The ER Stress Induced in Human Neuroblastoma Cells Can Be Reverted by Lumacaftor, a CFTR Corrector
Abstract
1. Introduction
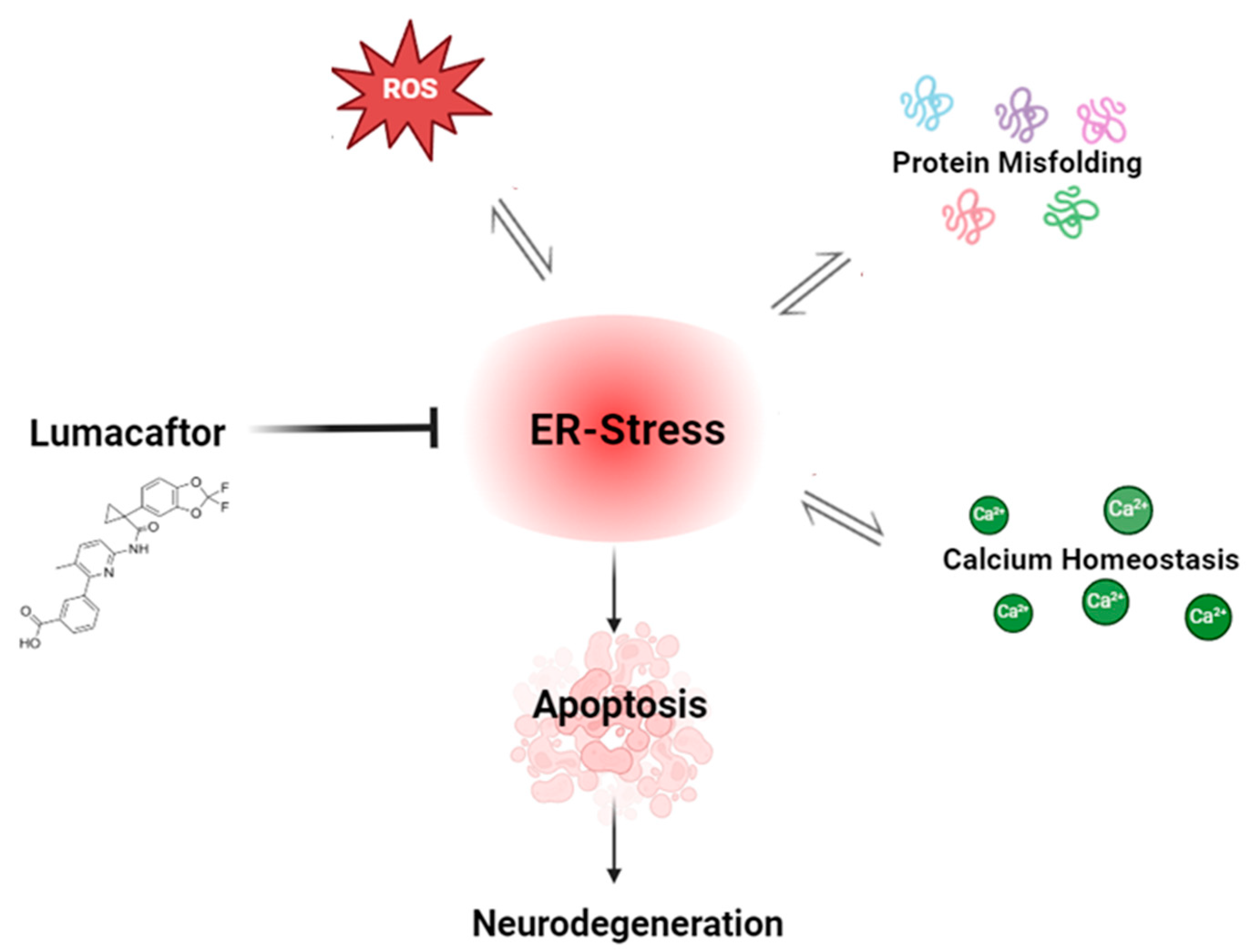
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting Assay
2.6. RNA Extraction and Real-Time RT-PCR Protocol
2.7. Calcium Signaling Assay
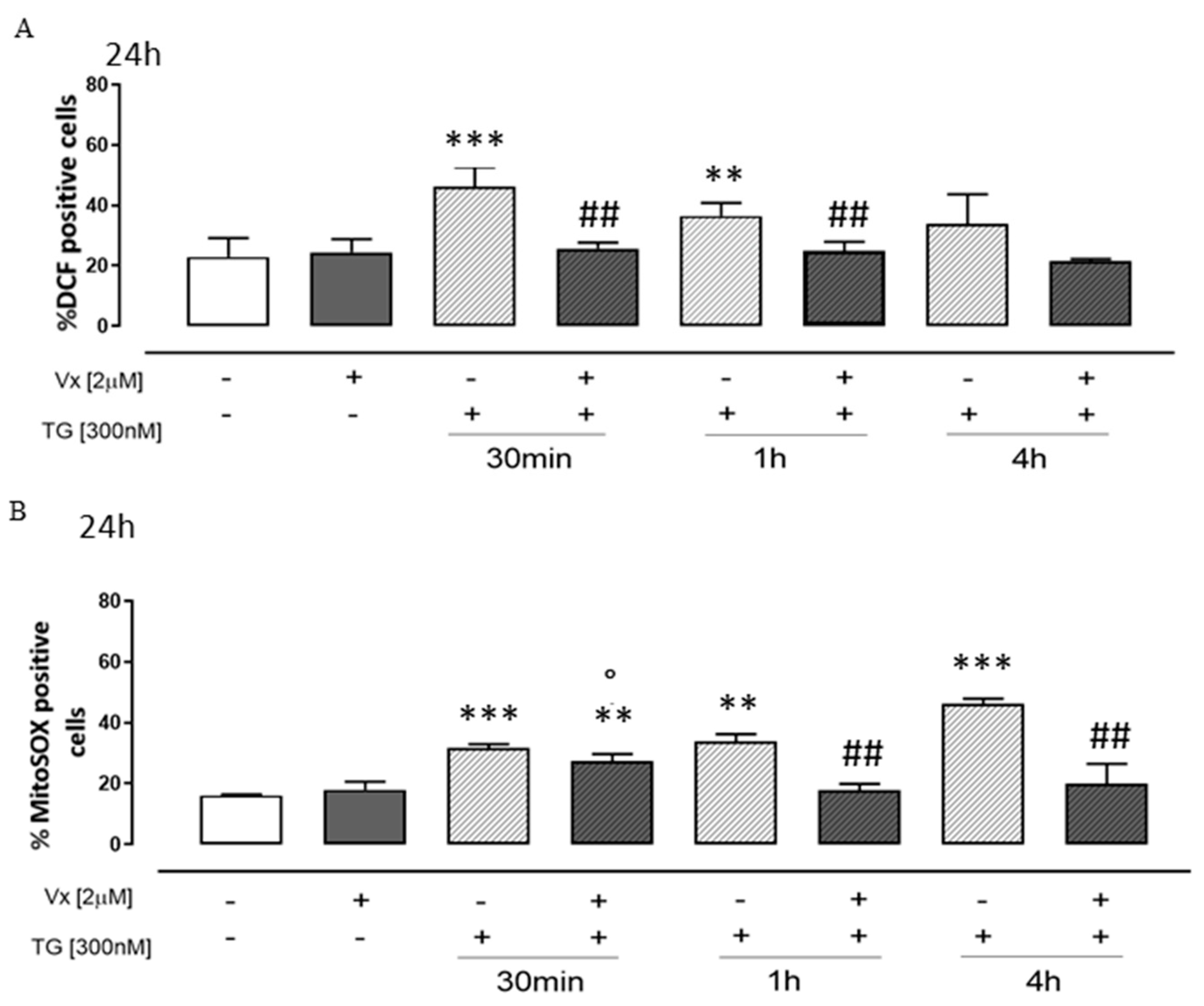
2.8. Intracellular and Mitochondrial ROS Detection
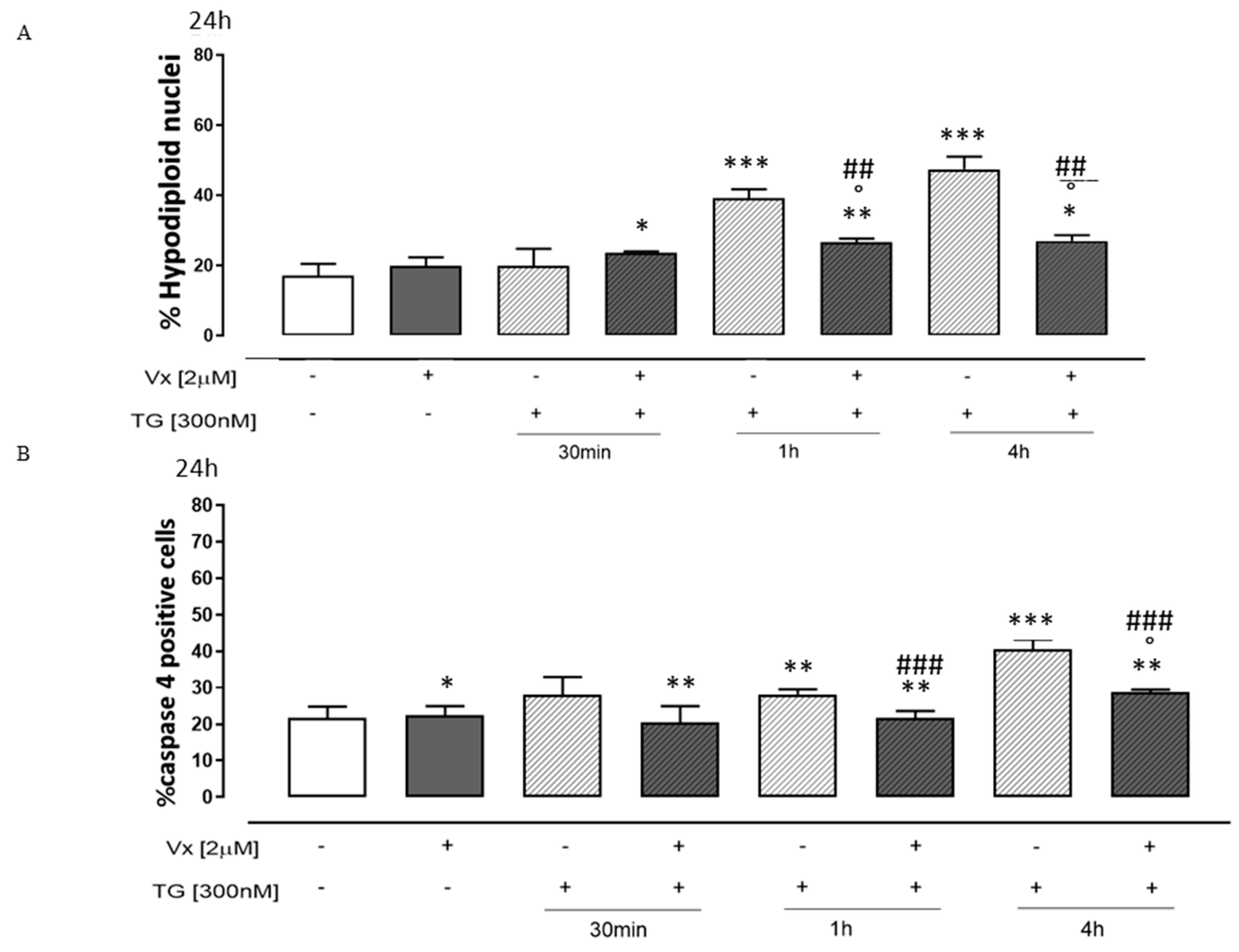
2.9. Caspase 4 Measurement
2.10. Hypodiploid DNA Detection
2.11. Analytical Statistics
3. Results
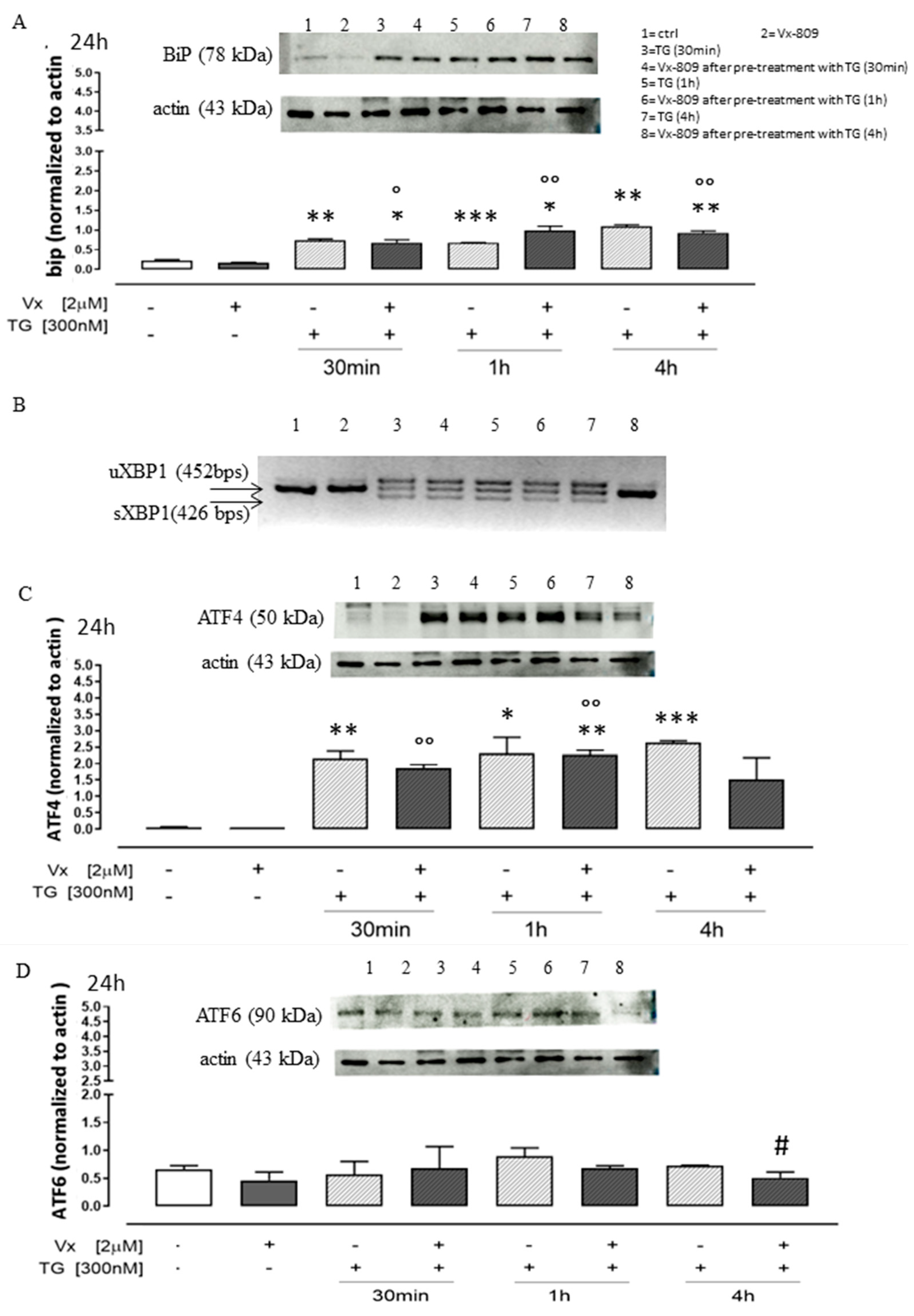
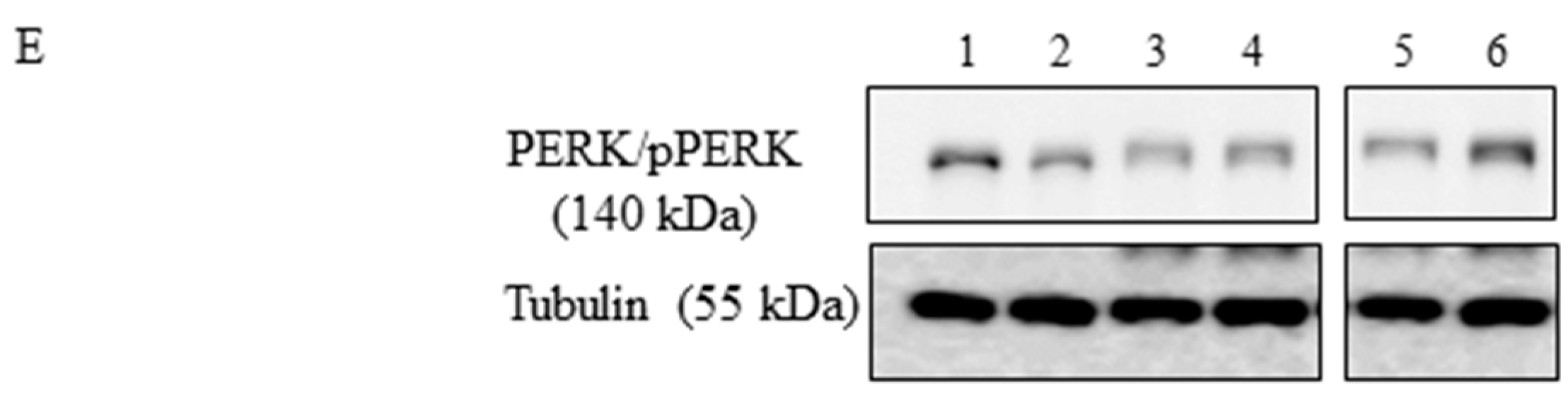
3.1. Role of Vx-809 in UPR Pathway
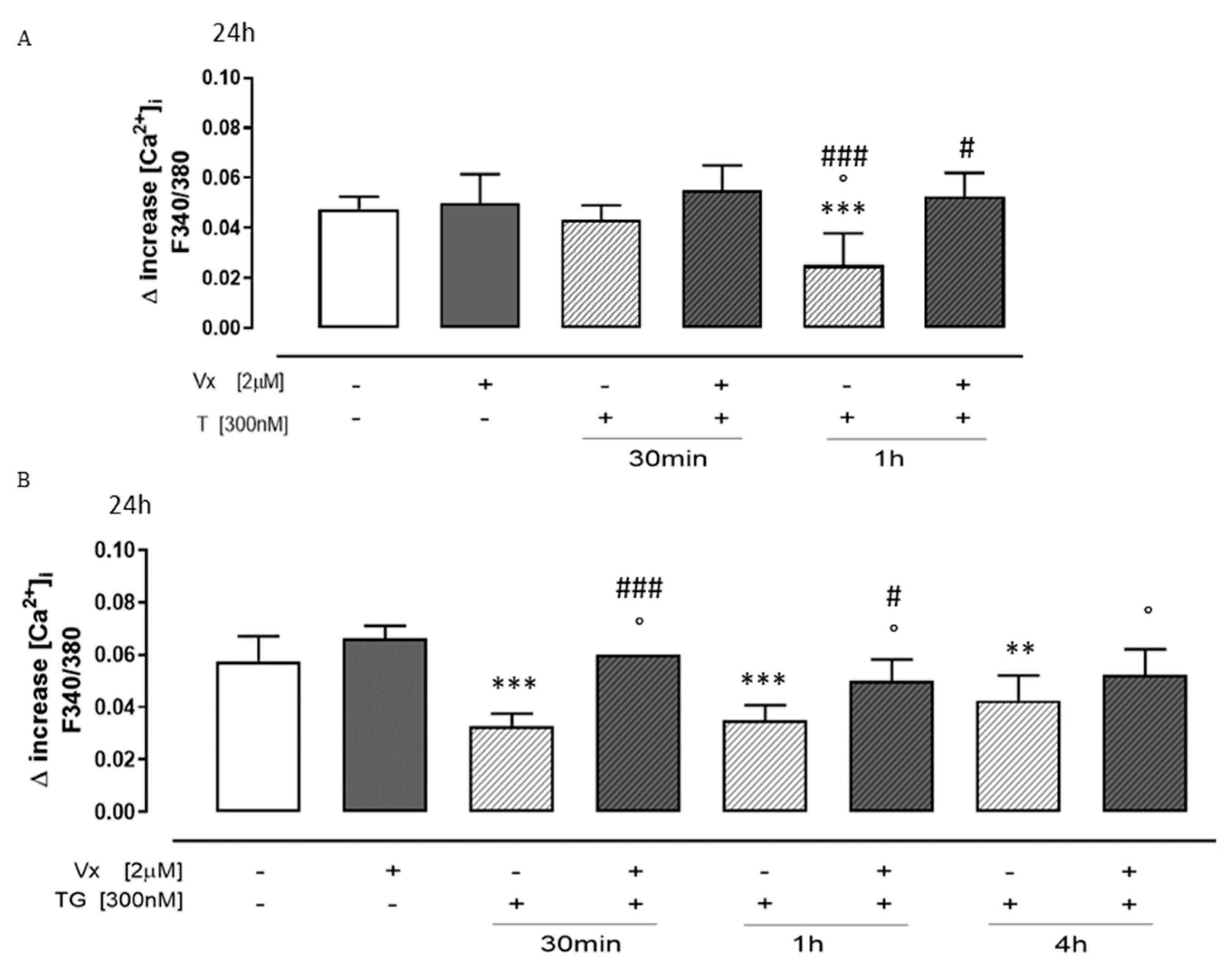
3.2. “Corrector” Vx-809 Interferes on Calcium Signaling
3.3. Vx-809 Counteract Thapsigargin-Induced Oxidative Stress
3.4. Vx-809 Interferes with the Apoptotic Pathway
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| IRE1α | Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 α |
| PERK | Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase |
| ATF6 | Activating transcription Factor 6 |
| GRP78/BiP | Glucose-regulated protein 78/binding immunoglobulin protein |
| eIF2α | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A |
| ATF4 | Activating transcription factor 4 |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| ERAD | ER-associated degradation |
| Vx-809 | Lumacaftor |
| CF | Cystic fibrosis |
| NBD1 | Nucleotide-binding domain 1 |
| TMD1 | Transmembrane domain 1 |
| TG | Thapsygargin |
| NDs | Neurodegenerative diseases |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PrD | Prion disease |
| Xbp1 | X-box binding protein 1 |
