Design, Synthesis, and In Silico Studies of New Norfloxacin Analogues with Broad Spectrum Antibacterial Activity via Topoisomerase II Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
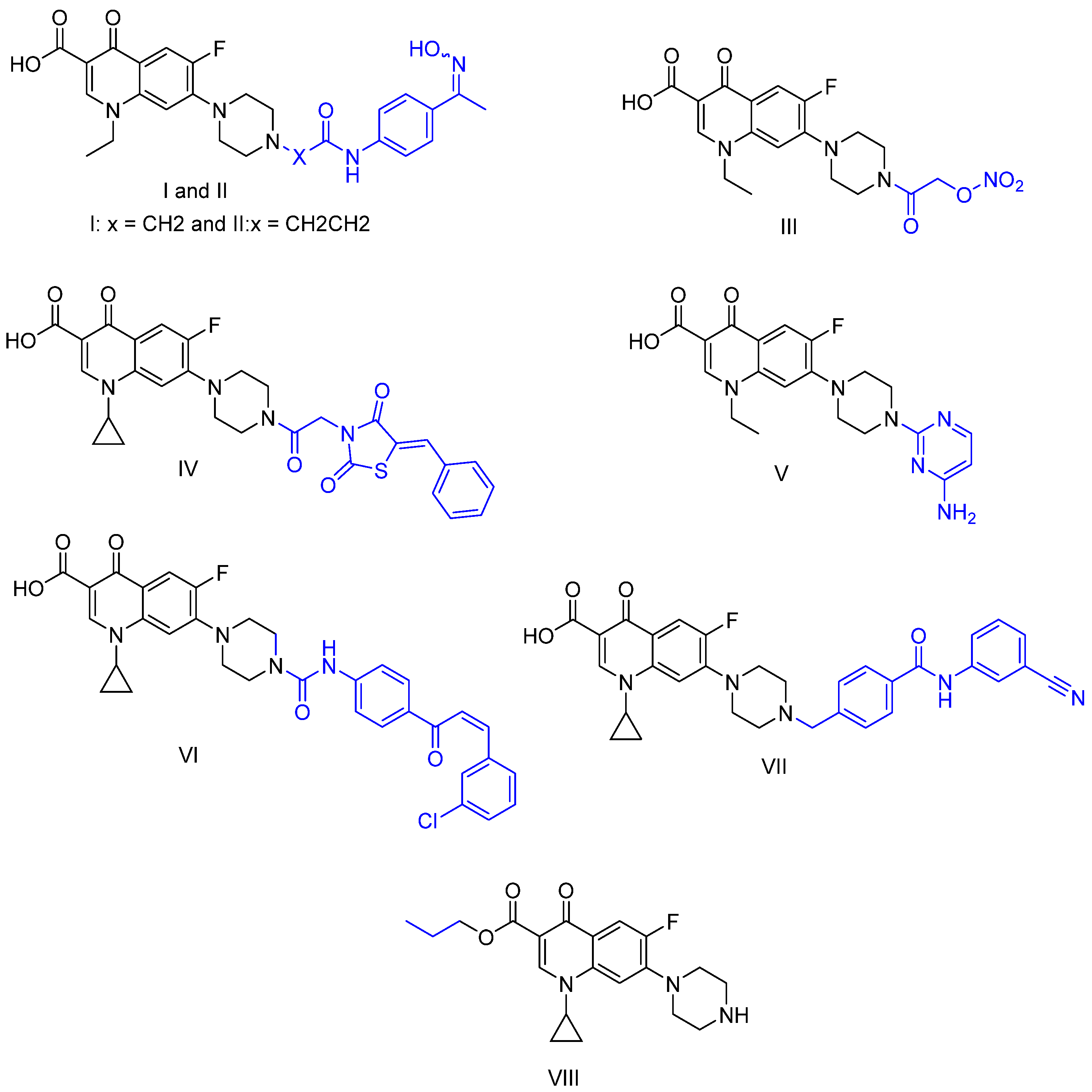
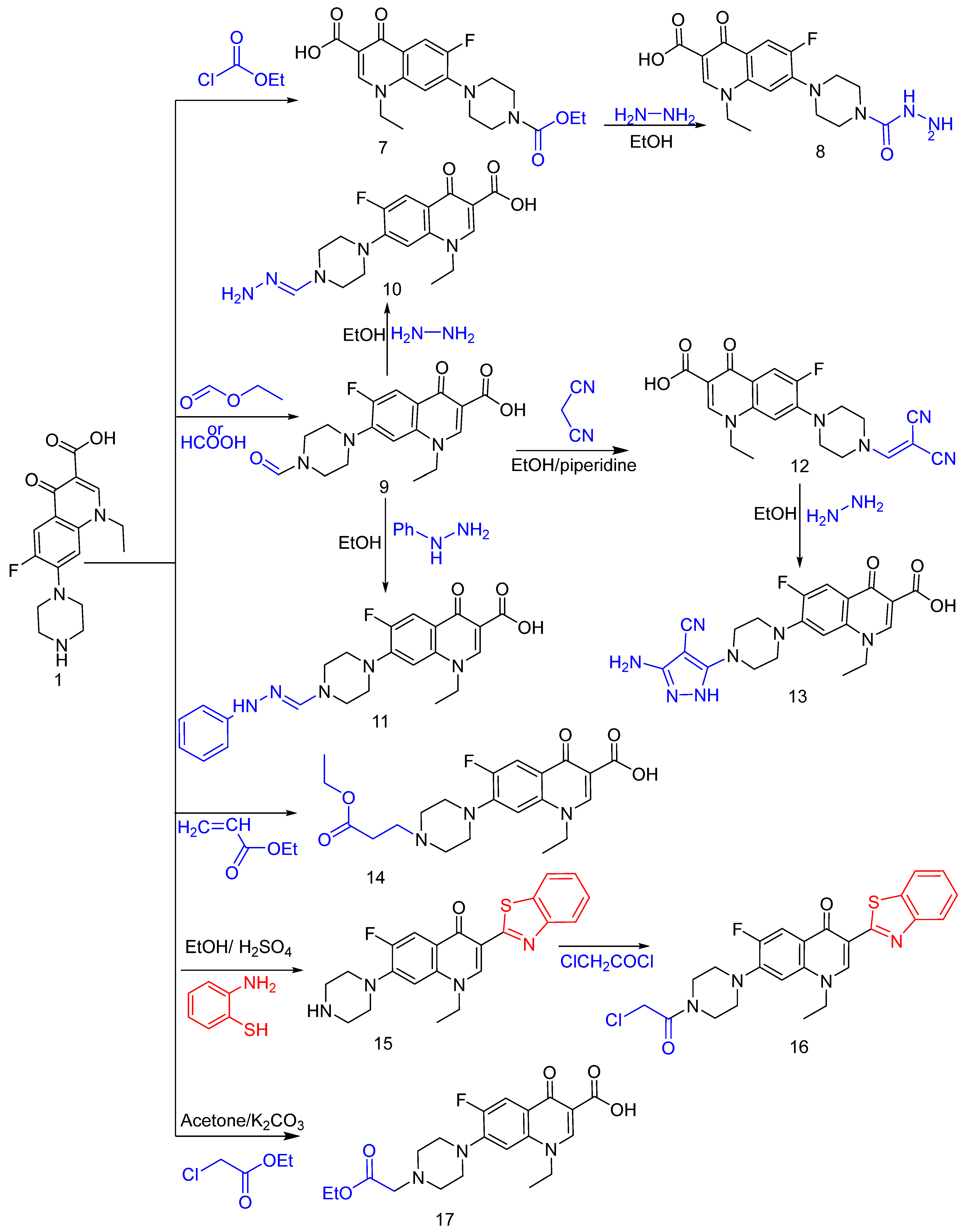
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Screening
2.2.1. Antimicrobial Evaluation
2.2.2. Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR)
2.2.3. DNA Cleavage Assay
2.2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. In Silico Studies
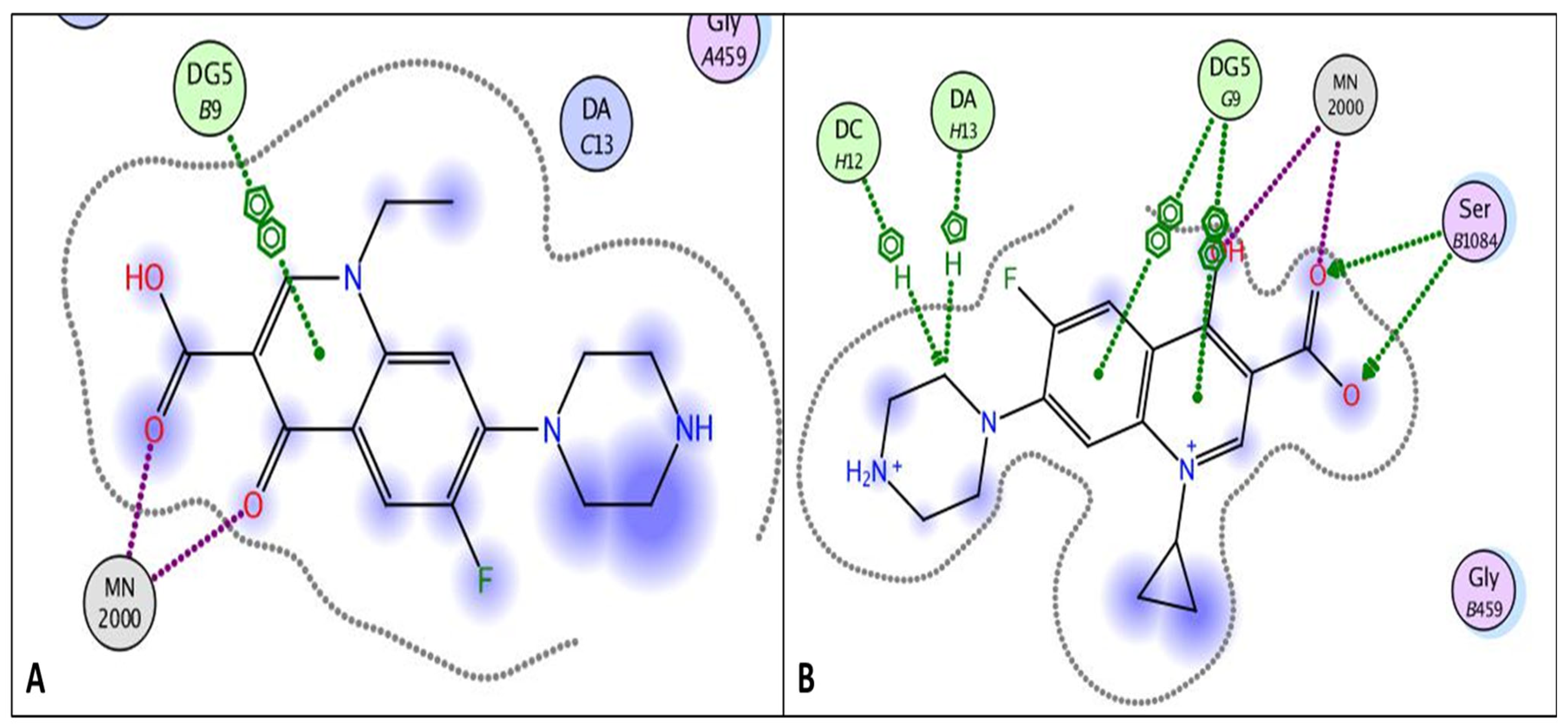
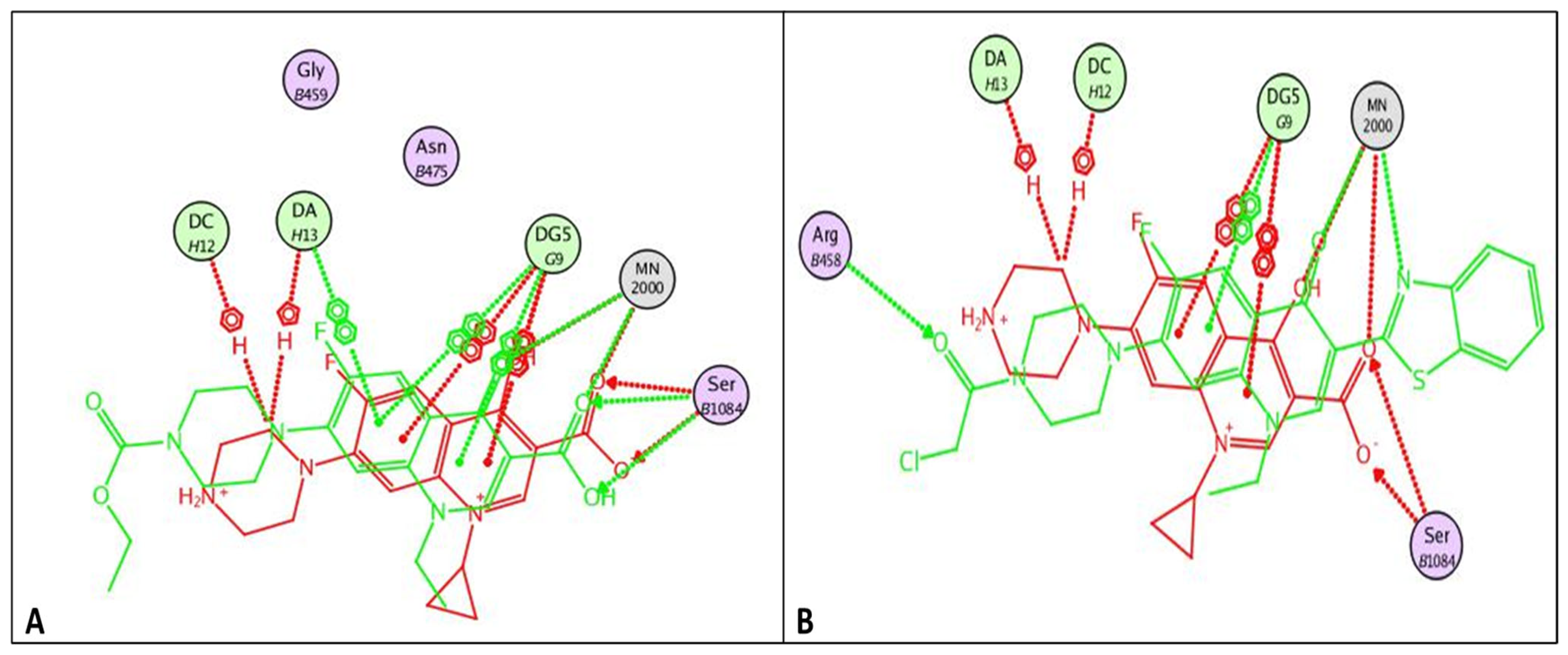
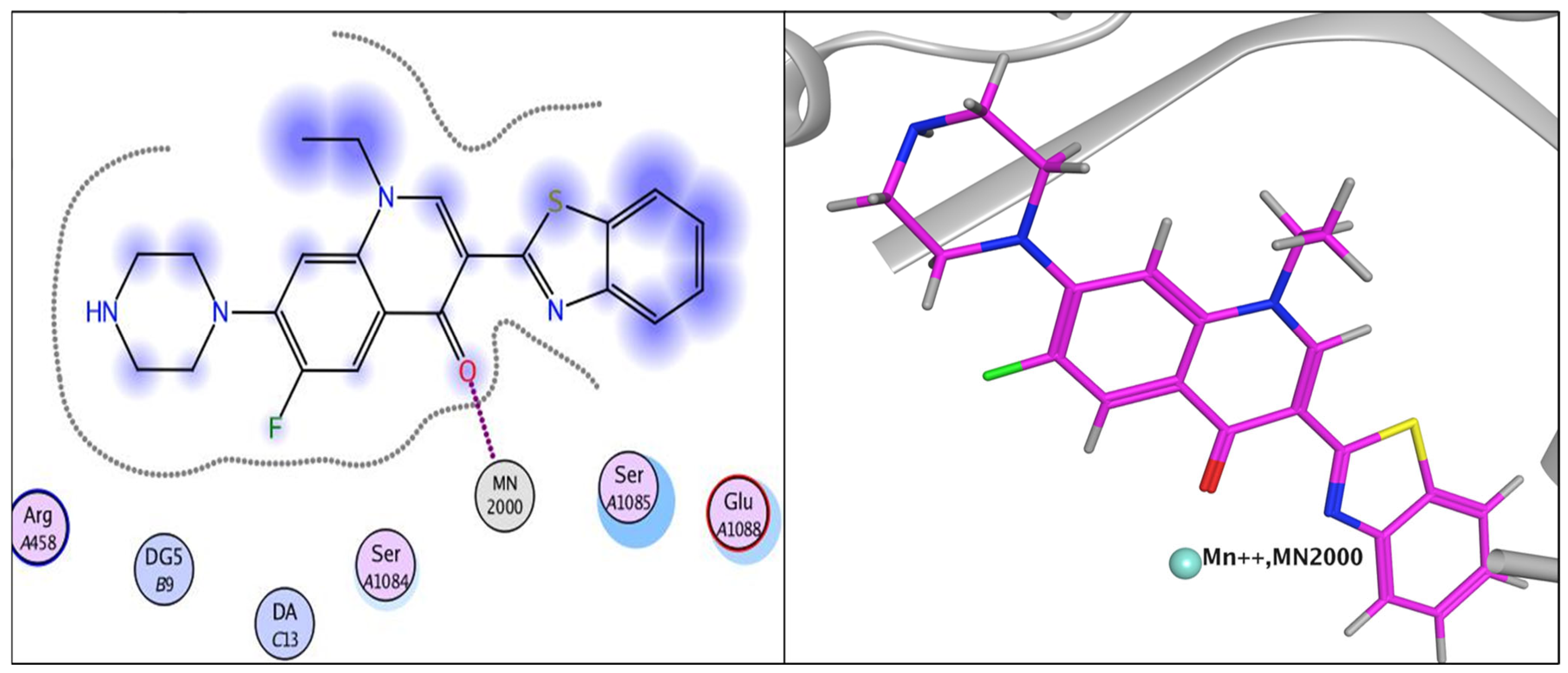
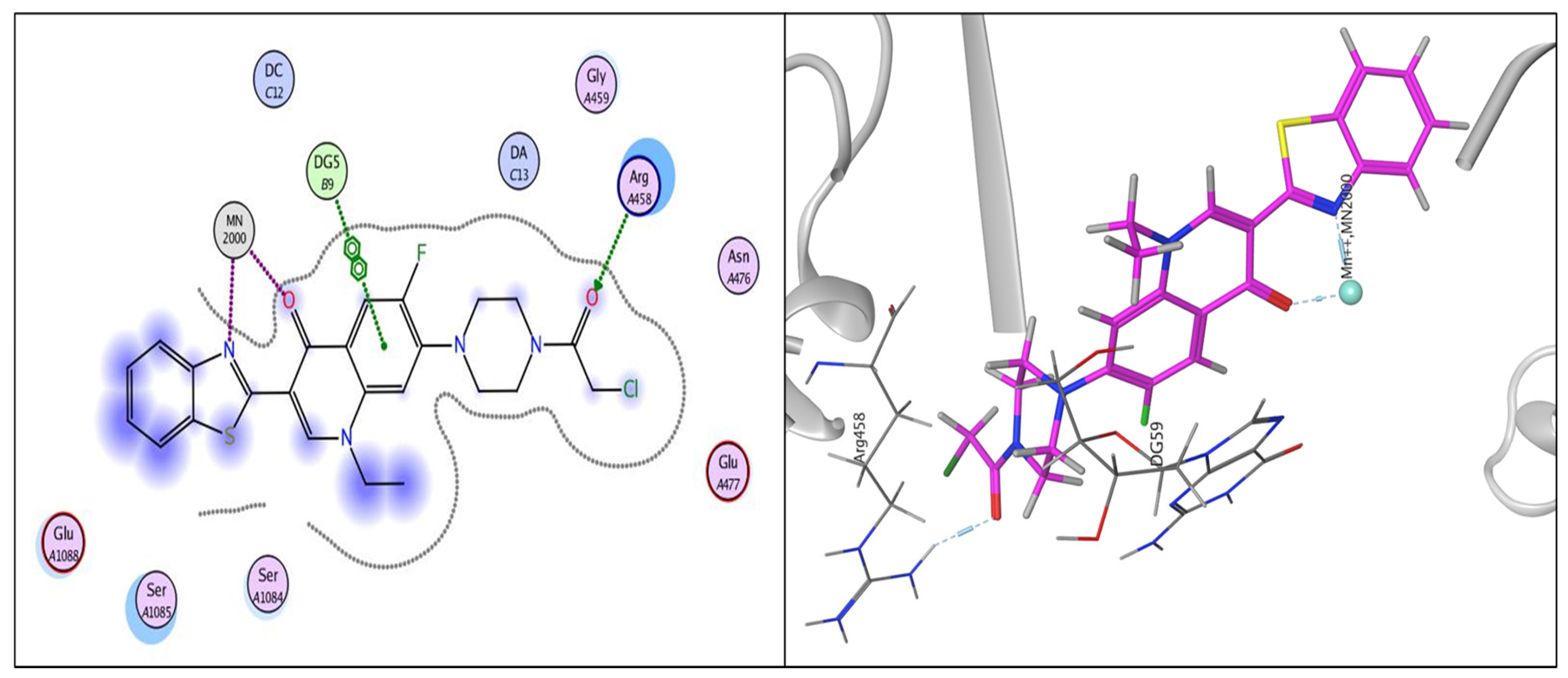
2.3.1. Docking Study
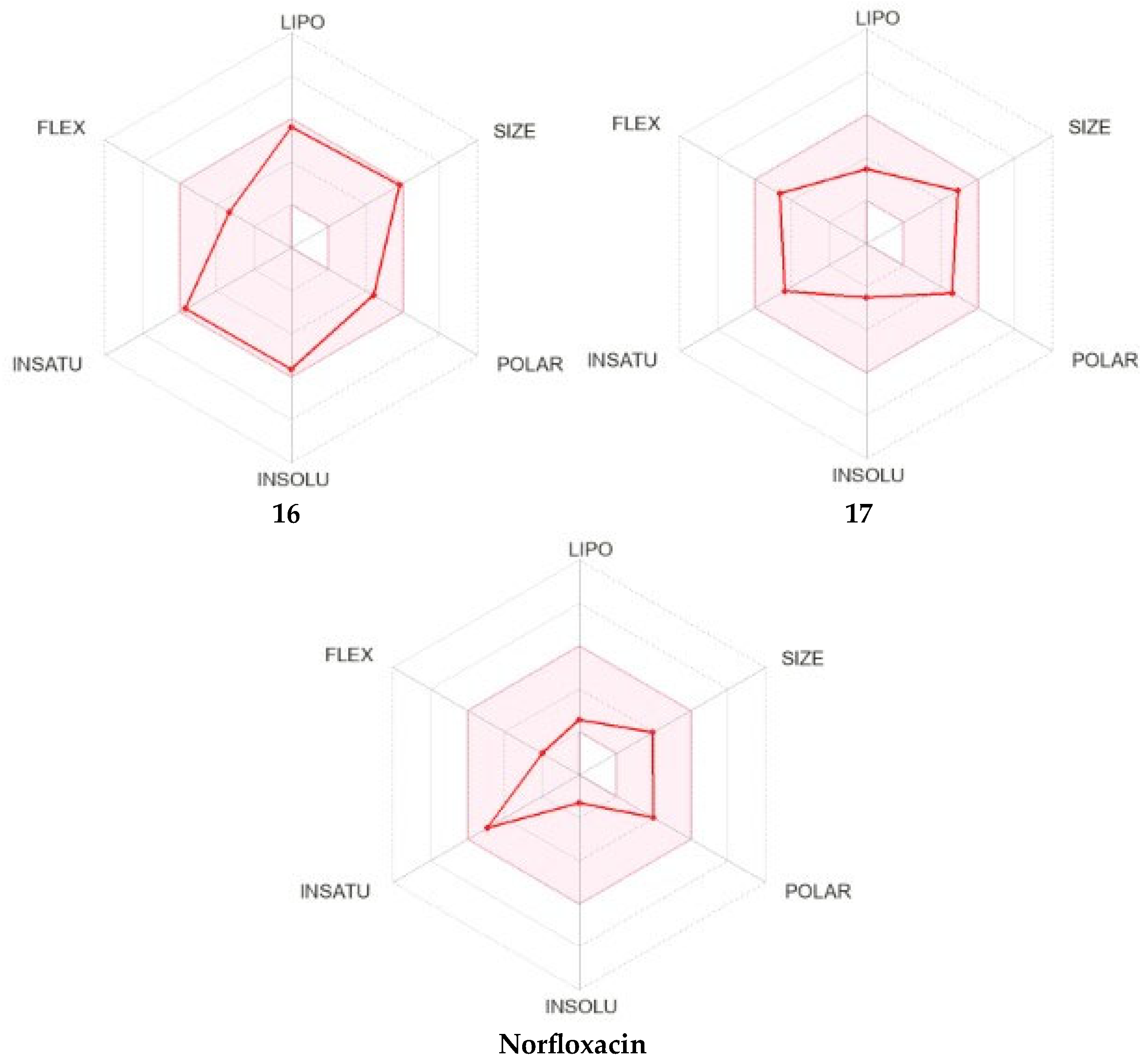
2.3.2. Physicochemical and Pharmacokinetic Prediction
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemistry
- Synthesis of compound 2
- 7-(4-(2-Chloroacetyl) piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 2
- Synthesis of compound 3
- 7-(4-(Aminoglycyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 3.
- Synthesis of compound 4
- 7-(4-((Benzylidene-amino)glycyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 4
- Synthesis of compound 5
- 7-(4-(2-(3-amino-4-cyano-5-phenyl-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)acetyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 5
- Synthesis of compound 6
- 7-(4-(2-Cyanoacetyl) piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 6
- Synthesis of compound 7
- 7-(4-(Ethoxy carbonyl) piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 7
- Synthesis of compound 8
- 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-(hydrazinecarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 8
- Synthesis of compound 9
- 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-formylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 9
- Synthesis of compound 10
- 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-(hydrazonomethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 10
- Synthesis of compound 11
- 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(4-((2-phenylhydrazono)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydro-quinolin-3-carboxylic acid 11
- Synthesis of compound 12
- 7-(4-(2,2-Dicyanovinyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 12
- Synthesis of compound 13
- 7-(4-(3-Amino-4-cyano-1H-pyrazol-5-yl) piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquin-oline-3-carboxylic acid 13
- Synthesis of compound 14
- 7-(4-(3-Ethoxy-3-oxopropyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinolin-3-carboxylic acid 14
