Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging in Macroalgae Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hyperspectral Camera
2.1.1. Setup and Camera Settings
2.1.2. Operation and Data Acquisition
2.1.3. Hyperspectral Camera Characterization
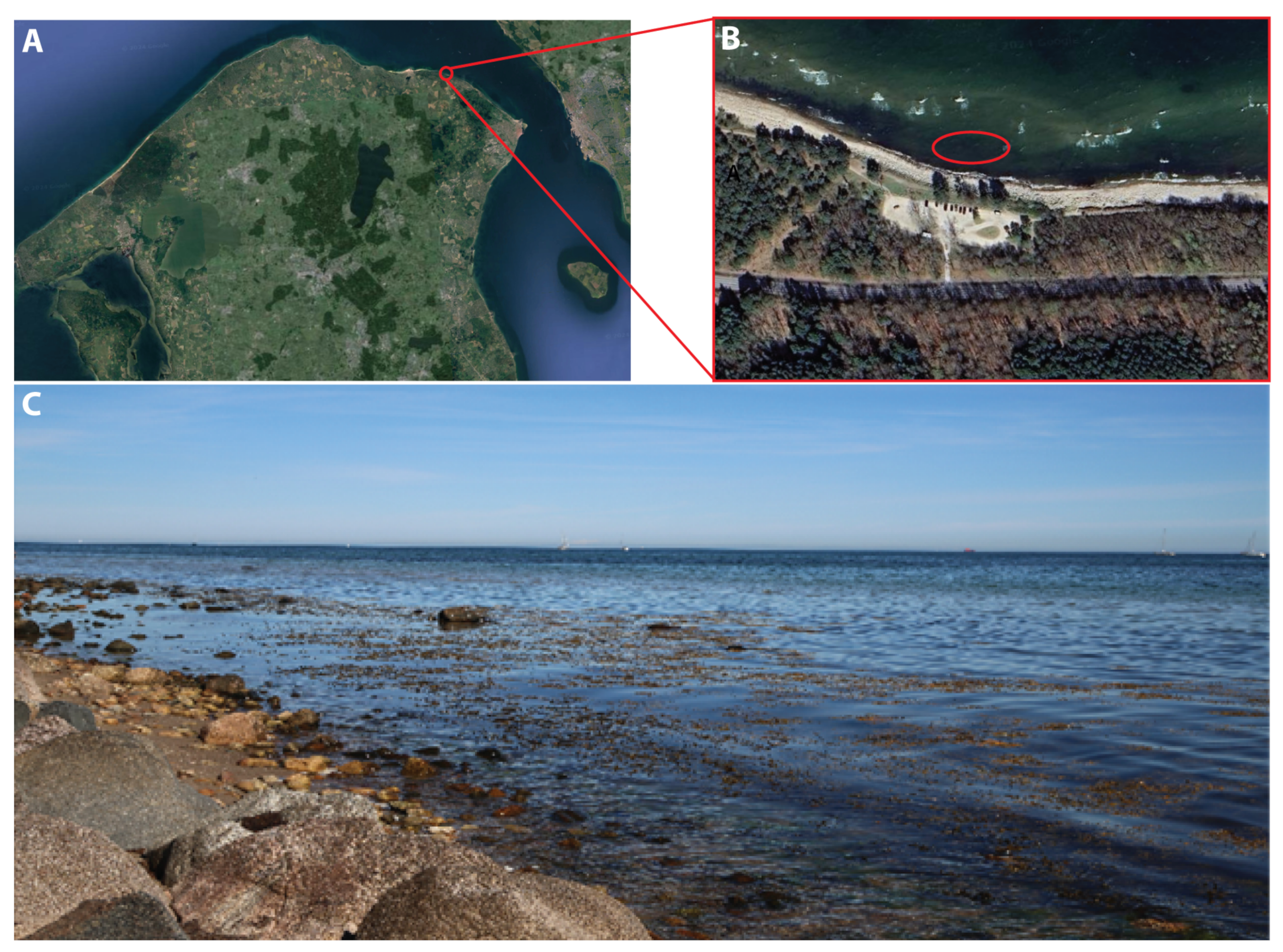
2.2. Study Area and Sample Collection
Taxonomic Identification
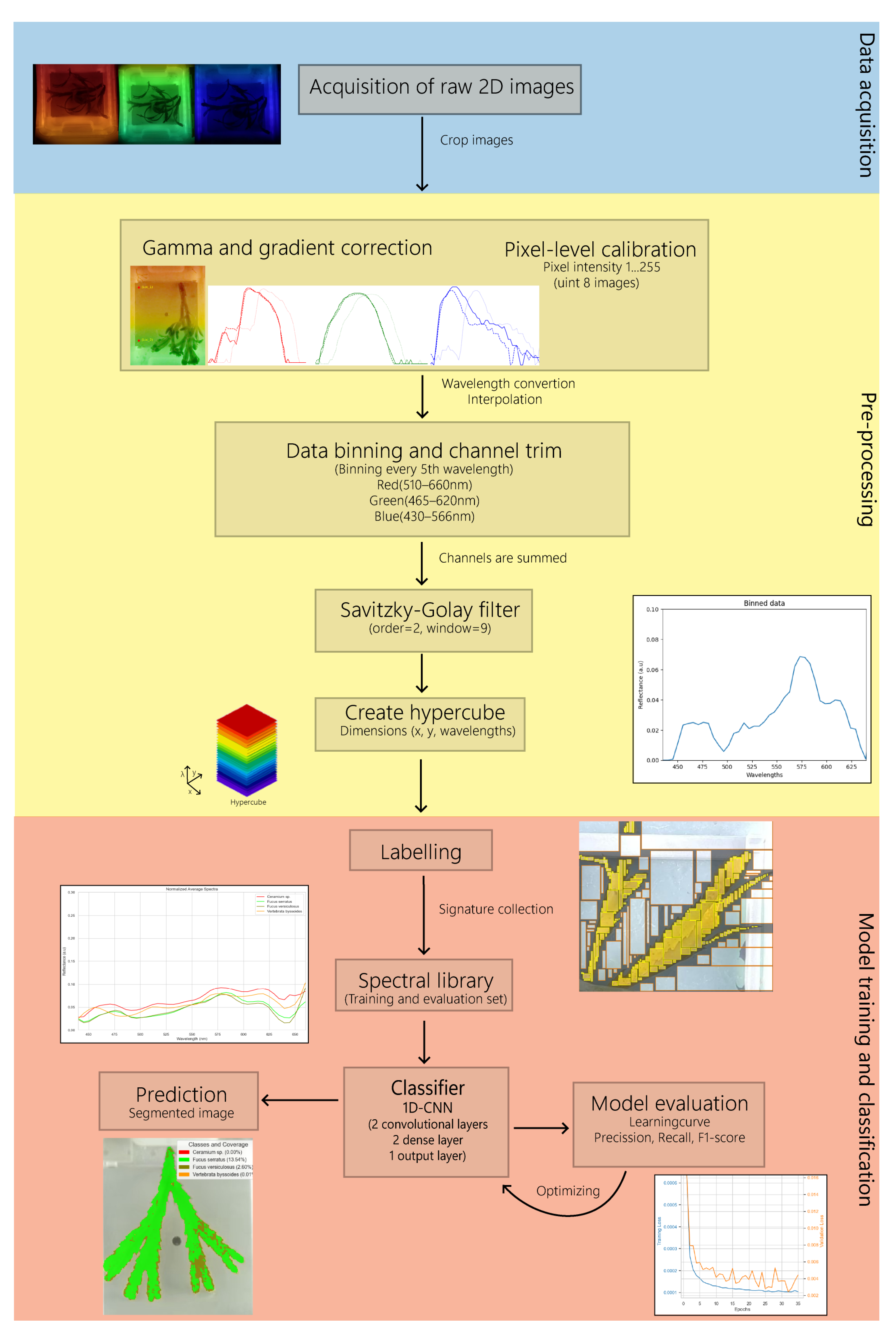
2.3. Pre-Processing of Hyperspectral Data
2.4. Classification Model
2.4.1. Software and Computer Specifications
2.4.2. Data Description
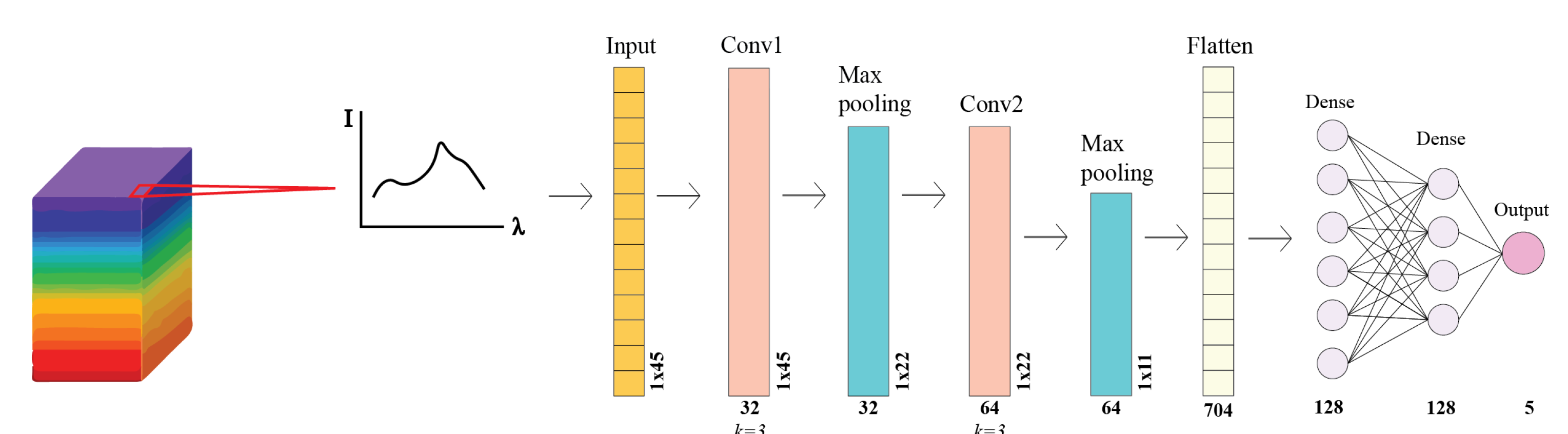
2.4.3. Model Description and Training Parameters
2.4.4. Model Evaluation
3. Results
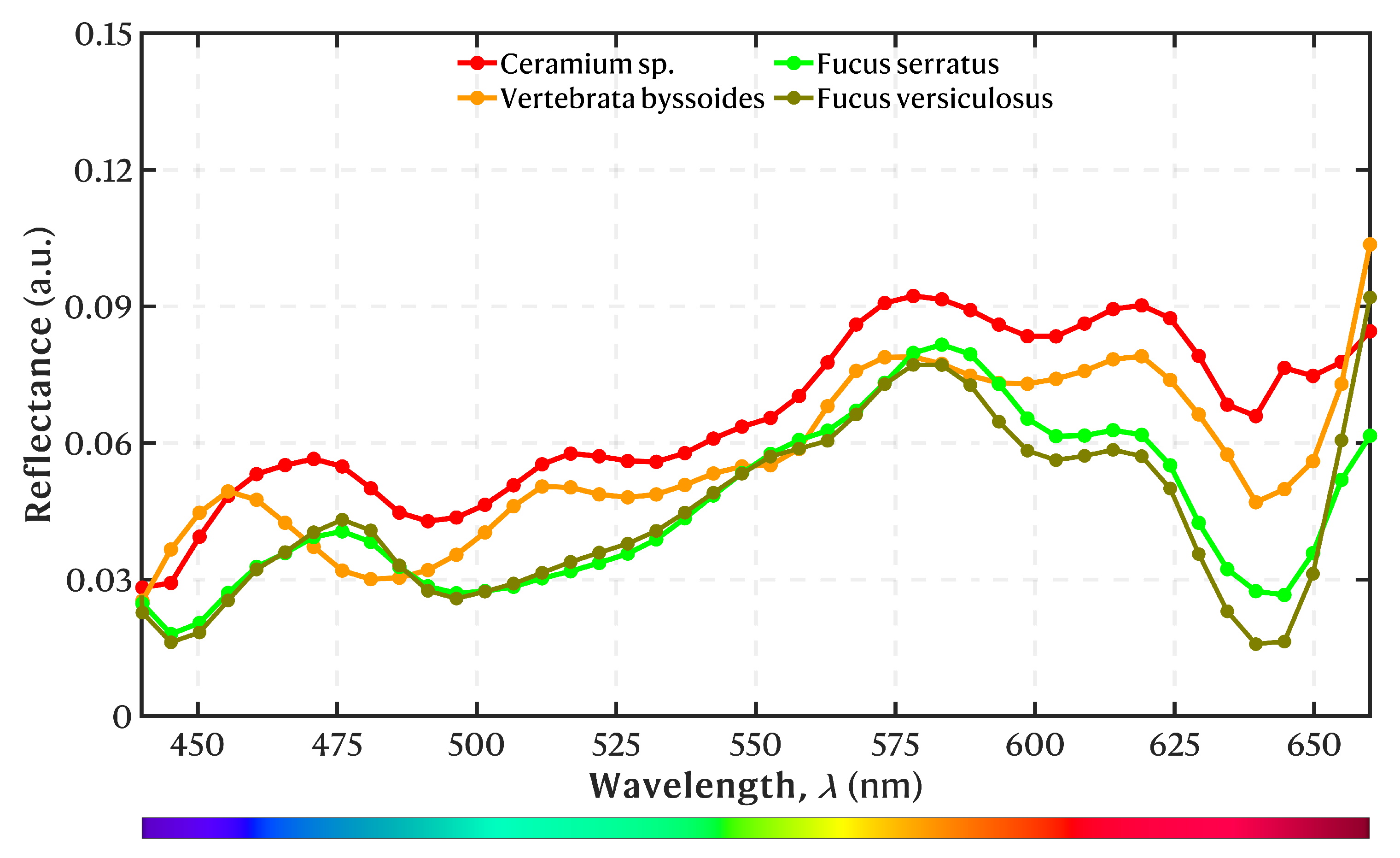
3.1. Spectral Library
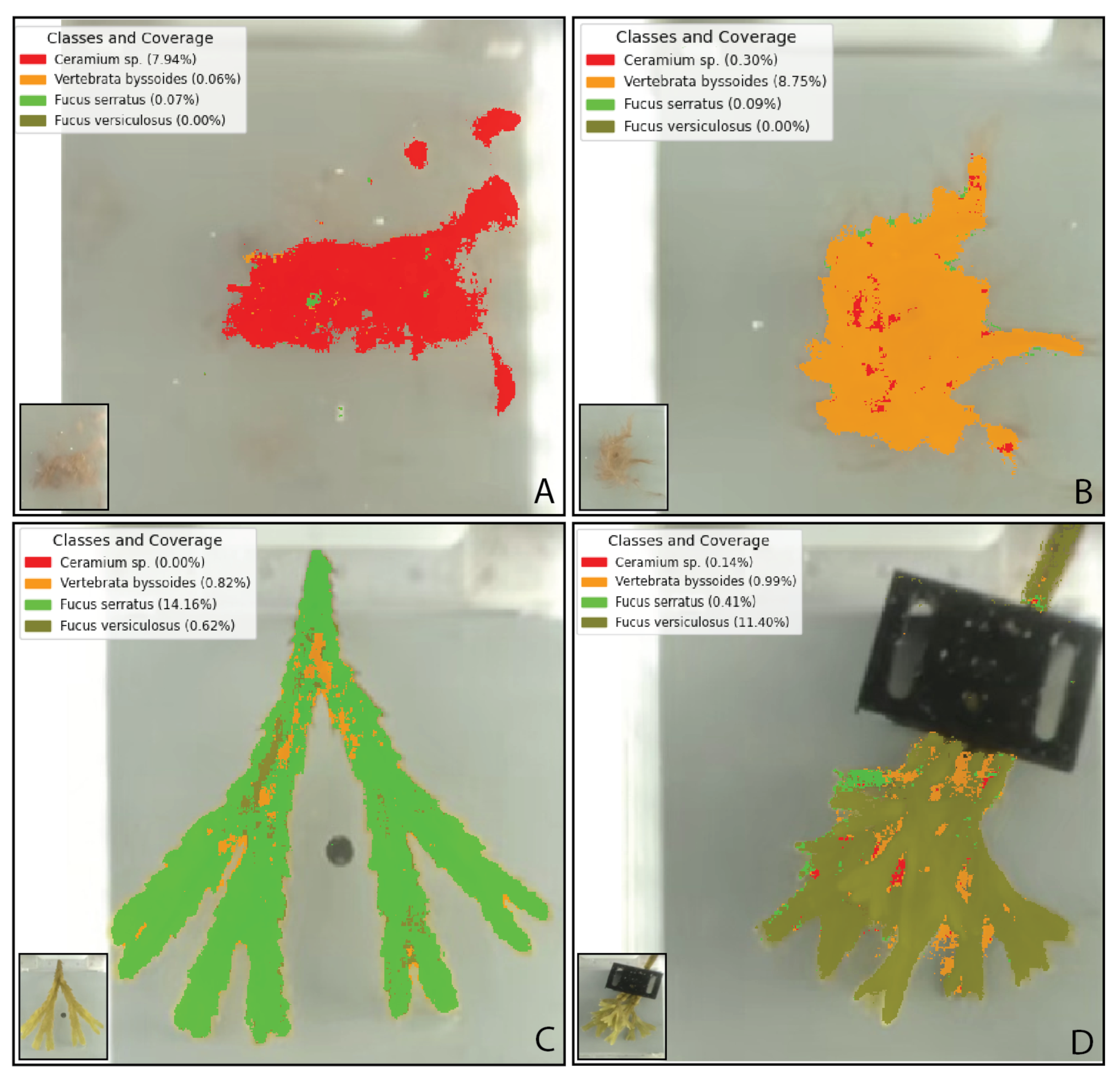
3.2. Model Performance and Classification
4. Discussion
4.1. Spectral Library
4.2. Model Performance and Classification
4.3. Implications and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CWL | Center Wavelength |
| FOV | Field-Of-View |
| FWHM | Full-Width at Half-Maximum |
| HSI | Hyperspectral Imaging |
| LED | Light-Emitting Diode |
| LVSBPF | Linear Variable Spectral Bandpass Filter |
| RGB | Red, Green, Blue |
| ROI | Region Of Interest |
| ROV | Remotely Operated Vehicle |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
References
- Monserrat, M.; Comeau, S.; Verdura, J.; Alliouane, S.; Spennato, G.; Priouzeau, F.; Romero, G.; Mangialajo, L. Climate change and species facilitation affect the recruitment of macroalgal marine forests. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheminée, A.; Sala, E.; Pastor, J.; Bodilis, P.; Thiriet, P.; Mangialajo, L.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Francour, P. Nursery value of Cystoseira forests for Mediterranean rocky reef fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 442, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause-Jensen, D.; Duarte, C.M. Substantial role of macroalgae in marine carbon sequestration. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D. Carbonate production by calcareous red algae and global change. Geodiversitas 2012, 34, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbee-Dexter, K.; Wernberg, T. Rise of Turfs: A New Battlefront for Globally Declining Kelp Forests. BioScience 2018, 68, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steneck, R.S.; Graham, M.H.; Bourque, B.J.; Corbett, D.; Erlandson, J.M.; Estes, J.A.; Tegner, M.J. Kelp forest ecosystems: Biodiversity, stability, resilience and future. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 436–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.L.; Bell, T.W.; Watson, J.R.; Grorud-Colvert, K.A.; Menge, B.A. Remote sensing: Generation of long-term kelp bed data sets for evaluation of impacts of climatic variation. Ecology 2020, 101, e03031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, K.C.; Bell, T.; Costa, M.; Eddy, N.E.; Gendall, L.; Gleason, M.G.; Hessing-Lewis, M.; Martone, R.; McPherson, M.; Pontier, O.; et al. A Review of the Opportunities and Challenges for Using Remote Sensing for Management of Surface-Canopy Forming Kelps. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 753531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditria, E.M.; Buelow, C.A.; Gonzalez-Rivero, M.; Connolly, R.M. Artificial intelligence and automated monitoring for assisting conservation of marine ecosystems: A perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 918104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, L.; Fragkopoulou, E.; Cavanaugh, K.C.; Houskeeper, H.F.; Assis, J. Artificial intelligence convolutional neural networks map giant kelp forests from satellite imagery. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, G.; Corsini, M.; Callieri, M.; Palma, M.; Scopigno, R. Semantic Segmentation of Benthic Communities from Ortho-moisaic Maps. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W10, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Herrera, J.C.; Cimoli, E.; Cummings, V.; Hill, N.; Lucieer, A.; Lucieer, V. Underwater hyperspectral imaging (UHI): A review of systems and applications for proximal seafloor ecosystem studies. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Fei, B. Medical hyperspectral imaging: A review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 010901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogstad, A.A.; Johnsen, G.; Ludvigsen, M. Shallow-Water Habitat Mapping using Underwater Hyperspectral Imaging from an Unmanned Surface Vehicle: A Pilot Study. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessios, H.A. Methods for Quantifying Abundance of Marine Organisms. In Methods and Techniques of Underwater Research, Proceedings of the American Academy of Underwater Sciences Scientific Diving Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 12–13 October 1996; Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogstad, A.A.; Johnsen, G. Spectral characteristics of coralline algae: A multi-instrumental approach, with emphasis on underwater hyperspectral imaging. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 9957–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, J.; Willans, J.; Allen, M.J.; Scott, T.B.; Day, J.C. Hyperspectral imaging as a tool for assessing in this issue: Preprocessing to compensate for packaging film/using neural nets to invert the prosail canopy model coral health utilising natural fluorescence. J. Spectr. Imaging 2019, 8, a7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimoli, E.; Lucieer, V.; Meiners, K.M.; Chennu, A.; Castrisios, K.; Ryan, K.G.; Lund-Hansen, L.C.; Martin, A.; Kennedy, F.; Lucieer, A. Mapping the in situ microspatial distribution of ice algal biomass through hyperspectral imaging of sea-ice cores. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, R.; Johnsen, G.; Bruheim, P.; Andreassen, T. Development of hyperspectral imaging as a bio-optical taxonomic tool for pigmented marine organisms. Org. Divers. Evol. 2014, 14, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, G.; Ludvigsen, M.; Sørensen, A.; Sandvik Aas, L.M. The use of underwater hyperspectral imaging deployed on remotely operated vehicles - methods and applications. