The Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Glimepiride—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
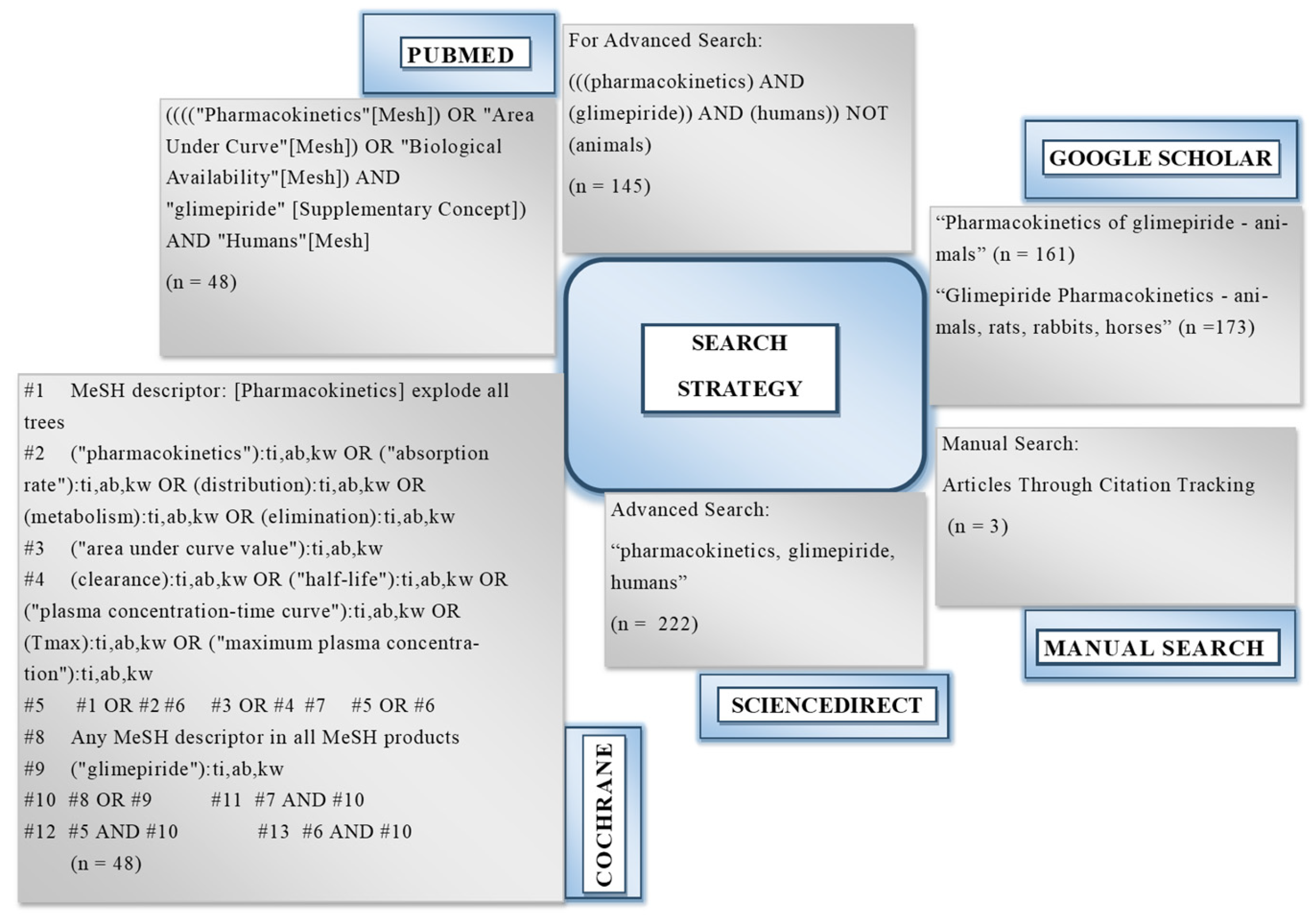
2.1. Results for the Literature Search
2.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
2.3. Quality of the Included Studies
2.4. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Healthy Populations
2.4.1. Data Following Oral Route of Administration
2.4.2. IV Administration
2.5. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Diseased Populations
Oral Administration
2.6. Studies with Pharmacodynamics of Glimepiride
2.7. Studies with the Interactions of Glimepiride
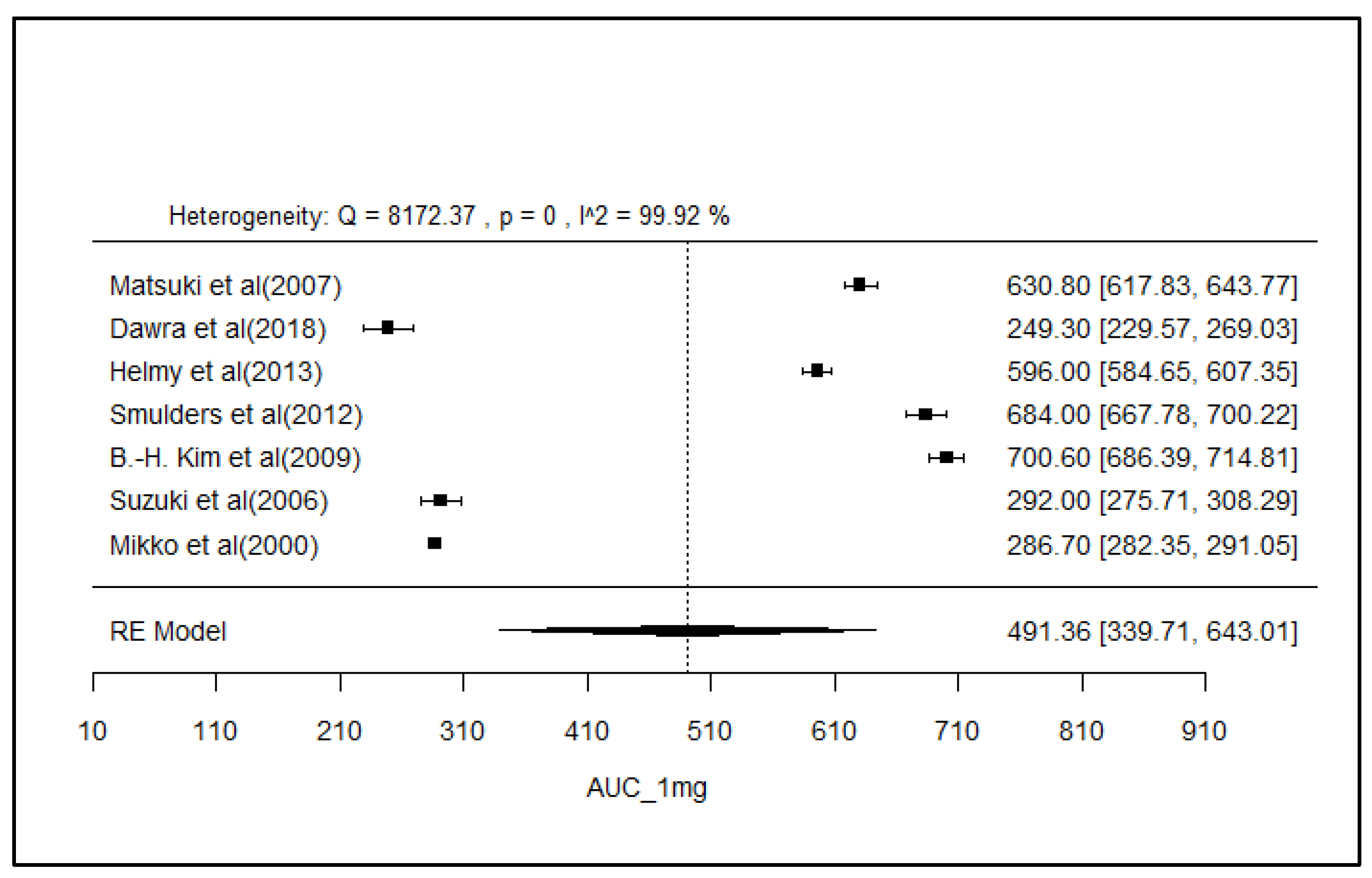
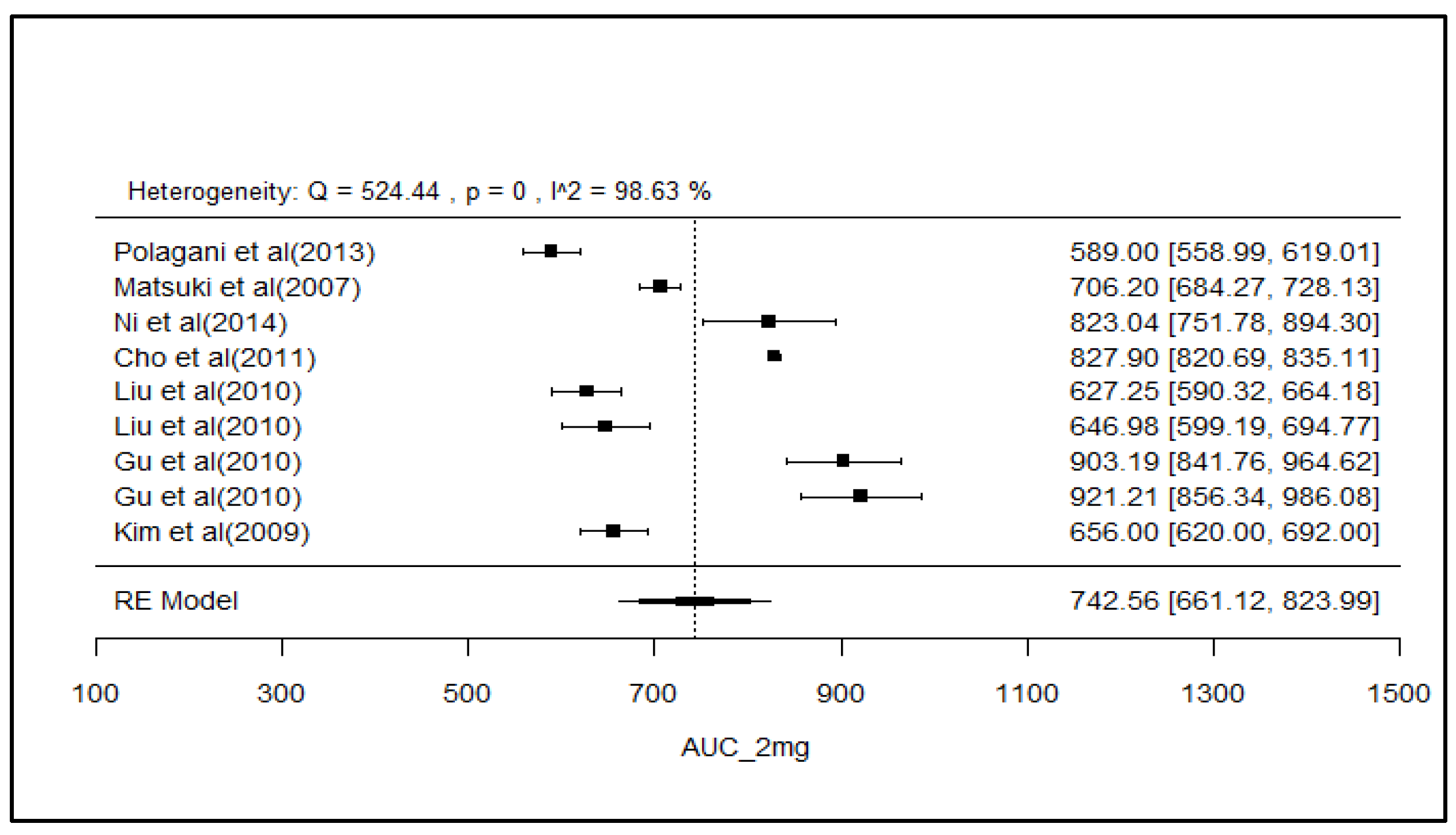
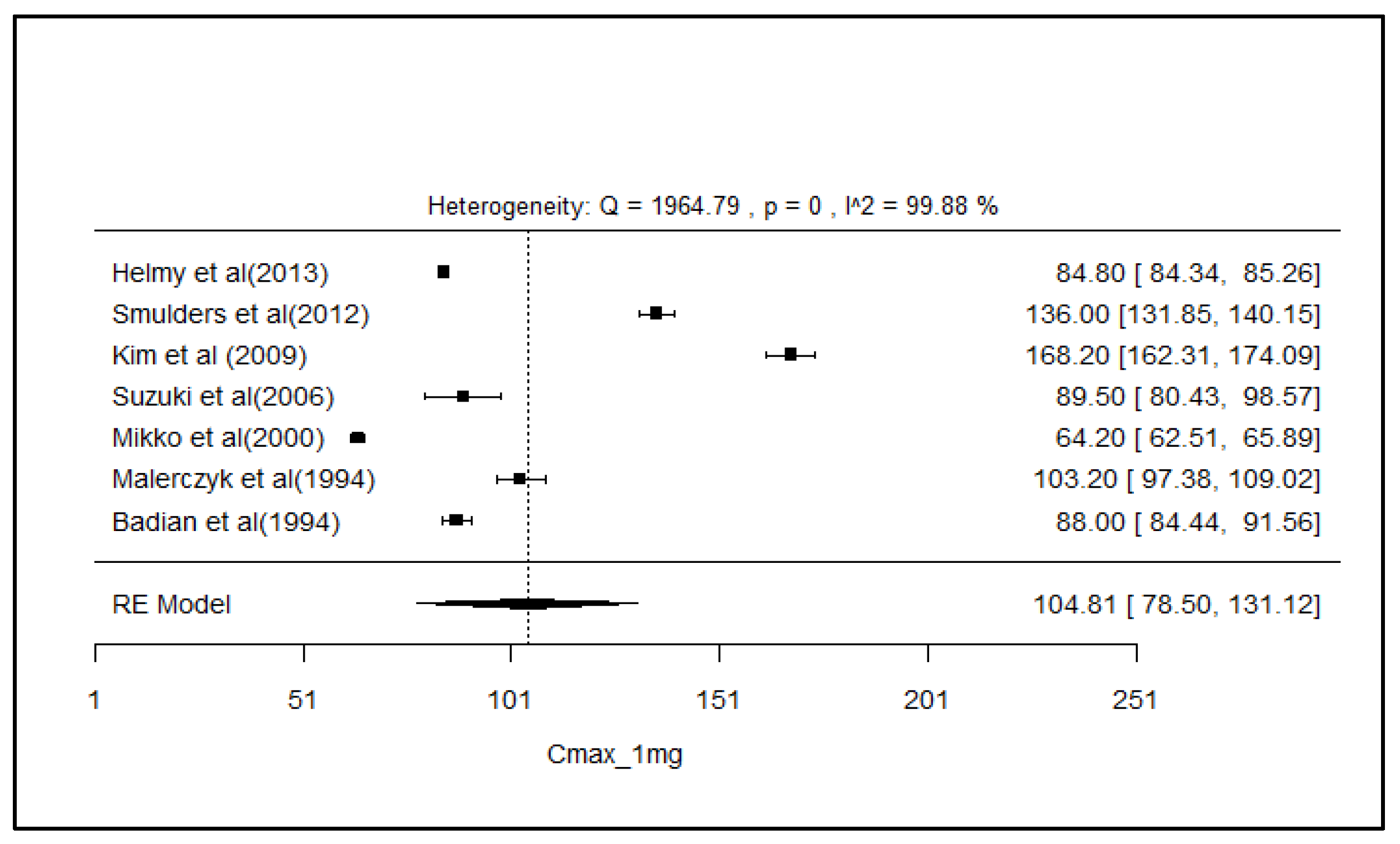
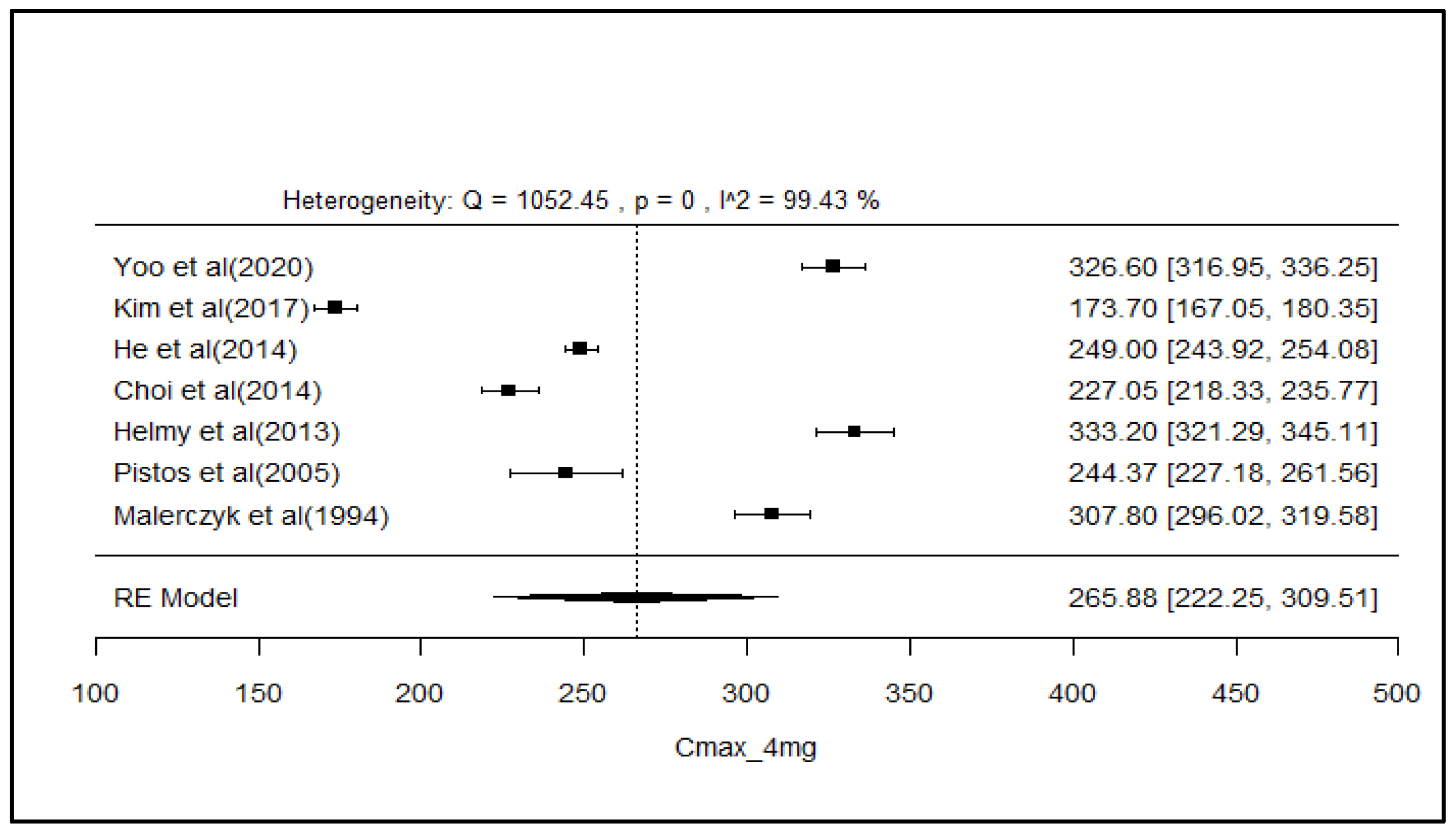
2.8. Analysis of Effect Size of PK Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design for Review
4.2. Search Strategy for the Literature
4.3. Eligibility Criteria
4.4. Procedure for Selection
4.5. Procedure for Extraction of Data
4.6. Assessment of Quality of Included Studies
4.7. Summary Measures for Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonfilio, R.; de Araújo, M.B.; Salgado, H.R.N. A review of analytical techniques for determination of glimepiride: Present and perspectives. Ther. Drug Monit. 2010, 32, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massi-Benedetti, M. Glimerpiride in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of the worldwide therapeutic experience. Clin. Ther. 2003, 25, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.K. Glimepiride: Role of a new sulfonylurea in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Pharmacother. 1998, 32, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, A.L. Clinical review of glimepiride. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2001, 2, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.N. The role of glimepiride in the effective management of type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2004, 18, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrie, M.Z.I.; Gul, A.; Hakeem, R.; Ahmadani, M.Y.; Basit, A. Glimepiride study on type-2 diabetic subjects. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 22, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Tanwar, D.K.; Surendrabhai, V.R.; Gill, M.S. An efficient and practical process for the synthesis of glimepiride. Synlett 2017, 28, 2495–2498. [Google Scholar]
- Chhajed, S.S.; Rajderkar, Y.R.; Tajanpure, A.B.; Ugale, J.B.; Kshirsagar, S.J. Synthesis of cocrystals of sulfonyl urea class drug using suitable coformers for enhancement of aqueous solubility. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Res. 2019, 1, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbic, S.; Parojcic, J.; Malenovic, A.; Djuric, Z.; Maksimovic, M. A contribution to the glimepiride dissociation constant determination. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaryl Glimepiride Tablets. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020496s021lbl.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Sola, D.; Rossi, L.; Schianca, G.P.C.; Maffioli, P.; Bigliocca, M.; Mella, R.; Corlianò, F.; Fra, G.P.; Bartoli, E.; Derosa, G. State of the art paper Sulfonylureas and their use in clinical practice. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glimepiride. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00222 (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Shukla, U.A.; Chi, E.M.; Lehr, K.-H. Glimepiride pharmacokinetics in obese versus non-obese diabetic patients. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Andrade, S.E.; Avalos, L.A.; Beaton, S.J.; Chiu, V.Y.; Davis, R.L.; Dublin, S.; Pawloski, P.A.; Raebel, M.A.; Smith, D.H. Prevalence, trends, and patterns of use of antidiabetic medications among pregnant women, 2001–2007. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 121, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lestari, M.L.; Indrayanto, G. Glimepiride. In Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 36, pp. 169–204. [Google Scholar]
- Remko, M. Theoretical study of molecular structure, pKa, lipophilicity, solubility, absorption, and polar surface area of some hypoglycemic agents. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem. 2009, 897, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, J.A. Use of oral antidiabetic agents during breastfeeding. J. Hum. Lact. 1997, 13, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langtry, H.D.; Balfour, J.A. Glimepiride: A review of its use in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 1998, 55, 563–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trerattanavong, K.; Tadi, P. Glimepiride. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Stott, K.E.; Pertinez, H.; Sturkenboom, M.G.G.; Boeree, M.J.; Aarnoutse, R.; Ramachandran, G.; Requena-Méndez, A.; Peloquin, C.; Koegelenberg, C.F.N.; Alffenaar, J.W.C.