- Synthesis of compound 15
- 3-(Benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(piperazin-1-yl)quinolin-4(1H)-one 15
- Synthesis of compound 16
- 3-(Benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-7-(4-(2-chloroacetyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoroquinolin-4(1H)-one 16
- Synthesis of compound 17
- 7-(4-(2-Ethoxy-2-oxoethyl) piperazin-1-yl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-3-carboxylic acid 17
3.2. Biological Evaluations
3.2.1. Screening of Antibacterial Activity
Microbial Strains and Culture Conditions
Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
3.2.2. Topoisomerase II Inhibition Assays
S. aureus Gyrase Supercoiling Assay
S. aureus Topoisomerase IV Decatenation Assay
3.2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.2.4. In Silico Studies
Docking Studies
Physicochemical and Pharmacokinetic Prediction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blondeau, J.M. The role of fluoroquinolones in skin and skin structure infections. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Legout, L.; Senneville, E.; Stern, R.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Savage, C.; Roussel-Delvalez, M.; Rosele, B.; Migaud, H.; Mouton, Y. Treatment of bone and joint infections caused by Gram-negative bacilli with a cefepime–fluoroquinolone, combination. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.R.; Hershberger, E.; Zervos, M.J. The role of fluoroquinolones in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infection. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2002, 4, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, R.K.; Jyoti, U.; Patil, R.K.; Patil, H.C. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: An overview. Adesh University. J. Med. Sci. Res. 2020, 2, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jasper, A.S.; Musuuza, J.S.; Tischendorf, J.S.; Stevens, V.W.; Gamage, S.D.; Osman, F.; Safdar, N. Are fluoroquinolones or macrolides better for treating Legionella pneumonia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Qurban, F.; Shahzad, S.A.; Khaskheli, M.S.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, S.A.; Rauf, W.; Islam, S.; Mannan, A. Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel norfloxacin analogs as potent anticancer and antioxidant agents. Future Med. Chem. 2024, 16, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Moustafa, G.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Hauk, G.; Siva Krishna, V.; Sriram, D.; Berger, J.M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E. New fluoroquinolones/nitric oxide donor hybrids: Design, synthesis and antitubercular activity. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, H.A.; Moustafa, G.A.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.; Rabea, S.M.; Hauk, G.; Krishna, V.S.; Sriram, D.; Berger, J.M.; Abbas, S.H. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of new nitric oxide-donating fluoroquinolone/oxime hybrids. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 354, 2000180. [Google Scholar]
- Bustos-Hamdan, A.; Bracho-Gallardo, J.I.; Hamdan-Partida, A.; Bustos-Martínez, J. Repositioning of Antibiotics in the Treatment of Viral Infections. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, H.A.; El-Saghier, A.M.; Badr, M.; Elsadek, B.E.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.; Shoman, M.E. Design, synthesis and mechanistic study of N-4-Piperazinyl Butyryl Thiazolidinedione derivatives of ciprofloxacin with Anticancer Activity via Topoisomerase I/II inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24101. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah, J.; Skinner-Adams, T.; Davis, T.M. In vitro antimalarial activity of trovafloxacin, a fourth-generation fluoroquinolone. Acta. Trop. 2000, 74, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaki, M.; Iwasawa, A.; Soda, M.; Yaguchi, S.; Koide, R. Cytotoxicity of five fluoroquinolone and two nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory benzalkonium chloride-free ophthalmic solutions in four corneo-conjunctival cell lines. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 20, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, S.B.; Orr, P.G.; Mazzola, J.L.; Brush, D.E.; Boyer, E.W. Levofloxacin-related seizure activity in a patient with Alzheimer’s disease: Assessment of potential risk factors. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 25, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Topoisomerase inhibitors: Fluoroquinolone mechanisms of action and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, 025320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettsch, W.; Van Pelt, W.; Nagelkerke, N.; Hendrix, M.G.; Buiting, A.G.; Petit, P.L.; Sabbe, L.J.; Van Griethuysen, A.J.; De Neeling, A.J. Increasing resistance to fluoroquinolones in Escherichia coli from urinary tract infections in the Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganduh, S.H. Spectrophotometric determination of metoclopramide-HCL in the standard raw and it compared with pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Negat. Results 2021, 12, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Nagshetty, K.; Manjula, N.G.; Math, G.C.; Mohan, A.S.; Shivannavar, C.T.; Gaddad, S.M. Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Other Antimicrobials in Culture—Positive Salmonella typhi Isolates in Gulbarga, South India. Adv. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, J., Jr.; Fish, D. The safety profile of the fluoroquinolones. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 798–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakkani, M.F.; Ahmed, N.; Abbas, A.A.; Hassan, M.H.; Aziz, H.A.; Elshamsy, A.M.; Khalifa, H.O.; Abdelshakour, M.A.; Saddik, M.S.; Elsayed, M.M.; et al. Synthesis, Physicochemical Characterization using a Facile Validated HPLC Quantitation Analysis Method of 4-Chloro-phenylcarbamoyl-methyl Ciprofloxacin and Its Biological Investigations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwatuyi, M.; Kaatz, G.W.; Gibbons, S. Antibacterial and resistance modifying activity of Rosmarinus officinalis. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokaber-Esfahani, M.; Eshghi, H.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Gholizadeh, M.; Mirzaie, Y.; Hakimi, M.; Lari, J. Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of New Pyrimidyl N-Ciprofloxacin Derivatives. Chem. Select. 2019, 4, 8930–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; El-Saghier, A.M.; Badr, M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.; Shoman, M.E. Thiazolidine-2,4-dione-linked ciprofloxacin derivatives with broad-spectrum antibacterial, MRSA and topoisomerase inhibitory activities. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 1743–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lungu, I.A.; Moldovan, O.L.; Biriș, V.; Rusu, A. Fluoroquinolones hybrid molecules as promising antibacterial agents in the fight against antibacterial resistance. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroumadi, A.; Emami, S.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Rajaee, M.; Sokhanvar, K.; Moshafi, M.H.; Shafiee, A. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of N-(5-benzylthio-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl) and N-(5-benzylsulfonyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl) piperazinyl quinolone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 44, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.M.; Li, D.; Li, F.F.; Ansari, M.F.; Fang, B.; Zhou, C.H. Pyrimidine-conjugated fluoroquinolones as new potential broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 73, 128885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monica, G.; Gallo, A.; Bono, A.; Alamia, F.; Lauria, A.; Alduina, R.; Martorana, A. Novel