Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy Followed by Lipiodol Infusion for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Temporary Infusion System
2.3. Regimen of Chemotherapy and Lipiodol Infusion
2.4. Study Assessment
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Efficacy
3.3. Prognostic Factors of Survival
3.4. Complications and Adverse Effects
3.5. Cause of Death
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.; Tillmann, T.; Banerjee, A. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.J.; Yang, Y.W.; Chen, J.D.; You, S.L.; Yang, H.I.; Lee, M.H. Significant reduction in end-stage liver diseases burden through the national viral hepatitis therapy program in Taiwan. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-W.; Chau, G.-Y.; Hung, H.-H.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Lei, H.-J.; Hsia, C.-Y. Impact of steatosis on prognosis of patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003, 37, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.-H.; Huo, T.-I.; Miksad, R.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor involvement: Best management strategies. Semin. Liver Dis. 2018, 38, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.N.; Wang, J.H.; Su, C.W.; Wang, T.E.; Dai, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, R.C.; Yang, S.S.; Hung, C.F.; Huang, S.F.; et al. Management consensus guideline for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2016 updated by the Taiwan Liver Cancer Association and the Gastroenterological Society of Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, D.; Aikata, H.; Honda, Y.; Naeshiro, N.; Nakahara, T.; Tanaka, M. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma according to Child-Pugh classification. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.-W.; Li, W.; Xie, X.-H.; Hu, H.-T.; Lu, M.-D.; Xie, X.-Y. Sorafenib versus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, Q.; Zou, R.; Shen, J.; Fang, W.; Tan, G. Sorafenib plus hepatic arterial infusion of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin vs sorafenib alone for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.L.; Huang, J.S.; Lin, Y.H.; Lai, K.H.; Yang, C.F.; Pan, H.B. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma by placing a temporary catheter via the subclavian route. Acta Radiol. 