A Comprehensive Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Predicting Vildagliptin Pharmacokinetics: Insights into Dosing in Renal Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
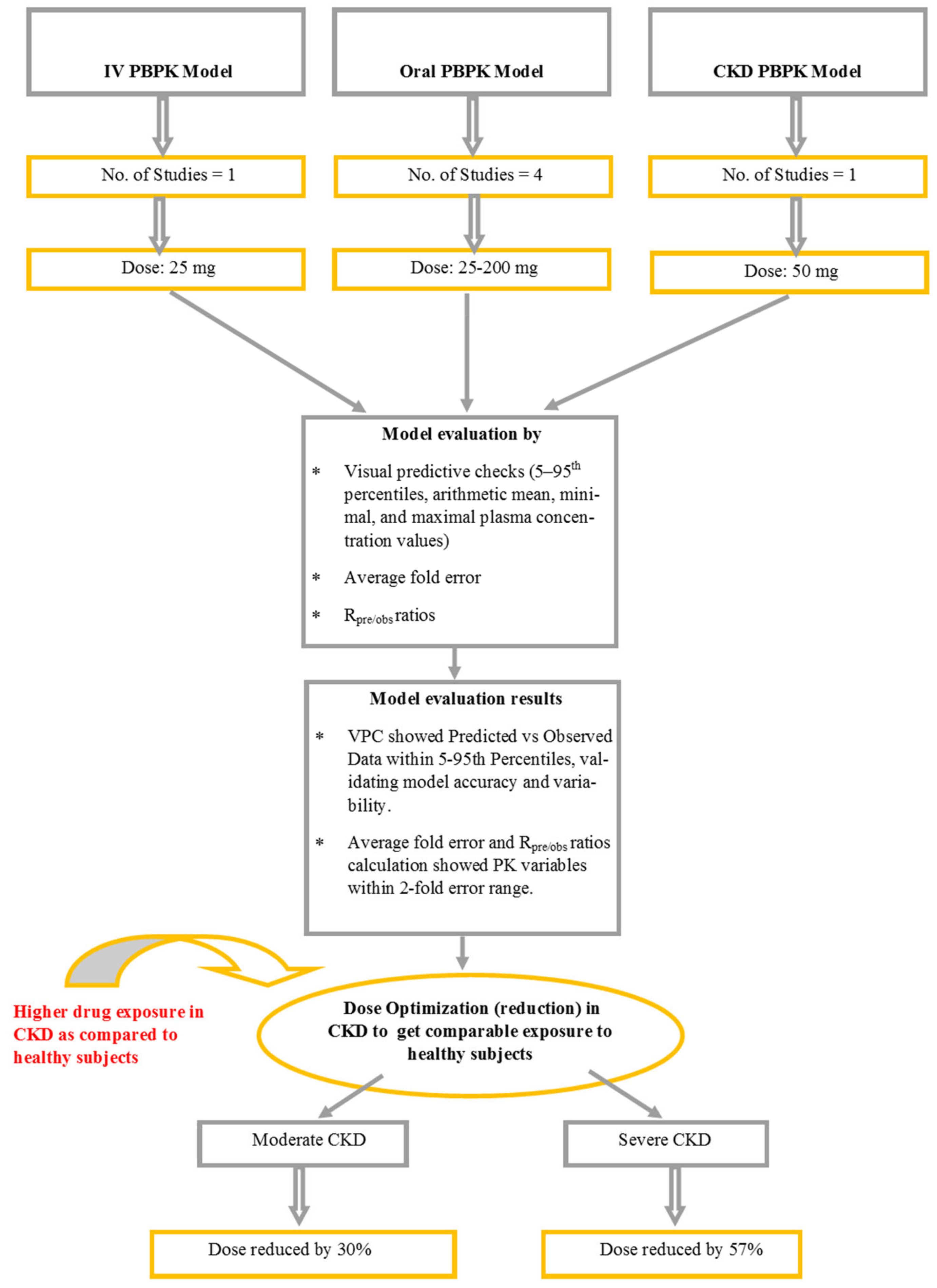
2. Results
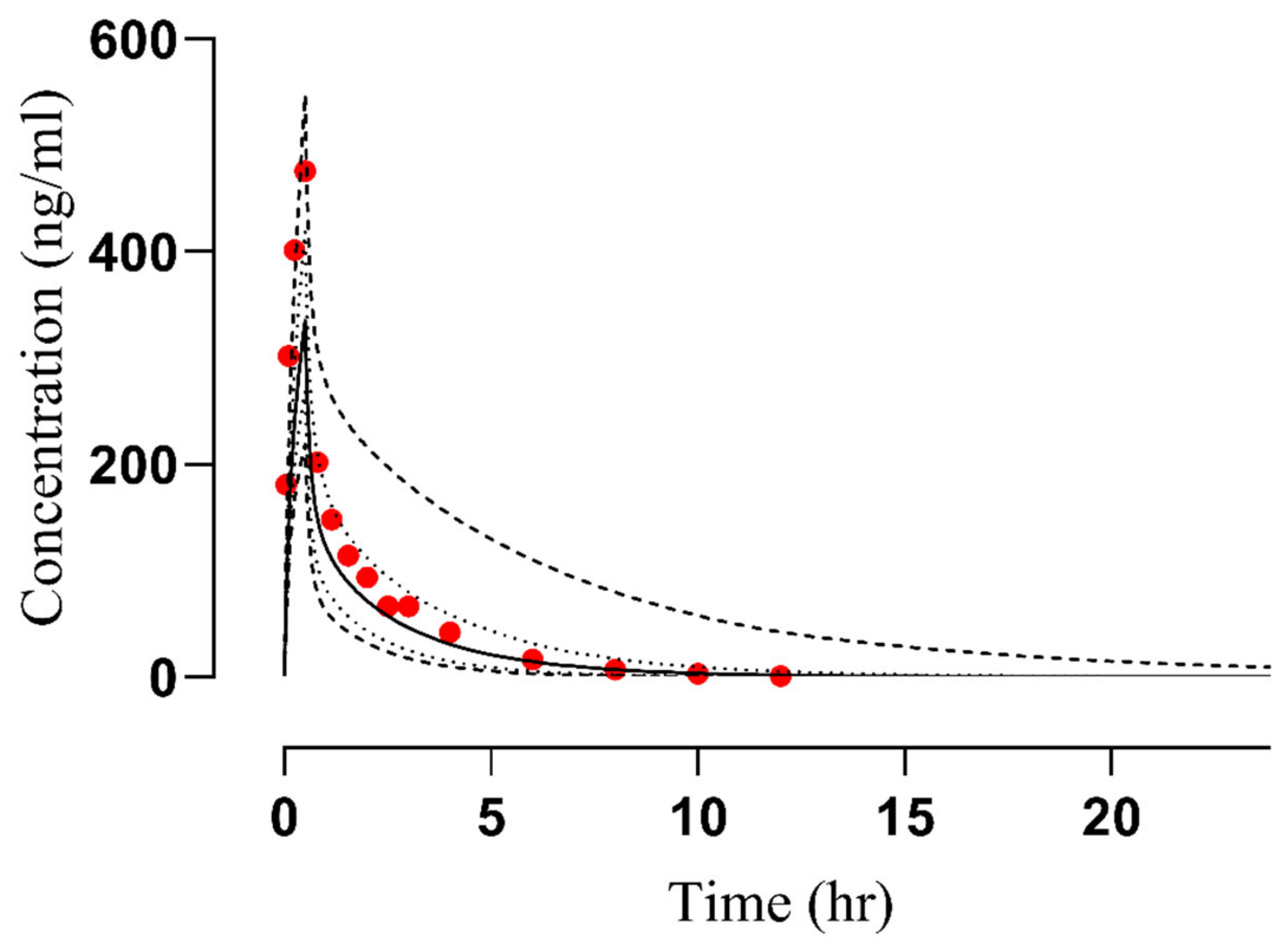
2.1. Evaluation of the PBPK Model in Healthy Subjects
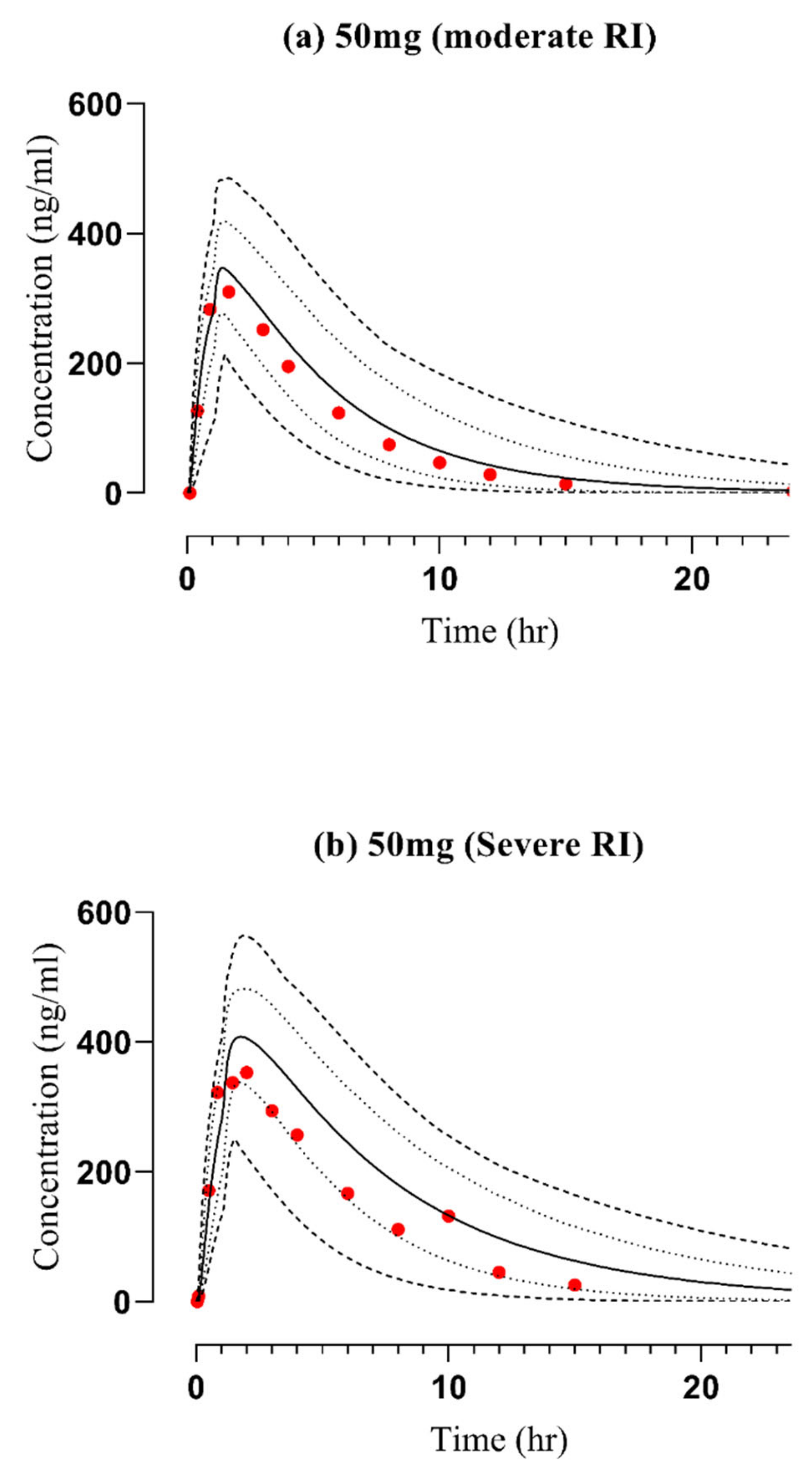
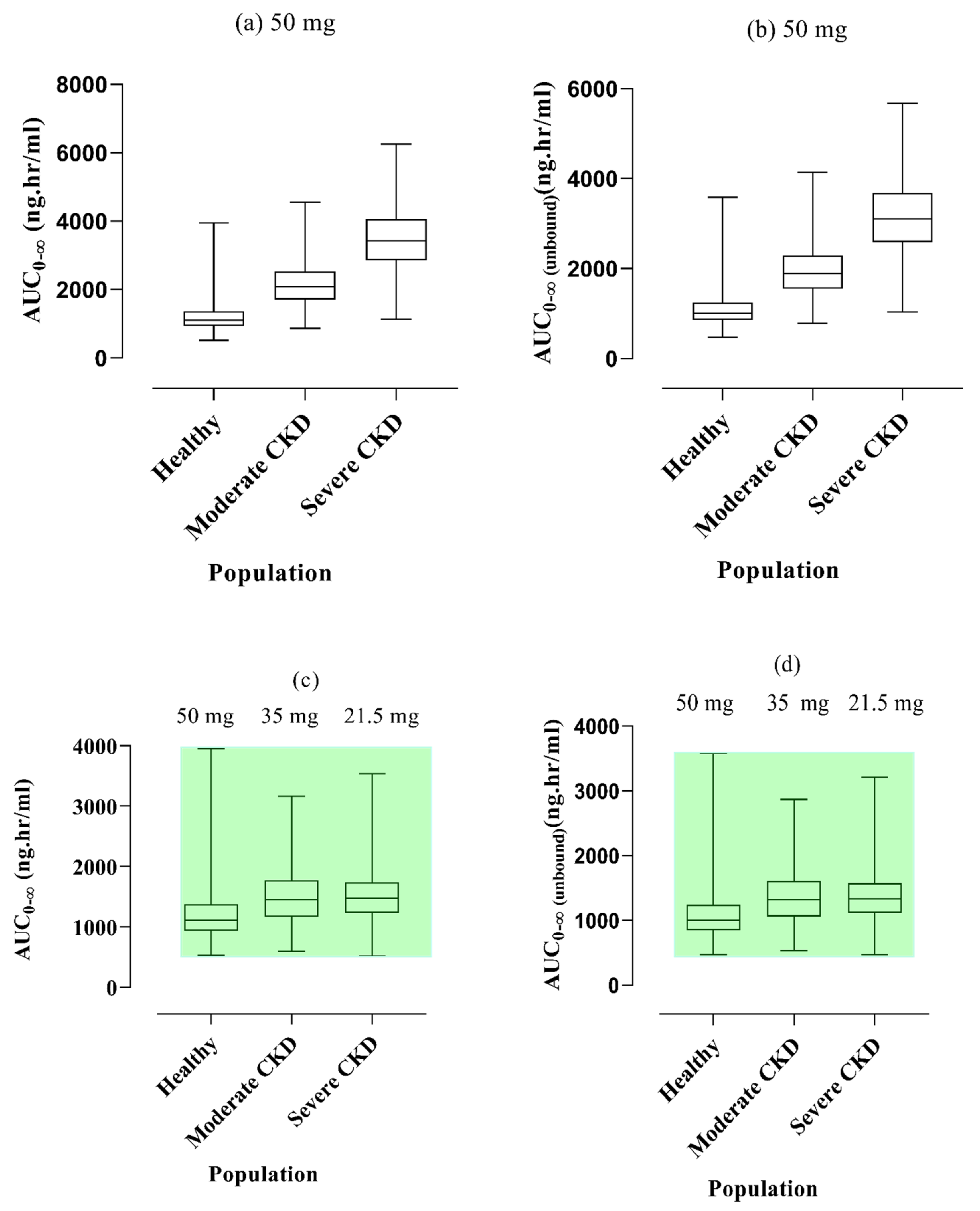
2.2. Assessment of the PBPK Model in CKD Patients
2.3. Vildagliptin Dose Modification in CKD Patients
3. Discussion
4. Limitations
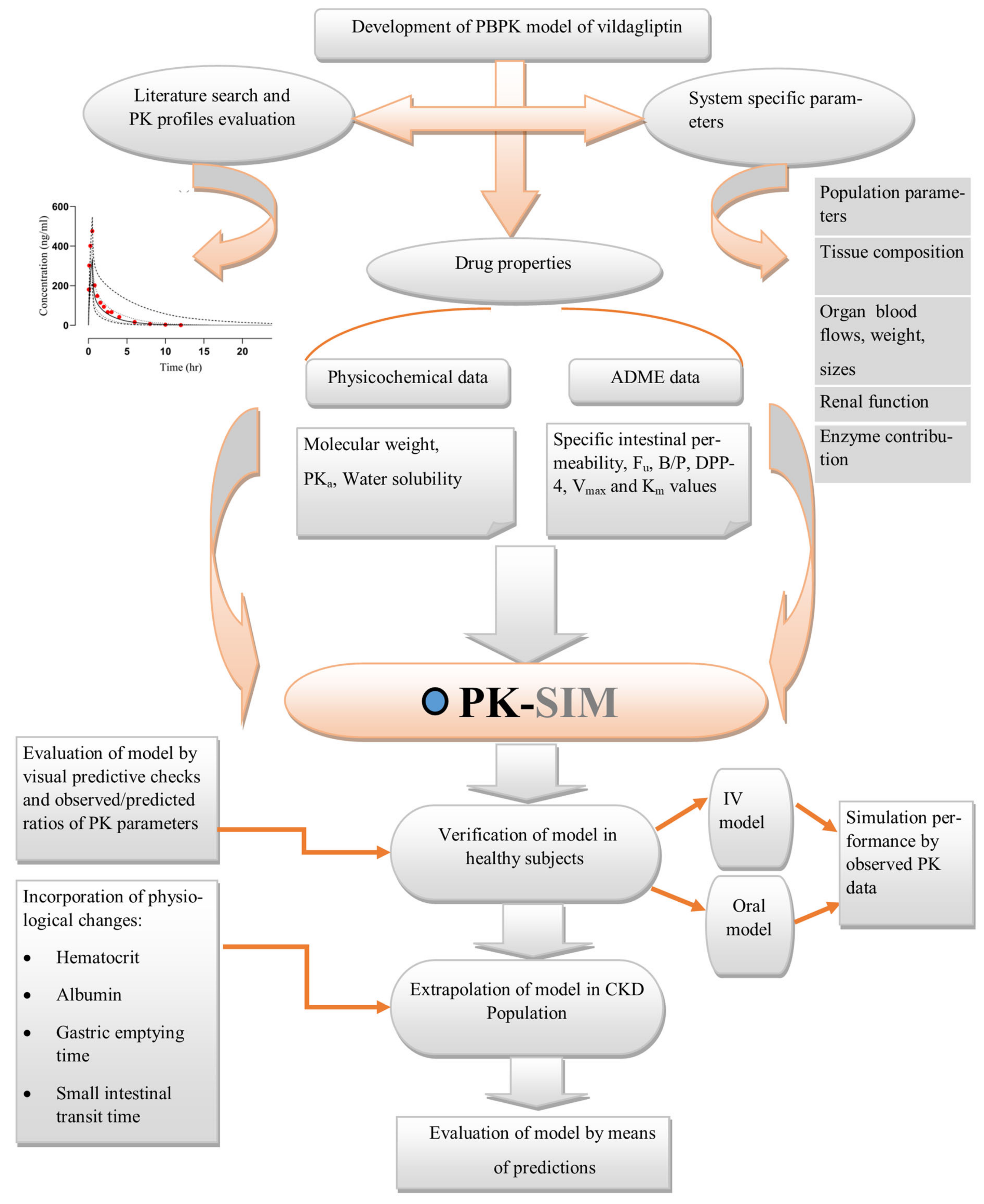
5. Methodology
5.1. Screening of Pharmacokinetic Parameters
5.2. Software System for Modeling
5.3. Building Blocks Creation
5.4. Model Development Strategy
5.5. Structure of Model
5.6. Configuration of the PBPK Model in the Diseased Population (CKD)
5.7. Verification of the Model
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, S.A. Evaluation of a Generic Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Lineshape Analysis. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 47, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.A.; Barton, H.A.; DeWoskin, R.S.; Schlosser, P.; Thompson, C.M.; Sonawane, B.; Lipscomb, J.C.; Krishnan, K. Evaluation of physiologically based pharmacokinetic models for use in risk assessment. J. Appl. Toxicol. Int. J. 2007, 27, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; Kostarelos, K.; Reineke, J. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6303–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmanshenn, C.; Scherholz, M.; Androulakis, I.P. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models: Approaches for enabling personalized medicine. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2016, 43, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Rasool, M.F.; Imran, I.; Majeed, A.; Saeed, H.; Rehman, A.U.; Ashraf, W.; Ahmad, T.; Bin Jardan, Y.A.; Alqahtani, F. A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Predicting Diazepam Pharmacokinetics after Intravenous, Oral, Intranasal, and Rectal Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clewell, R.A.; Clewell, H.J., III. Development and specification of physiologically based pharmacokinetic models for use in risk assessment. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 50, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, A.; Rasool, M.F.; Imran, I.; Saeed, H.; Khalid, S.; Majeed, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Ahmad, T.; Alasmari, F.; Alqahtani, F. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Predict Metoprolol Disposition in Healthy and Disease Populations. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 29302–29313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. Proposed Approach to Efficiently Develop Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) & Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic (PBPK-PD) Models for Pesticides. 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/pbpk.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Teorell, T. Kinetics of distribution of substances administered to the body, I: The extravascular modes of administration. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1937, 57, 205–225. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, M.F.; Läer, S. Development and evaluation of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to predict carvedilol-paroxetine metabolic drug–drug interaction in healthy adults and its extrapolation to virtual chronic heart failure patients for dose optimization. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.F.; Khalil, F.; Läer, S. A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Drug–Disease Model to Predict Carvedilol Exposure in Adult and Paediatric Heart Failure Patients by Incorporating Pathophysiological Changes in Hepatic and Renal Blood Flows. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 54, 943–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, E.M.; Rowland, A. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to predict the impact of metabolic changes associated with metabolic associated fatty liver disease on drug exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, E.M.; Rowland, A. Development and evaluation of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic drug-disease model of propranolol for suggesting model informed dosing in liver cirrhosis patients. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 23, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J. Pharmacokinetics and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Xenobiotic Disposition in Special Populations. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Nelson, C.; Paik, J.; Shirasaka, Y.; Amory, J.K.; Isoherranen, N. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of all-trans-retinoic acid with application to cancer populations and drug interactions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 361, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploeger, B.; Mensinga, T.; Sips, A.; Seinen, W.; Meulenbelt, J.; DeJongh, J. The pharmacokinetics of glycyrrhizic acid evaluated by physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. Drug Metab. Rev. 2001, 33, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-L. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Vildagliptin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sabo, R.; Campestrini, J.; Wang, Y.; Riviere, G.; Nielsen, J.C.; Rosenberg, M.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Howard, D.; Dole, W.P. The effect of age, gender, and body mass index on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, A.J.; Sharma, M.D. Update: Vildagliptin for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, M.; Karaki, F.; Fujii, H.; Atsuda, K.; Itoh, T.; Fujiwara, R. Vildagliptin and its metabolite M20.7 induce the expression of S100A8 and S100A9 in human hepatoma HepG2 and leukemia HL-60 cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, H.; Takubo, H.; Komura, H.; Kogayu, M.; Iwaki, M. Application of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model informed by a top-down approach for the prediction of pharmacokinetics in chronic kidney disease patients. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, P.; Remuzzi, G.; Glassock, R.; Levin, A.; Jager, K.J.; Tonelli, M.; Massy, Z.; Wanner, C.; Anders, H.J. Chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, P.R.; Yeung, C.H.; Ismaeil, S.; Advani, U.; Djie, S.; Edginton, A.N. A physiological approach to pharmacokinetics in chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 60, S52–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, K.R.; Aarabi, M.; Jamei, M.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Modeling and predicting drug pharmacokinetics in patients with renal impairment. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 4, 261–274. [Google Scholar]
