Industrial Internet of Things over 5G: A Practical Implementation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A 5G IoT end device that is retrofittable and provides the means to seamlessly and non-intrusively actuate and sense different aspects of various industrial assets as well as their surrounding environment;
- A 5G network deployed on the shop floor, supporting the industrial NPN, while the communication performance is tailored to the specific needs of the target industrial use cases;
- An intelligent assistant that collects and processes real-time data aiming to make future behaviour predictions and to detect anomalies;
- A practical implementation of the proposed infrastructure and application components that serves as a baseline and provides lessons learned for future deployments of IIoT over a 5G NPN.
2. Related Work
3. Use Cases and Requirements
3.1. Retrofit and Predictive Maintenance Use Case
3.2. Energy Management Use Case
3.3. System Requirements
4. Infrastructure and Application Components
4.1. 5G IoT End Device
4.2. Industrial 5G Network
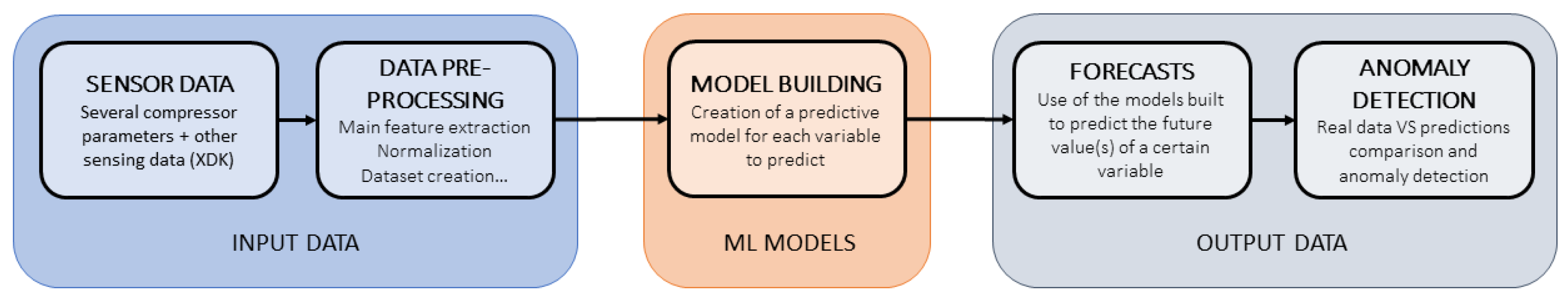
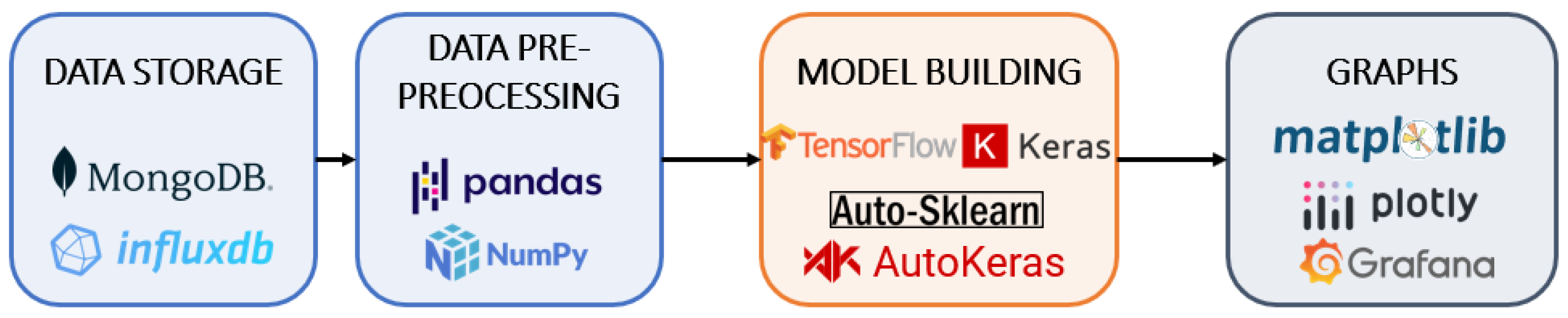
4.3. Intelligent Assistant
5. Validation Tests
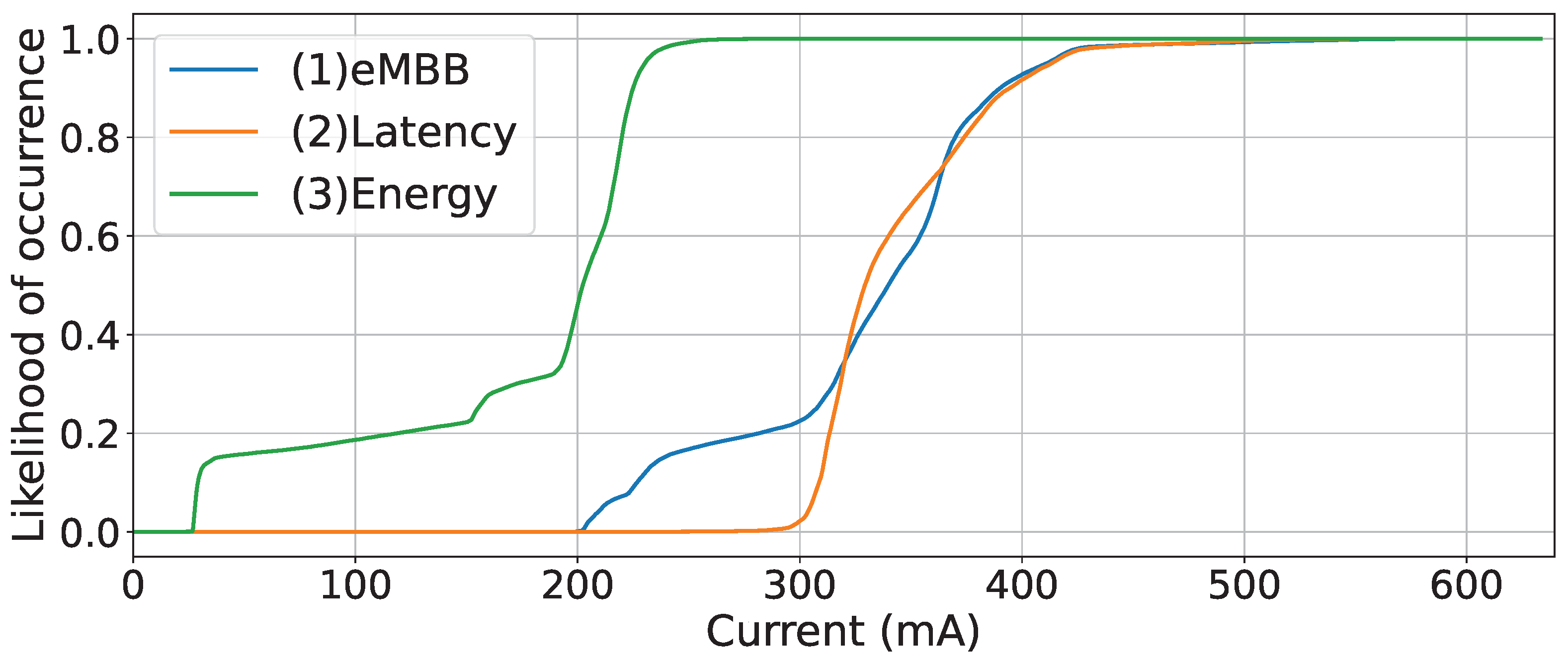
5.1. Capability Assessment of the Industrial 5G Network
5.2. Performance Assessment of the 5G IoT End Device
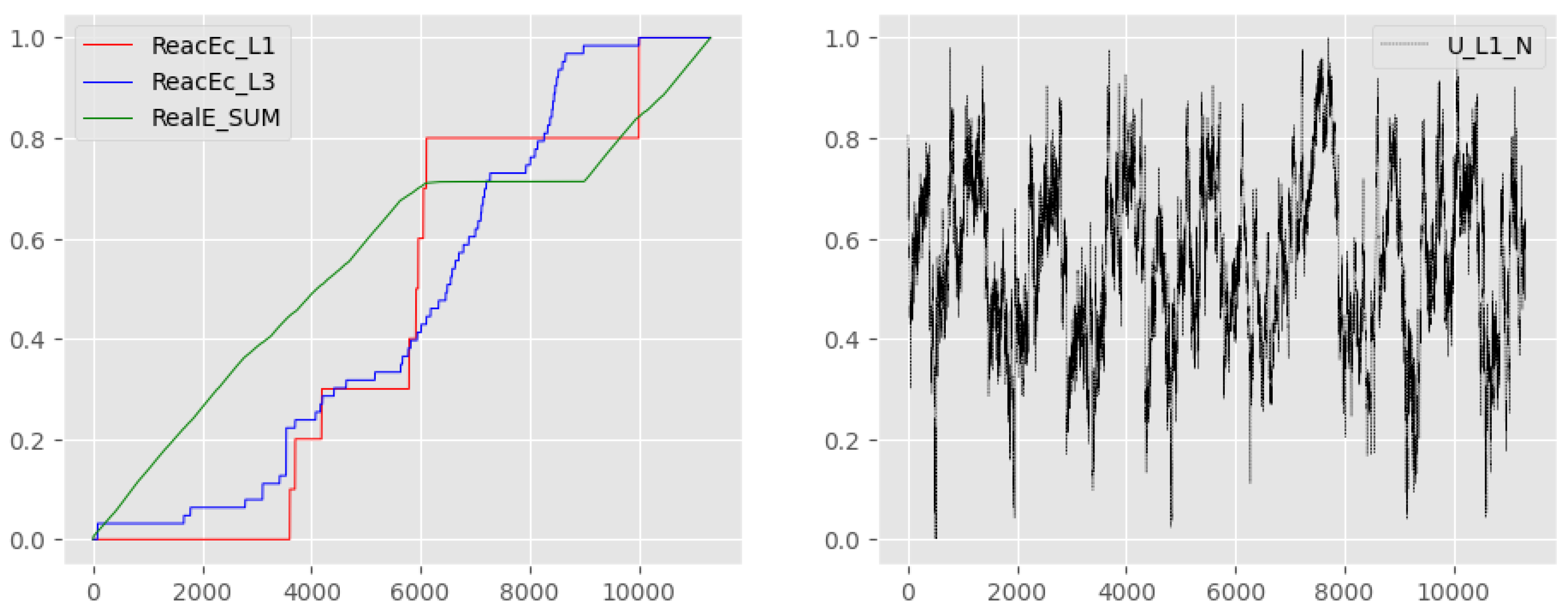
5.3. Intelligent Assistant
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3GPP | Third Generation Partnership Project |
| 5G-ACIA | 5G Alliance for Connected Industries and Automation |
| 5G SA | 5G Standalone |
| 5G NSA | 5G Non Standalone |
| 5G NR | 5G New Radio |
| AUSF | Authentication Server Function |
| AMF | Access and Mobility Management Function |
| BBU | Baseband Unit |
| BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy |
| Bosch TT | Bosch Termotecnologia |
| CDF | Cumulative Distribution Function |
| CPE | Customer-Premises Equipment |
| DNN | Data Network Name |
| eMBB | Enhanced Mobile Broadband |
| GPIO | General Purpose Input/Output |
| GSM | Global System for Mobile Communications |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit |
| IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| ITAV | Instituto de Telecomunicações in Aveiro |
| KPI | Key Performance Indicator |
| LADN | Local Area Data Network |
| LBO | Local BreakOut |
| LTE | Long-Term Evolution |
| LTE-M | Long-Term Evolution Machine Type Communication |
| MEC | Multi-access Edge Computing |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| mMTC | Massive Machine-Type Communications |
| MQTT | Message Queuing Telemetry Transport |
| NB-IoT | Narrow Band IoT |
| NFs | Network Functions |
| NFVI | NFV Infrastructure |
| NPN | Non-Public Network |
| NRF | Network Repository Function |
| NSSF | Network Slice Selection Function |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| PDU | Protocol Data Unit |
| PNI-NPN | Public Network Integrated Non-Public Network |
