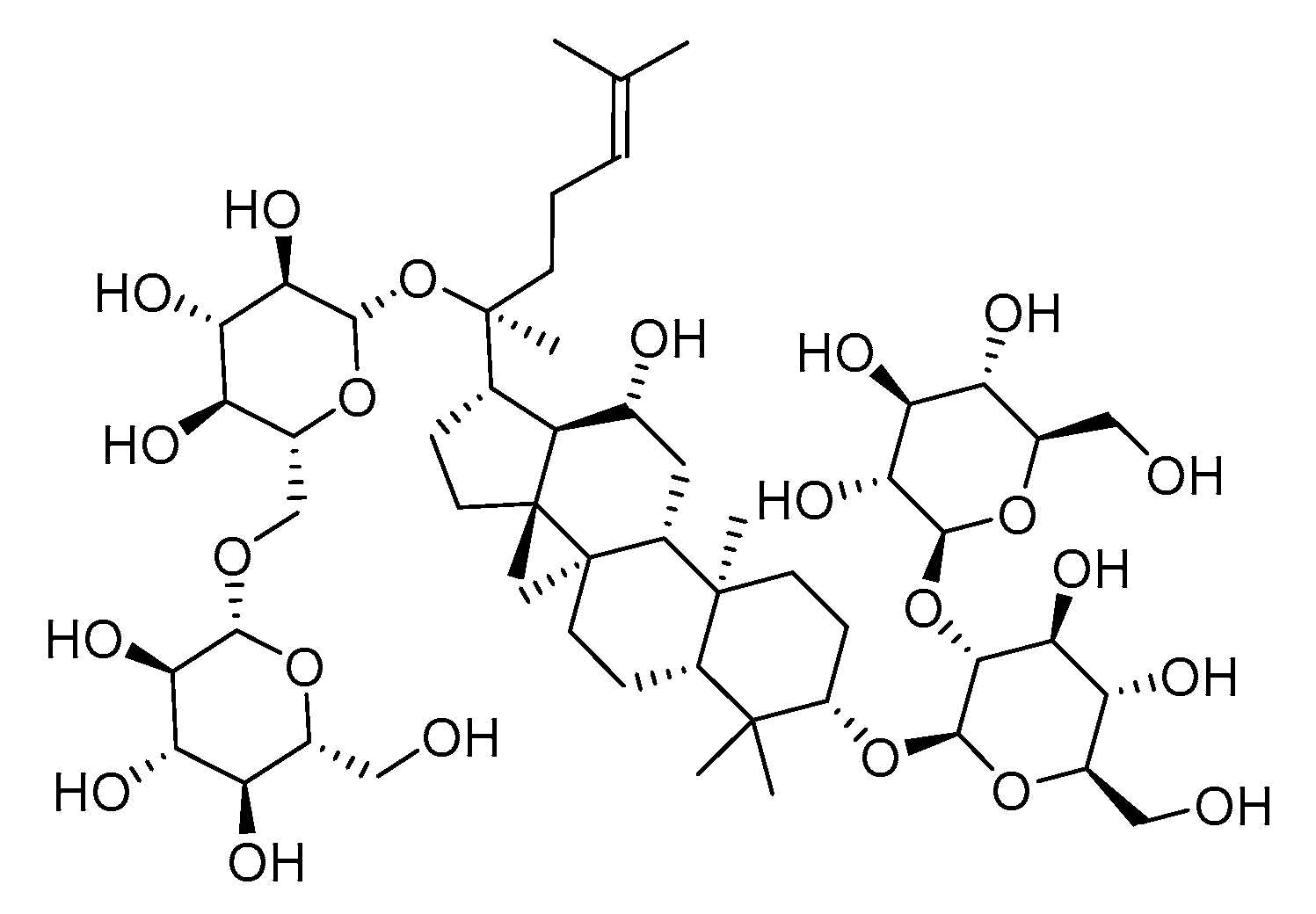
Ginsenoside Rb1 Ameliorates Heart Failure Ventricular Remodeling by Regulating the Twist1/PGC-1α/PPARα Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
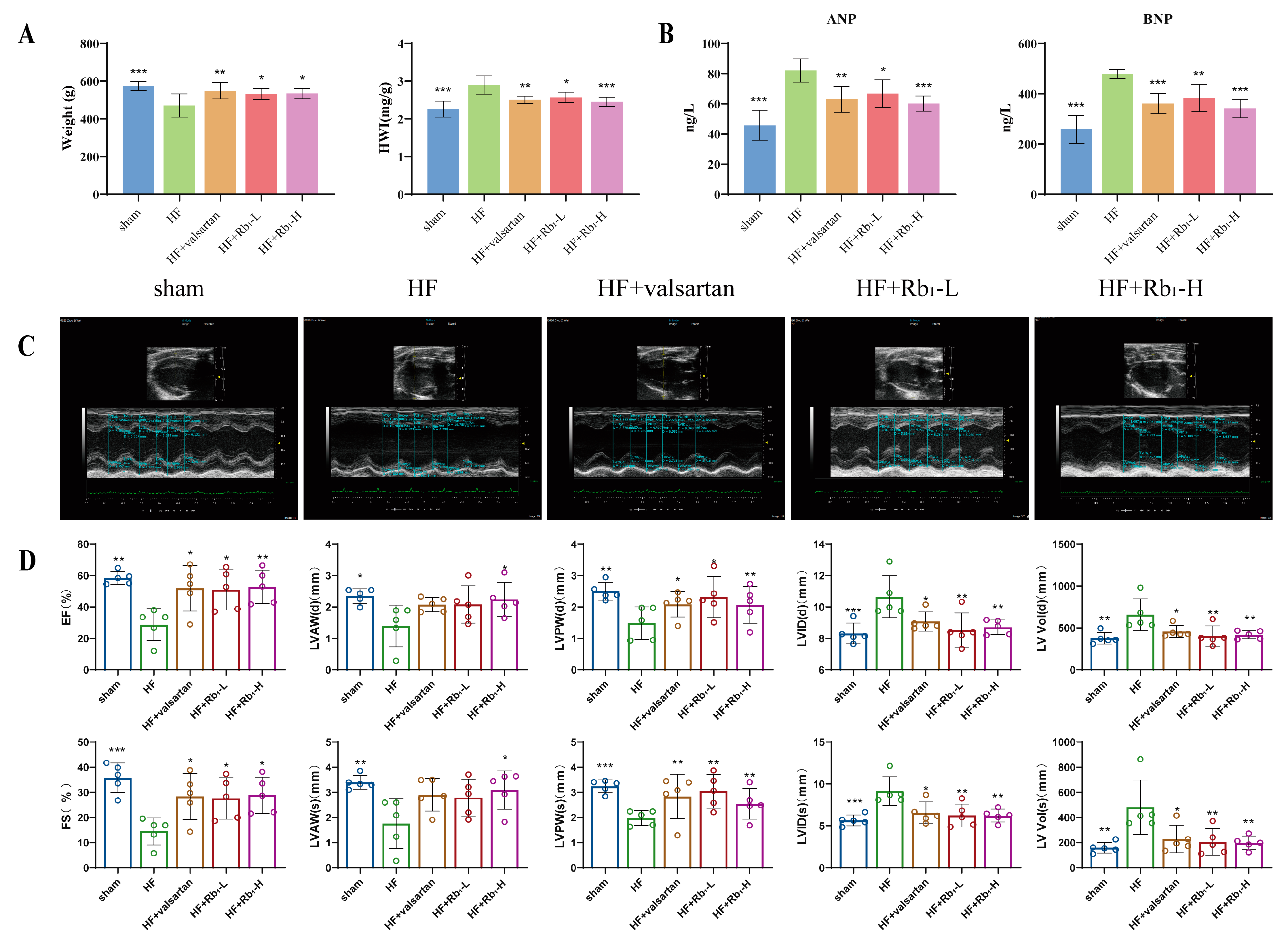
2.1. Ginsenoside Rb1 Can Improve Cardiac Function Damage in Rats with HF
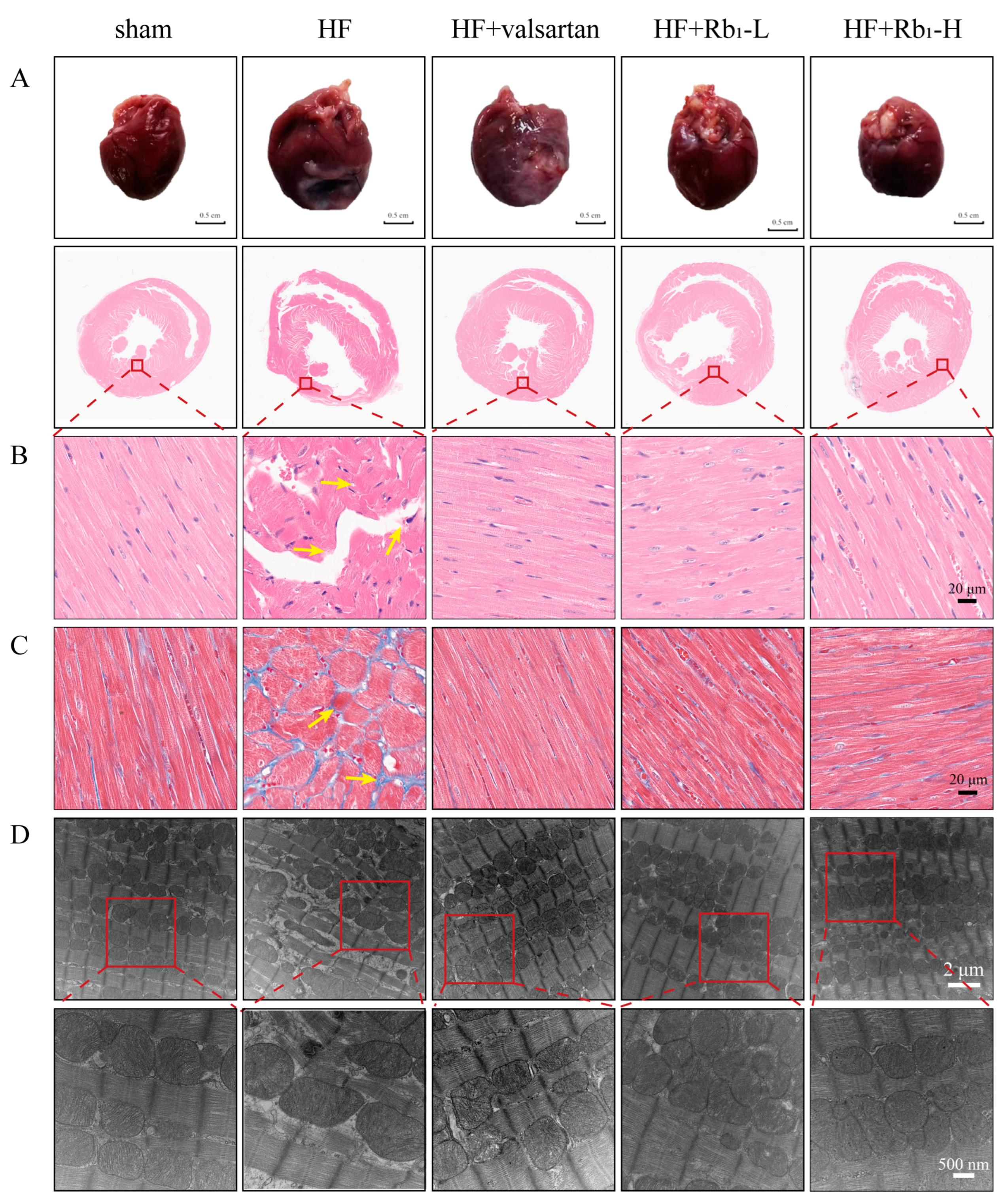
2.2. Ginsenoside Rb1 Can Improve the Pathological Changes in the Left Ventricle of Rats with HF
2.3. Ginsenoside Rb1 Can Improve the Myocardial Mitochondrial Ultrastructure in Rats with HF
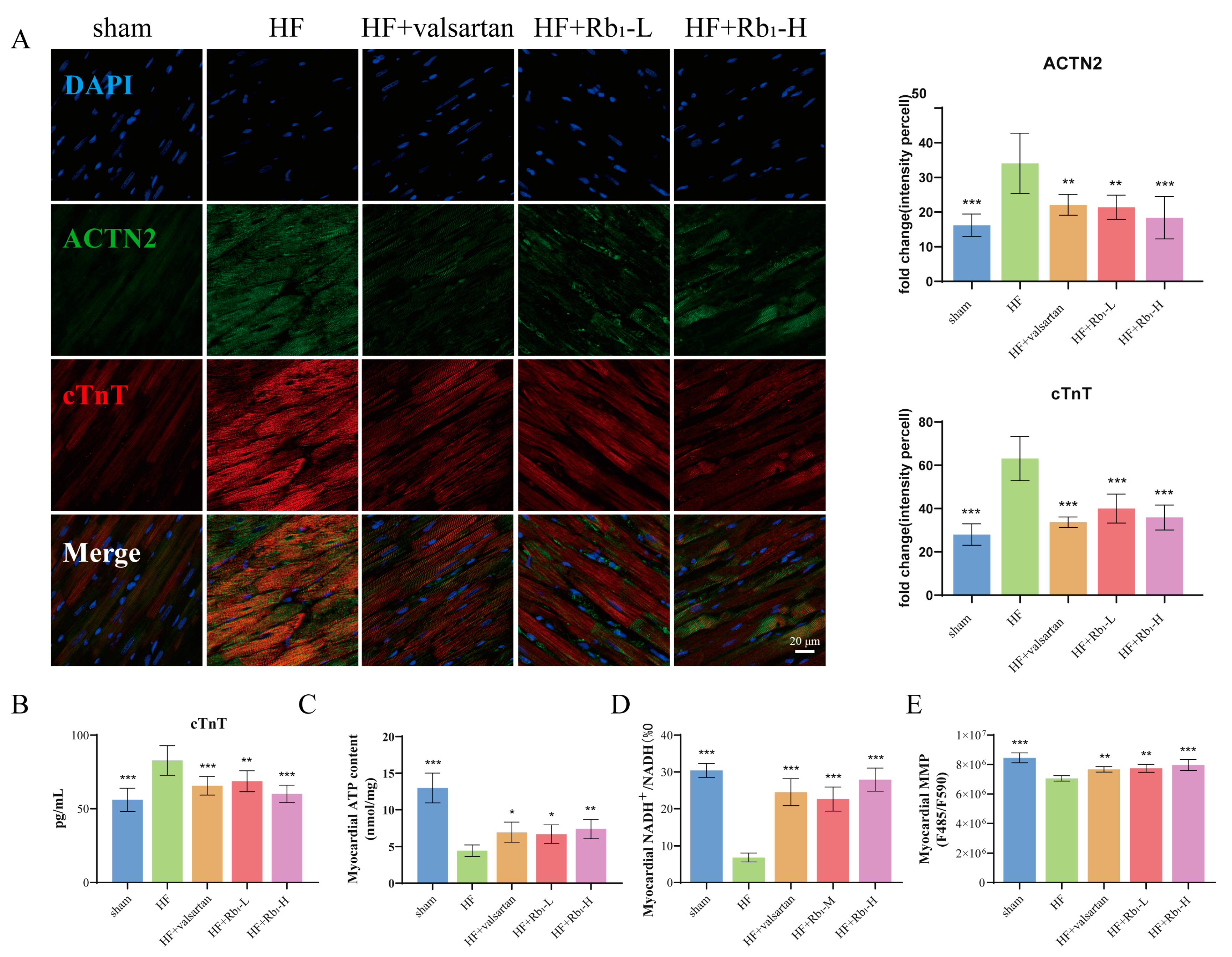
2.4. Ginsenoside Rb1 Can Reduce the Expression of cTnT and ACTN2 in Rats with HF
2.5. Ginsenoside Rb1 Can Improve Myocardial ATP Content, ETC Productivity Efficiency, and MMP Level in Rats with HF
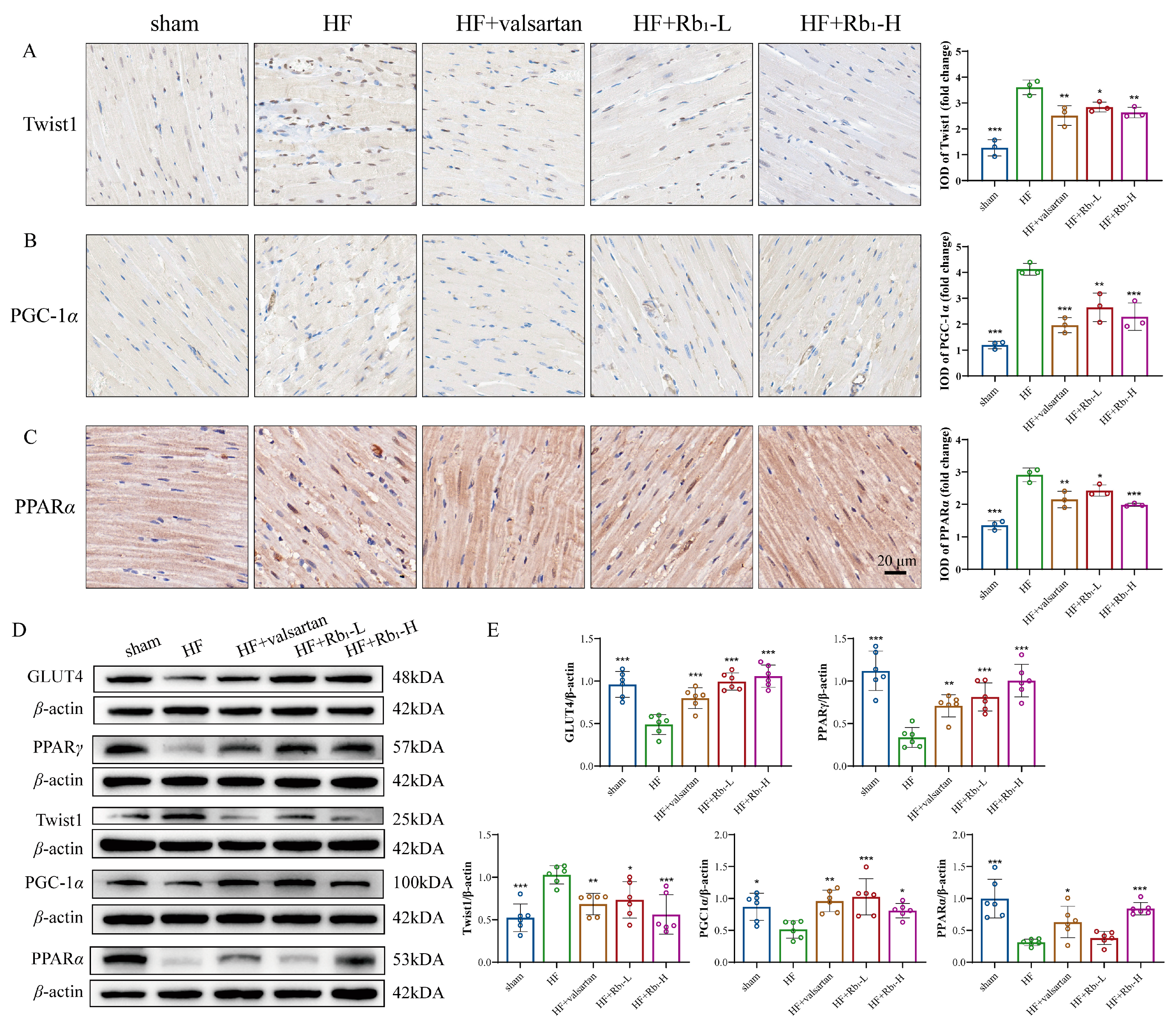
2.6. Ginsenoside Rb1 Improves Myocardial Energy Metabolism in HF by Inhibiting Twist1 and Activating PGC-1α
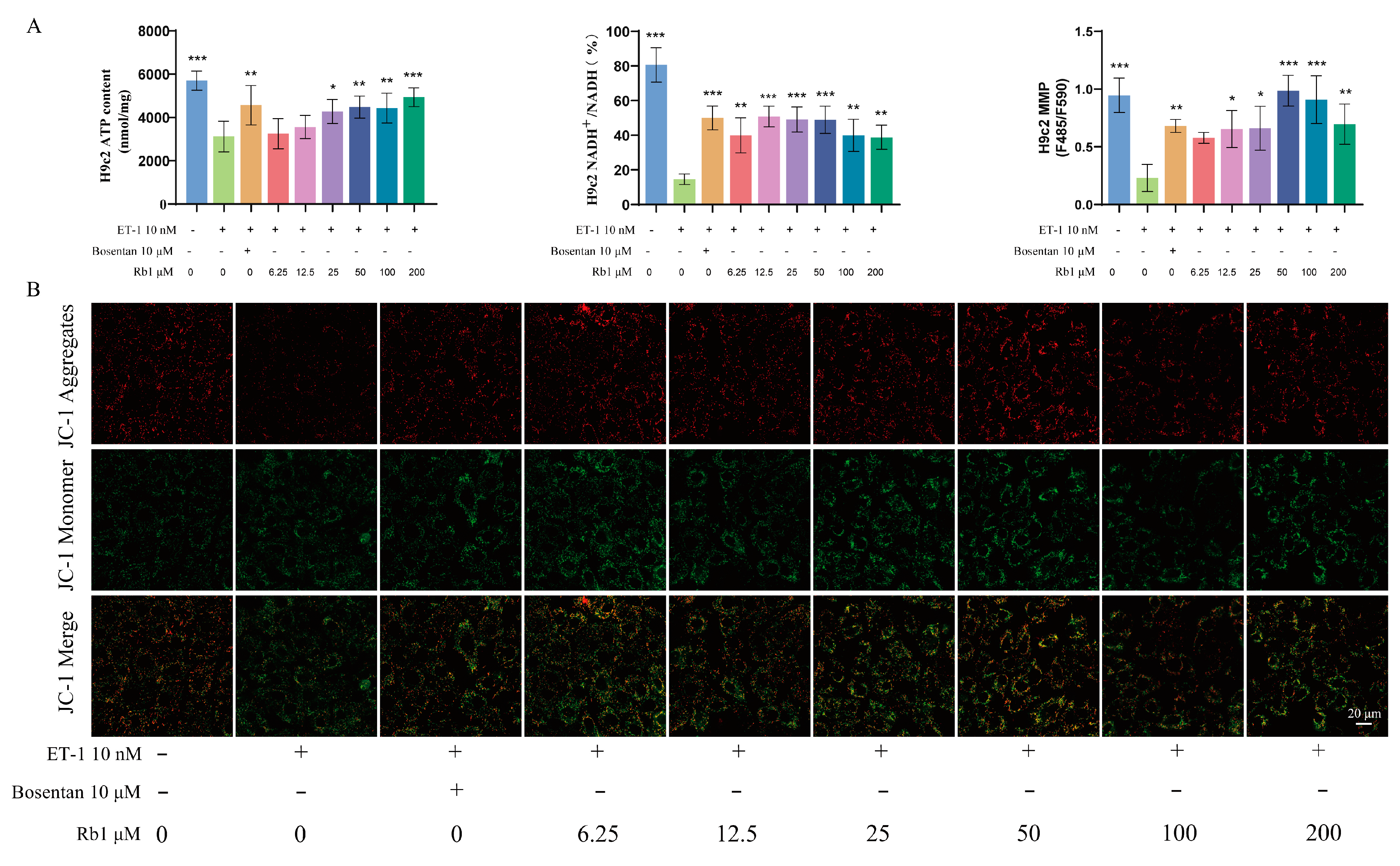
2.7. Ginsenoside Rb1 Can Improve the ATP Content, ETC Productivity Efficiency, and MMP Level in H9c2 Cells
2.8. Ginsenoside Rb1 Improves the Energy Metabolism of Injured H9c2 Cells by Regulating the Twist1/PGC-1α/PPARα Signaling Pathway
2.9. Molecular Docking
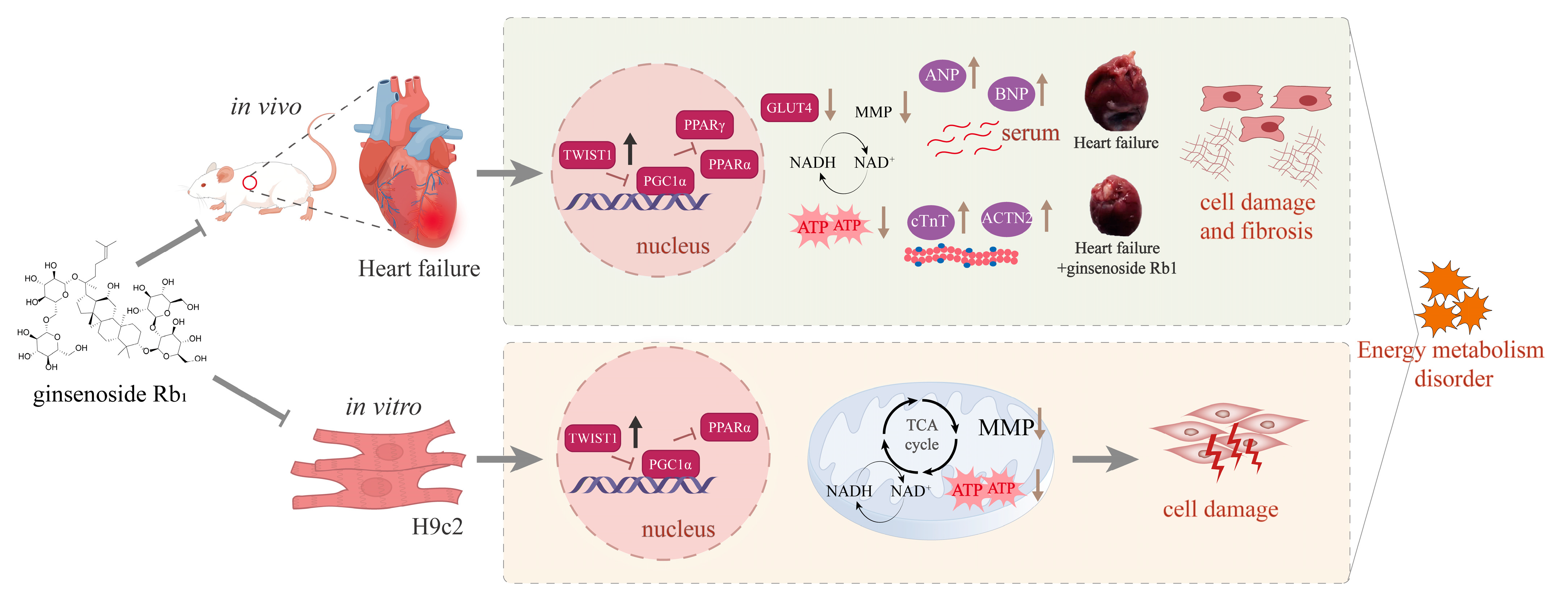
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Animal Models and Experimental Groups
4.3. Echocardiographic Detection
4.4. Animal Tissue Harvesting
4.5. Histopathological Examination
4.6. Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.7. Cell Culture
4.8. Cell Proliferation
4.9. Detection of Mitochondrial Structure and Function
4.9.1. Ultrastructure of Myocardial Mitochondria Was Observed by Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.9.2. Changes in Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.9.3. Detection of the Productivity Efficiency of ETC
4.9.4. ATP Level Detection
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Molecular Docking of Ginsenoside Rb1 with Key Targets
4.12. ELISA Measurement
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTN2 | Recombinant Actinin Alpha 2 |
