygen minimum zones [16,31,32].
The biomass results showed that relatively large species such as Ninoe chilensis were present in the shallow zones of the OMZ. Although the oxygen concentration is already low at this station, very low total wet weights were measured at the stations in the core of the OMZ (stns 26, 27, 28), where high abundance rates were mainly caused by few small-sized dominant species. This can be confirmed by previous studies from Gallardo et al. [30], who established the highest abundances of animals with low biomass and small average body size within the oxygen minimum zone on the continental margin off central Chile. The dominance of opportunistic species within the OMZ therefore appears to be an important pattern in the ecology of these hypoxic ecosystems. These key species play a crucial role through for example their contribution to essential ecosystem functions, such as bioturbation, their influence on community structure as keystone predators or prey species and as indicator species for the severity of hypoxia. As mentioned in the introduction, certain biological traits often develop as an adaptation in response to a lack of oxygen. Opportunistic species such as Paraprionospio pinnata and Magelona phyllisae dominate the OMZ among others due to their short lifespan and small body size. Other studies have already shown the relationship between these particular biological traits and typical characteristics of r-strategy species with hypoxic habitats [33,34]. In addition, the feeding strategy could also be an important adaptation to low oxygen concentrations. Although the relatively large and heavy omnivorous polychaetes Lumbrineris sp. and Nephtys ferruginea were mainly found at the stations in shallow water depths with low oxygen content, they showed significantly lower abundances than their opportunistic conspecifics. In the species-poor and bacteria-rich landscape of the OMZ, subsurface deposit feeders and interface feeders are likely to predominate, as the main food source is organic material that sinks down through the water column from the highly productive surface water. This is supported by the study of Bon et al. [13], who suggest that the greater number of permanent burrowers and bottom feeders is a life strategy to survive under hypoxic conditions. Deposit feeders facilitate the remineralisation of organic matter, contributing to benthic–pelagic coupling and serve as prey for demersal fish and invertebrate predators. Thereby, these taxa contribute to the maintenance of ecosystem functioning and energy flow in upwelling systems [35].
Outside the OMZ with significantly higher oxygen levels, a macrozoobenthic community could be discovered that consisted of completely different species. The lower slope below the OMZ was dominated by the polychaete families Cirratulidae, Amphinomidae, Oweniidae and Capitellidae. Additionally, members of the family Maldanidae also showed high abundances at greater water depths, in agreement with studies from Gallardo et al. [30].
The results of this study resonate with broader concerns about ocean deoxygenation, a global challenge exacerbated by climate change and anthropogenic nutrient loading. As OMZs expand and intensify, the ecological balance of affected regions could be disrupted, potentially leading to biodiversity loss and altered ecosystem services [36,37]. The study of benthic species communities in existing OMZs such as Concepción, Chile can therefore provide a preview of adaptations and processes that might prevail in the future [15]. The macrozoobenthic species communities are considered important regulators of the oceanic food webs, controlling benthic–pelagic energy transfer in the ecosystem through remineralisation and bioturbation of organic matter. Their diversity and abundance reflect broader environmental conditions, and they can provide insights into ecosystem stability [38,39]. Therefore, the study of benthic communities is of central importance to better understand the future changes in the structure and function of marine ecosystems in hypoxic waters.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d17040278/s1. The online version contains supplementary material with all abundance and biomass data (Tables S1 and S2) and the statistical results (Tables S3–S5). Table S1. Overview of the calculated abundance (ind./m2) data of all discovered species/species groups with the corresponding taxonomic classification of taxa at the 8 sampled stations. Table S2. Overview of the calculated biomass (fresh weight in g/m2) data of all discovered species/species groups with the corresponding taxonomic classification of taxa. classes and family level at the 8 sampled stations. Table S3. Results of the significance tests between the environmental factors oxygen, salinity and water depth and the species abundance. Table S4. Results of the significance tests between the 5 stations with high oxygen content (>100 µmol/L) and the 3 stations with low oxygen concentrations (<2 µmol/L) with regard to their species abundance. Table S5. Result of the SIMPER analysis of the 15 species with the highest proportions on the differences in species composition between the stations with low and those with higher oxygen content.