2007, 48, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.L.; Lai, K.H.; Liang, H.L.; Hsu, P.I.; Chan, H.H.; Chen, W.C. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for patients with huge unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamatsu, H.; Sumie, S.; Niizeki, T.; Tajiri, N.; Iwamoto, H.; Aino, H. Hepatic arterial infusion chemoembolization therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Multicenter phase II study. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.; Niizeki, T.; Nagamatsu, H.; Tanaka, M.; Kuromatsu, R.; Satani, M. Clinical effects and safety of intra-arterial infusion therapy of cisplatin suspension in lipiodol combined with 5-fluorouracil versus sorafenib, for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion without extra-hepatic spread: A prospective cohort study. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 7, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Osaki, Y.; Kita, R.; Kimura, T. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Cancers 2012, 4, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niizeki, T.; Sumie, S.; Torimura, T.; Kurogi, J.; Kuromatsu, R.; Iwamoto, H. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor as a predictor of response and survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, N.; Matsui, O.; Gabata, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Sanada, J.; Ueda, K. Accumulation of iodized oil within the non-neoplastic liver adjacent to hepatocellular carcinoma via the drainage routes of the tumor after transcatheter arterial embolization. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 24, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uka, K.; Aikata, H.; Takaki, S.; Shirakawa, H.; Jeong, S.C.; Yamashina, K. Clinical features and prognosis of patients with extrahepatic metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, Y.H.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, J.S.; Park, B.H.; Nam, K.J. Efficacy of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2012, 18, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, E.; Tanaka, M.; Yamashita, F.; Kuromatsu, R.; Yutani, S.; Fukumori, K. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: Analysis of 48 cases. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2002, 95, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lladó, L.; Virgili, J.; Figueras, J.; Valls, C.; Dominguez, J.; Rafecas, A. A prognostic index of the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer 2000, 88, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Kumada, H.