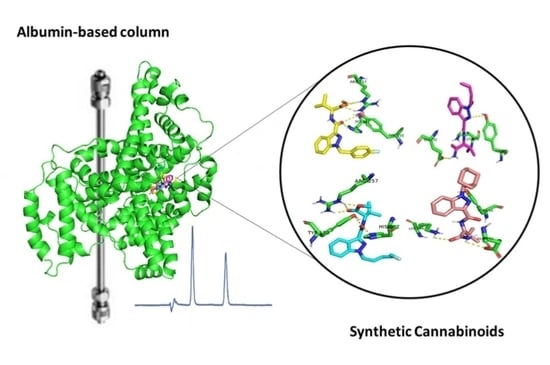
Binding Affinity of Synthetic Cannabinoids to Human Serum Albumin: Site Characterization and Interaction Insights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Determination of HSA Binding Affinity
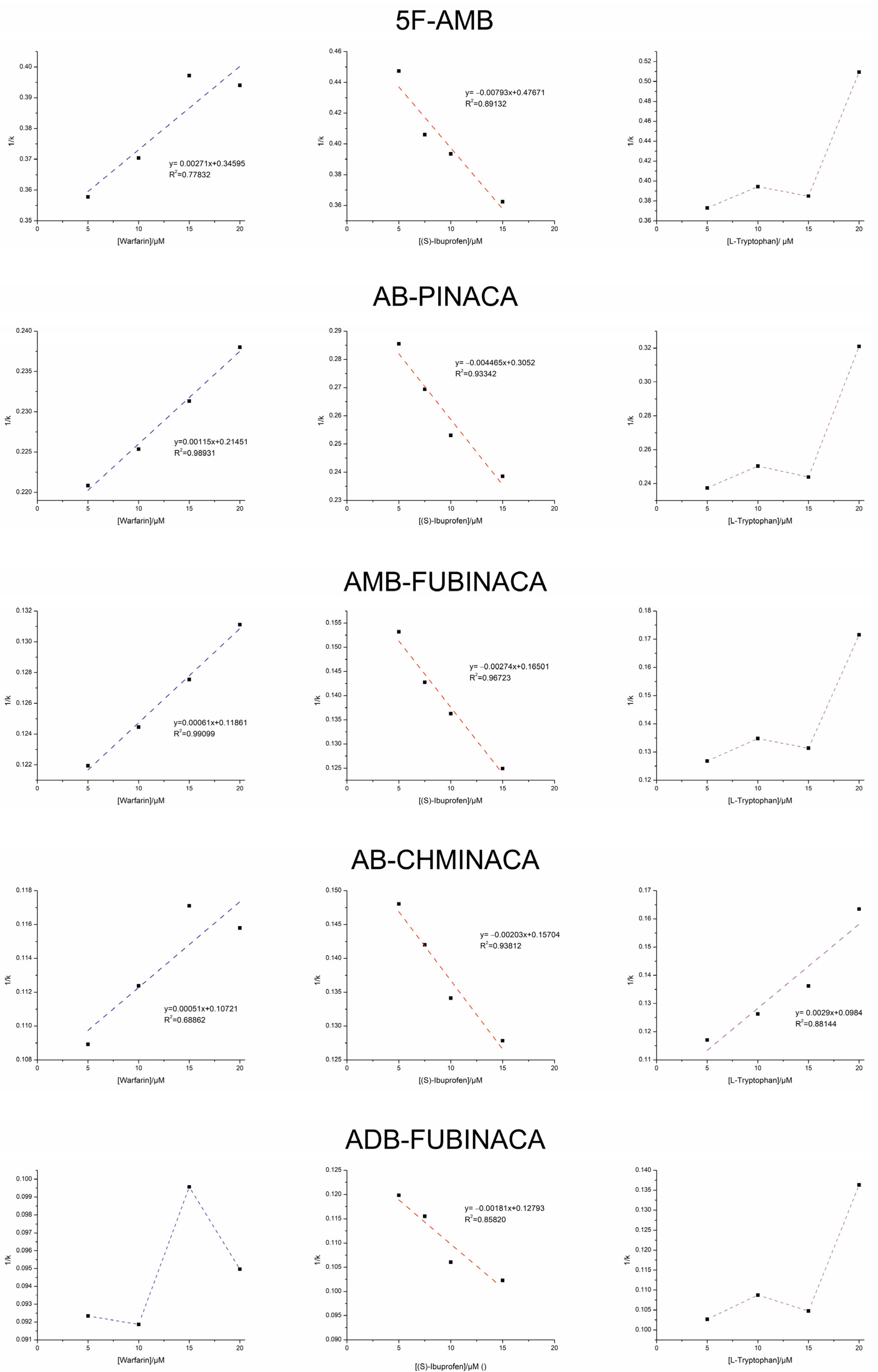
2.2. Displacement Studies
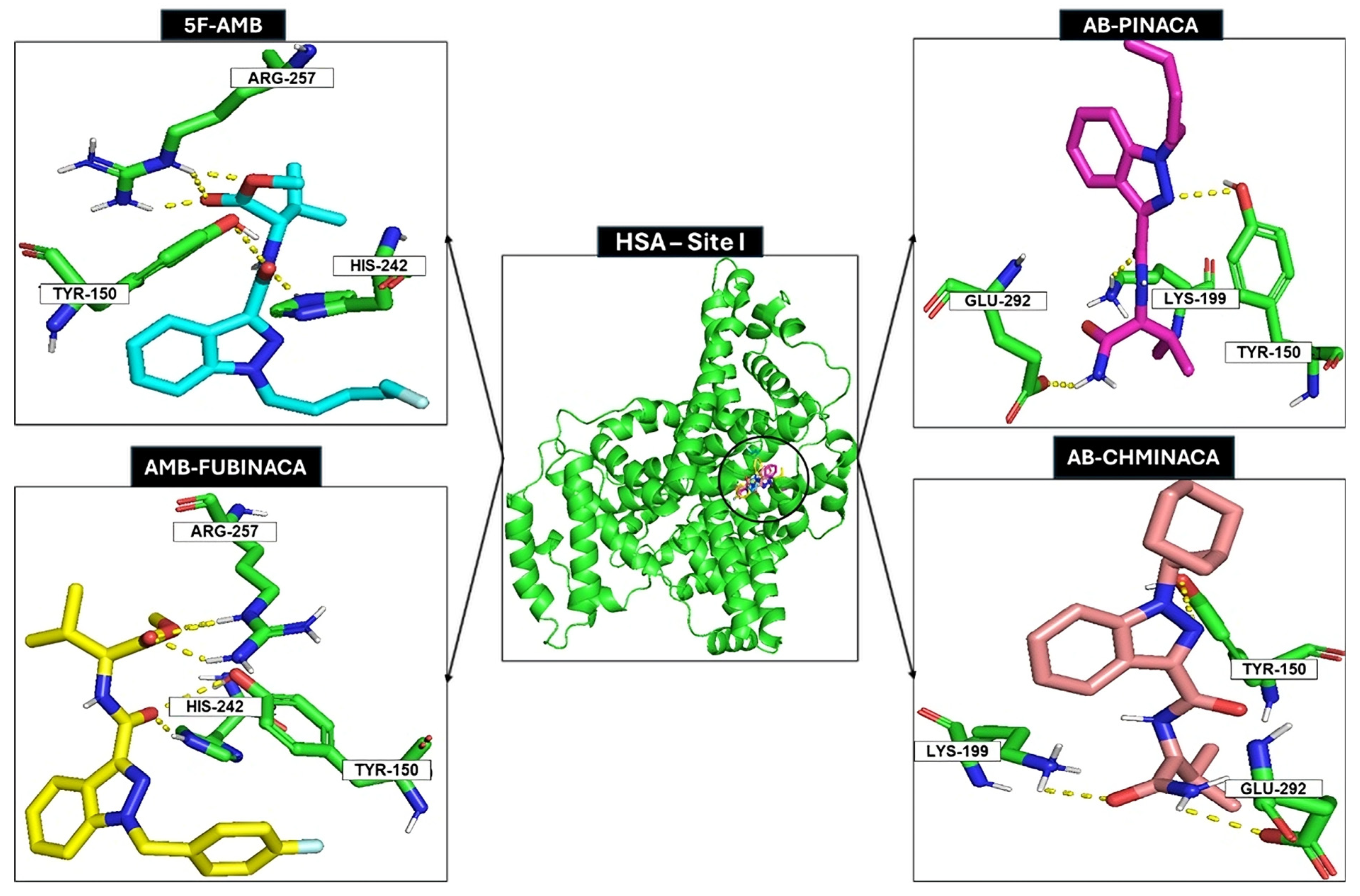
2.3. Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Instrumental and Chromatographic Conditions
3.3. Samples and Buffer Preparation
3.4. Bound Fraction Determination
3.5. Displacement Experiments
3.6. Computational
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roque-Bravo, R.; Silva, R.S.; Malheiro, R.F.; Carmo, H.; Carvalho, F.; Da Silva, D.D.; Silva, J.P. Synthetic Cannabinoids: A Pharmacological and Toxicological Overview. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.P.; Carvalho, F. The therapeutic use of cannabis and cannabinoids. Rev. Esp. Drogodepend. 2022, 47, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinotti, G.; Santacroce, R.; Papanti, D.; Elgharably, Y.; Prilutskaya, M.; Corazza, O. Synthetic Cannabinoids: Psychopharmacology, Clinical Aspects, Psychotic Onset. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2017, 16, 567–575. Available online: http://www.eurekaselect.com/151577/article (accessed on 20 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.L.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Aguiar, J.; Teixeira, H.M.; Câmara, J.S. The synthetic cannabinoids phenomenon: From structure to toxicological properties. A review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Boisselier, R.; Alexandre, J.; Lelong-Boulouard, V.; Debruyne, D. Focus on cannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 101, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Psychoactive Substances—The Current Situation in Europe (European Drug Report 2024). Available online: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/european-drug-report/2024/new-psychoactive-substances_en (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Shafi, A.; Berry, A.J.; Sumnall, H.; Wood, D.M.; Tracy, D.K. New psychoactive substances: A review and updates. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 10, 204512532096719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. Synthetic Cannabinoids in Europe: A Review. [Internet]. Publications Office: LU Luxemburg, Luxemburg. 2021. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2810/911833 (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Lobato-Freitas, C.; Brito-da-Costa, A.M.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carmo, H.; Carvalho, F.; Silva, J.P.; Dias-da-Silva, D. Overview of Synthetic Cannabinoids ADB-FUBINACA and AMB-FUBINACA: Clinical, Analytical, and Forensic Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, A.M.; Antonides, L.H.; Riley, J.; Epemolu, O.; McKeown, D.A.; Read, K.D.; McKenzie, C. A Systematic Study of the In Vitro Pharmacokinetics and Estimated Human In Vivo Clearance of Indole and Indazole-3-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Detected on the Illicit Drug Market. Molecules 2021, 26, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, A.M.; Baginski, S.R.; Peet, C.; Dugard, P.; Green, H.