Vancomycin-Induced Organizing Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
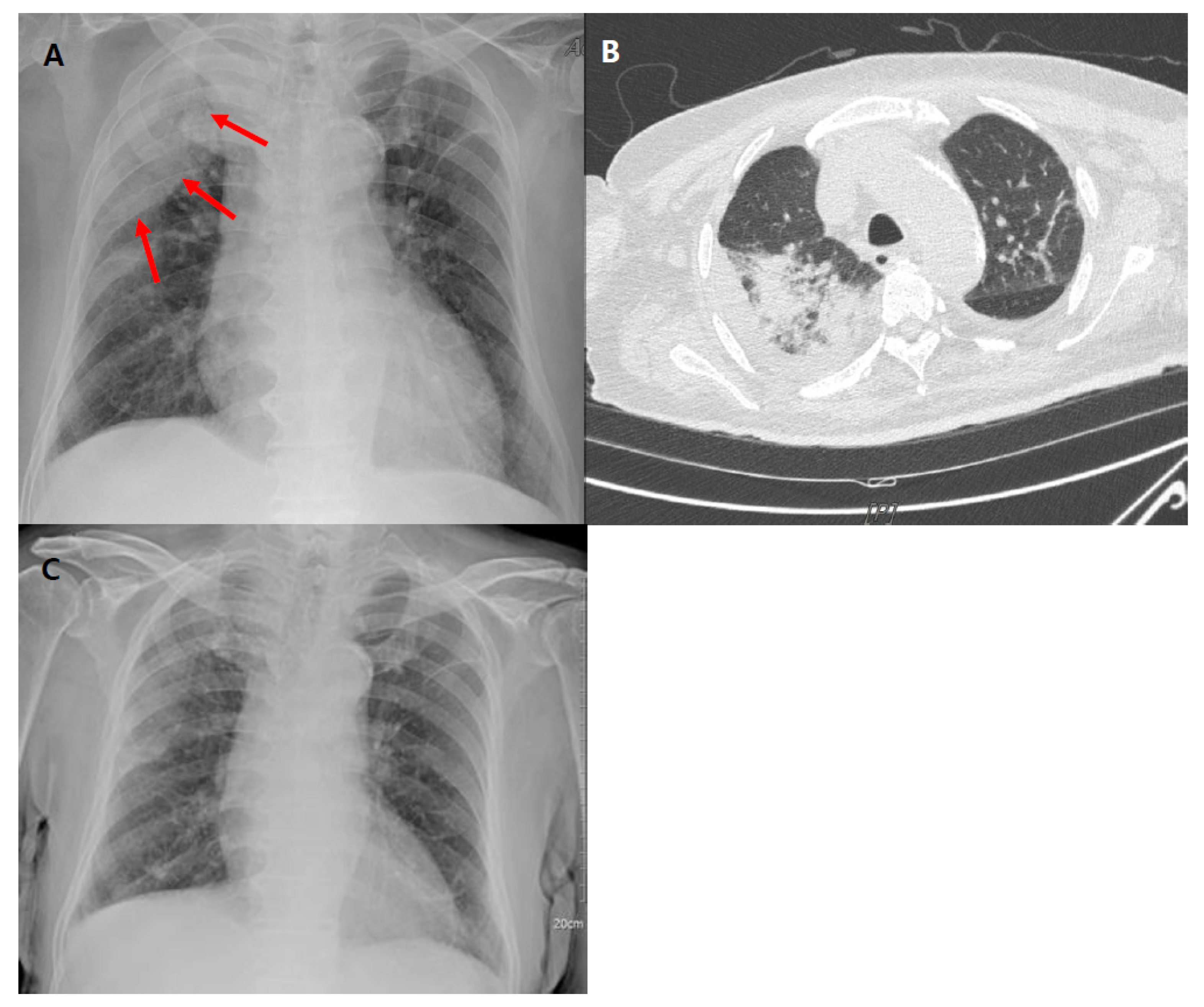
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruniera, F.R.; Ferreira, F.M.; Saviolli, L.R.; Bacci, M.R.; Feder, D.; da Luz Goncalves Pedreira, M.; Sorgini Peterlini, M.A.; Azzalis, L.A.; Campos Junqueira, V.B.; Fonseca, F.L. The use of vancomycin with its therapeutic and adverse effects: A review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Issa, K.; Diebo, B.G.; Faloon, M.; Naziri, Q.; Pourtaheri, S.; Paulino, C.B.; Emami, A. The Epidemiology of Vertebral Osteomyelitis in the United States from 1998 to 2013. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, E102–E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, L.M.; Fox, L.P. Vancomycin-associated drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordier, J.F. Organising pneumonia. Thorax 2000, 55, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobb, E.; Kimbrough, R.C.; Nugent, K.M.; Phy, M.P. Organizing pneumonia and pulmonary eosinophilic infiltration associated with daptomycin. Ann. Pharmacother. 2007, 41, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Ishizaki, M.; Masuda, Y.; Kimura, G.; Kawanami, O.; Masugi, Y. The role of intraalveolar fibrosis in the process of pulmonary structural remodeling in patients with diffuse alveolar damage. Am. J. Pathol. 1987, 126, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Song, W.J.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Min, K.U. A case of hypersensitivity syndrome to both vancomycin and teicoplanin. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, O.; Hassanein, M.; Armstrong, J.; Kassis, N. Case report: Atypical presentation of vancomycin induced DRESS syndrome: A case report and review of the literature. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazu, D.; Kodama, N.; Yamashita, D.; Tanaka, H.; Inoue, S.; Imakyure, O.; Hirakawa, M.; Shuto, H.; Kataoka, Y. DRESS Syndrome Caused by Cross-reactivity Between Vancomycin and Subsequent Teicoplanin Administration: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2016, 17, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, T.; Sawaguchi, H.; Kusumoto, H.; Shiono, H. Eosinophilic Pneumonia Putatively Induced by Vancomycin: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2019, 20, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Meara, P.; Borici-Mazi, R.; Morton, A.R.; Ellis, A.K. DRESS with delayed onset acute interstitial nephritis and profound refractory eosinophilia secondary to Vancomycin. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hewitson, L.J. Vancomycin induced DRESS syndrome (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) in a patient with tricuspid endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e229590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boet, S.; Noblet, C.; Haas-Hubscher, C.; Picard, D.; Musette, P.; Dureuil, B. Severe vancomycin-induced drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome imitating septic shock. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 26, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity | Eosinophilic Pneumonia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient (Age/Sex) | 79/Male | 50/Male | 66/Male | 57/Male | 38/Female | 65/Male |
| Relevant medical history | None | Alcoholic liver cirrhosis | Heterozygous hemochromatosis | Congenital heart disease (Aortic, pulmonary valve replacement) | None | IgA nephropathy |