| Xbp1s | Spliced Xbp1 |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| SODIII | Superoxide dismutase III |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s Medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-dimetiltiazol]-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide |
| Sp | Staurosporine |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| H2DCF-DA | 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate |
| MitoSOX | Mitochondrial superoxide |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| SERCA | Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase |
| ALSIDP | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosisIntrinsically disordered proteins |
References
- Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2015, 10, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebecca, B.; Berlow, H.; Dyson, J.; Peter, E. Wright, Expanding the Paradigm: Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Allosteric Regulation. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, C.; Pritzkow, S. Protein misfolding, aggregation, and conformational strains in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemrawi, R.; Khair, M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, G.; Greig, N.; Khan, T.; Hassan, I.; Tabrez, S.; Shakil, S.; Sheikh, I.; Zaidi, S.; Akram, M.; Jabir, N.; et al. Protein Misfolding and Aggregation in Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Saxena, S. ER stress and the unfolded protein response in neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frakes, A.E.; Dillin, A. The UPRER: Sensor and Coordinator of Organismal Homeostasis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Meng, Y. Integrated analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress regulators’ expression identifies distinct subtypes of autism spectrum disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 17, 1136154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, M.; Serra, A.; Pascale, M.; Franceschelli, S. Vx-809, a CFTR Corrector, Acts through a General Mechanism of Protein Folding and on the Inflammatory Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, O.J.; Mallucci, G.R. The UPR and synaptic dysfunction in neurodegeneration. Brain Res. 2016, 1648, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kaufman, R.J. Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature 2016, 529, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozada Ortiz, J.; Betancor, M.; Pérez Lázaro, S.; Bolea, R.; Badiola, J.J.; Otero, A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and ubiquitin-proteasome system impairment in natural scrapie. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1175364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, F.; Atkinson, R.; Cook, A.L.; Phipps, A.J.; King, A.E. The role of altered protein acetylation in neurodegenerative disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 14, 1025473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.A.; Halliday, M.; Molloy, C.; Radford, H.; Verity, N.; Axten, J.M.; Ortori, C.A.; Willis, A.E.; Fischer, P.M.; Barrett, D.A.; et al. Oral treatment targeting the unfolded protein response prevents neurodegeneration and clinical disease in prion-infected mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 206ra138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, P.R.; Ludtmann, M.H.R.; Horrocks, M.H.; Negoda, A.; Cremades, N.; Klenerman, D.; Dobson, C.M.; Wood, N.W.; Pavlov, E.V.; Gandhi, S.; et al. Ca2+ is a key factor in α-synuclein-induced neurotoxicity. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrinelli, F.; Mehta, S.