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Song, S.; Gui, S.; Chao, W.; Cheng, C.; Qin, R. Active and Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging for the Spectral Analysis of a Low-Light Environment. Sensors 2023, 23, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.B.; Davies, M.; Hobbs, M.J.; Pering, T.D.; McGonigle, A.J.; Willmott, J.R. High-Resolution Hyperspectral Imaging Using Low-Cost Components: Application within Environmental Monitoring Scenarios. Sensors 2022, 22, 4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Gibson, D.; Ahmadzadeh, S.; Chu, H.O.; Warden, B.; Overend, R.; Macfarlane, F.; Murray, P.; Marshall, S.; Aitkenhead, M.; et al. Low-cost hyper-spectral imaging system using a linear variable bandpass filter for agritech applications. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, A167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iga, M.; Kakuryu, N.; Tanaami, T.; Sajiki, J.; Isozaki, K.; Itoh, T. Development of thin-film tunable band-pass filters based hyper-spectral imaging system applied for both surface enhanced Raman scattering and plasmon resonance Rayleigh scattering. Rev. Sci. Instru. 2012, 83, 103707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinatake, K.; Ishinabe, T.; Shibata, Y.; Fujikake, H. High-speed Tunable Multi-Bandpass Filter for Real-time Spectral Imaging using Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Etalon. ITE Trans. Media Technol. Appl. 2020, 8, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shang, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Ni, H.; Qiao, D. Hyper-spectral imaging technology based on linear gradient bandpass filter for electricity power equipment status monitoring application. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2021, 2011, 012091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, R.M.; Fry, E.S. Absorption spectrum (380–700 nm) of pure water II Integrating cavity measurements. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 8710–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Xing, Z.; Hu, B.; Zheng, X. Automatic Registration of Remote Sensing High-Resolution Hyperspectral Images Based on Global and Local Features. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglini, F.; Grande, V.; Marchese, F.; Bracchi, V.A.; Prampolini, M.; Angeletti, L.; Castellan, G.; Chimienti, G.; Hansen, I.M.; Gudmundsen, M.; et al. Application of hyperspectral imaging to underwater habitat mapping, Southern Adriatic Sea. Sensors 2019, 19, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, A.; Køie, M. Havets Dyr og Planter; Gyldendal: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, R.; Lundsteen, S. Danmarks Havalger—Rødalger (Rhodophyta); Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab; Scientia Danica; Series B; Biologica: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.; Pedersen, M.L.; Ulusoy, B.; Weinell, C.E.; Pedersen, H.C.; Petersen, P.M.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Pedersen, C. A Tunable Hyperspectral Imager for Detection and Quantification of Marine Biofouling on Coated Surfaces. Sensors 2022, 22, 7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigo, J.M.; Babamoradi, H.; Elcoroaristizabal, S. Hyperspectral image analysis. A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 896, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.H.; Son, G.J.; Park, M.K.; Kim, Y.D. Rapid foreign object detection system on seaweed using vnir hyperspectral imaging. Sensors 2021, 21, 5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, B.; Nelson, J.; Hansen, T. Roboflow (Version 1.0), [Software]. 