| ANP | atrial natriuretic peptide |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BNP | brain natriuretic peptide |
| CMC-Na | sodium carboxymethyl cellulose |
| cTnT | cardiac troponin T |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| EF | ejection fraction |
| ET-1 | endothelin-1 |
| ETC | mitochondrial electron transfer chain |
| FS | fractional shortening |
| GLUT4 | glucose transporter 4 |
| HE | hematoxylin–eosin |
| HF | heart failure |
| HWI | heart weight index |
| JC-1 | 5,5′,6,6′-Tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine iodide |
| LVAW(d) | Left ventricular end-diastolic anterior wall thickness |
| LVAW(s) | Left ventricular end-systolic anterior wall thickness |
| LVID(d) | Left ventricular end-diastolic internal diameter |
| LVID(s) | Left ventricular end-systolic internal diameter |
| LVPW(d) | Left ventricular end-diastolic posterior wall thickness |
| LVPW(s) | Left ventricular end-systolic posterior wall thickness |
| LV Vol(d) | Left ventricular end-diastolic volume |
| LV Vol(s) | Left ventricular end-systolic volume |
| MI | myocardial infarction |
| MMP | mitochondrial membrane potential |
| NADH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α |
| PPARα | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| PPARs | proliferator-activated receptors |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SGLT2i | sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor |
| TCA cycle | tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| Twist1 | Twist homolog 1 |
References
- Savarese, G.; Becher, P.M.; Lund, L.H.; Seferovic, P.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Coats, A.J.S. Global burden of heart failure: A comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 118, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, M.C.; Campora, A.; Mandoli, G.E.; Lisi, M.; Benfari, G.; Ilardi, F.; Malagoli, A.; Sperlongano, S.; Henein, M.Y.; Cameli, M.; et al. Stress echocardiography in heart failure patients: Additive value and caveats. Heart Fail. Rev. 2024, 29, 1117–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, A.; di Mauro, G.; Cappetta, D.; De Angelis, A.; Torella, D.; Urbanek, K.; Berrino, L.