| PPP | Point-to-Point Protocol |
| pRRU | Pico Remote Radio Unit |
| R15 | Release 15 |
| RAN | Radio Access Network |
| RGB | RGB |
| RHUB | Remote HUB |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| RSRP | Reference Signal Received Power |
| RTT | Round-Trip Time |
| SCoT | Smart Cloud of Things |
| SIM | Subscriber Identity Module |
| SMF | Session Management Function |
| SMU | Source Meter Unit |
| SNPN | Stand-Alone Non-Public Network |
| SoC | System-on-Chip |
| SPI | Serial Peripheral Interface |
| TA | Tracking Area |
| TAI | Tracking Area Identifier |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| UART | Universal Asynchronous Receiver–Transmitter |
| UDM | Unified Data Management |
| UDP | User Datagram Protocol |
| UE | User Equipment |
| ULCL | Uplink Classifier |
| UPF | User Plane Function |
| URLLC | Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| USB-C | Universal Serial Bus Type-C |
References
- Aijaz, A. Private 5G: The future of industrial wireless. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2020, 14, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, M.; Collins, M.; Patel, M. The Internet of Things: Catching up to an Accelerating Opportunity. 2021. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/iot-value-set-to-accelerate-through-2030-where-and-how-to-capture-it (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- O’Connell, E.; Moore, D.; Newe, T. Challenges Associated with Implementing 5G in Manufacturing. Telecom 2020, 1, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G-ACIA. 5G-ACIA White Paper: 5G Non-Public Networks for Industrial Scenarios; 5G-ACIA: Hessen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lemes, M.T.; Alberti, A.M.; Both, C.B.; De Oliveira Júnior, A.C.; Cardoso, K.V. A Tutorial on Trusted and Untrusted Non-3GPP Accesses in 5G Systems—First Steps Toward a Unified Communications Infrastructure. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 116662–116685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Rouf, R.; Mazur, K.; Kontsos, A. The Industry Internet of Things (IIoT) as a Methodology for Autonomous Diagnostics in Aerospace Structural Health Monitoring. Aerospace 2020, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesjak, C.; Bock, H.; Hein, D.; Maritsch, M. Hardware-secured and transparent multi-stakeholder data exchange for industrial IoT. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 14th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Poitiers, France, 19–21 July 2016; pp. 706–713. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.D.; Vo, H.Q.; Le, L.N.; Eo, S.; Kim, L. An IoT hardware platform architecture for monitoring power grid systems based on heterogeneous multi-sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocero, L.; Amaxilatis, D.; Mylonas, G.; Chatzigiannakis, I. Open source IoT meter devices for smart and energy-efficient school buildings. HardwareX 2017, 1, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferagić, A.; Famaey, J.; De Poorter, E.; Hoebeke, J. Survey on wireless technology trade-offs for the industrial internet of things. Sensors 2020, 20, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, W.; Tao, F.; Lin, C.L. Industrial IoT in 5G environment towards smart manufacturing. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2018, 10, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Hao, F.; Cai, Z. An Efficient Approach to Sharing Edge Knowledge in 5G-Enabled Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, N. 5G Deployment: Standalone vs. Non-Standalone from the Operator Perspective. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Zemouri, S.; Verikoukis, C. Performance evaluation and comparison between SA and NSA 5G networks in indoor environment. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Mediterranean Conference on Communications and Networking (MeditCom), Athens, Greece, 7–10 September 2021; pp. 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Yang, Q. EcoSense: A Hardware Approach to On-Demand Sensing in the Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, S.; Marcon, M.; Milani, S.; Tubaro, S. Advanced assistive maintenance based on augmented reality and 5G networking. Sensors 2020, 20, 7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 3GPP TR 28.807. Study on Management of Non-Public Networks (NPN). V17.0.0, 2020-12. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/ftp/Specs/archive/28_series/28.807/ (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Ordonez-Lucena, J.; Chavarria, J.F.; Contreras, L.M.; Pastor, A. The use of 5G Non-Public Networks to support Industry 4.0 scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), Granada, Spain, 28–30 October 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Abedin, S.F.; Sauter, T.; Gidlund, M.; Landernäs, K. Factory 5G: A Review of Industry-Centric Features and Deployment Options. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2022, 16, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, R.S.; Rocha, A.D.; Coelho, A.; Oliveira, J.B. A highly flexible, distributed data analysis framework for industry 4.0 manufacturing systems. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2017, 694, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, D.; Costa, D.; Rocha, E.M.; Almeida, D.; Santos, J.P. Predictive maintenance on sensorized stamping presses by time series segmentation, anomaly detection, and classification algorithms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravin, P.; Tan, J.Z.M.; Yap, K.S.; Wu, Z. Hyperparameter optimisation strategies for machine learning-based stochastic energy efficient scheduling in cyber-physical production systems. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2022, 4, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallisto® Sensor Platform. Available online: https://sensry.