2024. Available online: https://roboflow.com (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Yu, S.; Jia, S.; Xu, C. Convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J. Application of Attention-Enhanced 1D-CNN Algorithm in Hyperspectral Image and Spectral Fusion Detection of Moisture Content in Orah Mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco). Information 2024, 15, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, H.; Lv, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Non-destructive detection and classification of textile fibres based on hyperspectral imaging and 1D-CNN. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1224, 340238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, E.M.; O’Kane, A.P.; Ford, L.; Sheldrake, G.N.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Dick, J.T.; Maggs, C.A.; Walsh, P.J. Temporal patterns of fucoxanthin in four species of European marine brown macroalgae. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Wang, L.J.; Fan, Y.; Parsons, R.L.; Hu, G.R.; Zhang, P.Y. A rapid method for the determination of fucoxanthin in diatom. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosumi, D.; Kusumoto, T.; Fujii, R.; Sugisaki, M.; Iinuma, Y.; Oka, N.; Takaesu, Y.; Taira, T.; Iha, M.; Frank, H.A.; et al. Ultrafast excited state dynamics of fucoxanthin: Excitation energy dependent intramolecular charge transfer dynamics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 10762–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Alberte, R.S. Characterization of in vivo absorption features of chlorophyte, phaeophyte and rhodophyte algal species. Mar. Biol. 1994, 118, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graiff, A.; Bartsch, I.; Glaser, K.; Karsten, U. Seasonal Photophysiological Performance of Adult Western Baltic Fucus vesiculosus (Phaeophyceae) Under Ocean Warming and Acidification. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 666493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Vazquez, J.; Mendez-Vazquez, A. A plug-and-play Hyperspectral Imaging Sensor using low-cost equipment. HardwareX 2020, 7, e00087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechlivani, E.M.; Papadimitriou, A.; Pemas, S.; Giakoumoglou, N.; Tzovaras, D. Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging Device for Portable Remote Sensing. Instruments 2023, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Color Class | Species | HS Images Train/Test | Training Datapoints | Testing Datapoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red macroalgae | Ceramium sp. | 8/1 | 278, 103 | 9648 |