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Latorre, A.; Edwards, M.J.; Balint, B.; Basu, P.; Kobylecki, C.; Groppa, S.; Hegde, A.; et al. Dissecting the Phenotype and Genotype of PLA2G6-Related Parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsteins, G.; Hakosalo, V.; Jaronen, M.; Keuters, M.H.; Lehtonen, Š.; Koistinaho, J. CNS Redox Homeostasis and Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, C.E.; Elborn, J.S.; Ramsey, B.W.; Marigowda, G.; Huang, X.; Cipolli, M.; Colombo, C.; Davies, J.C.; De Boeck, K.; Flume, P.A.; et al. Lumacaftor-Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for Phe508del CFTR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, M.; Franceschelli, S.; Pascale, M. Lumacaftor and Matrine: Possible Therapeutic Combination to Counteract the Inflammatory Process in Cystic Fibrosis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laselva, O.; Molinski, S.; Casavola, V.; Bear, C.E. Correctors of the Major Cystic Fibrosis Mutant Interact through Membrane-Spanning Domains. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardin, E.; Pastor, A.; Semeraro, M.; Golec, A.; Hayes, K.; Chevalier, B.; Berhal, F.; Prestat, G.; Hinzpeter, A.; Gravier-Pelletier, C.; et al. Modulators of CFTR. Updates on clinical development and future directions. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, M.; Pinto, A.; Popolo, A. Inhibition of Connexin 43 translocation on mitochondria accelerates CoCl2-induced apoptotic response in a chemical model of hypoxia. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 47, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, M.; Marzocco, S.; Belvedere, R.; Petrella, A.; Franceschelli, S.; Popolo, A. Simvastatin Reduces Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Effects beyond