Denser Mitogenomic Sampling for Exploring the Phylogeny of Tellinoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Next-Generation Sequencing
2.2. Mitochondrial Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Gene Order Analysis
2.4. Sequence Analysis and Alignment
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
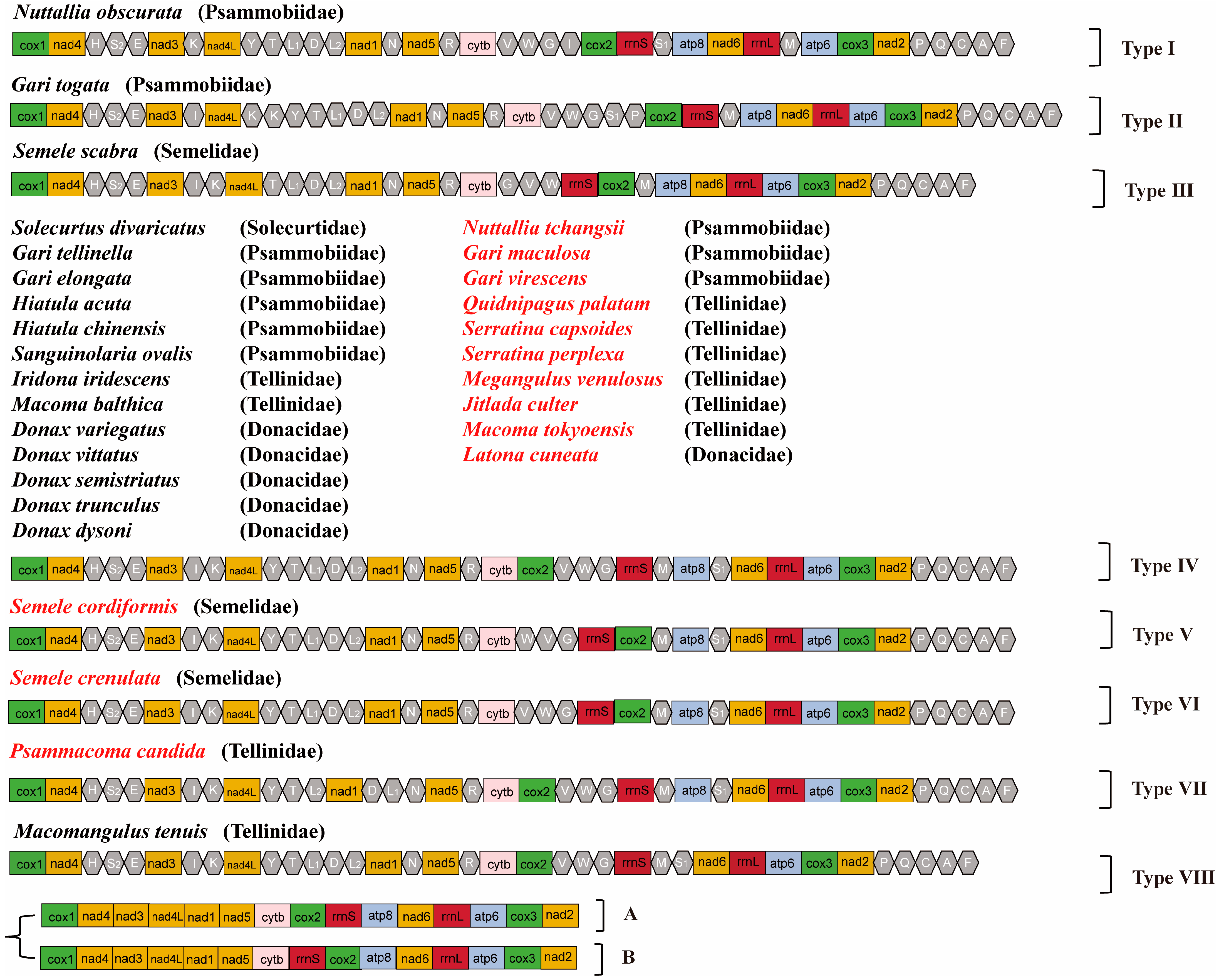
3.2. Gene Arrangements of the Mitochondrial Genome
3.3. Mitochondrial Genome Structure and Organization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MolluscaBase. Taxon Tree. Available online: https://www.molluscabase.org (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Moncada, E.; Lord, A.; Simone, L.R.L.; Adjei-Boateng, D.; Bouchet, P.; Strong, E.E.; Bieler, R.; Giribet, G. Marine surf to freshwater: A molecular phylogeny of Donacidae (Bivalvia: Heterodonta). Invertebr. Syst. 2022, 36, 984–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitonis, J.E.V.V.; Zaniratto, C.P.; Machado, F.M.; Passos, F.D. Comparative studies on the histology and ultrastructure of the siphons of two species of Tellinidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia) from Brazil. Zoologia 2012, 29, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, H.; Ohnishi, M. Fatty acid compositions of various tissue lipids in the marine bivalves, Megangulus venulosus and Megangulus zyonoensis, from coastal waters of Hokkaido, Northern Japan. J. Oleo Sci. 2003, 52, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pérez, J.; Nantón, A.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Camacho, J.P.M.; Méndez, J. First complete female mitochondrial genome in four bivalve species genus Donax and their phylogenetic relationships within the Veneroida order. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.D.; Williams, S.T.; Glover, E.A.; Dyal, P. A molecular phylogeny of heterodont bivalves (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Heterodonta): New analyses of 18S and 28S rRNA genes. Zool. Scr. 2007, 36, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combosch, D.J.; Collins, T.M.; Glover, E.A.; Graf, D.L.; Harper, E.M.; Healy, J.M.; Kawauchi, G.Y.; Lemer, S.; McIntyre, E.; Strong, E.E.; et al. A family-level tree of life for bivalves based on a Sanger-sequencing approach. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 107, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, G.; Shimamura, S.; Takaki, Y.; Yokobori, S.; Ohara, Y.; Takishita, K.; Maruyama, T.; Fujikura, K.; Yoshida, T. Updated mitochondrial phylogeny of Pteriomorph and Heterodont Bivalvia, including deep-sea chemosymbiotic Bathymodiolus mussels, vesicomyid clams and the thyasirid clam Conchocele cf. bisecta. Mar. Genom. 2017, 31, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Kong, L. The complete mitochondrial genomes of six heterodont bivalves (Tellinoidea and Solenoidea): Variable gene arrangements and phylogenetic implications. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Jiang, L.; Kong, L.; Li, Q. Comparative mitogenomic analysis of the superfamily Tellinoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia): Insights into the evolution of the gene rearrangements. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D 2020, 36, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, L.R.L.; Wilkinson, S. Comparative morphological study of some Tellinidae from Thailand (Bivalvia: Tellinoidea). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 154, 167–191. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, R.C.; Da Silva, A.M.; Simone, L.R.L. Cladistic analysis of the transisthmian genus Eurytellina (Bivalvia: Tellinoidea) based on morphological and morphometric data. Organ. Divers. Evol. 2022, 22, 857–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistão, A.R.; Audino, J.A.; Passos, F.D. Comparative anatomy of siphons in tellinoidean clams (Bivalvia, Tellinoidea). J. Morphol. 