Biomedical Promise of Aspergillus Flavus-Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach to Antiviral, Anticancer, Anti-Biofilm, and Antibacterial Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
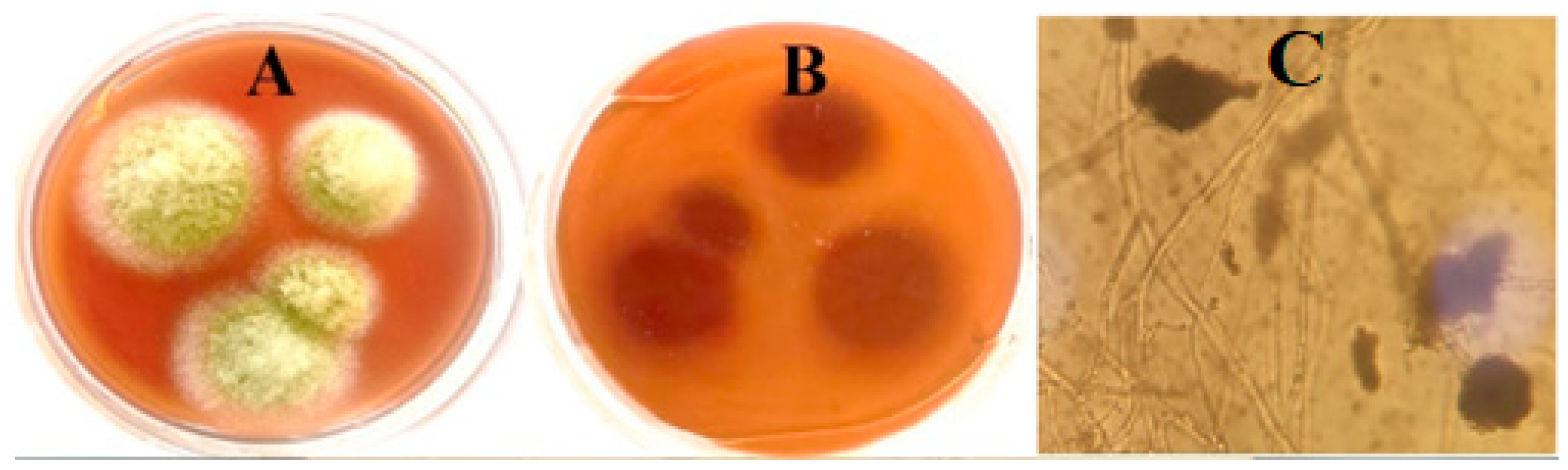
2.1. The Fungal Isolate Identification
GC-MS Analysis
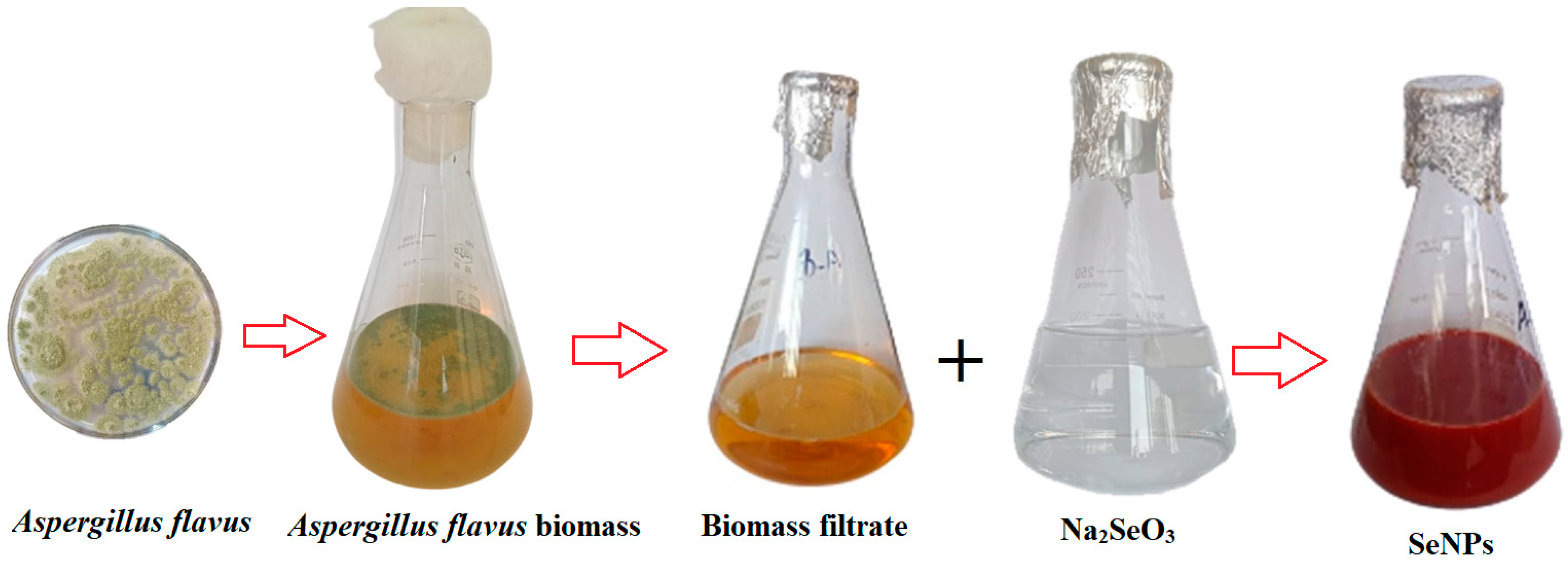
2.2. Se-NPs Bio Fabrication
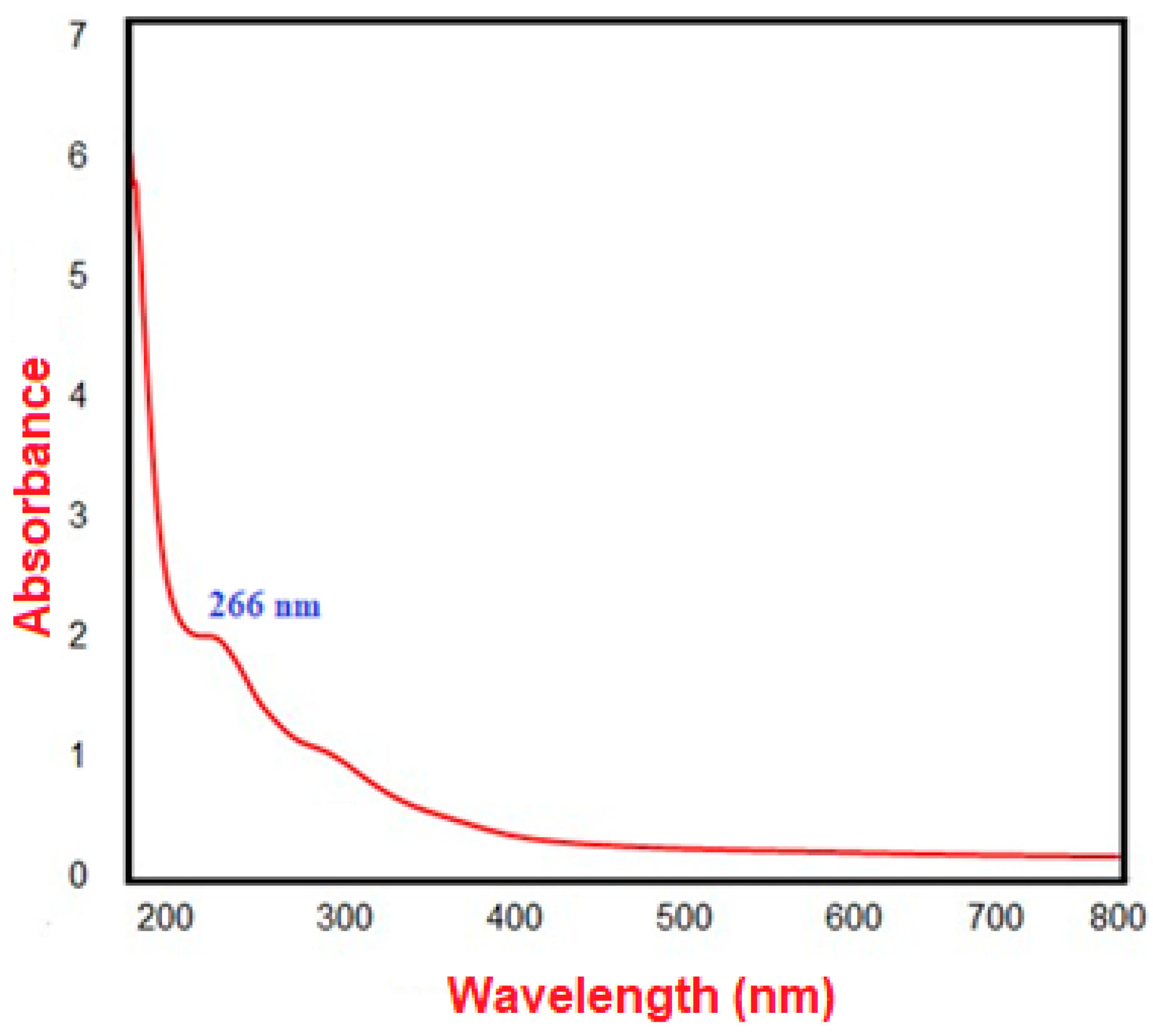
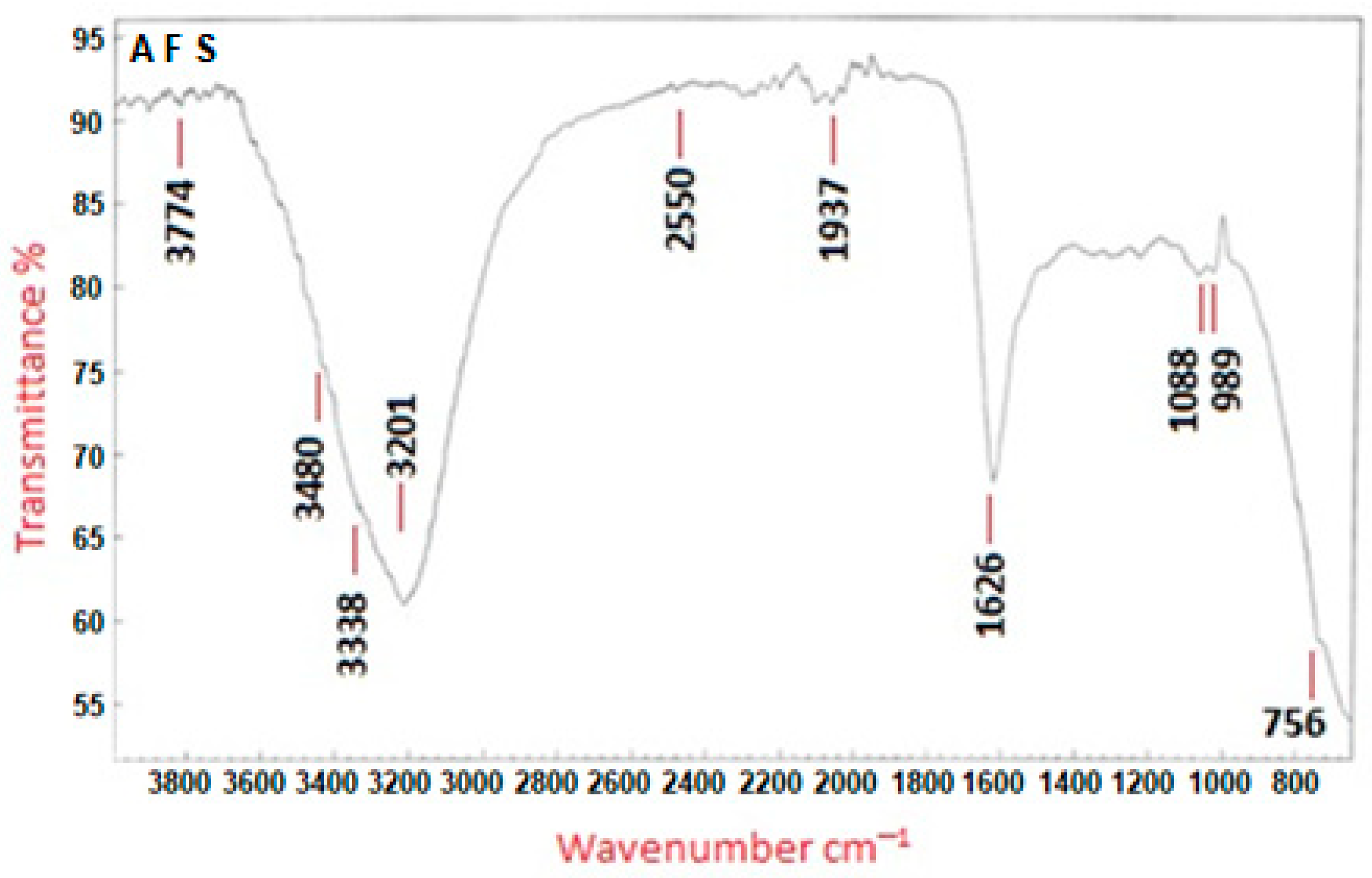
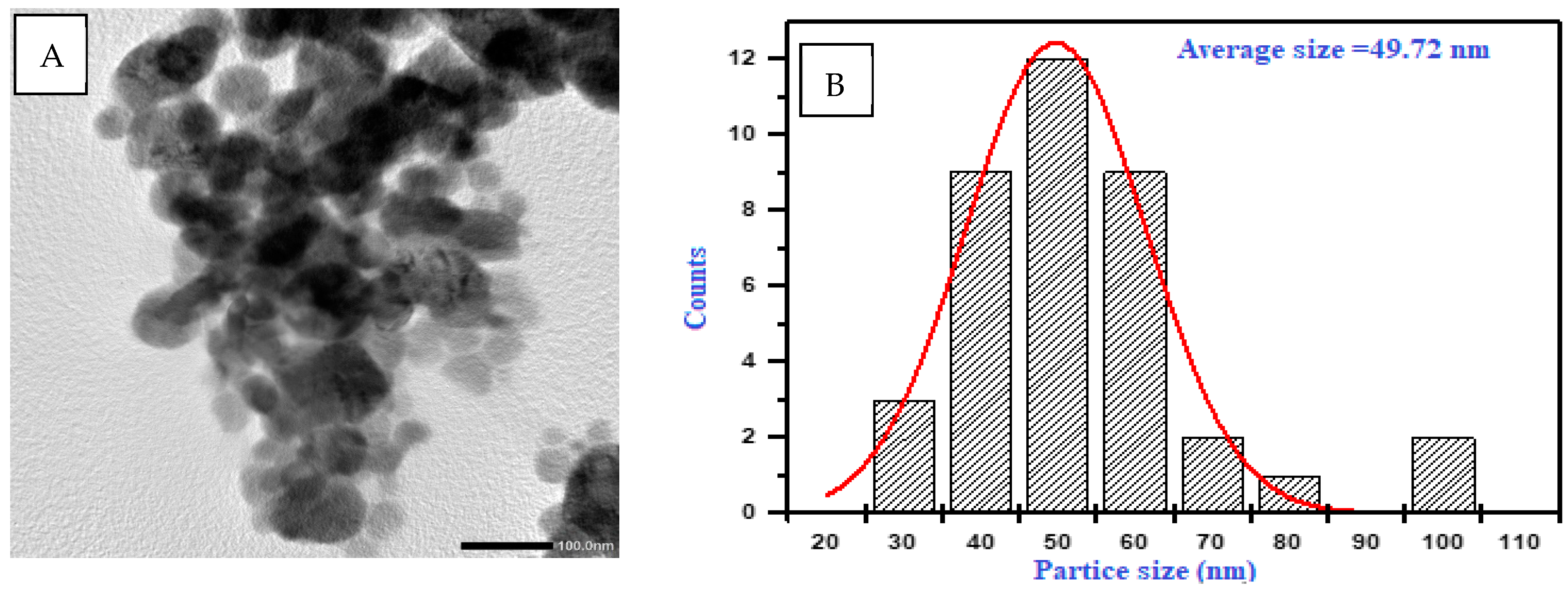
2.2.1. Characterization
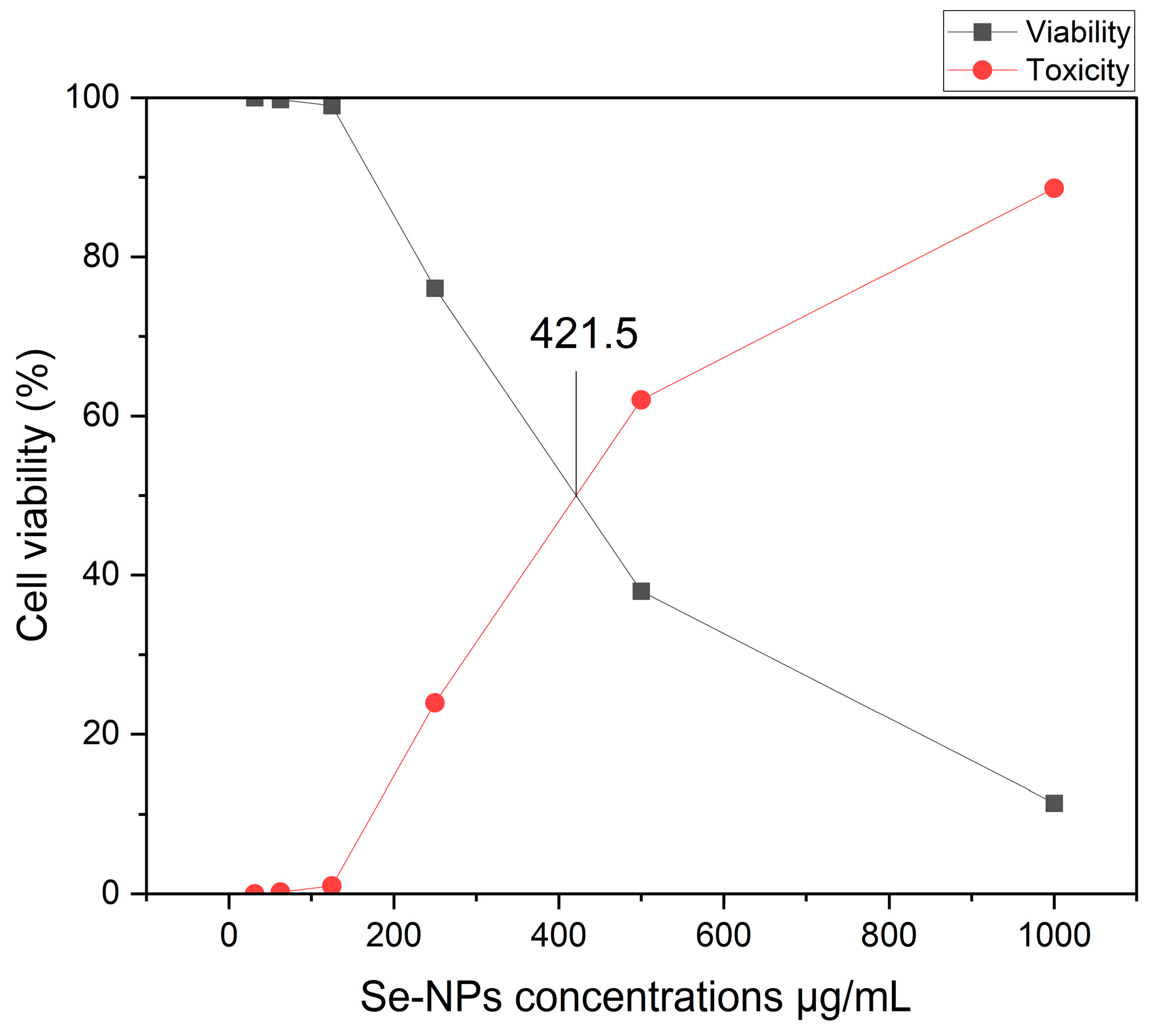
2.2.2. The Cytotoxic Effect
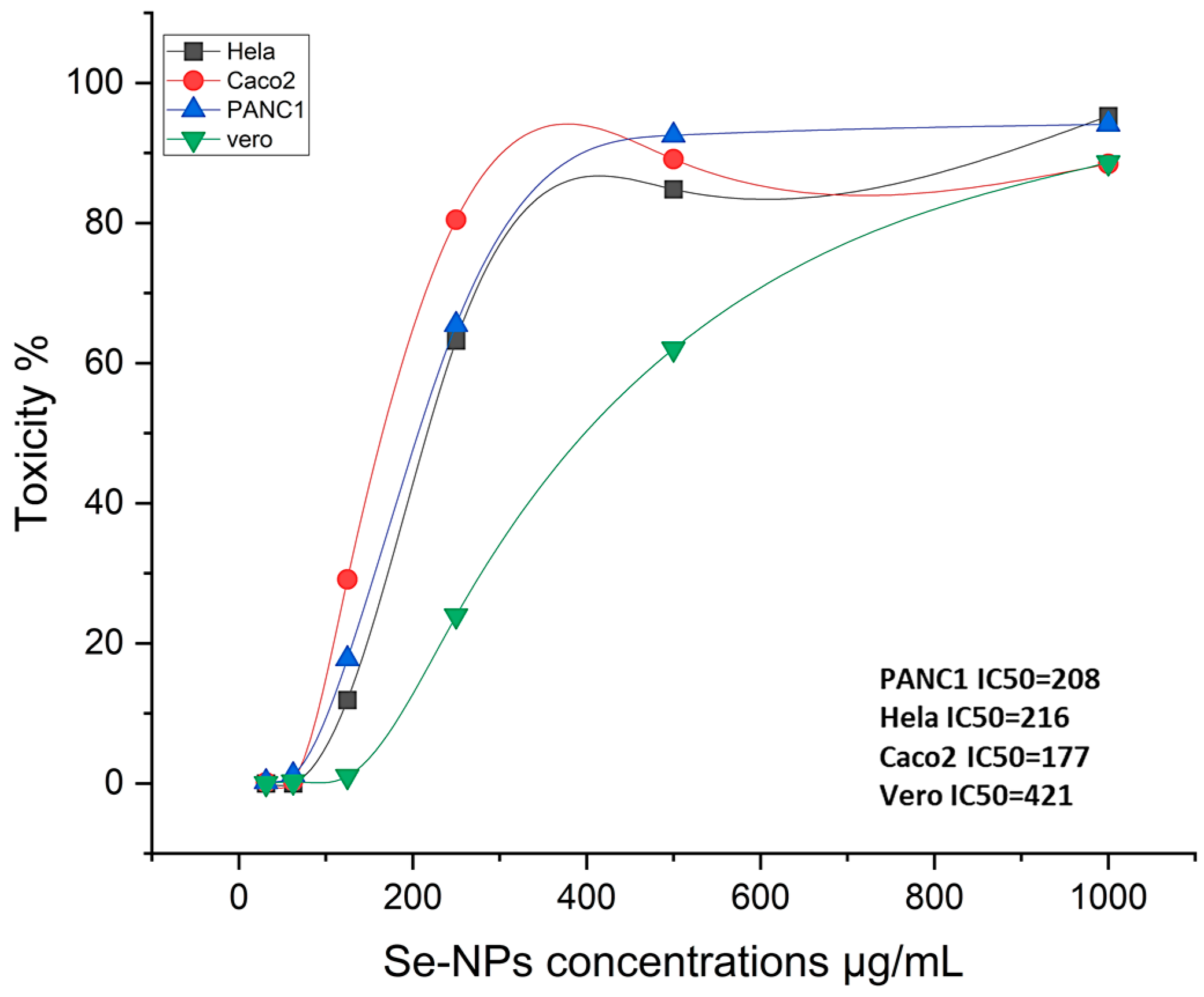
2.3. Anticancer Activity
2.4. Antibacterial Assay
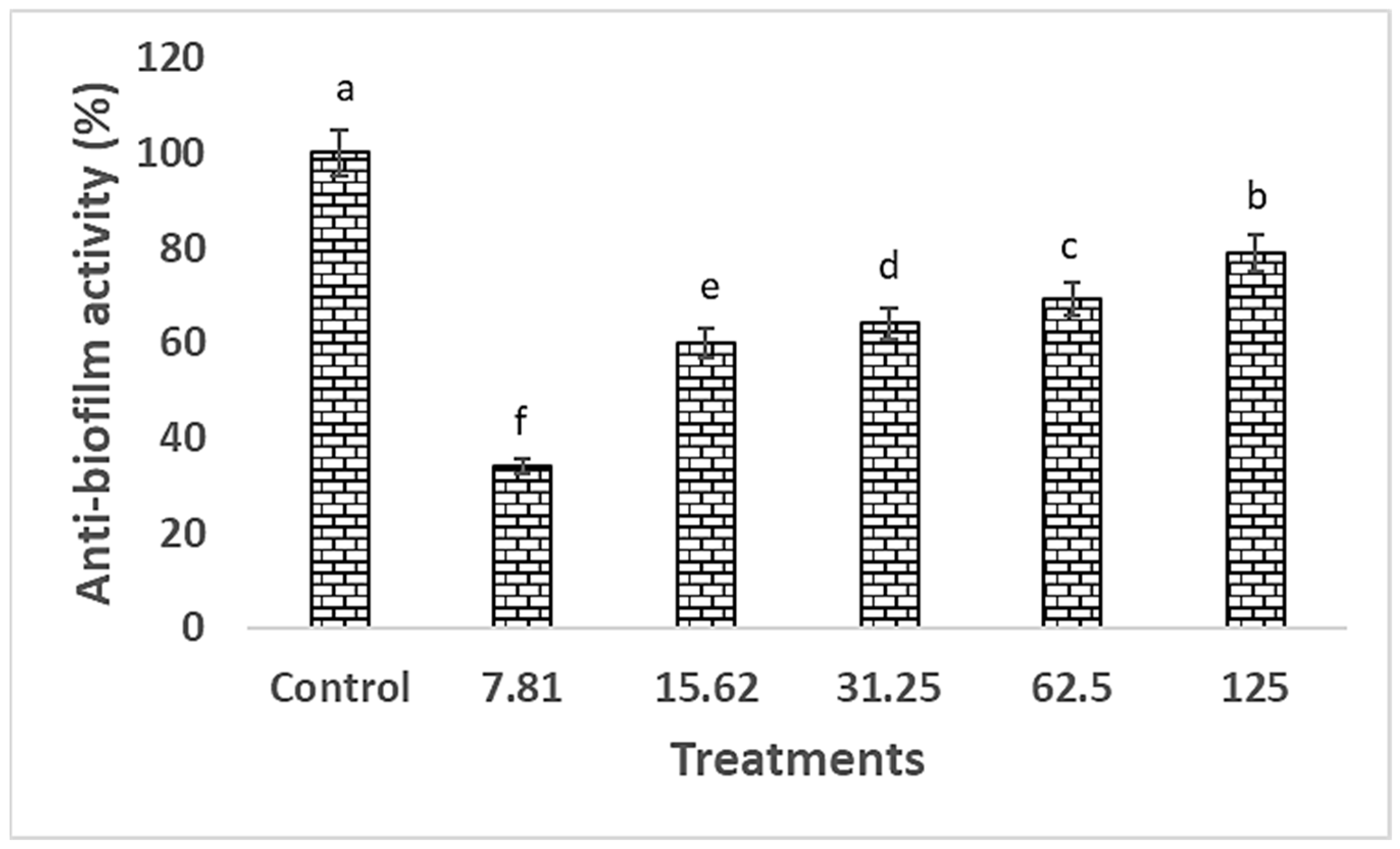
2.5. Anti-Biofilm Activity
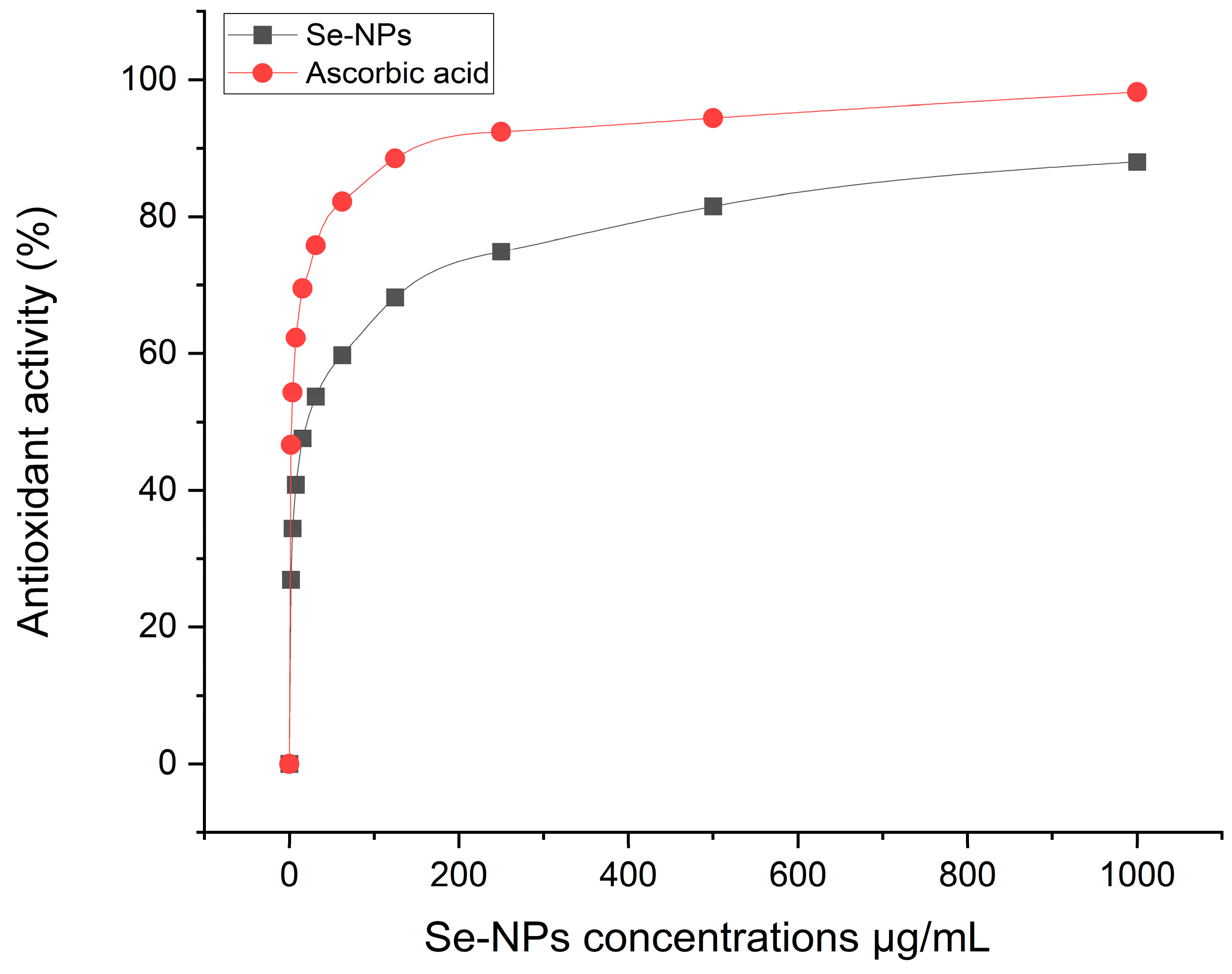
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
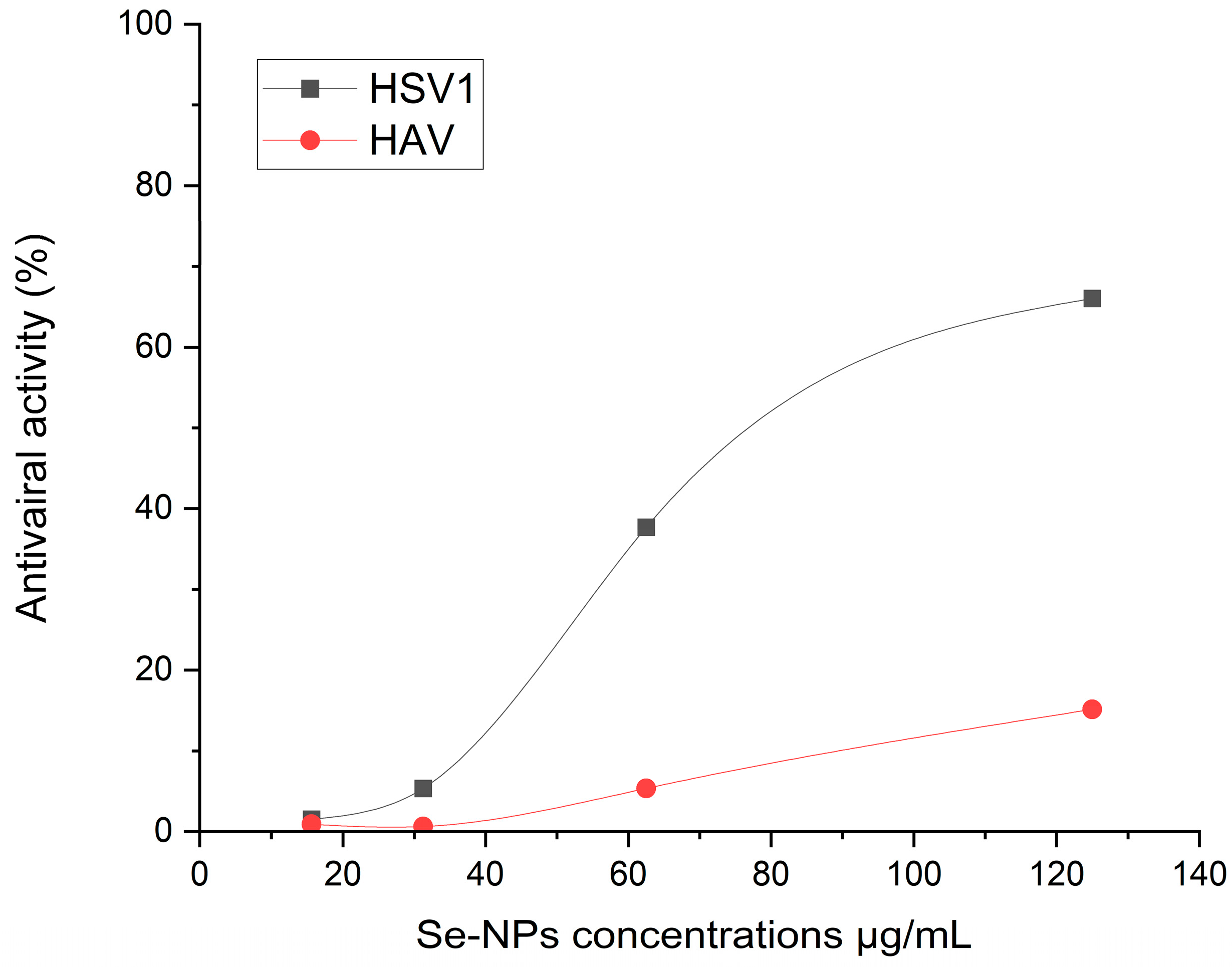
2.7. Antiviral Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fungal Isolation and Identification
4.2. Bio Fabrication of Se-NPs
4.2.1. Generating the Fungal Filtrate
4.2.2. GC–MS Assay
4.2.3. Creation of Se-NPs
4.2.4. Se-NPs Characterization
4.3. Anti-Tumor and Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. Antibacterial Activity
4.4.1. Assay for Broth Microdilution
4.4.2. Assay for Biofilm Inhibition
4.5. Antioxidant Activity
4.6. Experiment to Evaluate the Antiviral Effects of Se-NPs on Hepatitis A Virus (HAV), Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) and Vero Cell
4.7. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaoui Mdarhri, H.; Benmessaoud, R.; Yacoubi, H.; Seffar, L.; Guennouni Assimi, H.; Hamam, M.; Boussettine, R.; Filali-Ansari, N.; Lahlou, F.A.; Diawara, I.; et al. Alternatives therapeutic approaches to conventional antibiotics: Advantages, limitations and potential application in medicine. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Barroco, C.; Rivas-García, L.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V. Tackling multidrug resistance in streptococci–From novel biotherapeutic strategies to nanomedicines. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 579916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minarini, L.A.D.R.; Andrade, L.N.d.; De Gregorio, E.; Grosso, F.; Naas, T.; Zarrilli, R.; Camargo, I.L.B.C. antimicrobial resistance as a global public health problem: How can we address it? Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 612844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parupudi, A.; Mulagapati, S.H.R.; Subramony, J.A. Nanoparticle technologies: Recent state of the art and emerging opportunities. In Production Technologies, Types of Nanoparticles, and Regulatory Aspects; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 3–46. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Application of nanomaterials in biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Hammad, E.N.; Mohamed, A.A.; El-Dougdoug, W. A comprehensive review of nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, characterization, and applications. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, S.; Dharmaraj, S. Selenium and selenoproteins: It’s role in regulation of inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 667–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: An updated overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, W.; Baj, J.; Maciejewski, R. Antioxidants: Classification, natural sources, activity/capacity measurements, and usefulness for the synthesis of nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Roh, Y.J.; Han, S.