Its Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, P.; Szalai, P.; Olesen, C.; Praetorius, H.A.; Nissen, P.; Christensen, S.B.; Engedal, N.; Møller, J.V. Inhibition of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+-ATPase by thapsigargin analogs induces cell death via ER Ca2+ depletion and the unfolded protein response. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 19656–19673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. Effects of GRP78 on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Inflammatory Response in Macrophages of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kim, K.S.; Iyirhiaro, G.O.; Marcogliese, P.C.; Callaghan, S.M.; Qu, D.; Kim, W.J.; Slack, R.S.; Park, D.S. DJ-1 modulates the unfolded protein response and cell death via upregulation of ATF4 following ER stress. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Sheng, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.L.; Glembotski, C.C.; Warneret, D.S.; Paschen, W.; Yang, W. Activation of the ATF6 branch of the unfolded protein response in neurons improves stroke outcome. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.T.; Li, R.; Yu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.R.; Sheng, H.X.; Yang, W.V. Activation of the ATF6 (Activating Transcription Factor 6) signaling pathway in neurons improves outcome after cardiac arrest in mice. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, S.; Gu, L.; Jian, Z.; Wang, H. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Unfolded Protein Response in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 864426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, G.; Castillo, V.; Soto, P.; Sidhu, A. ER stress and Parkinson’s disease: Pathological inputs that converge into the secretory