In-Motion Alignment with MEMS-IMU Using Multilocal Linearization Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To the best of the authors’ knowledge, the maximum likelihood of the generalized Schweppe likelihood ratio method is applied for the first time to replace the coarse alignment process. The proposed method only requires satellite signals at two-time instants to make the initial estimates.
- The proposed quasi-uniform quaternion method in this study significantly reduces the number of initial estimates required.
- The vehicle experiment is designed and implemented to evaluate the proposed method.
2. Mathematical Models and Problem Statement
2.1. Mathematical Models
2.2. Problem Statement
3. Multilocal Linearization and Maximum Likelihood Estiamtion
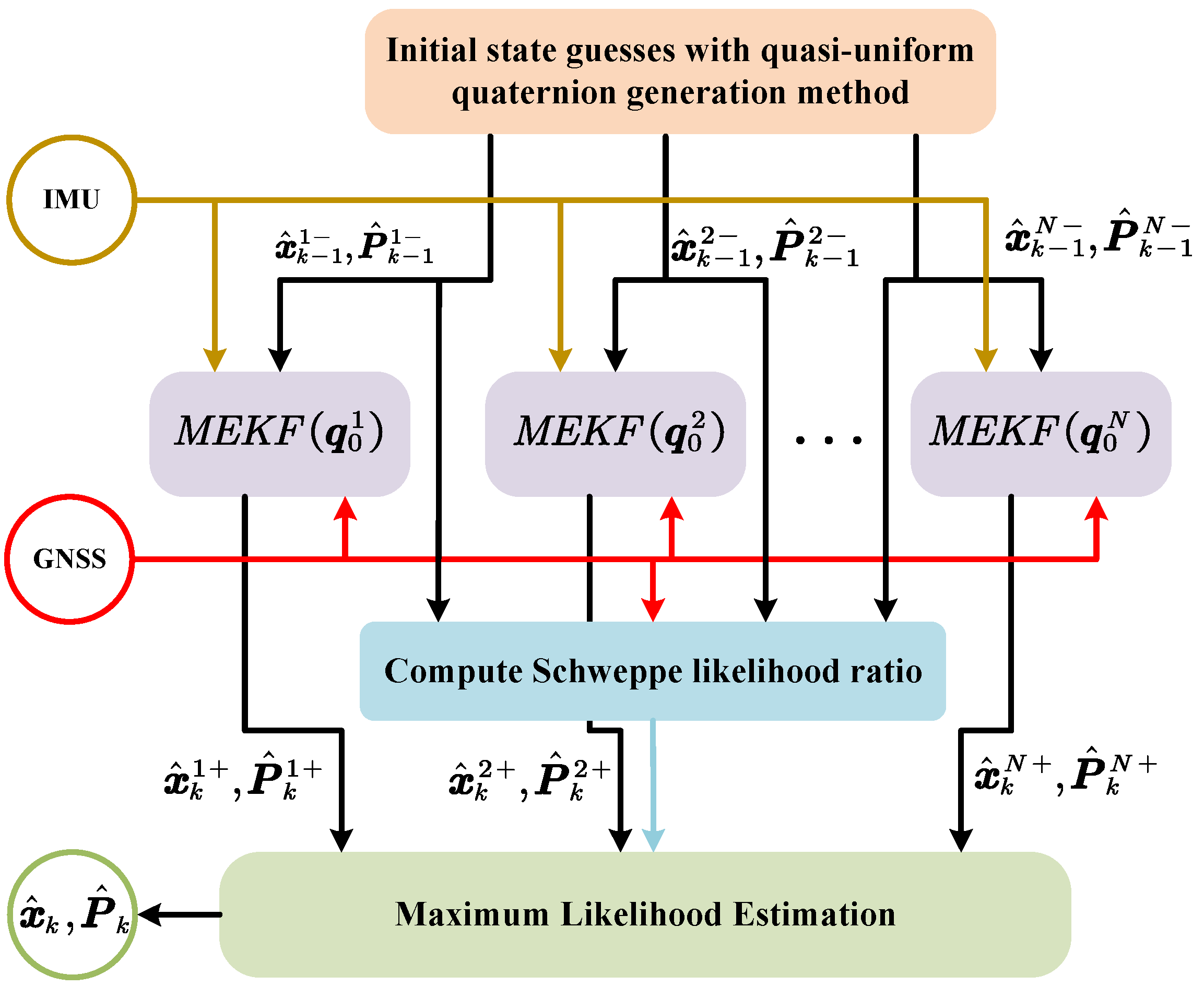
3.1. The Proposed Method Framework
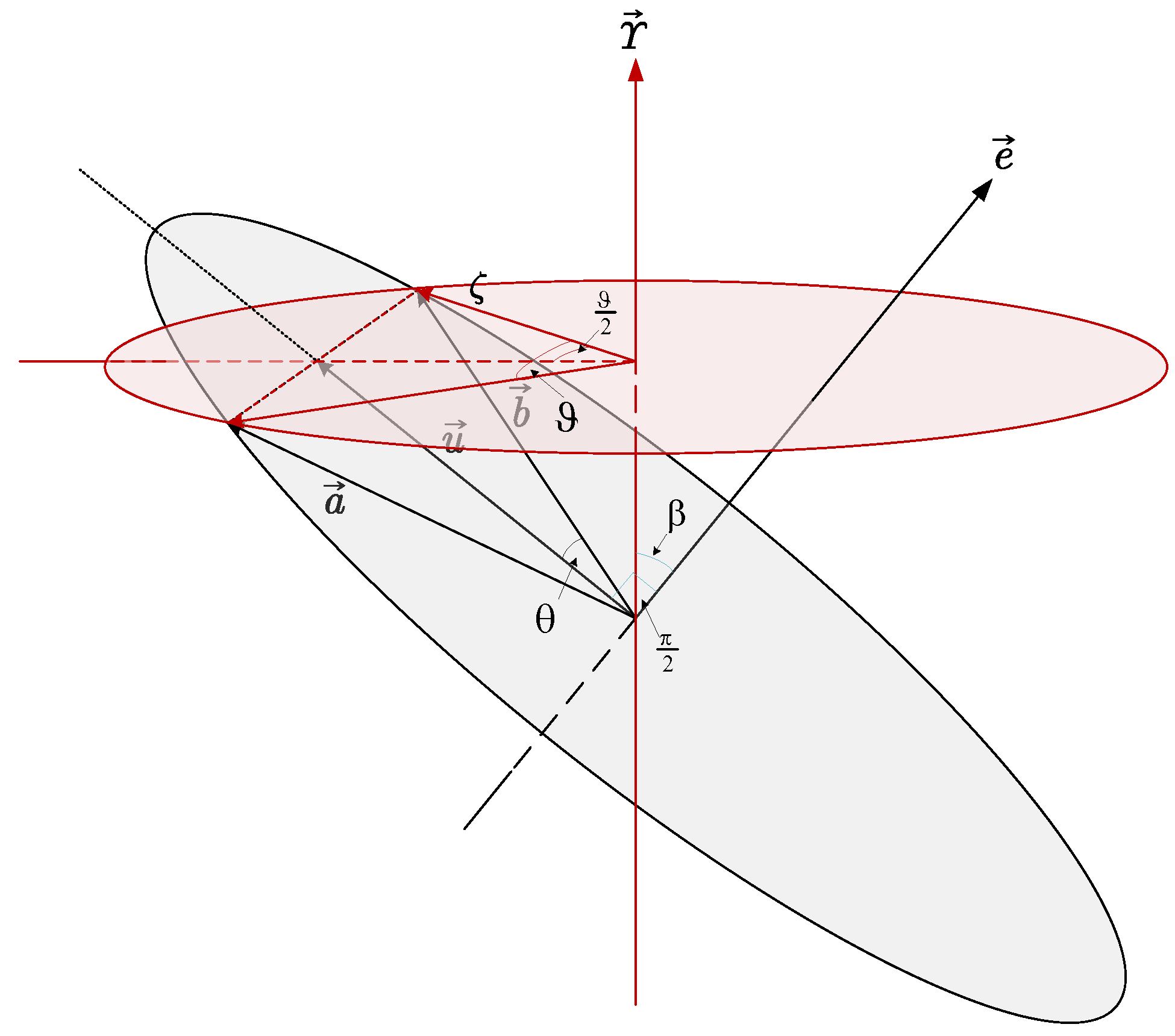
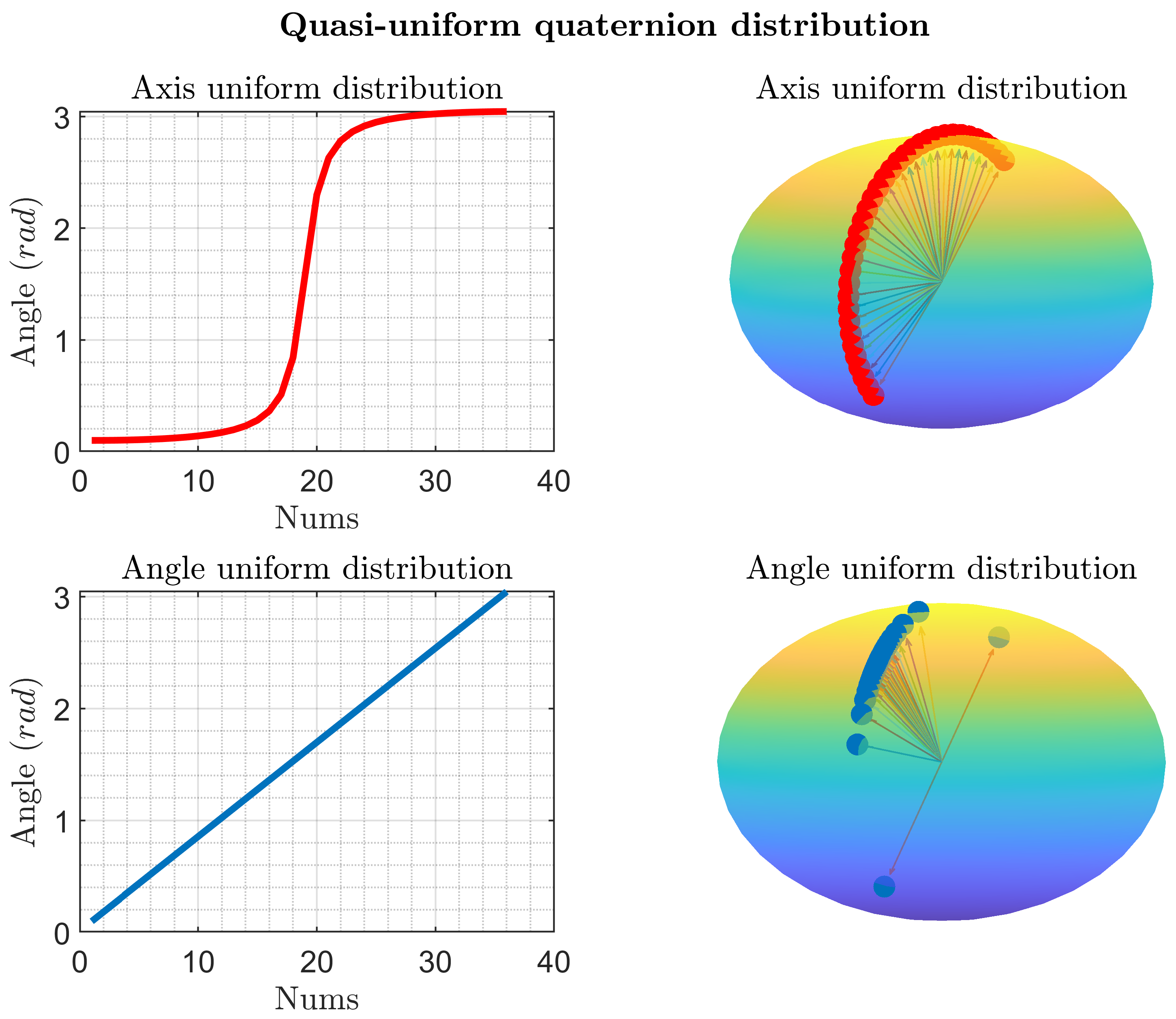
3.2. Initial Quasi-Uniform Quaternion Generation Method for Multilocal Linearization
