Specificity of the Associations between Indices of Cardiovascular Health with Health Literacy and Physical Literacy; A Cross-Sectional Study in Older Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Variables and Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Health Literacy, Physical Literacy, and Lipid Profile
4.2. Physical Literacy, Health Literacy, and Physical Activity Levels
4.3. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornish, K.; Fox, G.; Fyfe, T.; Koopmans, E.; Pousette, A.; Pelletier, C.A. Understanding physical literacy in the context of health: A rapid scoping review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutbeam, D. The evolving concept of health literacy. Soc. Sci. Med. 2008, 67, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bruin, W.B. Judgment and decision making in adolescents. In Judgment and Decision Making as a Skill: Learning, Development and Evolution; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, K.; Van den Broucke, S.; Fullam, J.; Doyle, G.; Pelikan, J.; Slonska, Z.; Brand, H. Health literacy and public health: A systematic review and integration of definitions and models. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinker, C.D.; Aaby, A.; Ringgaard, L.W.; Hjort, A.V.; Hawkins, M.; Maindal, H.T. Health Literacy is Associated with Health Behaviors in Students from Vocational Education and Training Schools: A Danish Population-Based Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yu, X.; Davis, E.; Armstrong, R.; Naccarella, L. Health Literacy: An Interactive Outcome Among Secondary Students in Beijing. Health Lit. Res. Pract. 2021, 5, e1–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.; Schillmöller, Z.; Nienhaus, A. How Does Health Literacy Modify Indicators of Health Behaviour and of Health? A Longitudinal Study with Trainees in North Germany. Healthcare 2021, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Wang, X.; Qin, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, N.; Xu, F. The relationship between health literacy and health-related quality of life among school-aged children in regional China. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Onofre, M.; Mota, J.; Murphy, C.; Repond, R.-M.; Vost, H.; Cremosini, B.; Svrdlim, A.; Markovic, M.; Dudley, D. International approaches to the definition, philosophical tenets, and core elements of physical literacy: A scoping review. Prospects 2021, 50, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, J.; Dudley, D.; Kwan, M.; Bulten, R.; Kriellaars, D. Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Health: Toward an Evidence-InforMed. Conceptual Model. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geets, K.M.; Peric, M.; Gilic, B.; Manojlovic, M.; Drid, P.; Modric, T.; Znidaric, Z.; Zenic, N.; Pajtler, A. Are Health Literacy and Physical Literacy Independent Concepts? A Gender-Stratified Analysis in Medical School Students from Croatia. Children 2022, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar]
