Mixed Medicinal Mushroom Mycelia Attenuates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathologies In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Aqueous Extract of MMMM
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. TUNEL Assay
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Intracellular ROS Detection
2.8. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT) Activity Assay
2.9. Animals and MMMM Administration
2.10. Y-Maze Test (Y-MT)
2.11. Passive Avoidance Test (PAT)
2.12. Brain Tissue Preparation
2.13. Thioflavin S Staining
2.14. Immunohistochemistry
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
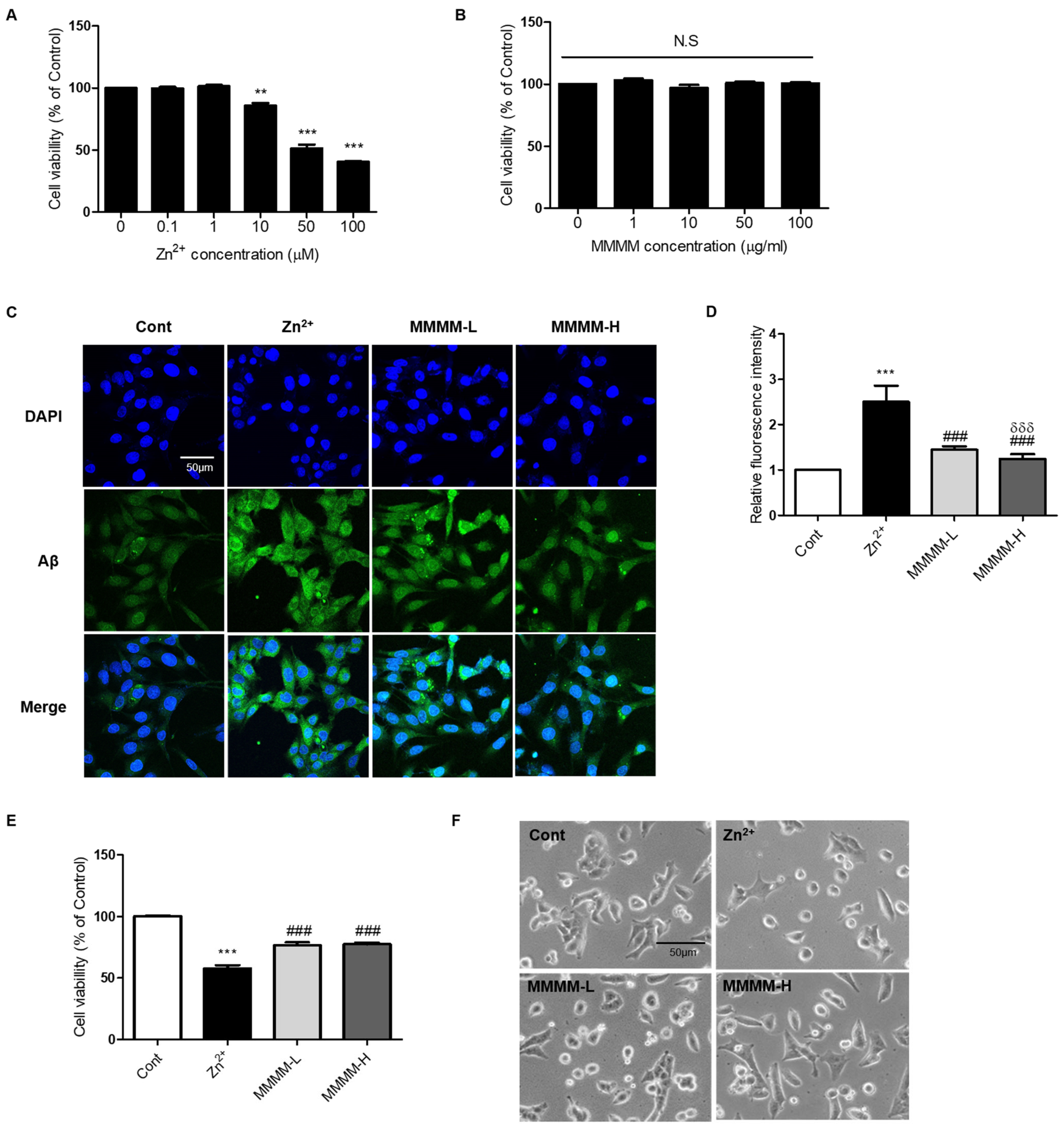
3.1. MMMM Impedes Aβ Aggregation and Mitigates Associated Cell Death in PC12 Cells
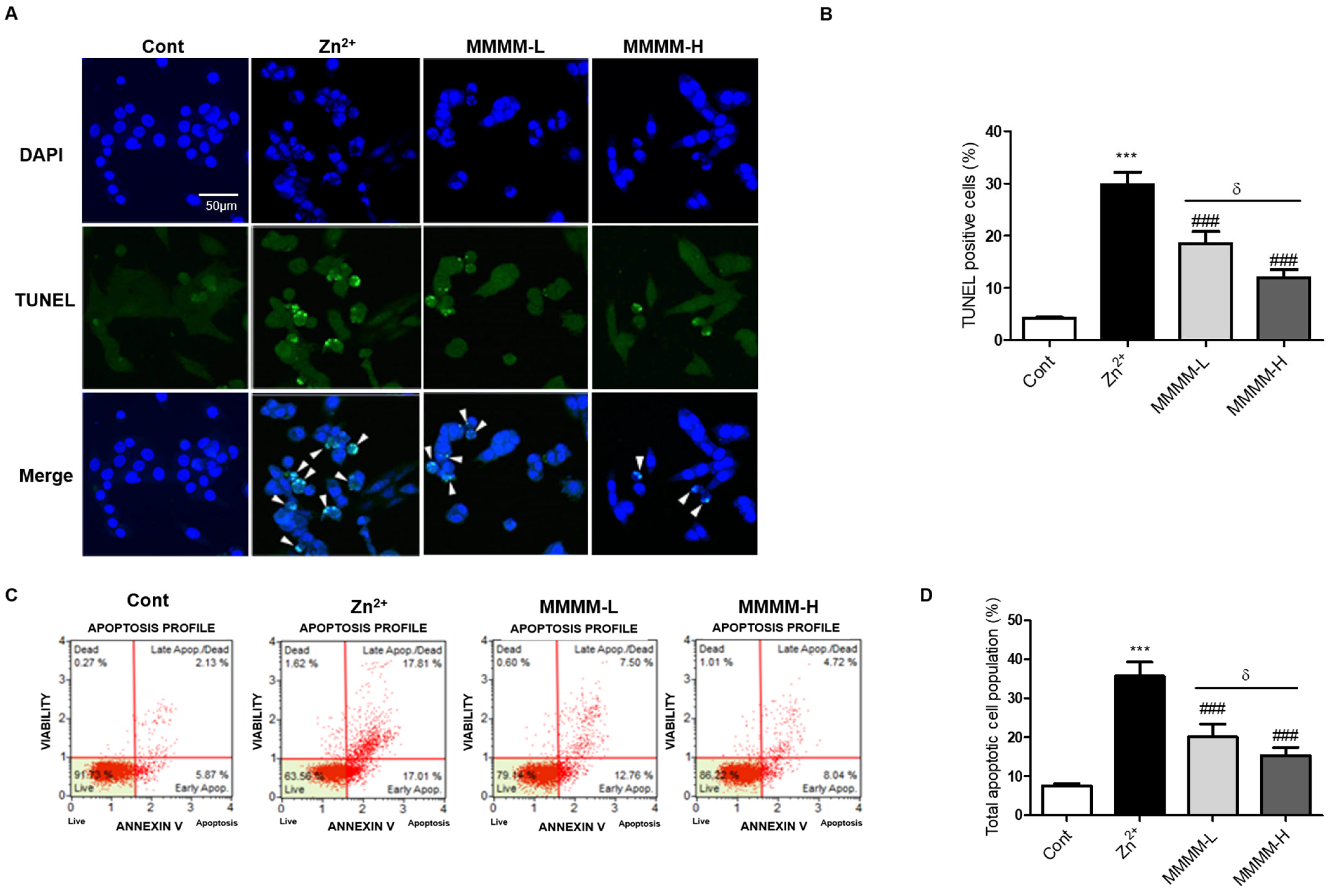
3.2. MMMM Attenuates Aβ-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis
3.3. MMMM Inhibits Aβ-Induced Oxidative Stress in Neuronal Cells
3.4. MMMM Prevents Memory Impairments in 5XFAD Mice
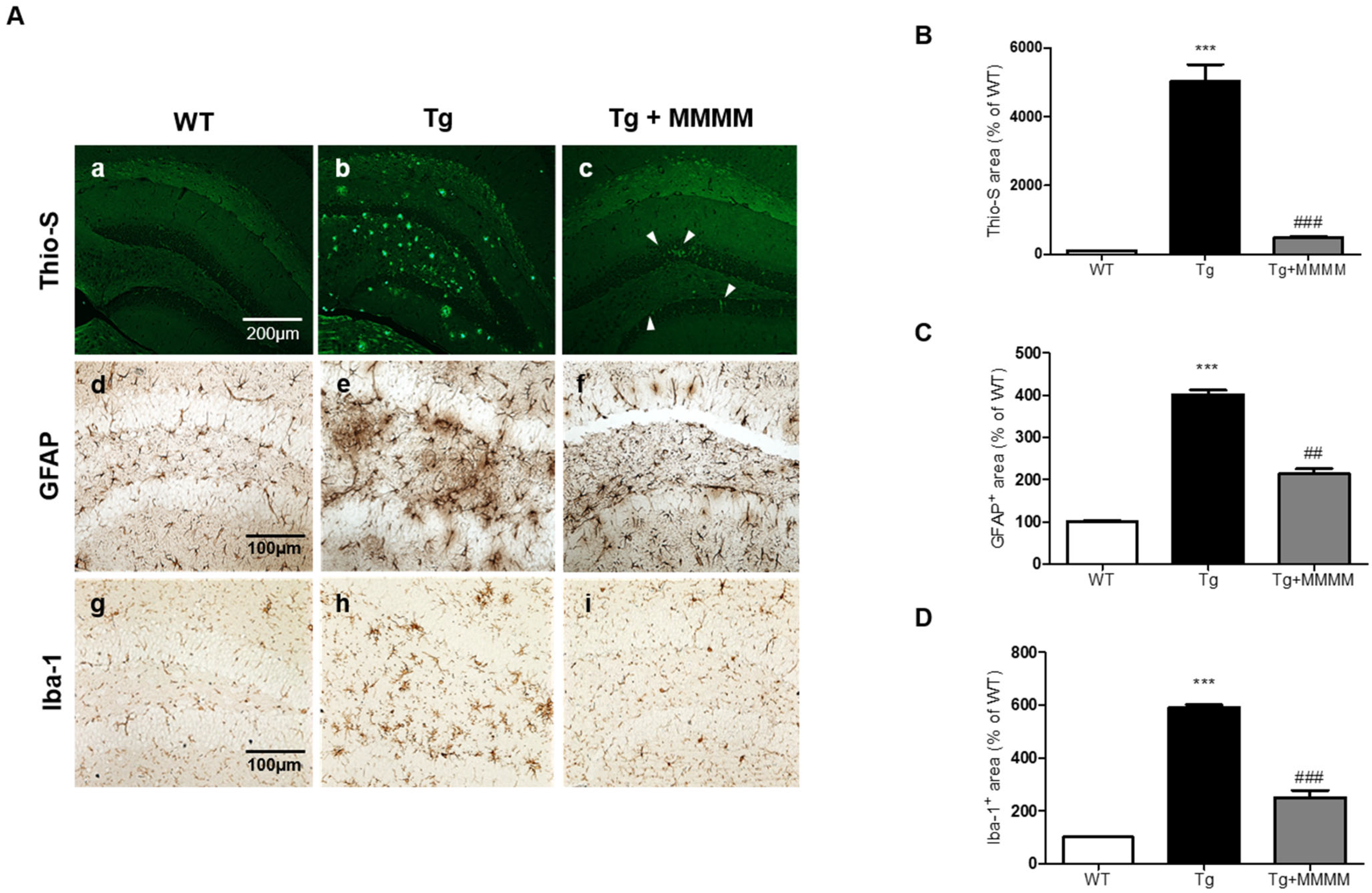
3.5. MMMM Inhibits Aβ Accumulation, Plaque Formation, and Neuroinflammation in the Hippocampus of 5XFAD Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, C.; Kivipelto, M.; von Strauss, E. Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease: Occurrence, determinants, and strategies toward intervention. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 11, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarawneh, R.; Holtzman, D.M. The clinical problem of symptomatic Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, J.Y.; Lewis, S.J. Current Treatment Options for Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease Dementia. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Srivastav, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Srikrishna, S.; Perry, G. Overview of Alzheimer’s Disease and Some Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Abeta by Using Several Synthetic and Herbal Compounds. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7361613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bharadwaj, P.R.; Dubey, A.K.; Masters, C.L.; Martins, R.N.; Macreadie, I.G. Abeta aggregation and possible implications in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, G.; Mannini, B.; Vecchi, G.; Cascella, R.; Cecchi, C.; Dobson, C.M.; Vendruscolo, M.; Chiti, F. Abeta Oligomers Dysregulate Calcium Homeostasis by Mechanosensitive Activation of AMPA and NMDA Receptors. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tong, H.; Lei, M.; Zhou, M.; Guo, W.; Li, G.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Mo, M.; Zhang, X.; et al. Astrocytic glutamatergic transporters are involved in Abeta-induced synaptic dysfunction. Brain Res. 2018, 1678, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coan, E.J.; Irving, A.J.; Collingridge, G.L. Low-frequency activation of the NMDA receptor system can prevent the induction of LTP. Neurosci. Lett. 1989, 105, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerpa, W.; Gambrill, A.; Inestrosa, N.C.; Barria, A. Regulation of NMDA-receptor synaptic transmission by Wnt signaling. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9466–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samidurai, M.; Ramasamy, V.S.; Jo, J. β-amyloid inhibits hippocampal LTP through TNFR/IKK/NF-kappaB pathway. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Shukla, R.; Ali, S.; Najmi, A.K.; Nath, C. Okadaic acid-induced Tau phosphorylation in rat brain: Role of NMDA receptor. Neuroscience 2013, 238, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Kamat, P.K.; Nath, C.; Shukla, R. A study on neuroinflammation and NMDA receptor function in STZ (ICV) induced memory impaired rats. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 254, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Kalani, A.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Tota, S.; Nath, C.; Tyagi, N. Mechanism of Oxidative Stress and Synapse Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Understanding the Therapeutics Strategies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parihar, M.S.; Brewer, G.J. Amyloid-beta as a modulator of synaptic plasticity. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 22, 741–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, L.; Masliah, E. Molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, R12–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, C. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant properties from mushrooms. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanic, M.; Rankovic, B.; Dasic, M. Mushrooms as possible antioxidant and antimicrobial agents. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rowaiye, A.; Wilfred, O.I.; Onuh, O.A.; Bur, D.; Oni, S.; Nwonu, E.J.; Ibeanu, G.; Oli, A.N.; Wood, T.T. Modulatory Effects of Mushrooms on the Inflammatory Signaling Pathways and Pro-inflammatory Mediators. Clin. Complement. Med. Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Sahoo, G.; Swain, S.S.; Luyten, W. Anticancer Activities of Mushrooms: A Neglected Source for Drug Discovery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tan, H.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L. A Review: The Bioactivities and Pharmacological Applications of Phellinus linteus. Molecules 2019, 24, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wachtel-Galor, S.; Yuen, J.; Buswell, J.A.; Benzie, I.F.F. Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi or Reishi): A Medicinal Mushroom. In Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects, 2nd ed.; Benzie, I.F.F., Wachtel-Galor, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xue, Z.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Recent Developments in Inonotus obliquus (Chaga mushroom) Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structural Characteristics, Biological Activities and Application. Polymers 2021, 13, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigemori, H.; Aihara, Y.; Kawaguchi, A.; Hanaki, M.; Murakami, K.; Irie, K. Inhibitory Activity Of Hispidin Derivatives Isolated From Inonotus Obliquus On Amyloid β Aggregation. Heterocycles 2017, 94, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ahn, N.H.; Choi, S.B.; Kwon, Y.; Yang, S.H. Natural Products Targeting Amyloid Beta in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, F.; Luo, J.; Zhu, Y. Ganoderma lucidum Triterpenoids (GLTs) Reduce Neuronal Apoptosis via Inhibition of ROCK Signal Pathway in APP/PS1 Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9894037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letti, L.; Vítola, F.; Pereira, G.; Karp, S.; Medeiros, A.; Scopel Ferreira da Costa, E.; Bissoqui, L.; Soccol, C. Solid-State Fermentation for the Production of Mushrooms. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 285–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, M.N.; Park, J.Y.; Park, H.Y.; Song, C.E.; Moon, J.H.; Choi, A.; Kim, K.D.; Lee, N.S.; et al. Water Extract of Mixed Mushroom Mycelia Grown on a Solid Barley Medium Is Protective against Experimental Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Lan, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Screening a specific Zn(ii)-binding peptide for improving the cognitive decline of Alzheimer’s disease in APP/PS1 transgenic mice by inhibiting Zn(2+)-mediated amyloid protein aggregation and neurotoxicity. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 5197–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Boughey, J.G.F.; Graff-Radford, N.R. Chapter 65—Alzheimer’s Disease. In Neurology and Clinical Neuroscience; Schapira, A.H.V., Byrne, E., DiMauro, S., Frackowiak, R.S.J., Johnson, R.T., Mizuno, Y., Samuels, M.A., Silberstein, S.D., Wszolek, Z.K., Eds.; Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Prince, A.C.-H.; Martin, K.; Maëlenn, G.; Maria, K. World Alzheimer Report 2016; Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI): London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mormino, E.C.; Papp, K.V. Amyloid Accumulation and Cognitive Decline in Clinically Normal Older Individuals: Implications for Aging and Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, S633–S646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, M. Aspects of communication in Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical features and treatment options. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2013, 25, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, C.J.; Kitazawa, M. Infection, systemic inflammation, and Alzheimer’s disease. Microbes. Infect 2015, 17, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariot, P.N.; Cummings, J.L.; Katz, I.R.; Mintzer, J.; Perdomo, C.A.; Schwam, E.M.; Whalen, E. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in the nursing home setting. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2001, 49, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Jiang, H. Efficacy and adverse effects of memantine treatment for Alzheimer’s disease from randomized controlled trials. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, P. Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials on the Efficacy and Safety of Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine, and Memantine for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzi, G.M.; Petraglia, T.; Latronico, T.; Crescenzi, A.; Rossano, R. Antioxidant Compounds from Edible Mushrooms as Potential Candidates for Treating Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambri, A.; Srivastava, M.; Mahale, V.G.; Mahale, S.; Karn, S.K. Mushrooms as Potential Sources of Active Metabolites and Medicines. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 837266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Kawamata, T.; Okada, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Hori, T. Filtrate of Phellinus linteus Broth Culture Reduces Infarct Size Significantly in a Rat Model of Permanent Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011, 2011, 326319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giridharan, V.V.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Konishi, T. Amelioration of scopolamine induced cognitive dysfunction and oxidative stress by Inonotus obliquus—A medicinal mushroom. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Tang, Y.P.; Xiang, J.; Wua, P.; Jin, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Mori, M.; Cai, D.F. Neuroprotective effects of water-soluble Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on cerebral ischemic injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.J.; Cho, S.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, H.B.; Park, Y.I. Neuroprotective effects of the Phellinus linteus ethyl acetate extract against H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death of SK-N-MC cells. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Z.; Liao, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, L.M. Neuroprotective effects of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides against oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. Neural. Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.X.; Wang, X.B.; Lv, T.M.; Hou, Z.L.; Lin, B.; Huang, X.X.; Song, S.J. Flavan derivative enantiomers and drimane sesquiterpene lactones from the Inonotus obliquus with neuroprotective effects. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugasani, S.; Pichika, M.R.; Nadarajah, V.D.; Balijepalli, M.K.; Tandra, S.; Korlakunta, J.N. Comparative antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of [6]-gingerol, [8]-gingerol, [10]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.Y.; Luo, Y.L.; Cheng, H.Y.; Hsieh, W.C.; Liao, J.C.; Peng, W.H. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of [6]-gingerol. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.F.; Zong, S.H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Fu, S.W.; Li, K.K.; Fang, Y.; Lu, L.; Xiao, D.Q. The Role of 6-Gingerol on Inhibiting Amyloid beta Protein-Induced Apoptosis in PC12 Cells. Rejuvenation Res. 2015, 18, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, C.; Kang, M.; Han, Y.; Zhang, T.; Quan, W.; Gao, J. 6-Gingerols (6G) reduces hypoxia-induced PC-12 cells apoptosis and autophagy through regulation of miR-103/BNIP3. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaspar, J.W.; Niture, S.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, M.; Yang, H. Microglia in the Neuroinflammatory Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 856376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, L.; Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Chang, S.; Wen, J.; Sun, J.; Li, H. Role of Abeta in Alzheimer’s-related synaptic dysfunction. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 964075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacosta, A.M.; Insua, D.; Badi, H.; Pesini, P.; Sarasa, M. Neurofibrillary Tangles of Abetax-40 in Alzheimer’s Disease Brains. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 58, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, J.H.; Hong, G.-L.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lee, N.S.; Kim, D.K.; Park, J.Y.; Park, M.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, Y.E.; Yoo, Y.C.; et al. Mixed Medicinal Mushroom Mycelia Attenuates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathologies In Vitro and In Vivo. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6775-6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080428
Jeong JH, Hong G-L, Jeong YG, Lee NS, Kim DK, Park JY, Park M, Kim HM, Kim YE, Yoo YC, et al. Mixed Medicinal Mushroom Mycelia Attenuates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathologies In Vitro and In Vivo. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(8):6775-6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080428
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Ji Heun, Geum-Lan Hong, Young Gil Jeong, Nam Seob Lee, Do Kyung Kim, Jong Yea Park, Mina Park, Hyun Min Kim, Ya El Kim, Yung Choon Yoo, and et al. 2023. "Mixed Medicinal Mushroom Mycelia Attenuates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathologies In Vitro and In Vivo" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 8: 6775-6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080428
APA StyleJeong, J. H., Hong, G. -L., Jeong, Y. G., Lee, N. S., Kim, D. K., Park, J. Y., Park, M., Kim, H. M., Kim, Y. E., Yoo, Y. C., & Han, S. Y. (2023). Mixed Medicinal Mushroom Mycelia Attenuates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathologies In Vitro and In Vivo. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(8), 6775-6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080428