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of rifampicin in adult TB patients and healthy volunteers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Murray, M.; McLachlan, A.J. Influence of genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sulfonylurea drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, F.; Matson, K.L.; Mohammadpour, A.H.; Kelly, M.; Karimani, A. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antihyperglycemic medications in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; He, Y.; Ji, Y.; Ge, Y.; Feng, Y.; Huo, M.; Li, H.; Xue, F.; Liu, Y. Comparative efficacy and safety of glucose-lowering drugs in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 897776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amate, J.M.; Lopez-Cuadrado, T.; Almendro, N.; Bouza, C.; Saz-Parkinson, Z.; Rivas-Ruiz, R.; Gonzalez-Canudas, J. Effectiveness and safety of glimepiride and iDPP4, associated with metformin in second line pharmacotherapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 69, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schwartz, S.L. Treatment of elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of the benefits and risks of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Am. J. Geriatr. Pharmacother. 2010, 8, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Kim, Y.; Jang, I.-J.; Yu, K.-S.; Lee, S. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic interactions between evogliptin and glimepiride in healthy male subjects. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 5179–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawra, V.K.; Cutler, D.L.; Zhou, S.; Krishna, R.; Shi, H.; Liang, Y.; Alvey, C.; Hickman, A.; Saur, D.; Terra, S.G. Assessment of the drug interaction potential of ertugliflozin with sitagliptin, metformin, glimepiride, or simvastatin in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2019, 8, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.A.; Suhail, M.A.; Hosny, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.I. Clinical pharmacokinetic study for the effect of glimepiride matrix tablets developed by quality by design concept. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.O.; Oh, E.S.; Kim, H.; Park, M.S. Pharmacokinetic interactions between glimepiride and rosuvastatin in healthy Korean subjects: Does the SLCO1B1 or CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism affect these drug interactions? Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.A.; Khalid, M.; Aljaeid, B.M.; Fahmy, U.A.; Abd-Allah, F.I. Transdermal glimepiride delivery system based on optimized ethosomal nano-vesicles: Preparation, characterization, in vitro, ex vivo and clinical evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 500, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalat, Z.A. Study of Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interaction between Glimepiride and Gemfibrozil in Healthy Subjects. Medicine 2015, 4, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, R.-A. Simultaneous determination of bosentan and glimepiride in human plasma by ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 95, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.-J.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Shang, D.-W.; Zhang, M.; Hu, J.-Q.; Qiu, C.; Wen, Y.-G. Simultaneous determination of glimepiride and pioglitazone in human plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and its application to pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 960, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon, J.S.; Woo, C.J.; Jeong, S.B.; Kwang-Il, K. Bioequivalence comparison of two formulations of fixed-dose combination glimepiride/metformin (2/500 mg) tablets in healthy volunteers. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Wickremasingha, P.; Lee, J.; Tao, B.; Mendell-Harary, J.; Walker, J.; Wight, D. The effects of colesevelam HCl on the single-dose pharmacokinetics of glimepiride, extended-release glipizide, and olmesartan medoxomil. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 54, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.H.; Bang, K.; Han, S.; Lim, H.-S.; Bae, K.-S. Evaluation of pharmacokinetic drug interactions between gemigliptin (dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitor) and glimepiride (sulfonylurea) in healthy volunteers. Drugs R&D 2014, 14, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Polagani, S.R.; Pilli, N.R.; Gajula, R.; Gandu, V. Simultaneous determination of atorvastatin, metformin and glimepiride in human plasma by LC–MS/MS and its application to a human pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Anal. 2013, 3, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmy, S.A.; El Bedaiwy, H.M.; Mansour, N.O. Dose linearity of glimepiride in healthy human Egyptian volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2013, 2, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smulders, R.; Zhang, W.; Veltkamp, S.; van Dijk, J.; Krauwinkel, W.; Keirns, J.; Kadokura, T. No pharmacokinetic interaction between ipragliflozin and sitagliptin, pioglitazone, or glimepiride in healthy subjects. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lim, M.s.; Lee, J.; Jegal, M.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, W.K.; Jang, I.J.; Shin, J.G.; Yoon, Y.R. Frequency of CYP2C9 variant alleles, including CYP2C9* 13 in a Korean population and effect on glimepiride pharmacokinetics. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2012, 37, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, L.; Ahmad, S.I.; Mishra, S.; Khuroo, A.; Monif, T. Selective, sensitive, and rapid liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of Glimepiride in human plasma. Clin. Res. Regul. Aff. 2012, 29, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-G.; Oh, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Huh, W.-S.; Ko, J.-W.; Kim, H.-G. Effect of genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics and efficacy of glimepiride in a Korean population. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1831–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.; Kim, E.; Jeong, T.; Na, M.; Baek, M.-C.; Liu, K.-H.; Park, P.-H.; Shin, B.S.; Kang, W. Simultaneous determination of glimepiride and its metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography coupled to a tandem mass spectrometry. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2011, 34, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotagiri, H.; Gannu, R.; Palem, C.R.; Yamsani, S.K.; Yamsani, V.V.; Yamsani, M.R. Simultaneous determination of glimepiride and atorvastatin in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography: Application to pharmacokinetic study. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2011, 34, 2420–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.-q.; Zhu, J.-m.; Jia, J.-y.; Liu, Y.-m.; Liu, G.-y.; Li, S.; Weng, L.-p.; Yu, C. Bioequivalence and pharmacokinetic evaluation of two formulations of glimepiride 2 mg: A single-dose, randomized-sequence, open-label, two-way crossover study in healthy Chinese male volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasichayanula, S.; Liu, X.; Shyu, W.; Zhang, W.; Pfister, M.; Griffen, S.; Li, T.; LaCreta, F.; Boulton, D. Lack of pharmacokinetic interaction between dapagliflozin, a novel sodium–glucose transporter 2 inhibitor, and metformin, pioglitazone, glimepiride or sitagliptin in healthy subjects. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, N.; Kim, B.-H.; Rhim, H.; Chung, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-R.; Shin, H.-S.; Yoon, S.-H.; Cho, J.-Y.; Shin, S.-G.; Jang, I.-J. Comparison of the bioavailability and tolerability of fixed-dose combination glimepiride/metformin 2/500-mg tablets versus separate tablets: A single-dose, randomized-sequence, open-label, two-period crossover study in healthy Korean volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-H.; Shin, K.-H.; Kim, J.; Lim, K.S.; Kim, K.-p.; Kim, J.-R.; Cho, J.-Y.; Shin, S.-G.; Jang, I.-J.; Yu, K.-S. Pharmacokinetic comparison of a new glimepiride 1-mg+ metformin 500-mg combination tablet formulation and a glimepiride 2-mg + metformin 500-mg combination tablet formulation: A single-dose, randomized, open-label, two-period, two-way crossover study in healthy, fasting Korean male volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuki, M.; Matsuda, M.; Kohara, K.; Shimoda, M.; Kanda, Y.; Tawaramoto, K.; Shigetoh, M.; Kawasaki, F.; Kotani, K.; Kaku, K. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glimepiride in type 2 diabetic patients: Compared effects of once-versus twice-daily dosing. Endocr. J. 2007, 54, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Zhao, Z.; Slater, M.; Bradford, D.; Schuster, J.; Laurent, A. Replicate study design in bioequivalency assessment, pros and cons: Bioavailabilities of the antidiabetic drugs pioglitazone and glimepiride present in a fixed-dose combination formulation. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Yanagawa, T.; Shibasaki, T.; Kaniwa, N.; Hasegawa, R.; Tohkin, M. Effect of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms on the efficacy and pharmacokinetics of glimepiride in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 72, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, D.; Stojšić, D.; Zlatković, M.; Jović-Stošić, J.; Jovanović, M. Bioequivalence assessment of the two brands of glimepiride tablets. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2006, 63, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbaa-Khabbaz, L.; Abi Daoud, R.; Karam-Sarkis, D.; Atallah, C.; Zoghbi, A. A simple and sensitive method for determination of glimepiride in human serum by HPLC. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 3255–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistos, C.; Koutsopoulou, M.; Panderi, I. Improved liquid chromatographic tandem mass spectrometric determination and pharmacokinetic study of glimepiride in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2005, 19, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-K.; Maeng, J.-E.; Hwang, H.-R.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, B.-C.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, C.-K. Determination of glimepiride in human plasma using semi-microbore high performance liquid chromatography with column-switching. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 810, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, I.I.; Idrees, J.; Al Tamimi, J.I. Determination of glimepiride in human plasma by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 799, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, M.; Cascorbi, I.; Timm, R.; Kroemer, H.K.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Kivistö, K.T. Glyburide and glimepiride pharmacokinetics in subjects with different CYP2C9 genotypes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 72, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, M.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Kivistö, K.T. Effect of gemfibrozil on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glimepiride. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 70, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, M.; Backman, J.T.; Neuvonen, M.; Laitila, J.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Kivistö, K.T. Effects of fluconazole and fluvoxamine on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glimepiride. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, M.; Kivistö, K.T.; Backman, J.T.; Neuvonen, P.J. Effect of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glimepiride. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 50, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, B.; Profozic, V.; Metelko, Z.; Mrzljak, V.; Lange, C.; Malerczyk, V. Pharmacokinetics and safety of glimepiride at clinically effective doses in diabetic patients with renal impairment. Diabetologia 1996, 39, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malerczyk, V.; Badian, M.; Korn, A.; Lehr, K.-H.; Waldhäusl, W. Dose linearity assessment of glimepiride (Amaryl) tablets in healthy volunteers. Drug Metab. Drug Interact. 1994, 11, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badian, M.; Korn, A.; Lehr, K.-H.; Malerczyk, V.; Waldhäusl, W. Absolute bioavailability of glimepiride (Amaryl) after oral administration. Drug Metab. Drug Interact. 1994, 11, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Lehr, K.; Damm, P. Simultaneous determination of the sulphonylurea glimepiride and its metabolites in human serum and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1990, 526, 497–505. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, L. Flurbiprofen Therapy and CYP2C9 Genotype; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.A.; French, D.P.; Brooks, J.M. Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Res. Methods Med. Health Sci. 2020, 1, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 5.1. 0 [updated March 2011]; The Cochrane Collaboration. Available online: www.cochrane-handbook.org (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, J.L.; Holder-Pearson, L.; Chase, J.G. Insulin units and conversion factors: A story of truth, boots, and faster half-truths. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, H.D.; Wells, G.A.; Huët, C.; McAlister, F.A.; Salmi, L.R.; Fergusson, D.; Laupacis, A. Assessing the quality of randomized trials: Reliability of the Jadad scale. Control. Clin. Trials 1999, 20, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A.B.E.; Pawluk, S.A.; Wilby, K.J.; Rachid, O. The use of a modified Delphi technique to develop a critical appraisal tool for clinical pharmacokinetic studies. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2022, 44, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savović, J.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; Turner, L.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Higgins, J.P. Evaluation of the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias in randomized trials: Focus groups, online survey, proposed recommendations and their implementation. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Scheme | Age (Years) | Gender | Population | Drug | Dose (mg) | Brand Name | Method of Analysis | Dosage Form | Frequency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19–45 | Male 100% | HP (Korean) | GLM EVO | 4 5 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | LC-MS | Tab | OD | [26] |
| 2 | 18–55 | Male 55% Female 44% | HP (European) | GLM ERT | 1 15 | N/S | HPLC-MS | Tab | SD | [27] |
| 3 | 25–45 a | Male 100% | HP (Egyptian) | GLM | 1 a | Amaryl®, Hoechst Marion Roussel | HPLC | Tab | OD | [28] |
| 4 | 20–45 b | Male 100% | HP (Korean) | GLM ROS | 4 20 | N/S | HPLC-MS | Tab | OD | [29] |