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Daéid, N.N.; Nisbet, L.A.; Read, K.D.; McKenzie, C. Log D7.4 and plasma protein binding of synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists and a comparison of experimental and predicted lipophilicity. Drug Test. Anal. 2024, 16, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardal, M.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Leibnitz, S.; Castiglioni, S.; Meyer, M.R. Toxicokinetics of new psychoactive substances: Plasma protein binding, metabolic stability, and human phase I metabolism of the synthetic cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 studied using in vitro tools and LC-HR-MS/MS. Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 8, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuignier, K.; Schappler, J.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Carrupt, P.-A.; Martel, S. Drug–protein binding: A critical review of analytical tools. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehvar, R. Role of Protein Binding in Pharmacokinetics. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2005, 69, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.; Loadman, P.; Abraham, M.H.; Liu, X. Structural properties governing drug-plasma protein binding determined by high-performance liquid chromatography method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, C.; Domenici, E. Reversible and Covalent Binding of Drugs to Human Serum Albumin: Methodological Approaches and Physiological Relevance. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 1463–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Pea, F.; Lipman, J. The Clinical Relevance of Plasma Protein Binding Changes. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, M.; Matin, S.B. Kinetics of drug-drug interactions. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1973, 1, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.M.; Lima, R.; Almeida, A.S.; Fernandes, P.A.; Remião, F.; Fernandes, C.; Tiritan, M.E. Binding studies of promethazine and its metabolites with human serum albumin by high-performance affinity chromatography and molecular docking in the presence of codeine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 4605–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, D.S.; Jackson, A.; Sobansky, M.R.; Schiel, J.E.; Yoo, M.J.; Joseph, K.S. Characterization of drug–protein interactions in blood using high-performance affinity chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xue, J.; Shao, J.; Jia, L. Compilation of 222 drugs’ plasma protein binding data and guidance for study designs. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascoli, G.A.; Domenici, E.; Bertucci, C. Drug binding to human serum albumin: Abridged review of results obtained with high-performance liquid chromatography and circular dichroism. Chirality 2006, 18, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, G.L. The importance of plasma protein binding in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2007, 2, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratih, R.; Wätzig, H.; Stein, M.; El