Evaluation of Choroidal Melanoma Vascularization by Color Doppler Flow Imaging: An Option for Follow-Up Tumor Control Assessment after CyberKnife®?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Clinical Data
2.4. Color Doppler Flow Imaging
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Course of Tumor Vascularization during Treatment
3.3. Course of Tumor Height during Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. Course of Choroidal Melanoma Vascularization during Treatment
4.2. Course of Choroidal Melanoma Height during Treatment
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krantz, B.A.; Dave, N.; Komatsubara, K.M.; Marr, B.P.; Carvajal, R.D. Uveal melanoma: Epidemiology, etiology, and treatment of primary disease. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 11, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilborn, M.D.; Munk, P.L.; Lin, D.T.; Vellet, A.D.; Poon, P.Y. Sonography of Ocular Choroidal Melanomas. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1993, 161, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliki, S.; Shields, C.L. Uveal melanoma: Relatively rare but deadly cancer. Eye 2017, 31, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virgili, G.; Gatta, G.; Ciccolallo, L.; Capocaccia, R.; Biggeri, A.; Crocetti, E.; Lutz, J.M.; Paci, E.; Eurocare Working Group. Incidence of Uveal Melamona in Europe. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.; Arnold-Wörner, N.; Zimmermann, F.B.; Gross, M.W. Uveale Melanome und Metastasen. Info Onkol. 2011, 14, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthoff, R.; Frischmuth, J.; Jensen, O.A.; Bjerrum, K.; Prause, J.U. Eine retrospektive randomisierte Vergleichsstudie Ruthenium-Bestrahiung vs Enukleation. Klin. Mon. Augenheilkd. 1992, 200, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüler, A.O.; Bornfeld, N. Aktuelle Therapieaspekte intraokularer Tumoren. Der Ophthalmol. 2000, 97, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bois, A.Z.-D.; Debus, J. Methodik und Technik der stereotaktischen Radiochirurgie. In Strahlentherapie; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, U.; Niendorf, T.; Graessl, A.; Rieger, J.; Krüger, P.C.; Langner, S.; Guthoff, R.F.; Stachs, O. Ultrahigh Field Magnetic Resonance and Colour Doppler Real-Time Fusion Imaging of the Orbit–A Hybrid Tool for Assessment of Choroidal Melanoma. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthoff, R.; Winkler, P.; Helmke, K.; Berger, R. Diagnosis and treatment control of choroidal melanomas–The role of B-scan and Doppler-technique. Acta Ophthalmol. 