A Novel LC-APCI-MS/MS Approach for the Trace Analysis of 3,4-Difluoronitrobenzene in Linezolid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
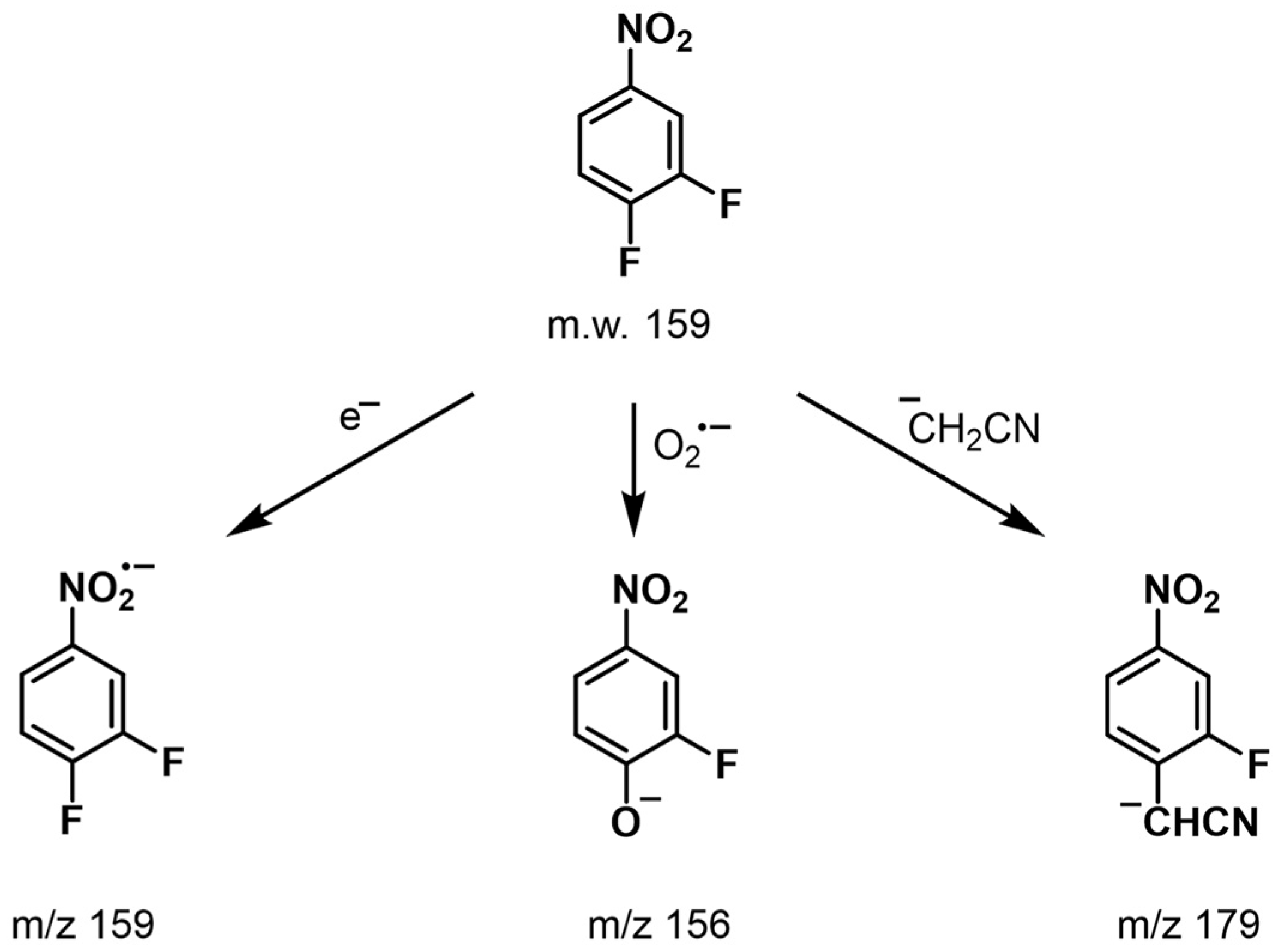
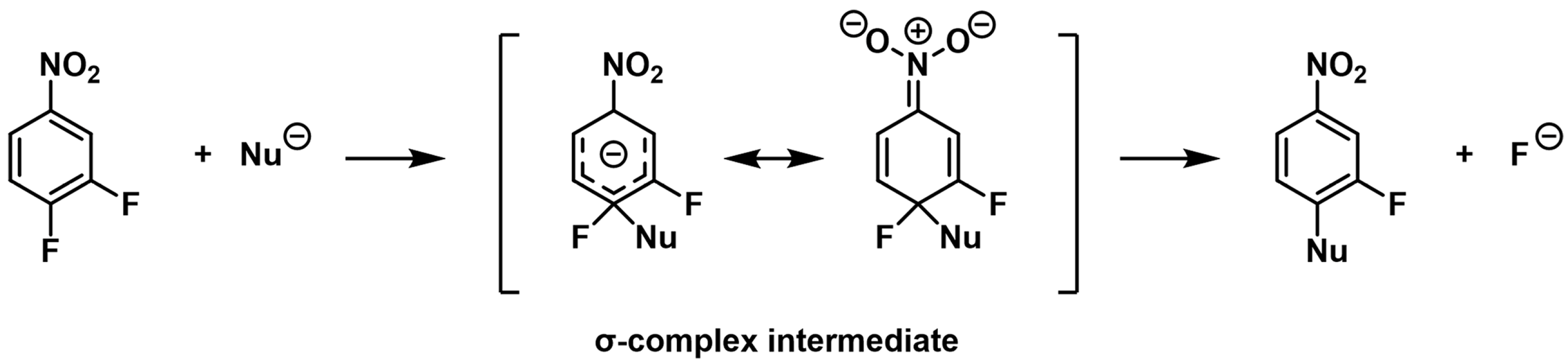
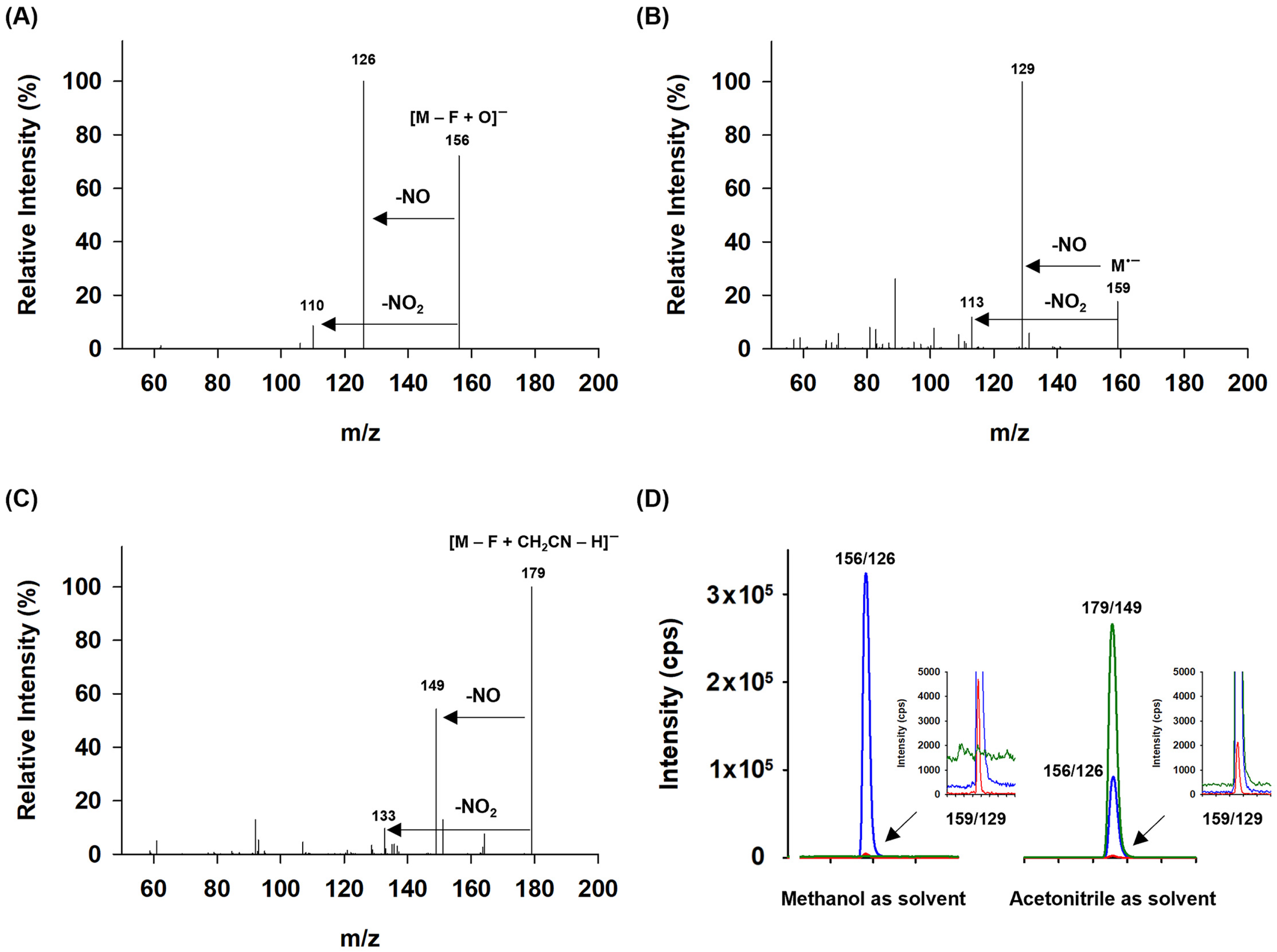
2.1. Optimization of the MS Conditions
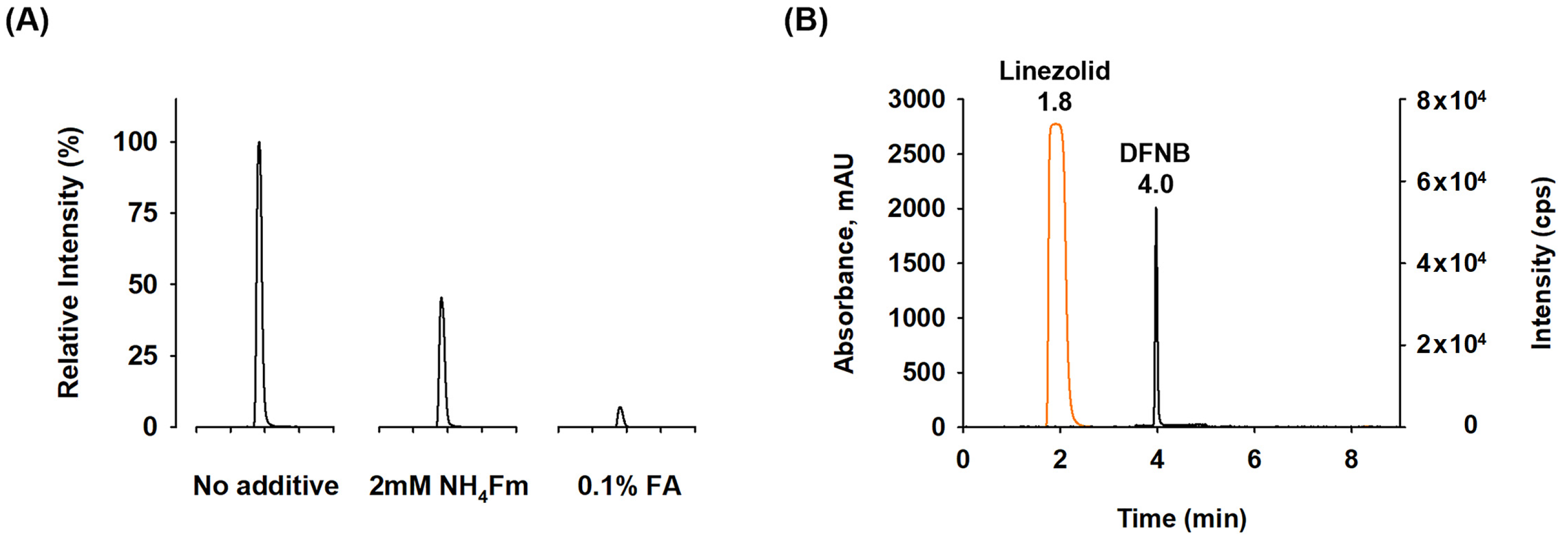
2.2. Optimization of LC Conditions
2.3. Method Validation
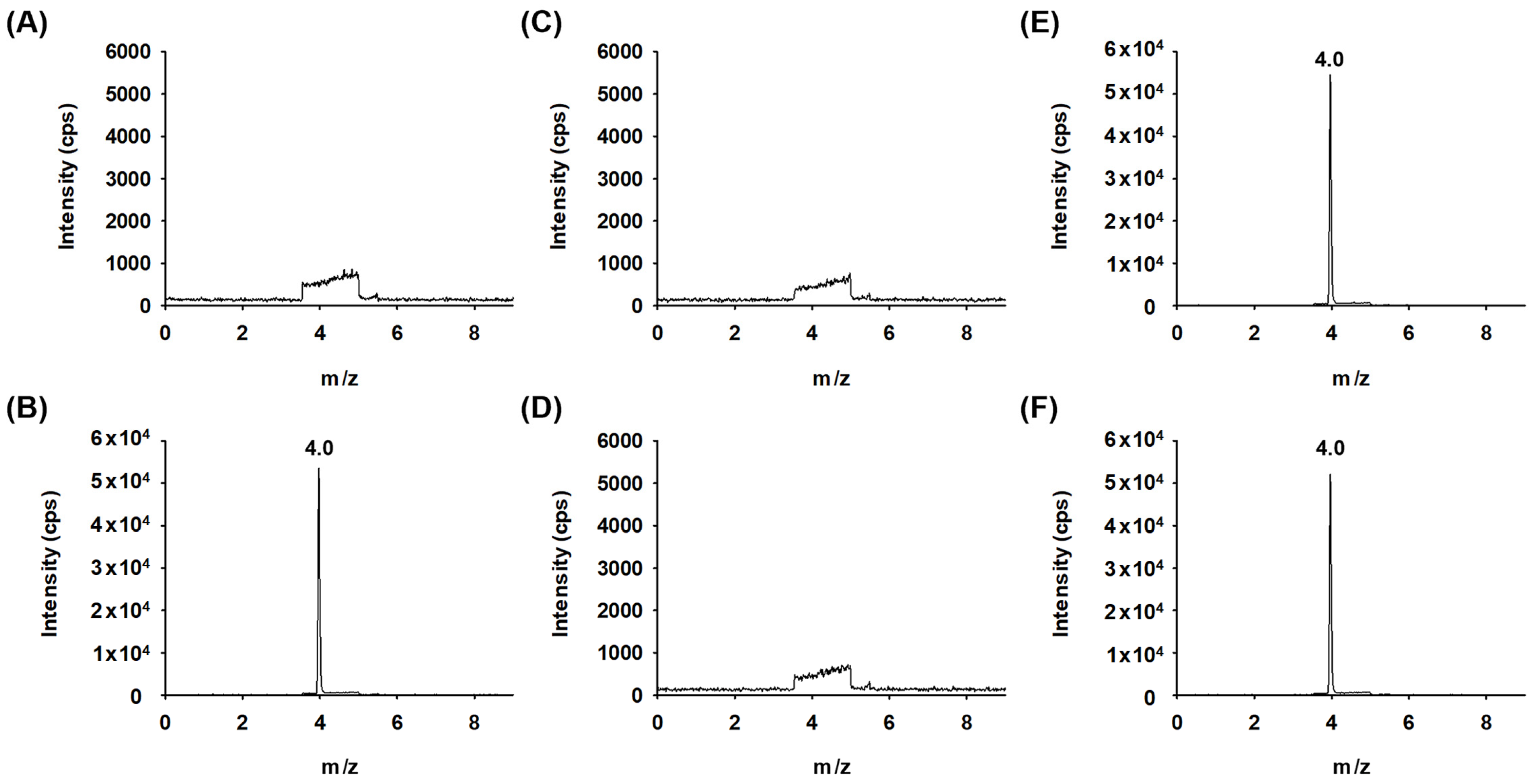
2.3.1. System Suitability and Specificity
2.3.2. Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
2.3.3. Recovery
2.3.4. Precision (Repeatability) and Intermediate Precision
2.3.5. Robustness and Stability
2.3.6. Analysis of Drug Samples and Regulatory Considerations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. HPLC Conditions
3.3. Mass Spectrometer Conditions
3.4. Standard Solution Preparation
3.5. Sample Preparation
3.5.1. Drug Substance
3.5.2. Drug Product
3.6. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozdogan, B.; Appelbaum, P.C. Oxazolidinones: Activity, mode of action, and mechanism of resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, C.; Piperno, A.; Scala, A.; Giuffrè, O. Oxazolidinone Antibiotics: Chemical, Biological and Analytical Aspects. Molecules 2021, 26, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, A.; Schito, G.C. The oxazolidinones as a new family of antimicrobial agent. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.F.S.; Scarim, C.B.; Kim, S.-H.; Wu, J.; Castagnolo, D. Oxazolidinones as versatile scaffolds in medicinal chemistry. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 823–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickner, S.J.; Hutchinson, D.K.; Barbachyn, M.R.; Manninen, P.R.; Ulanowicz, D.A.; Garmon, S.A.; Grega, K.C.; Hendges, S.K.; Toops, D.S.; Ford, C.W.; et al. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of U-100592 and U-100766, Two Oxazolidinone Antibacterial Agents for the Potential Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Nitrobenzene; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Washington, DC, USA; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. In Some Nitrobenzenes and Other Industrial Chemicals; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Lou, C.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. Computational Approaches to Identify Structural Alerts and Their Applications in Environmental Toxicology and Drug Discovery. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, K.L. Fluorination in Medicinal Chemistry: Methods, Strategies, and Recent Developments. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2008, 12, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henary, E.; Casa, S.; Dost, T.L.; Sloop, J.C.; Henary, M. The Role of Small Molecules Containing Fluorine Atoms in Medicine and Imaging Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lu, Y.; Sheng, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. Discovery of Fluorine-Containing Benzoxazinyl-oxazolidinones for the Treatment of Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renslo, A.R.; Luehr, G.W.; Gordeev, M.F. Recent developments in the identification of novel oxazolidinone antibacterial agents. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 4227–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Assessment and Control of DNA Reactive (Mutagenic) Impurities in Pharmaceuticals to Limit Potential Carcinogenic Risk M7 (R2); ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Zeng, H.; Gu, X.; Zheng, J. Determination of nitrobenzene potential genotoxic impurities in nifedipine with GC-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 248, 116274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Shang, J.; Guo, J.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, S. Determination of Seven Nitrobenzene Compounds in Mainstream Cigarette Smoke with Heart-Cutting Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 50, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteil-Rivera, F.; Beaulieu, C.; Deschamps, S.; Paquet, L.; Hawari, J. Determination of explosives in environmental water samples by solid-phase microextraction–liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1048, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borch, T.; Gerlach, R. Use of reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection for complete separation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene metabolites and EPA Method 8330 explosives: Influence of temperature and an ion-pair reagent. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1022, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.S.; Gerk, P.M. Simultaneous determination of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, 2,4-dinitrophenyl-S-glutathione and its metabolites for human placental disposition studies by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 859, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Li, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, T.; Liang, Y.; Shi, G. Simultaneous determination of nitroaromatic compounds in water using capillary electrophoresis with amperometric detection on an electrode modified with a mesoporous nano-structured carbon material. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüí, L.; Vega-Montenegro, D.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Rapid voltammetric determination of nitroaromatic explosives at electrochemically activated carbon-fibre electrodes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Li, Q.; Jia, J.; Deng, D. Electrochemical determination of nitrobenzene using bismuth-film modified carbon paste electrode in the presence of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Ahmad, S. Molecular structure, anharmonic vibrational analysis and electronic spectra of o-, m-, p-iodonitrobenzene using DFT calculations. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1059, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Yao, L. Substituent effect on electronic structures of halonitrobenzenes. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 71, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierbach, A.; Groh, K.J.; Schönenberger, R.; Schirmer, K.; Suter, M.J.F. LC-APCI(−)-MS Determination of 1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, a Model Substrate for Glutathione S-Transferases. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmiche, M.; Colin, A.; Clavos, M.-C.; Pallez, C.; Rosin, C.; Dauchy, X. Determination of nitroaromatic explosive residues in water by stir bar sorptive extraction-gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, J.; Schuster, D.I. The Anomalous Reactivity of Fluorobenzene in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and Related Phenomena. J. Chem. Educ. 2003, 80, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachon, R.; Pichon, V.; Borgne, M.B.L.; Minet, J.-J. Use of porous graphitic carbon for the analysis of nitrate ester, nitramine and nitroaromatic explosives and by-products by liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1154, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, C.N.; Larsen, B.S. Ionization mechanisms related to negative Ion APPI, APCI, and DART. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayen, H.; Jachmann, N.; Vogel, M.; Karst, U. LC-Electron capture APCI-MS for the determination of nitroaromatic compounds. Analyst 2002, 127, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppila, T.J.; Kotiaho, T.; Kostiainen, R.; Bruins, A.P. Negative ion-atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzidic, I.; Carroll, D.I.; Stillwell, R.N.; Horning, E.C. Atmospheric pressure ionization (API) mass spectrometry. Formation of phenoxide ions from chlorinated aromatic compounds. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudlawar, S.K.; Dwivedi, J. Substitution Reactions in Apci Negative Mass Spectrometry: Analysis of 1-Chloro-2-Nitrobenzene in Quetiapine Fumarate. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 37, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cooks, R.G. Atmospheric pressure ion/molecule reactions for the selective detection of nitroaromatic explosives using acetonitrile and air as reagents. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 3130–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danikiewicz, W.; Bieńkowski, T.; Kozłowska, D.; Zimnicka, M. Aromatic nucleophilic substitution (SNAr) Reactions of 1,2- and 1,4-halonitrobenzenes and 1,4-dinitrobenzene with carbanions in the gas phase. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Validation of Analytical Procedures Q2 (R2); ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Retention time (RT, min) | 4.0 | |
| Theoretical plate number (N) | 36,594 | |
| HETP (mm) | 0.0027 | |
| Capacity factor (k’) | 5.67 | |
| Symmetry factor | 1.23 | |
| System precision (%RSD, N = 6) | Area | 1.17 |
| Retention time | 0.13 | |
| Nominal Conc. (ng/mL) | Drug Substance (n = 3) | Drug Product (n = 3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Conc. (ng/mL, Mean ± SD) | Recovery (%) | RSD % | Measured Conc. (ng/mL, Mean ± SD) | Recovery (%) | RSD % | |
| 5 | 5.14 ± 0.18 | 102.78 | 3.54 | 5.20 ± 0.48 | 99.71 | 2.36 |
| 25 | 24.31 ± 0.78 | 97.24 | 3.22 | 25.59 ± 0.46 | 102.38 | 1.78 |
| 50 | 47.54 ± 1.02 | 95.08 | 2.15 | 51.92 ± 0.50 | 103.84 | 0.97 |
| 75 | 74.43 ± 1.50 | 99.24 | 2.01 | 77.01 ± 0.80 | 102.68 | 1.04 |
| Overall | - | 98.59 | 3.86 | - | 102.15 | 2.08 |
| Matrix | Analyst | Retention Time (min) | Calculated Conc. (ng/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | %RSD | Mean | SD | %RSD | ||
