Vision-Based Localization Method for Picking Points in Tea-Harvesting Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Data
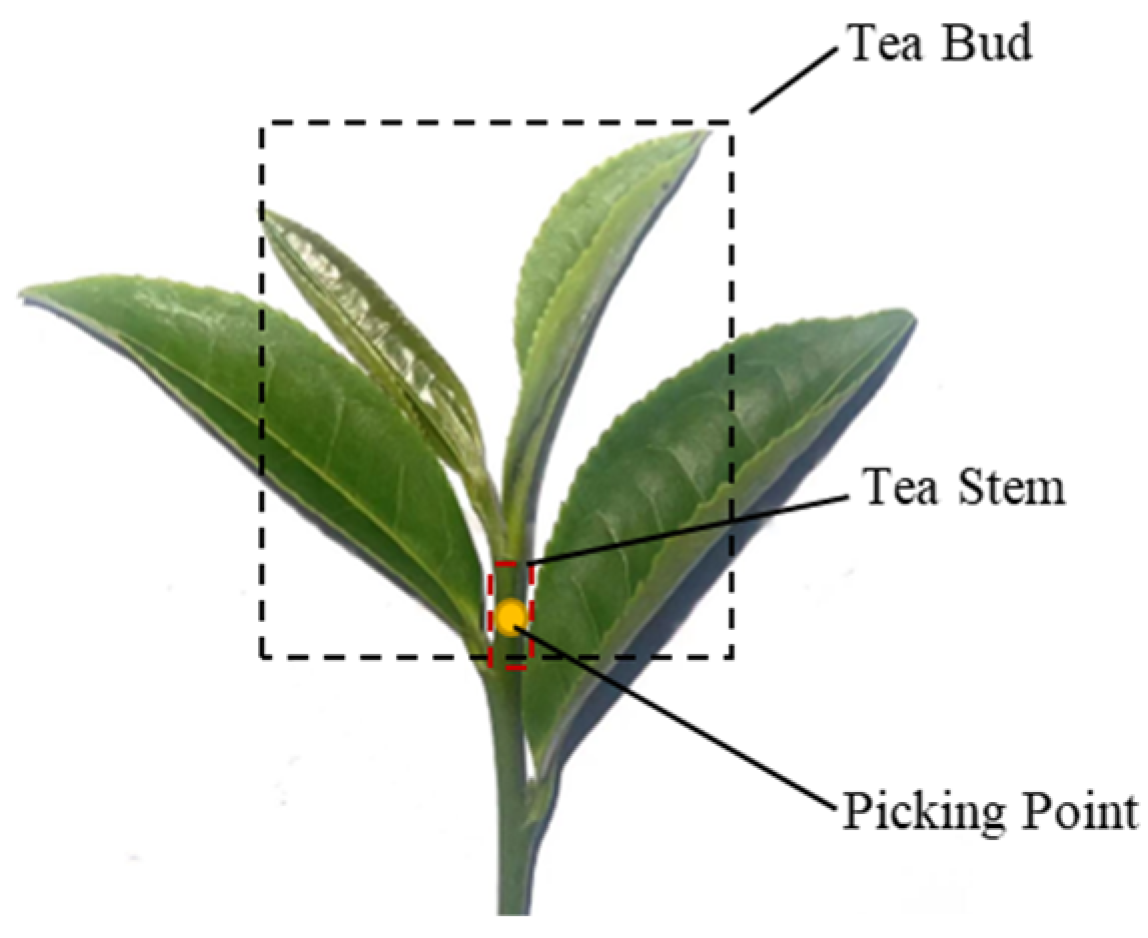
2.1. Premium Tea-Picking Standards
2.2. Data Collection and Construction
3. Methods
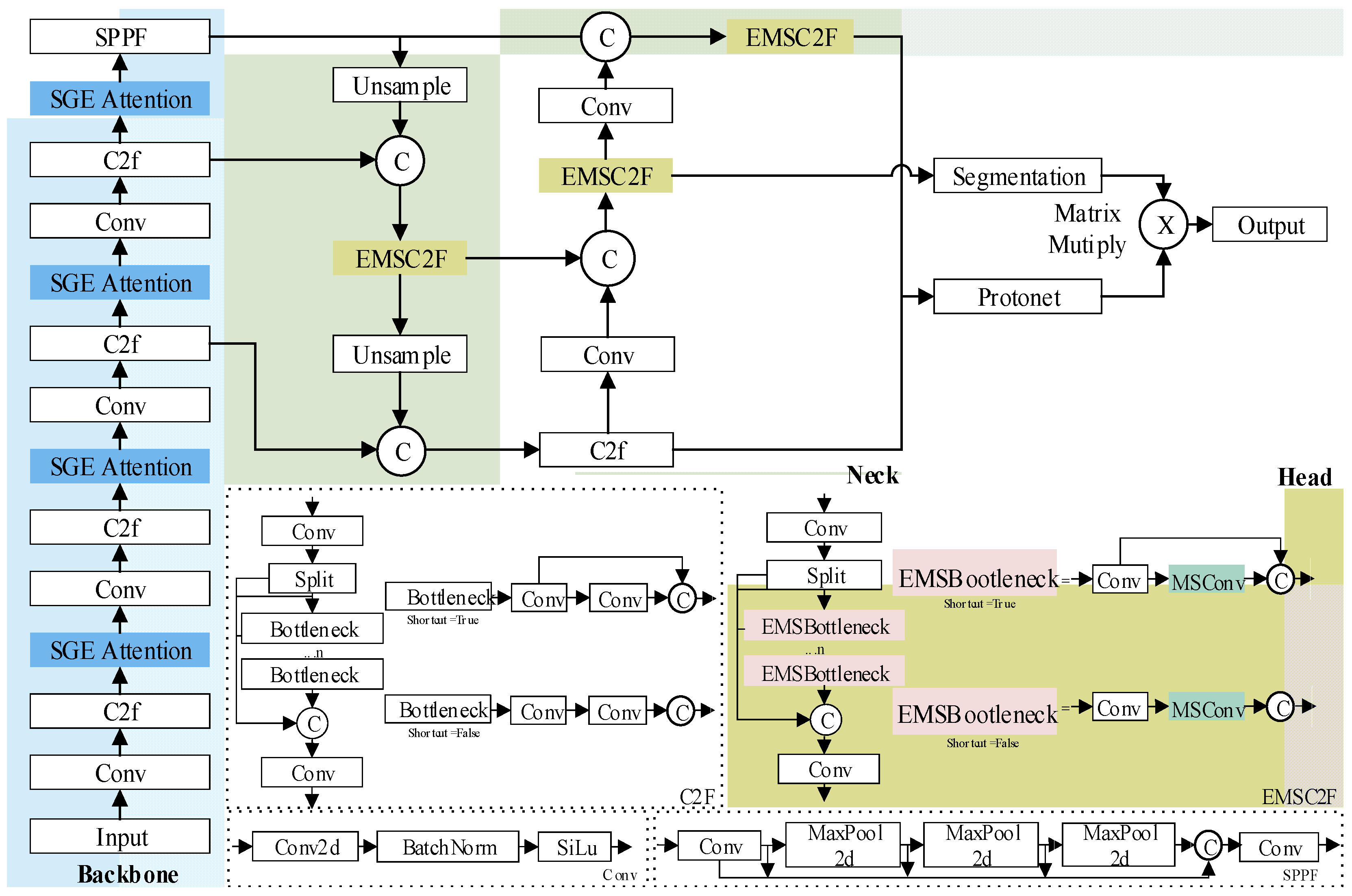
3.1. T-YOLOv8n: A Tea-Picking Key Structure Recognition and Segmentation Model Based on an Improved YOLOv8n-Seg
3.1.1. Feature-Enhanced Backbone Network
3.1.2. EMSC2F Feature Fusion Module
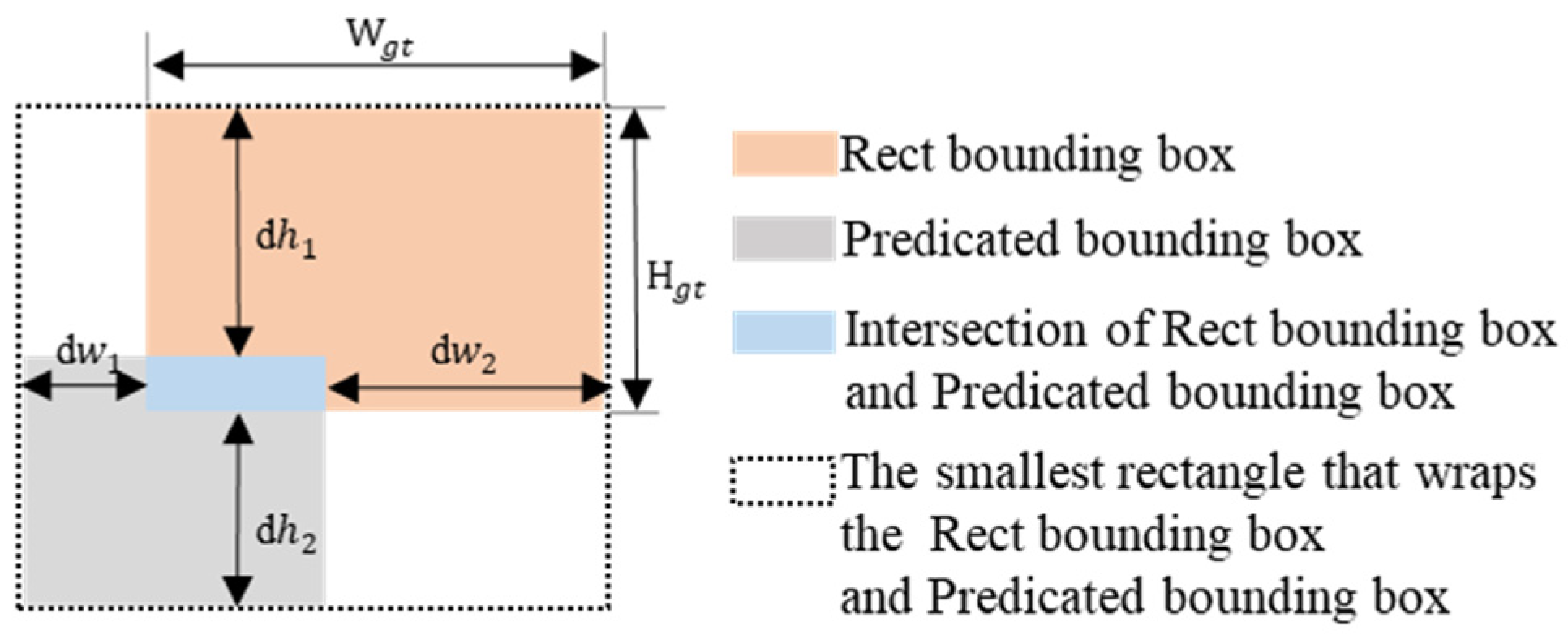
3.1.3. Scale-Adaptive Loss Function
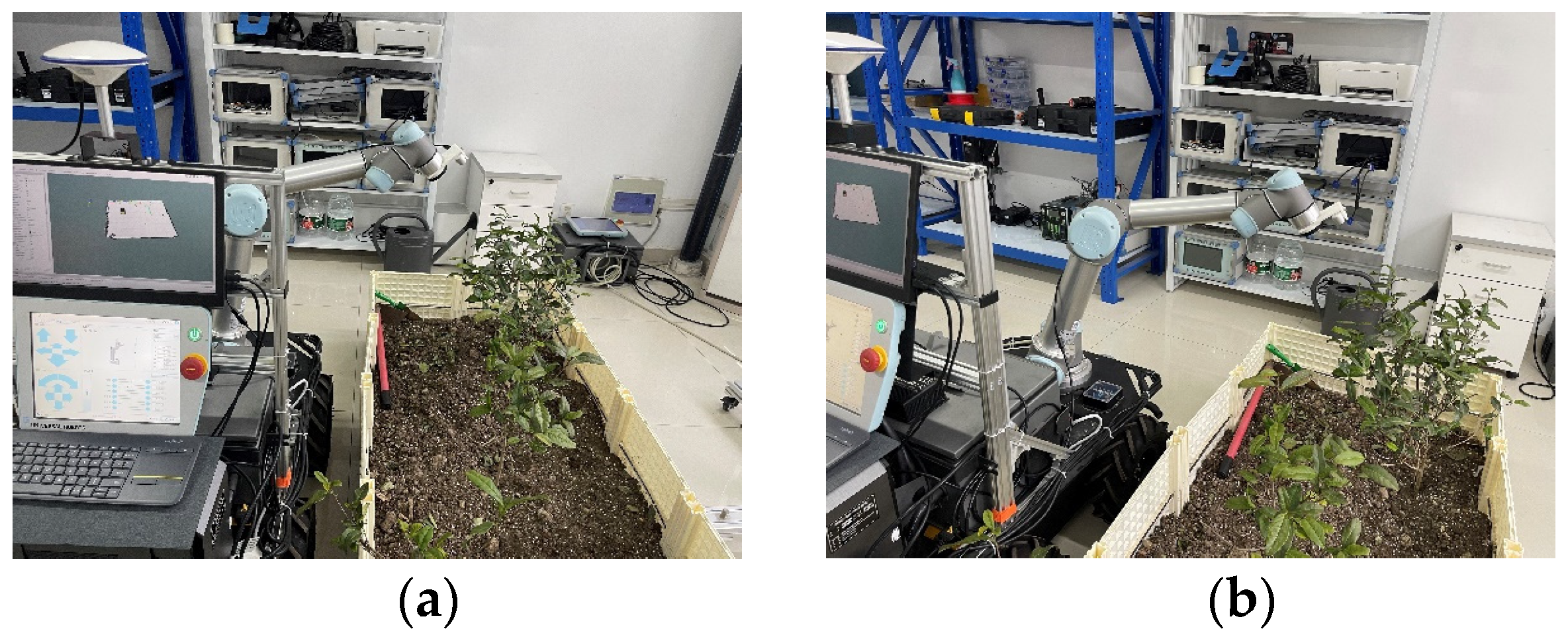
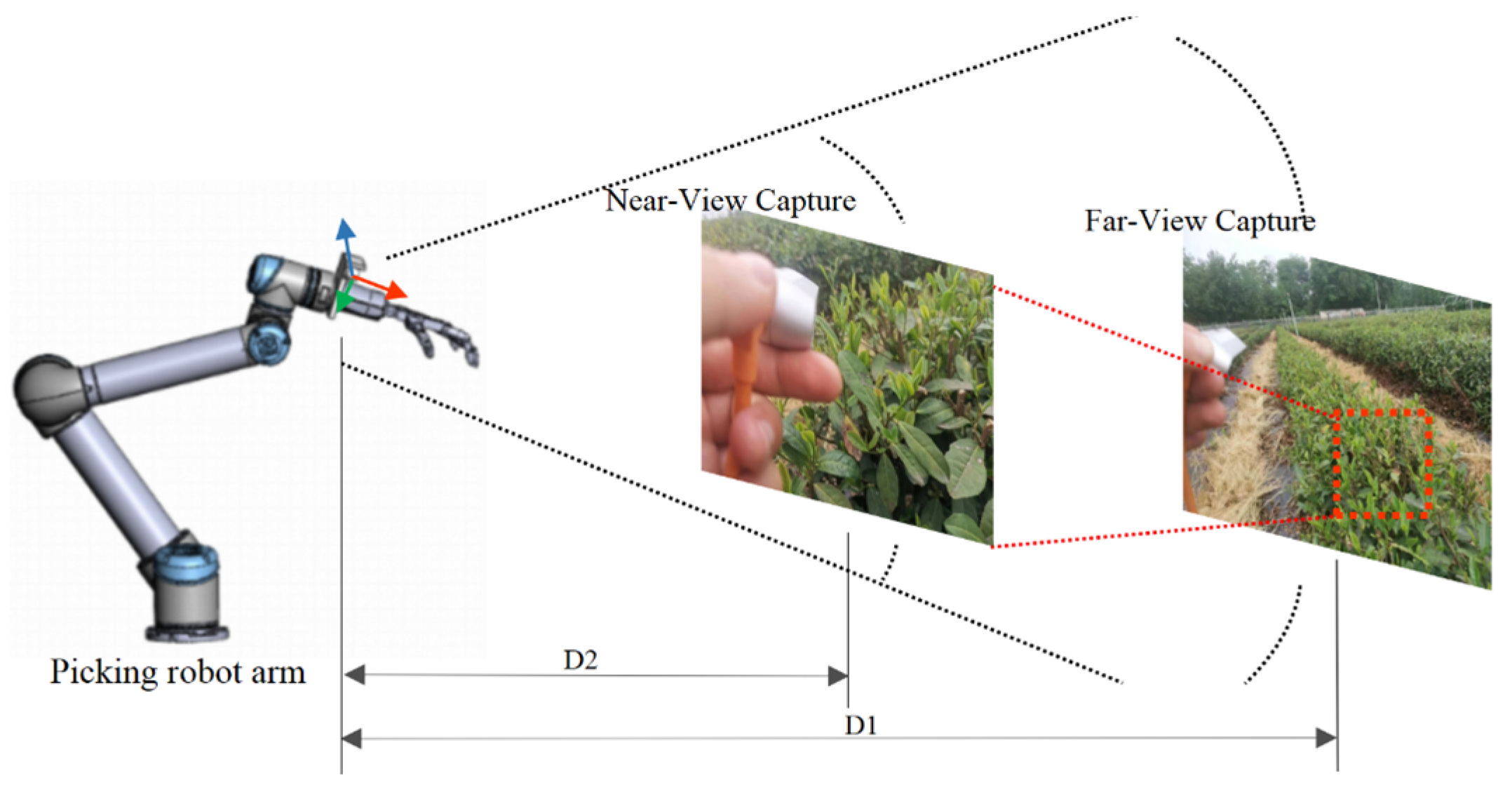
3.2. A Layered Visual Servoing Strategy for Picking Point Localization Integrating Far and near Views
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. T-YOLOv8n Performance Experiments
4.1.1. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Indexes
4.1.2. Ablation Experiment
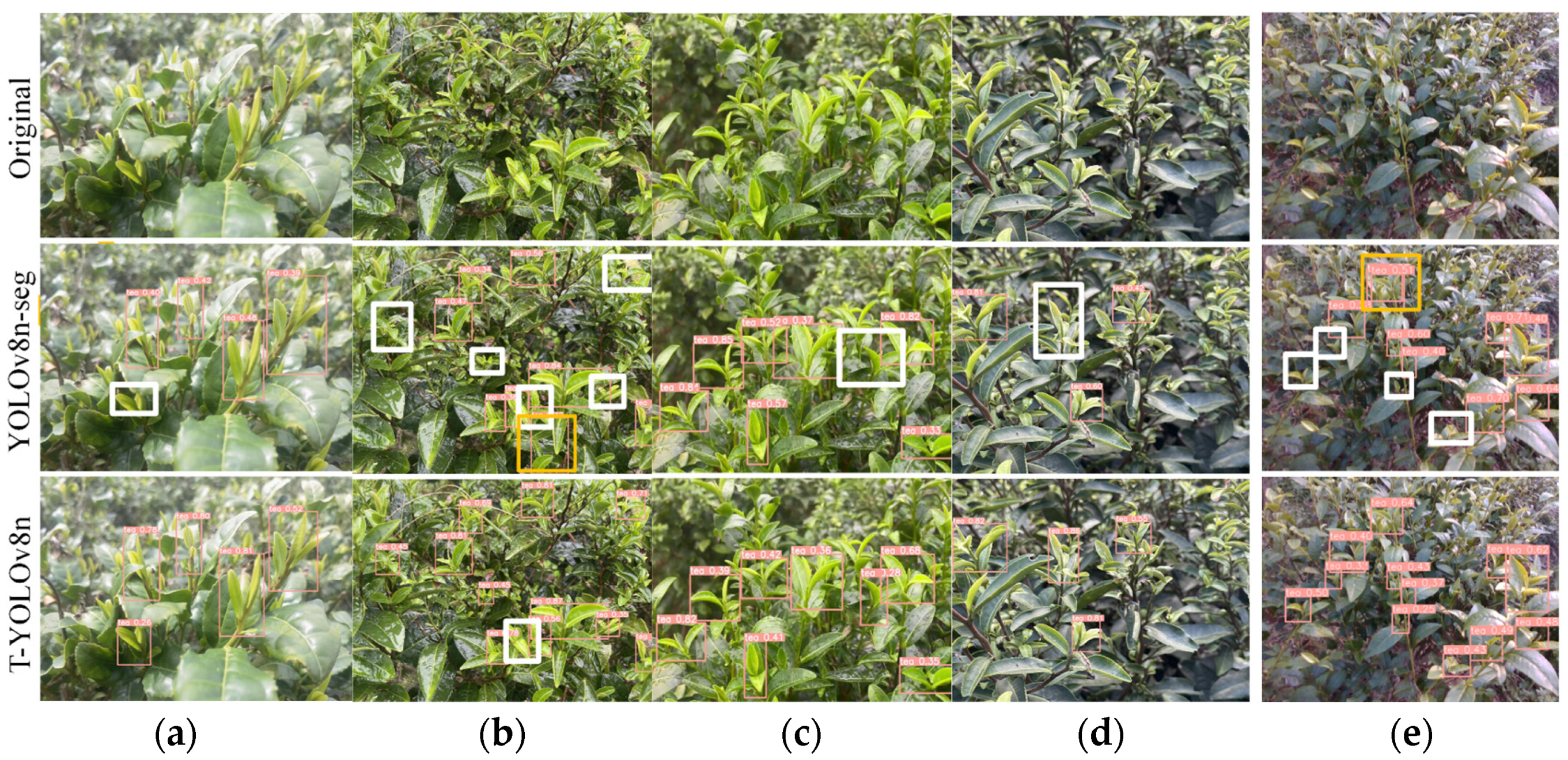
4.1.3. Comparative Experiments
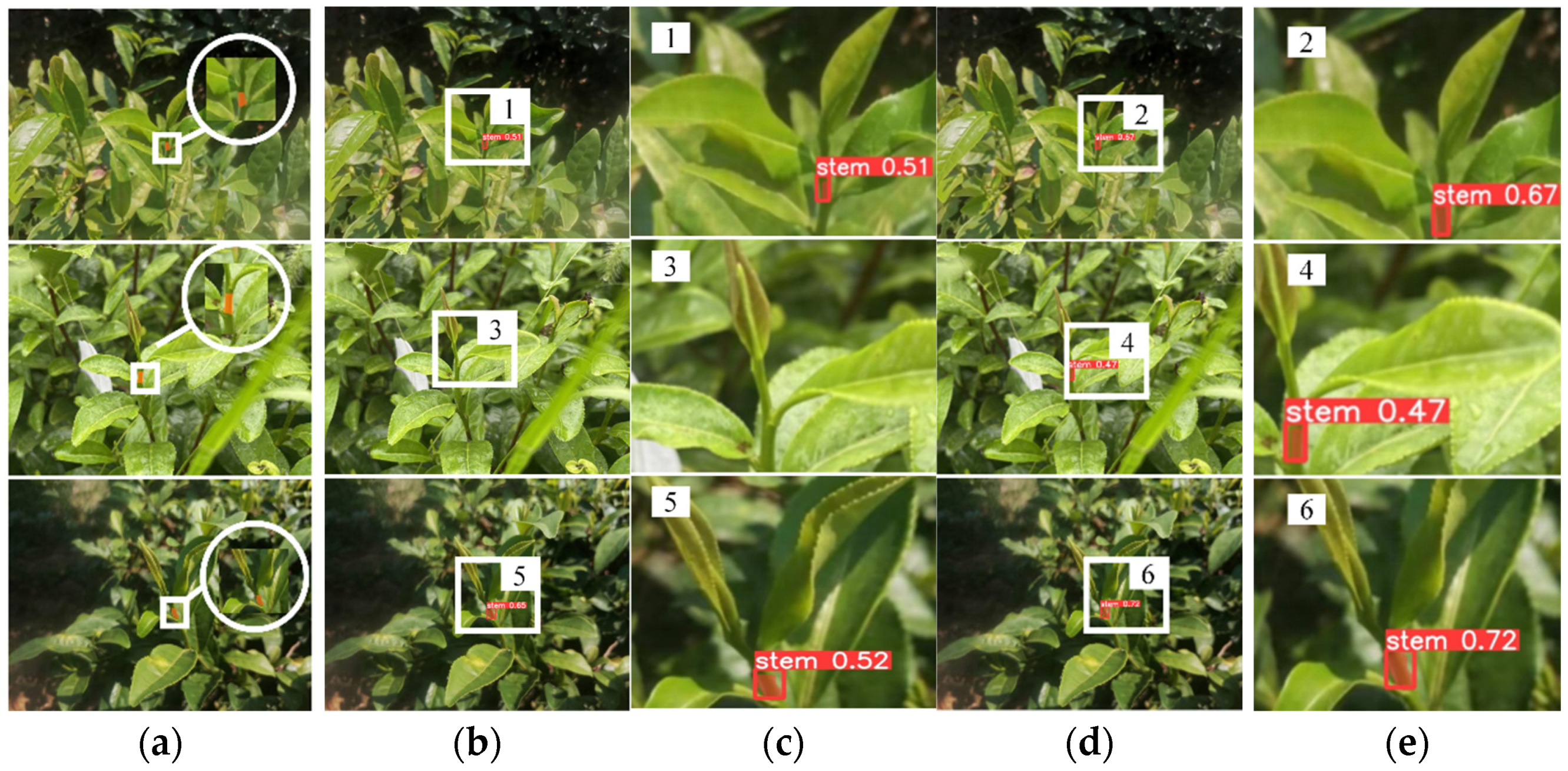
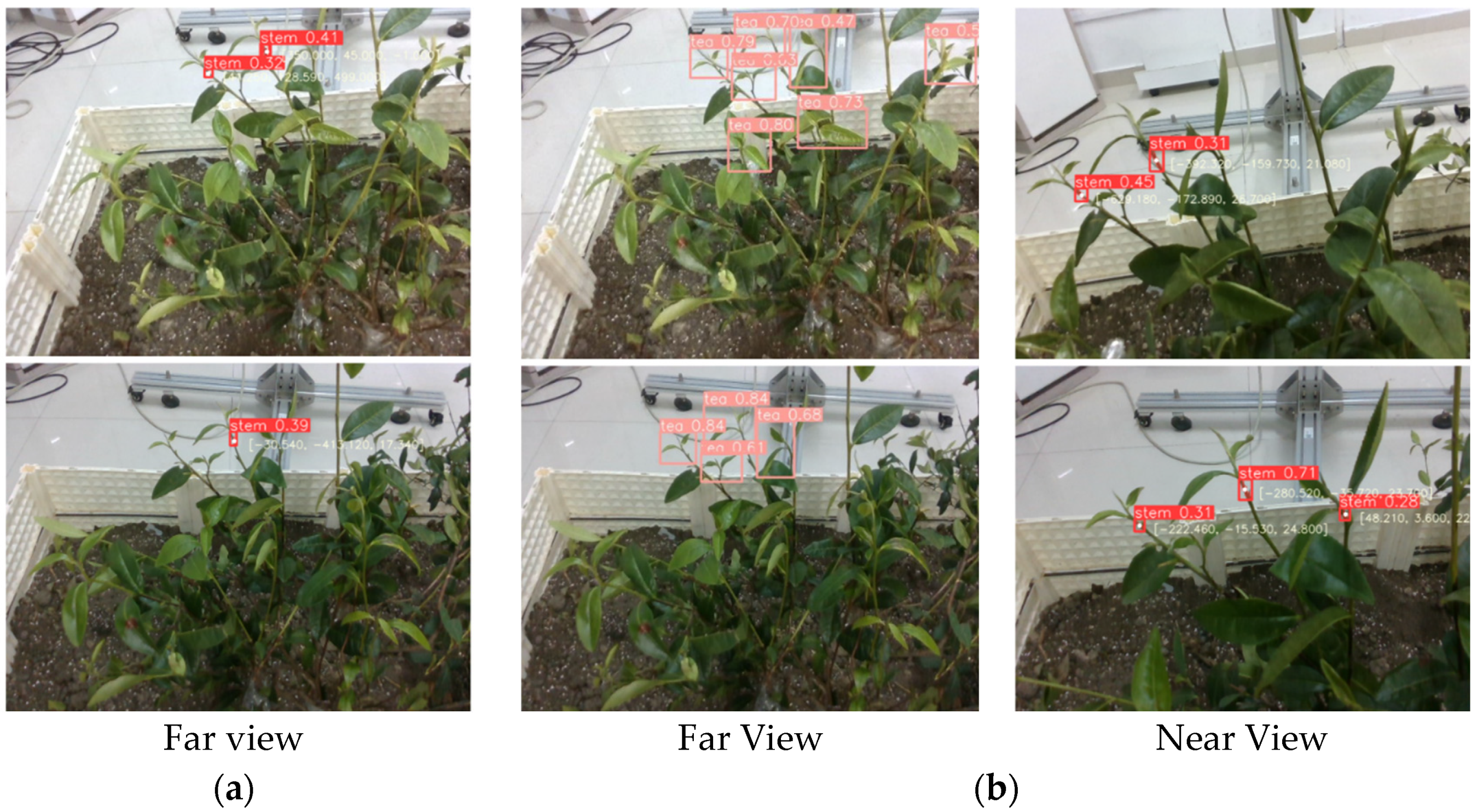
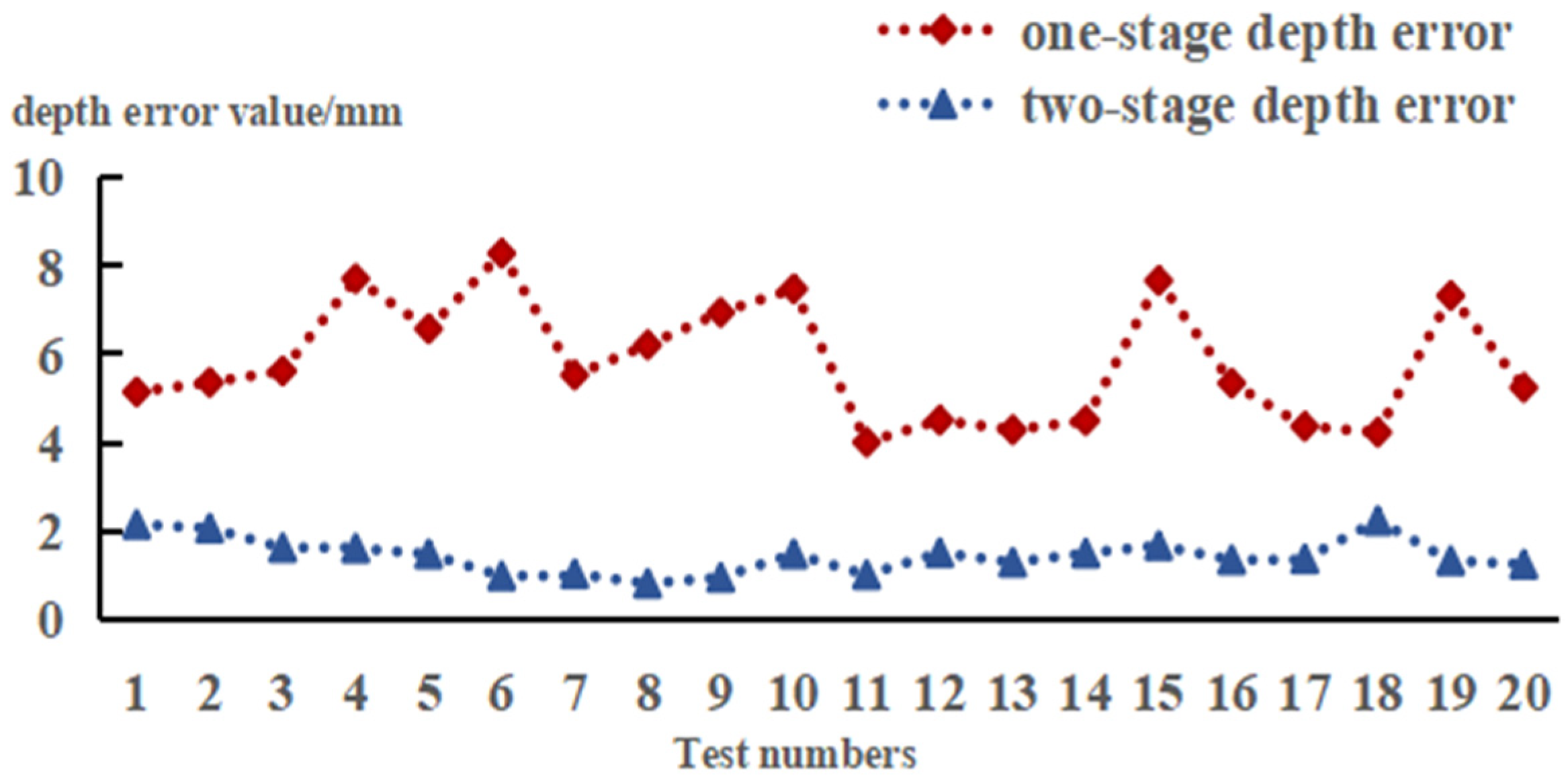
4.2. Picking Point Localization Experiment
5. Conclusions
- Designed and optimized the T-YOLOv8n model for identifying and segmenting key structures for picking: Based on YOLOv8n-seg, structural optimizations were made, including backbone network reconstruction, feature fusion module design, and the introduction of a scale-adaptive loss function, improving the model’s performance in recognizing and segmenting key tea-picking structures in multi-scale scenarios. In the MFN composite test set, the tea buds in the far-view test set reached 80.8%, and in the near-view test set, the mAP0.5 for tea stem detection in bounding boxes and masks reached 93.6% and 93.7%, an improvement of 9.1% and 14.1% compared to the original model, laying a visual perception foundation for accurate picking point localization.