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Bredin, S.S.D. Health benefits of physical activity: A systematic review of current systematic reviews. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.A.; Zanesco, A. Early sport practice is related to lower prevalence of cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes in adults independently of overweight and current physical activity. Medicina 2015, 51, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buja, A.; Rabensteiner, A.; Sperotto, M.; Grotto, G.; Bertoncello, C.; Cocchio, S.; Baldovin, T.; Contu, P.; Lorini, C.; Baldo, V. Health Literacy and Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2020, 17, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys with 1·9 million participants. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1077–e1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whooten, R.; Kerem, L.; Stanley, T. Physical activity in adolescents and children and relationship to metabolic health. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2019, 26, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, L.; Behme, N.; Breuer, C. Physical Activity of Children and Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic-A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, E.L.; Reichert, F.F. Studies of Physical Activity and COVID-19 During the Pandemic: A Scoping Review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2020, 17, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenic, N.; Taiar, R.; Gilic, B.; Blazevic, M.; Maric, D.; Pojskic, H.; Sekulic, D. Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekulic, D.; Blazevic, M.; Gilic, B.; Kvesic, I.; Zenic, N. Prospective Analysis of Levels and Correlates of Physical Activity during COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Rules of Social Distancing; Gender Specific Study among Adolescents from Southern Croatia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Fashi, M.; Eskandari, A.; Villafaina, S.; Murillo-Garcia, Á.; Pérez-Gómez, J. Effect of COVID-19 on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adolescents and Children: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riiser, K.; Helseth, S.; Haraldstad, K.; Torbjørnsen, A.; Richardsen, K.R. Adolescents’ health literacy, health protective measures, and health-related quality of life during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idrizovic, K.; Ahmeti, G.B.; Sekulic, D.; Zevrnja, A.; Ostojic, L.; Versic, S.; Zenic, N. Indices of Cardiovascular Health, Body Composition and Aerobic Endurance in Young Women; Differential Effects of Two Endurance-Based Training Modalities. Healthcare 2021, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL-Ashker, S.; Pednekar, M.S.; Narake, S.S.; Albaker, W.; Al-Hariri, M. Blood Pressure and Cardio-Metabolic Risk Profile in Young Saudi Males in a University Setting. Medicina 2021, 57, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.; Beedie, C.; Jimenez, A. Differential effects of aerobic exercise, resistance training and combined exercise modalities on cholesterol and the lipid profile: Review, synthesis and recommendations. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, M.D.; Kit, B.K.; Lacher, D.A. Total and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2009–2010. NCHS Data Brief 2012, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Earnest, C.P.; Artero, E.G.; Sui, X.; Lee, D.C.; Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N. Maximal estimated cardiorespiratory fitness, cardiometabolic risk factors, and metabolic syndrome in the aerobics center longitudinal study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Malina, R.M.; Bouchard, C. Physical activity, physical fitness, and coronary heart disease risk factors in youth: The Québec Family Study. Prev. Med. 1999, 29, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, J.; Weres, A.; Czenczek-Lewandowska, E.; Wyszyńska, J.; Łuszczki, E.; Dereń, K.; Sobek, G.; Więch, P. Blood lipid profile and body composition in a pediatric population with different levels of physical activity. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, N.K. Gender Differences in Health Literacy Among Korean Adults: Do Women Have a Higher Level of Health Literacy Than Men? Am. J. Mens. Health 2015, 9, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, H.A.T.; Proudfoot, N.A.; DiCristofaro, N.A.; Cairney, J.; Bray, S.R.; Timmons, B.W. Preschool to School-Age Physical Activity Trajectories and School-Age Physical Literacy: A Longitudinal Analysis. J. Phys. Act. Health 2022, 19, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchengast, S. Gender Differences in Body Composition from Childhood to Old Age: An Evolutionary Point of View. J. Life Sci. 2010, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E. Gender differences in fat metabolism. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2001, 4, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geets Kesic, M.; Penjak, A.; Sekulic, D. Reliability and validity of the croatian version of the european health literacy survey questionnaire. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Scientific Conference of Montenegrin Sports Academy “Sport, Physical Activity and Health: Contemporary perspectives”, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 7–10 April 2022; Volume 11, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, K.; Van den Broucke, S.; Pelikan, J.M.; Fullam, J.; Doyle, G.; Slonska, Z.; Kondilis, B.; Stoffels, V.; Osborne, R.H.; Brand, H. Measuring health literacy in populations: Illuminating the design and development process of the European Health Literacy Survey Questionnaire (HLS-EU-Q). BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferies, P.; Bremer, E.; Kozera, T.; Cairney, J.; Kriellaars, D. Psychometric properties and construct validity of PLAYself: A self-reported measure of physical literacy for children and youth. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunda, M.; Gilic, B.; Sekulic, D.; Matic, R.; Drid, P.; Alexe, D.I.; Cucui, G.G.; Lupu, G.S. Out-of-School Sports Participation Is Positively Associated with Physical Literacy, but What about Physical Education? A Cross-Sectional Gender-Stratified Analysis during the COVID-19 Pandemic among High-School Adolescents. Children 2022, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilic, B.; Malovic, P.; Sunda, M.; Maras, N.; Zenic, N. Adolescents with Higher Cognitive and Affective Domains of Physical Literacy Possess Better Physical Fitness: The Importance of Developing the Concept of Physical Literacy in High Schools. Children 2022, 9, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.C.; Crocker, P.R.; Donen, R.M. The Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C) and Adolescents (PAQ-A) Manual; College of Kinesiology, University of Saskatchewan: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2004; Volume 87, pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, A.; Greig-Pylypczuk, R.; Huisman, A. The state of point-of-care testing: A European perspective. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 120, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; De Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, e1082–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigdel, M.; Yadav, B.K.; Gyawali, P.; Regmi, P.; Baral, S.; Regmi, S.R.; Jha, B. Non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol versus low density lipoprotein cholesterol as a discriminating factor for myocardial infarction. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calling, S.; Johansson, S.-E.; Wolff, M.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K. Total cholesterol/HDL-C ratio versus non-HDL-C as predictors for ischemic heart disease: A 17-year follow-up study of women in southern Sweden. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents: Summary report. Pediatrics 2011, 128 (Suppl. 5), S213–S256. [CrossRef]
- Mearns, G.J.; Chepulis, L.; Britnell, S.; Skinner, K. Health and Nutritional Literacy of New Zealand Nursing Students. J. Nurs. Educ. 2017, 56, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, S.F.; Liu, C.H.; Liao, L.L.; Osborne, R.H. Health literacy and the determinants of obesity: A population-based survey of sixth grade school children in Taiwan. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.M.; Jacobson, T.A. The role of health literacy in narrowing the treatment gap for hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Manag. Care 2000, 6, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, H.A.T.; Di Cristofaro, N.A.; Cairney, J.; Bray, S.R.; MacDonald, M.J.; Timmons, B.W. Physical Literacy, Physical Activity, and Health Indicators in School-Age Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.J.; Chaput, J.P.; Longmuir, P.E.; Barnes, J.D.; Belanger, K.; Tomkinson, G.R.; Anderson, K.D.; Bruner, B.; Copeland, J.L.; Gregg, M.J.; et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with physical literacy in a large sample of Canadian children aged 8 to 12 years. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, A.; Grotto, G.; Montecchio, L.; De Battisti, E.; Sperotto, M.; Bertoncello, C.; Cocchio, S.; Baldovin, T.; Baldo, V. Association between health literacy and dietary intake of sugar, fat and salt: A systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmuir, P.E.; Tremblay, M.S. Top 10 Research Questions Related to Physical Literacy. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2016, 87, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, K.; Barnes, J.D.; Longmuir, P.E.; Anderson, K.D.; Bruner, B.; Copeland, J.L.; Gregg, M.J.; Hall, N.; Kolen, A.M.; Lane, K.N.; et al. The relationship between physical literacy scores and adherence to Canadian physical activity and sedentary behaviour guidelines. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, E.; Graham, J.D.; Bedard, C.; Rodriguez, C.; Kriellaars, D.; Cairney, J. The Association Between PLAYfun and Physical Activity: A Convergent Validation Study. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2020, 91, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.M.; Sum, R.K.W.; Leung, E.F.L.; Ng, R.S.K. Relationship between perceived physical literacy and physical activity levels among Hong Kong adolescents. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, J.; Barratt, J.; Wanner, P.; Töpfer, C.; Cairney, J.; Pfeifer, K. The Effectiveness of Physical Literacy Interventions: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, L.C.; Bryant, A.S.; Keegan, R.J.; Morgan, K.; Jones, A.M. Definitions, Foundations and Associations of Physical Literacy: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faigenbaum, A.D.; Rebullido, T.R. Understanding physical literacy in youth. Strength Cond. J. 2018, 40, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paakkari, L.; Kokko, S.; Villberg, J.; Paakkari, O.; Tynjälä, J. Health literacy and participation in sports club activities among adolescents. Scand J. Public Health 2017, 45, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademakers, J.; Hahnraths, M.T.H.; van Schayck, O.C.P.; Heijmans, M. Children’s Health Literacy in Relation to Their BMI z-Score, Food Intake, and Physical Activity: A Cross-Sectional Study among 8-11-Year-Old Children in The Netherlands. Children 2022, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumith, S.C.; Gigante, D.P.; Domingues, M.R.; Kohl, H.W., 3rd. Physical activity change during adolescence: A systematic review and a pooled analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maric, D.; Kvesic, I.; Lujan, I.K.; Bianco, A.; Zenic, N.; Separovic, V.; Terzic, A.; Versic, S.; Sekulic, D. Parental and Familial Factors Influencing Physical Activity Levels in Early Adolescence: A Prospective Study. Healthcare 2020, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
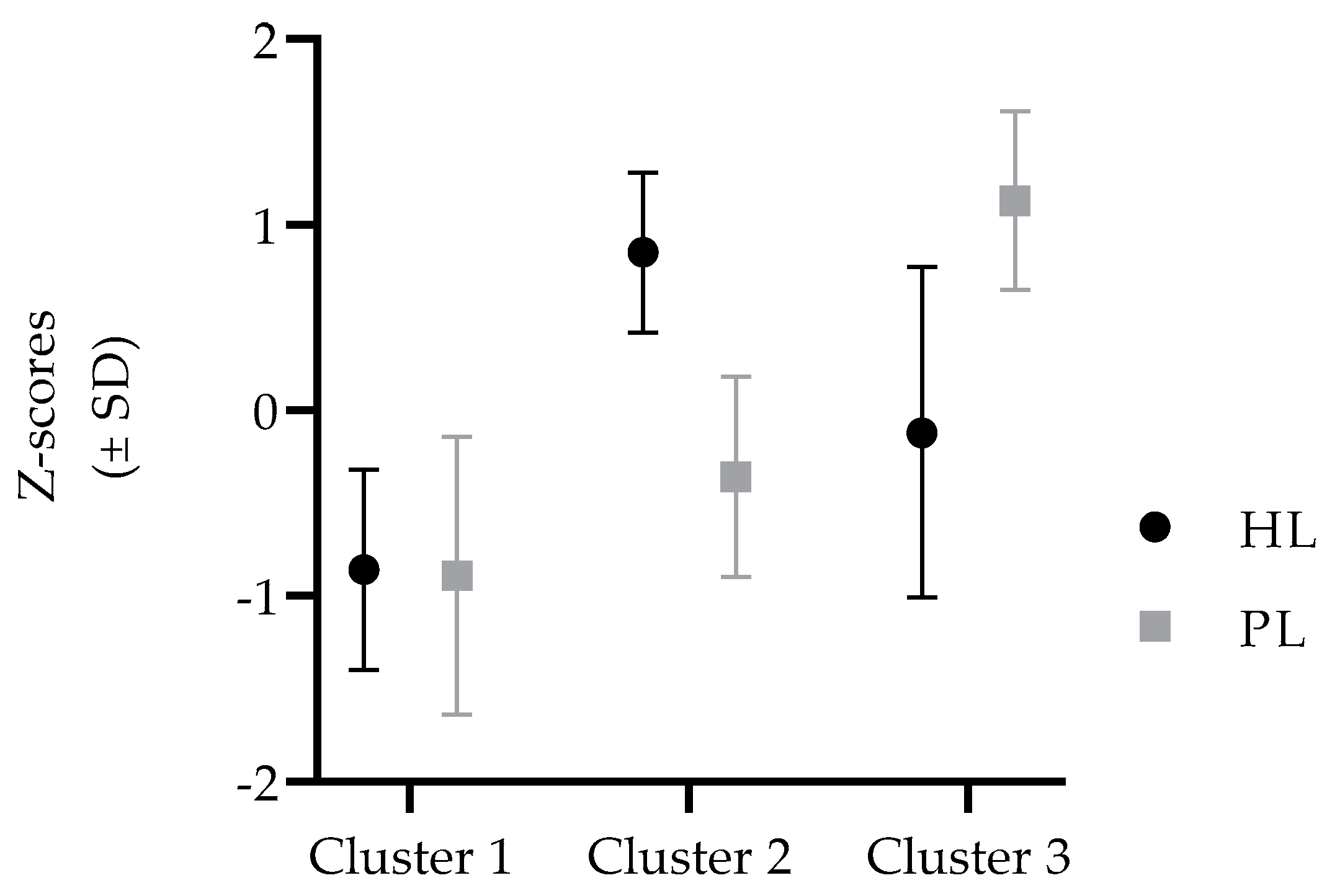
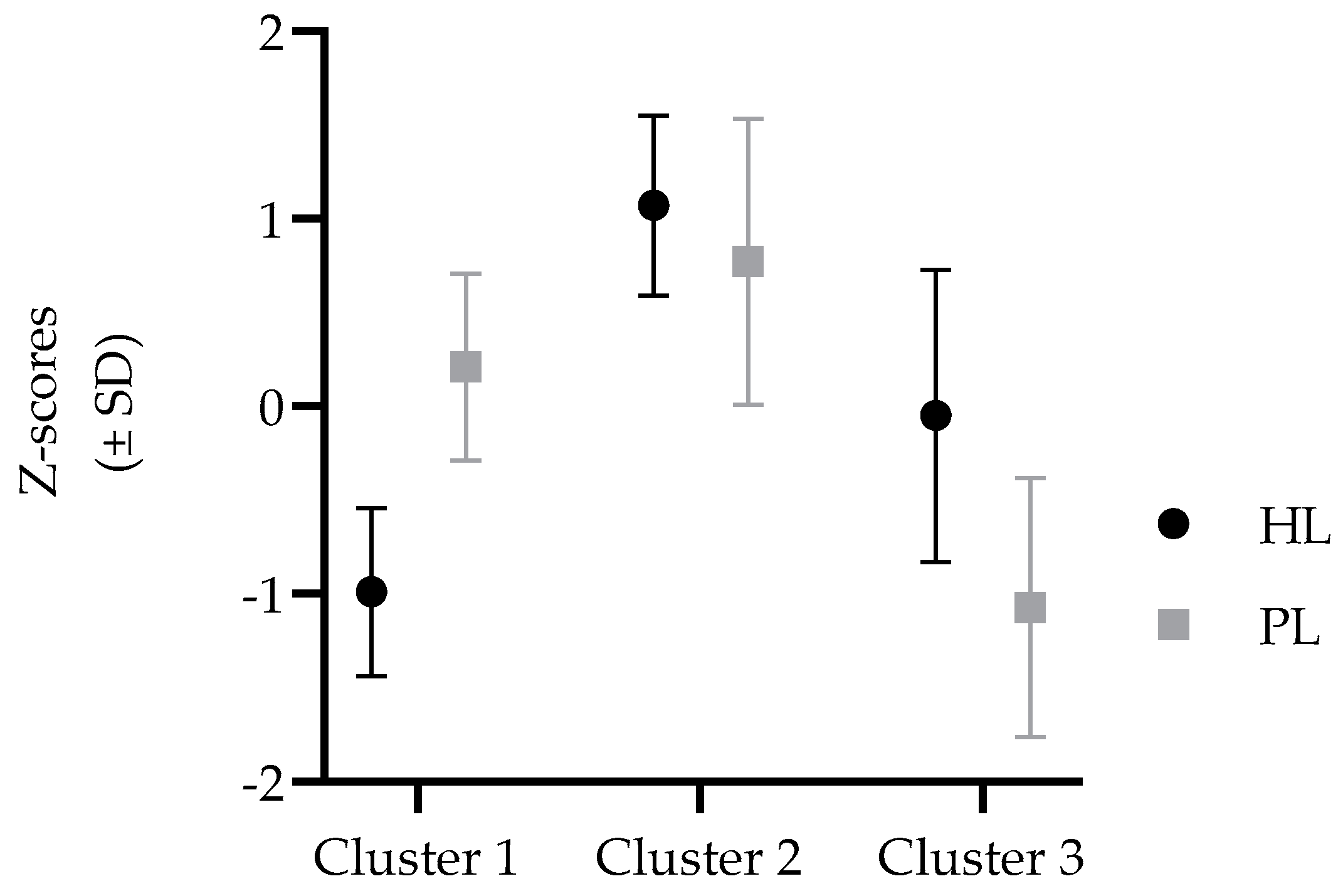
| Category | Acceptable mg/dL (mmol/L) | Borderline mg/dL (mmol/L) | High mg/dL (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCHOL | <170 (4.4) | 170 to 199 (4.4 to 5.2) | ≥200 (5.2) |
| LDL-C | <110 (2.8) | 110 to 129 (2.8 to 3.3) | ≥130 (3.4) |
| Non-HDL-C | <120 (3.1) | 120 to 144 (3.1 to 3.7) | ≥145 (3.8) |
| TG | <90 (1 mmol/L) | 90 to 129 (1 to 1.5) | ≥130 (1.5) |
| HDL-C | <40 (1) | 40 to 45 (1 to 1.2) | >45 (1.2) |
| High F (%) | Borderline F (%) | Acceptable F (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCHOL | 2 (1) | 15 (6) | 230 (93) |
| TG | 16 (7) | 48 (20) | 183 (73) |
| HDL-C | 47 (19) | 20 (8) | 181 (73) |
| non-HDL-C | 4 (2) | 13 (5) | 231 (93) |
| LDL-C | 2 (1) | 9 (4) | 236 (95) |
| Total Sample (n = 247) | Boys (n = 70) | Girls (n = 177) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body height (cm) | 1.71 ± 0.18 | 1.81 ± 0.14 | 1.68 ± 0.18 |
| Body mass (kg) | 67.01 ± 12.27 | 74.4 ± 12.49 | 64.48 ± 11.15 |
| PAL (score) | 2.51 ± 0.72 | 2.64 ± 0.72 | 2.47 ± 0.72 |
| PL (score) | 69.1 ± 11.11 | 69.05 ± 11.04 | 68.91 ± 11.40 |
| HL (score) | 37.91 ± 6.31 | 37.78 ± 6.53 | 38.07 ± 6.42 |
| TCHOL (mg/dL) | 132.58 ± 24.63 | 120.9 ± 23.82 | 136.25 ± 23.78 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 82.89 ± 29.86 | 82.25 ± 33.99 | 83.09 ± 28.53 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 51.46 ± 13.68 | 40.12 ± 13.17 | 55.02 ± 11.79 |
