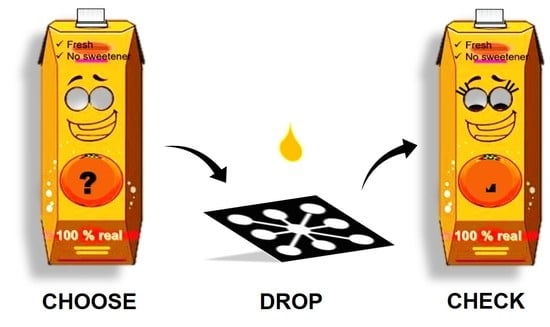
Multiplexed Paper Microfluidics for Titration and Detection of Ingredients in Beverages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Paper Microfluidics for Titration Experiments
2.3. Design of Paper Microfluidics to Identify Biochemical Compounds in Packaged Fruit Juices
2.4. Designing Multiplexed Test Strips
2.5. UV-VIS Spectrophotometry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Titration on Paper Microfluidics
3.2. Identifying Biochemical Compounds in Packaged Fruit Juices
3.3. Multiplexed Test Strips to Identify the Components of Fruit Juices
3.4. UV Spectrophotometry
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hua, M.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. Detecting Chemical Hazards in Foods Using Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices (μPADs): The Real-World Application. Micromachines 2018, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busa, L.; Mohammadi, S.; Maeki, M.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Tokeshi, M. Advances in microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for food and water analysis. Micromachines 2016, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, Z.; Shah, M.P.; Wikswo, M.E.; Barclay, L.; Kisselburgh, H.; Kambhampati, A.; Cannon, J.L.; Parashar, U.D.; Vinjé, J.; Hall, A.J. Epidemiology of Foodborne Norovirus Outbreaks–United States, 2009–2015. Food Saf. 2018, 6, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.; Reuhs, B.L.; Nielsen, S.S. Analysis of food contaminants, residues, and chemical constituents of concern. In Food Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 317–349. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Lantigua, D.; Meka, A.; Taing, S.; Pandher, M.; Camci-Unal, G. Based Sensors: Emerging Themes and Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, J.A.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical detection in paper-based analytical devices using microwire electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 891, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunney, J.; Williamson, S.; Atkin, D.; Jeanneret, M.; Cozzolino, D.; Chapman, J. The Use of Electrochemical Biosensors in Food Analysis. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2017, 5, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A.; Bakker, E. based thin-layer coulometric sensor for halide determination. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokerst, J.C.; Adkins, J.A.; Bisha, B.; Mentele, M.M.; Goodridge, L.D.; Henry, C.S. Development of a paper-based analytical device for colorimetric detection of select foodborne pathogens. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.Z.; Luckham, R.E.; McFadden, M.J.; Brennan, J.D. Reagentless bidirectional lateral flow bioactive paper sensors for detection of pesticides in beverage and food samples. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9055–9064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J. Electroanalytical sensors and devices for multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogen microorganisms. Sensors 2009, 9, 5503–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Weng, X.; Tah, A.; Cordero, J.; Ragavan, K. Nano-biosensor platforms for detecting food allergens–New trends. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2018, 18, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhang, W. Microarray technology for major chemical contaminants analysis in food: Current status and prospects. Sensors 2012, 12, 9234–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Moodley, K.; Govender, U.; Chen, H.; Fourie, L.; Ngwenya, S.; Kumar, S.; Mjwana, P.; Cele, H.; Mbanjwa, M.B. Based smart microfluidics for education and low-cost diagnostics. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2015, 111, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.M.; Tarn, M.D.; Choudhury, T.A.; Hewitt, L.C.; Mayo, A.J.; Rubin, T.A.; Waller, M.R.; Christensen, M.G.; Dawson, A.; Pamme, N. Lab-on-a-chip workshop activities for secondary school students. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrilho, E.; Phillips, S.T.; Vella, S.J.; Martinez, A.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper microzone plates. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5990–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Prasad, A.; Maurya, P.; Chandra, P. Nanobiosensors: Next generation point-of-care biomedical devices for personalized diagnosis. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2016, 7, e125. [Google Scholar]