- Proposed a far–near layered visual servoing strategy: To address the limitations of single-stage visual methods in accurately locating slender tea stems and the inherent shortcomings of low-cost depth cameras in capturing small target information, this study proposes this strategy. This method effectively combines the region of interest (ROI) of tea buds output by the T-YOLOv8n model with the coarse segmentation results of tea stems, enabling accurate localization of the 3D coordinates of picking points.
- Experimental validation shows that by using this two-stage visual method, the success rate of picking point localization reached 86.4%, with an average depth error of only 1.43 mm, confirming the potential application value of this method in precise robotic operations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Zhao, B.; Gao, X.; Meng, N.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, W.; Sun, B. Chemical components and health benefits of Rubus suavissimus S. Lee (Chinese sweet tea) and the production method of rubusoside. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Gong, L.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.M. Current status and development trends of agricultural robots. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 1–22+55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zou, L.; Wu, C.; Jia, J.; Chen, J. Method of famous tea sprout identification and segmentation based on improved watershed algorithm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 184, 106108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, R.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; He, X.; Zhao, Z. YOLOv7-Branch: A Jujube Leaf Branch Detection Model for Agricultural Robot. Sensors 2024, 24, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, B.; Liao, S.; Huo, Z.; Yang, Z. A method for litchi picking points calculation in natural environment based on main fruit bearing branch detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 189, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liu, C.