Quick Detection of Proteus and Pseudomonas in Patients’ Urine and Assessing Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Using Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
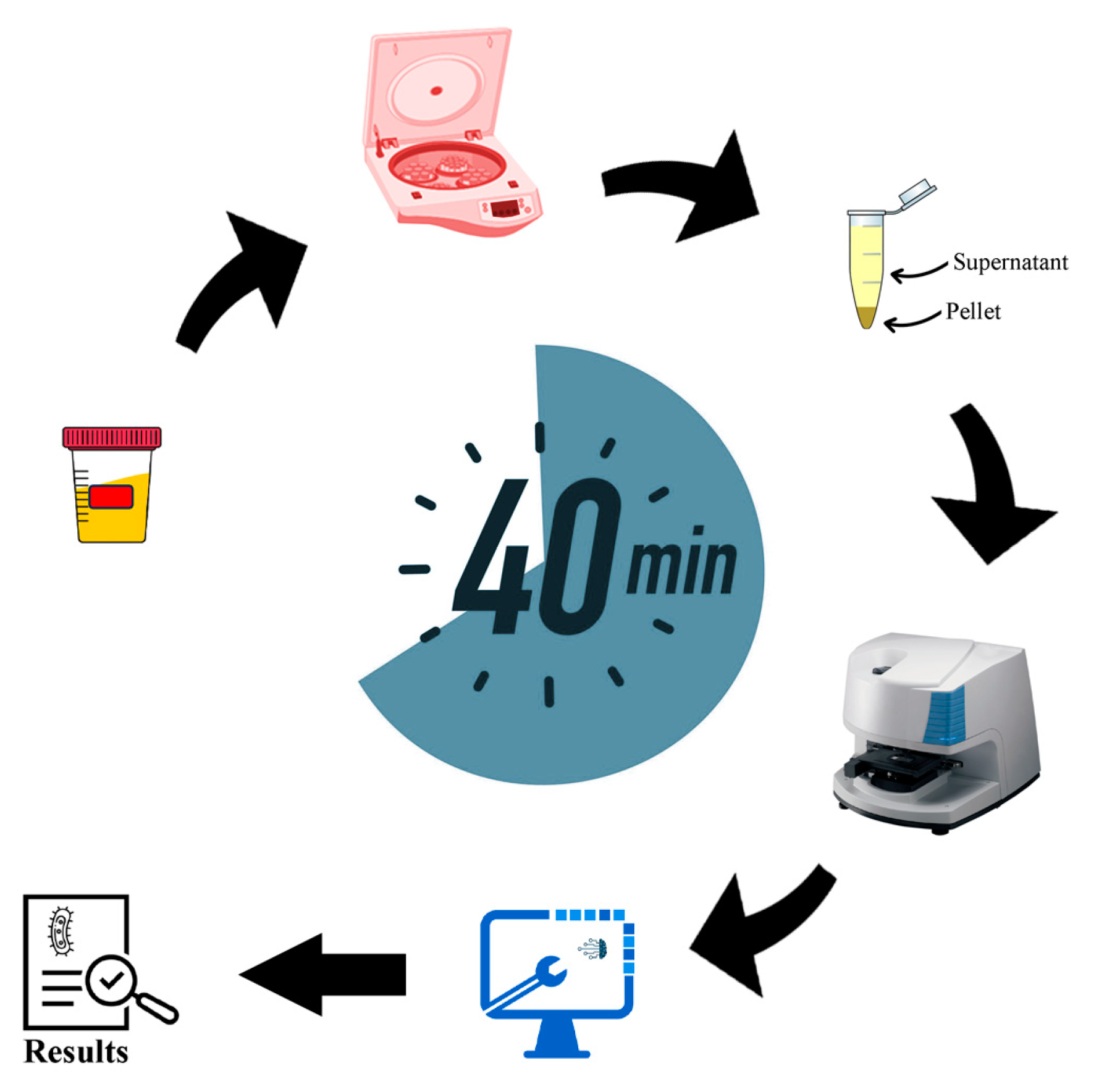
2.1. Collection of Bacterial Samples
2.2. Preparation of Bacterial Samples
2.3. FTIR Measurements
2.4. Pre-Processing of the FTIR Measurements
2.5. Analysis
3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Random Forest (RF)
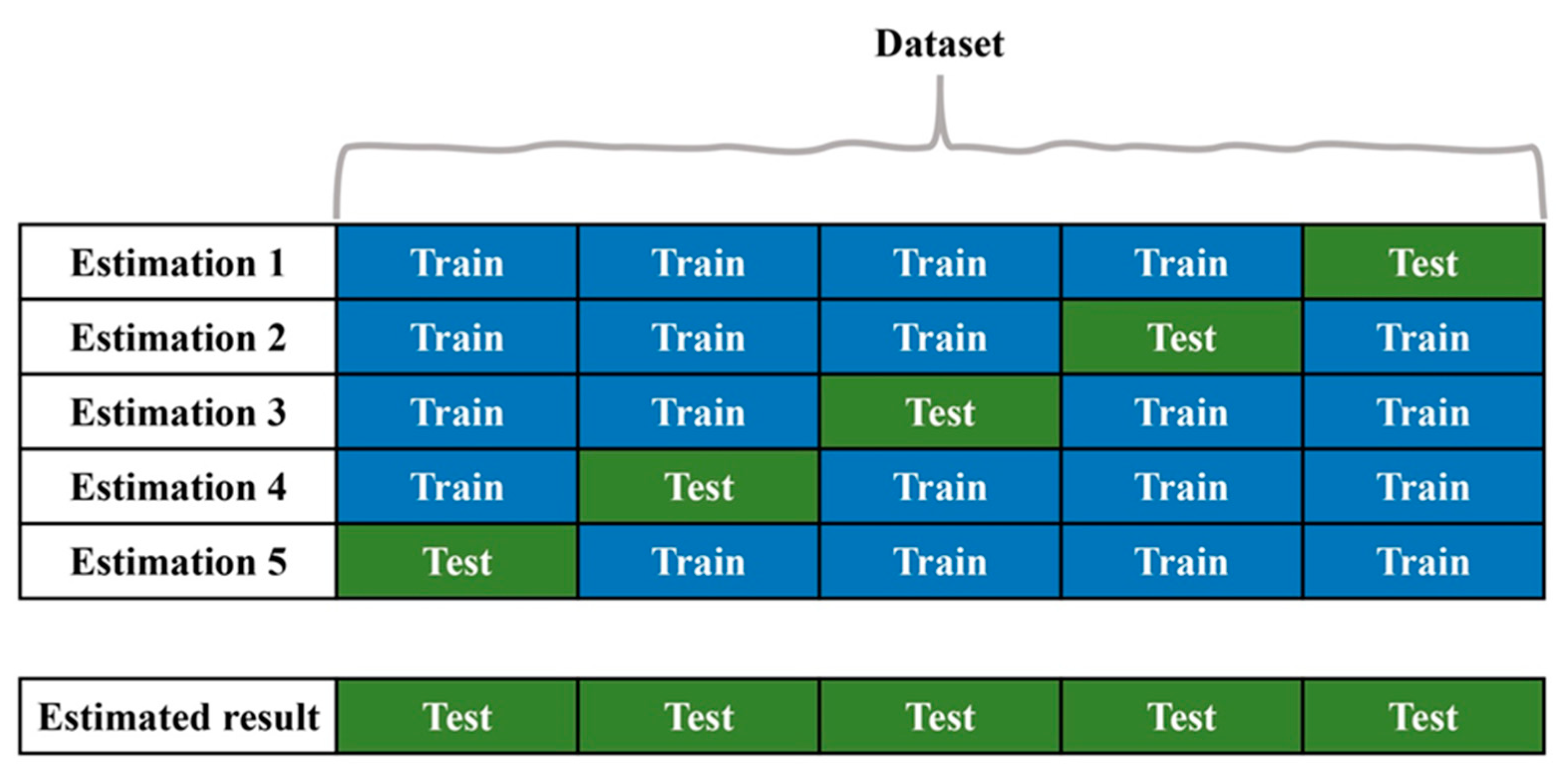
5. Validation
6. Statistical Parameters
7. Results and Discussion
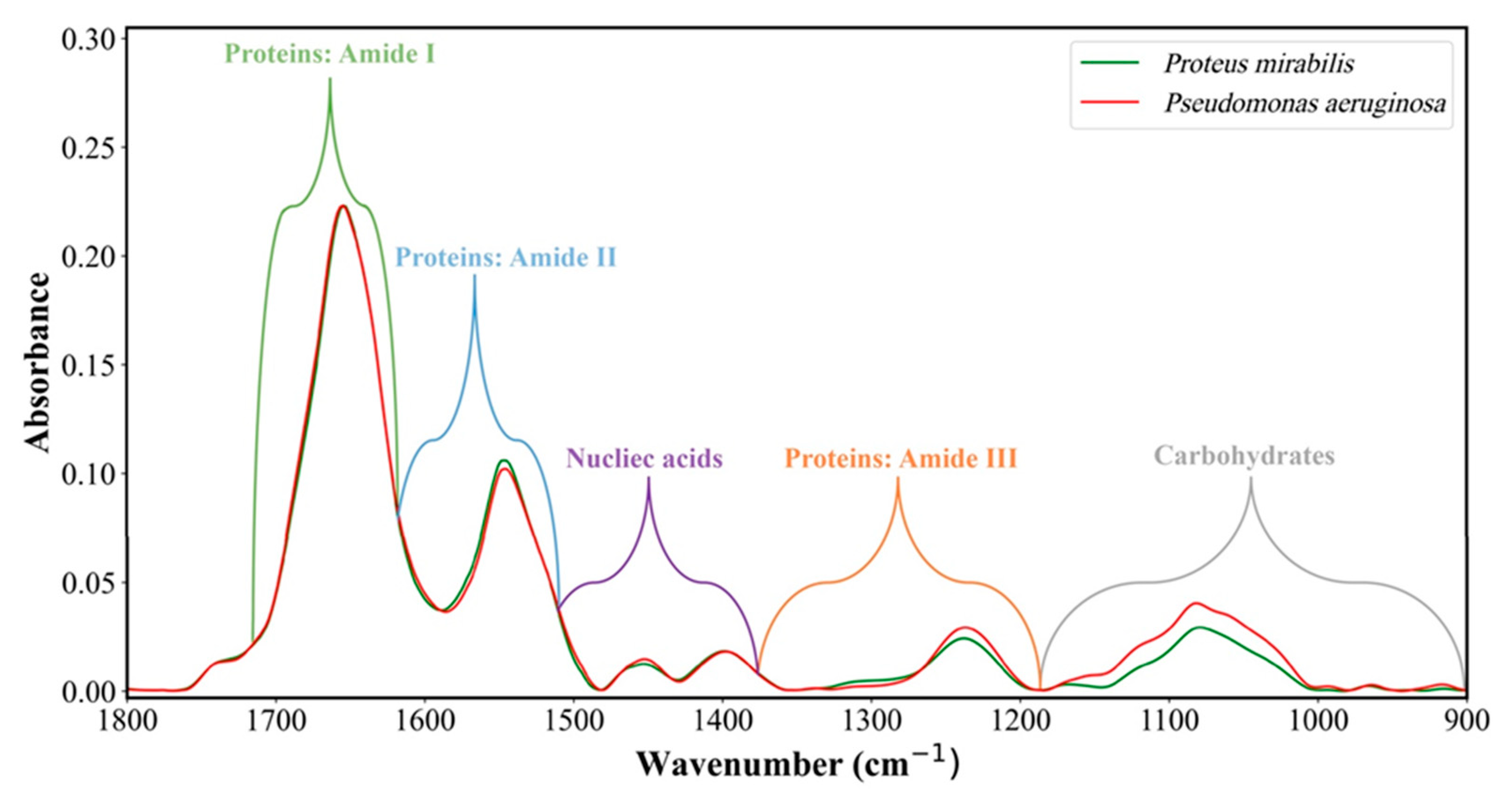
8. Representative IR Absorption Spectra
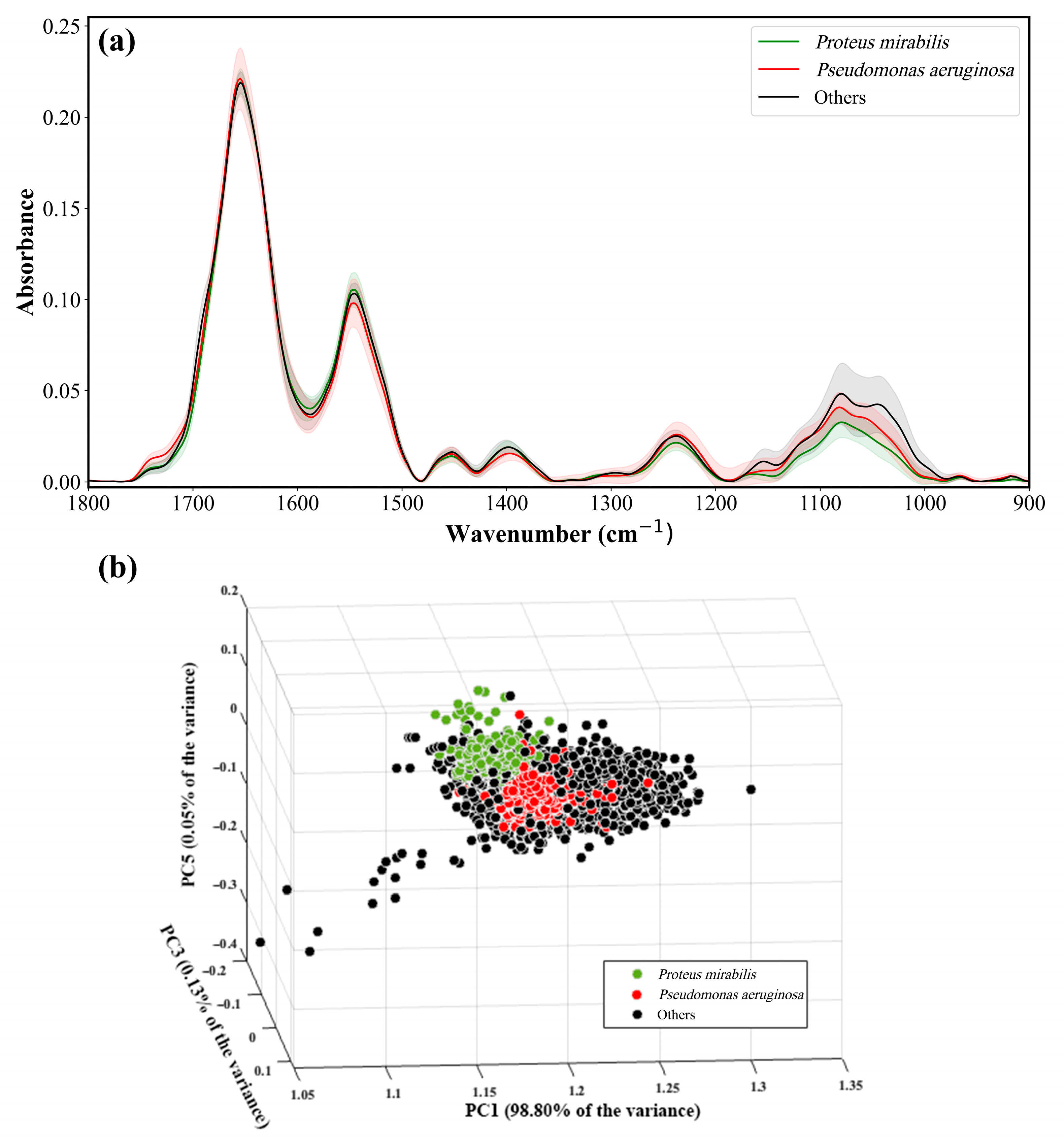
9. Identification of Proteus and Pseudomonas from Other Bacteria
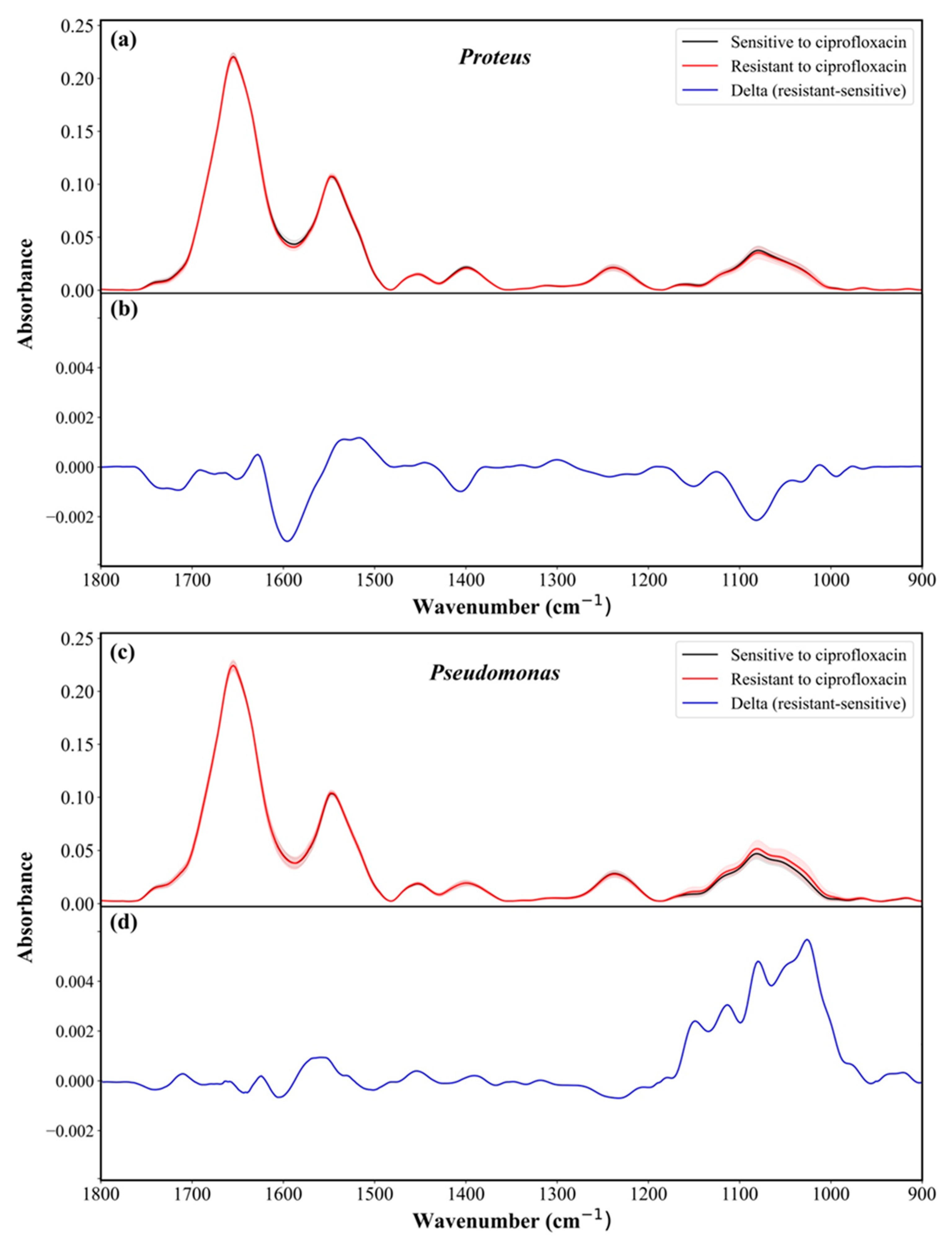
10. Susceptibility Determination of Proteus and Pseudomonas to Antibiotics
11. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alos, J.-I. Antibiotic resistance: A global crisis. Enfermedades Infecc Y Microbiol. Clin. 2014, 33, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, R.C.; San Millan, A. The evolution of antibiotic resistance. Science 2019, 365, 1082–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R. Antibiotic resistance: A crisis in the making. Emerg. Nurse 2012, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coxeter, P.; Looke, D.; Hoffmann, T.; Lowe, J.; Del Mar, C. The antibiotic crisis: Charting Australia’s path towards least resistance. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2013, 37, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A. Tackling the crisis of antibiotic resistance. South Asian J. Cancer 2013, 2, 003–004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary tract infections: Epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheerin, N.S. Urinary tract infection. Medicine 2011, 39, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motarjemi, Y.; Moy, G.; Todd, E. Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Li, X. Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In Molecular Medical Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1547–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Armbruster, C.E.; Mobley, H.L.; Pearson, M.M. Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis infection. EcoSal Plus 2018, 8, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelling, H.; Nzakizwanayo, J.; Milo, S.; Denham, E.L.; MacFarlane, W.M.; Bock, L.J.; Sutton, J.M.; Jones, B.V. Bacterial biofilm formation on indwelling urethral catheters. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Huang, Z.; Yang, T.; Wang, G.; Li, P.; Yang, B.; Li, J. Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis in Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections. Urol. Int. 2021, 105, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.Á.; Stickler, D.; Mobley, H.; Shirtliff, M. Complicated catheter-associated urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 26–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, L.E. Catheter-related urinary tract infection. Drugs Aging 2005, 22, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lu, P.-L.; Lin, W.-R.; Chen, T.-C.; Lin, C.-Y. Proteus mirabilis urinary tract infection and bacteremia: Risk factors, clinical presentation, and outcomes. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2012, 45, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E. Comparative Epidemiology and Resistance Trends of Proteae in Urinary Tract Infections of Inpatients and Outpatients: A 10-Year Retrospective Study. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, K.R.; Lee, G.C.; Frei, C.R. Trends in catheter-associated urinary tract infections among a national cohort of hospitalized adults, 2001–2010. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooton, T.M.; Bradley, S.F.; Cardenas, D.D.; Colgan, R.; Geerlings, S.E.; Rice, J.C.; Saint, S.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Tambayh, P.A.; Tenke, P. Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of catheter-associated urinary tract infection in adults: 2009 International Clinical Practice Guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 625–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzakizwanayo, J.; Hanin, A.; Alves, D.R.; McCutcheon, B.; Dedi, C.; Salvage, J.; Knox, K.; Stewart, B.; Metcalfe, A.; Clark, J.; et al. Bacteriophage Can Prevent Encrustation and Blockage of Urinary Catheters by Proteus mirabilis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasfi, R.; Hamed, S.M.; Amer, M.A.; Fahmy, L.I. Proteus mirabilis Biofilm: Development and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, R.T.; Foris, L.A.; Snowden, J. Proteus Mirabilis Infections; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, P.; McCulloch, J.; Mamizuka, E.; Lincopan, N. PSEUDOMONAS| Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Pier, G.B. Pseudomonas and related Gram-negative bacillary infections. In Goldman’s Cecil Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1877–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Okeke, I.N.; Ihekweazu, C. The importance of molecular diagnostics for infectious diseases in low-resource settings. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukumbuzya, M.; Schmid, M.; Pjevac, P.; Daims, H. A Multicolor Fluorescence in situ Hybridization Approach Using an Extended Set of Fluorophores to Visualize Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogomolny, E.; Huleihel, M.; Suproun, Y.; Sahu, R.K.; Mordechai, S. Early spectral changes of cellular malignant transformation using Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, D.; Helm, D.; Labischinski, H. Microbiological characterizations by FT-IR spectroscopy. Nature 1991, 351, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswani, S.M.; Chandrashekar, U.; Shivashankara, K.; Pruthvi, B. Clinical profile of urinary tract infections in diabetics and non-diabetics. Australas. Med. J. 2014, 7, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Kazarian, S.G.; Chan, K.A. ATR-FTIR spectroscopic imaging: Recent advances and applications to biological systems. Analyst 2013, 138, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyanfif, A.; Liyanage, S.; Hequet, E.