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; Chayama, K. Effect of repeated transcatheter arterial embolization on the survival time in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis by the Cox proportional hazard model. Cancer 1991, 68, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, R.; Sato, M.; Kawabata, M.; Nakatsuka, H.; Nakamura, K.; Takashima, S. Hepatic artery embolization in 120 patients with unresectable hepatoma. Radiology 1983, 148, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Chung, W.J.; Bae, S.H.; Song, M.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yim, H.J. Randomized, prospective, comparative study on the effects and safety of sorafenib vs. hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.S.; Bae, S.H.; Song, M.J.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamasaki, T.; Kimura, T.; Kurokawa, F.; Aoyama, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Tajima, K. Prognostic factors in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchino, K.; Tateishi, R.; Shiina, S.; Kanda, M.; Masuzaki, R.; Kondo, Y. Hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: Clinical features and prognostic factors. Cancer 2011, 117, 4475–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Hung, C.-F.; Chen, W.-T.; Lin, S.-M. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: Impact of early response to 4 weeks of treatment. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Liu, J.B.; Wu, T.M.; Fu, D. New Therapeutic Options for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Control 2020, 27, 1073274820945975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Y.; Yu, W.; Ren, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, T. Stereotactic body radiotherapy based treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with extensive portal vein tumor thrombosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, R.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Riaz, A.; Ryu, R.K.; Ibrahim, S. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using Yttrium-90 microspheres: A comprehensive report of long-term outcomes. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Raoul, J.-L.; Sherman, M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Bolondi, L.; Craxi, A. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Subanalyses of a phase III trial. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuma, M.; Uojima, H.; Hiraoka, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T. Analysis of efficacy of lenvatinib treatment in highly advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus in the main trunk of the portal vein or tumor with more than 50% liver occupation: A multicenter analysis. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-M.; Han, M.-Z.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, T.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Cheng, P.-N. Real-world outcome of immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular tumor thrombosis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, M.; Yang, G.; Ye, X.; Wu, M. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with sorafenib versus TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shi, J.; Mou, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shen, A. Systematic review of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus sorafenib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient Characteristics | Statistic |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 64 (40–84) |
| Gender (M/F) | 26/6 |
| Etiology | |
| HBV/HCV/HBV + HCV/non-viral | 17/6/2/7 |
| Child-Pugh classification (A/B) | 27/5 |
| BCLC staging C | 32 (100%) |
| Portal venous thrombosis a | |
| Vp2/Vp3/Vp4 | 5/21/6 |
| Maximal tumor size (cm) | |
| <10/≥10 | 6/26 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 5 (15.6%) |
| PT (INR) | 1.04 (0.93–1.26) |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.96 (0.4–3.6) |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 (2.8–4.7) |
| Platelet count (×103/mL) | 161 (54–469) |
| Alpha-fetoprotein (ng/mL) | |
| (≤1000/1000~10,000/>10,000) | 18/5/9 |
| Sorafenib | 19 (59.4%) |
| Previous treatment | |
| (TACE/TACE + RFA/conservative treatment) | 3/2/27 |
| Response after Two HAIC Cycles, n (%) | Response after Completing HAIC, n (%) | Overall Treatment Response, n (%) a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complete response | 2 (6.3%) | 8 (25%) | 5 (15.6%) |
| Partial response | 14 (43.8%) | 9 (28.1%) | 7 (21.9%) |
| Stable disease | 9 (28.1%) | 6 (18.8%) | 4 (12.5%) |
| Progressive disease | 7 (21.9%) | 9 (28.1%) | 16 (50%) |