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, T.; Zhao, C. MTA-YOLACT: Multitask-aware network on fruit bunch identification for cherry tomato robotic harvesting. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 146, 126812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, C.; Dong, C. A lightweight tea bud detection model based on Yolov5. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.; Mu, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. An improved YOLOv5-based method for multi-species tea shoot detection and picking point location in complex backgrounds. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 231, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, R.-W.; Oladipo, M. Mask YOLOv7-Based Drone Vision System for Automated Cattle Detection and Counting. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2024, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gu, Z.; He, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Mo, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, Z.; Wu, F. A Lightweight Improved YOLOv5s Model and Its Deployment for Detecting Pitaya Fruits in Daytime and Nighttime Light-Supplement Environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fu, L.; Gao, C.; Fang, W.; Zhao, G.; Shi, F.; Dhupia, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, R.; Cui, Y. Multi-Class Detection of Kiwifruit Flower and Its Distribution Identification in Orchard Based on YOLOv5l and Euclidean Distance. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 201, 107342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Chen, S.F. Localizing plucking points of tea leaves using deep convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 171, 105298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tong, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; An, Y.; Kang, F. Tea Bud and Picking Point Detection Based on Deep Learning. Forests 2023, 14, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Extracting Tea Bud Contour and Location of Picking Points in Large Scene Using Case