Itaconic Acid: A Regulator of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
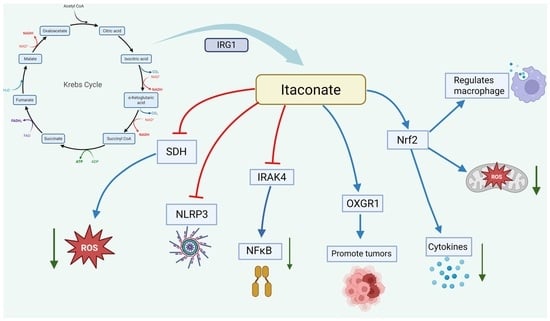
2. Biosynthesis of Itaconic Acid and Its Inhibitory Effect on Succinate Dehydrogenase
3. Role of Itaconic Acid in Immune Regulation
3.1. Regulation of Macrophage Function by Itaconic Acid and Its Role in Anti-Tumor Immunity
3.2. Effects of Itaconic Acid on Other Immune Cells Such as T Cells and B Cells
4. Role of Itaconic Acid in Inflammatory Metabolism
4.1. Regulatory Effects of Itaconic Acid and Its Derivatives on Inflammatory Factors
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Itaconic Acid in Sepsis
- (A)
- Early Hyperinflammatory Phase:Pathogen Recognition: LPS or other pathogen-associated molecular patterns activate macrophages, upregulating IRG1 and triggering itaconate synthesis from cis-aconitate in the TCA cycle.Nrf2/HO-1 Activation: Itaconate (or its derivative, 4-OI) modifies KEAP1, releasing Nrf2 to translocate into the nucleus. This upregulates HO-1 and NQO-1 (NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1) to reduce oxidative stress.Nrf2 activation leads to subsequent inhibition of NF-κB-mediated cytokine production.
- (B)
- Immunoparalysis Phase:Persistent SDH inhibition disrupts the TCA cycle, reducing ATP production.Energy depletion impairs immune cell function, leading to immunosuppression.
4.3. Effect of Itaconic Acid on Inflammatory Metabolic Pathways
4.4. Effect of Itaconic Acid on Lipid Metabolism
4.5. Role of Itaconic Acid in Anemia
5. Mechanism of Action of Itaconic Acid
5.1. Itaconic Acid Covalently Modifies Proteins Through a Michael Addition Reaction
5.2. Competitive Binding of Itaconic Acid to α-Ketoglutarate Affects Epigenetic Modifications
5.3. Itaconic Acid Acts as a Paracrine Signaling Molecule Through the G Protein-Coupled Receptor OXGR1
6. Biological Roles and Mechanisms of Itaconyl-CoA
7. Pharmacological Effects and Clinical Potential of Itaconic Acid
7.1. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Itaconic Acid Derivatives
7.2. The Application Prospect of Itaconic Acid in Clinical Treatment
7.3. Safety and Efficacy of Itaconic Acid as a Drug Candidate
8. Role of Itaconic Acid in Bacterial and Viral Infections and Autoimmune Diseases
9. Future Research Directions, Challenges, and Prospects
9.1. Non-Inflammatory Functions and Therapeutic Potential
9.2. Long-Term Safety and Clinical Application
9.3. Summary and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, X.; Tang, C. Itaconate: An emerging determinant of inflammation in activated macrophages. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Bambouskova, M.; Nair, S.; Vincent, E.E.; Loginicheva, E.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Ma, X.; Huang, S.C.; Griss, T.; et al. Itaconate links inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase with macrophage metabolic remodeling and regulation of inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Noh, M.H.; Moon, J.H.; Milito, A.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.W.; Yang, J.S.; Jung, G.Y. Kinetic compartmentalization by unnatural reaction for itaconate production. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Elgaher, W.A.M.; Winterhoff, M.; Büssow, K.; Waqas, F.H.; Graner, E.; Pires-Afonso, Y.; Casares Perez, L.; de la Vega, L.; Sahini, N.; et al. Citraconate inhibits ACOD1(IRG1) catalysis, reduces interferon responses and oxidative stress, and modulates inflammation and cell metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 534–546. [Google Scholar]
- Michelucci, A.; Cordes, T.; Ghelfi, J.; Pailot, A.; Reiling, N.; Goldmann, O.; Binz, T.; Wegner, A.; Tallam, A.; Rausell, A.; et al. Immune-responsive gene 1 protein links metabolism to immunity by catalyzing itaconic acid production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7820–7825. [Google Scholar]
- Strelko, C.L.; Lu, W.Y.; Dufort, F.J.; Seyfried, T.N.; Chiles, T.C.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Roberts, M.F. Itaconic acid is a mammalian metabolite induced during macrophage activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16386–16389. [Google Scholar]
- Cordes, T.; Metallo, C.M. Itaconate alters succinate and coenzyme a metabolism via inhibition of mitochondrial complex II and methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. Metabolites 2021, 11, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, W.W.; Potter, V.R. Enzyme inhibition in relation to chemotherapy. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1949, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, P.; Kofman, S.B.; Smith, J.R.; Norris, G.T.; Snyder, A.G.; Kolb, J.P.; Gao, X.; Locasale, J.W.; Martinez, J.; Gale, M.; et al. The nucleotide sensor ZBP1 and kinase RIPK3 induce the enzyme IRG1 to promote an antiviral metabolic state in neurons. Immunity 2019, 50, 64–76.e64. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, A.; Nonnenmacher, Y.; Henne, A.; Khalil, M.A.; Bejkollari, K.; Dostert, C.; Hosseini, S.; Goldmann, O.; He, W.; Palorini, R.; et al. Itaconate controls its own synthesis via feedback-inhibition of reverse TCA cycle activity at IDH2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166530. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, H.; Wei, J.; Mo, W.; Li, Q.; Lv, X. The signaling pathways and therapeutic potential of itaconate to alleviate inflammation and oxidative stress in inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 2022, 58, 102553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swain, A.; Bambouskova, M.; Kim, H.; Andhey, P.S.; Duncan, D.; Auclair, K.; Chubukov, V.; Simons, D.M.; Roddy, T.P.; Stewart, K.M.; et al. Comparative evaluation of itaconate and its derivatives reveals divergent inflammasome and type I interferon regulation in macrophages. Nat. Metab. 2022, 2, 594–602. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, N.; Madore, V.; Albalakhi, A.; Lin, S.; Stimpson, T.; Xu, Y.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Bakshi, R. Microglia-dependent neuroprotective effects of 4-octyl itaconate against rotenone-and MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Pang, C.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhan, H. Regulation of newly identified lysine lactylation in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2024, 587, 216680. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Huang, H.; Xie, Z.; Ma, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Shi, P.; et al. Octyl itaconate inhibits osteoclastogenesis by suppressing Hrd1 and activating Nrf2 signaling. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 12929–12940. [Google Scholar]
- Bourner, L.A.; Chung, L.A.; Long, H.; McGettrick, A.F.; Xiao, J.; Roth, K.; Bailey, J.D.; Strickland, M.; Tan, B.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Endogenously produced itaconate negatively regulates innate-driven cytokine production and drives global ubiquitination in human macrophages. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114570. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, C.; Castro-Dopico, T.; Richoz, N.; Tuong, Z.K.; Ferdinand, J.R.; Lok, L.S.C.; Loudon, K.W.; Banham, G.D.; Mathews, R.J.; Cader, Z.; et al. Macrophage metabolic reprogramming presents a therapeutic target in lupus nephritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15160–15171. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Zhang, P.; Yin, Y.; Tao, K.; Li, R. Protective effects of IRG1/itaconate on acute colitis through the inhibition of gasdermins-mediated pyroptosis and inflammation response. Genes Dis. 2022, 10, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, N.; Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Wei, R.; Yang, Q.; He, F.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; Feng, M. Artificial cells delivering itaconic acid induce anti-inflammatory memory-like macrophages to reverse acute liver failure and prevent reinjury. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101132. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Kong, X.; Feng, Z.; Jin, Z.; Wang, M.; Lu, H.; Chen, G. 4-Octyl itaconate protects chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 methylation in osteoarthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 137, 112531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Jiao, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, X.; Jia, H.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, Y. Dimethyl Itaconate alleviates the inflammatory responses of macrophages in sepsis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shi, B.; Suo, R.; Xiong, S.; Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Li, G. Itaconate regulates macrophage function through stressful iron-sulfur cluster disrupting and iron metabolism rebalancing. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakkala, J.R.; Yao, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Mao, Z.; Lu, L.; Gao, C. Dimethyl Itaconate-loaded nanofibers rewrite macrophage polarization, reduce inflammation, and enhance repair of myocardic infarction. Small 2021, 17, e2006992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- An, L.; Zhai, Q.; Tao, K.; Xiong, Y.; Ou, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X.; Ji, J.; Lu, M. Quercetin induces itaconic acid-mediated M1/M2 alveolar macrophages polarization in respiratory syncytial virus infection. Phytomedicine 2024, 130, 155761. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, N.; Guo, J.; Liu, W.; Guo, K.; Ling, X.; Zhang, L. 4-octyl itaconate improves the viability of D66H cells by regulating the KEAP1-NRF2-GCLC/HO-1 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 962–975. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Kang, J.; Jiang, H.; Gong, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Liu, M.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. 4-octyl itaconate as a metabolite derivative inhibits inflammation via alkylation of STING. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Qian, S.; Wu, P.; Yu, B.; Yin, D.; Peng, X.; Li, S.; Xiao, Z.; Xie, Z. Tumor-associated macrophage-derived itaconic acid contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by promoting immune escape via TET2. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 413. [Google Scholar]