Author Contributions
M.L.Z. Sampling at sea; A.S.K. and M.L.Z.: taxonomy and lab work on land; A.S.K. and M.L.Z.: writing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The sampling cruise SO296 was part of the Mapuche project funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (grant no. 03G0296A).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval was not required for the nature of this work.
Data Availability Statement
Underlying data are available as Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We thank the officers and crew of the RV Sonne for their help at sea. The present study was part of the research expedition SO296. Thanks to Frank Pohl and Mayya Gogina (Rostock) for helping during the cruise.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Breitburg, D.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.; Grégoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Garçon, V.; Gilbert, D.; Gutiérrez, D.; Isensee, K.; et al. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, eaam7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.A.; Ekau, W.; Gooday, A.J.; Jorissen, F.; Middelburg, J.J.; Naqvi, S.W.A.; Neira, C.; Rabalais, N.N.; Zhan, J. Effects of natural and human-induced hypoxia on coastal benthos. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2063–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A.; Ekau, W.; Gooday, A.J.; Jorissen, F.; Middelburg, J.J.; Naqvi, W.; Neira, C.; Rabalais, N.N.; Zhang, J. Environmental Influences on Regional Deep-Sea Species Diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 51–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, O.; Pantoja, S. The oxygen minimum zone of the eastern South Pacific. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2009, 56, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstensen, J.; Stramma, L.; Visbeck, M. Oxygen minimum zones in the eastern tropical Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Prog. Oceanogr. 2008, 77, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, M.; Macaya, E.; Acuna, E.; Arntz, W.; Bastias, H.; Brokordt, K.; Camus, P.; Castilla, J.; Castro, L.; Cortés, M.; et al. The Humboldt Current System of Northern and Central Chile. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2007, 45, 195–345. [Google Scholar]
- Helly, J.J.; Levin, L.A. Global distribution of naturally occurring marine hypoxia on continental margins. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Espinoza, C. New communities of large filamentous sulfur bacteria in the eastern South Pacific. Int. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, H.N.; Strotmann, B.; Gallardo, V.A.; Jørgensen, B.B. Population study of the filamentous sulfur bacteria Thioploca spp. off the Bay of Concepción, Chile. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 200, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossing, H.; Gallardo, V.A.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Huttel, M.; Nielsen, L.P.; Schulz, H.; Canfield, D.E.; Forster, S.; Glud, R.N.; Gundersen, J.K.; et al. Concentration and transport of nitrate by the mat-forming sulphur bacterium Thioploca. Nature 1995, 374, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høgslund, S.; Revsbech, N.P.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Gallardo, V.A.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Nielsen, J.L.; Holmkvist, L.; Arning, E.T.; Nielsen, L.P. Physiology and behaviour of marine Thioploca. ISME J. 2009, 3, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Fonseca, A.; Musleh, S.; Espinoza, C. Extrapolations of Standing-Stocks of Big Bacteria in Humboldt Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystem (HEBCE). Ocean. Mar. Biol. 2013, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bon, M.; Grall, J.; Gusmao, J.B.; Fajardo, M.; Harrod, C.; Pacheco, A.S. Functional changes in benthic macrofaunal communities along a natural gradient of hypoxia in an upwelling system. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2021, 164, 112056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, E.; Quiñones, R.; Palma, M.; Sellanes, J.; Gallardo, V.A.; Gerdes, D.; Rowe, G. Biomass size-spectra of microbenthic communities in the oxygen minimum zone off Chile. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A. Oxygen minimum zone benthos: Adaptation and community response to hypoxia. Ocean. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 2003, 41, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, E.; Quiñones, R.A.; González, R.R.; Gallardo, V.A.; Jessen, G. Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of Paraprionospio pinnata (Polychaeta: Spionidae) in central Chile. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2007, 87, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.R.; Quiñones, R.A. Pyruvate Oxidoreductases Involved in Glycolytic Anaerobic Metabolism of Polychaetes from the Continental Shelf off Central-South Chile. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, P.A.; Gage, J.D. Morphological responses of macrobenthic polychaetes to low oxygen on the Oman continental slope, NW Arabian Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, K.; Loick-Wilde, N.; Yuen, B.; Osvatic, J.T.; Wäge-Recchioni, J.; Hausmann, B.; Petersen, J.M.; Fabian, J.; Wodarg, D.; Zettler, M.L. Chemoautotrophy, symbiosis and sedimented diatoms support high biomass of benthic molluscs in the Namibian shelf. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellanes, J.; Krylova, E. A new species of Calyptogena (Bivalvia: Vesicomyidae) from a recently discovered methane seepage area off Concepción Bay, Chile (~36°S). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, O.; Sellanes, J. New species of Thyasiridae from a methane seepage area off Concepción, Chile. Zootaxa 2005, 1092, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sellanes, J.; Quiroga, E.; Neira, C.; Gutiérrez, D. Changes of macrobenthos composition under different ENSO cycle conditions on the continental shelf off central Chile. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006; Volume 29, pp. 1060–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Huettel, M.; Forster, S.; Klöser, S.; Fossing, H. Vertical migration in the sediment-dwelling sulfur bacteria Thioploca spp. in overcoming diffusion limitations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, F.; Gallardo, V.A.; Baltazar, M. The structure of the benthic macrofauna collected across a transect at the central chile shelf and relationships with giant sulfur bacteria Thioploca spp. mats. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1999, 40, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zettler, M.L.; Bochert, R.; Pollehne, F. Macrozoobenthos diversity in an oxygen minimum zone off northern Namibia. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A.; Gage, J.D.; Martin, C.; Lamont, P.A. Macrobenthic community structure within and beneath the oxygen minimum zone, NW Arabian Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 189–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, K.; Zettler, M.L. Gradients and instability: Macrozoobenthic communities in the Benguela Upwelling System off Namibia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 291, 108421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, M.; Quiroga, E.; Gallardo, V.A.; Arntz, W.; Gerdes, D.; Schneider, W.; Hebbeln, D. Macrobenthic animal assemblages of the continental margin off Chile (22° to 42° S). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2005, 85, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Palma, M.; Carrasco, F.D.; Gutiérrez, D.; Levin, L.A.; Cañete, J.I. Macrobenthic zonation caused by the oxygen minimum zone on the shelf and slope off central Chile. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; Gallardo, V.A.; Mayor, S.; Neira, C.; Vásquez, C.; Sellanes, J.; Rivas, M.; Soto, A.; Carrasco, F.; Baltazar, M. Bioturbation potential of macrofauna in sublitoral organic-rich sediments off central Chile: Spatial and temporal variation under ‘El Niño’ 1997/98. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 202, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Carrasco, F.D.; Roa, R.; Cañete, J.I. Ecological patterns in the benthic macrobiota across the continental shelf off central Chile. Ophelia 1995, 40, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.S.; González, M.T.; Bremner, J.; Oliva, M.; Heilmayer, O.; Laudien, J.; Riascos, J.M. Functional diversity of marine macrobenthic communities from sublittoral soft-sediment habitats off northern Chile. Helgol. Mari. Res. 2011, 65, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, D.M.; Maybury, C.A.; Ewing, R.M. Feeding behavior and general ecology of several Spionid polychaetes from the Chesapeake Bay. J. Exp. Mar. Ecol. Biol. 1981, 54, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M. Thresholds of hypoxia for marine biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 107, 15452–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramma, L.; Schmidtko, S.; Levin, L.A.; Johnson, G.C. Ocean oxygen minima expansions and their biological impacts. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villnäs, A.; Norkko, J.; Lukkari, K.; Hewitt, J.; Norkko, A. Consequences of increasing hypoxic disturbance on benthic communities and ecosystem functioning. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Marine benthic hypoxia: A review of its ecological effects and the behavioural responses of benthic macrofauna. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 1995, 33, 245–303. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).