- Lisowski, P.; Zarzycki, P.K. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) and micro total analysis systems (μTAS): Development, applications and future trends. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, H.G.; Tobin, G. Nutrition and Food Processing; Croom Helm: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.; Hasan, S.M.A.; Grouchy, S.; Gartia, M.R. DNA microarray analysis using a smartphone to detect the BRCA-1 gene. Analyst 2019, 144, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, Á.; Vicente, J.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.; Casquel, R.; Santamaría, B.; Maigler, M.; Hernández, A.; Ramírez, Y. On the determination of uncertainty and limit of detection in label-free biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.A.; Pry, T. Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2008, 29, S49. [Google Scholar]
- Karita, S.; Kaneta, T. Acid–base titrations using microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12108–12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.M.; Kernisan, E.N.; Lieberman, M. Lab on paper: Iodometric titration on a printed card. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3764–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y. A Low-Cost and High Sensitive Paper-Based Microfluidic Device for Rapid Detection of Glucose in Fruit. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardane, B.M.; Wei, S.; McKelvie, I.D.; Kolev, S.D. Microfluidic paper-based analytical device for the determination of nitrite and nitrate. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7274–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Rasband, W. ImageJ user guide. Imagej/Fiji 2012, 1, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- De Quirós, A.R.-B.; Fernández-Arias, M.; López-Hernández, J. A screening method for the determination of ascorbic acid in fruit juices and soft drinks. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand. Survey of Nitrates and Nitrites in Food and Beverages in Australia; Food Standards Australia New Zealand: Canberra, Australia, 2013.
- Bahadoran, Z.; Mirmiran, P.; Jeddi, S.; Azizi, F.; Ghasemi, A.; Hadaegh, F. Nitrate and nitrite content of vegetables, fruits, grains, legumes, dairy products, meats and processed meats. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 51, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carwile, J.; Willett, W.; Spiegelman, D.; Hertzmark, E.; Rich-Edwards, J.; Frazier, A.; Michels, K. Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and age at menarche in a prospective study of US girls. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gregg, E.W.; Flanders, W.D.; Merritt, R.; Hu, F.B. Added sugar intake and cardiovascular diseases mortality among US adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Konno, M.; Shimura, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Takahashi, H.; Hashizume, K. Formation of Guaiacol by Spoilage Bacteria from Vanillic Acid, a Product of Rice Koji Cultivation, in Japanese Sake Brewing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4599–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Analyte | Common Beverages | Amount Present | Concentration (C) | Present Study (LOD) | C/LOD | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Low citric fruit juice | 23–66 mg/125 mL | 1–3 mM | 1.47 µM | ~1000 | [29] |
| Fruit & Vegetable mixed juice | 35–73 mg/12 mL | 16–34 mM | 1.47 µM | ~1000 | ||
| Nitrite | Fruit & Vegetable juice | 0.71 mg/100 g | 0.1 mM | 0.06 mM | 1.5 | [30,31] |
| Sugar | Sodas, Fruit juice, Ice Tea | 11 g/100 mL | 600 mM | 20 mM | 30 | [32,33] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prasad, A.; Tran, T.; Gartia, M.R. Multiplexed Paper Microfluidics for Titration and Detection of Ingredients in Beverages. Sensors 2019, 19, 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061286
Prasad A, Tran T, Gartia MR. Multiplexed Paper Microfluidics for Titration and Detection of Ingredients in Beverages. Sensors. 2019; 19(6):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061286
Chicago/Turabian StylePrasad, Alisha, Tiffany Tran, and Manas Ranjan Gartia. 2019. "Multiplexed Paper Microfluidics for Titration and Detection of Ingredients in Beverages" Sensors 19, no. 6: 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061286
APA StylePrasad, A., Tran, T., & Gartia, M. R. (2019). Multiplexed Paper Microfluidics for Titration and Detection of Ingredients in Beverages. Sensors, 19(6), 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061286