| Infectious disease | Wound infection after femur fracture | Vertebral osteomyelitis with epidural abscess | Implant infection at pelvis | Infective endocarditis | Infective endocarditis | Empyema with pneumothorax |
| Microorganism | Methicillin resistant Staphylcoccus aureus | - | Methicillin resistant Staphylcoccus aureus | Penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis | Streptococcus oralis | Methicillin-resistant Staphylcoccus aureus |
| History of antibiotics | Vancomycin for 29 days then, Teicoplanin was initiated | Vancomycin for 18 days, then switched to Ceftriaxone, then switched to Teicoplanin | Vancomycin for 4 weeks | Vancomycin for 4 weeks | Amoxicillin, Gentamicin, and Vancomycin for 3 weeks Rifampicin, Teicoplanin | Vancomycin for 2 days Piperacillin/tazobactam Meropenem |
| Involved organs | Skin, Lung | Skin, Lung | Skin, Lung, Liver | Skin, Lung, Gastrointestinal tract | Skin, Lung, Kidney | Lung |
| Clinical manifestations | Fever Eosinophilia Skin rash Diffuse pneumonic infiltrates | Skin rash High fever up to 39 °C Eosinophilia Hypersensitivity pneumonitis | Skin rash High fever up to 40 °C Cervical lymphadenopathy Eosinophilia Abnormal liver enzymes Eosinophilic pneumonitis | Fever Epigastric pain Diarrhoea Maculopapular pruritic rash Severe hypoxia Peripheral eosinophilia Acalculous cholecystitis | Fever Upper body erythema Renal failure with dialysis Mechanical ventilation | Peripheral eosinophilia Eosinophil dominant in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| Treatment | Prednisolone 50 mg for 6 days Switched to linezolid | Methylprednisolone 30 mg q 6 h Stop antibiotics Switched to linezolid | Stop antibiotics Topical steroid with antihistamine Prednisolone 60 mg | Prednisolone 40 mg | Methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg/day | Switched to linezolid Prednisolone 30 mg |
| Outcome | Resolved | Resolved | Resolved | Resolved | Resolved | Resolved |
| Reference | DRESS syndrome caused by cross reactivity between vancomycin and subsequent teicoplanin administration [9] | A Case of Hypersensitivity syndrome to both vancomycin and teicoplanin [7] | DRESS with delayed onset acute interstitial nephritis and profound refractory eosinophilia secondary to vancomycin [11] | Vancomycin induced DRESS syndrome in a patient with tricuspid endocarditis [12] | Severe vancomycin-induced drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome imitating septic shock [13] | Eosinophilic pneumonia putatively induced by vancomycin: a case report [10] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.-M. Vancomycin-Induced Organizing Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina 2021, 57, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060610
Lee Y-S, Lee Y-M. Vancomycin-Induced Organizing Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina. 2021; 57(6):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060610
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Young-Shin, and Yu-Mi Lee. 2021. "Vancomycin-Induced Organizing Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review" Medicina 57, no. 6: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060610
APA StyleLee, Y.-S., & Lee, Y.-M. (2021). Vancomycin-Induced Organizing Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina, 57(6), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57060610