| 5 | 25–45 c | Male 100% | HP (Egyptian) | GLM | 1 | Amaryl® | LC-MS/MS | Tab | SD | [30] |
| 6 | 18–27 | Male 100% | HP | GLM GMF | 3 600 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | UV-Visible Spectroscopy | Tab | SD | [31] |
| 7 | N/S | N/S | HP (Chinese) | GLM | 2 | N/S | UPLC-MS | N/S | OD | [32] |
| 8 | 19–28 | Male 100% | HP (Chinese) | GLM | 2 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | LC-MS | Tab | SD | [33] |
| 9 | 19–30 d | Male 100% | HP (Korean) | FDC | 2/500 | N/S | HPLC-LC/MS/MS | Tab | SD | [34] |
| 10 | 18–45 | Male Female | HP (American) | GLM COL | 4 | N/S | LC-MS | N/S | SD | [35] |
| 11 | 20–45 | Male 100% | HP (Korean) | GLM GEMI | 4 60 | N/S | LC-MS/MS | Tab | SD | [36] |
| 12 | N/S | Male 100% | HP (Indian) | GLM | 2 | TRIPILL (Cipla Limited | MS | N/S | OD | [37] |
| 13 | 18–29 | Male 100% | HP (Egyptian) | GLM | 1–6 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | HPLC-UV | Tab | SD | [38] |
| 14 | 18–55 | Male 50% Female 50% | HP (Egyptian) | GLM IPRA | 1, 2 150 | N/S | LC-MS | Tab | SD Multiple- SD | [39] |
| 15 | 22–29 | Male 100% | HP (Korean) | GLM | 2 | Amadiem; Dongsung Pharmaceutical Co | LC-MS | Tab | SD | [40] |
| 16 | N/S | N/S | HP (Korean) | GLM | 1 | N/S | LC-MS | N/S | N/S | [41] |
| 17 | 20–28 | Male 100% | HP (Korean) | GLM | 2 | Amaryl, Handok/Aventis Pharma | LC-MS/MS | Tab | SD | [42] |
| 18 | N/S | N/S | HP (Korean) | GLM | 2 | N/S | LC-MS | Tab | SD | [43] |
| 19 | N/S | N/S | Disease (Korean) | GLM | 2 | Amaryl, Aventis | HPLC | Tab | N/S | [44] |
| 20 | 18–26 e | Male 100% | HP (Japanese) | GLM | 2 | Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd.; Amaryl® (Sanofi-Aventis Pharma | LC-MS | Tab | SD | [45] |
| 21 | 18–45 | Male 67% Female 33% | HP (African American or Caucasian) | GLM DAPA | 4 20 | N/S | LC/MS-MS | Tab | SD | [46] |
| 22 | M = 18–26 F = 20–38 | Male 50% Female 50% | HP (Korean) | FDC d GLM, MET | 2/500 2, 500 | Amaryl®-M 2/500, Handok Pharmaceutical Co.; Amaryl® Handok Pharmaceutical Co. | LC/MS-MS | Tab | SD | [47] |
| 23 | 20–36 | Male 100% | HP (Korean) | FDC d, e | 1/500, 2/500 2/500, 1/500 | Amaryl®-M 1/500, Handok Pharmaceutical Co.; Amaryl®-M 2/500, Handok Pharmaceutical Co. | HPLC-MS/MS | Tab | SD | [48] |
| 24 | 62–65 | Male 75% Female 25% | Disease (Japanese) | GLM | 1, 2 | N/S | LC-MS | N/S | OD/BID | [49] |
| 25 | 18–55 | Male 49% Female 51% | HP | FDC f GLM | 4/30 4 | N/S | LC-MS/MS | Tab | SD | [50] |
| 26 | 35–85 | Male Female | Disease (Japanese) | GLM | 1 | Amaryl, Aventis | N/S | Tab | SD | [51] |
| 27 | 20–50 | Male 62.5% Female 37.5% | HP (Caucasian) | GLM e | 6 | Amaryl®, Aventis Pharma; Remevita | HPLC | Tab | SD | [52] |
| 28 | N/S | Male 100% | HP (Lebanese) | GLM | 3 | Amaryl®, Aventis | HPLC | Tab | SD | [53] |
| 29 | 25–26 | Male Female | HP (Caucasian) | GLM | 4 | N/S | LC-MS | Tab | SD | [54] |
| 30 | 23–25 | Male 100% | HP (Asian) | GLM | 2 | Amaryl®, Handok-Aventis | HPLC | Tab | SD | [55] |
| 31 | 18–70 | Male 50% Female 50% | Disease | GLM | 8 | N/S | HPLC | Tab | SD | [13] |
| 32 | N/S | N/S | HP | GLM | 3 | N/S | LC-MS | Tab | SD | [56] |
| 33 | (19–36) (19–27) g | Male 33% Female 66% | HP (Caucasian) | GLM GLY | 0.5 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | N/S | Tab | SD | [57] |
| 34 | 20–26 | Male 20% Female 80% | HP | GLM GMF | 0.5 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | N/S | Tab | SD | [58] |
| 35 | 19–27 | Male 50% Female 50% | HP | GLM FLC FLV | 0.5 200, 400 100 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | N/S | Tab | SD | [59] |
| 36 | 19–26 | Male 50% Female 50% | HP | GLM RIF | 1 | Amaryl®, Sanofi-Aventis | N/S | Tab | SD | [60] |
| 37 | (44–70) h (49–75) i | Male 47% Female 53% | Disease | GLM | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 | N/S | N/S | Tab | SD | [61] |
| 38 | 23–32 | Male 100% | HP (Caucasian) | GLM | 1, 2, 4, 8 | Amaryl® | N/S | Tab | SD | [62] |
| 39 | 18–40 | Male 100% | HP (Caucasian) | GLM | 1 | Amaryl® | HPLC | Tab, Inj | SD | [63] |
| 40 | N/S | N/S | N/S | GLM | 3 | N/S | HPLC | Tab | SD | [64] |
| Sr | Ref. | Dose (mg) | (AUC)0-∞ (ng.× h/mL) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | t½ (h) | CL/F (mL/min) | CLʀ (mL/min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [28] | 1 a | 178.988 | 147.7 | 4 | N/S | N/S | N/S | |
| 2.19 | 32.47 | 2.5 | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 15.967 | 135.77 | 2.5 | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 2 | [30] | 1 b | 3.595 | 21.533 | 4 | 4.006 | N/S | N/S | |
| 19.791 | 46.09 | 2.5 | 4.911 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 6.626 | 135.16 | 2.5 | 3.55 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 3 | [33] | 2 | 823.04 ± 290.87 | 163.77 ± 45.73 | 2.53 ± 0.62 | 7.37 ± 2.24 | N/S | N/S | |
| 4 | [32] | 2 | 4452.06 ± 539.78 | 414.83 ± 20.45 | N/S | 8.22 ± 2.50 | N/S | 7.67 ± 1 | |
| 5 | [34] | 2/500 c | N/S | 144.0 ± 49.8 | 2.2 ± 0.8 | 3.0 ± 2.0 | N/S | N/S | |