Segmentation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2024, 40, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Sun, H. Tea-YOLOv8s: A Tea Bud Detection Model Based on Deep Learning and Computer Vision. Sensors 2023, 23, 6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Hu, C.; Hu, X.; Xu, M. Picking point recognition for ripe tomatoes using semantic segmentation and morphological processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 210, 107923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, L. Optimization strategies of fruit detection to overcome the challenge of unstructured background in field orchard environment: A review. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 1183–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zou, X.; Wu, M.; Tang, W.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, H. Adaptive Active Positioning of Camellia oleifera Fruit Picking Points: Classical Image Processing and YOLOv7 Fusion Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Duan, J.; Ai, P.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zou, X. Rachis detection and three-dimensional localization of cut off point for vision-based banana robot. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Yuan, Y. Far-near combined positioning of picking-point based on depth data features for horizontal-trellis cultivated grape. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 194, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, L.; Song, L.; Han, T.; Song, Y.; Pang, Y.; Su, B. Identifying and positioning grape compound buds using RGB-D images. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, Z.; Li, K.; Ding, X.; Li, H.; Gong, W.; Cui, Y. Object detection and spatial positioning of kiwifruits in a wide-field complex environment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 223, 109102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, L.; Jia, J.; Lv, J.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X.; Wu, C. In-field tea shoot detection and 3D localization using an RGB-D camera. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 185, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, J.; Zhou, M.; Yi, J.; Liao, M.; Gao, Z. A YOLOv3-based computer vision system for identification of tea buds and the picking point. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Gao, F.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q. Application of consumer RGB-D cameras for fruit detection and localization in field: A critical review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 177, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnsen, C.H.; Johansen, A.S.; Philipsen, M.P.; Henriksen, J.W.; Nasrollahi, K.; Moeslund, T.B. 3D Sensors for Sewer Inspection: A Quantitative Review and Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Walsh, K.B.; Verma, B. On-Tree Mango Fruit Size Estimation Using RGB-D Images. Sensors 2017, 17, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z. Kiwifruit Detection and Localization Methods Based on Multi-Source Information Fusion. Master’s Thesis, College of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Syed, T.N. Experiments and Analysis of Close-Shot Identification of On-Branch Citrus Fruit with RealSense. Sensors 2018, 18, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Luo, L.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, J. Dynamic visual servo control methods for continuous operation of a fruit harvesting robot working throughout an orchard. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C. A review of key techniques of vision-based control for harvesting robot. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 311–323. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:30904888 (accessed on 1 January 2020). [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Tang, Y. A Study on Long-Close Distance Coordination Control Strategy for Litchi Picking. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, A.; Russell, B.C.; Yuen, J. LabelMe: Online Image Annotation and Applications. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1467–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G. Ultralytics YOLOv8 [EB/OL]. GitHub. 11 January 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Gu, Z.; He, D.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, B.; Dong, T.; Yang, Q.; Li, H. Simultaneous Detection of Fruits and Fruiting Stems in Mango Using Improved YOLOv8 Model Deployed by Edge Device. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lv, J.; Zhang, C. MAE-YOLOv8-Based Small Object Detection of Green Crisp Plum in Real Complex Orchard Environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huo, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H. USSC-YOLO: Enhanced Multi-Scale Road Crack Object Detection Algorithm for UAV Image. Sensors 2024, 24, 5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Spatial Group-wise Enhance: Improving Semantic Feature Learning in Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09646. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.09646 (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861 (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- Xue, J.; Cheng, F.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Mao, T. Detection of Farmland Obstacles Based on an Improved YOLOv5s Algorithm by Using CIoU and Anchor Box Scale Clustering. Sensors 2022, 22, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, K.; Ma, H. Powerful-IoU: More straightforward and faster bounding box regression loss with a nonmonotonic focusing mechanism. Neural Netw. 2024, 170, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E.; Masters, B.R. Digital Image Processing, Third Edition. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 029901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, Z.; Gao, N.; Zhang, Z. Advancements in fusion calibration technology of lidar and camera. Infrared Laser Eng. 2023, 52, 20230427-1–20230427-14. Available online: https://www.sciengine.com/IRLA/doi/10.3788/IRLA20230427 (accessed on 22 