-J.; Park, I.; Lee, H.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, S.-R. Role of selenoproteins in redox regulation of signaling and the antioxidant system: A review. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Selenium Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis and Biomedical Application. Molecules 2023, 28, 8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchielli, G.; Capperucci, A.; Tanini, D. The role of selenium in pathologies: An updated review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, C.; Hu, H.; Yin, S. Food sources of selenium and its relationship with chronic diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambonino, M.C.; Quizhpe, E.M.; Mouheb, L.; Rahman, A.; Agathos, S.N.; Dahoumane, S.A. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles in biomedical sciences: Properties, current trends, novel opportunities and emerging challenges in theranostic nanomedicine. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.-F.; Pi, J. The advancing of selenium nanoparticles against infectious diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 682284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serov, D.A.; Khabatova, V.V.; Vodeneev, V.; Li, R.; Gudkov, S.V. A review of the antibacterial, fungicidal and antiviral properties of selenium nanoparticles. Materials 2023, 16, 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, A.; Al-Otaibi, W.A.; Saber, T.; AlMotwaa, S.M.; Alshallash, K.S.; Elhady, M.; Badr, N.F.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.J. Antimicrobial, antiviral, and in-vitro cytotoxicity and mosquitocidal activities of Portulaca oleracea-based green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.-R.A.; Eid, A.M.; Atta, H.M.; El Naghy, W.S.; Fouda, A. Exploring the antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, biocompatibility, and larvicidal activities of selenium nanoparticles fabricated by endophytic fungal strain Penicillium verhagenii. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, C.; Florindo, H.F.; Santos, H.A. Selenium nanoparticles for biomedical applications: From development and characterization to therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridopoulou, K.; Aindelis, G.; Pappa, A.; Chlichlia, K. Anticancer activity of biogenic selenium nanoparticles: Apoptotic and immunogenic cell death markers in colon cancer cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, A.; Chang, K.; Hossainy, S.; Mansurov, A.; Rowan, S.J.; Hubbell, J.A.; Guler, M.O. Therapeutic synthetic and natural materials for immunoengineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1789–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, N.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K. Selenium nanoparticles: A review on synthesis and biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, L.H. Eco-friendly Green Biosynthesized Metallic Nanoparticles and Biotechnological Applications in Pharmaceuticals Sciences. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 13, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Elazab, N.T.; Younis, S.A.; Abdelgalil, S.A. Biogenic Synthesis of Nanoparticles Mediated by Fungi. In Plant Mycobiome Diversity, Interactions and Uses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 241–265. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, R.; Sun, K.; Li, M.; Gu, J.; Zhuang, G.J.C. Colorectal cancer burden and trends: Comparison between China and major burden countries in the world. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 33, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Ansari, M.A.; Al-Dossary, H.A.; Fatima, Z.; Hameed, S.; Ahmad, W.; Ali, A. Current perspectives on mycosynthesis of nanoparticles and their biomedical application. In Modeling and Control of Drug Delivery Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Bafghi, M.H.; Nazari, R.; Darroudi, M.; Zargar, M.; Zarrinfar, H. The effect of biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles on the expression of CYP51A and HSP90 antifungal resistance genes in Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2022, 38, e3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, A.H.; Khalil, A.M.A.; Reyad, A.M.; Salem, S.S. Biomedical applications of mycosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using Penicillium expansum ATTC 36200. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2021, 199, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevam, E.C.; Griffin, S.; Nasim, M.J.; Denezhkin, P.; Schneider, R.; Lilischkis, R.; Dominguez-Alvarez, E.; Witek, K.; Latacz, G.; Keck, C.J. Natural selenium particles from Staphylococcus carnosus: Hazards or particles with particular promise? J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowndarya, P.; Ramkumar, G.; Shivakumar, M. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles conjugated Clausena dentata plant leaf extract and their insecticidal potential against mosquito vectors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshtmand, Z.; Khademian, E.; Jafroodi, P.P.; Abtahi, M.S.; Yaraki, M.T. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Artemisia chamaemelifolia: Toxicity effects through regulation of gene expression for cancer cells and bacteria. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2023, 36, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, S.; Kuppusamy, S.J. Eco-friendly formulation of selenium nanoparticles and its functional characterization against breast cancer and normal cells. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.; Esakkiraj, P.; Annamalai, A.; Lakra, A.K.; Naik, S.; Arul, V.J. Synthesis, optimization, and physicochemical characterization of selenium nanoparticles from polysaccharide of mangrove Rhizophora mucronata with potential bioactivities. J. Trace Elements Miner. 2022, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saied, E.; Mekky, A.E.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Hagag, A.F.; El-bana, A.A.; Ashraf, M.; Walid, A.; Nour, T.; Fawzi, M.M.; Arishi, A.A. Aspergillus terreus-mediated selenium nanoparticles and their antimicrobial and photocatalytic activities. Crystals 2023, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, C.; Roy, A.; Ghotekar, S.; Khusro, A.; Islam, M.N.; Emran, T.B.; Lam, S.E.; Khandaker, M.U.; Bradley, D.A.J. Biological agents for synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Keskin, N.O.; Akbal Vural, O.; Abaci, S. Biosynthesis of noble selenium nanoparticles from Lysinibacillus sp. NOSK for antimicrobial, antibiofilm