Challenging Molecular Diagnosis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: Case Series and Novel Variants of CYP21A2 Gene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Copy Number Variation (CNV) Detection
2.2. Analysis of the CYP21A2 Downstream of the TNXB Gene
2.3. Detection of the CYP21A2 Downstream of the TNXA Gene
3. Case Series
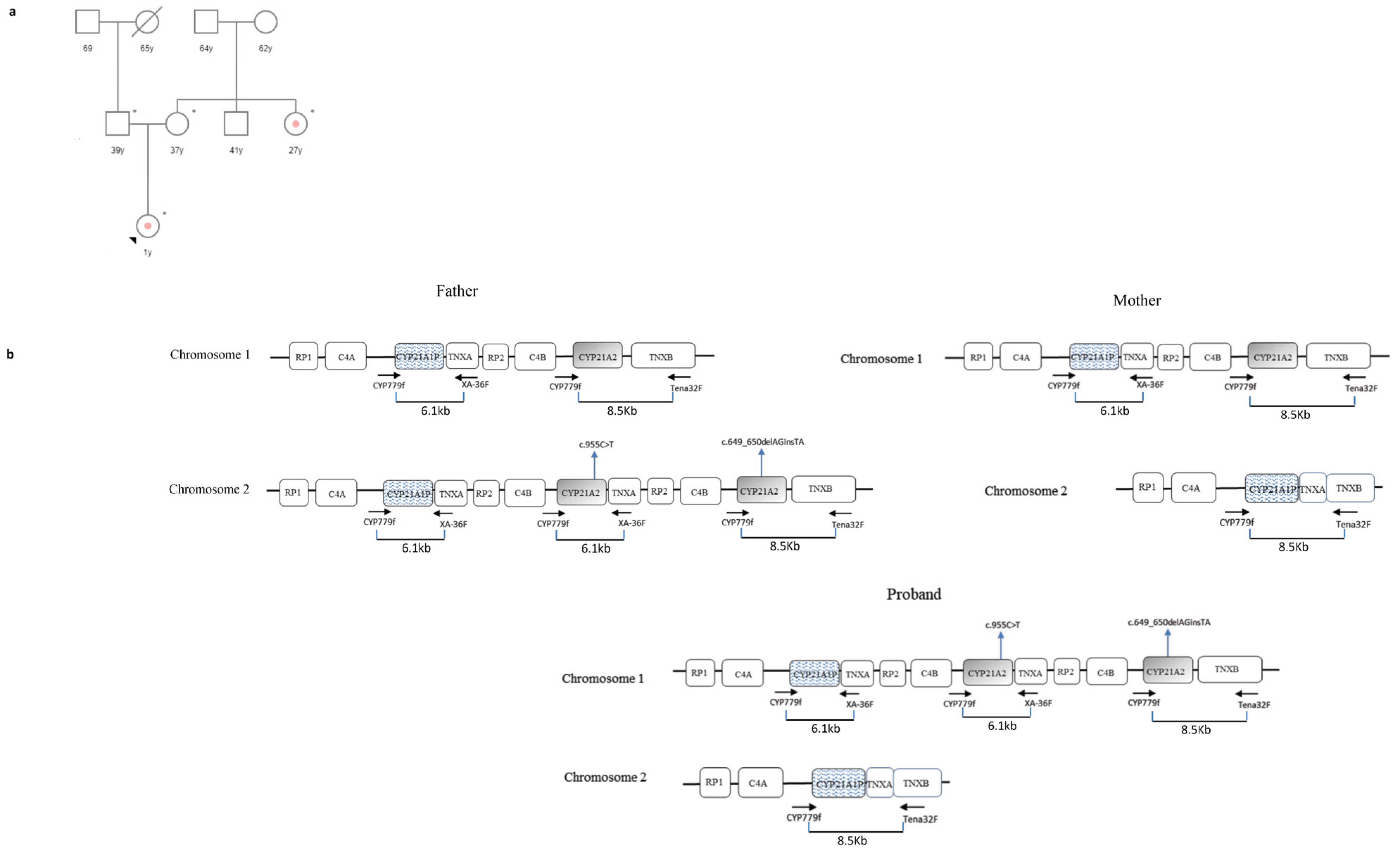
3.1. Case 1
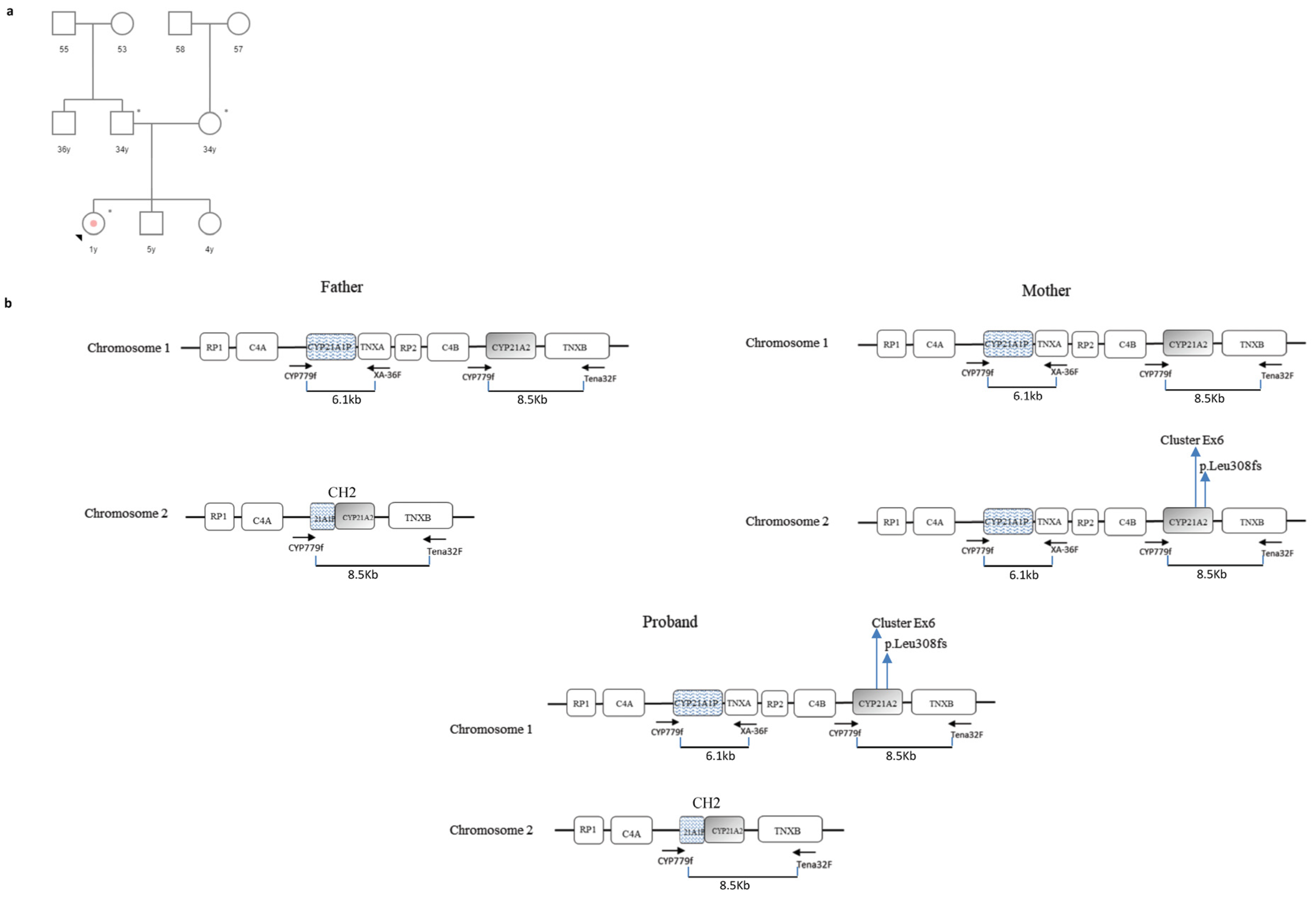
3.2. Case 2
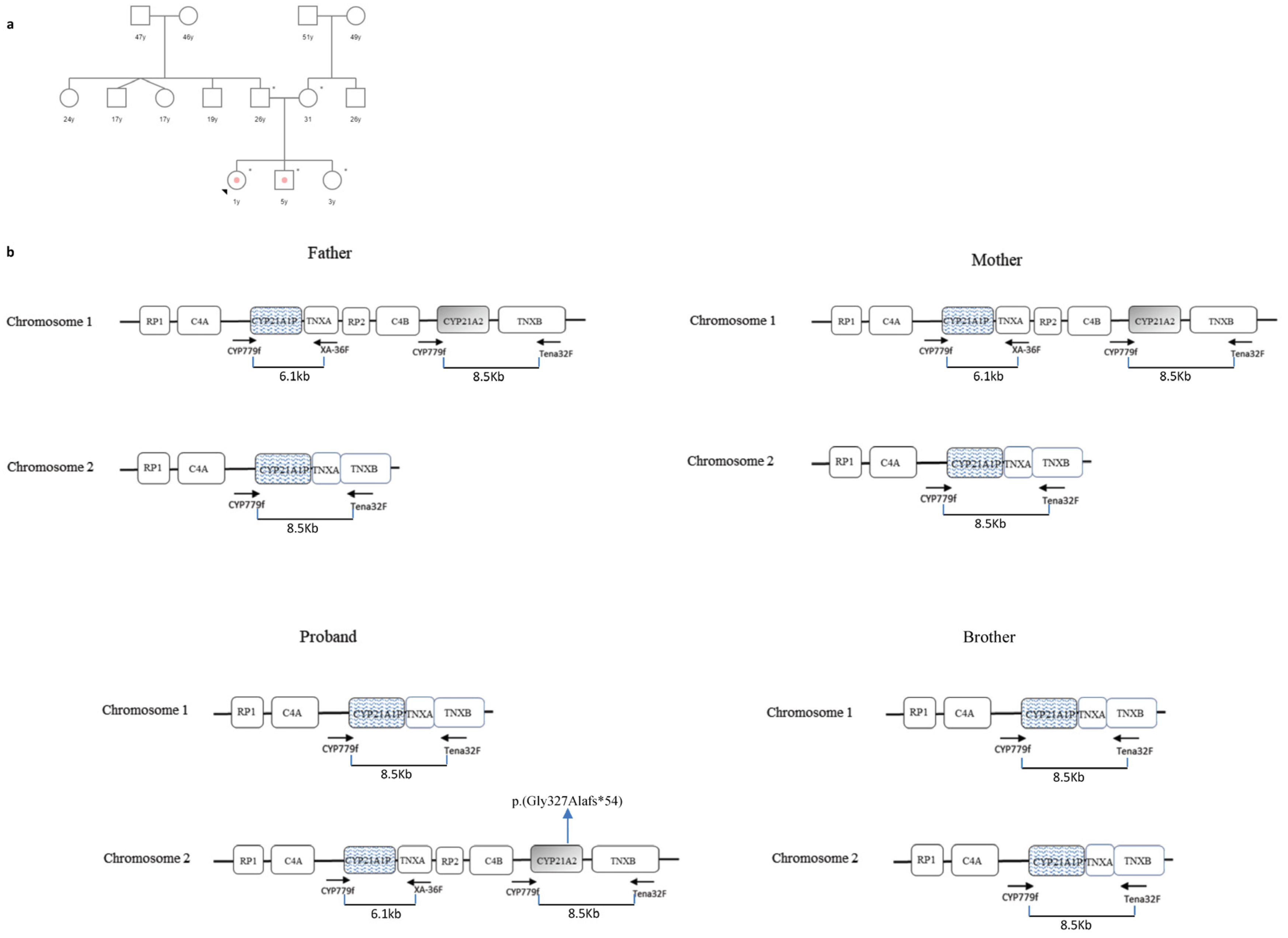
3.3. Case 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, P.C.; Speiser, P.W. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 245–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, A.A.; New, M.I. Steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 165, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, M.K.; Nordenström, A.; Lajic, S.; Reisch, N. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet 2023, 401, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maouche, D.; Arlt, W.; Merke, D.P. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet 2017, 390, 2194–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, P.W.; Arlt, W.; Auchus, R.J.; Baskin, L.S.; Conway, G.S.; Merke, D.P.; Meyer-Bahlburg, H.F.L.; Miller, W.L.; Murad, M.H.; Oberfield, S.E.; et al. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4043–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah-Shmouni, F.; Morissette, R.; Sinaii, N.; Elman, M.; Prezant, T.R.; Chen, W.; Pulver, A.; Merke, D.P. Revisiting the prevalence of nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia in US Ashkenazi Jews and Caucasians. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, S.; Weinrib, L.; Weintrob, N.; Miller, K.; Brautbar, C. Distribution of the V281L mutation of the CYP21 gene in Israeli congenital adrenal hyperplasia patients and its association with HLA-B14. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2006, 3, 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Speiser, P.W.; Dupont, B.; Rubinstein, P.; Piazza, A.; Kastelan, A.; New, M.I. High frequency of nonclassical steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1985, 37, 650–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrozza, C.; Foca, L.; De