- Bundhun, P.K.; Janoo, G.; Teeluck, A.R.; Huang, F. Adverse drug effects observed with vildagliptin versus pioglitazone or rosiglitazone in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landersdorfer, C.B.; He, Y.L.; Jusko, W.J. Mechanism-based population pharmacokinetic modelling in diabetes: Vildagliptin as a tight binding inhibitor and substrate of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 73, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhari, M.; Vahidi, O. Mechanism based pharmacokinetic pharmacodynamic modeling of vildagliptin as an add-on to metformin for subjects with type 2 Diabetes. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2018, 114, 153–171. [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis, S.D.; Han, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mita, S.; Zhao, R.; Sunkara, G.; Kulmatycki, K. Population pharmacokinetic modeling and noncompartmental analysis demonstrated bioequivalence between metformin component of metformin/vildagliptin fixed-dose combination products and metformin immediate-release tablet sourced from various countries. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2016, 5, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; Sadler, B.M.; Sabo, R.; Balez, S.; Wang, Y.; Campestrini, J.; Laurent, A.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Howard, D. The absolute oral bioavailability and population-based pharmacokinetic modelling of a novel dipeptidylpeptidase-IV inhibitor, vildagliptin, in healthy volunteers. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 46, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Kong, F.; Xie, N.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J.; Chen, X. Mechanistic Study on the Effect of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of Vildagliptin and its Carboxylic Acid Metabolite. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 2147–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madny, M.A.; Deshpande, P.; Tumuluri, V.; Borde, P.; Sangana, R. Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Vildagliptin Modified Release (MR) Tablets to Predict In Vivo Performance and Establish Clinically Relevant Dissolution Specifications. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Yu, S.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Li, B.; Liu, Y. Prediction of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of trelagliptin and omarigliptin in healthy humans and in patients with renal impairment using physiologically based pharmacokinetic combined DPP-4 occupancy modeling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, D.; Parrott, N.J.; Manevski, N.; Zhang, J.D. Another string to your bow: Machine learning prediction of the pharmacokinetic properties of small molecules. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Yin, Q.; Deckert, F.; Jiang, J.; Liu, D.; Kjems, L.; Dole, W.P.; He, Y. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin in healthy Chinese volunteers. In Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics; Nature Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.-L.; Kulmatycki, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Reynolds, C.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Taylor, A. Pharmacokinetics of vildagliptin in patients with varying degrees of renal impairment. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 51, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tran, P.; Yin, H.; Smith, H.; Batard, Y.; Wang, L.; Einolf, H.; Gu, H.; Mangold, J.B.; Fischer, V.; et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of [14C] vildagliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, G.; Sabo, R.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Campestrini, J.; Rosenberg, M.; Howard, D.; Dole, W.P. Dose proportionality and the effect of food on vildagliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor, in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyakova, E.B.; Sabirzyanov, D.R.; Prozorova, N.A.; Foteeva, A.V. Physicochemical Properties and Methods of Analysis of Vildagliptin. Pharm. Chem. J. 2022, 56, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Penno, G.; Del Prato, S. Managing diabetic patients with moderate or severe renal impairment using DPP-4 inhibitors: Focus on vildagliptin. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2013, 6, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barghash, S.; El-Razeq, S.A.; Elmansi, H.; Elmorsy, M.A.; Belal, F. Intermolecular Interactions of Saxagliptin and Vildagliptin with Human Serum Albumin. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2022, 88, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 6918537. 23 September 2023. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Galvus (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Sarafidis, P.A.; Bakris, G.L. Antihypertensive treatment with beta-blockers and the spectrum of glycaemic control. QJM Int. J. Med. 2006, 99, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vildagliptin (HMDB0015596). Human Metabolome Database. Available online: https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015596 (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Arar, S.; Al-Qudah, E.; Alzweiri, M.; Sweidan, K. New forced degradation products of vildagliptin: Identification and structural elucidation using LC-MS, with proposed formation mechanisms. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2020, 43, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Koley, T.K.; Singh, S.K.; Tripathi, Y.B. The tuber extract of pueraria tuberosa Linn. competitively inhibits DPP-IV activity in normoglycemic rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrand, M.; Hooker, A.C.; Wallin, J.E.; Karlsson, M.O. Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J. 2011, 13, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Dose (mg) | Cmax (ng/mL) | AUC0–∞ (ng·h/mL) | CL/F (L/h) | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OV | PV | R Ratio | OV | PV | R Ratio | OV | PV | R Ratio | ||
| Oral administration in Healthy individuals | ||||||||||
| 25 a | 140 | 127 | 0.90 | 566 | 507 | 0.89 | 44 | 49 | 1.11 | [35] |
| 25 b | 138 | 125 | 0.90 | 541 | 507 | 0.93 | 46 | 49 | 1.06 | [35] |
| 25 | 112 | 127 | 1.13 | 475 | 499 | 1.05 | 50 | 50 | 1.00 | [38] |
| 50 a | 294 | 254 | 0.86 | 1269 | 980 | 0.77 | 39 | 50 | 1.28 | [35] |
| 50 b | 339 | 250 | 0.73 | 1241 | 962 | 0.77 | 40 | 50 | 1.25 | [35] |
| 50 | 212 | 242 | 1.14 | 1164 | 989 | 0.84 | 42.9 | 50 | 1.16 | [38] |
| 50 | 191 | 243 | 1.27 | 1097 | 1019 | 0.92 | 45 | 49 | 1.08 | [30] |