| N/S | 143.3 ± 51.3 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 2.9 ± 1.9 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 6 | [37] | 2 | 589 ± 75 | 62.8 ± 7.9 | 5.33 ± 0.52 | 8.55 ± 1.87 | N/S | N/S | |
| 7 | [38] | 1 | 596.0 ± 141.9 | 84.8 ± 3.81 | 2.4 ± 1.7 | 8.81 ± 1.1 | 121.8 ± 29.4 | N/S | |
| 2 | 7.07 ± 1.41 | 173.9 ± 38.0 | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 7.07 ± 1.41 | 116.9 ± 25.9 | N/S | |||
| 3 | 8.54 ± 3.31 | 254.7 ± 54.5 | 2.19 ± 0.83 | 8.54 ± 3.31 | 114.1 ± 32.2 | N/S | |||
| 4 | 2894.8 ± 1105.2 | 333.2 ± 99.2 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 7.63 ± 1.5 | 112 ± 44.1 | N/S | |||
| 6 | 3993.2 ± 1550.5 | 512.2 ± 100.2 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 8.75 ± 1.3 | 123.9 ± 56.7 | N/S | |||
| 8 | [40] * | CYP2C9 Genotypes | |||||||
| 2 | *1/*1 | 892.7 | 218.5 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 42.4583 | N/S | ||
| *1/*3 | 832.9 | 161.3 | 3 | 2.9 | 40.0217 | N/S | |||
| *3/*3 | 4371.9 | 267.8 | 4 | 12.3 | 7.625 | N/S | |||
| 9 | [41] * | 1 d | 881.69 | 83.56 | 13.45 | 0.74 | 18.9 | N/S | |
| 795.7 | 106.84 | 13.44 | 0.53 | 20.95 | N/S | ||||
| 10 | [42] | CYP2C9 Genotypes | |||||||
| 2 | Total | 827.9 ± 49.9 | 188.3 ± 9.5 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | N/S | N/S | ||
| *1/*1 | 806.1 ± 48.9 | 184.6 ± 9.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 6.2 ± 0.4 | N/S | N/S | |||
| *1/*3 | 1309.65 | 270.55 | 3.25 | 5.6 | N/S | N/S | |||
| 11 | [43] * | 2 e | Parent drug | N/S | 184.7 ± 91.2 | 2.8 ± 1.3 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | N/S | N/S |
| M 1 | N/S | 29.3 ± 4.9 | 3.5 ± 1.3 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | N/S | N/S | |||
| M 2 | N/S | 4.9 ± 1.9 | 6.7 ± 1.2 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | N/S | N/S | |||
| 12 | [45] | 2 f | Parent drug | 627.25 ± 184.61 | 75.71 ± 21.11 | 5.76 ± 2.07 | 4.74 ± 1.66 | N/S | N/S |
| 646.98 ± 238.92 | 74.05 ± 24.95 | 4.93 ± 2.81 | 4.08 ± 1.18 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| M 1 | 288.76 ± 63.09 | 25.13 ± 5.06 | 7.07 ± 2.45 | 5.74 ± 1.45 | N/S | N/S | |||
| 303.46 ± 61.86 | 24.83 ± 5.13 | 6.78 ± 2.43 | 5.05 ± 1.13 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 13 | [47] | 2/500 c | 903.19 ± 250.72 | 205.14 ± 56.08 | 1.0 1 | 6.89 ± 2.46 | 39.333 ± 10 | N/S | |
| 2 | 921.21 ± 264.77 | 201.81 ± 50.75 | 3.0 1 | 6.39 ± 1.77 | 38.5 ± 9.33 | N/S | |||
| 14 | [48] | 1/500 c | 700.6 ± 198.6 | 168.2 ± 54.9 | 1.75 1 (1.0–4.0) 2 | 8.2 ± 2.5 | N/S | N/S | |
| 2/500 c | 656.0 ± 201.2 | 149.9 ± 47.4 | 2.02 1 (1.0–4.0) 2 | 8.5 ± 2.7 | N/S | N/S | |||
| 15 | [50] 3* | 4/30 g | 2363.39 | 285.29 | 3.02 | 13.05 | 112.85 | N/S | |
| 4 | 2334.51 | 304.60 | 2.33 | 18.07 | 114.22 | N/S | |||
| 16 | [52] 3 | 6 d | 4399.6 ± 1491.8 | 532.5 ± 190.1 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 8.8 ± 3.0 | N/S | N/S | |
| 4260.7 ± 1330.0 | 518.6 ± 218.6 | 2.5 ± 0.7 | 8.9 ± 2.5 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 17 | [53] 3* | 3 | 1301.85 | 220.58 | 2.69 | 5.04 | 115.22 | N/S | |
| 18 | [54] | 4 | 1549.9 ± 299.54 | 244.37 ± 71.6 | 2.9 ± 0.98 | 4.61 ± 0.83 | N/S | N/S | |
| 19 | [55] | 2 | N/S | 232.8 ± 28.4 | 2.14 ± 0.38 | 2.16 ± 0.21 | N/S | 32.8 ± 7.9 | |
| 20 | [56] * | 3 | 1044.38 | 210.82 | 1.56 | 15.485 | 143.63 | N/S | |
| 21 | [57] | CYP2C9 Genotype | 116.1 1 (60.1–171.1) 2 | 29.9 1 (23.1–51.2) 2 | 1.25 1 (1.0–5.0) 2 | 1.9 1 (1.1–2.5) 2 | N/S | N/S | |
| 0.5 | *1/*1 | ||||||||
| *1/*2 | 125.1 1 (94.7–170.5) 2 | 31.6 1 (17.5–35.8) 2 | 2.0 1 (1.5–4.0) 2 | 1.9 1 (1.8–3.2) 2 | N/S | N/S | |||
| *1/*3 or *2/*3 | 310.1 1 (151.2–313.3) 2 | 37.8 1 (2951.4) 2 | 2.5 1 (1.5–4) 2 | 3 1 (2.5–4) 2 | N/S | N/S | |||
| 22 | [62] 3 | 1 f 2 f 4 f 8 f | Parent drug | N/S | 103.2 ± 34.3 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | N/S | 55.3 ± 16.3 |
| N/S | 176.8 ± 44.1 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | N/S | 53.5 ± 15.5 | ||||
| N/S | 307.8 ± 69.4 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | N/S | 53.6 ± 10.6 | ||||
| N/S | 550.8 ± 151.9 | 2.8 ± 1.2 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | N/S | 65.5 ± 21.1 | ||||
| 1 f 2 f 4 f 8 f | M 1 | N/S | 24.0 ± 5.7 | 2.8 ± 0.8 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | N/S | 146 ± 72 | ||
| N/S | 42.1 ± 9.6 | 2.8 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.7 | N/S | 170 ± 48 | ||||
| N/S | 76.7 ± 19.9 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 3.0 ± 0.8 | N/S | 166 ± 90 | ||||
| N/S | 135.0 ± 40.4 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | 3.2 ± 1.1 | N/S | 169 ± 47 | ||||
| 23 | [63] 3 | 1 f | N/S | 88 ± 21 | 2.7 ± 1.4 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | N/S | 45 ± 16 | |
| N/S | 20 ± 6 | 3.9 ± 1.9 | 3.3 ± 1.2 | N/S | 143 ± 48 | ||||
| 24 | [64] 3 | 3 e | 634.36 | 348 | 0.77 | 1.09 | 236.46 | N/S | |
| 383.12 | 91.2 | 1.50 | 2.39 | 436.522 | N/S | ||||
| 173.59 | 35.2 | 3.01 | 2.39 | 864.08 | N/S | ||||