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wen, J. An Improved Mask RCNN Model for Segmentation of ‘Kyoho’ (Vitis labruscana) Grape Bunch and Detection of Its Maturity Level. Agriculture 2023, 13, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. YOLACT: Real-Time Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9156–9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; NanoCode012; Kwon, Y.; Michael, K.; TaoXie; Fang, J.; Imyhxy; et al. ultralytics/yolov5: v7.0—YOLOv5 SOTA Realtime Instance Segmentation. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Research on the Visual Detection and Localization Technology of Tea Harvesting Robot. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
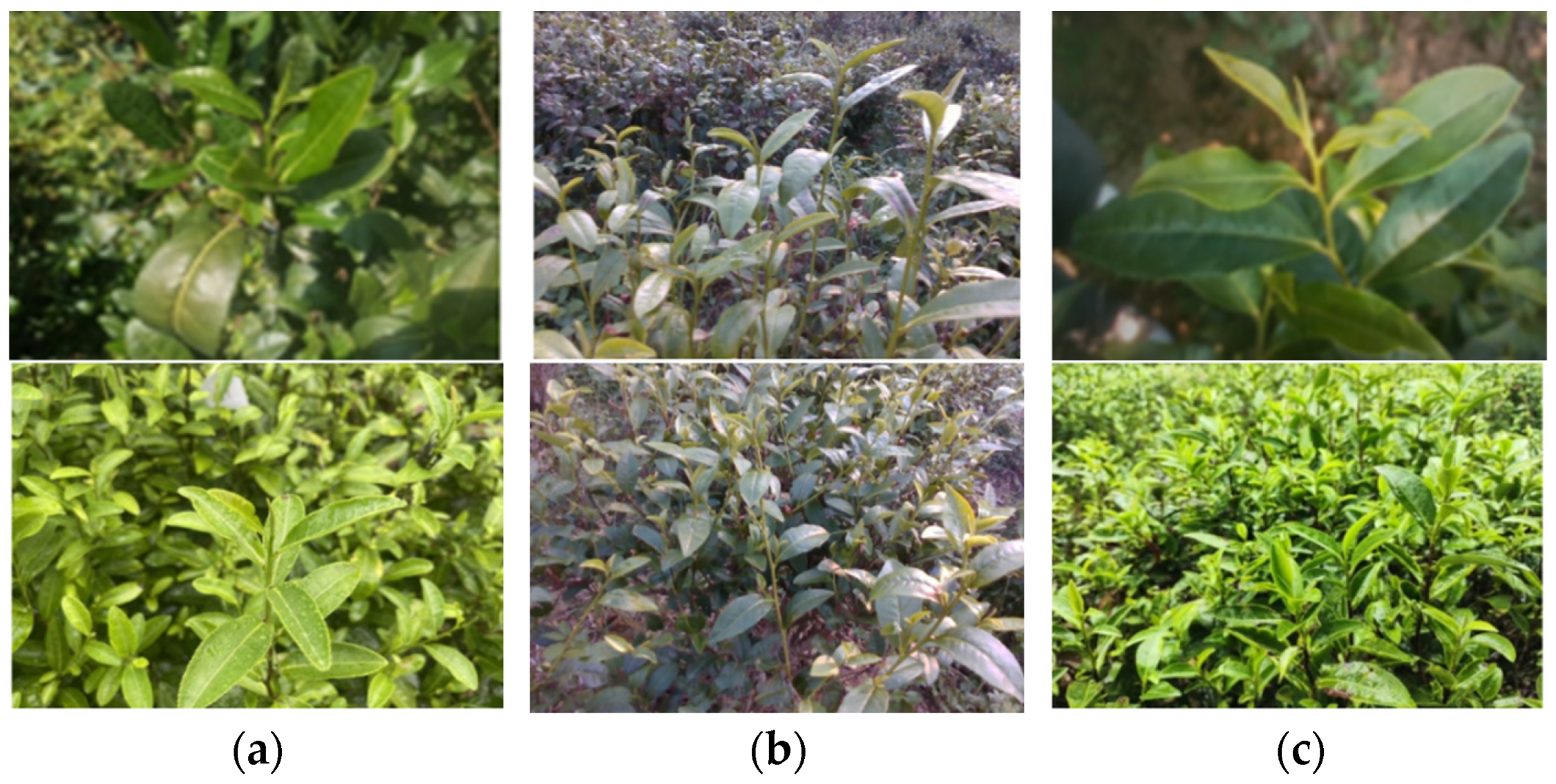









| Type of Dataset | Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Training set | 1687 | |
| Validation set | 422 | |
| MFN test set | Far-view test set A | 170 |
| Near-view test set B | 150 | |
| Total | 2429 | |
| Dataset (Class) | Add Modules | Bounding Box/% | Mask/% | Parmas/106 | GFLOPS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIoUv2 | EMSC2F | SGE | P | R | mAP0.5 | P | R | mAP0.5 | |||
| Test A (Tea) | 74.6 | 74.8 | 74.6 | - | - | - | 3.26 | 12.1 | |||
| √ | 78.6 | 77.7 | 78.1 | - | - | - | 3.26 | 12.1 | |||
| √ | 73.8 | 77.1 | 78.2 | - | - | - | 3.13 | 11.4 | |||
| √ | 78.4 | 76.5 | 78.9 | - | - | - | 3.30 | 11.7 | |||
| √ | √ | √ | 80.8 | 76.2 | 81 | - | - | - | 3.16 | 11.4 | |
| Test B (Stem) | 88.5 | 77.3 | 84.5 | 84.9 | 71.8 | 79.6 | 3.26 | 12.1 | |||
| √ | 88.6 | 80.3 | 88.1 | 85.8 | 81.4 | 86.1 | 3.26 | 12.1 | |||
| √ | 89.4 | 81.7 | 87.9 | 89.8 | 74.6 | 80.8 | 3.13 | 11.4 | |||
| √ | 78.8 | 78.3 | 83.3 | 82.9 | 82.1 | 84.1 | 3.30 | 11.7 | |||
| √ | √ | √ | 95.4 | 88.5 | 93.6 | 95.5 | 89.5 | 93.7 | 3.16 | 11.4 | |
| Dataset (Class) | Model | Bounding Box/% | Mask/% | Parmas /106 | GFLOPS | Model Size /MB | FPS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | mAP0.5 | P | R | mAP0.5 | ||||||
| Test A (Tea) | YOLOv5n-seg | 79.2 | 72.0 | 73.1 | - | - | - | 2.76 | 11.1 | 5.9 | 189 |
