Research on Influence of Switching Angle on the Vibration of Switched Reluctance Motor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
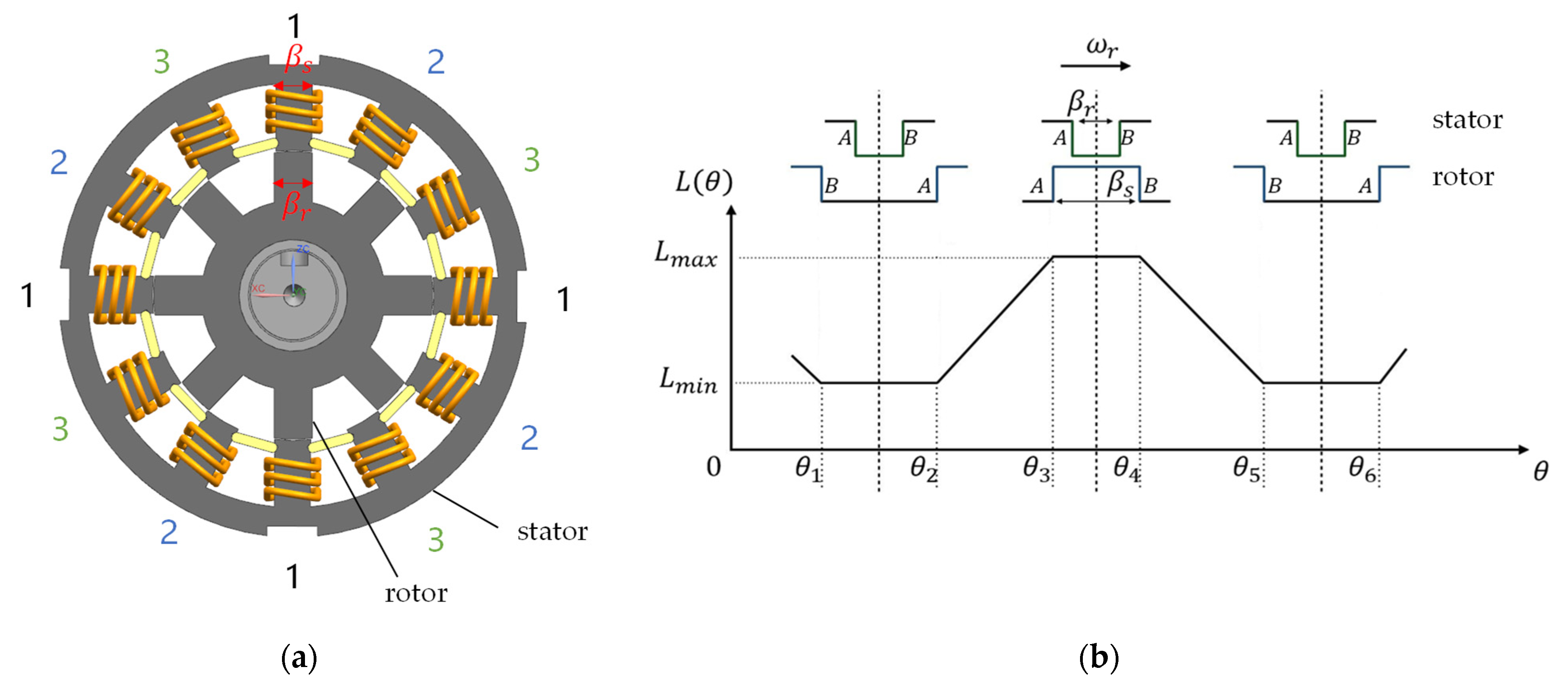
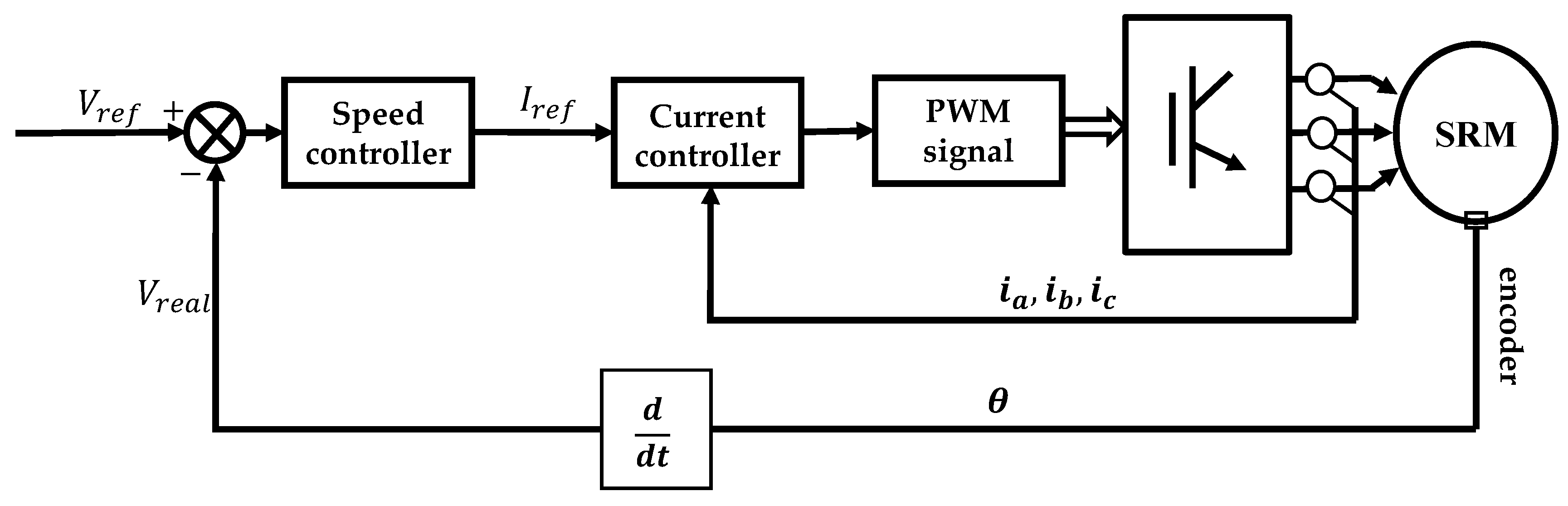
2. Principle of Switching Angle control Method
3. Influence of Switching Angle on Vibration
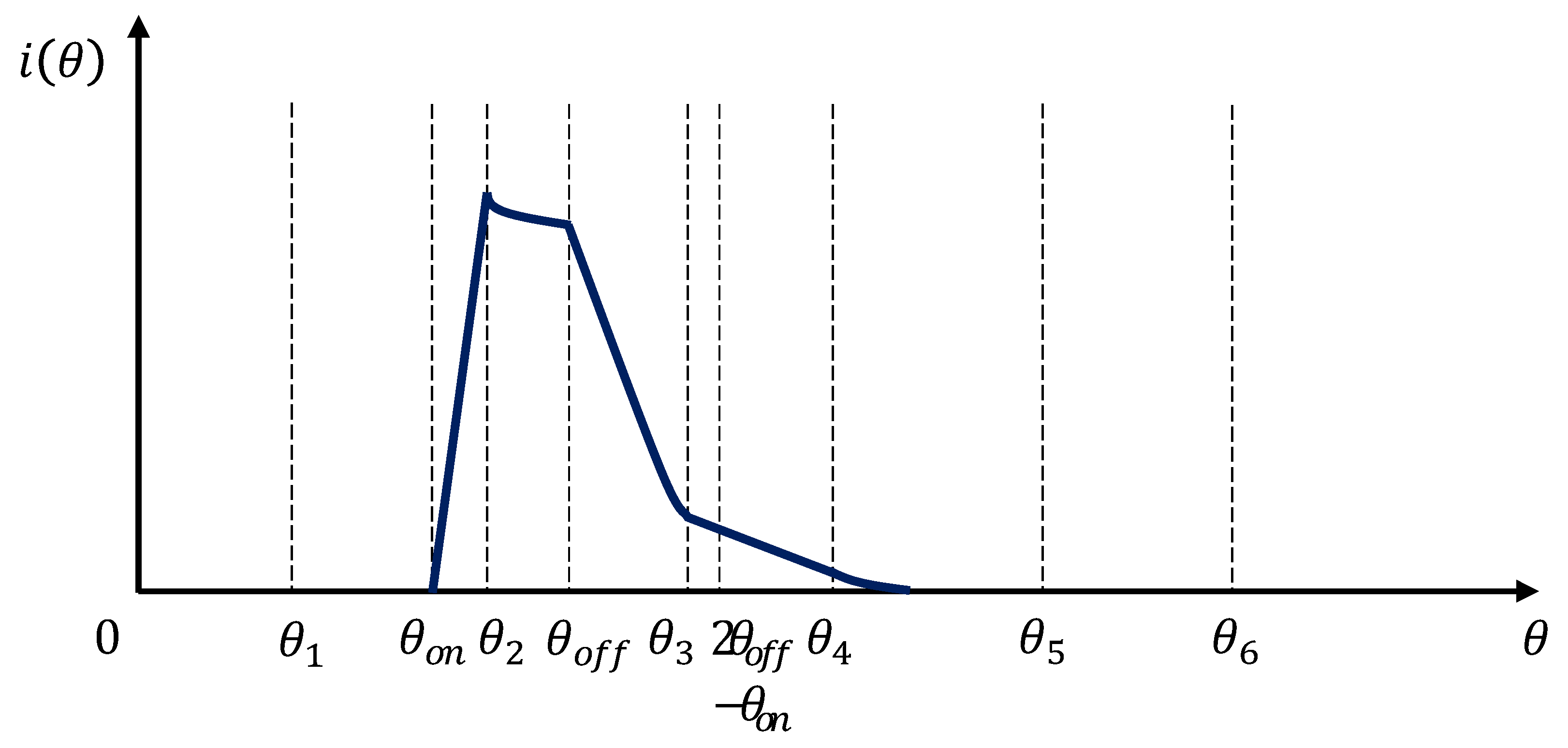
3.1. Current Harmoinc Model
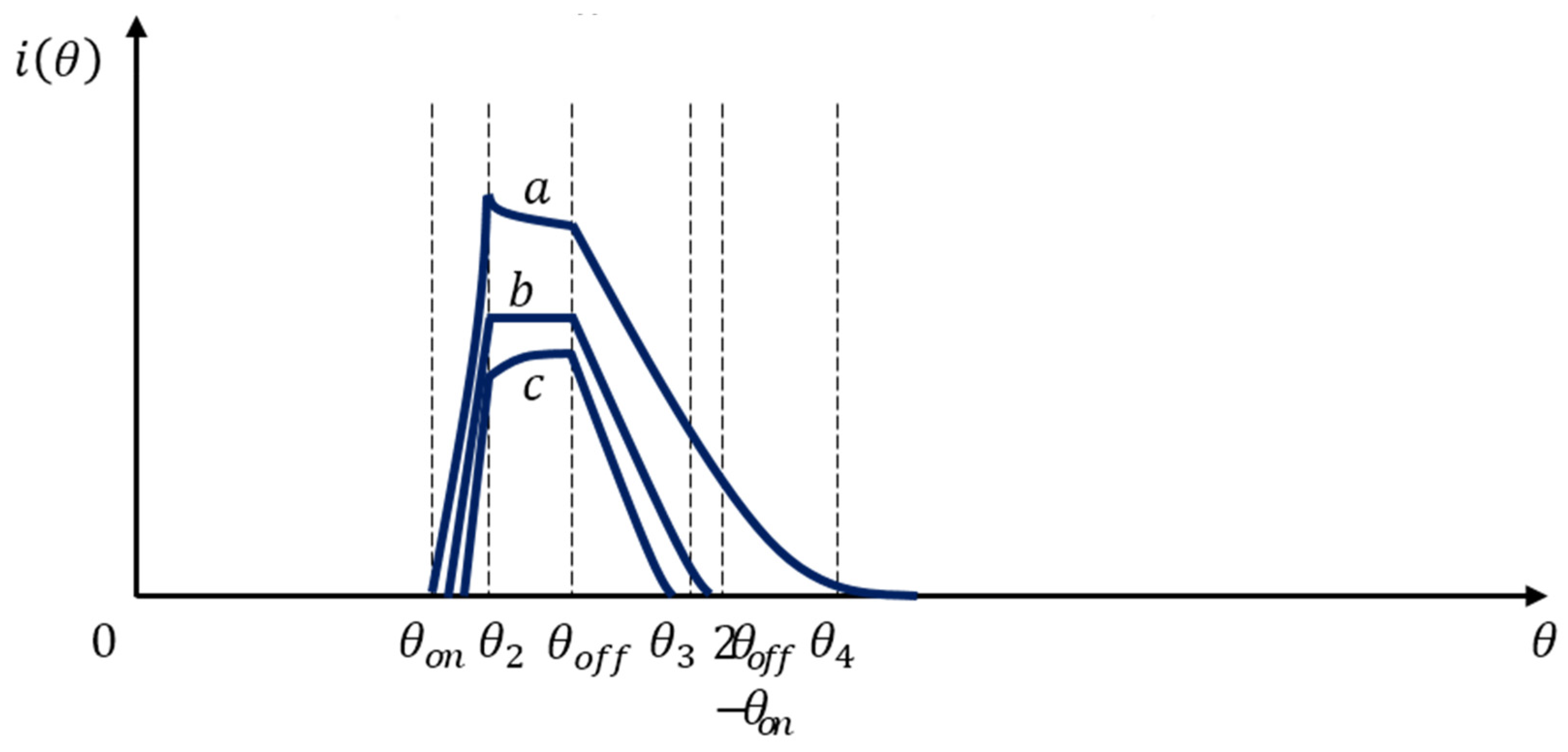
3.2. Influence of Switching Angle on Current
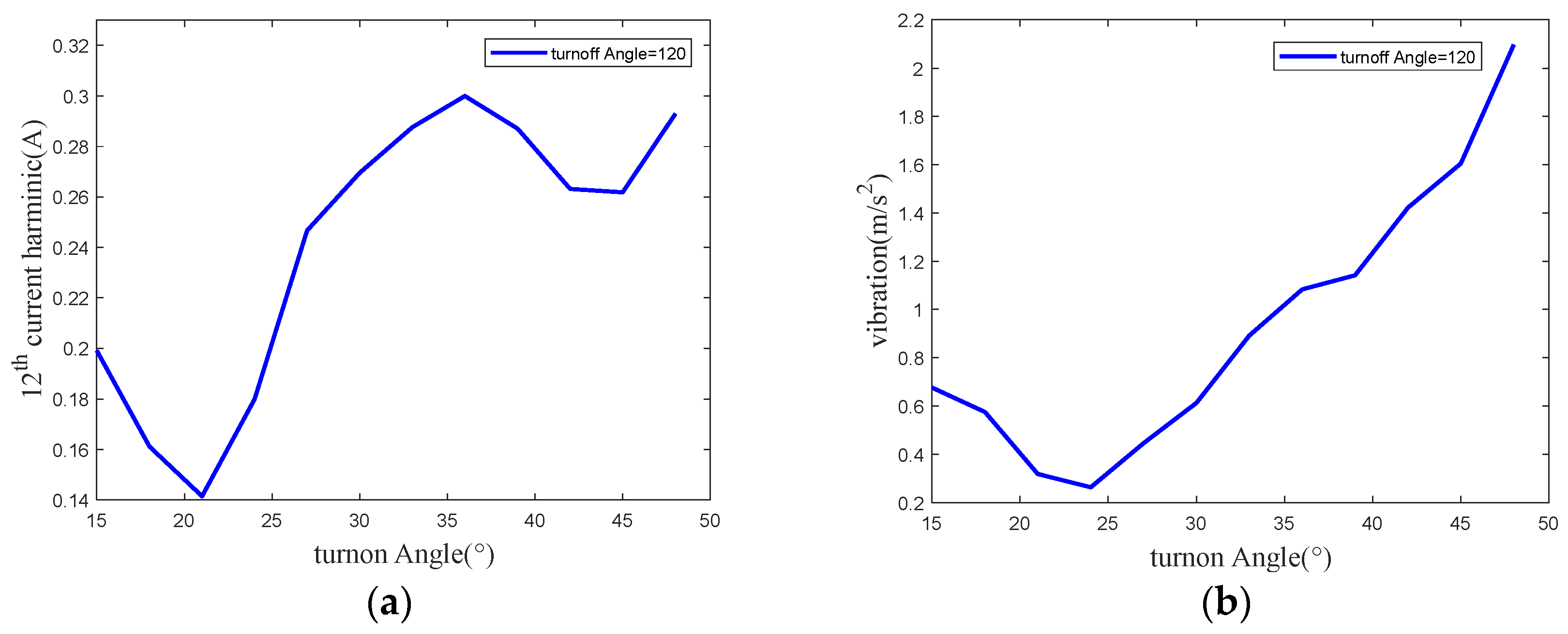
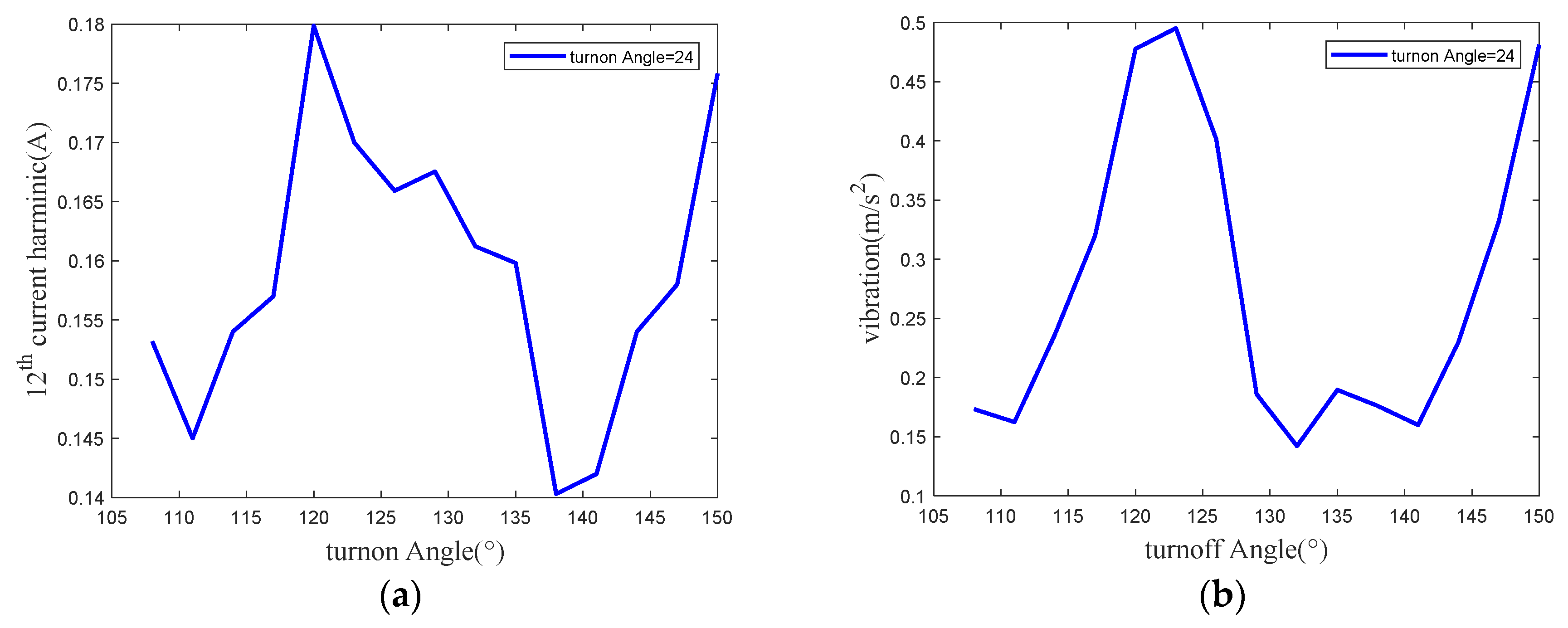
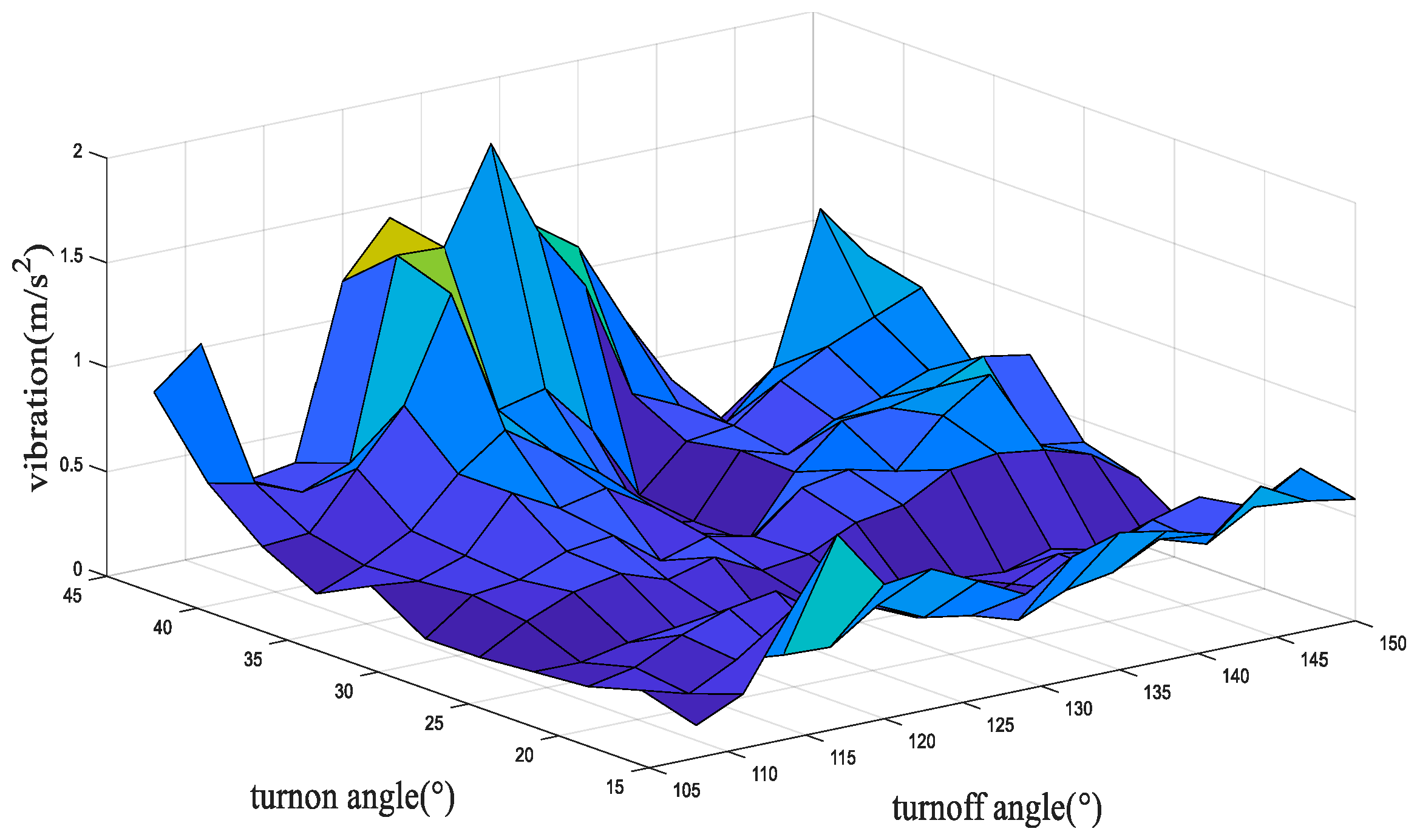
3.3. Influence of Switching Angle on Vibration
4. Experimental Verification and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, G.; Scalcon, F.P.; Xiao, D.; Vieira, R.P.; Grundling, H.A.; Emadi, A. Advanced Control of Switched Reluctance Motors (SRMs): A Review on Current Regulation, Torque Control and Vibration Suppression. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2021, 2, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, M.; Chiba, A.; Hoshi, N.; Ogasawara, S.; Takemoto, M.; Rahman, M.A. Test Results and Torque Improvement of the 50-kW Switched Reluctance Motor Designed for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Tao, J.; Li, B.; Qin, C.; Liu, C. A Multi-Physics Modeling-Based Vibration Prediction Method for Switched Reluctance Motors. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bostanci, E.; Moallem, M.; Parsapour, A.; Fahimi, B. Opportunities and Challenges of Switched Reluctance Motor Drives for Electric Propulsion: A Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Shi, G.; Tao, J.; Yu, H.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C. An adaptive hierarchical decomposition-based method for multi-step cutterhead torque forecast of shield machine. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 175, 109148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-Y.; Lim, Y.-C.; Kim, H.-C. Acoustic Noise/Vibration Reduction of a Single-Phase SRM Using Skewed Stator and Rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 4292–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Yang, S.; Hu, Y.; Cao, W. Investigation of Skewing Effects on the Vibration Reduction of Three-Phase Switched Reluctance Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isfahani, A.H.; Fahimi, B. Comparison of Mechanical Vibration Between a Double-Stator Switched Reluctance Machine and a Conventional Switched Reluctance Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, J.D.; Mecrow, B.C. Optimized Segmental Rotor Switched Reluctance Machines with a Greater Number of Rotor Segments Than Stator Slots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, N.; Bayless, J.; Sugimoto, H.; Chiba, A. Noise Reduction of Switched Reluctance Motor with High Number of Poles by Novel Simplified Current Waveform at Low Speed and Low Torque Region. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Lin, Y.; Liaw, C. Comparative study of switching controls in vibration and acoustic noise reductions for switched reluctance motor. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 2006, 153, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, X.; Pan, Z. Analytical Model for Predicting Maximum Reduction Levels of Vibration and Noise in Switched Reluctance Machine by Active Vibration Cancellation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 26, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiguchi, M.; Sugimoto, H.; Kurihara, N.; Chiba, A. Acoustic Noise and Vibration Reduction of SRM by Elimination of Third Harmonic Component in Sum of Radial Forces. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Zhong, Y. Predictive Current Control for Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Local Linear Phase Voltage Model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvirdilu-Asl, R.; Nalakath, S.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. A Finite Control Set Model Predictive Torque Control for Switched Reluctance Motor Drives with Adaptive Turn-off Angle. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019—45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Xiao, D.; Tao, J.; Yu, H.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C. Concentrated velocity synchronous linear chirplet transform with application to robotic drilling chatter monitoring. Measurement 2022, 194, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.R.D.C.; de Araujo, W.R.H.; Gomes, V.M.; Silva, F.D.S.E.; Ganzaroli, C.A.; Gomes, F.A.; Wainer, G.A.; Calixto, W.P. Optimized techniques for driving and control of the switched reluctance motor to improve efficiency. Control Eng. Pract. 