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Capuano, A.; Rossi, F. Current and future therapeutic perspective in chronic heart failure. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, C. Heart failure: A major public health problem. Presse Med. 2024, 53, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, F. Vericiguat for the Treatment of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction Following a Worsening Heart Failure Event: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis from the Perspective of Chinese Healthcare Providers. Clin. Drug Investig. 2023, 43, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Tian, R. Mitochondrial dysfunction in pathophysiology of heart failure. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3716–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.E.; Arias-Durán, C.; Ávalos-Guajardo, Y.; Aedo, G.; Verdejo, H.E.; Parra, V.; Lavandero, S. Emerging role of mitophagy in cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Mol. Aspects Med. 2020, 71, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedkova, E.N.; Seidlmayer, L.K.; Blatter, L.A. Mitochondria-mediated cardioprotection by trimetazidine in rabbit heart failure. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2013, 59, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouquet, F.; Rousseau, D.; Domergue-Dupont, V.; Grynberg, A.; Liao, R. Effects of trimetazidine, a partial inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation, on ventricular function and survival after myocardial infarction and reperfusion in the rat. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 24, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Lu, K.; Zong, G.; Xia, Y.; Han, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Y. Ginseng polysaccharides: Potential antitumor agents. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y. Therapeutic Potential of Ginsenoside Rb1-PLGA Nanoparticles for Heart Failure Treatment via the ROS/PPARα/PGC1α Pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Liu, Z.; Xie, J.; Yu, C.-Y.; Wei, H. Enhancing myocardial infarction treatment through bionic hydrogel-mediated spatial combination therapy via mtDNA-STING crosstalk modulation. J. Control. Release 2024, 371, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Chang, X. Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates heart failure through DUSP-1-TMBIM-6-mediated mitochondrial quality control and gut flora interactions. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, S.-Y.; Liu, D.-H.; Wu, L.; Yu, X.-G.; Wang, M.; Shi, G.-Y.; Wen, R.-H.; Zhou, B.; Hao, B.-S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 Ameliorates Age-Related Myocardial Dysfunction by Regulating the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Zeng, J.; Wen, M.; Pan, L.; Lv, D.; Liu, M.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 promotes the activation of PPARα pathway via inhibiting FADD to ameliorate heart failure. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 947, 175676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, E.L.; Yutzey, K.E. Twist1 function in endocardial cushion cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation during heart valve development. Dev. Biol. 2008, 317, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Tong, H.; Lang, J. Fucoxanthin Mitigates High-Fat-Induced Lipid Deposition and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle through Inhibiting PKM1 Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 18013–18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, U.P.; Pichiah, P.B.T.; Arunachalam, S. Adriamycin downregulates the expression of KLF4 in cardiomyocytes in vitro and contributes to impaired cardiac energy metabolism in Adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. 3 Biotech. 2023, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ning, X.