activity, and biocompatibility. Geomicrobiology 2020, 37, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Protein–nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today 2020, 3, 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarshini, E.; Priyadarshini, S.S.; Cousins, B.G.; Pradhan, N. Metal-Fungus interaction: Review on cellular processes underlying heavy metal detoxification and synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Chiang, Y.W.; Santos, R.M. X-ray diffraction techniques for mineral characterization: A review for engineers of the fundamentals, applications, and research directions. Minerals 2022, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminśki, E.; Libbey, L.; Stawicki, S.; Wasowicz, E. Identification of the predominant volatile compounds produced by Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelghany, T.; Hassan, M.M.; El-Naggar, M.A.; Abd El-Mongy, M. GC/MS analysis of Juniperus procera extract and its activity with silver nanoparticles against Aspergillus flavus growth and aflatoxins production. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 27, e00496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anneken, D.J.; Both, S.; Christoph, R.; Fieg, G.; Steinberner, U.; Westfechtel, A. Fatty acids. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shaaban, M.T.; Ghaly, M.F.; Fahmi, S.M. Antibacterial activities of hexadecanoic acid methyl ester and green-synthesized silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T. Phytochemical screening and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy analysis of bioactive compounds and biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using sprout extracts of Vigna radiata L. and their antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2019, 12, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Khaled, J.M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Mothana, R.A.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Alobaidi, A.S. Biochemical profile by GC–MS of fungal biomass produced from the ascospores of Tirmania nivea as a natural renewable resource. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adan, A.; Kiraz, Y.; Baran, Y. Cell proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Filip, J.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Natural inorganic nanoparticles–Formation, fate, and toxicity in the environment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8410–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, M.M.; Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; Al-Olayan, E.M.; Allam, A.A.; Shaheen, T.I. Antibacterial, cytotoxicity and larvicidal activity of green synthesized selenium nanoparticles using Penicillium corylophilum. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Thamer, N.; Tareq Barakat, N. Cytotoxic activity of green synthesis copper oxide nanoparticles using cordia myxa L. aqueous extract on some breast cancer cell lines. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1294, 062104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunti, L.; Dass, R.S.; Mahata, P.K. Multifaceted role of phyto-assisted selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) in biomedical and human therapeutics. In Selenium and Nano-Selenium in Environmental Stress Management and Crop Quality Improvement; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 437–458. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, S.R.; Seyedabadi, M.; Montazeri, M.; Khan, B.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A. Allium paradoxum extract mediated green synthesis of SeNPs: Assessment of their anticancer, antioxidant, iron chelating activities, and antimicrobial activities against fungi, ATCC bacterial strains, Leishmania parasite, and catalytic reduction of methylene blue. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 296, 127240. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, G.; Tang, J.; Wang, D.; Zuo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, H. Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) have potent antitumor activity against prostate cancer cells through the upregulation of miR-16. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibi, M.; Agaei, S.S.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Nazari, R.; Zolfaghari, M.R. Antibacterial, antioxidant, and anticancer activities of biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using two indigenous halophilic bacteria. Arch. Hyg. Sci. 2020, 9, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.F.; Keskin, C.; Baran, A.; Kurt, K.; İpek, P.; Eftekhari, A.; Khalilov, R.; Fridunbayov, I.; Cho, W.C. Green synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles (Se NPs) from the skin (testa) of Pistacia vera L. (Siirt pistachio) and investigation of antimicrobial and anticancer potentials. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.H.; Salem, S.S. Green and ecofriendly biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Urtica dioica (stinging nettle) leaf extract: Antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Biotecnol. J. 2022, 17, 2100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosaiah, G.; Mangamuri, U.K.; Sikharam, A.S.; Devaraj, K.; Kalagatur, N.K.; Kadirvelu, K.; Vardhan, S. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles from Annona muricata fruit aqueous extract and investigation of their antioxidant and antimicrobial potentials. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2022, 16, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mosallam, F.M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Fathy, R.M.; El-Batal, A.I. Biomolecules-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Aspergillus oryzae fermented Lupin extract and gamma radiation for hindering the growth of some multidrug-resistant bacteria and pathogenic fungi. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 122, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Ramírez, M.C.; Castañeda-Ovando, A.; Pérez-Escalante, E.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.M.; Ramírez-Moreno, E.; Quintero-Lira, A.; Contreras-López, E.; Añorve-Morga, J.; Jaimez-Ordaz, J.; González-Olivares, L.G. Antimicrobial activity of Se-nanoparticles from bacterial biotransformation. Fermentation 2021, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, J. Bacteria-responsive biomimetic selenium nanosystem for multidrug-resistant bacterial infection detection and inhibition. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13965–13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, H.H.; Guisbiers, G.; Mendoza, J.; Mimun, L.C.; Vincent, B.A.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L.; Nash, K.L. Synergistic antifungal effect of chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquids against Candida albicans biofilms. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Golińska, P. Mycosynthesis of Nanomaterials; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Jounaki, K.; Pishgahzadeh, E.; Morad, H.; Vahidi, H. Penicillium species as an Innovative Microbial Platform for Bioengineering of Biologically Active Nanomaterials. In Mycosynthesis of Nanomaterials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 50–80. [Google Scholar]
- Almalki, M.A.; Varghese, R.J. Prevalence of catheter associated biofilm producing bacteria and their antibiotic sensitivity pattern. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaie, M.; Forootanfar, H.; Golkari, Y.; Mohammadi-Khorsand, T.; Shakibaie, M.R. Anti-biofilm activity of biogenic selenium nanoparticles and selenium dioxide against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus mirabilis. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khiralla, G.M.; El-Deeb, B.A. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of selenium nanoparticles on some foodborne pathogens. LWT 2015, 63, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkusre, P.; Cameotra, S.S. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles inhibit Staphylococcus aureus adherence on different surfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Fan, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, Y.-L.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.-F. Using nano-selenium to combat Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)? Nano Today 2021, 36, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhao, M.; Xia, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, T.; Zhu, B. Inhibition of H1N1 influenza virus-induced apoptosis by functionalized selenium nanoparticles with amantadine through ROS-mediated AKT signaling pathways. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Gong, G.; Xia, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Hua, L.; Zhong, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X. Restriction of H1N1 influenza virus infection by selenium nanoparticles loaded with ribavirin via resisting caspase-3 apoptotic pathway. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5787–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Guo, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, M.; Chen, H.; Kuang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 by selenium nanoparticles loaded with siRNA through bax signaling pathways. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12495–12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhayay, A.; Ling, J.; Pal, D.; Xie, Y.; Ping, F.-F.; Kumar, A. Resistance-proof antimicrobial drug discovery to combat global antimicrobial resistance threat. Drug Resist. Updat. 2023, 66, 100890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, M.K.; Salem, S.S.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Azab, M.S. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their efficacy towards antibacterial, antibiofilm, cytotoxicity, and antioxidant activities. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 1158–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zothanpuia Passari, A.K.; Leo, V.V.; Chandra, P.; Kumar, B.; Nayak, C.