Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Analogs as a Potential Molecular Biology Reagent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties of SDS, Sarkosyl and SLG
3. Effects on Native Proteins
4. Effects on Protein Refolding
5. Amyloid Fractionation by Sarkosyl or SDS
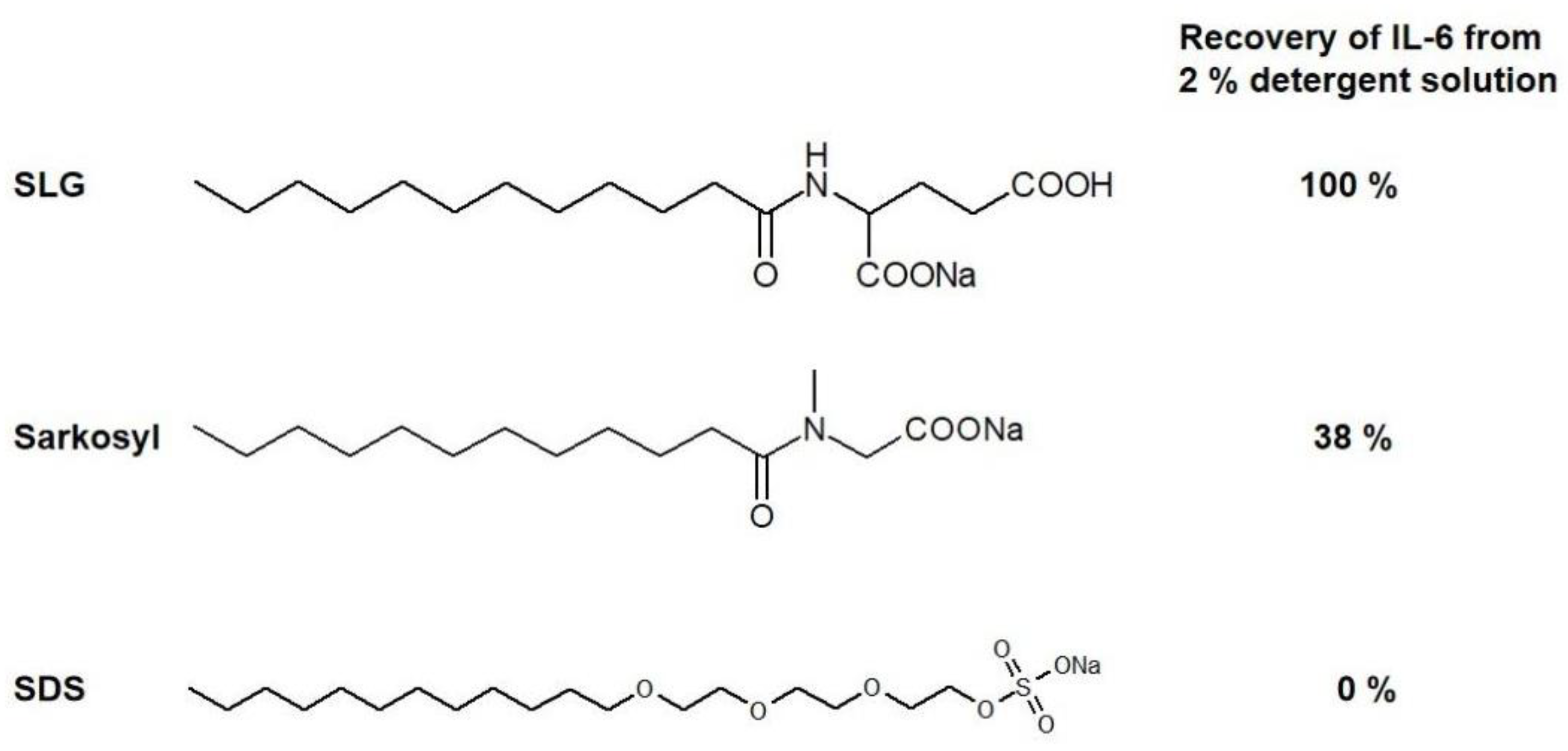
6. Cell Lysis
7. Mechanism
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Izumida, K.; Hara, Y.; Furukawa, Y.; Ishida, K.; Tabata, K.; Morita, E. Purification of hepatitis C virus core protein in non-denaturing condition. J. Virol. Mthods 2023, 323, 114852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.; Sasi, S.; Kodakkattumannil, P.; Senaani, S.; Lekshmi, G.; KOttackal, M.; Amiri, K.M.A. Cationic and anionic detergent buffers in sequence yield high-quality genomic DNA from diverse plant species. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 1, 115372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebling, S.; Burastero, O.; Garcia-Alai, M. Biophysical characterization of membrane proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2652, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, D. Detergents: An overview. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 463, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, J.; Ochiai-Yanagi, S.; Kasumi, T.; Takagi, T. Isolation of a membrane protein from R rubrun chromatophores and its abnormal behavior in SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis due to a high binding capacity for SDS. J. Biochem. 1978, 83, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neset, L.; Takayidza, G.; Berven, F.S.; Hernandez-Valladares, M. Comparing effciency of lysis buffer solutions and sample preparation methods for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of human cells and plasma. Molecules 2022, 27, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Isemura, T.; Takagi, T. Electrophoretic behavior of micellar and monomeric sodium dodecyl sulfate in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with reference to those of SDS-protein complexes. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 92, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, C.; Nakagawa, M.; Tomioka, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Entzminger, K.; Fleming, J.K.; Shibata, T.; Kurosawa, Y.; Okumura, C.J.; Arakawa, T. Western blotting of native proteins from agarose gels. Biotechniques 2022, 72, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuta, T.; Maruyama, T.; Sakuma, C.; Nakagawa, M.; Tomioka, Y.; Entzminger, K.; Fleming, J.K.; Sato, R.; Shibata, T.; Kurosawa, Y. A new method to characterize conformation-specific antibody by a combination of agarose native gel electrophoresis and contact blotting. Antibodies 2022, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, D.V.; Valkenburg, F.; Kolen, K.V.; Pintelon, I.; Timmermans, J.-P.; Deyn, P.P.D. Behavioral and neuropathological phenotyping of the Tau58.2 and Tau58/4 transgenic mouse models for FTDP-17. Life 2023, 13, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, H.; Mandai, S.; Shiwaku, H.; Koide, T.; Takahashi, N.; Yanagi, T.; Inaba, S.; Ida, S.; Fujiki, T.; Mori, Y.; et al. Chronic kidney disease causes blood-brain barrier breakdown via urea-activated matrix metalloproteinase-2 and insolubility of tau protein. Aginig 2023, 25, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, S.O.; Tsaka, G.; Ronisz, A.; Ospitalieri, S.; Gawor, K.; Gomes, L.A.; Otto, M.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; Damme, P.V.; Bosch, L.V.D. TDP-43 pathology is associated with increased tau buerdens and seeding. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisnall, B.; Johnson, C.; Kulaberoglu, Y. Insoluble protein purification with Sarkosyl: Facts and precautions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1091, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, B.H.; Koening, P.H.; Shen, J.K. Self-assembly and bilayer-micelle transition of fatty acids studied by replica-exchange constant molecular dynamics. Langmiur 2013, 29, 14823–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordes, R.; Tropsch, J.; Holmberg, K. Role of an amide bond for self-assembly of surfactants. Langmuir 2010, 26, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Nnanna, I.A.; Sakamoto, K. Amino acid surfactants: Chemistry, synthesis, and properties. In Protein-Based Surfactants. Synthesis, Physicochemical Properties, and Applications; Nnanna, I.A., Xia, J., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 75–122. Available online: https://books.google.co.jp/books?hl=ja&lr=lang_ja%7Clang_en&id=CWK1DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA75&ots=fEoUpD7MJE&sig=XcfIl8ys3o410mGlCPLT26tMoYc&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 4 March 2014).