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Abidi, N. Review of FTIR microspectroscopy applications to investigate biochemical changes in C. elegans. Vib. Spectrosc. 2018, 96, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, Á.; Yáñez, J.; Contreras, D.; Saavedra, R.; Sáez, P.; Amarasiriwardena, D. Propellant’s differentiation using FTIR-photoacoustic detection for forensic studies of improvised explosive devices. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 280, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, R. FTIR and NIRS in Forensic Chemical Sensing. In Forensic Analytical Methods; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 164–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Qi, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, M.; He, Y.; Huang, K.; Chen, P. Metal ions-regulated chemical vapor generation of Hg2+: Mechanism and application in miniaturized point discharge atomic emission spectrometry assay of oxalate in clinical urolithiasis samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1262, 341223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuffo, C.A.; Schmitt, J.; Wenning, M.; von Stetten, F.; Scherer, S. Reliable and rapid identification of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria species by artificial neural network-based Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.J.; Trevisan, J.; Bassan, P.; Bhargava, R.; Butler, H.J.; Dorling, K.M.; Fielden, P.R.; Fogarty, S.W.; Fullwood, N.J.; Heys, K.A.; et al. Using Fourier transform IR spectroscopy to analyze biological materials. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1771–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthäus, C.; Bird, B.; Miljković, M.; Chernenko, T.; Romeo, M.; Diem, M. Infrared and Raman microscopy in cell biology. Methods Cell Biol. 2008, 89, 275–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.J.; Gazi, E.; Brown, M.D.; Shanks, J.H.; Gardner, P.; Clarke, N.W. FTIR-based spectroscopic analysis in the identification of clinically aggressive prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Aqil, G.; Suleiman, M.; Sharaha, U.; Riesenberg, K.; Lapidot, I.; Huleihel, M.; Salman, A. Fast identification and susceptibility determination of E. coli isolated directly from patients’ urine using infrared-spectroscopy and machine learning. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 285, 121909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Aqil, G.; Sharaha, U.; Suleiman, M.; Riesenberg, K.; Lapidot, I.; Salman, A.; Huleihel, M. Culture-independent susceptibility determination of E. coli isolated directly from patients’ urine using FTIR and machine-learning. Analyst 2022, 147, 4815–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaha, U.; Abu-Aqil, G.; Suleiman, M.; Riesenberg, K.; Lapidot, I.; Huleihel, M.; Salman, A. Rapid determination of Proteus mirabilis susceptibility to antibiotics using infrared spectroscopy in tandem with random forest. J. Biophotonics 2023, 16, e202200198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, M.; Abu-Aqil, G.; Sharaha, U.; Riesenberg, K.; Lapidot, I.; Salman, A.; Huleihel, M. Infra-red spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms enables early determination of Pseudomonas aeruginosa’s susceptibility to antibiotics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 274, 121080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C. Fundamentals of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, A.; Katariya, R.; Patel, V. A review on random forest: An ensemble classifier. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things, Bengaluru, India, 5–7 January 2023; pp. 758–763. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, I.; Dokukin, M.E.; Kalaparthi, V.; Miljkovic, M.; Wang, A.; Seigne, J.D.; Grivas, P.; Demidenko, E. Noninvasive diagnostic imaging using machine-learning analysis of nanoresolution images of cell surfaces: Detection of bladder cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12920–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstajic, D.; Buturovic, L.J.; Leahy, D.E.; Thomas, S. Cross-validation pitfalls when selecting and assessing regression and classification models. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Motoda, H. Computational Methods of Feature Selection; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paraskevaidi, M.; Matthew, B.J.; Holly, B.J.; Hugh, B.J.; Thulya, C.P.V.; Loren, C.; StJohn, C.; Peter, G.; Callum, G.; Sergei, K.G.; et al. Clinical applications of infrared and Raman spectroscopy in the fields of cancer and infectious diseases. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2021, 56, 804–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekes, M.; Lasch, P.; Naumann, D. Analytical applications of Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy in microbiology and prion research. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 123, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamudio Cañas, R.; Zaca Moran, O.; Jaramillo Flores, M.E.; Vallejo Ruiz, V.; Reyes Leyva, J.; Delgado Macuil, R.; Lopez Gayou, V. Characterization and differentiation of cervical cancer cell lines using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 86, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaha, U.; Suleiman, M.; Abu-Aqil, G.; Riesenberg, K.; Lapidot, I.; Salman, A.; Huleihel, M. Determination of Klebsiella pneumoniae Susceptibility to Antibiotics Using Infrared Microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13426–13433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaha, U.; Rodriguez-Diaz, E.; Riesenberg, K.; Bigio, I.J.; Huleihel, M.; Salman, A. Using infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis to detect antibiotics’ resistant Escherichia coli bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8782–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, M.; Abu-Aqil, G.; Sharaha, U.; Riesenberg, K.; Sagi, O.; Lapidot, I.; Huleihel, M.; Salman, A. Rapid detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing extended spectrum β lactamase enzymes by infrared microspectroscopy and machine learning algorithms. Analyst 2021, 146, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charretier, Y.; Dauwalder, O.; Franceschi, C.; Degout-Charmette, E.; Zambardi, G.; Cecchini, T.; Bardet, C.; Lacoux, X.; Dufour, P.; Veron, L.; et al. Rapid Bacterial Identification, Resistance, Virulence and Type Profiling using Selected Reaction Monitoring Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Elangovan, R.; Vivekanandan, P. Antibiotic Resistance and Epigenetics: More to It than Meets the Eye. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drancourt, M. Detection of microorganisms in blood specimens using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: A review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasala, A.; Hytönen, V.P.; Laitinen, O.H. Modern Tools for Rapid Diagnostics of Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Park, S. Current and Emerging Methods of Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, W. Emerging Microtechnologies and Automated Systems for Rapid Bacterial Identification and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing. SLAS Technol. 2017, 22, 585–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Prediction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteus | Pseudomonas | Others | ||
| True | Proteus | 0.99 (355) | 0.01 (4) | 0.00 (1) |
| Pseudomonas | 0.00 (1) | 1.00 (352) | 0.00 (0) | |
| Others | 0.01 (14) | 0.00 (6) | 0.99 (2713) | |
| Antibiotic | Bacteria | Sensitive | Resistant | Features | AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceftazidime | Proteus | 291 | 69 | 469 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.91 | 0.51 |