| Sr. no. | Ref | Dose (mg) | (AUC) 0-∞ (ng × h/mL) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | t½ (h) | CL/F (mL/min) | CL (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [63] 1 | 1 a | N/S | 243 ± 33 | N/S | 3.4 ± 2.0 | N/S | 48 ± 20 |
| N/S | 24 ± 5 | 1.6 ± 0 4 | 2.7 ± 1.0 | N/S | 175 ± 94 |
| Sr. | Ref. | Patient Characteristics | Dose (mg) | (AUC)0-∞ (ng × h/mL) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | t½ (h) | CL/F (mL/min) | CLʀ (mL/min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [44] * | DP (Southeast Asian) | 2 | 51.9400 | 7.306 | 6.032 | 2.001 | 1283.53 | N/S | ||
| 2 | [49] | DP (Japanese) | 2 a | 706.2 ± 63.3 | N/S | 1.88± 0.21 | 3.28 ± 0.21 | N/S | N/S | ||
| 1 b | 630.8 ± 93.6 | N/S | 2.15 ± 0.4 | N/S | N/S | N/S | |||||
| 3 | [51] 3 | DP (Japanese) | 1 | *1/*1 | 292 ± 101.8 * | 89.5 ± 37.8 | N/S | N/S | 2 63 ± 24 | N/S | |
| *1/*3 | 762.7 (654.6–870.9) 1 | 141.5 (123.8–159.2) 1 | N/S | N/S | 2 22.5 (25.33–19.67) 1 | N/S | |||||
| 4 | [13] | DP | 8 | Parent drug c | 4004 ± 1319 | 547 ± 218 | 2.89 ± 0.90 | 12.6 ± 12.8 (2.80–54.85) 1 | 20.20 ± 7.23 | N/S | |
| 3281 ± 1362 | 410 ± 124 | 2.90 ± 0.89 | 8.89 ± 3.91 | 20.35 ± 8.9 | N/S | ||||||
| M 1 d | 1887 ± 754 | 180 ± 63 | 4.50 ± 0.78 | 9.76 ± 3.24 | N/S | N/S | |||||
| 1686 ± 476 | 135 ± 52 | 4.33 ± 0.82 | 11.6 ± 5.2 | N/S | N/S | ||||||
| M 2 e | 549 ± 212 | 50.3 ± 15.7 | 5.00 ± 1.14 | 7.09 ± 3.89 | N/S | N/S | |||||
| 383 ± 211 | 36.5 ± 14.7 | 5.36 ± 1.45 | 6.37 ± 4.87 | N/S | N/S | ||||||
| 5 | [61] | DP with Renal Impairment | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 | Parent drug | |||||||
| f | S | 1357 ± 452 | 359.2 ± 98.3 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.28 ± 0.79 | 41.6 ± 18.5 | N/S | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 5.6 ± 3.0 | 68.1 ± 26.4 | N/S | |||||
| g | S | 622 ± 106 | 205.3 ± 29.0 | 2.7 ± 1.3 | 1.06 ± 0.23 | 81.1 ± 12.8 | N/S | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 3.2 ± 2.2 | 71.4 ± 17.5 | N/S | |||||
| h | S | 622 ± 226 | 194.0 ± 42.4 | 2.2 ± 1.0 | 2.19 ± 1.13 | 91.1 ± 36.5 | N/S | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 3.6 ± 1.9 | 97.8 ± 48.7 | N/S | |||||
| M 1 | |||||||||||
| f | S | N/S | 70.8 ± 14.0 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 2.79 ± 0.86 | 132.1 ± 66.4 | 49.6 ± 48.9 | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 3.75 ± 1.3 | 100.2 ± 30.4 | 31.8 ± 21.1 | |||||
| g | S | N/S | 93.0 ± 12.5 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 2.32 ± 0.93 | 107.0 ± 33.7 | 9.2 ± 7.0 | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 3.96 ± 1.8 | 80.6 ± 21.1 | 11.8 ± 8.3 | |||||
| h | S | N/S | 103.6 ± 24.1 | 4.1 ± 2.3 | 4.88 ± 2.92 | 67.5 ± 39.6 | 4.9 ± 7.5 | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 8.0 ± 4.6 | 59.7 ± 33.3 | 2.1 | |||||
| M 2 | |||||||||||
| f | S | N/S | 21.8 ± 8.5 | 4.8 ± 1.5 | 4.91 ± 2.94 | 306.5 ± 63.6 | 52.7 ± 40.7 | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 3.5 ± 1.1 | 184.2 ± 51.8 | 89.7 ± 61.0 | |||||
| g | S | N/S | 42.0 ± 2.6 | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 3.06 ± 0.50 | 140.8 ± 36.5 | 20.5 ± 12.7 | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 4.2 ± 1.2 | 111.9 ± 38.3 | 27.6 ± 9.4 | |||||
| h | S | N/S | 61.7 ± 25.9 | 7.0 ± 1.2 | 8.37 ± 1.90 | 61.5 ± 30.6 | 3.7 ± 7.5 | ||||
| M | N/S | N/S | N/S | 14.9 ± 12.3 | 62.0 ± 32.9 | 3.9 ± 3.5 | |||||
| Sr. | Ref. | Dose (mg) | HbA1c Levels (%) | Serum Glucose | Serum Insulin | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gmax (mmol/L) | AUGC (mmol × h/L) | Decremental AUC (0-3) (mmol × h/L) | Decremental AUC (0–7) (mmol × h/L) | Emax (pmol/L) | AUEC (pmol × h/L) | Incremental AUC (0–3) (pmol × h/L) | Incremental AUC (0–7) (pmol × h/L) | ||||||
| 1 | [26] | 4 | GLM | N/S | 7.5 ± 1.9 | 16.17 ± 2.68 | N/S | N/S | 518.4 ± 262.8 | 850.2 ± 393 | N/S | N/S | |
| EVO | N/S | 7.0 ± 0.83 | 14.79 ± 1.76 | N/S | N/S | 633 ± 400.8 | 990.6 ± 636 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 2 | OD | 6.9 ± 0.2 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | |||
| 1 | BID | 7.1 ± 0.1 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | |||
| 3 | [57] 1 | 0.5 | CYP2C9 Genotypes | ||||||||||
| *1/*1 3 | N/S | N/S | N/S | −0.6 (−2.0–2.95) | −4.3 (−9.9–1.1) | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||||
| *1/*2 3 | N/S | N/S | N/S | −0.9 (−1.9–3.6) | −8.0 (−10.2–3.4) | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||||
| *1/*3 or *2/*3 3 | N/S | N/S | N/S | −0.1 (−−2.0–0.2) | −8.8 (−12.1–(−3.2)) | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 4 | [58] | 0.5 | GLM | N/S | N/S | N/S | −0.88 ± 1.27 | 1.96 ± 3.65 | N/S | N/S | 0.382 ± 0.182 | 0.964 ± 0.614 | |
| GMF | N/S | N/S | N/S | −1.05 ± 2.13 | 1.5 ± 3.70 | N/S | N/S | 0.413 ± 0.303 | 0.88 ± 0.654 | ||||
| 5 | [59] | 0.5 | GLM | N/S | N/S | N/S | 0.63 ± 1.45 | 0.40 ± 3.35 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | |
| 100 | FLV | N/S | N/S | N/S | –0.15 ± 2.10 | –0.50 ± 4.92 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | |||
| 200, 400 | FLC | N/S | N/S | N/S | 1.15 ± 1.07 | 1.43 ± 3.48 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | |||
| 6 | [60] | 1 | GLM | N/S | N/S | N/S | 0.57 ± 0.5 | 4.51 ± 1.07 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | |
| RIF | N/S | N/S | N/S | 0.26 ± 0.55 | 5.05 ± 1.34 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 7 | [61] 2 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 | 6.99 ± 1.2 | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||
| Sr. | Ref. | Dose (mg) | Drug | (AUC) 0-∞ (ng × h/mL) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | t½ (h) | CL/F (mL/min) | CLʀ (mL/min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [26] 1 | 4 | Parent drug | GLM | 1672.7 ± 623. 9 (783.9–3293.8) | 326.6 ± 98.5 (143.8–562.9) | 3 2 (1.5–5) 3 | 4.7 ± 2.2 (1.7–4.2) | 45 ± 16.67 (20–85) | N/S |
| GLM + EVO | 1794.9 ± 653.2 (883.6–3282.8) | 350.9 ± 97.4 (185.1–547.8) | 4 2 (1–6) 3 | 4.2 ± 2.0 (1.7–8.4) | 41.67 ± 13.33 (20–75) | N/S | ||||
| M 1 | GLM | 611.9 ± 180.7 (309.4–1179.5) | 81.3 ± 20.6 (47.7–135.3) | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | |||
| GLM + EVO | 652.6 ± 197.7 (387–1331.4) | 84.2 ± 19 (55.8–137) | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 2 | [27] | 1 | GLM | 249.3 ± 213.55 | 34.35 ± 19.9 | 3 2 (1.0–12.0) 3 | 5.89 ± 2.79 | N/S | N/S | |
| GLM + ERT | 296.7 ± 306.9 | 33.47 ± 15.79 | 4 2 (1.5–12.0) 3 | 6.68 ± 4.02 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 3 | [29] | 4 | GLM | N/S | 173.7 ± 55.4 | 4.0 2 (2.0–6.0) 3 | 13.3 ± 12.3 | 4.5 ± 1.3 | N/S | |
| GLM + ROS | N/S | 180.5 ± 65.3 | 3.0 2 (1.5–5.0) 3 | 11.7 ± 5.0 | 4.4 ± 1.5 | N/S | ||||
| 4 | [31] | 3 | GLM | 1498 ± 21.6 | 327.1 ± 3.4 | 1.5 | 2.6 ± 0.195 | 33.38 ± 0.4773 | N/S | |
| GLM + GMF | 3619.124 ± 58.0 | 1108.5 ± 44.52 | 1.5 | 4.1 ± 0.215 | 13.82 ± 0.2167 | N/S | ||||
| 5 | [35] | 4 | GLM | 1215 ± 311 | 249 ± 56 | 1.0 2 (0.9–3.93) 3 | 5.98 2 | 58.5 ± 14.97 | N/S | |
| GLM + COL | 971 ± 244 | 233 ± 73 | 1.0 2 (1.0–9.02) 3 | 6.59 2 | 72.67 ± 16.62 | N/S | ||||
| GLM 4hr before COL | 1139 ± 318 | 256 ± 56 | 1.0 2 (1.0–5.0) 3 | 5.52 2 | 62.67 ± 15.5 | N/S | ||||
| 6 | [36] | 4 | Parent drug | GLM + GEMI | N/S | 231.32 ± 71.58 | 3 2 | 6.54 ± 2.30 | N/S | N/S |
| GLM | N/S | 227.05 ± 72.64 | 4 2 | 6.37 ± 2.9 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| M 1 | GLM + GEMI | N/S | 29.58 ± 8.23 | 4 2 | 5.87 ± 2.19 | N/S | N/S | |||
| GLM | N/S | 28.26 ± 8.4 | 4 2 | 6.42 ± 2.18 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 7 | [39] | 1–2 | ||||||||
| GLM | 684 ± 211 | 136 ± 36 | 1.50 2 (1.0–5.0) 3 | 6.8 ± 1.6 | 53.33 ± 16.67 | N/S | ||||
| GLM + IPRA | 720 ± 22 | 150 ± 41 | 1.00 2 (1.0–5.0) 3 | 7.1 ± 1.8 | 50 ± 15 | N/S | ||||
| 8 | [46] * | 4 | GLM | 4771.269 | 699.489 | 7.8742 | 16.1423 | 55.89 | N/S | |
| GLM + DAPA | 5375.324812 | 565.628 | 8.06713 | 16.751 | 49.6 | N/S | ||||
| 9 | [58] | 0.5 | GLM | 137.9 ± 69.2 | 31.3 ± 5.2 | 1.52 (1–4) 3 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | N/S | N/S | |
| GLM + GMF | 169.9 ± 82.7 | 35.6 ± 13.6 | 1.52 (1–3) 3 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 10 | [59] | 0.5 | GLM | 132.2 ± 61.4 | 32.7 ± 10.5 | 1.5 2 (1–5) 3 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | N/S | N/S | |
| GLM + FLV | 175.4 ± 93.3 | 46.7 ± 18.6 | 1.5 2 (1–1.5) 3 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| GLM + FLC | 314.9 ± 122.2 | 49.2 ± 9.6 | 2.0 2 (1.5–5) 3 | 3.3 ± 0.9 | N/S | N/S | ||||
| 11 | [60] | 1 | GLM | 286.7 ± 35.1 | 64.2 ± 9.1 | 1.5 2 (1.0–3.0) 3 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | N/S | N/S | |
| GLM + RIF | 190.3 ± 25.2 | 55.5 ± 7.2 | 1.0 2 (1.0–2.0) 3 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | N/S | N/S | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azhar, M.; Alasmari, M.S.; Zamir, A.; Saeed, H.; Alqahtani, F.; Ahmad, T.; Rasool, M.F. The Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Glimepiride—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010122
Azhar M, Alasmari MS, Zamir A, Saeed H, Alqahtani F, Ahmad T, Rasool MF. The Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Glimepiride—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(1):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010122
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzhar, Mubara, Mohammed S. Alasmari, Ammara Zamir, Hamid Saeed, Faleh Alqahtani, Tanveer Ahmad, and Muhammad Fawad Rasool. 2025. "The Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Glimepiride—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 1: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010122
APA StyleAzhar, M., Alasmari, M. S., Zamir, A., Saeed, H., Alqahtani, F., Ahmad, T., & Rasool, M. F. (2025). The Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Glimepiride—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(1), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010122