- Muri, J.; Wolleb, H.; Broz, P.; Carreira, E.M.; Kopf, M. Electrophilic Nrf2 activators and itaconate inhibit inflammation at low dose and promote IL-1β production and inflammatory apoptosis at high dose. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101647. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Cai, X.; Yu, N.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z. 4-Octyl Itaconate activates Nrf2 signaling to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 979–990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Teng, D.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Jiang, T.; Feng, A.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Frederick, D.T.; Gu, L.; et al. Myeloid-derived itaconate suppresses cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells and promotes tumour growth. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Long, R.; Han, Y. The role of exosomes in the tumour microenvironment on macrophage polarization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Yang, F.; Zeng, Y.X.; Sun, P.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Itaconate is a lysosomal inducer that promotes antibacterial innate immunity. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2844–2857.e2810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McGettrick, A.F.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Two for the price of one: Itaconate and its derivatives as an anti-infective and anti-inflammatory immunometabolite. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2023, 80, 102268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Runtsch, M.C.; Angiari, S.; Hooftman, A.; Wadhwa, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Spina, J.S.; Ruzek, M.C.; Argiriadi, M.A.; McGettrick, A.F.; et al. Itaconate and itaconate derivatives target JAK1 to suppress alternative activation of macrophages. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 487–501.e488. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, L.M.; Leighton, I.; Schwarz, B.; Wehrly, T.D.; Evans, T.J.; Bosio, C.M. Itaconate indirectly influences expansion of effector T cells following vaccination with Francisella tularensis live vaccine strain. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 373, 104485. [Google Scholar]
- Aso, K.; Kono, M.; Kanda, M.; Kudo, Y.; Sakiyama, K.; Hisada, R.; Karino, K.; Ueda, Y.; Nakazawa, D.; Fujieda, Y.; et al. Itaconate ameliorates autoimmunity by modulating T cell imbalance via metabolic and epigenetic reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 984. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Artyomov, M.N. Itaconate: The poster child of metabolic reprogramming in macrophage function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Chen, F.; Wang, N. ACOD1 in immunometabolism and disease. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 822–833. [Google Scholar]
- Hooftman, A.; O’Neill, L.A.J. The immunomodulatory potential of the metabolite itaconate. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 687–698. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, B.; Xiao, X.; Qian, Q.; Wang, R.; Lyu, Z.; Chen, R.; Cui, N.; Ou, Y.; Pu, X.; et al. Itaconate inhibits CD103+ TRM cells and alleviates hepatobiliary injury in mouse models of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2024, 79, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Zeng, L.; Yu, C.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Billiar, T.R.; Jiang, J.; Tang, D.; et al. Aconitate decarboxylase 1 is a mediator of polymicrobial sepsis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo2028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, P.; Li, R.; Yin, Y.; Xie, G.; Shi, L.; Zhang, P.; Tao, K. Investigating the role of itaconate in macrophage activation and oxidative stress injury in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Su, Q.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Ren, H.; Zheng, S.; Hui, S.; et al. 4-Octyl itaconate attenuates renal tubular injury in db/db mice by activating Nrf2 and promoting PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2403653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Han, C.; Xu, D.; Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, L. 4-Octyl itaconate inhibits aerobic glycolysis by targeting GAPDH to exert anti-inflammatory effects. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5091. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Xu, T.; Feng, X.; Lai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, H.; He, X.; Wei, G.; Liao, W.; Liao, Y.; et al. Itaconate prevents abdominal aortic aneurysm formation through inhibiting inflammation via activation of Nrf2. EBioMedicine 2020, 57, 102832. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Shi, L.; Yin, Y.; Tao, K.; Li, R. Immune-responsive gene 1 protects against liver injury caused by concanavalin A via the activation Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibition of ROS activation pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 182, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, R.; Tao, K. Immune Response Gene-1 [IRG1]/itaconate protect against multi-organ injury via inhibiting gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis and inflammatory response. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 419–432. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Su, W.; Chen, F.; Lai, T.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D. Mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of 4-octyl itaconate in treating sepsis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1056405. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, W.; Liao, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, M.; Li, X.; Lin, Q.; Cao, C. Molecular mechanisms underlying the renal protective effects of coenzyme Q10 in acute kidney injury. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022, 27, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Zou, L.; Lang, S. 4-Octyl itaconate (4-OI) attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppress ing PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways in mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Peng, Q.; Jin, Y.; Shi, G.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, Z. Four-Octyl itaconate protects chondrocytes against H2O2 induced oxidative injury and attenuates osteoarthritis progression by activating Nrf2 signaling. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 2206167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Han, C.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; et al. Immune responsive gene 1 (IRG1) promotes endotoxin tolerance by increasing A20 expression in macrophages through reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 16225–16234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Long, D.; Zabalawi, M.; Ingram, B.; Yoza, B.K.; Stacpoole, P.W.; McCall, C.E. Stimulating pyruvate dehydrogenase complex reduces itaconate levels and enhances TCA cycle anabolic bioenergetics in acutely inflamed monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Novakovic, B.; Li, Y.; Scicluna, B.P.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Arts, R.J.; Oosting, M.; Moorlag, S.J.C.F.M.; Groh, L.A.; Zwaag, J.; et al. The itaconate pathway is a central regulatory node linking innate immune tolerance and trained immunity. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 211–220.e5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.S.; Chang, H.H. Emerging role of the itaconate-mediated rescue of cellular metabolic stress. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2021, 34, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, J.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Song, Y.; Dong, D.; Shi, L.; Xu, D. ATF3 positively regulates antibacterial immunity by modulating macrophage killing and migration functions. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 839502. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gong, W.; Li, W.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, T.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. The IRG1-Itaconate axis: A regulatory hub for immunity and metabolism in macrophages. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 42, 364–378. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Liu, H.; Cai, W.; Han, D.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xie, S. 4-Octyl Itaconate supplementation relieves soybean diet-induced liver inflammation and glycolipid metabolic disorders by activating the Nrf2-Pparγ pathway in juvenile gibel carp. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 520–531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhi, Y.; Zan, X.; Fan, K.; Chen, K.; Zhao, S.; Dai, X.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Hu, K.; et al. Immune response gene 1 deficiency aggravates high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via promotion of redox-sensitive AKT suppression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166656. [Google Scholar]
- Cordes, T.; Wallace, M.; Michelucci, A.; Divakaruni, A.S.; Sapcariu, S.C.; Sousa, C.; Koseki, H.; Cabrales, P.; Murphy, A.N.; Hiller, K.; et al. Immunoresponsive Gene 1 and Itaconate Inhibit Succinate Dehydrogenase to Modulate Intracellular Succinate Levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 14274–14284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bambouskova, M.; Gorvel, L.; Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Loginicheva, E.; Johnson, K.; Korenfeld, D.; Mathyer, M.E.; Kim, H.; Huang, L.H.; et al. Electrophilic properties of itaconate and derivatives regulate the IκBζ-ATF3 inflammatory axis. Nature 2018, 556, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, B.; Peng, L.; Chen, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. S-glycosylation-based cysteine profiling reveals regulation of glycolysis by itaconate. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.M.; Palmieri, E.M.; Gonzalez-Cotto, M.; Bettencourt, I.A.; Megill, E.L.; Snyder, N.W.; McVicar, D.W. Itaconic acid underpins hepatocyte lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in male mice. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 981–995. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, D.G.; Murphy, M.P.; Frezza, C.; Prag, H.A.; Chouchani, E.T.; O’Neill, L.A.; Mills, E.L. Coupling Krebs cycle metabolites to signalling in immunity and cancer. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 16–33. [Google Scholar]