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Singh, B.P. Bioprospection of actinobacteria derived from freshwater sediments for their potential to produce antimicrobial compounds. Microb. Cell Factories 2018, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Loosdrecht, A.; Beelen, R.; Ossenkoppele, g.; Broekhoven, M.; Langenhuijsen, M.J. A tetrazolium-based colorimetric MTT assay to quantitate human monocyte mediated cytotoxicity against leukemic cells from cell lines and patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 1994, 174, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Ambler, J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Castanheira, M.; Dingle, T.; Hindler, J.A.; Koeth, L.; Sei, K. CLSI methods development and standardization working group best practices for evaluation of antimicrobial susceptibility tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C. Antibiotic assay by agar-well diffusion method. Acta Biol. Med. Exp. 1990, 15, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kosikowska, U.; Andrzejczuk, S.; Grywalska, E.; Chwiejczak, E.; Winiarczyk, S.; Pietras-Ożga, D.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D. Prevalence of susceptibility patterns of opportunistic bacteria in line with CLSI or EUCAST among Haemophilus parainfluenzae isolated from respiratory microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshikh, M.; Ahmed, S.; Funston, S.; Dunlop, P.; McGaw, M.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Resazurin-based 96-well plate microdilution method for the determination of minimum inhibitory concentration of biosurfactants. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, A.M.; Abo-Taleb, H.A.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; El-Tabakh, M.A.; El-Feky, M.M.; Abu-Elghait, M. Daphnia magna and Gammarus pulex, novel promising agents for biomedical and agricultural applications. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, M.K.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Salem, S.S.; Azab, M.S. Multifunctional properties of silver and gold nanoparticles synthesis by Fusarium pseudonygamai. Biomass Convers. Bio. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Khaleil, M.; Hashem, A. Fungal endophytes from leaves of Avicennia marina growing in semi-arid environment as a promising source for bioactive compounds. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desselberger, U. Antiviral Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Medicine, Volume 24.: Kinchington D, Schinazi RF, eds. ($99.00.) Humana Press, 2000. ISBN 0 896 03561 1. Mol. Pathol. 2000, 53, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No | RT | Compound Name | Peak Area% | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Molecular Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.43 | 9-Octadecenoic acid (Z), 3-[(1-oxohexadecyl)oxy]-2-[(1-oxooctadecyl)oxy]propyl ester | 0.31 | 861.4 | C55H104O6 |
| 2 | 6.32 | Cyclohexanone, 4-[[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl] oxy]- | 0.35 | 268.33 | C13H16O4S |
| 3 | 10.21 | 3-tert-Butylsulfanyl-3-fluoro-2-trifluoromethyl-acrylic acid methyl ester | 1.06 | 260.25 | C9H12F4O2S |
| 4 | 20.99 | 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural | 1.76 | 126.11 | C6H6O3 |
| 5 | 31.45 | 3-Furanacetic acid, 4-hexyl-2,5-dihydro-2,5-dioxo | 0.57 | 240.25 | C12H16O5 |
| 6 | 40.53 | 1,4-Diaza-2,5-dioxobicyclo[4.3.0]Nonane | 4.43 | 154.17 | C7H10N2O2 |