Deeb, S. Investigation of the enantioselective interaction between selected drug enantiomers and human serum albumin by mobility shift-affinity capillary electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3960–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Liu, W.; Dai, H.; Yu, Y. Fluorescence Spectroscopic Investigation of Competitive Interactions between Quercetin and Aflatoxin B1 for Binding to Human Serum Albumin. Toxins 2019, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, T.; Almeida, A.S.; Remião, F.; Fernandes, C. Enantioresolution and Binding Affinity Studies on Human Serum Albumin: Recent Applications and Trends. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hage, D.S. Analysis of stereoselective drug interactions with serum proteins by high-performance affinity chromatography: A historical perspective. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 144, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofia Almeida, A.; Cardoso, T.; Cravo, S.; Elizabeth Tiritan, M.; Remião, F.; Fernandes, C. Binding studies of synthetic cathinones to human serum albumin by high-performance affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2023, 1227, 123836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, D.S. High-performance affinity chromatography: A powerful tool for studying serum protein binding. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 768, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular Docking: A Powerful Approach for Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided-Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Carmo, J.P.; Phyo, Y.Z.; Palmeira, A.; Tiritan, M.E.; Afonso, C.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Fernandes, C. Enantioseparation, Recognition Mechanisms and Binding of Xanthones on Human Serum Albumin by Liquid Chromatography. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1255–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguizola, J.; Debolt, E.; Suresh, D.; Hage, D.S. Chromatographic analysis of the effects of fatty acids and glycation on binding by probes for Sudlow sites I and II to human serum albumin. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1021, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Hage, D.S. Characterization of interaction kinetics between chiral solutes and human serum albumin by using high-performance affinity chromatography and peak profiling. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6892–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Wainer, I.W. Rapid analysis of the interactions between drugs and human serum albumin (HSA) using high-performance affinity chromatography (HPAC). J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 870, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkó, K.L. Lipophilicity and biomimetic properties measured by HPLC to support drug discovery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Beeram, S.R.; Bi, C.; Suresh, D.; Zheng, X.; Hage, D.S. High-Performance Affinity Chromatography. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–39. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S187616231500070X (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Kim, H.; Kye, Y.; Hage, D. Development and evaluation of N-hydroxysuccinimide-activated silica for immobilizing human serum albumin in liquid chromatography columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1049, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, C.; Cimitan, S.; Riva, A.; Morazzoni, P. Binding studies of taxanes to human serum albumin by bioaffinity chromatography and circular dichroism. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 42, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, C.; Tedesco, D. Human Serum Albumin as Chiral Selector in Enantioselective High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haginaka, J. Recent progresses in protein-based chiral stationary phases for enantioseparations in liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 875, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, T.A.G.; Wainer, I.W. The Use of Displacement Chromatography to Alter Retention and Enantioselectivity on a Human Serum Albumin-Based HPLC Chiral Stationary Phase: A Mini-Review. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1993, 16, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, J.; Zunszain, P.A.; Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Otagiri, M.; Curry, S. Structural Basis of the Drug-binding Specificity of Human Serum Albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, E.; Lowe, P.J.; Briand, X.; Faller, B. New Approach To Measure Protein Binding Based on a Parallel Artificial Membrane Assay and Human Serum Albumin. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, Z. Coupling microdialysis with flow-injection chemiluminescence detection for a protein–drug interaction study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.S.; Anandakumar, S.; Ilanchelian, M. In vitro investigation of domain specific interactions of phenothiazine dye with serum proteins by spectroscopic and molecular docking approaches. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36267–36281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.J.; Wade, D.N. The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1975, 11, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, J.; Bulmer, M. Human Serum Albumin: A Multifunctional Plasma Protein. In Production of Plasma Proteins for Therapeutic Use, 1st ed.; Bertolini, J., Goss, N., Curling, J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 159–183. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781118356807.ch12 (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Bertucci, C.; Pistolozzi, M.; Felix, G.; Danielson, U.H. HSA binding of HIV protease inhibitors: A high-performance affinity chromatography study. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, K.S.; Hage, D.S. The effects of glycation on the binding of human serum albumin to warfarin and l-tryptophan. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Hage, D.S. Characterization of Minor Site Probes for Human Serum Albumin by High-Performance Affinity Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3821–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitos, I.; Visy, J.; Simonyi, M.; Hermansson, J. Stereoselective allosteric binding interaction on human serum albumin between ibuprofen and lorazepam acetate. Chirality 1999, 11, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh-Hansen, U. Octanoate binding to the indole- and benzodiazepine-binding region of human serum albumin. Biochem. J. 1991, 273 Pt 3, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Qaiser, H.; Tariq, S.; Khalid, A.; Makeen, H.A.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Ul-Haq, Z. Unraveling the versatility of human serum albumin—A comprehensive review of its biological significance and therapeutic potential. Curr. Res. Struct. Biol. 2023, 6, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, D.I.; Pistolozzi, M.; Palomo, V.; Redondo, M.; Fortugno, C.; Gil, C.; Felix, G.; Martinez, A.; Bertucci, C. 5-Imino-1,2-4-thiadiazoles and quinazolines derivatives as glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) and phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) inhibitors: Determination of blood–brain barrier penetration and binding to human serum albumin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh-Hansen, U.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Otagiri, M. Practical Aspects of the Ligand-Binding and Enzymatic Properties of Human Serum Albumin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghaei, H.; Norouzi, S.; Zakariazadeh, M.; Soltani, S. Investigation of Atorvastatin interaction with human serum albumin: Evaluation of pH effect and competitive binding with warfarin. J. Res. Pharm. 2022, 26, 1386–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, D.S.; Anguizola, J.; Barnaby, O.; Jackson, A.; Yoo, M.J.; Papastavros, E.; Pfaunmiller, E.; Sobansky, M.; Tong, Z. Characterization of Drug Interactions with Serum Proteins by Using High-Performance Affinity Chromatography. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistolozzi, M.; Fortugno, C.; Franchini, C.; Corbo, F.; Muraglia, M.; Roy, M.; Félix, G.; Bertucci, C. Species-dependent binding of tocainide analogues to albumin: Affinity chromatography and circular dichroism study. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 968, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.J.; Smith, Q.R.; Hage, D.S. Studies of imipramine binding to human serum albumin by high-performance affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.W.; Prlić, A.; Bi, C.; Bluhm, W.F.; Christie, C.H.; Dutta, S.; Green, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Westbrook, J.D.; Woo, J.; et al. The RCSB Protein Data Bank: Views of structural biology for basic and applied research and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D345–D356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, G.; Morley, C.; James, C.; Swain, C.; Winter, H.; Vandermeersch, T. Boyle Open Babel Documentation. 1 January 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265572051 (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, L.L. O Sistema Gráfico Molecular PyMOL. 1–8 edn; Schrödinger LL: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]