- Medlock, A.E.; Dailey, H.A. New Avenues of Heme Synthesis Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7467. [Google Scholar]
- Marcero, J.R.; Cox, J.E.; Bergonia, H.A.; Medlock, A.E.; Phillips, J.D.; Dailey, H.A. The immunometabolite itaconate inhibits heme synthesis and remodels cellular metabolism in erythroid precursors. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar]
- Meiser, J.; Kraemer, L.; Jaeger, C.; Madry, H.; Link, A.; Lepper, P.M.; Hiller, K.; Schneider, J.G. Itaconic acid indicates cellular but not systemic immune system activation. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 32098–32107. [Google Scholar]
- Burch, J.S.; Marcero, J.R.; Maschek, J.A.; Cox, J.E.; Jackson, L.K.; Medlock, A.E.; Phillips, J.D.; Dailey, H.A. Glutamine via alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase provides succinyl-CoA for heme synthesis during erythropoiesis. Blood 2018, 132, 987–998. [Google Scholar]
- Day, E.A.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Protein targeting by the itaconate family in immunity and inflammation. Biochem. J. 2022, 479, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, P.; Wang, L. Lipase-catalyzed phospha-michael addition reactions under mild conditions. Molecules 2022, 27, 7798. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.; Jing, X.; Yao, S.; Su, W.; Ye, B.; Qu, Y.; Gao, F.; Sun, T.; Guo, X. Multifunctional hydrogel loaded with 4-octyl itaconate exerts antibacterial, antioxidant and angiogenic properties for diabetic wound repair. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 139, 212979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milanović, M.; Bekić, M.; Đokić, J.; Vučević, D.; Čolić, M.; Tomić, S. Exogenous α-ketoglutarate modulates redox metabolism and functions of human dendritic cells, altering their capacity to polarise T cell response. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 1064–1087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Cai, J.; Li, C.; Yang, M.; Duan, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xi, Y.; Sun, L.; He, L.; Tang, C.; et al. 4-Octyl itaconate attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by activating Nrf2 and inhibiting STAT3 signaling. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.L.; Morcelle, C.; Cheng, Z.L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Smith, M.D.; Shi, M.; et al. Itaconate inhibits TET DNA dioxygenases to dampen inflammatory responses. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, R.; Siddique, M.N.A.A. Control of immune cell signaling by the immuno-metabolite itaconate. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352165. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Yak OXGR1 promotes fibroblast proliferation via the PI3K/AKT pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6729–6740. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.R.; Song, J.B.; Wang, D.; Huang, Z.X.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.P.; Shu, G.; Xiong, Y.; Guan, K.L.; Ye, D.; et al. The immunometabolite itaconate stimulates OXGR1 to promote mucociliary clearance during the pulmonary innate immune response. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e160463. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, J.M.; Davies, L.C.; Karwan, M.; Ileva, L.; Ozaki, M.K.; Cheng, R.Y.; Ridnour, L.A.; Annunziata, C.M.; Wink, D.A.; McVicar, D.W. Itaconic acid mediates crosstalk between macrophage metabolism and peritoneal tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3794–3805. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Nan, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, J. Synthesis and characterization of pH-sensitive poly(itaconic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol)-folate-poly(l-histidine) micelles for enhancing tumor therapy and tunable drug release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Tokizane, K.; Konishi, H.; Yu, H.R.; Kiyama, H. Agonists for G-protein-coupled receptor 84 (GPR84) alter cellular morphology and motility but do not induce pro-inflammatory responses in microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naujoks, J.; Tabeling, C.; Dill, B.D.; Hoffmann, C.; Brown, A.S.; Kunze, M.; Kempa, S.; Peter, A.; Mollenkopf, H.J.; Dorhoi, A.; et al. IFNs modify the proteome of Legionella-containing vacuoles and restrict infection via IRG1-derived itaconic acid. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruetz, M.; Campanello, G.C.; Purchal, M.; Shen, H.; McDevitt, L.; Gouda, H.; Wakabayashi, S.; Zhu, J.; Rubin, E.J.; Warncke, K.; et al. Itaconyl-CoA forms a stable biradical in methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and derails its activity and repair. Science 2019, 366, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olagnier, D.; Farahani, E.; Thyrsted, J.; Blay-Cadanet, J.; Herengt, A.; Idorn, M.; Hait, A.; Hernaez, B.; Knudsen, A.; Iversen, M.B.; et al. SARS-CoV2-mediated suppression of NRF2-signaling reveals potent antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity of 4-octyl-itaconate and dimethyl fumarate. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4938. [Google Scholar]