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SY020-PCB-FLY001.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- nRF52840. Available online: https://www.nordicsemi.com/products/nrf52840 (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Zephyr Project. Available online: https://www.zephyrproject.org (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- 5G RG50xQ Series. Available online: https://www.quectel.com/product/5g-rg50xq-series (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Meyer, G. RFC1968: The PPP Encryption Control Protocol (ECP); IETF: Wilmington, DE, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Abracon. 5G NR/4G/LTE Ceramic Chip Antenna. 2020. Available online: https://abracon.com/datasheets/5G-NR-_4G_-LTE-Ceramic-Chip-Antenna.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- ICS-43434. Available online: https://product.tdk.com/system/files/dam/doc/product/sw_piezo/mic/mems-mic/data_sheet/ds-000069-ics-43434-v1.2.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- KX134-1211. Available online: https://www.kionix.com/product/KX134-1211 (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Quectel. RG50xQ Series Hardware Design. 2021. Available online: https://forums.quectel.com/uploads/short-url/gZbwan0OT4teshliYw6xhFmI1yh.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Quevedo, J.; Perdigão, A.; Santos, D.; Silva, R.; Aguiar, R.L. 5GAIner: Taking the verticals into the 5G road. In Proceedings of the EuCNC & 6G Summit-OPE, Gothenburg, Sweden, 6–9 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP ETSI TS 23.501. System Architecture for the 5G System (5GS). V16.6.0, 2020-10. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3144 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Antunes, M.; Santiago, A.R.; Manso, S.; Regateiro, D.; Barraca, J.P.; Gomes, D.; Aguiar, R.L. Building an IoT Platform Based on Service Containerisation. Sensors 2021, 21, 6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendeiro, P.M.B.S. Energy Management Solution for Industrial IoT. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Camarneiro, D.J. Industrial Internet of Things and Connectivity, in Bosch. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- De Matos, G.A.V. Web Services for Shop-Floor Energetic Consumption Monitoring, Based on the Eclipse IoT Platforms: Bosch and SCoT. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, P.M.R. Agente Inteligente Para Gestão de Eletricidade. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Veedu, S.N.K.; Mozaffari, M.; Höglund, A.; Yavuz, E.A.; Tirronen, T.; Bergman, J.; Wang, Y.P.E. Toward Smaller and Lower-Cost 5G Devices with Longer Battery Life: An Overview of 3GPP Release 17 RedCap. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2022, 6, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G RedCap RG255C Series. Available online: https://www.quectel.com/product/5g-redcap-rg255c-series (accessed on 10 April 2023).