Antibacterial 4-Piperazinylquinoline Hybrid Derivatives Against Staphylococcus aureus: Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro and In Silico Insights. Molecules 2024, 30, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peytam, F.; Norouzbahari, M.; Saadattalab, T.; Şanlıtürk, G.; Firoozpour, L.; Emamgholipour, Z.; Dogaheh, M.G.; Nikou, M.; Tehrani, M.B.; Bijanzadeh, H.R.; et al. Novel fluoroquinolones analogues bearing 4-(arylcarbamoyl)benzyl: Design synthesis, and antibacterial evaluation. Mol. Divers. 2024, 28, 1577–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaifan, G.A.; Mohammed, A.A. Fluoroquinolones structural and medicinal developments 2013–2018): Where are we now? Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3005–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; MMEl-Saghier, A.; AAbuo-Rahma, G.E.; Mai, E.S. Design Synthesis, Antibacterial Screening and Cytotoxicity Measurement of new N-4 piperazinyl Derivative of Ciprofloxacin. J. Pharm. Appl. Chem. 2022, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, H.A.; Moustafa, G.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Derayea, S.M.; Abuo, G.E. New norfloxacin/nitric oxide donor hybrids: Synthesis and nitric oxide release measurement using a modified Griess colorimetric method European. J. Chem. 2017, 8, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentese, M.Y.; Bayrak, H.; Uygun, Y.; Mermer, A.; Ulker, S.; Karaoglu, S.A.; Demirbas, N. Microwave assisted synthesis of some hybrid molecules derived from norfloxacin and investigation of their biological activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 67, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzgrabe, U.; Branch, S.K. 1H, 19F and 13C NMR spectral data of fifteen gyrase inhibitors and some metabolites. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1994, 32, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryhoriv, H.; Mariutsa, I.; Kovalenko, S.M.; Georgiyants, V.; Perekhoda, L.; Filimonova, N.; Geyderikh, O.; Sidorenko, L. The search for new antibacterial agents among 1,2,3–triazole functionalized ciprofloxacin and Norfloxacin hybrids: Synthesis, docking studies, and biological activity evaluation. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 90, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgrave, L.S.; Sutton, S.B.; Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J. Fluoroquinolone resistance: Mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, V.E.; Osheroff, N. Type II topoisomerases as targets for quinolone Antibacterials turning Dr. Jekyll into Mr. Hyde. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoux, J.J. DNA topoisomerases: Structure, function, and mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 369–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Badr, M.; Hassan, H.A.; Abdelhamid, D.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E. Novel 4-(piperazin-1-yl) quinolin-2 1H)-one bearing thiazoles with antiproliferative activity through VEGFR-2-TK inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 40, 116–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.M.; Aziz, H.A.; Bräse, S.; Al Bahir, A.; Alkhammash, A.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.; Elshamsy, A.M.; Hashem, H.; Abdelmagid, W.M. Unveiling the Anticancer Potential of a New Ciprofloxacin—Chalcone Hybrid as an Inhibitor of Topoisomerases I & II and Apoptotic Inducer. Molecules 2024, 29, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, G.; Araniciu, C.; Oniga, S.D.; Vlase, L.; Pîrnău, A.; Nadăș, G.C.; Novac, C.Ș.; Matei, I.A.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Măruțescu, L.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new piperazin-4-yl-(acetyl-thiazolidine-2,4-dione) norfloxacin analogues as antimicrobial agents. Molecules 2019, 24, 3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qandil, A.M.; Al-Zoubi, L.O.; Al-Bakri, A.G.; Amawi, H.A.; Al-Balas, Q.A.; Alkatheri, A.M.; Albekairy, A.M. Synthesis, antibacterial evaluation and QSAR of α-substituted-N4-acetamides of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 244–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuo-Rahma, G.E.; Sarhan, H.A.; Gad, G.F. Design, synthesis, antibacterial activity and physi- cochemical parameters of novel N-4-piperazinyl derivatives of norfloxacin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3879–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Q.D.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.J.; Guo, Q.L.; Chen, X.G.; He, X.G.; Li, T.K.; Chern, J.W. Discovery of a novel series of quinolone and naphthyridine derivatives as potential topoisomerase I inhibitors by scaffold modification. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5649–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Sakamoto, F.; Inoue, Y.; Tsukamoto, G. Studies on prodrugs. 10. Possible mechanism of N-dealkylation of N-masked norfloxacin’s having several active methylene groups. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Alt, S.; Mitchenall, L.A.; Maxwell, A.; Heide, L. Inhibition of DNA gyrase and DNA topoisomerase IV of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by aminocoumarin antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar]