2019, 90, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mademlis, C.; Kioskeridis, I. Performance optimization in switched reluctance motor drives with online commutation angle control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, T.; Elrayyah, A.; Sozer, Y.; Husain, I. Unified Control for Switched Reluctance Motors for Wide Speed Operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 3401–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhong, R.; Zhang, M.-S.; Ding, D.-S.; Sun, W. Resonance Reduction by Optimal Switch Angle Selection in Switched Reluctance Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayless, J.; Kurihara, N.; Sugimoto, H.; Chiba, A. Acoustic Noise Reduction of Switched Reluctance Motor with Reduced RMS Current and Enhanced Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 31, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.C.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Schofield, N.; Emadi, A. Novel Switched Reluctance Machine Configuration with Higher Number of Rotor Poles Than Stator Poles: Concept to Implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhong, R.; Chen, L.; Lu, S. Analytical method to optimise turn-on angle and turn-off angle for switched reluctance motor drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2012, 6, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.F.S.; Mamede, A.; Araújo, R.E. Switched Reluctance Motor Drives: Fundamental Control Methods; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dong, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C. Analysis on accuracy of rotor-locked transient-response-based vibration model for switched reluctance machines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2022, 16, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

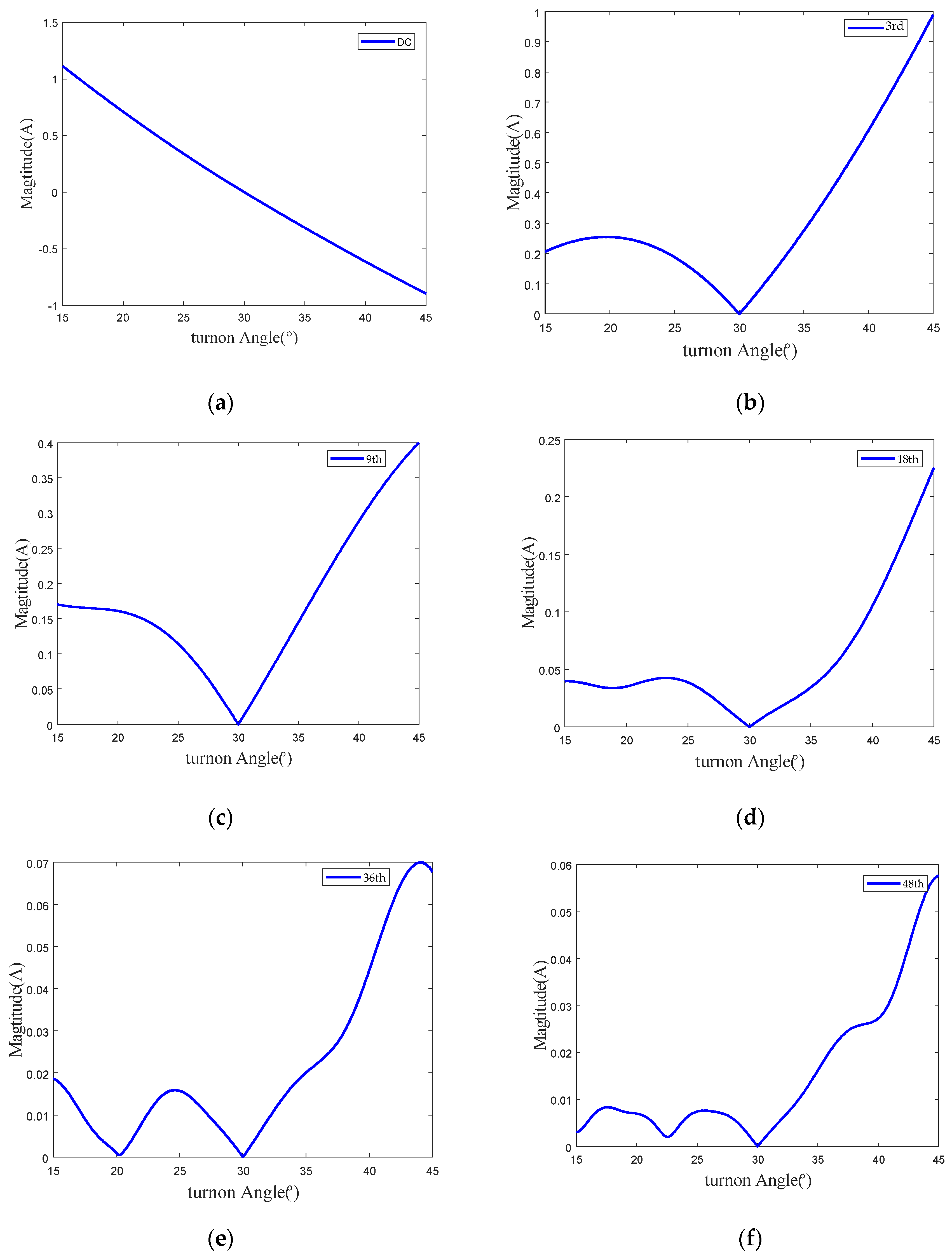

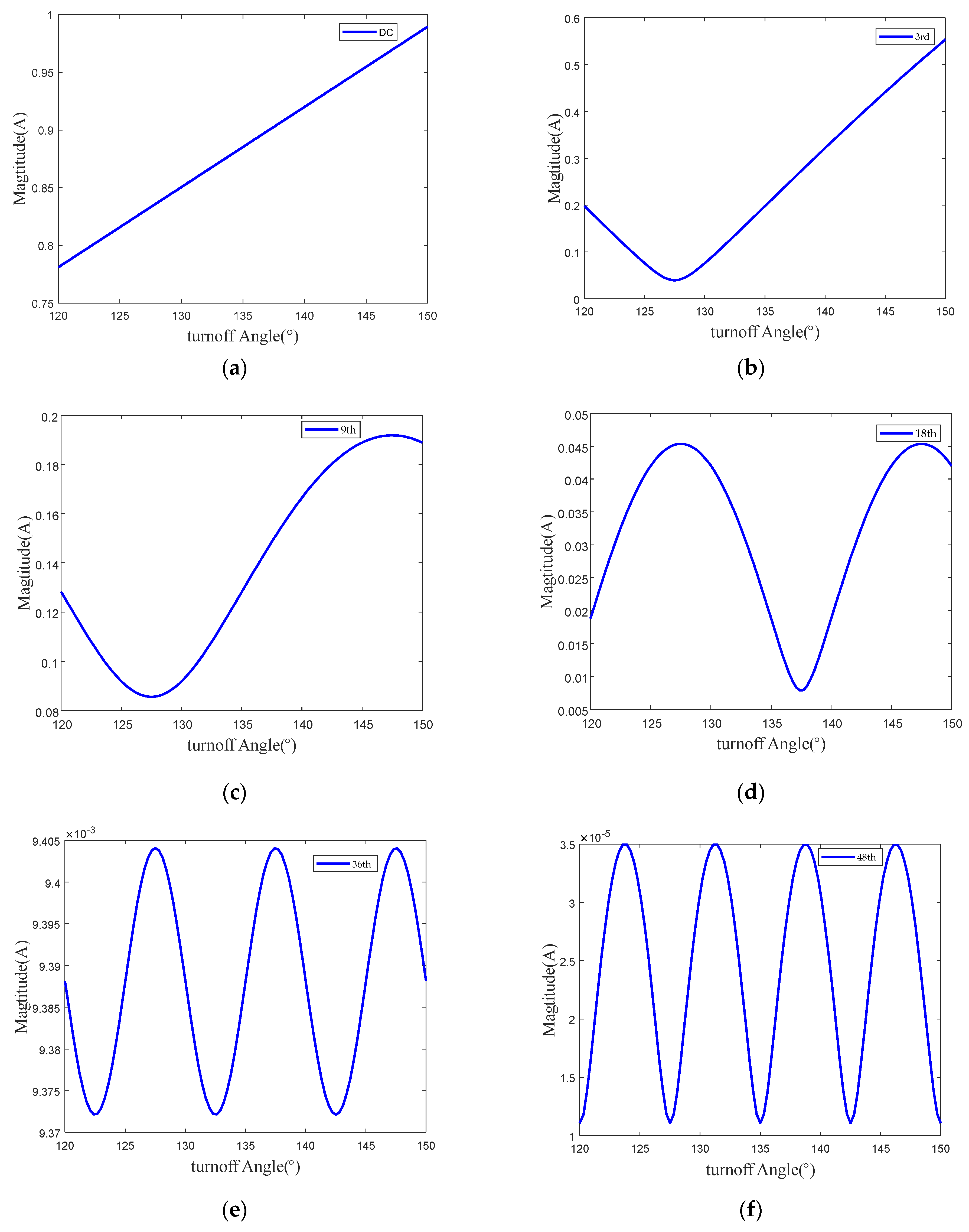
| Harmonic Order, k = 3 m | Speed |
|---|---|
| m = 1, 3rd | 2034 r/min |
| m = 2, 6th | 1017 r/min |
| m = 3, 9th | 915 r/min |
| m = 4, 12th | 763 r/min |
| m = 5, 15th | 610 r/min |
| m = 6, 18th | 508 r/min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, X.; Zhou, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. Research on Influence of Switching Angle on the Vibration of Switched Reluctance Motor. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094793
Ling X, Zhou C, Yang L, Zhang J. Research on Influence of Switching Angle on the Vibration of Switched Reluctance Motor. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094793
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Xiao, Chenhao Zhou, Lianqiao Yang, and Jianhua Zhang. 2022. "Research on Influence of Switching Angle on the Vibration of Switched Reluctance Motor" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094793
APA StyleLing, X., Zhou, C., Yang, L., & Zhang, J. (2022). Research on Influence of Switching Angle on the Vibration of Switched Reluctance Motor. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094793