| Objective response | 16 (50%) | 17 (53.1%) | 12 (37.5%) |
| Disease control rate | 25 (78.1%) | 23 (71.9%) | 16 (50%) |
| Crude HR | Adjusted HR a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (95% CI) | p-Value | (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Pre HAIC prognostic factor | ||||
| Age (≤65/>65) | 0.63 (0.25–1.63) | 0.344 | 0.52(0.13–2.15) | 0.369 |
| Sex (F/M) | 0.41 (0.15–1.14) | 0.087 | 0.12 (0.01–1.28) | 0.079 |
| Tumor size (≤10/>10) | 1.1 (0.36–3.38) | 0.869 | 0.75 (0.21–2.62) | 0.649 |
| Child-Pugh score (A/B) | 0.36 (0.18–0.69) | 0.002 * | 0.28 (0.1–0.76) | 0.013 * |
| PVTT (nonVp4/Vp4) | 1.32 (0.43–4.04) | 0.624 | 0.67 (0.13–3.37) | 0.628 |
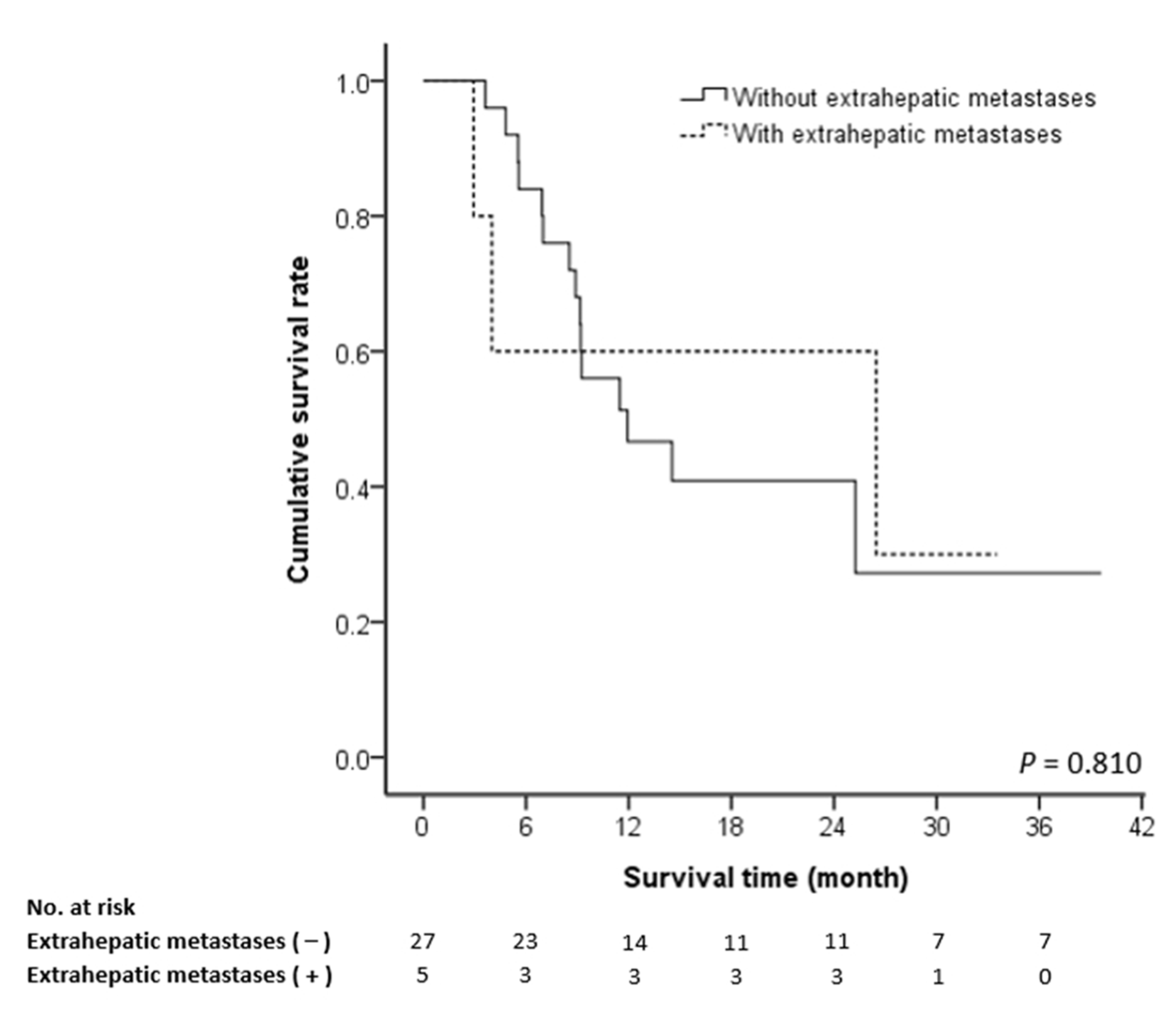
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 0.86 (0.24–3.08) | 0.81 | 0.74 (0.18–3.39) | 0.781 |
| AFP level (AFP ≤ 1000/>1000) | 0.79 (0.29–2.15) | 0.649 | 0.31 (0.06–1.47) | 0.14 |
| Sorafenib | 0.68 (0.27–1.71) | 0.414 | 1.1 (0.34–3.55) | 0.87 |
| Post HAIC prognostic factor | ||||
| After two cycles of HAIC | ||||
| Objective response | ||||
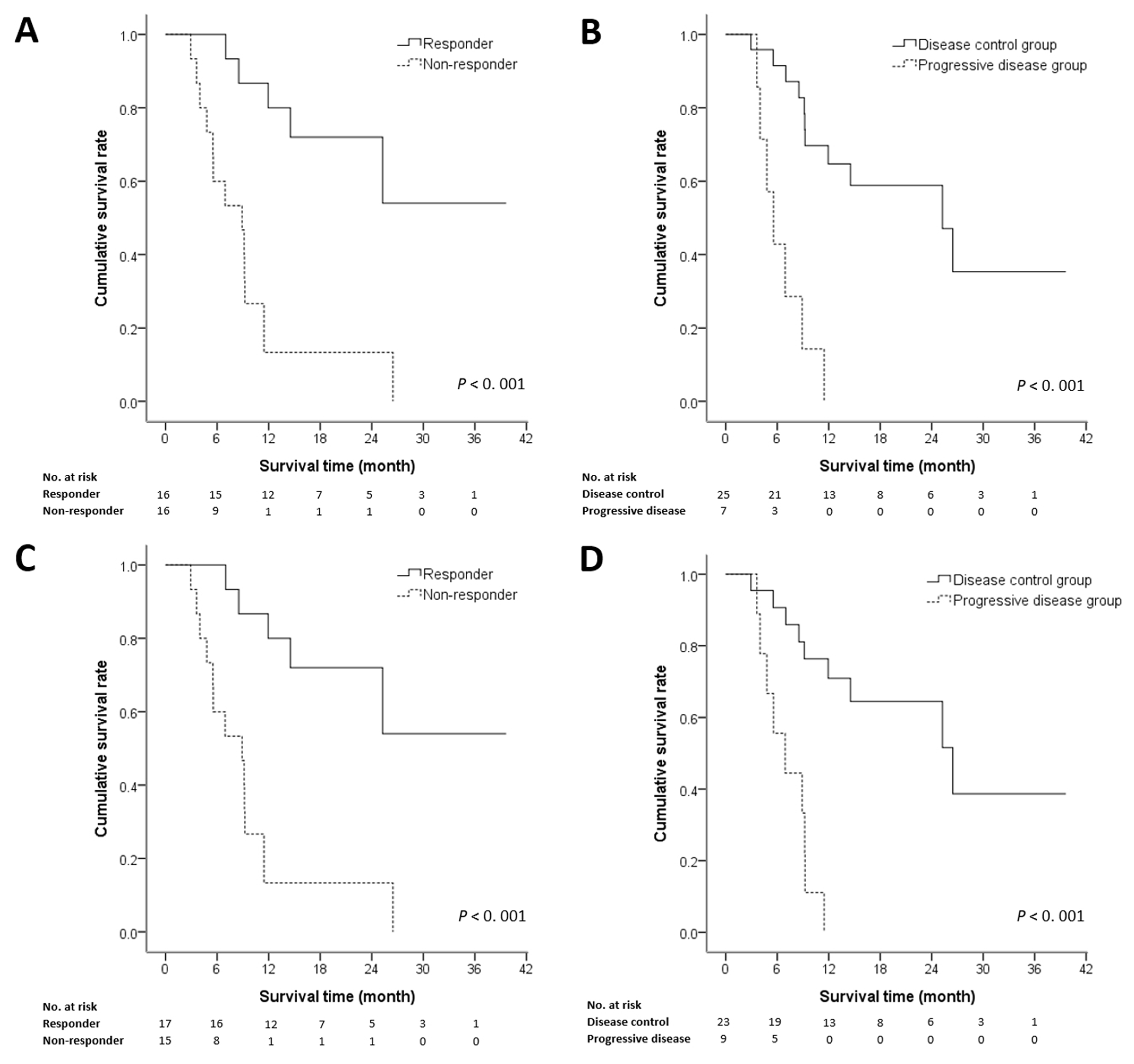
| Responder | 0.15 (0.05–0.46) | 0.001 * | 0.10 (0.03–0.35) | 0.009 * |
| Non-responder | 1 | |||
| Tumor control | ||||
| Control group | 0.12 (0.43–0.39) | 0.001 * | 0.41 (0.04–3.92) | 0.44 |
| Progressive group | 1 | |||
| After completing HAIC | ||||
| Objective response | ||||
| Responder | 0.14 (0.05–0.40) | 0.001 * | 0.13 (0.02–0.74) | 0.02 * |
| Non-responder | 1 | |||
| Tumor control | ||||
| Control group | 0.13 (0.04–0.40) | 0.001 * | 0.17 (0.02–0.31) | 0.001 * |
| Progressive group | 1 | |||
| Grade 1/2, n (%) | Grade 3/4, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Leukopenia | 5 (15.6%) | 0 |
| Anemia | 1 (3.1%) | 0 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 5 (15.6%) | 0 |
| Elevated liver function | 8 (25.0%) | 1 (3.1%) |
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 5 (15.6%) | 2 (6.3%) |
| Elevated serum creatinine | 1 (3.1%) | 0 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 13 (40.6%) | 2 (6.3%) |
| Diarrhea | 2 (6.3%) | 3 (9.4%) |
| Fever | 9 (28.1%) | 0 |
| Study Reference | Treatment Modality | Patient Number | Response Rate | Disease Control Rate | Overall Survival | Progression Free Survival |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
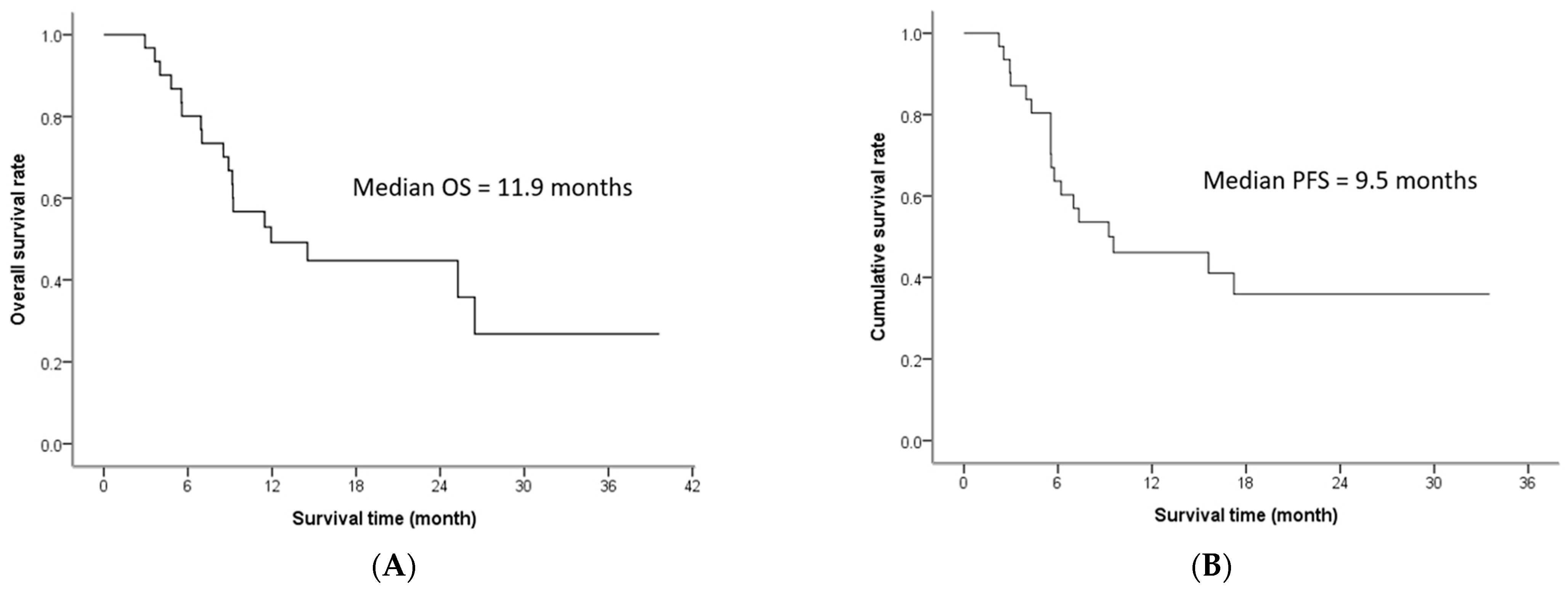