- Borenfreund, E.; Babich, H.; Martin-Alguacil, N. Comparisons of two in vitro cytotoxicity assays—The neutral red NR and tetrazolium MTT tests. Toxicol. Vitro 1988, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfat, M.; Hakami, M.A.; Hazazi, A.; Mahmood AKhalid, A.; Alqurashi, R.S.; Abdalla, A.N.; Hu, J.; Wadood, A.; Huang, X. Identification of novel NLRP3 inhibitors as therapeutic options for epilepsy by machine learning-based virtual screening, molecular docking and biomolecular simulation studies. Heliyon 2024, 15, 10. [Google Scholar]






| Compounds | Bacterial Strain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram +ve Strains | Gram −ve Strains | |||
| S. aureus ATCC 6538 | E. coli ATCC 25922 | K. pneumoniae ATCC 10031 | P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | |
| 2 | >10 | 3.16 ± 0.10 | 1.58 ± 0.06 | 1.58 ± 0.05 |
| 3 | >10 | 6.62 ± 0.22 | 3.31 ± 0.11 | 3.31 ± 0.12 |
| 4 | >10 | 5.21 ± 0.19 | 1.30 ± 0.04 | 1.30 ± 0.06 |
| 5 | >10 | 4.58 ± 0.17 | >10 | 4.58 ± 0.21 |
| 6 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 1.69 ± 0.10 | 1.69 ± 0.08 | 0.85 ± 0.03 |
| 7 | 1.60 ± 0.06 | 1.60 ± 0.04 | 1.60 ± 0.08 | 0.80 ± 0.02 |
| 8 | 1.66 ± 0.07 | 3.31 ± 0.10 | 1.66 ± 0.07 | 0.83 ± 0.04 |
| 9 | 3.61 ± 0.15 | 3.61 ± 0.13 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.90 ± 0.04 |
| 10 | 3.46 ± 0.11 | 3.46 ± 0.09 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | 0.86 ± 0.02 |
| 11 | 2.86 ± 0.09 | 2.86 ± 0.10 | 1.43 ± 0.06 | 2.86 ± 0.11 |
| 12 | 1.58 ± 0.05 | 3.16 ± 0.12 | 3.16 ± 0.10 | 1.58 ± 0.06 |
| 13 | 1.47 ± 0.05 | 5.88 ± 0.21 | 2.94 ± 0.09 | 1.47 ± 0.06 |
| 14 | 1.49 ± 0.07 | 2.98 ± 0.13 | 2.98 ± 0.11 | 0.75 ± 0.02 |
| 15 | 1.58 ± 0.06 | 0.40 ± 0.19 | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| 16 | 1.28 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.14 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.01 |
| 17 | 1.54 ± 0.04 | >10 | 0.77 ± 0.02 | 1.54 ± 0.06 |
| norfloxacin 1 | 7.83 ± 0.30 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| Compound | MIC Against Staphylococcus MRSA AUMC 261 (µM) |
|---|---|
| 6 | >20 |
| 7 | 0.80 ± 0.04 |
| 15 | 6.33 ± 0.22 |
| 16 | >20 |
| Norfloxacin | 1.60 ± 0.08 |
| Compound | Topoisomerase IV IC50 (µM ± SD) | DNA Gyrase IC50 (µM) ±SD |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 3.00 ± 0.12 | 7.10 ± 0.29 |
| 7 | 2.40 ± 0.07 | 4.07 ± 0.16 |
| 15 | 9.99 ± 0.19 | 17.17 ± 0.69 |
| 16 | 1.91 ± 0.04 | 3.57 ± 0.14 |
| Norfloxacin | 11.92 ± 0.42 | 2.28 ± 0.09 |
| Compound | Cytotoxicity Against Normal Cell Line WI 38 IC50 uM | SD ± |