- Hooftman, A.; Angiari, S.; Hester, S.; Corcoran, S.E.; Runtsch, M.C.; Ling, C.; Ruzek, M.C.; Slivka, P.F.; McGettrick, A.F.; Banahan, K.; et al. The immunomodulatory metabolite itaconate modifies NLRP3 and inhibits inflammasome activation. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 468–478.e7. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, A.K.; Huang, S.C.; Sergushichev, A.; Lampropoulou, V.; Ivanova, Y.; Loginicheva, E.; Chmielewski, K.; Stewart, K.M.; Ashall, J.; Everts, B.; et al. Network integration of parallel metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity 2015, 42, 419–430. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Jiang, P.; Sun, H.; Yuan, X.; Gao, S.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y. Dimethyl itaconate protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced endometritis by inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB and activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, E.; Xing, H.; Pei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Shen, C.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, J.; et al. Itaconic acid facilitates inflammation abatement and alleviates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3/caspase-1inflammasome axis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 861. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xu, S. The emerging role of ACOD1/itaconate pathway in atherosclerosis. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 797–799. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.; Ke, Q.; Wu, N.; Lu, L.; Wu, J.; Sun, S.; Jin, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. 4-Octyl itaconate attenuates glycemic deterioration by regulating macrophage polarization in mouse models of type 1 diabetes. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Raj, R.; Kumar, D.; Bhattacharya, B.; Rajinikanth, P.S.; Chidambaram, K.; Mahata, T.; Maity, B.; Saha, S. Preclinical evaluation of Dimethyl Itaconate against hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of the e/iNOS-Mediated NF-κB-Dependent apoptotic pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 823285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Tong, X.; Zeng, X.; Yin, Y.; Tao, K.; Li, R.; et al. Hepatoprotective role of 4-Octyl Itaconate in Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 5766434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Shi, L.; Li, R.; Tao, K. 4-Octyl itaconate regulates immune balance by activating Nrf2 and negatively regulating PD-L1 in a mouse model of sepsis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 6189–6209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- You, M.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, H.; Ma, F.; Zhou, X. 4-Octyl itaconate inhibits inflammation to attenuate psoriasis as an agonist of oxeiptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124 Pt B, 110915. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, R.; Blackburn, G.; Best, C.; Goodyear, C.S.; Mudaliar, M.; Burgess, K.; Stirling, A.; Porter, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Barrett, M.P.; et al. Changes in plasma itaconate elevation in early rheumatoid arthritis patients elucidates disease activity associated macrophage activation. Metabolites 2020, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Wu, M.; Tu, M.; Tan, X.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, M. 4-octyl itaconate inhibits high glucose induced renal tubular epithelial cell fibrosis through TGF-β-ROS pathway. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2024, 44, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Duan, C.; Ma, H.; Nong, C.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, N.; Mou, X.; Liu, T.; Zou, S.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of itaconyl-CoA hydratase and citramalyl-CoA lyase involved in itaconate metabolism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Structure 2024, 32, 941–952.e3. [Google Scholar]
- Elkasaby, T.; Hanh, D.D.; Kahar, P.; Kawaguchi, H.; Sazuka, T.; Kondo, A.; Ogino, C. Utilization of sweet sorghum juice as a carbon source for enhancement of itaconic acid production in engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2024, 172, 110345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, G.; Guo, F. Irg1-itaconate axis protects against acute kidney injury via activation of Nrf2. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Cordes, T.; Lucas, A.; Divakaruni, A.S.; Murphy, A.N.; Cabrales, P.; Metallo, C.M. Itaconate modulates tricarboxylic acidand redox metabolism to mitigate reperfusion injury. Mol. Metab. 2020, 32, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Long, D. Nrf2 and Ferroptosis: A new research direction for neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nosenko, M.; Anisov, D.; Gubernatorova, E.; Gorshkova, E.; Zeng, Y.R.; Ye, D.; Wang, P.; Finlay, D.; Drutskaya, M.; Nedospasov, S.; et al. Itaconate and dimethyl itaconate upregulate IL-6 production in the LPS-induced inflammation in mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024, 116, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Ren, J.; Zhu, B.; Dai, Y.; Gao, D.S.; Xia, S.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yu, L. Dimethyl Itaconate attenuates CFA-induced inflammatory pain via the NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 938979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diankristanti, P.A.; Ng, I.S. Microbial itaconic acid bioproduction towards sustainable development: Insights, challenges, and prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129280. [Google Scholar]