1992, 70, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthoff, R.; Terwey, B.; Burk, R.; von Domarus, D. Attempt at preoperative differentiation of malignant melanoma of the choroid. A comparison of nuclear magnetic resonance tomography, ultrasound echography and histopathology. Klin. Mon. Augenheilkd. 1987, 191, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthoff, R.; Heller, M.; Hallermann, D.; Hagemann, J. First experiences with serial computed tomography in choroidal melanomas. Ophthalmologica 1981, 183, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthoff, R. Ultrasound in Ophthalmologic Diagnosis: A Practical Guide; Thieme Verlag Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Guthoff, R.; Pauleikhoff, D.; Hingst, V. Bildgebende Diagnostik in der Augenheilkunde; Ferdinand Enke Verlag Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.M.; Huang, Y.F.; Chen, H.H.; Cheng, Y.M.; Chou, C.Y. Three-Dimensional Power Doppler Ultrasound Is Useful to Monitor the Response to Treatment in a Patient with Primary Papillary Serous Carcinoma of the Peritoneum. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proniewska-Skretek, E.; Zalewska, R.; Ustymowicz, A.; Kraśnicki, P.; Mariak, Z. An application of Color Doppler ultrasonography in evaluate of brachytherapy in patients with uveal melanomas. Klin. Ocz. 2007, 109, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff-Kormann, P.G.; Kormann, B.A.; Riedel, K.G.; Hasenfratz, G.C.; Stefani, F.H.; Spengel, F.A.; Lund, O.E. Quantitative Color Doppler Imaging in Untreated and Irradiated Choroidal Melanoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 1928–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Muacevic, A.; Nentwich, M.; Wowra, B.; Staerk, S.; Kampik, A.; Schaller, U. Development of a Streamlined, Non-Invasive Robotic Radiosurgery Method for Treatment of Uveal Melanoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 7, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibl-Lindner, K.; Fürweger, C.; Nentwich, M.; Foerster, P.; Wowra, B.; Schaller, U.; Muacevic, A. Robotic Radiosurgery for the Treatment of Medium and Large Uveal Melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damato, B.; Patel, I.; Campbell, I.R.; Mayles, H.M.; Errington, R.D. Local Tumor Control after 106Ru Brachytherapy of Choroidal Melanoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 63, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouberol, F.; Roy, P.; Kodjikian, L.; Gerard, J.; Jean-Louis, B.; Grange, J. Survival, Anatomic, and Functional Long-Term Results in Choroidal and Ciliary Body Melanoma after Ruthenium Brachytherapy (15 Years’ Experience with Beta-Rays). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
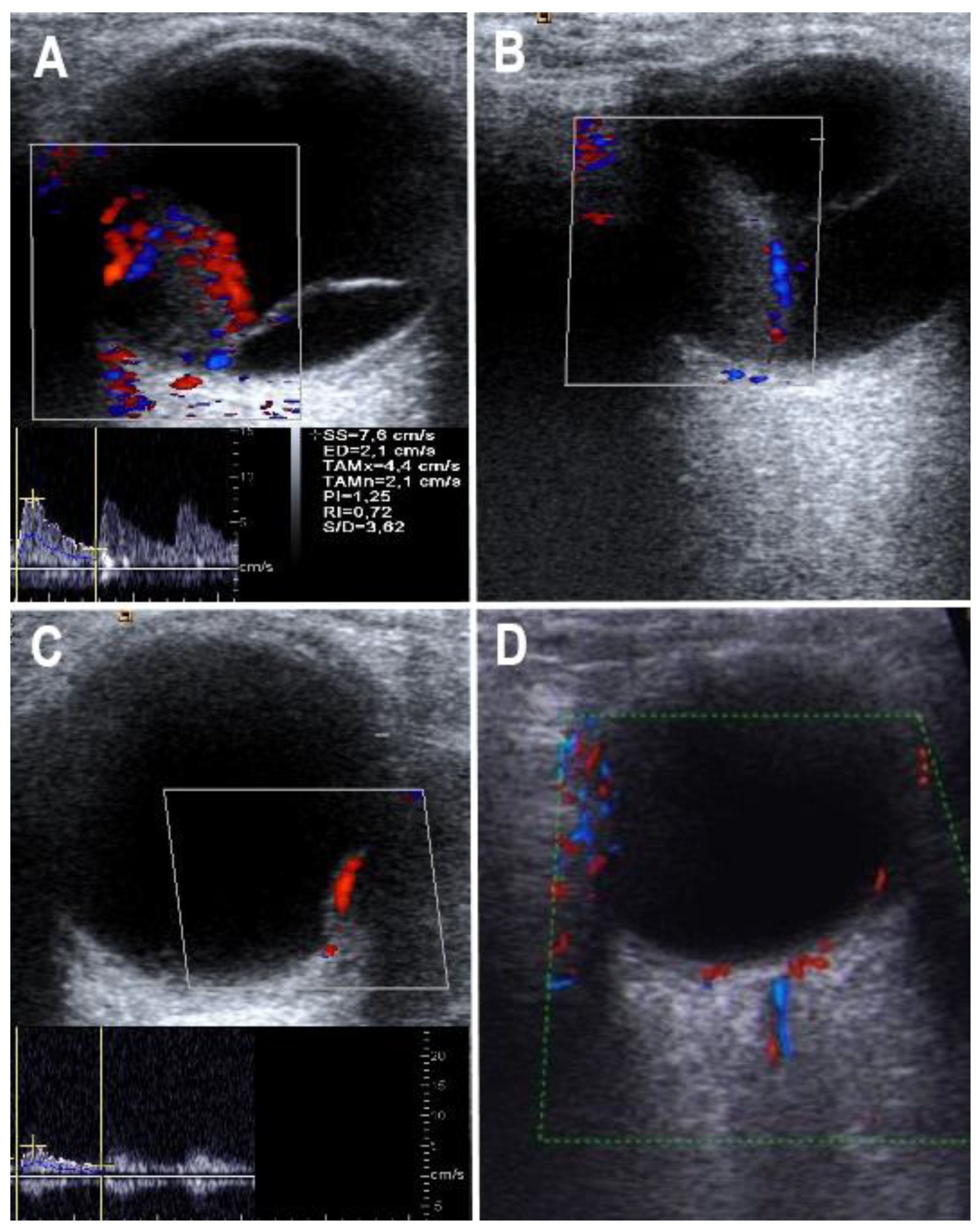


