Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia in a Patient with X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: A Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
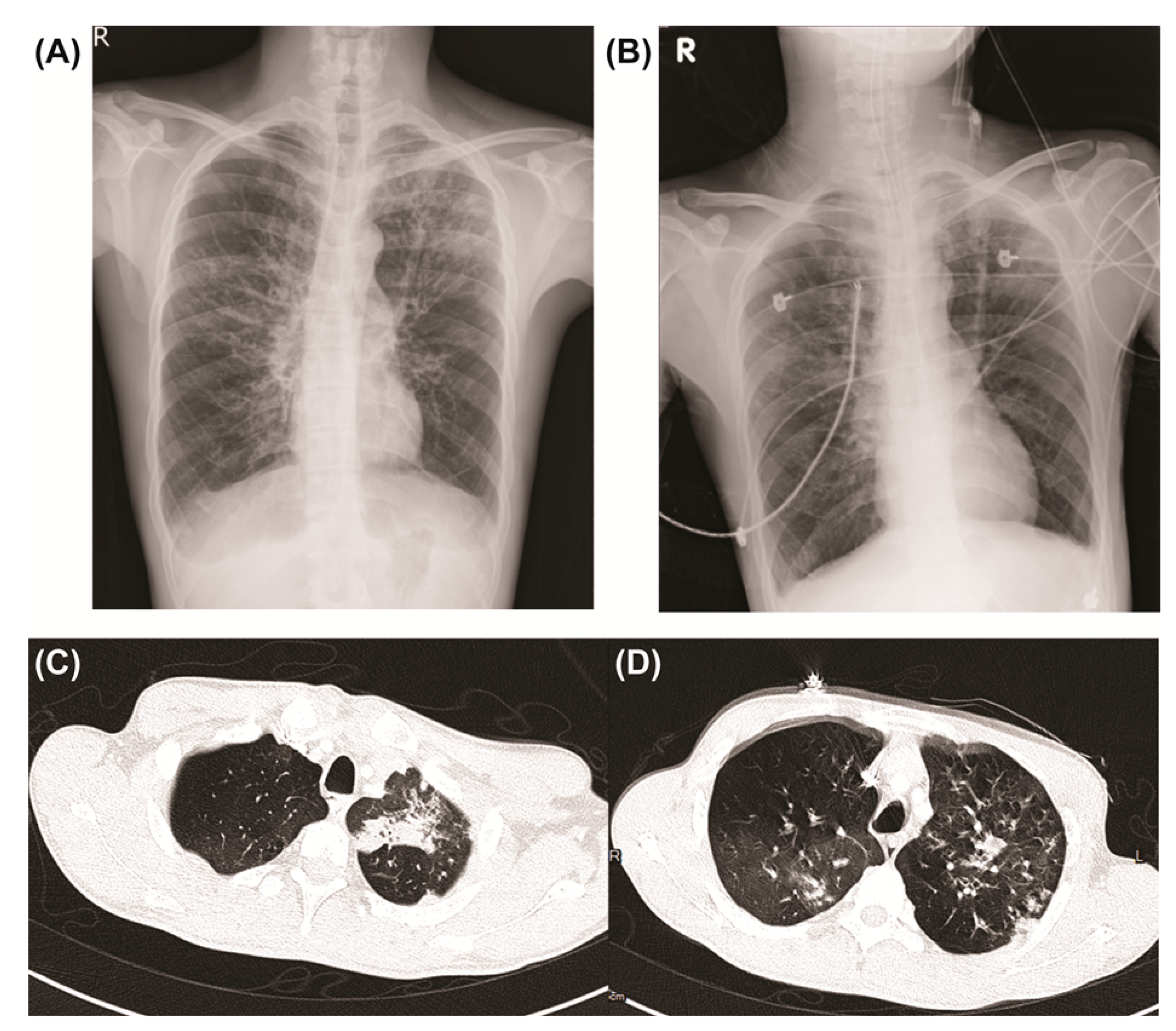
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kainulainen, L.; Nikoskelainen, J.; Vuorinen, T.; Tevola, K.; Liippo, K.; Ruuskanen, O. Viruses and bacteria in bronchial samples from patients with primary hypogammaglobulinemia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahuma, A.; Mansonb, D.; Nganc, B. Atypical presentation and manifestations in X-linked agammaglobulinemia patients with novel BTK mutations. LymphoSign J. 2015, 2, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, L.M.; Chang, J.M.; Wang, I.F.; Chang, W.C.; Hwang, D.Y.; Chen, H.C. Atypical X-linked agammaglobulinaemia caused by a novel BTK mutation in a selective immunoglobulin M deficiency patient. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kornfeld, S.J.; Kratz, J.; Haire, R.N.; Litman, G.W.; Good, R.A. X-linked agammaglobulinemia presenting as transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 95, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.M.; Mayne, A.; Joyce, H.; Smith, C.I.; Granoff, D.M.; Kumararatne, D.S. A mutation in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase as a cause of selective anti-polysaccharide antibody deficiency. J. Pediatr. 2001, 139, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.M.; Tian, L.; Nelson, D.L. A case of X-linked agammaglobulinemia diagnosed in adulthood. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 99, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungman, P.; Boeckh, M.; Hirsch, H.H.; Josephson, F.; Lundgren, J.; Nichols, G.; Pikis, A.; Razonable, R.R.; Miller, V.; Griffiths, P.D.; et al. Definitions of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in transplant patients for use in clinical trials. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arroyo-Martinez, Y.M.; Saindon, M.; Raina, J.S. X-linked agammaglobulinemia presenting with multiviral pneumonia. Cureus 2020, 12, e7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qing, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Niu, X.; Tan, Y.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Bruton’s agammaglobulinemia in an adult male due to a novel mutation: A case report. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E1207–E1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razonable, R.R.; Humar, A. Cytomegalovirus in solid organ transplant recipients-Guidelines of the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayatte, C.; Schneider-Ohrum, K.; Wang, Z.; Irrinki, A.; Nguyen, N.; Lu, J.; Nelson, C.; Servat, E.; Gemmell, L.; Citkowicz, A.; et al. Cytomegalovirus vaccine strain towne-derived dense bodies induce broad cellular immune responses and neutralizing antibodies that prevent infection of fibroblasts and epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11107–11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Britt, W.J.; Prichard, M.N. New therapies for human cytomegalovirus infections. Antivir. Res. 2018, 159, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugliesi, F.; Coscia, A.; Griffante, G.; Galitska, G.; Pasquero, S.; Albano, C.; Biolatti, M. Where do we stand after decades of studying human Cytomegalovirus? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waqas, Q.A.; Abdullah, H.M.A.; Khan, U.I.; Oliver, T. Human cytomegalovirus pneumonia in an immunocompetent patient: A very uncommon but treatable condition. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungman, P.; Reusser, P.; de la Camara, R.; Einsele, H.; Engelhard, D.; Ribaud, P.; Ward, K. Management of CMV infections: Recommendations from the infectious diseases working party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004, 33, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponsford, M.J.; Price, C.; Farewell, D.; Greene, G.; Moore, C.; Perry, M.; Price, N.; Cottrell, S.; Steven, R.; El-Shanawany, T.; et al. Increased respiratory viral detection and symptom burden among patients with primary antibody deficiency: Results from the BIPAD study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, N.; Shiraki, A.; Yajima, M.; Oyama, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Ohno, A.; Yamada, H.; Takemoto, M.; Daikoku, T.; Shiraki, K. Interaction of immunoglobulin with cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Viral Immunol. 