| Mask R-CNN | 80.1 | 82.3 | 80.3 | - | - | - | - | - | 53.7 | 30 | |
| YOLACT | 76.3 | 80 | 79.7 | - | - | - | - | - | 45.84 | 94 | |
| YOLOv8n-seg | 74.6 | 74.8 | 74.6 | - | - | - | 3.26 | 12.1 | 6.72 | 151 | |
| T-YOLOv8n | 80.8 | 76.2 | 81 | - | - | - | 3.16 | 11.4 | 6.3 | 178 | |
| Test B (Stem) | YOLOv5n-seg | 91.5 | 76.3 | 89.4 | 86.6 | 73 | 84.6 | 2.76 | 11.1 | 5.9 | 189 |
| Mask R-CNN | 72.3 | 95.6 | 84.6 | 71.1 | 97.1 | 85.4 | - | - | 53.7 | 30 | |
| YOLACT | 70 | 89.7 | 68.7 | 72.3 | 79.4 | 52.6 | - | - | 45.84 | 94 | |
| YOLOv8n-seg | 88.5 | 77.3 | 84.5 | 84.9 | 71.8 | 79.6 | 3.26 | 12.1 | 6.72 | 151 | |
| T-YOLOv8n | 95.4 | 88.5 | 93.6 | 95.5 | 89.5 | 93.7 | 3.16 | 11.4 | 6.3 | 178 | |
| Method | First Target | Second Target | Tea Count (Statistical) | Tea Count (Detected) | Stem Count (Statistical) | Stem Count (Detected) | Number of Successful Picking Poin Localizations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-stage visual scheme | Stem | - | - | - | 59 | 38 | 14 |
| Two-stage visual scheme | Tea | Stem | 71 | 64 | 59 | 54 | 51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Fu, L.; Li, S. Vision-Based Localization Method for Picking Points in Tea-Harvesting Robots. Sensors 2024, 24, 6777. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216777
Yang J, Li X, Wang X, Fu L, Li S. Vision-Based Localization Method for Picking Points in Tea-Harvesting Robots. Sensors. 2024; 24(21):6777. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216777
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jingwen, Xin Li, Xin Wang, Leiyang Fu, and Shaowen Li. 2024. "Vision-Based Localization Method for Picking Points in Tea-Harvesting Robots" Sensors 24, no. 21: 6777. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216777
APA StyleYang, J., Li, X., Wang, X., Fu, L., & Li, S. (2024). Vision-Based Localization Method for Picking Points in Tea-Harvesting Robots. Sensors, 24(21), 6777. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216777