|---|---|---|
| Norfloxacin | 54.57 | 1.94 |
| 6 | 34.06 | 1.21 |
| 7 | 47.92 | 1.71 |
| 15 | 39.16 | 1.39 |
| 16 | 51.24 | 1.82 |
| Doxorubicin | 14.11 | 0.50 |
| Compound | Energy Score (kcal/mol) | Amino Acid Residue | Interaction Type | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| norfloxacin | −8.33 | DG 59 | Pi-Pi | 3.92 |
| MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 1.69 | ||
| MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 2.31 | ||
| 6 | −10.32 | MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 1.63 |
| DG 9 | Pi-Pi | 3.68 | ||
| MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 2.01 | ||
| 7 | −9.80 | DG 9 | Pi-Pi | 3.84 |
| SER 1048 | Hydrogen bond | 3.13 | ||
| SER 1048 | Hydrogen bond | 2.79 | ||
| MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 2.52 | ||
| MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 1.75 | ||
| DG 9 | Pi-Pi | 3.97 | ||
| DA 13 | Pi-Pi | 3.85 | ||
| 15 | −7.84 | MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 1.61 |
| 16 | −10.94 | ARG 458 | Hydrogen bond | 2.85 |
| DG 9 | Pi-Pi | 3.88 | ||
| MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 2.11 | ||
| MN 2000 | Metal interaction | 1.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Saghier, A.M.; Abosella, L.; Hassan, A.; Elakesh, E.O.; Bräse, S.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.-D.A.; Aziz, H.A. Design, Synthesis, and In Silico Studies of New Norfloxacin Analogues with Broad Spectrum Antibacterial Activity via Topoisomerase II Inhibition. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040545
El-Saghier AM, Abosella L, Hassan A, Elakesh EO, Bräse S, Abuo-Rahma GE-DA, Aziz HA. Design, Synthesis, and In Silico Studies of New Norfloxacin Analogues with Broad Spectrum Antibacterial Activity via Topoisomerase II Inhibition. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040545
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Saghier, Ahmed M., Laila Abosella, Abdelfattah Hassan, Esmail O. Elakesh, Stefan Bräse, Gamal El-Din A. Abuo-Rahma, and Hossameldin A. Aziz. 2025. "Design, Synthesis, and In Silico Studies of New Norfloxacin Analogues with Broad Spectrum Antibacterial Activity via Topoisomerase II Inhibition" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040545
APA StyleEl-Saghier, A. M., Abosella, L., Hassan, A., Elakesh, E. O., Bräse, S., Abuo-Rahma, G. E.-D. A., & Aziz, H. A. (2025). Design, Synthesis, and In Silico Studies of New Norfloxacin Analogues with Broad Spectrum Antibacterial Activity via Topoisomerase II Inhibition. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040545