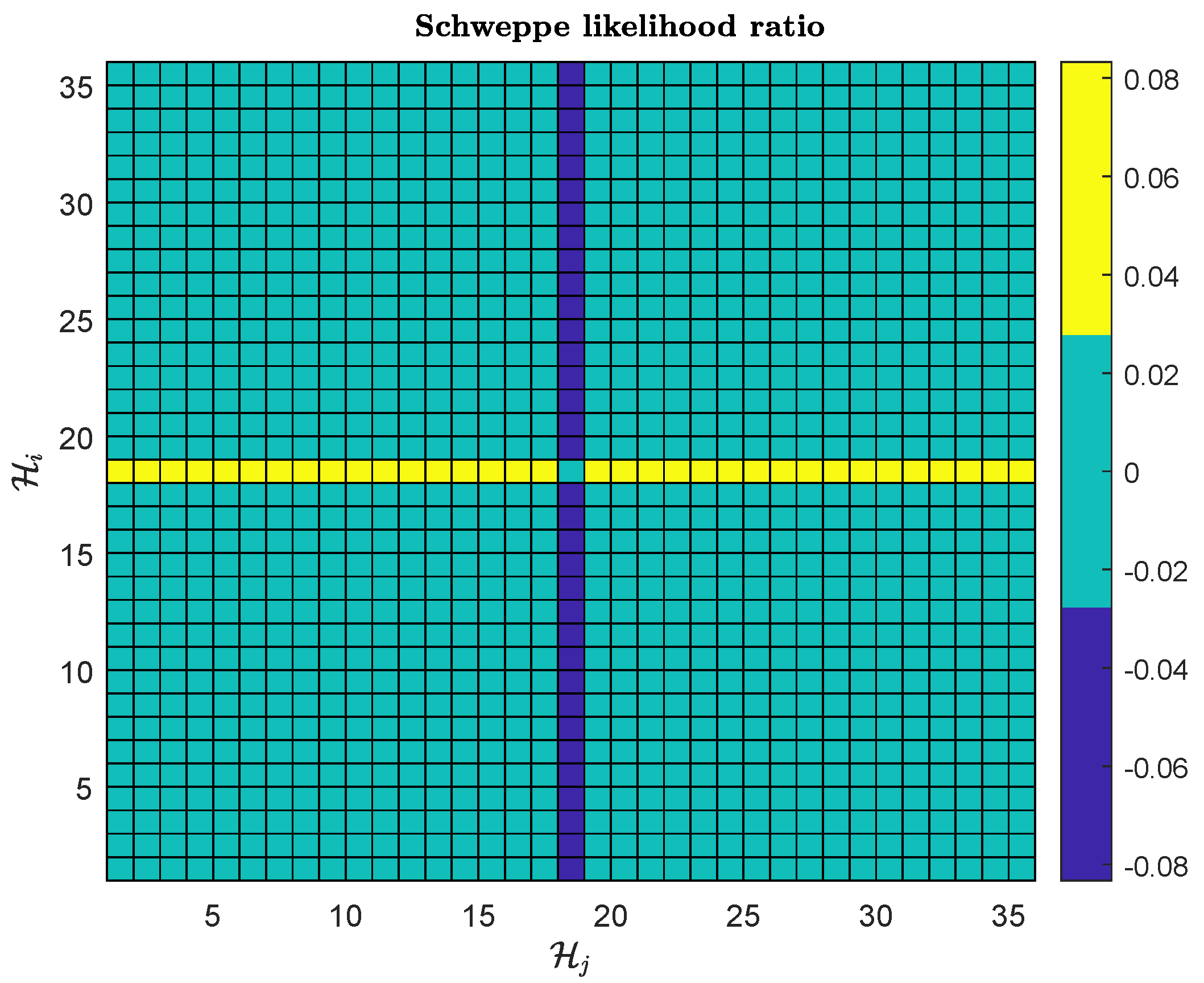
3.3. Generalized Schweppe Likelihood and Maximum Likelihood Estiamtion
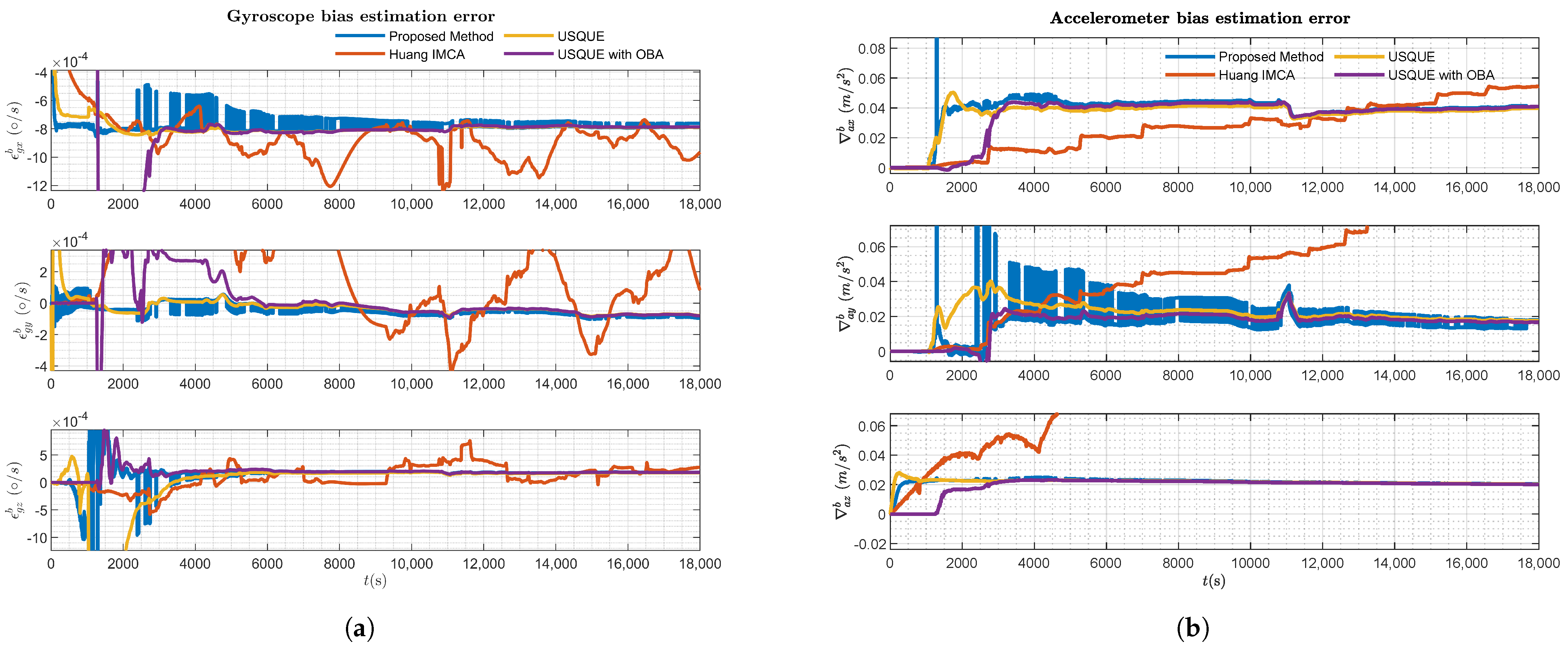
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Experiment Setup
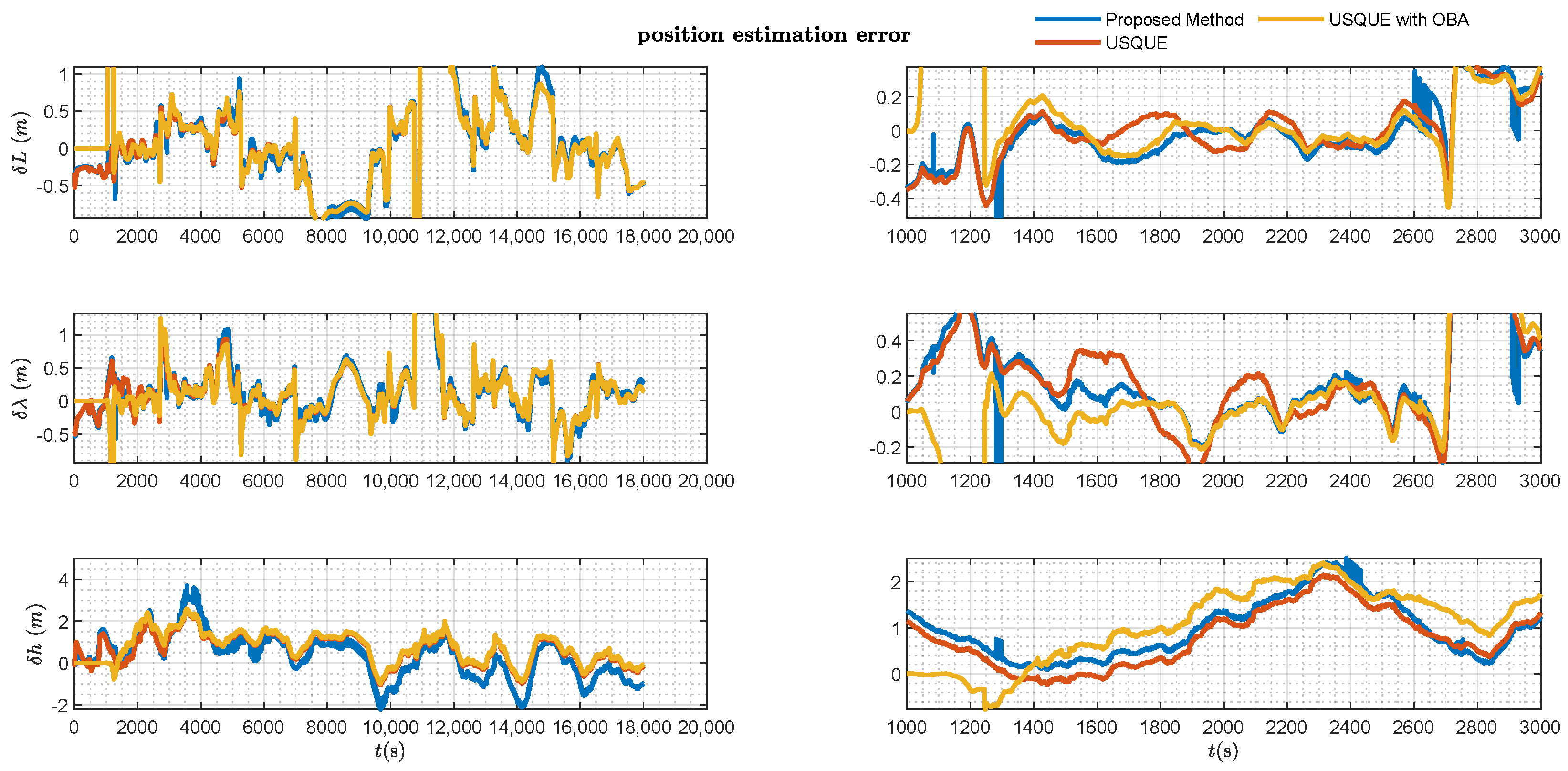
4.2. Vehicle Experiment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groves, P.D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems; Artech House: Norwood, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Markley, F.L.; Crassidis, J.L. Fundamentals of Spacecraft Attitude Determination and Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Pan, X. Velocity/position integration formula, Part I: Application to in-flight coarse alignment. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 1006–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.L.; Hu, D.W. A New Technique for INS/GNSS Attitude and Parameter Estimation Using Online Optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 