| This study | HAIC followed by lipiodol infusion | 32 | 53.1% | 71.9% | 11.9 m | 9.5 m |
| He et al. [13] | Sorafenib | 122 | 5.7% | 50.8% | 7.13 m | 2.6 m |
| Bruix et al. [35] | sorafenib | 108 | NR | 38.9% | 8.1 m | 4.1 m |
| Chuma et al. [36] | Lenvatinib | 61 | 29.3% | 61% | 6.7 m | 3.4 m |
| Tsai et al. [37] | Nivolumab or pembrolizumab | 45 | 20.6% | 41.2% | 8.9 m | NR |
| Zhang et al. [38] | TACE | 131 | 0–32% | 0–68% | 4.1–6 m | 2.4–3.0 m |
| Salem et al. [34] | Radioembolization with yttrium-90 | Child-Pugh A: 35 | 50% | NR | 10.4 m | 5.6 m |
| Child-Pugh B: 57 | 28% | NR | 5.6 m | 5.9 m | ||
| Liu et al. [39] | HAIC | 181 | 26–43.8% | 46.3–93.8% | 5.3–14.9 m | 3.3–4.4 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.-T.; Tsai, K.-F.; Leung, H.W.C.; Chan, A.L.F.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liang, H.-L.; Tang, S.-Y.; Chou, C.-K.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chan, S.-H.; et al. Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy Followed by Lipiodol Infusion for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Single-Center Experience. Medicina 2021, 57, 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080779
Chen K-T, Tsai K-F, Leung HWC, Chan ALF, Wang S-Y, Liang H-L, Tang S-Y, Chou C-K, Chen H-Y, Chan S-H, et al. Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy Followed by Lipiodol Infusion for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Single-Center Experience. Medicina. 2021; 57(8):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080779
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kuan-Ting, Kun-Feng Tsai, Henry W. C. Leung, Agnes L. F. Chan, Shyh-Yau Wang, Huei-Lung Liang, Sheng-Yeh Tang, Chu-Kuang Chou, Hsin-Yu Chen, Shan-Ho Chan, and et al. 2021. "Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy Followed by Lipiodol Infusion for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Single-Center Experience" Medicina 57, no. 8: 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080779
APA StyleChen, K.-T., Tsai, K.-F., Leung, H. W. C., Chan, A. L. F., Wang, S.-Y., Liang, H.-L., Tang, S.-Y., Chou, C.-K., Chen, H.-Y., Chan, S.-H., & Li, M.-F. (2021). Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy Followed by Lipiodol Infusion for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Single-Center Experience. Medicina, 57(8), 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080779