| 0 | No vascularization |
| 1 | Low vascularization (a small internal artery can be visualized) |
| 2 | Moderate vascularization (two to three internal arteries can be visualized) |
| 3 | Strong vascularization (paying, partly strong internal arteries can be shown) |
| Ruthenium-106 Brachytherapy | Robot-Assisted Radiotherapy Using CyberKnife® | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 4 | 11 |
| Age at diagnosis | Ø 67.5 ± 12.13 years | Ø 62 ± 13.68 years |
| Gender ♀/♂ | 4:0 | 2:9 |
| Tumor entity | 100% Choroidal melanoma | 100% Choroidal melanoma |
| Tumor localization right/left | 3:1 | 4:7 |
| Tumor apex prominence at diagnosis | Sonography: Ø 3.735 ± 1.22 mm CDFI: Ø 4.55 ± 0.64 mm | Sonography: Ø6.55 ± 3.66 mm CDFI: Ø 8.35 ± 3.92 mm |
| Scleral radiation dose | Ø 798.5 Gy | Ø 55 Gy |
| Follow-up period | Ø 50.25 ± 26.19 months | Ø 43.3 ± 24.82 months |
| Adjuvant therapy | Transpupillary thermotherapy: in 100% Ø 2 therapy sessions | None |
| Metastases | None | 27.3% |
| Recurrence | None | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaak, C.; Kakkassery, V.; Scheef, B.O.; Zschoche, M.; Rommel, F.; Hildebrandt, G.; Emmert, S.; Junghanß, C.; Guthoff, R.F.; Jünemann, A.M.; et al. Evaluation of Choroidal Melanoma Vascularization by Color Doppler Flow Imaging: An Option for Follow-Up Tumor Control Assessment after CyberKnife®? Medicina 2021, 57, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060553
Kaak C, Kakkassery V, Scheef BO, Zschoche M, Rommel F, Hildebrandt G, Emmert S, Junghanß C, Guthoff RF, Jünemann AM, et al. Evaluation of Choroidal Melanoma Vascularization by Color Doppler Flow Imaging: An Option for Follow-Up Tumor Control Assessment after CyberKnife®? Medicina. 2021; 57(6):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060553
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaak, Cinja, Vinodh Kakkassery, Björn O. Scheef, Marco Zschoche, Felix Rommel, Guido Hildebrandt, Steffen Emmert, Christian Junghanß, Rudolf F. Guthoff, Anselm M. Jünemann, and et al. 2021. "Evaluation of Choroidal Melanoma Vascularization by Color Doppler Flow Imaging: An Option for Follow-Up Tumor Control Assessment after CyberKnife®?" Medicina 57, no. 6: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060553
APA StyleKaak, C., Kakkassery, V., Scheef, B. O., Zschoche, M., Rommel, F., Hildebrandt, G., Emmert, S., Junghanß, C., Guthoff, R. F., Jünemann, A. M., & Walter, U. (2021). Evaluation of Choroidal Melanoma Vascularization by Color Doppler Flow Imaging: An Option for Follow-Up Tumor Control Assessment after CyberKnife®? Medicina, 57(6), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060553