2642–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.B.; Li, J.S.; Chen, S.Y. Initial Alignment by Attitude Estimation for Strapdown Inertial Navigation Systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 63, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, L.B.; Li, J.S.; Li, K.L. Optimization-based alignment for strapdown inertial navigation system: Comparison and extension. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 1697–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.G.; Chang, L.B. A New Fast In-Motion Coarse Alignment Method for GPS-Aided Low-Cost SINS. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2018, 23, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.; Du, S.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.G. A High-Accuracy GPS-Aided Coarse Alignment Method for MEMS-Based SINS. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 7914–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, F.L. Attitude Error Representations for Kalman Filtering. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2003, 26, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterton, D.H.; Weston, J.L. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Technology, 2nd ed.; The Institute of Electrical Engineers: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Chang, L. MEKF with Navigation Frame Attitude Error Parameterization for INS/GPS. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crassidis, J.L. Sigma-point Kalman filtering for integrated GPS and inertial navigation. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Contol Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Merwe, R.; Wan, E.A.; Julier, S. Sigma-Point Kalman Filters for Nonlinear Estimation and Sensor-Fusion-Applications to Integrated Navigation. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Contol Conference, Providence, RI, USA, 16–19 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Crassidis, J.L.; Markley, F.L. Unscented filtering for spacecraft attitude estimation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2003, 26, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crassidis, J.L. Sigma-Point Kalman Filtering for Integrated GPS and Inertial Navigation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2006, 42, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Chen, X.Y.; Liu, J.G.; Zhu, X.F.; Zhong, Y.L. A Robust Backtracking CKF Based on Krein Space Theory for In-Motion Alignment Process. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 1909–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.C.; Wang, J.W. Adaptive Particle Filtering with Variational Bayesian and Its Application for INS/GPS Integrated Navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 19757–19770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Strong Tracking UKF-Based Hybrid Algorithm and Its Application to Initial Alignment of Rotating SINS with Large Misalignment Angles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 8334–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweppe, F. Evaluation of likelihood functions for Gaussian signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1965, 11, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, T.H. Analytic example of a Schweppe likelihood-ratio detector. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1989, 25, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, M.S.; Andrews, A.P. Kalman Filtering: Theory and Practice with MATLAB, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, A.P. The Accuracy of Navigation Using Magnetic Dipole Beacons. Navigation 1991, 38, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. An Improved Fuzzy Adaptive Iterated SCKF for Cooperative Navigation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2024, 29, 3774–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
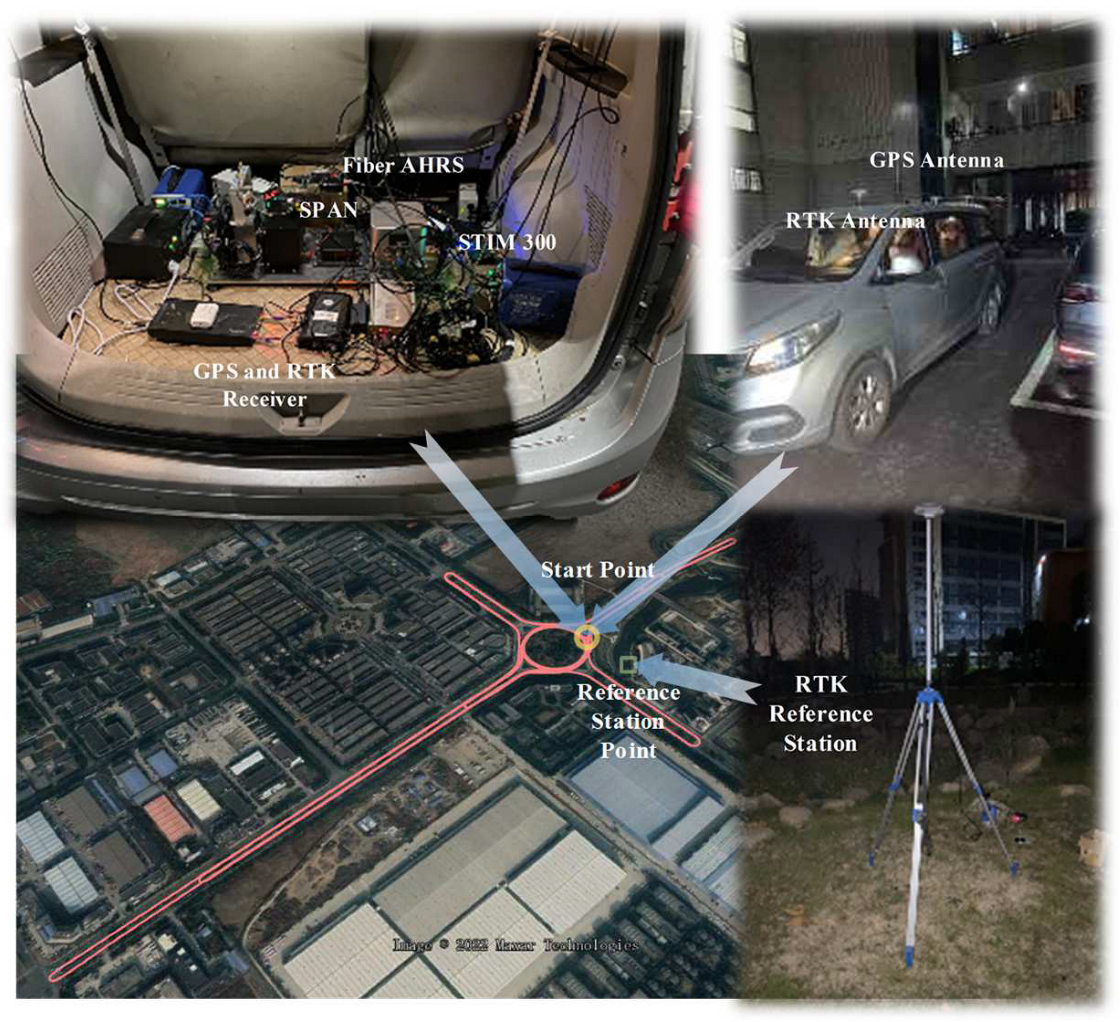




| Experiment Equipments Parameters (Allan Analysis) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| MEMS-IMU | gyroscope | Bias | −250°/h∼250°/h |