Paolis, E.; Concolino, P. Genes and Pseudogenes: Complexity of the RCCX Locus and Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 709758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.C.; Grossberger, D.; Onufer, B.J.; Chaplin, D.D.; New, M.I.; Dupont, B.; Strominger, J.L. Two Genes Encoding Steroid 21-Hydroxylase are Located Near the Genes Encoding the Fourth Component of Complement in Man. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.C.; New, M.I.; Dupont, B. Structure of Human Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 5111–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y.; Tanae, A.; Inoue, H.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Evidence for Frequent Gene Conversion in the Steroid 21-Hydroxylase P-450(C21) Gene: Implications for Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1988, 42, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tusié-Luna, M.T.; White, P.C. Gene Conversions and Unequal Crossovers Between CYP21 (Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Gene) and CYP21P Involve Different Mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10796–10800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatelli, D.; Carvalho, B.L.; Palmeiro, A.; Barros, A.; Guerreiro, S.G.; Macut, D. The Complexities in Genotyping of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concolino, P.; Costella, A. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: A Comprehensive Focus on 233 Pathogenic Variants of CYP21A2 Gene. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 22, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Gupta, N. Navigating the Complex Landscape of CYP21A2 Variants. Indian J. Pediatr. 2024, 91, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, L.; Bruque, C.D.; Fernández, C.S.; Benavides-Mori, B.; Delea, M.; Kolomenski, J.E.; Espeche, L.D.; Buzzalino, N.D.; Nadra, A.D.; Dain, L. CYP21A2 Mutation Update: Comprehensive Analysis of Databases and Published Genetic Variants. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xu, Z.; Sullivan, A.; Finkielstain, G.P.; Van Ryzin, C.; Merke, D.P.; McDonnell, N.B. Junction Site Analysis of Chimeric CYP21A1P/CYP21A2 Genes in 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrat, M.; Riahi, A.; Maazoul, F.; M’rad, R.; Chaabouni, H. Detection of a Frequent Duplicated CYP21A2 Gene Carrying a Q318X Mutation in a General Population with Quantitative PCR Methods. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2011, 20, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concolino, P.; Mello, E.; Minucci, A.; Giardina, B.; Capoluongo, E. Genes, Pseudogenes and Like Genes: The Case of 21-Hydroxylase in Italian Population. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2013, 424, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, R.; Moresco, A.; Perez Garrido, N.; Ramirez, P.; Belgorosky, A. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 803226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Q.; Merke, D.P. Molecular genetic testing of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency should include CAH-X chimeras. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 1047–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concolino, P.; Perrucci, A.; Carrozza, C.; Urbani, A. Genetic Characterization of a Cohort of Italian Patients with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2023, 27, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocova, M.; Concolino, P.; Falhammar, H. Characteristics of In2G Variant in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 788812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lin, C.Y. PCR-based detection of the CYP21 deletion and TNXA/TNXB hybrid in the RCCX module. Genomics 2004, 83, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.P.; Cheng, C.F.; Chuang, S.H.; Lee, H.H. Analysis of the CYP21A1P pseudogene: Indication of mutational diversity and CYP21A2-like and duplicated CYP21A2 genes. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 413, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, M.I.; Abraham, M.; Gonzalez, B.; Dumic, M.; Razzaghy-Azar, M.; Chitayat, D.; Sun, L.; Zaidi, M.; Wilson, R.C.; Yuen, T. Genotype-phenotype correlation in 1,507 families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia owing to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concolino, P. Issues with the Detection of Large Genomic Rearrangements in Molecular Diagnosis of 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concolino, P.; Mello, E.; Minucci, A.; Zuppi, C.; Capoluongo, E. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification analysis is useful for diagnosing congenital adrenal hyperplasia but requires a deep knowledge of CYP21A2 genetics. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, N.; Song, X.; Wang, X.Y.; Qin, S.F.; He, G.N.; Sun, L.L.; Chen, X.M. 2+0 CYP21A2 deletion carrier—A limitation of the genetic testing and counseling: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases. 2021, 9, 6789–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajes, S.; Quinteiro, C.; Domínguez, F.; Loidi, L. High frequency of copy number variations and sequence variants at CYP21A2 locus: Implication for the genetic diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppens, P.F.; Hoogenboezem, T.; Degenhart, H.J. Duplication of the CYP21A2 gene complicates mutation analysis of steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: Characteristics of three unusual haplotypes. Hum. Genet. 2002, 111, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; Witsch-Baumgartner, M.; Hoeppner, W. EMQN best practice guidelines for molecular genetic testing and reporting of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 1341–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriba, M.; Ezquieta, B. Molecular Diagnosis of Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: A Practical Approach. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 834549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquieta, B.; Beneyto, M.; Muñoz-Pacheco, R.; Barrio, R.; Oyarzabal, M.; Lechuga, J.L.; Luzuriaga, C.; Hermoso, F.; Quinteiro, S.; Martinez, S. Gene duplications in 21-hydroxylase deficiency: The importance of accurate molecular diagnosis in carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis. Prenat. Diagn. 2006, 26, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekarev, O.; Tafuri, K.; Lane, A.H.; Zhu, G.; Nakamoto, J.M.; Buller-Burckle, A.M.; Wilson, T.A.; New, M.I. Erroneous prenatal diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia owing to a duplication of the CYP21A2 gene. J. Perinatol. 2013, 33, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SALSA MLPA Probe | Exon Position |