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, F.; Bai, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, S. Twist1 downregulation of PGC-1α decreases fatty acid oxidation in tubular epithelial cells, leading to kidney fibrosis. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3758–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, e876–e894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhor, M.; Law, W.; Pavlovic, M.; Aksentijevic, D.; McGrath, K.; McClements, L. Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers reflective of cardiac remodelling in diabetes mellitus: A scoping review. Diabet. Med. 2023, 40, e15064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Z.; Matos Pires, N.M.; Lin, Q.; Jing, W.; Zhao, L.; Wei, X.; Jiang, Z. Advances in heart failure monitoring: Biosensors targeting molecular markers in peripheral bio-fluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 255, 116090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta-Aho, J.; Olive, M.; Vandroux, M.; Roticiani, G.; Dominguez, C.; Johari, M.; Torella, A.; Böhm, J.; Turon, J.; Nigro, V.; et al. Mutation update for the ACTN2 gene. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, H.; Guo, F.; Yu, Y.; Wei, J.; Geng, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Yang, H. Identification of active components in Yixinshu Capsule with protective effects against myocardial dysfunction on human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes by an integrative approach. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, B.; Song, L.; Hu, L.; Guo, D.; Ren, G.; Peng, T.; Liu, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; et al. Cardiac-specific overexpression of Ndufs1 ameliorates cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction by alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-Q.; Han, Y.-Y.; Gao, F.; Tian, J.-Y.; Bai, R.; Guo, Q.-H.; Liu, X.-C. Shengxian decoction protects against chronic heart failure in a rat model via energy regulation mechanisms. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-Q.; Xiao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, Z.-G.; Liao, H.-H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.-X.; Yang, Z.; Deng, W.; Tang, Q.-Z. Mechanisms contributing to cardiac remodelling. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2319–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Tian, R.; Wende, A.R.; Abel, E.D. Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1487–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, X.; Hu, Y.; Fan, X. Chemical constituents of Panax ginseng and Panax notoginseng explain why they differ in therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, D.; Wu, T.; Lee, H.; Zheng, F.; Dai, Y.; Yue, H. A novel glycopeptide from mountain-cultivated ginseng residue protects type 2 diabetic symptoms-induced heart failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 336, 118723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Gong, M. Overview of Panax ginseng and its active ingredients protective mechanism on cardiovascular diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 334, 118506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Han, H.; Shan, X.; Zhao, P.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Xu, M.; Lu, R.; Guo, W. Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates lipotoxicity-induced myocardial injury in diabetes mellitus by regulating Mfn2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 974, 176609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.-l.; Li, Z.-q.; Zhao, Y.-j.; Zhao, S.-m.; Zhu, L.; Li, T.; Fu, Y.; Li, H.-j. Ginsenoside Rb1 protects cardiomyocytes against CoCl2-induced apoptosis in neonatal rats by inhibiting mitochondria permeability transition pore opening. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yan, W.; Gao, E.; Cheng, H.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; et al. Branched chain amino acids exacerbate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion vulnerability via enhancing GCN2/ATF6/PPAR-α pathway-dependent fatty acid oxidation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5623–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B.M. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xing, Y.; Ning, X.; Yu, Z.; Bai, X.; Liu, L.; Sun, S. Roles of Twist1 in lipid and glucose metabolism. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Fujimoto, M.; Lopes, A.; Wang, Y.-X. Twist-1 is a PPARdelta-inducible, negative-feedback regulator of PGC-1alpha in brown fat metabolism. Cell 2009, 137, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonhögen, I.G.C.; El Azzouzi, H.; Olieslagers, S.; Vasilevich, A.; de Boer, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; da Costa Martins, P.A.; de Windt, L.J.; Murri, M. MiR-337-3p Promotes Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting TWIST1. Cells 2020, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhong, W.; Li, M.; Zong, S.; Li, M.; Tao, H.; et al. Thymidine phosphorylase promotes malignant progression in hepatocellular carcinoma through pentose Warburg effect. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Li, Z.Q.; Kong, J.J. Effect and mechanism of miR-223 on fibrosis-related signaling pathway in rat cardiomyocytes. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 100, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Kim, H.R.; Xing, R.; Hsiao, S.; Mammoto, A.; Chen, J.; Serbanovic-Canic, J.; Feng, S.; Bowden, N.P.; Maguire, R.; et al. TWIST1 Integrates Endothelial Responses to Flow in Vascular Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Q.; Liu, M.; Sun, S. Emerging role of Twist1 in fibrotic diseases. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Wirrig, E.E.; Hinton, R.B.; Merrill, W.H.; Spicer, D.B.; Yutzey, K.E. Twist1 promotes heart valve cell proliferation and extracellular matrix gene expression during development in vivo and is expressed in human diseased aortic valves. Dev. Biol. 2010, 347, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, H.; Yin, L.