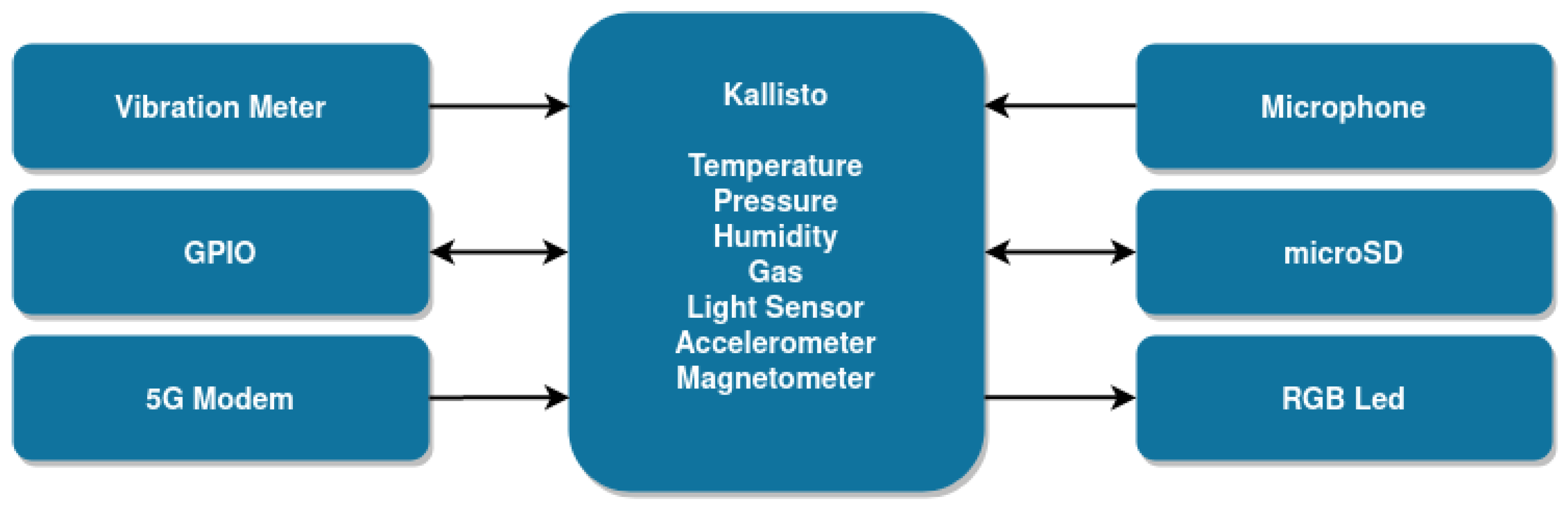
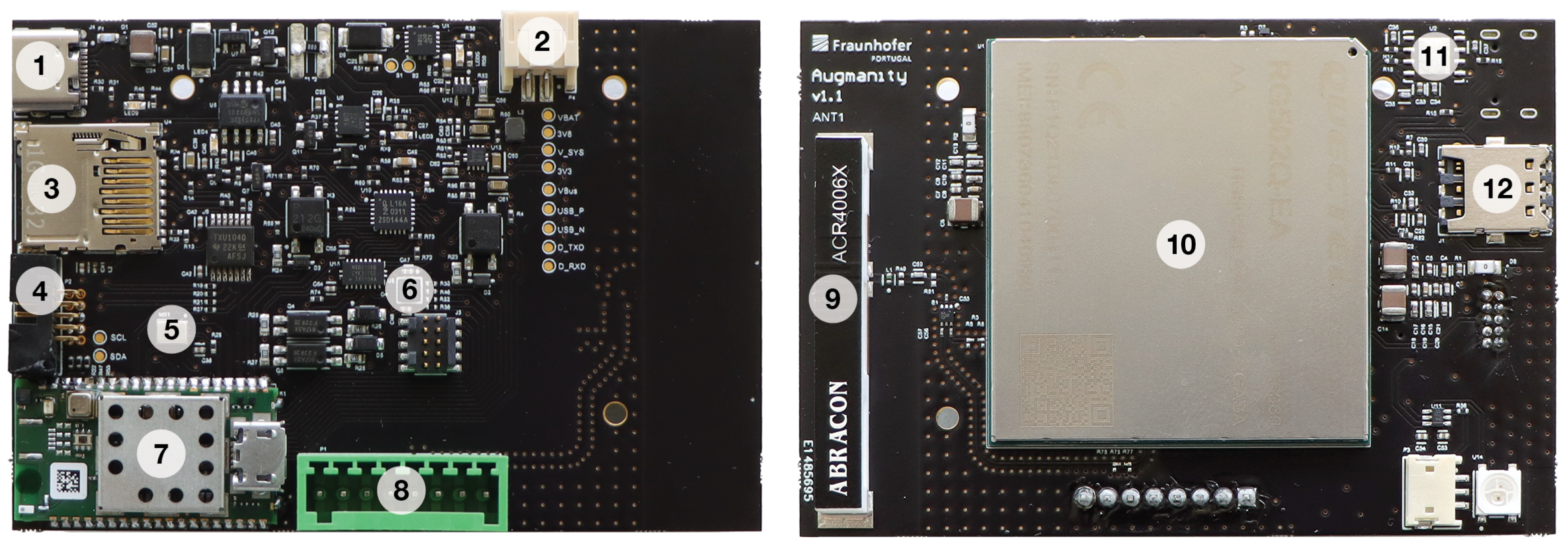

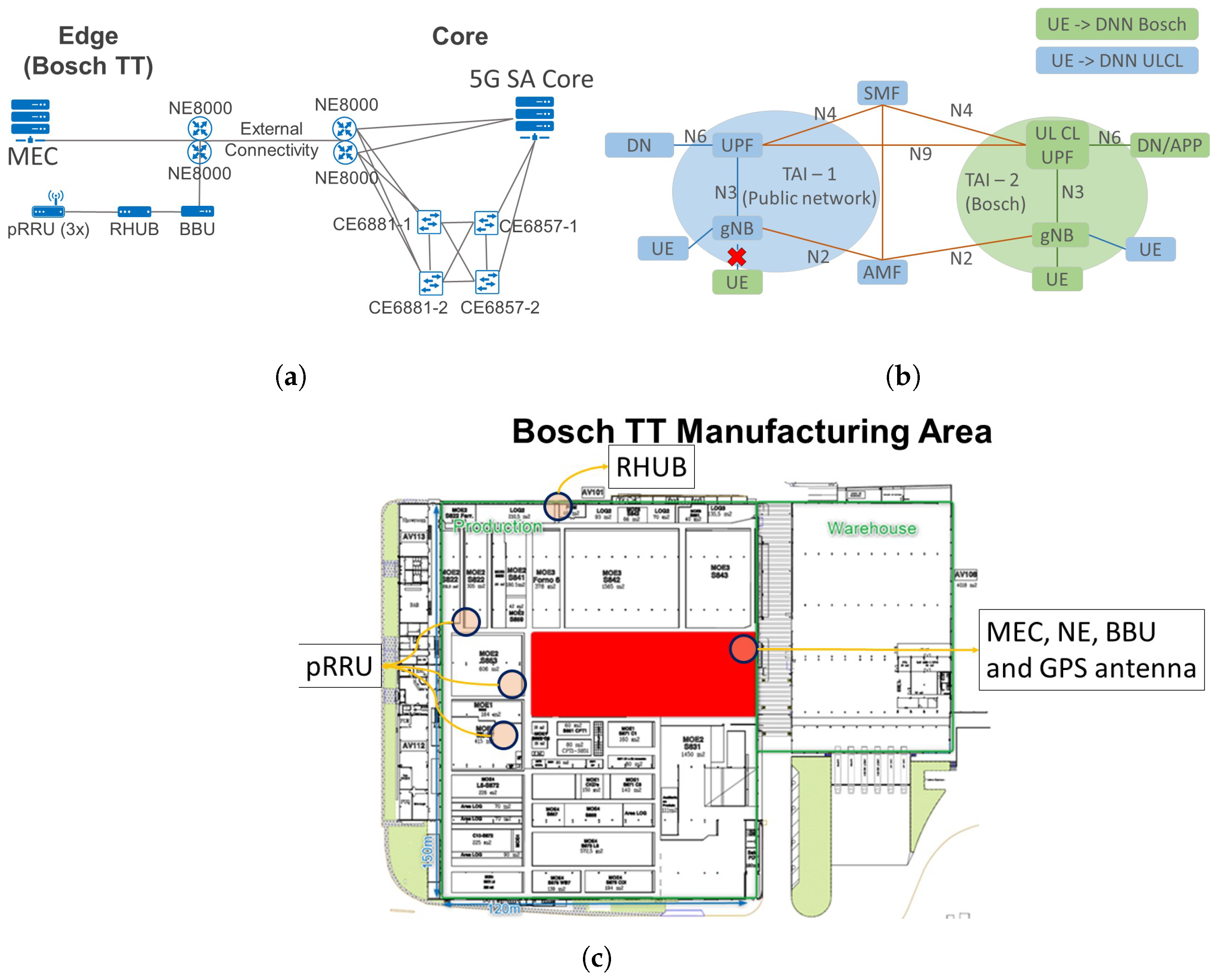
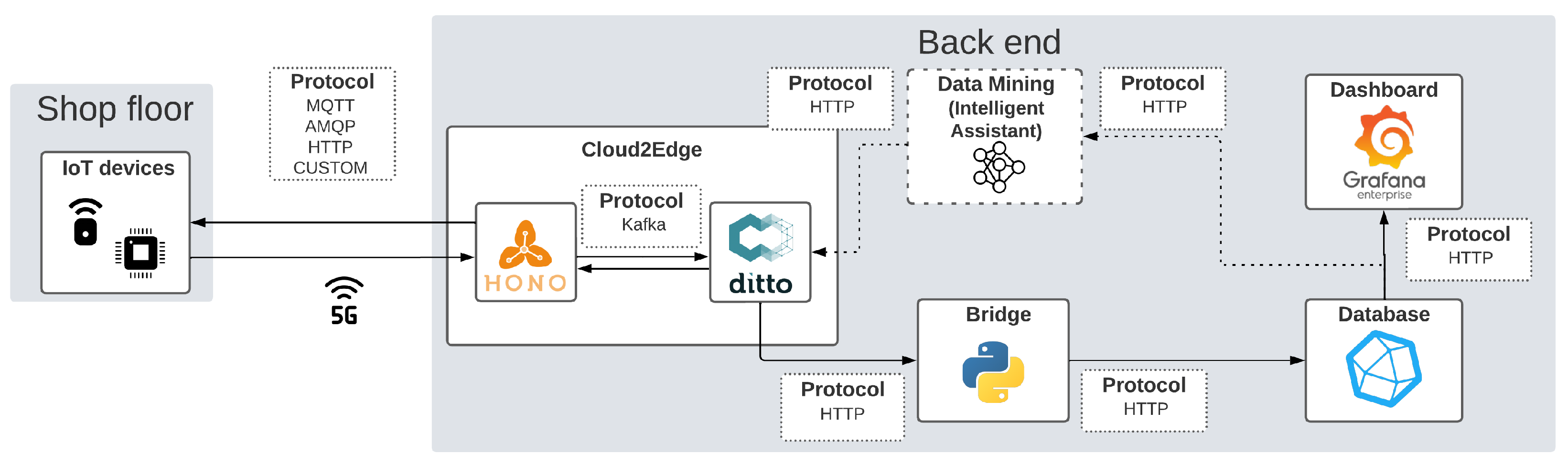




| Component | Retrofit and Predictive Maintenance | Energy Management |
|---|---|---|
| 5G IoT end device | 5G NR support | |
| Multiple sensing capabilities | ||
| Low energy consumption | ||
| Modular and retrofittable | ||
| MQTT support | ||
| Actuate on industrial assets | ||
| Protective and easily accessible enclosure | ||
| Industrial 5G Network | Guaranteed Throughput | High density of devices |
| Low energy consumption | ||
| Reliable communication | ||
| Industrial data needs to remain in factory premises | ||
| Industrial MEC needs to be logically isolated from the public network | ||
| All industrial communications need to be secure | ||
| Intelligent Assistant | Fault prediction | |
| Anomaly detection | ||
| Alarm/report creation | ||
| Specification | Values |
|---|---|
| Maximum bandwidth | 20 MHz with 30 kHz subcarrier spacing |
| Frequency band | Centre frequency of 3790.02 MHz (n78 band) |
| Output power per port | 24 dBm |
| Demultiplexing | TDD |
| DL Modulation | BPSK; QPSK; 16/64/256QAM |