|---|---|
| Gene | |
| (■) CYP21A2 probe 22959-L32396 | Exon 4, p.(Ile173Asn) location |
| (▲) CYP21A2 probe 15221-L20261 | Exon 3, p.(Gly111fs) location |
| (►) CYP21A2 probe 17261-L21169 | Exon 7, p.(Leu308fs) location |
| (▼) CYP21A2 probe 17270-L16990 | Exon 6, p.(Val238Glu) location |
| (◄) CYP21A2 probe 17271-L16989 | Exon 6, p.(Met240Lys) location |
| (◊) CYP21A2 probe 21552-L20299 * | Intron 2, c. 293-13A allele |
| (○) CYP21A2 probe 21552-L32321 * | Intron 2, c. 293-13C allele |
| (●) CYP21A2 probe 22964-L32402 | Promoter region, c.-113G>A location |
| Pseudogene | |
| (♦) CYP21A1P probe 22961-L32398 | Exon 4, p.(Ile173Asn) location |
| (□) CYP21A1P probe 15221-L20262 | Exon 3, p.(Gly111fs) location |
| (◙) CYP21A1P probe 17261-L21170 | Exon 7, p.(Leu308fs) location |
| (⸙) CYP21A1P probe 22963-L32401 | Promoter region, c.-113G>A location |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Concolino, P. Challenging Molecular Diagnosis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: Case Series and Novel Variants of CYP21A2 Gene. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4832-4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050291
Concolino P. Challenging Molecular Diagnosis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: Case Series and Novel Variants of CYP21A2 Gene. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(5):4832-4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050291
Chicago/Turabian StyleConcolino, Paola. 2024. "Challenging Molecular Diagnosis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: Case Series and Novel Variants of CYP21A2 Gene" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 5: 4832-4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050291
APA StyleConcolino, P. (2024). Challenging Molecular Diagnosis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: Case Series and Novel Variants of CYP21A2 Gene. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(5), 4832-4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050291