pathway. Brain Res. 2016, 1648, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.K.; Jeong, S.; Lee, J. The Common Cellular Events in the Neurodegenerative Diseases and the Associated Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Gao, N.; Hu, X.; Luo, H.; Peng, J.; Xia, Y. SOD3 overexpression alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e00831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, S.; Patergnani, S.; Missiroli, S.; Morciano, G.; Rimessi, A.; Wieckowski, M.R.; Giorgi, C.; Pinton, P. Mitochondrial and Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Homeostasis and Cell Death. Cell Calcium 2018, 69, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, M. ROS and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pulmonary Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 879204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Jiang, J. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and drug targets via apoptotic signaling. Mitochondrion 2019, 49, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, E.; Formichi, P.; Battisti, C.; Federico, A. Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42 (Suppl. S3), S125–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukai, Y.; Ito, G.; Konno, M.; Sakata, Y.; Ozaki, T. Mitochondrial calpain-5 truncates caspase-4 during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 608, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.M.M.; Park, J. LONRF2 is a gatekeeper against protein aggregation in aging neurons. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 913–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelise, N.; Scaricamazza, S.; Salvatori, I.; Ferri, A.; Valle, C.; Manganelli, V.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; Misasi, R. Protein Aggregation Landscape in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Clinical Relevance and Future Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, O.I.; Haller, D. ER Stress and the UPR in Shaping Intestinal Tissue Homeostasis and Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.; Castillo, K.; Armisén, R.; Stutzin, A.; Soto, C.; Hetz, C. Prion protein misfolding affects calcium homeostasis and sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Lindholm, D.; Ren, J.; Pratico, D. ER stress and UPR in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, pathogenesis, treatments. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regard, L.; Martin, C.; Burnet, E.; Da Silva, J.; Burgel, P.R. CFTR Modulators in People with Cystic Fibrosis: Real-World Evidence in France. Cells 2022, 11, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Lan, T.H.; Shiau, J.P.; Chen, K.L.; Jeng, J.H.; Yen, C.Y.; Chang, H.W. Oxidative-Stress-Mediated ER Stress Is Involved in Regulating Manoalide-Induced Antiproliferation in Oral Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmer, I.L.; Willemsen, N.; Hilal, N.; Bartelt, A. A guide to understanding endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disorders. Mol. Metab. 2021, 47, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.; Encina, G.; Soto, C.; Hetz, C. Abnormal calcium homeostasis and protein folding stress at the ER: A common factor in familial and infectious prion disorders. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, Y.; Yarjanli, Z.; Pakniya, F.; Bidram, E.; Łos, M.J.; Eshraghi, M.; Klionsky, D.J.; Ghavami, S.; Zarrabi, A. Targeting autophagy, oxidative stress, and ER stress for neurodegenerative disease treatment. J. Control Release 2022, 345, 