| non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 78.32 ± 28.02 | 76.94 ± 30.29 | 78.76 ± 27.32 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 58.98 ± 30.32 | 52.33 ± 35.58 | 61.07 ± 28.25 |
| CHOL/HDL ratio (ratio) | 2.5 ± 1.6 | 2.48 ± 1.68 | 2.51 ± 1.58 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body height (1) | − | |||||||||
| Body mass (2) | 0.00 | − | ||||||||
| PAL (3) | −0.10 | 0.02 | − | |||||||
| PL (4) | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.43 * | − | ||||||
| HL (5) | −0.11 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07 | − | |||||
| TCHOL (6) | −0.13 | 0.08 | 0.03 | −0.07 | −0.03 | − | ||||
| TG (7) | 0.06 | 0.29 * | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.06 | 0.53 * | − | |||
| HDL-C (8) | 0.04 | −0.23 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.14 | −0.20 | − | ||
| non-HDL-C (9) | −0.15 | 0.19 | −0.03 | −0.18 | −0.15 | 0.86 * | 0.59 * | −0.39 * | − | |
| LDL-C (10) | −0.18 | −0.01 | 0.04 | −0.21 | −0.02 | 0.84 * | 0.32 * | 0.05 | 0.76 * | − |
| CHOL/HDL ratio (11) | −0.14 | 0.03 | 0.00 | −0.23 | −0.01 | 0.71 * | 0.36 * | −0.08 | 0.71 * | 0.96 * |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body height (1) | - | |||||||||
| Body mass (2) | 0.54 * | - | ||||||||
| PAL (3) | −0.08 | 0.07 | - | |||||||
| PL (4) | −0.01 | −0.05 | 0.51 * | - | ||||||
| HL (5) | −0.01 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.31 * | - | |||||
| TCHOL (6) | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.20 * | - | ||||
| TG (7) | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.01 | −0.09 | 0.11 | 0.28 * | - | |||
| HDL-C (8) | −0.04 | −0.19 * | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.21 * | −0.15 | - | ||
| non-HDL-C (9) | 0.03 | 0.21 * | 0.02 | 0.04 | −0.25 * | 0.88 * | 0.35 * | −0.25 * | - | |
| LDL-C (10) | 0.02 | 0.17 * | 0.00 | 0.01 | −0.24 * | 0.84 * | 0.18 * | −0.09 | 0.88 * | - |
| CHOL/HDL ratio (11) | −0.07 | 0.07 | −0.03 | −0.04 | 0.07 | 0.32 * | 0.12 | −0.13 | 0.39 * | 0.47 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kesic, M.G.; Savicevic, A.J.; Peric, M.; Gilic, B.; Zenic, N. Specificity of the Associations between Indices of Cardiovascular Health with Health Literacy and Physical Literacy; A Cross-Sectional Study in Older Adolescents. Medicina 2022, 58, 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101316
Kesic MG, Savicevic AJ, Peric M, Gilic B, Zenic N. Specificity of the Associations between Indices of Cardiovascular Health with Health Literacy and Physical Literacy; A Cross-Sectional Study in Older Adolescents. Medicina. 2022; 58(10):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101316
Chicago/Turabian StyleKesic, Marijana Geets, Anamarija Jurcev Savicevic, Mia Peric, Barbara Gilic, and Natasa Zenic. 2022. "Specificity of the Associations between Indices of Cardiovascular Health with Health Literacy and Physical Literacy; A Cross-Sectional Study in Older Adolescents" Medicina 58, no. 10: 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101316
APA StyleKesic, M. G., Savicevic, A. J., Peric, M., Gilic, B., & Zenic, N. (2022). Specificity of the Associations between Indices of Cardiovascular Health with Health Literacy and Physical Literacy; A Cross-Sectional Study in Older Adolescents. Medicina, 58(10), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101316