| UL Modulation | BPSK; QPSK; 16/64QAM |
| MIMO | 4T4R |
| Network Slicing | eMBB Slices |
| Slot assignment | 4 Downlink: 1 Uplink (Slot structure 2) |
| Model | Linear Regression | AutoSKLearn | AutoKeras |
|---|---|---|---|
| C_phi_L3 | 0.055232 | 0.044430 | 0.052167 |
| F | 0.040205 | 0.039560 | 0.041842 |
| H_TDH_I_L3_N | 0.046060 | 0.034610 | 0.050411 |
| H_TDH_U_L2_N | 0.030794 | 0.030430 | 0.032300 |
| I_SUM | 0.065990 | 0.057850 | 0.069731 |
| P_SUM | 0.079265 | 0.063210 | 0.144370 |
| ReacEc_L1 | 0.000090 | 0.014230 | 0.098168 |
| ReacEc_L3 | 0.000133 | 0.004760 | 0.188699 |
| RealE_SUM | 0.000004 | 0.044310 | 0.340505 |
| U_L1_N | 0.031372 | 0.030960 | 0.031636 |
| Model | TP | FP | TN | FN | Recall | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C_phi_L3 | 26 | 26 | 3888 | 1 | 0.962963 | 0.500000 | 0.658228 |
| F | 26 | 26 | 3888 | 1 | 0.962963 | 0.500000 | 0.658228 |
| H_TDH_I_L3_N | 26 | 10 | 3904 | 1 | 0.962963 | 0.722222 | 0.825397 |
| H_TDH_U_L2_N | 27 | 1 | 3913 | 0 | 1.000000 | 0.964286 | 0.981818 |
| I_SUM | 26 | 26 | 3888 | 1 | 0.962963 | 0.500000 | 0.658228 |
| P_SUM | 26 | 6 | 3908 | 1 | 0.962963 | 0.812500 | 0.881356 |
