As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Key Materials and Equipment
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. CCK-8 Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Flow Cytometric Detection of Apoptosis Levels
2.5. Detection of Cell Cycle Distribution by Flow Cytometry
2.6. Detection of ROS Accumulation Levels by Flow Cytometry and Immunofluorescence
2.7. Protein Immunoblotting for Protein Expression Levels
2.8. q-PCR to Detect mRNA Transcription Levels
2.9. Statistical Analysis Methods
3. Results
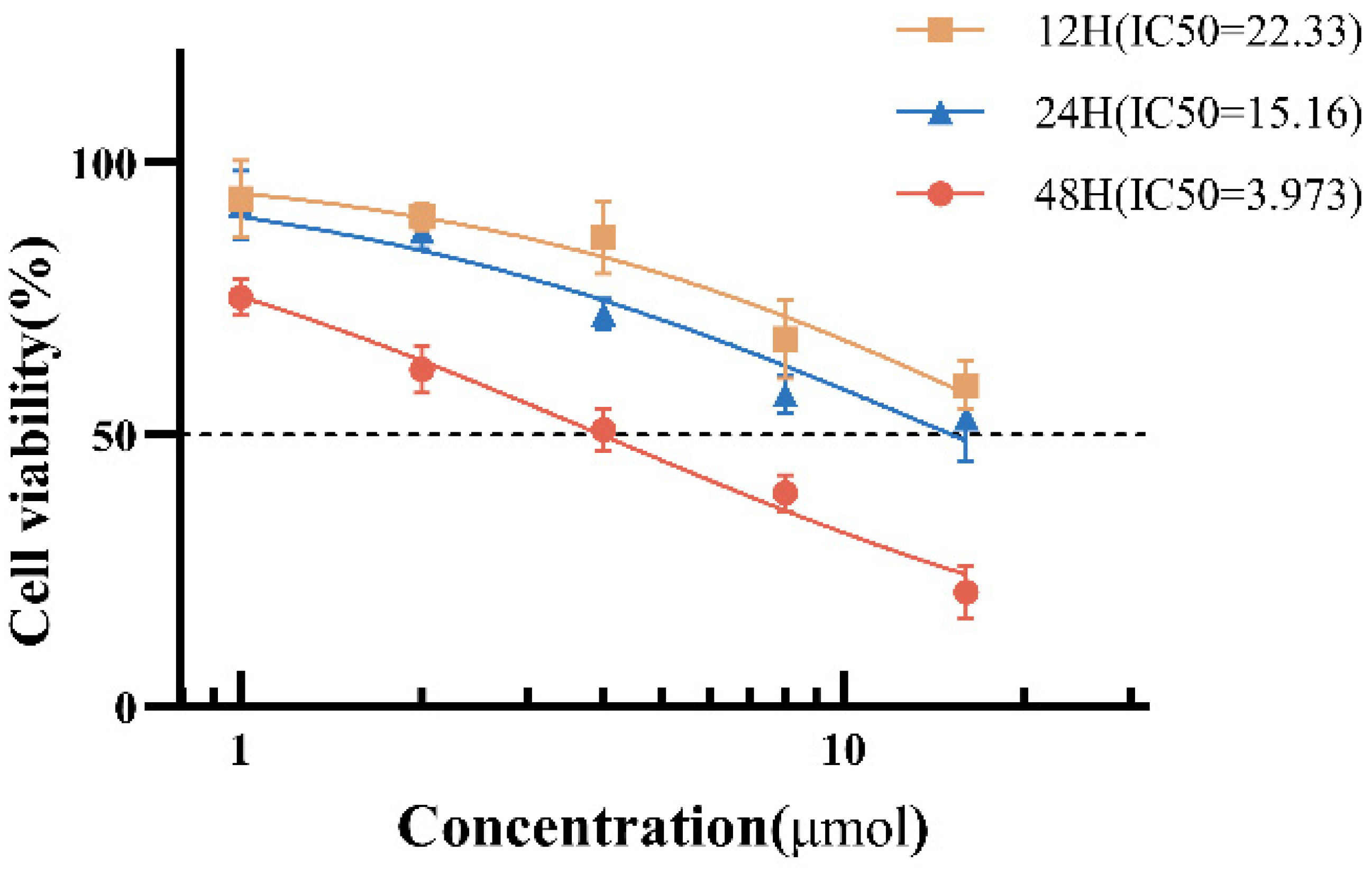
3.1. As2S2 Inhibits SKM-1 Cell Proliferation
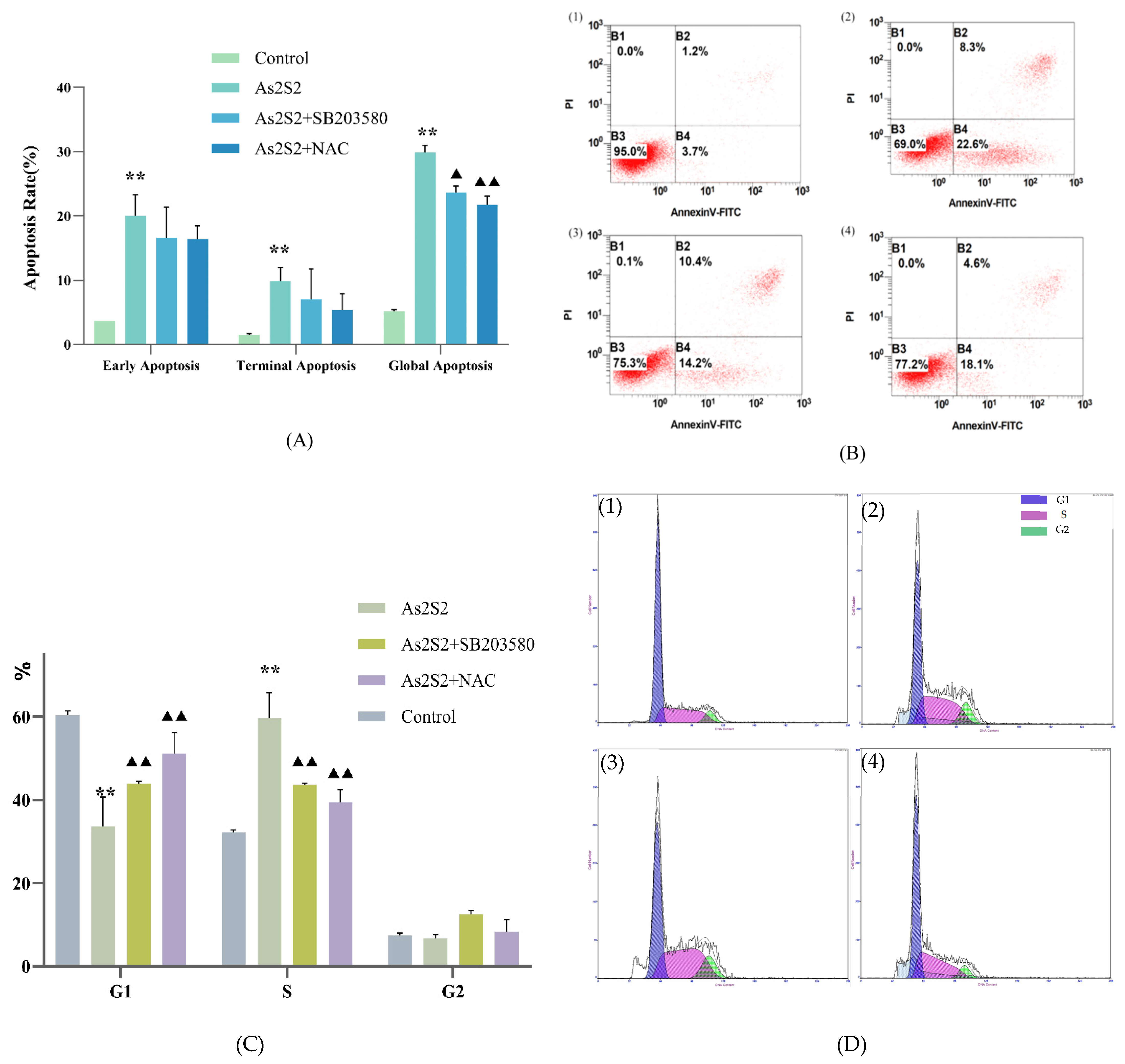
3.2. As2S2 Induces S-Phase Arrest and Apoptosis in the SKM-1 Cell Cycle
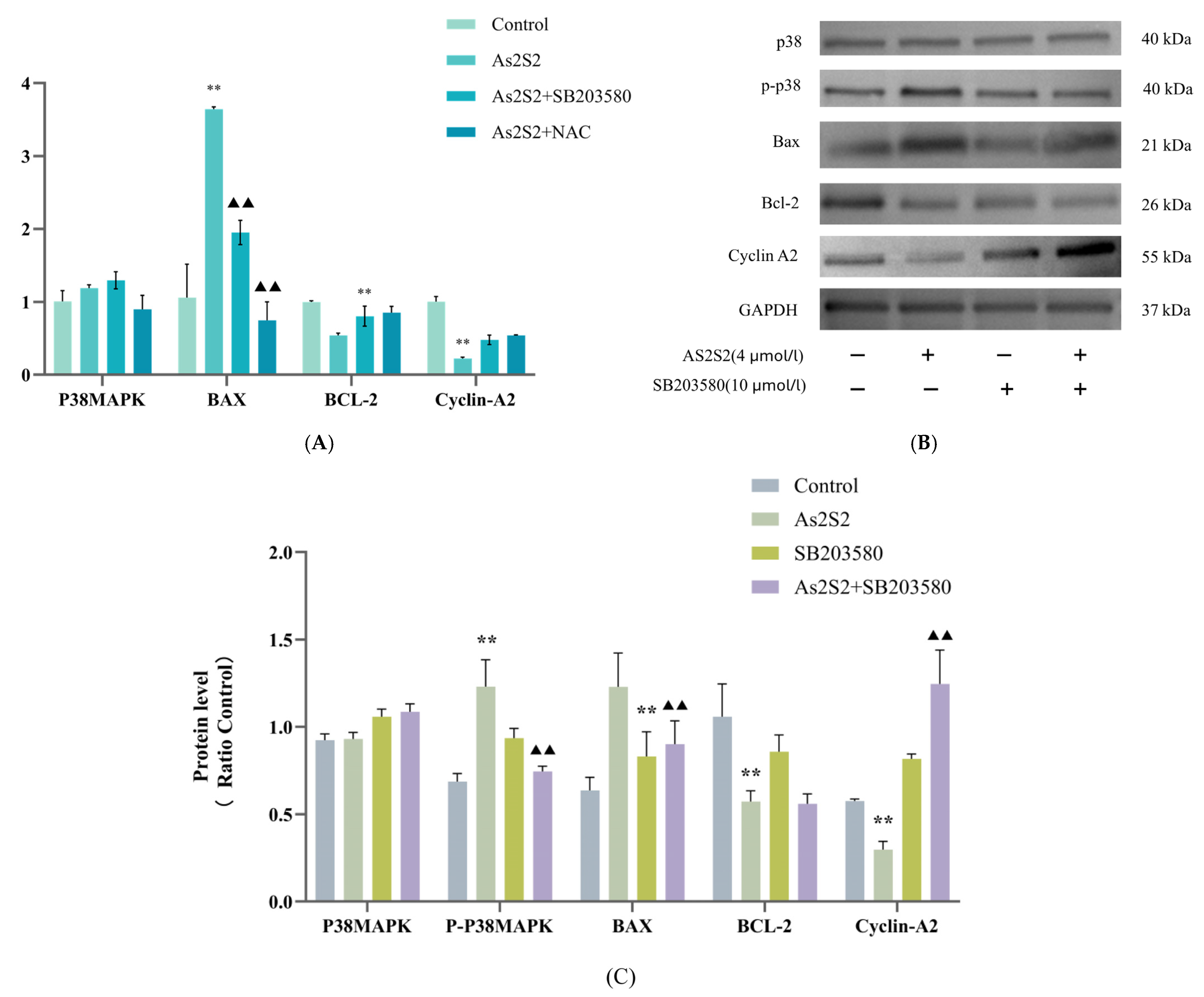
3.3. Effect of As2S2 on Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Regulatory Proteins in SKM-1 Cells
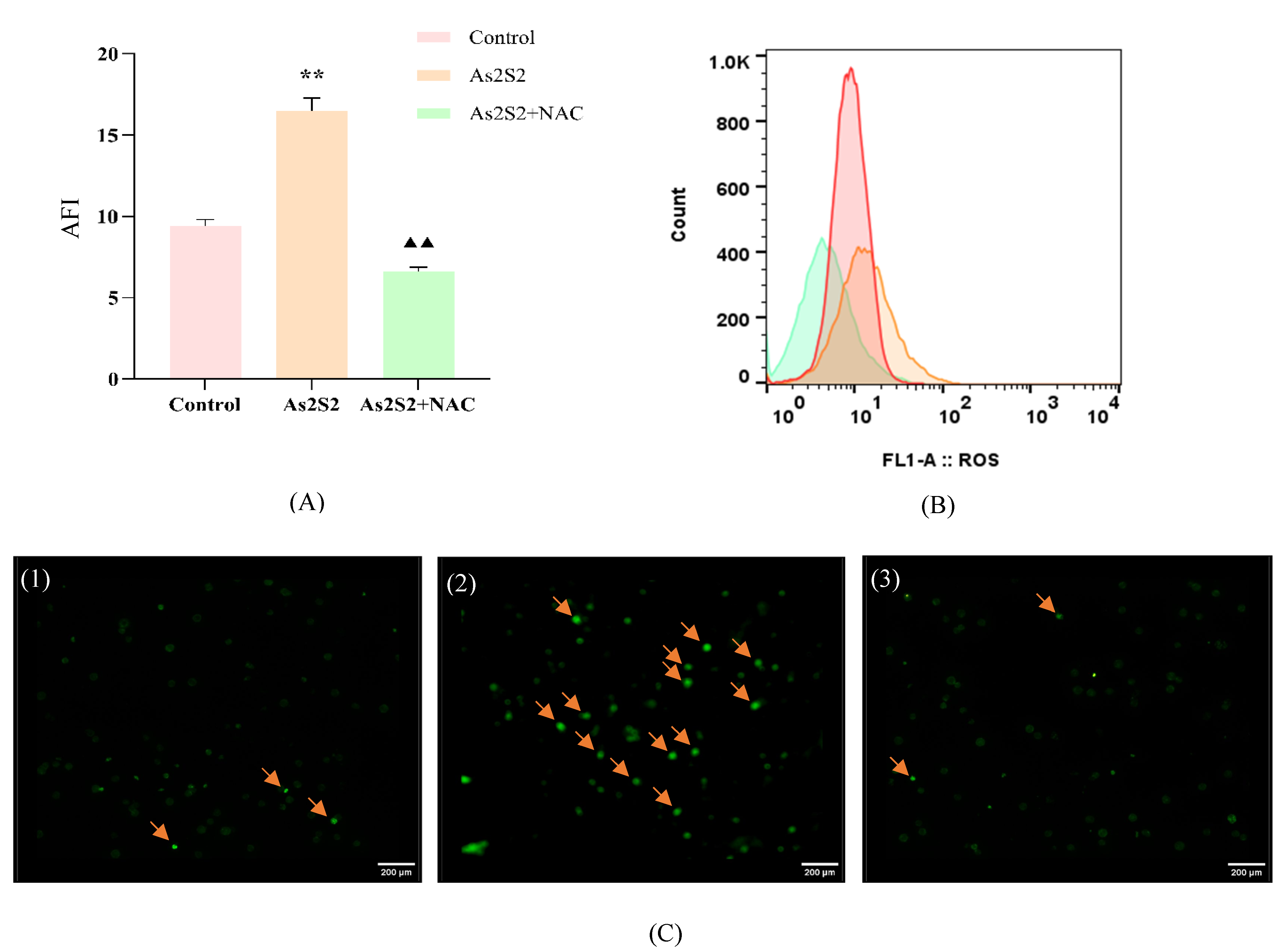
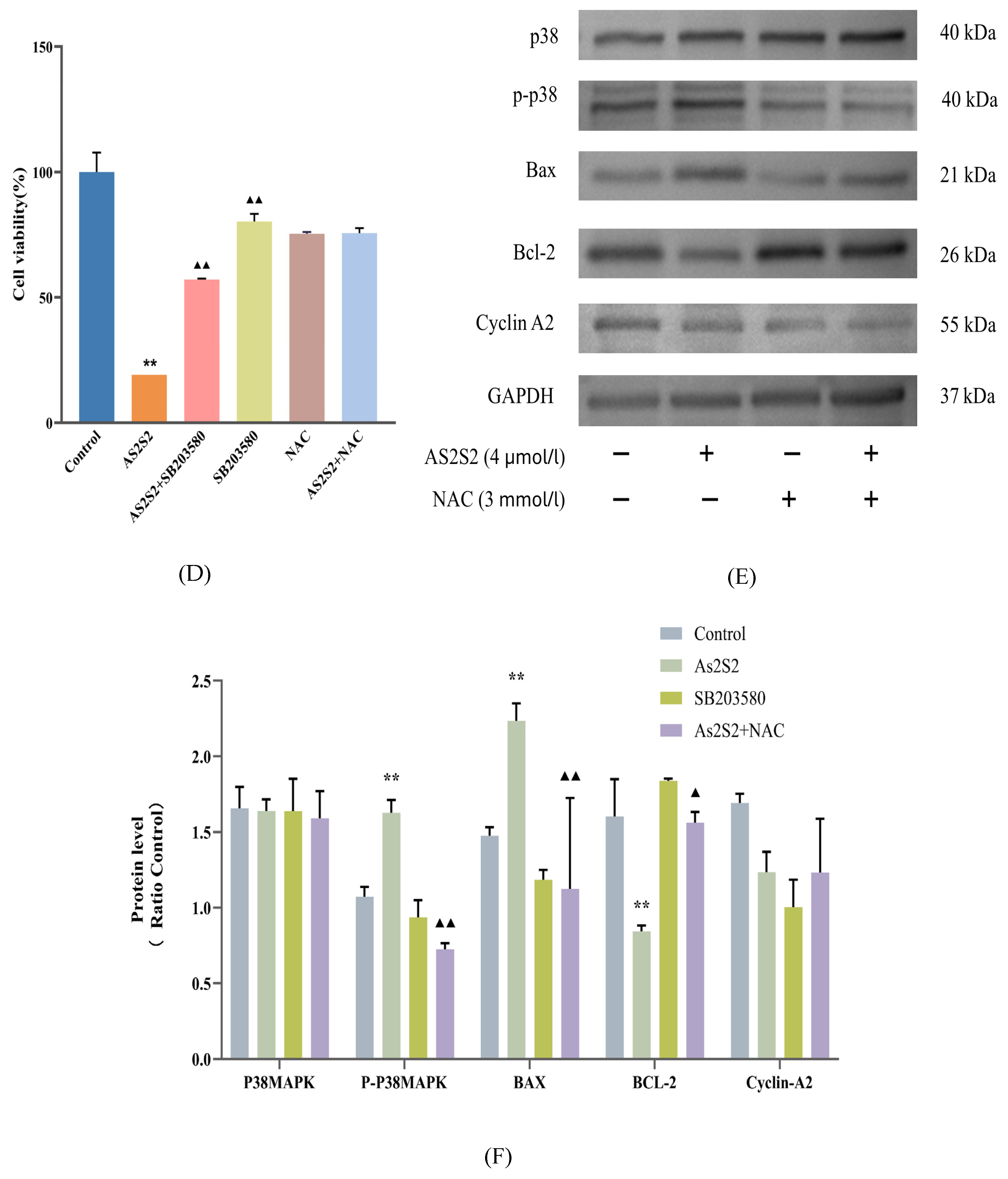
3.4. As2S2 Promotes ROS Accumulation to Activate the P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cazzola, M. Myelodysplastic Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1358–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckstein, R.J. Integrating patient-centered factors in the risk assessment of MDS. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2019, 2019, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekeres, M.A.; Taylor, J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndromes. JAMA 2022, 328, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.-M.; Yuan, B.; Tanaka, S.; Song, M.-M.; Onda, K.; Tohyama, K.; Zhou, A.-X.; Toyoda, H.; Hirano, T. Arsenic disulfide-triggered apoptosis and erythroid differentiation in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia cell lines. Hematology 2013, 19, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, S.-Q.; Li, H.-W.; DU, S.-H.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Li, B.-B.; Liu, C.; Jiao, J.; Teng, Q.-L. Effects of Arsenic Disulfide Combined with Itraconazole on Proli-feration and Apoptosis and Hedgehog Pathway of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2021, 29, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ming, J.; Ming, J.; Liu, W.-Y.; Liu, W.-Y.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Xu, Y.-G.; Xu, Y.-G.; Ma, R.; Ma, R.; et al. Oral Arsenic-Containing Qinghuang Powder: A Potential Drug for Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 28, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, T.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Yin, F.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, D.; Sun, M.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, B.; et al. Arsenic sulfide induces apoptosis and autophagy through the activation of ROS/JNK and suppression of Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in osteosarcoma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 106, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Yuan, B.; Sugiyama, K.; Onda, K.; Kiyomi, A.; Takagi, N.; Sugiura, M.; Hirano, T. Arsenic Disulfide Combined with L-Buthionine-(S, R)-Sulfoximine Induces Synergistic Antitumor Effects in Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Models of MCF-7 Breast Carcinoma Cells Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 1149–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-B.; Liu, Z.-T.; Wang, H.-Z.; Guo, X.-Q.; Xu, Y.-G.; Hu, X.-M. Arsenic Disulfide Promoted Hypomethylation by Increasing DNA Methyltransferases Expression in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Onda, K.; Sugiyama, K.; Yuan, B.; Tanaka, S.; Takagi, N.; Hirano, T. Antitumor effects of arsenic disulfide on the viability, migratory ability, apoptosis and autophagy of breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 41, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boese, A.C.; Kang, S. Mitochondrial metabolism-mediated redox regulation in cancer progression. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Cueto, R.; Effi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, H.; Qin, X.; Ji, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H. Biochemical basis and metabolic interplay of redox regulation. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.-M.; Tang, Y.-J.; Cao, J.-L.; Hou, W.-S.; Wang, A.-Q.; Wang, C.; Jin, C.-H. Jaceosidin induces apoptosis and inhibits migration in AGS gastric cancer cells by regulating ROS-mediated signaling pathways. Redox Rep. 2024, 29, 2313366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Nan, J.; Si, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Guo, T. Exploring the therapeutic potential of rabdoternin E in lung cancer treatment: Targeting the ROS/p38 MAPK/JNK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 30, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Liu, F.; Ma, R. Application and assessment of Chinese arsenic drugs in treating malignant hematopathy in China. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2010, 16, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, B.; Onda, K.; Sugiyama, K.; Tanaka, S.; Takagi, N.; Hirano, T. Anticancer efficacies of arsenic disulfide through apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest, and pro-survival signal inhibition in human breast cancer cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 366–386. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Kim, S.; Ding, W.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, M. Arsenic sulfide inhibits cell migration and invasion of gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5579–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.-B.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Huang, J.-M.; Xie, Y.-J.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Fan, X.-X.; Yao, X.-J.; Xie, C.; et al. Plumbagin suppresses non-small cell lung cancer progression through downregulating ARF1 and by elevating CD8+ T cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 169, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulavin, D.V.; Higashimoto, Y.; Popoff, I.J.; Gaarde, W.A.; Basrur, V.; Potapova, O.; Appella, E.; Fornace, A.J. Initiation of a G2/M checkpoint after ultraviolet radiation requires p38 kinase. Nature 2001, 411, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, C.H.; Fung, T.K.; Poon, R.Y.C. Cyclin A in cell cycle control and cancer. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatat, A.-A.S.; Mahgoup, E.M.; Rashed, M.H.; Saleh, I.G.; Akool, E.-S. Molecular mechanisms of extracellular-ATP-mediated colorectal cancer progression: Implication of purinergic receptors-mediated nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HuR. Purinergic Signal 2024, 20, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.K.; Shah, M.A. Targeting the Cell Cycle: A New Approach to Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 9408–9421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Xia, W.; Neuzil, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Wu, K. Bid integrates intrinsic and extrinsic signaling in apoptosis induced by α-tocopheryl succinate in human gastric carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 288, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesik, S.W. Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, L.A.; Tavallai, S.; Hamed, H.A.; Cruickshanks, N.; Dent, P. The role of cell signalling in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Signal 2013, 26, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; Gwak, D.S.; Shin, S.Y.; Jun, D.Y.; Kim, Y.H. L-Cysteine mitigates ROS-induced apoptosis and neurocognitive deficits by protecting against endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in mouse neuronal cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, F.; Handali, S.; Rezaei, M. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the cytotoxic synergistic effect of gemcitabine and arsenic on breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0312424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tong, X.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, Y. Role of reactive oxygen species in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato-Nagaoka, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, S.; Takahashi, S. Combination of triciribine and p38 MAPK inhibitor PD169316 enhances the differentiation effect on myeloid leukemia cells. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Lv, Y.; Hong, F.; Wu, D.; Wang, T.; Gao, G.; Lin, Z.; Yang, R.; Hu, J.; He, A.; et al. Peroxiredoxin 6 maintains mitochondrial homeostasis and promotes tumor progression through ROS/JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in multiple myeloma. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Sequence 5’ → 3’ |
|---|---|
| P38 MAPK | TGCGTCTGACAGGAACACCTCTTCTCCAGCAAGTCGACAG |
| BAX | GCCCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTTCCACTCGCTCAGCTTCTTGGT |
| BCL-2 | TGTCCCTTTGACCTTGTTTCTTCATTTGCCATCTGGATTTT |
| Cyclin-A2 | CTGCTCCAACAGTAAATCAGTTTCAAGGCAGCTCCAGCATAAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Yu, L.; Yang, R.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X. As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040253
Chen P, Yu L, Yang R, Zeng W, Chen Y, Wang F, Xu Y, Yang X. As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(4):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040253
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pengjie, Li Yu, Rui Yang, Wen Zeng, Yanxi Chen, Fengmei Wang, Yonggang Xu, and Xiupeng Yang. 2025. "As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 4: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040253
APA StyleChen, P., Yu, L., Yang, R., Zeng, W., Chen, Y., Wang, F., Xu, Y., & Yang, X. (2025). As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(4), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040253