| 100 a | 654 | 509 | 0.77 | 2799 | 2010 | 0.71 | 35 | 49.7 | 1.42 | [35] |
| 100 b | 610 | 509 | 0.83 | 2667 | 1987 | 0.74 | 37 | 50 | 1.35 | [35] |
| 100 | 446 | 484 | 1.08 | 2670 | 1871 | 0.70 | 37 | 53 | 1.43 | [38] |
| 100 | 350 | 410 | 1.17 | 1630 | 1767 | 1.08 | 60 | 56 | 0.93 | [37] |
| 200 a | 1247 | 1019 | 0.81 | 5776 | 4073 | 0.70 | 34.6 | 49 | 1.41 | [35] |
| 200 b | 1173 | 1001 | 0.85 | 5760 | 4125 | 0.71 | 34 | 48 | 1.41 | [35] |
| 200 | 902 | 953 | 1.05 | 5314 | 3525 | 0.66 | 37.6 | 56 | 1.48 | [38] |
| IV administration in Healthy individuals | ||||||||||
| 25 | 476 | 337 | 0.70 | 660 | 479 | 0.73 | 51 | 52.1 | 1.02 | [30] |
| Oral administration in the CKD population | ||||||||||
| 50 | 224 | 277 | 1.23 | 976 | 1204 | 1.23 | 51 | 40 | 0.78 | [36] |
| 50 (Mod) | 310 | 342 | 1.10 | 1792 | 2107 | 1.17 | 27.8 | 23.6 | 0.84 | [36] |
| 50 (severe) | 353 | 406 | 1.15 | 2366 | 3519 | 1.48 | 21 | 14.2 | 0.67 | [36] |
| PK Parameters | AFE |
|---|---|
| Oral healthy | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1.03 |
| AUC0–∞ (ng·h/mL) | 1.21 |
| CL (L/h) | 1.23 |
| Renal failure | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1.15 |
| AUC0–∞ (ng·h/mL) | 1.28 |
| CL (L/h) | 1.30 |
| Sr. No. | Reference | Gender | Female Proportion (%) | Age (Years) | Population | Route | Dose (mg) | Study Size | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [30] | M and F | 45 | 18–45 | HT | PO | 50 | 11 | 68.1 ± 7.1 c |
| IV | 25 | ||||||||
| 2 | [35] | M and F | 48 | 18–45 | HT | PO | 25, 50, 100, or 200 | 60 | 58.6 ± 5.6 c |
| 3 | [38] | M and F | 65 | 18–45 | HT | PO | 25, 50, 100, 200 | 20 | 70.9 ± 8.6 c |
| 4 | [37] | M | 0 | 18–45 | HT | PO | 100 | 4 | 77–93 a |
| 5 | [36] | M and F | Mild: 56 | 18–85 | CKD | PO | 50 | 96 | Mild: 63.1 b |
| Moderate: 62 | Moderate: 62.4 b | ||||||||
| Severe: 61 | Severe: 63.7 b |
| Parameters for Model | Values of Literature | Input Values | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical and Chemical Properties | |||
| Plasma protein binding | Albumin | Albumin | [41] |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) | 303.4 | 303.4 | [42] |
| Water solubility (mg/mL) at pH 7 | 60 | 60 | [43] |
| pKa (base) | 9.7 | 9.7 | [37] |