147–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvandi, M.S.; Sheikhzadeh Hesari, F.; Aref, A.R.; Mahdavi, M. The neuroprotective effects of targeting key factors of neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative diseases: The role of ER stress, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochneva, A.; Zorkina, Y.; Abramova, O.; Pavlova, O.; Ushakova, V.; Morozova, A.; Zubkov, E.; Pavlov, K.; Gurina, O.; Chekhonin, V. Protein Misfolding and Aggregation in the Brain: Common Pathogenetic Pathways in Neurodegenerative and Mental Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pecoraro, M.; Serra, A.; Pascale, M.; Franceschelli, S. The ER Stress Induced in Human Neuroblastoma Cells Can Be Reverted by Lumacaftor, a CFTR Corrector. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9342-9358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090553
Pecoraro M, Serra A, Pascale M, Franceschelli S. The ER Stress Induced in Human Neuroblastoma Cells Can Be Reverted by Lumacaftor, a CFTR Corrector. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(9):9342-9358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090553
Chicago/Turabian StylePecoraro, Michela, Adele Serra, Maria Pascale, and Silvia Franceschelli. 2024. "The ER Stress Induced in Human Neuroblastoma Cells Can Be Reverted by Lumacaftor, a CFTR Corrector" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 9: 9342-9358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090553
APA StylePecoraro, M., Serra, A., Pascale, M., & Franceschelli, S. (2024). The ER Stress Induced in Human Neuroblastoma Cells Can Be Reverted by Lumacaftor, a CFTR Corrector. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(9), 9342-9358. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090553