2024, 285, e21762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Kocot, K.M.; Yang, Y.; Qi, L.; Li, Q.; Halanych, K.M. Mitogenomics reveals phylogenetic relationships of Arcoida (Mollusca, Bivalvia) and multiple independent expansions and contractions in mitochondrial genome size. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 150, 106857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Kong, L.; Sasaki, T.; Li, Q. Phylogenomic resolution of Imparidentia (Mollusca: Bivalvia) diversification through mitochondrial genomes. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kwak, H.; Shin, J.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, T.; Park, J.K. A mitochondrial genome phylogeny of Mytilidae (Bivalvia: Mytilida). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 139, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Park, C.; Kijima, A. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in the Pacific abalone, Haliotis discus hannai. J. Shellfish Res. 2002, 21, 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single—Cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, e18. [Google Scholar]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, K.; Parkhill, J.; Crook, J.; Horsnell, T.; Rice, P.; Rajandream, M.-A.; Barrell, B. Artemis: Sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L.; Macey, J.R.; Medina, M. Sequencing and comparing whole mitochondrial genomes of animals. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 395, 311–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laslett, D.; Canbäck, B. ARWEN: A program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemer, S.; Bieler, R.; Giribet, G. Resolving the relationships of clams and cockles: Dense transcriptome sampling drastically improves the bivalve tree of life. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20182684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrash, A.; Arick, M.; Peterson, D.G. Quack: A quality assurance tool for high throughput sequence data. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 548, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forni, G.; Puccio, G.; Bourguignon, T.; Evans, T.; Mantovani, B.; Rota-Stabelli, O.; Luchetti, A. Complete mitochondrial genomes from transcriptomes: Assessing pros and cons of data mining for assembling new mitogenomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Uribe, J.E.; Zardoya, R. Conidae phylogenomics and evolution. Zool. Scr. 2019, 48, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Qi, L.; Kong, L.; Li, Q. Mitogenomics reveals phylogenetic relationships of Patellogastropoda (Mollusca, Gastropoda) and dynamic gene rearrangements. Zool. Scr. 2022, 51, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Merkle, D.; Ramsch, K.; Fritzsch, G.; Perseke, M.; Bernhard, D.; Schlegel, M.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M. CREx: Inferring genomic rearrangements based on common intervals. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2957–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieler, R.; Mikkelsen, P.M.; Collins, T.M.; Glover, E.A.; González, V.L.; Graf, D.L.; Harper, E.M.; Healy, J.; Kawauchi, G.Y.; Sharma, P.P.; et al. Investigating the bivalve tree of life—An exemplar—Based approach combining molecular and novel morphological characters. Invertebr. Syst. 2014, 28, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE7: New and improved tools for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kück, P.; Meusemann, K. FASconCAT: Convenient handling of data matrices. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 56, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ—TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum—likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.4. 