| Vertebrata byssoides | 10/1 | 205,100 | 15,807 | |
| Brown macroalgae | Fucus serratus | 10/1 | 269,536 | 16,555 |
| Fucus versiculosus | 11/1 | 212,982 | 15,693 | |
| Total | 39/4 | 965,721 | 57,703 |
| Label (Species) | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramium sp. | 1.0000 | 0.9010 | 0.9479 |
| Vertebrata byssoides | 1.0000 | 0.8895 | 0.9415 |
| Fucus serratus | 0.9999 | 0.9121 | 0.9540 |
| Fucus versiculosus | 0.9987 | 0.8794 | 0.9353 |
| Average score | 0.9997 | 0.8955 | 0.9447 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allentoft-Larsen, M.C.; Santos, J.; Azhar, M.; Pedersen, H.C.; Jakobsen, M.L.; Petersen, P.M.; Pedersen, C.; Jakobsen, H.H. Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging in Macroalgae Monitoring. Sensors 2025, 25, 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092652
Allentoft-Larsen MC, Santos J, Azhar M, Pedersen HC, Jakobsen ML, Petersen PM, Pedersen C, Jakobsen HH. Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging in Macroalgae Monitoring. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092652
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllentoft-Larsen, Marc C., Joaquim Santos, Mihailo Azhar, Henrik C. Pedersen, Michael L. Jakobsen, Paul M. Petersen, Christian Pedersen, and Hans H. Jakobsen. 2025. "Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging in Macroalgae Monitoring" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092652
APA StyleAllentoft-Larsen, M. C., Santos, J., Azhar, M., Pedersen, H. C., Jakobsen, M. L., Petersen, P. M., Pedersen, C., & Jakobsen, H. H. (2025). Low-Cost Hyperspectral Imaging in Macroalgae Monitoring. Sensors, 25(9), 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092652