| Log P | 1.12 | 1.55 * | [44] |
| Absorption | |||
| Specific intestinal permeability (cm/s) | 5 × 10−4 | 5 × 10−4 | [32] |
| Formulation method | Weibull | ||
| Dissolution Time (50% dissolved) (minutes) | 50 | Optimized | |
| Distribution | |||
| Fraction unbound (fu) | 90.7% | 90.7% | [45] |
| Partition Coefficient Model | Poulin Theil | ||
| Cellular Permeability Model | PK Sim Standard | ||
| Metabolism | |||
| Vildagliptin Km (uM) | 190 | 190 | [46] |
| Vildagliptin Vmax (nmol/L/s) | 23.31 | 23.31 | [46] |
| Excretion | |||
| Renal clearance (L/h) | 13 | 13 ** | [30] |
| Healthy | CKD | ||
| eGFR | >60 mL/min | Moderate: 48 mL/min Severe: 29 mL/min | [24] |
| Gastric Emptying Time | 15 min | Moderate: 20.63 min Severe: 39 min | [24] |
| GIT Transit Time | 2.1 h | Moderate: 2.94 h Severe: 4.12 h | [24] |
| Hematocrit | 0.47 | Moderate: 0.42 Severe: 0.37 | [24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasha, M.; Zamir, A.; Rasool, M.F.; Saeed, H.; Ahmad, T.; Alqahtani, N.S.; Alqahtani, L.S.; Alqahtani, F. A Comprehensive Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Predicting Vildagliptin Pharmacokinetics: Insights into Dosing in Renal Impairment. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070924
Pasha M, Zamir A, Rasool MF, Saeed H, Ahmad T, Alqahtani NS, Alqahtani LS, Alqahtani F. A Comprehensive Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Predicting Vildagliptin Pharmacokinetics: Insights into Dosing in Renal Impairment. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070924
Chicago/Turabian StylePasha, Mahnoor, Ammara Zamir, Muhammad Fawad Rasool, Hamid Saeed, Tanveer Ahmad, Nawaf Shalih Alqahtani, Lamya Saif Alqahtani, and Faleh Alqahtani. 2024. "A Comprehensive Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Predicting Vildagliptin Pharmacokinetics: Insights into Dosing in Renal Impairment" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070924
APA StylePasha, M., Zamir, A., Rasool, M. F., Saeed, H., Ahmad, T., Alqahtani, N. S., Alqahtani, L. S., & Alqahtani, F. (2024). A Comprehensive Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Predicting Vildagliptin Pharmacokinetics: Insights into Dosing in Renal Impairment. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070924