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. The paired-related homeobox protein 1 promotes cardiac fibrosis via the Twist1-Prrx1-tenascin-C loop. Cell Biol. Int. 2023, 47, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Guo, F.; Zhang, M.; Xian, M.; Wang, T.; Gao, J.; Wu, H.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Signature-oriented investigation of the efficacy of multicomponent drugs against heart failure. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Xian, M.; Wang, T.; Wu, H.; Wei, J.; Huang, Y.; Cui, X.; Wu, S.; et al. Yi-Xin-Shu capsule ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy by regulating RB/HDAC1/GATA4 signaling pathway based on proteomic and mass spectrometry image analysis. Phytomedicine 2022, 103, 154185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Morgunova, E.; Naqvi, S.; Goovaerts, S.; Bader, M.; Koska, M.; Popov, A.; Luong, C.; Pogson, A.; Swigut, T.; et al. DNA-guided transcription factor cooperativity shapes face and limb mesenchyme. Cell 2024, 187, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Song, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Gong, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 Ameliorates Heart Failure Ventricular Remodeling by Regulating the Twist1/PGC-1α/PPARα Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040500
Zhou Z, Song Z, Guo X, Wang Q, Li M, Zhang M, Gong M. Ginsenoside Rb1 Ameliorates Heart Failure Ventricular Remodeling by Regulating the Twist1/PGC-1α/PPARα Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040500
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ziwei, Zhimin Song, Xiaomeng Guo, Qi Wang, Meijing Li, Minyu Zhang, and Muxin Gong. 2025. "Ginsenoside Rb1 Ameliorates Heart Failure Ventricular Remodeling by Regulating the Twist1/PGC-1α/PPARα Signaling Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040500
APA StyleZhou, Z., Song, Z., Guo, X., Wang, Q., Li, M., Zhang, M., & Gong, M. (2025). Ginsenoside Rb1 Ameliorates Heart Failure Ventricular Remodeling by Regulating the Twist1/PGC-1α/PPARα Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040500