2014. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzyński, A.; Śmietanka, B.; Fernández-Pérez, J.; Lubośny, M. The Absence of Canonical Respiratory Complex I Subunits in Male-Type Mitogenomes of Three Donax Species. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Shen, X.; Jiang, F.; Liu, B. The mitochondrial genomes of two scallops, Argopecten irradians and Chlamys farreri (Mollusca: Bivalvia): The most highly rearranged gene order in the family Pectinidae. J. Mol. Evol. 2010, 70, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Heng, X.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, A.; Yang, Y. Comparative mitogenomic analyses of the infraclass Pteriomorphia (Mollusca: Bivalvia) provides novel insights into gene rearrangement and phylogeny. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D 2024, 53, 101361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantatore, P.; Gadaleta, M.N.; Roberti, M.; Saccone, C.; Wilson, A.C. Duplication and remoulding of tRNA genes during the evolutionary rearrangement of mitochondrial genomes. Nature 1987, 329, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissi, C.; Iannelli, F.; Pesole, G. Evolution of the mitochondrial genome of Metazoa as exemplified by comparison of congeneric species. Heredity 2008, 101, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śmietanka, B.; Burzyński, A.; Wenne, R. Comparative genomics of marine mussels (Mytilus spp.) gender associated mtDNA: Rapidly evolving atp8. J. Mol. Evol. 2010, 71, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Gao, S.; Zhao, M.; Lv, H.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, J. Mitochondrial genomic analyses provide new insights into the “missing” atp8 and adaptive evolution of Mytilidae. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.T.; Foster, P.G.; Hughes, C.; Harper, E.M.; Taylor, J.D.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Dyal, P.; Hopkins, K.P.; Briscoe, A.G. Curious bivalves: Systematic utility and unusual properties of anomalodesmatan mitochondrial genomes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 110, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, B.T.; Kerr, L.J.; McKiernan, J.M.; Jansen, E.S.; Hanna, P.J. Mitochondrial DNA sequence and gene organization in the Australian blacklip abalone Haliotis rubra (Leach). Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capt, C.; Bouvet, K.; Guerra, D.; Robicheau, B.M.; Stewart, D.T.; Pante, E.; Breton, S. Unorthodox features in two venerid bivalves with doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondria. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, H.; Steiner, G. The complete sequences and gene organisation of the mitochondrial genomes of the heterodont bivalves Acanthocardia tuberculata and Hiatella arctica—And the first record for a putative ATPase subunit 8 gene in marine bivalves. Front. Zool. 2006, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Fujiwara, M. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Japanese cockle Fulvia mutica (Cardiidae). Fish. Sci. 2013, 79, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, W.; Yu, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the giant clam Tridacna derasa (Tridacnidae: Tridacna). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 3, 911–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of giant clam, Hippopus hippopus (Cardiidae: Tridacninae). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2019, 11, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Ye, Y. Complete sequence and gene organization of the mitochondrial genome of clam Donax dysoni. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2023, 54, 246–258. [Google Scholar]