| drug substance | Analyst 1, day 1 (n = 6) | 4.0 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 48.70 | 0.93 | 1.91 |
| Analyst 2, day 2 (n = 6) | 4.0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 48.94 | 2.22 | 4.53 | |
| Combined (n = 12) | 4.0 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 48.82 | 1.63 | 3.33 | |
| drug product | Analyst 1, day 1 (n = 6) | 4.0 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 51.56 | 0.91 | 1.76 |
| Analyst 2, day 2 (n = 6) | 4.0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 49.44 | 3.01 | 6.09 | |
| Combined (n = 12) | 4.0 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 50.50 | 2.39 | 4.74 | |
| Robustness (%RSD, n = 3) | Solution Stability (% Difference, n = 3) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column Temp. (40 ± 4 °C) | Flow Rate (0.3 ± 0.03 mL/min) | Standard Solution | In Drug Substance | In Drug Product | |||||
| Area | RT | Area | RT | 9 h | 18 h | 9 h | 18 h | 9 h | 18 h |
| 2.60 | 1.49 | 4.00 | 3.59 | −6.44 | −2.97 | −5.76 | 6.87 | 0.51 | 5.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, Y.; Kim, A.; Shin, E.; Cho, H. A Novel LC-APCI-MS/MS Approach for the Trace Analysis of 3,4-Difluoronitrobenzene in Linezolid. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040465
Lim Y, Kim A, Shin E, Cho H. A Novel LC-APCI-MS/MS Approach for the Trace Analysis of 3,4-Difluoronitrobenzene in Linezolid. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040465
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Yujin, Aelim Kim, Eunyeong Shin, and Hwangeui Cho. 2025. "A Novel LC-APCI-MS/MS Approach for the Trace Analysis of 3,4-Difluoronitrobenzene in Linezolid" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040465
APA StyleLim, Y., Kim, A., Shin, E., & Cho, H. (2025). A Novel LC-APCI-MS/MS Approach for the Trace Analysis of 3,4-Difluoronitrobenzene in Linezolid. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040465