- Arakawa, T.; Kita, Y.; Ejima, D. Refolding technology for scFv using a new detergent, N-lauroyl-L-glutamate and arginine. Antibodies 2012, 1, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariki, R.; Hirano, A.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Drug solubilization effect of lauroyl-L-glutamate. J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumioka, R.; Shimada, M.; Takino, K.; Ejima, D. Evaluation Method for Detergents. Japan Patent JP 2006292686, 26 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kudou, M.; Yumioka, R.; Ejima, D.; Arakawa, T.; Tsumoto, K. A novel protein refolding system using lauroyl-L-glutamate as a solubilizing detergent and arginine as a folding assisting agent. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 75, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratalá, J.V.; Atienza-Garriga, J.; López-Laguna, H.; Vázquez, E.; Villaverde, A.; Sánchez, J.M.; Ferrer-Miralles, N. Enhanced recombinant protein capture, purity and yield from crude bacterial cell extracts by N-Lauroylsarcosine-assisted affinity chromatography. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.M.; Lee, S.; Jung, H.S. Effective non-denaturing purification method for improving the solubility of recombinant actin-binding proteins produced by bacterial expression. Protein Expr. Purif. 2017, 133, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peternel, S.; Grdadolnik, J.; Garberc-Porekar, V.; Komel, R. Engineering inclusion bodies for non denaturing extraction of functional proteins. Microb. Cell Fact. 2008, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, D.R.; Burgess, R.R. Overproduction and purification of the ω subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Protein Expr. Purifi. 1990, 1, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, R.R. Purification of overproduced Escherichia coli RNA polymerase sigma factors by solubilizing and refolding from Sarkosyl. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 273, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.S.; Clogston, C.L.; Narhi, L.O.; Merewether, L.A.; Pearl, W.R.; Boone, T.S. Folding and oxidation of recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor produced in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 8770–8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltoni, G.; Scutteri, L.; Mensitieri, F.; Piaz, F.D.; Hochkoeppler, A. High-yield production in Escherichia coli and convenient purification of a candidate vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Biotechnol. Lett. 2022, 44, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhiar, A.A.; Chanda, W.; Joseph, T.P.; Guo, X.; Liu, M.; Sha, L.; Batool, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M. Comparative study to develop a single method for retrieving wide class of recombinant proteins from classical inclusion bodies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, R.M.; Syngkli, S.; Nongkhlaw, J.; Das, B. Expression and characterization of human glycerol kinase: The role of solubilizing agents and molecular chaperones. Biosci. Rep. 2023, 43, BSR20222258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Sato, A. Improved refolding of a human IgG Fc (CH2-CH3) scaffold from its inclusion body in E. coli by alkaline solubilization. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storrs, S.B.; Tou, J.S.; Ballinger, J.M. Method for Solubilization and Renaturation of Somatotropins. U.S. Patent US6410694B, 15 December 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Yumioka, R.; Ejima, D. Protein Refolding Method. Japan Patent WO 2009136568A1, 12 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kudou, M.; Ejima, D.; Sato, H.; Yumioka, R.; Arakawa, T.; Tsumoto, K. Refolding single-chain antibody (scFv) using lauroyl-L-glutamate as a solubilizing detergent and arginine as a refolding additive. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 77, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melki, R.; Carlier, M.F.; Pantaloni, D.; Timasheff, S.N. Cold depolymerization of microtubules to double rings: Geometric stabilization of assemblies. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 9143–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, C.; Bretteville, A.; Planel, E. Biochemical isolation of insoluble tau in transgenic mouse models of tauopathies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 849, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, S.G.; Davies, P. A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5827–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, J.; Honda, T.; Mori, H.; Hamada, Y.; Miura, R.; Ogawa, M.; Ihara, Y. The carboxyl third of tau is tightly bound to paired helical filaments. Neuron 1988, 1, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarutani, A.; Adachi, T.; Akatsu, H.; Hashizume, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Saito, Y.; Robinson, A.C.; Mann, D.M.A.; Yoshida, M.; Maruyama, S. Ultrastrucrural and biochemical classification of pathogenic tau, α-synuclein and TDP-43. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 143, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, A.W.P.; Falcon, B.; He, S.; Murzin, A.G.; Murshudov, G.; Garringer, H.J.; Crowther, R.A.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S.H.W. Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments frin Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2017, 547, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, A.M.; Yang, Y.; Jin, S.; Yamashita, K.; Meunier, A.L.; Liu, W.; Cai, Y.; Ericsson, M.; Liu, L.; Goedert, M. Abundant Aß fibrils in ultracentrifugal supernatants of aqueous extracts from Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neuron 2012, 111, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryndushkin, D.; Pripuzova, N.; Shewmaker, F.P. Isolation and analysis of prion and amyloid aggregates. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2017, 2, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizhnikov, A.A.; Alexandrov, A.I.; Ryzhova, T.A.; Mitkevich, O.V.; Dergalev, A.A.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Galkin, A.P. Proteomic screening for amyloid proteins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belashova, T.A.; Valina, A.A.; Sysoev, E.L.; Velizhanina, M.E.; Zelensky, A.A.; Galkin, A.P. Search and identification of amyloid proteins. Methods Protoc. 2023, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhova, T.A.; Sopova, J.V.; Zadorsky, S.P.; Siniukova, V.A.; Sergeeva, A.V.; Galkina, S.A.; Nizhnikov, A.A.; Shenfeld, A.A.; Volkov, K.V.; Galkin, A.P. Screening for amyloid proteins in the yeast proteome. Curr. Genet. 2018, 64, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, A.V.; Galkin, A.P. Functional amyloids of eukaryotes: Criteria, classification, and biological significance. Curr. Genet. 2020, 66, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sopova, J.V.; Koshel, E.I.; Belashova, T.A.; Zadorsky, S.P.; Sergeeva, A.V.; Siniukova, V.A.; Shenfeld, A.A.; Velizhanina, M.E.; Volkov, K.V.; Nizhnikov, A.A. RNA-binding protein FXR1 is presented in rat brain in amyloid form. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonets, K.S.; Belousov, M.V.; Sulatskaya, A.I.; Belousova, M.E.; Kosolapova, A.O.; Sulatsky, M.I.; Andreeva, E.A.; Zykin, P.A.; Malovichko, Y.V.; Shtark, O.Y. Accumulation of storage proteins in plant seeds is mediated by amyloid formation. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidan, A.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Lashmet, M.; Smith, L.J.; Hara, H.; Cooper, D.K.C.; Ekser, B. Decellularization methods for developing porcine corneal xenografts and future perspectives. Xenotransplantation 2019, 26, e12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Palma, R.K.; Fratini, P.; Schiavo Matias, G.S.; Cereta, A.D.; Guimarães, L.L.; Anunciação, A.R.A.; de Oliveira, L.V.F.; Farre, R.; Miglino, M.A. Equine lung decellularization: A potential approach for in vitro modeling the role of the extracellular matrix in asthma. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, 2041731418810164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, W. Rapid porcine corneal decellurization through the use of sodium N-lauroyl glutamate and supernuclease. J. Tissue Eng. 2019, 10, 2041731419875876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gin, J.W.; Wang, Y.; de Raad, M.; Tan, S.; Hillson, N.J.; Northen, T.R.; Adams, P.D.; Petzold, J. Alkaline-SDS cell lysis of microbes with acetone protein precipitation for proteomic sample preparation in 96-well plate format. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCaprio, J.; Kohl, T.O. Denaturing lysis of cells for immunoprecipitation. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2020, 2020, 098616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massiah, M.A.; Wright, K.M.; Du, H. Obtaining soluble folded proteins from inclusion bodies using Sarkosyl, Triton X-100, and CHAPS: Application to LB and M9 minimal media. Curr. Proto. Protein Sci. 2016, 84, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gill, C.O.; Yang, X. Use of sodium lauroyl sarcosinate (Sarkosyl) in viable real-time PCR for enumeration of Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 98, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.N.; Romine, M.F.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Smith, R.D.; Lipton, M.S. Mapping the subcellular proteome of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 using Sarkosyl-based fractionation and LC-MS/MS protein identification. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4454–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, K.S.; Kuyukina, M.S.; Heidbrink, S.; Philp, J.C.; Aw, D.W.; Ivshina, I.B.; Christofi, N. Identification and environmental detection of Rhodococcus species by 1S rDNA-targeted PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 87, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elke, C.; Vögtli, M.; Rauch, P.; Spindler-Barth, M.; Lezzi, M. Expression of EcR and USP in Escherichi coli: Purification and functional studies. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1997, 35, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, S.; Sohn, R.; Leinwand, L. The use of salkosyl in generating soluble protein after bacterial expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-H.; Guidotti, G. Purification of membrane proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 463, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M. Strategies for the purification of membrane proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1485, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmeister, F. Zur Lehre von der wirkung der salze. Arch. Expt. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1888, 24, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Timasheff, S.N. Mechanism of protein salting in and salting out by divalent cation salts: Balance between hydration and salt binding. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 5912–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Timasheff, S.N. Protein stabilization and destabilization by guanidinium salts. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 5924–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petyaev, I.M.; Zigangirova, N.A.; Tsibezov, V.V.; Ross, A.; Bashmakov, Y.K. Monoclonal antibodies against lipopolysaccharide of Chlamydia trachomatis with cross reactivity to human ApoB. Hybridoma 2011, 30, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impeller, D. Hemoglobin Binding Protein from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae: A novel Method for Extraction and Isolation. 2007. Available online: https://escholarship.mcgill.ca/concern/thesis/z029p754m (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Nandy, A.; Shekhar, S.; Paul, B.K.; Mukherjee, S. Exploring the nucleobase-specific hydrophobic interaction of cryptolepine hydrate with RNA and its subsequenct sequestration. Langmuir 2021, 37, 11176–11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, C. SARKOSYL-PAGE: A new electrophoretic method for the separation and immunological detection of PEGylated proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 869, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Kuo, X.; Zheng, W.; Xiao, X.; Li, C.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L. 05SAR-PAGE: Separation of protein dimerization and modification using a gel with 0.5% Sarkosyl. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1101, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Liu, W.; Simmons, B.N.; Harris, H.K.; Cox, T.C.; Massiah, M.A. Purifying natively folded proteins from inclusion bodies using sarkosyl, Triton X-100, and CHAPS. BioTechniques 2010, 48, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Sha, W.; Yuan, S.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y. Aggregation, transmission, and toxicity of the microtubule-associated protein tau. A complex comprehension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Sahara, N.; Saito, Y.; Murayama, M.; Yoshiike, Y.; Kim, Y.; Miyasaka, T.; Murayama, S.; Ikai, A.; Takashima, A. Granular tau oligomers as intermediates of tau filaments. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 3856–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Detergent | CMC | Aggregation Number | MW |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDS | 8.2 mM in water 1.4 mM in 0.1 M NaCl | ~80 in water | 288.4 |
| Sarkosyl | 14.57 mM | 2 | 293.4 |
| SLG | 10.6 mM | ~80 | 351.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arakawa, T.; Niikura, T.; Kita, Y.; Akuta, T. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Analogs as a Potential Molecular Biology Reagent. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010040
Arakawa T, Niikura T, Kita Y, Akuta T. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Analogs as a Potential Molecular Biology Reagent. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(1):621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleArakawa, Tsutomu, Takako Niikura, Yoshiko Kita, and Teruo Akuta. 2024. "Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Analogs as a Potential Molecular Biology Reagent" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 1: 621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010040
APA StyleArakawa, T., Niikura, T., Kita, Y., & Akuta, T. (2024). Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Analogs as a Potential Molecular Biology Reagent. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(1), 621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010040