2017, 30, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schampera, M.S.; Schweinzer, K.; Abele, H.; Kagan, K.O.; Klein, R.; Rettig, I.; Jahn, G.; Hamprecht, K. Comparison of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific neutralization capacity of hyperimmunoglobulin (HIG) versus standard intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) preparations: Impact of CMV IgG normalization. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 90, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, L.; Perera, M.M.; Torres-Miñana, L.; Pena-López, M.J. CMV viral load in bronchoalveolar lavage for diagnosis of pneumonia in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckh, M.; Stevens-Ayers, T.; Travi, G.; Huang, M.L.; Cheng, G.S.; Xie, H.; Leisenring, W.; Erard, V.; Seo, S.; Kimball, L.; et al. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA quantitation in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with CMV pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, F.A.; Khan, D.A.; Ballas, Z.K.; Chinen, J.; Frank, M.M.; Hsu, J.T.; Keller, M.; Kobrynski, L.J.; Komarow, H.D.; Mazer, B.; et al. Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1186–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Sayed, Z.A.; Abramova, I.; Aldave, J.C.; Al-Herz, W.; Bezrodnik, L.; Boukari, R.; Bousfiha, A.A.; Cancrini, C.; Condino-Neto, A.; Dbaibo, G.; et al. X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA): Phenotype, diagnosis, and therapeutic challenges around the world. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballow, M. Optimizing immunoglobulin treatment for patients with primary immunodeficiency disease to prevent pneumonia and infection incidence: Review of the current data. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111 (Suppl. S6), S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borte, M.; Kriván, G.; Derfalvi, B.; Maródi, L.; Harrer, T.; Jolles, S.; Bourgeois, C.; Engl, W.; Leibl, H.; McCoy, B.; et al. Efficacy, safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of a novel human immune globulin subcutaneous, 20%: A Phase 2/3 study in Europe in patients with primary immunodeficiencies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 187, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, P.; Karmacharya, P.; Wang, Z.; Donato, A.; Joshi, A.Y. Impact of IVIG vs. SCIG on IgG trough level and infection incidence in primary immunodeficiency diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kainulainen, L.; Vuorinen, T.; Rantakokko-Jalava, K.; Österback, R.; Ruuskanen, O. Recurrent and persistent respiratory tract viral infections in patients with primary hypogammaglobulinemia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 120–126.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lougaris, V.; Baronio, M.; Vitali, M.; Tampella, G.; Cattalini, M.; Tassone, L.; Soresina, A.; Badolato, R.; Plebani, A. Bruton tyrosine kinase mediates TLR9-dependent human dendritic cell activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1644–1650.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ref. | Patient Age (Years) | Serum IgG (Normal Range) | Pathogen | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arroyo-Martinez et al. [8] | 20 | <108 (540–1822 mg/dL) | CMV, RSV, and rhinovirus | Vancomycin, piperacillin/tazobactam, and IVIG | Discharged |
| Xu et al. [9] | 22 | 5.55 g/L (7.23–16.85 g/L) | Staphylococcus epidermidis, Candida albicans, and CMV | Teicoplanin, voriconazole, ganciclovir, and IVIG | Discharged |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, Y.-X.; Shyur, S.-D. Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia in a Patient with X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: A Case Report. Medicina 2022, 58, 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101457
Wong Y-X, Shyur S-D. Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia in a Patient with X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: A Case Report. Medicina. 2022; 58(10):1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101457
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Yao-Xian, and Shyh-Dar Shyur. 2022. "Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia in a Patient with X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: A Case Report" Medicina 58, no. 10: 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101457
APA StyleWong, Y.-X., & Shyur, S.-D. (2022). Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia in a Patient with X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: A Case Report. Medicina, 58(10), 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101457