| Bias Instability | 0.5269°/h | ||
| Random Walk | 0.1426°/h | ||
| accelerometer | Bias | 750 μg | |
| Bias Instability | 0.068 mg | ||
| Random Walk | 0.079 m/s/h | ||
| GPS | Position White Noise | 3 m | |
| Velocity White Noise | 0.15 m/s | ||
| AHRS | gyroscope Bias Instability | 0.01°/h | |
| Angular Random Walk | 0.003°/h | ||
| Accelerometer Bias Instability | μg | ||
| RTK | Velocity Random Walk | 0.003 m/s/h | |
| Horizontal position accuracy | 8 mm | ||
| Vertical position accuracy | 15 mm | ||
| Items | Proposed Method (1300 s∼end) | Wu OBA (1300 s∼end) | Huang IMCA (1300 s∼end) | USQUE (1300 s∼end) | USQUE with OBA (1300 s∼end) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pitch (°) | 0.2620 | 7.5328 | 0.4194 | 0.2668 | 0.2694 |
| Roll (°) | 0.2057 | 6.3555 | 0.7417 | 0.2270 | 0.2267 |
| Yaw (°) | 22.2248 | 128.2715 | 29.7970 | 26.2894 | 24.0499 |
| Eastern Velocity (m/s) | 0.4158 | \ | \ | 0.4382 | 0.4311 |
| Northern Velocity (m/s) | 0.4329 | \ | \ | 0.4524 | 0.4448 |
| Up Velocity (m/s) | 0.0977 | \ | \ | 0.0850 | 0.0825 |
| Eastern Position (m) | 2.7577 | \ | \ | 2.7616 | 2.7622 |
| Northern Position (m) | 2.2062 | \ | \ | 2.2041 | 2.2046 |
| Up Position (m) | 1.1242 | \ | \ | 1.0067 | 1.0973 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, N.; Jiao, Z. In-Motion Alignment with MEMS-IMU Using Multilocal Linearization Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092645
Zhong Y, Chen X, Gao N, Jiao Z. In-Motion Alignment with MEMS-IMU Using Multilocal Linearization Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092645
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yulu, Xiyuan Chen, Ning Gao, and Zhiyuan Jiao. 2025. "In-Motion Alignment with MEMS-IMU Using Multilocal Linearization Detection" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092645
APA StyleZhong, Y., Chen, X., Gao, N., & Jiao, Z. (2025). In-Motion Alignment with MEMS-IMU Using Multilocal Linearization Detection. Sensors, 25(9), 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092645