| 7 | 48.29 | Hexadecaoic acid, Methyl ester | 9.59 | 270.5 | C17H34O2 |
| 8 | 50.12 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 22.97 | 256.42 | C16H32O2 |
| 9 | 53.81 | 1-Dodecanol, 3,7,11-trimethyl- | 1.32 | 228.41 | C15H32O |
| 10 | 54.66 | Octadecenoic acid, Methyl ester | 9.29 | 298.5 | C19H38O2 |
| 11 | 56.45 | Octadecanoic acid | 6.23 | 284.5 | C18H36O2 |
| 12 | 61.81 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z) | 2.43 | 281.5 | C18H35NO |
| 13 | 72.90 | Tetraacosanoic acid, Methyl ester | 0.85 | 382.7 | C25H50O2 |
| 14 | 73.30 | 13-Docosenamide, (Z) | 3.43 | 337.6 | C22H43NO |
| 15 | 77.62 | 9,12-Octadecenoic acid (Z,Z)-, 2,3-bis[(trimethyl silyl) oxy]propyl ester | 0.82 | 498.9 | C27H54O4Si2 |
| 16 | 85.83 | Hexadecanoic acid, octadecyl ester | 3.05 | 508.9 | C34H68O2 |
| 17 | 85.90 | 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2-(3,4-dimthoxyphenyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy | 1.67 | 462.4 | C22H22O11 |
| No. | Isolate Name | Antibacterial Assay of Se-NPs 100 µL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MICs µg/mL | Diameter of Inhibition Zone (mm) | Mean Growth Inhibition Percentage % | ||
| 1 | S. aureus | 500 ± 0.32 | 28 ± 0.36 | 100 ± 0.03 |
| 2 | C. sporogenes | 125 ± 0.41 | 29 ± 0.32 | 100 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | S. typhimurium | 125 ± 0.44 | 30 ± 0.7 | 100 ± 0.021 |
| 4 | B. subtilis | 64 ± 0.14 | 31 ± 0.2 | 100 ± 0.03 |
| 5 | E. coli | 500 ± 0.28 | 27 ± 0.45 | 100 ± 0.02 |
| 6 | B. pumilus | 1000 ± 0.54 | 25 ± 0.49 | 100 ± 0.024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammed, E.J.; Abdelaziz, A.E.M.; Mekky, A.E.; Mahmoud, N.N.; Sharaf, M.; Al-Habibi, M.M.; Khairy, N.M.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Youssef, F.S.; Gaber, M.A.; et al. Biomedical Promise of Aspergillus Flavus-Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach to Antiviral, Anticancer, Anti-Biofilm, and Antibacterial Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070915
Mohammed EJ, Abdelaziz AEM, Mekky AE, Mahmoud NN, Sharaf M, Al-Habibi MM, Khairy NM, Al-Askar AA, Youssef FS, Gaber MA, et al. Biomedical Promise of Aspergillus Flavus-Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach to Antiviral, Anticancer, Anti-Biofilm, and Antibacterial Applications. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070915
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammed, Eman Jassim, Ahmed E. M. Abdelaziz, Alsayed E. Mekky, Nashaat N. Mahmoud, Mohamed Sharaf, Mahmoud M. Al-Habibi, Nehal M. Khairy, Abdulaziz A. Al-Askar, Fady Sayed Youssef, Mahmoud Ali Gaber, and et al. 2024. "Biomedical Promise of Aspergillus Flavus-Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach to Antiviral, Anticancer, Anti-Biofilm, and Antibacterial Applications" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070915
APA StyleMohammed, E. J., Abdelaziz, A. E. M., Mekky, A. E., Mahmoud, N. N., Sharaf, M., Al-Habibi, M. M., Khairy, N. M., Al-Askar, A. A., Youssef, F. S., Gaber, M. A., Saied, E., AbdElgayed, G., Metwally, S. A., & Shoun, A. A. (2024). Biomedical Promise of Aspergillus Flavus-Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles: A Green Synthesis Approach to Antiviral, Anticancer, Anti-Biofilm, and Antibacterial Applications. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070915