| Compound | k [a] | Bound Fraction (%b) [a] | Log Po/w [b] | Molecular Weight (g/mol) [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5F-AMB | 87.30 | 98.9 | 3.40 | 363.43 |
| AB-PINACA | 79.11 | 98.7 | 2.58 | 330.42 |
| AMB-FUBINACA | 326.38 | 99.7 | 3.50 | 383.42 |
| AB-CHMINACA | 294.40 | 99.7 | 2.89 | 356.46 |
| ADB-FUBINACA | 619.87 | 99.8 | 3.10 | 382.43 |
| FUBIMINA | 968.23 | 99.9 | 3.67 | 360.42 |
| Synthetic Cannabinoid | HSA Site I | HSA Site II |
|---|---|---|
| 5F-AMB | Binding occurs (competition with warfarin). | Binding does not occur (no competition with L-tryptophan). Allosterically interacts with (S)-ibuprofen. |
| AB-PINACA | Binding occurs (competition with warfarin). | Binding does not occur (no competition with L-tryptophan). Allosterically interacts with (S)-ibuprofen. |
| AMB-FUBINACA | Binding occurs (competition with warfarin). | Binding does not occur (no competition with L-tryptophan). Allosterically interacts with (S)-ibuprofen. |
| AB-CHMINACA | Binding occurs (competition with warfarin). | Binding occurs (competition with L-tryptophan). Allosterically interacts with (S)-ibuprofen. |
| ADB-FUBINACA | Binding does not occur (no competition with warfarin). | Binding does not occur (no competition with L-tryptophan). Allosterically interacts with (S)-ibuprofen. |
| Synthetic Cannabinoid | KI Warfarin (M−1) (Lit. 3.3 × 105 M−1) [55] | KI (S)-Ibuprofen (M−1) (Lit. 2.7 × 106 M−1) [55] | KI L-Tryptophan (M−1) (Lit. 4.4 × 104 M−1) [55] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5F-AMB | 1.27 × 102 | 6.0 × 101 | - |
| AB-PINACA | 1.86 × 102 | 6.8 × 101 | - |
| AMB-FUBINACA | 1.94 × 102 | 6.8 × 101 | - |
| AB-CHMINACA | 2.1 × 102 | 7.7 × 101 | 3.3 × 101 |
| ADB-FUBINACA | - | 7.0 × 101 | - |
| Synthetic Cannabinoid | Binding Free Energy, Site I (kcal/mol) | Amino Acid Residues |
|---|---|---|
| 5F-AMB | −8.4 | His242; Tyr150; Arg257 |
| AB-PINACA | −8.2 | Tyr150; Lys199; Glu292 |
| AMB-FUBINACA | −9.6 | His242; Tyr150; Arg257 |
| AB-CHMINACA | −9.0 | Lys199; Glu292; Tyr150 |
| ADB-FUBINACA | −9.5 | Tyr150; Arg257 |
| Warfarin | −9.8 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, R.M.G.; Lima, R.; Cravo, S.; Fernandes, P.A.; Remião, F.; Fernandes, C. Binding Affinity of Synthetic Cannabinoids to Human Serum Albumin: Site Characterization and Interaction Insights. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040581
Santos RMG, Lima R, Cravo S, Fernandes PA, Remião F, Fernandes C. Binding Affinity of Synthetic Cannabinoids to Human Serum Albumin: Site Characterization and Interaction Insights. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040581
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Rita M. G., Rita Lima, Sara Cravo, Pedro Alexandrino Fernandes, Fernando Remião, and Carla Fernandes. 2025. "Binding Affinity of Synthetic Cannabinoids to Human Serum Albumin: Site Characterization and Interaction Insights" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040581
APA StyleSantos, R. M. G., Lima, R., Cravo, S., Fernandes, P. A., Remião, F., & Fernandes, C. (2025). Binding Affinity of Synthetic Cannabinoids to Human Serum Albumin: Site Characterization and Interaction Insights. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040581