| ReacEc_L1 | 27 | 50 | 3860 | 0 | 1.000000 | 0.350649 | 0.519231 |
| ReacEc_L3 | 26 | 26 | 3888 | 1 | 0.962963 | 0.500000 | 0.658228 |
| RealE_SUM | 27 | 326 | 3588 | 0 | 1.000000 | 0.076487 | 0.142105 |
| U_L1_N | 27 | 322 | 3592 | 0 | 1.000000 | 0.077364 | 0.143617 |
| Model | TP | FP | TN | FN | Recall | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C_phi_L3 | 37 | 6 | 3737 | 161 | 0.186869 | 0.860465 | 0.307054 |
| F | 173 | 8 | 3735 | 25 | 0.873737 | 0.955801 | 0.912929 |
| H_TDH_I_L3_N | 157 | 0 | 3743 | 41 | 0.792929 | 1.000000 | 0.884507 |
| H_TDH_U_L2_N | 180 | 1 | 3742 | 18 | 0.909091 | 0.994475 | 0.949868 |
| I_SUM | 179 | 3 | 3740 | 19 | 0.904040 | 0.983516 | 0.942105 |
| P_SUM | 182 | 6 | 3737 | 6 | 0.919192 | 0.968085 | 0.943005 |
| ReacEc_L1 | 27 | 9 | 3734 | 171 | 0.136364 | 0.750000 | 0.230769 |
| ReacEc_L3 | 18 | 0 | 3743 | 180 | 0.090909 | 1.000000 | 0.166667 |
| RealE_SUM | 193 | 123 | 3620 | 5 | 0.974747 | 0.610759 | 0.750973 |
| U_L1_N | 191 | 164 | 3579 | 7 | 0.964646 | 0.538028 | 0.690778 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meira, J.; Matos, G.; Perdigão, A.; Cação, J.; Resende, C.; Moreira, W.; Antunes, M.; Quevedo, J.; Moutinho, R.; Oliveira, J.; et al. Industrial Internet of Things over 5G: A Practical Implementation. Sensors 2023, 23, 5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115199
Meira J, Matos G, Perdigão A, Cação J, Resende C, Moreira W, Antunes M, Quevedo J, Moutinho R, Oliveira J, et al. Industrial Internet of Things over 5G: A Practical Implementation. Sensors. 2023; 23(11):5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115199
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeira, José, Gonçalo Matos, André Perdigão, José Cação, Carlos Resende, Waldir Moreira, Mário Antunes, José Quevedo, Ruben Moutinho, João Oliveira, and et al. 2023. "Industrial Internet of Things over 5G: A Practical Implementation" Sensors 23, no. 11: 5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115199
APA StyleMeira, J., Matos, G., Perdigão, A., Cação, J., Resende, C., Moreira, W., Antunes, M., Quevedo, J., Moutinho, R., Oliveira, J., Rendeiro, P., Oliveira, P., Oliveira-Jr, A., Santos, J., & Aguiar, R. L. (2023). Industrial Internet of Things over 5G: A Practical Implementation. Sensors, 23(11), 5199. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115199