- Saunier, A.; Garcia, P.; Becquet, V.; Marsaud, N.; Escudié, F.; Pante, E. Mitochondrial genomes of the Baltic clam Macoma balthica (Bivalvia: Tellinidae): Setting the stage for studying mito-nuclear incompatibilities. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2014, 14, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Order | Genbank | Length (bp) | Locality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latona cuneata | Donacidae | PQ851673 | 16,921 | Lingshui, Hainan, China |
| Semele crenulata | Semelidae | PQ238728 | 16,671 | Lingshui, Hainan, China |
| Semele cordiformis | Semelidae | PQ238729 | 16,260 | Beihai, Gangxi, China |
| Macoma tokyoensis | Tellinidae | PQ851675 | 16,606 | Qingdao, Shandong, China |
| Megangulus venulosus | Tellinidae | PQ306545 | 16,143 | Qingdao, Shandong, China |
| Jitlada culter | Tellinidae | PQ306547 | 16,483 | Rizhao, Shandong, China |
| Psammacoma candida | Tellinidae | PQ221920 | 16,933 | Qingdao, Shandong, China |
| Serratina perplexa | Tellinidae | PQ356192 | 16,673 | Fangchenggang, Gangxi, China |
| Serratina capsoides | Tellinidae | PQ839686 | 16,590 | Wenchang, Hainan, China |
| Quidnipagus palatam | Tellinidae | PQ851674 | 16,650 | Sanya, Hainan, China |
| Gari maculosa | Psammobiidae | PQ276911 | 16,555 | Fangchenggang, Gangxi, China |
| Nuttallia tchangsii | Psammobiidae | PQ306546 | 16,695 | Lingao, Hainan, China |
| Gari virescens | Psammobiidae | PQ306548 | 16,116 | Wenchang, Hainan, China |
| Species | (A+T) % | AT Skew | GC Skew | rRNA Length | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitogenome | PCGs | Mitogenome | PCGs | Mitogenome | PCGs | rrnS | rrnL | |
| Latona cuneata | 62.2 | 61.4 | −0.212 | −0.274 | 0.323 | 0.328 | 858 | 1255 |
| Semele crenulata | 60.6 | 60.1 | −0.261 | −0.341 | 0.442 | 0.455 | 892 | 1373 |
| Semele cordiformis | 62 | 62 | −0.252 | −0.313 | 0.465 | 0.484 | 915 | 1301 |
| Macoma tokyoensis | 63.1 | 62.5 | −0.217 | −0.299 | 0.441 | 0.355 | 878 | 1330 |
| Megangulus venulosus | 58 | 57.3 | −0.262 | −0.33 | 0.357 | 0.362 | 892 | 1331 |
| Jitlada culter | 65.4 | 65.5 | −0.223 | −0.282 | 0.372 | 0.374 | 894 | 1362 |
| Psammacoma candida | 60.3 | 60 | −0.23 | −0.29 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 883 | 1349 |
| Serratina perplexa | 63.1 | 62.8 | −0.261 | −0.322 | 0.377 | 0.382 | 891 | 1466 |
| Serratina capsoides | 63 | 63.1 | −0.283 | −0.341 | 0.395 | 0.408 | 893 | 1440 |
| Quidnipagus palatam | 61.3 | 61.5 | −0.272 | −0.34 | 0.39 | 0.387 | 894 | 1458 |
| Gari maculosa | 63.3 | 62.5 | −0.261 | −0.338 | 0.341 | 0.376 | 880 | 1438 |
| Nuttallia tchangsii | 60.8 | 60.5 | −0.128 | −0.289 | 0.303 | 0.301 | 880 | 1367 |
| Gari virescens | 62.4 | 61.9 | −0.24 | −0.318 | 0.307 | 0.312 | 865 | 1323 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, W.; Xu, T.; Gong, J.; Kong, L. Denser Mitogenomic Sampling for Exploring the Phylogeny of Tellinoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Diversity 2025, 17, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050303
Tang W, Xu T, Gong J, Kong L. Denser Mitogenomic Sampling for Exploring the Phylogeny of Tellinoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Diversity. 2025; 17(5):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050303
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Weikang, Tao Xu, Jihang Gong, and Lingfeng Kong. 2025. "Denser Mitogenomic Sampling for Exploring the Phylogeny of Tellinoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia)" Diversity 17, no. 5: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050303
APA StyleTang, W., Xu, T., Gong, J., & Kong, L. (2025). Denser Mitogenomic Sampling for Exploring the Phylogeny of Tellinoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Diversity, 17(5), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050303