| Pseudomonas | 287 | 63 | 150 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.89 | 0.33 | |
| Ciprofloxacin | Proteus | 236 | 124 | 200 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.75 |
| Pseudomonas | 283 | 68 | 50 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.53 | 0.87 | 0.37 | |
| Gentamicin | Proteus | 284 | 76 | 100 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 0.62 | 0.90 | 0.56 |
| Pseudomonas | 301 | 50 | 300 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 0.93 | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu-Aqil, G.; Lapidot, I.; Salman, A.; Huleihel, M. Quick Detection of Proteus and Pseudomonas in Patients’ Urine and Assessing Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Using Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 8132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198132
Abu-Aqil G, Lapidot I, Salman A, Huleihel M. Quick Detection of Proteus and Pseudomonas in Patients’ Urine and Assessing Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Using Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning. Sensors. 2023; 23(19):8132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198132
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu-Aqil, George, Itshak Lapidot, Ahmad Salman, and Mahmoud Huleihel. 2023. "Quick Detection of Proteus and Pseudomonas in Patients’ Urine and Assessing Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Using Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning" Sensors 23, no. 19: 8132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198132
APA StyleAbu-Aqil, G., Lapidot, I., Salman, A., & Huleihel, M. (2023). Quick Detection of Proteus and Pseudomonas in Patients’ Urine and Assessing Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Using Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning. Sensors, 23(19), 8132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198132