- Ki, N.; Kim, J.; Jo, I.; Hyun, Y.; Ryu, S.; Ha, N.C. Isocitrate binds to the itaconic acid-responsive LysR-type transcriptional regulator RipR in Salmonella pathogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102562. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, S.; Huynh, J.P.; Lampropoulou, V.; Loginicheva, E.; Esaulova, E.; Gounder, A.P.; Boon, A.C.M.; Schwarzkopf, E.A.; Bradstreet, T.R.; Edelson, B.T.; et al. Irg1 expression in myeloid cells prevents immunopathology during M. tuberculosis infection. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Mitochondrial ACOD1/IRG1 in infection and sterile inflammation. J. Intensive Med. 2022, 2, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yin, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Zeng, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, R.; Tang, Y.; Shi, L.; et al. Maresin 1 mitigates concanavalin A-induced acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting ROS-mediated activation of NF-κB signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 147, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bambouskova, M.; Potuckova, L.; Paulenda, T.; Kerndl, M.; Mogilenko, D.A.; Lizotte, K.; Swain, A.; Hayes, S.; Sheldon, R.D.; Kim, H.; et al. Itaconate confers tolerance to late NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108756. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.W.; Lam, S.M.; Fan, X.; Cao, W.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Tian, H.; Chua, G.H.; Zhang, C.; Meng, F.P.; Xu, Z.; et al. Omics-driven systems interrogation of metabolic dysregulation in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 188–202.e185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Tao, K.; Zeng, L.; Zeng, X.; Wan, Y.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P. IRG1/Itaconate inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of CD69+CD103+CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells in autoimmune hepatitis by regulating the JAK3/STAT3/P53 signalling pathway. Apoptosis 2024, 29, 1738–1756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Sheng, Z.; Hu, L.; Shi, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, W.; Xiao, Z.; Shen, D.; Wu, W.; et al. Targeted macrophage phagocytosis by Irg1/itaconate axis improves the prognosis of intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke and peritonitis. EBioMedicine 2024, 101, 104993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Fan, K.R.; Chen, K.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, G. Deficiency of IRG1/ itaconate aggravates endotoxemia-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting autophagy in mice. Exp. Anim. 2023, 72, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, L.; Li, R.; Yin, Y.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Tao, K.; Zhang, P. IRG1/itaconate alleviates acute liver injury in septic mice by suppressing NLRP3 expression and its mediated macrophage pyroptosis via regulation of the Nrf2 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112277. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle, C.; Green, J.P.; Allan, S.M.; Brough, D.; Lemarchand, E. Itaconate and fumarate derivatives inhibit priming and activation of the canonical NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. Immunology 2022, 165, 460–480. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.V.; Kostidis, S.; Groh, L.A.; Koeken, V.A.C.M.; Bruno, M.; Baydemir, I.; Kilic, G.; Bulut, Ö.; Andriopoulou, T.; Spanou, V.; et al. Dimethyl itaconate induces long-term innate immune responses and confers protection against infection. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112658. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, K.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.; Tao, K.; Zhang, P. Itaconic Acid: A Regulator of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Metabolism. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070534
Ma K, Zhou P, Zhang W, Zeng L, Tao K, Zhang P. Itaconic Acid: A Regulator of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Metabolism. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070534
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Kai, Pei Zhou, Wei Zhang, Liwu Zeng, Kaixiong Tao, and Peng Zhang. 2025. "Itaconic Acid: A Regulator of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Metabolism" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070534
APA StyleMa, K., Zhou, P., Zhang, W., Zeng, L., Tao, K., & Zhang, P. (2025). Itaconic Acid: A Regulator of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Metabolism. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070534