Custom-Made Implants in Ankle Bone Loss: A Retrospective Assessment of Reconstruction/Arthrodesis in Sequelae of Septic Non-Union of the Tibial Pilon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
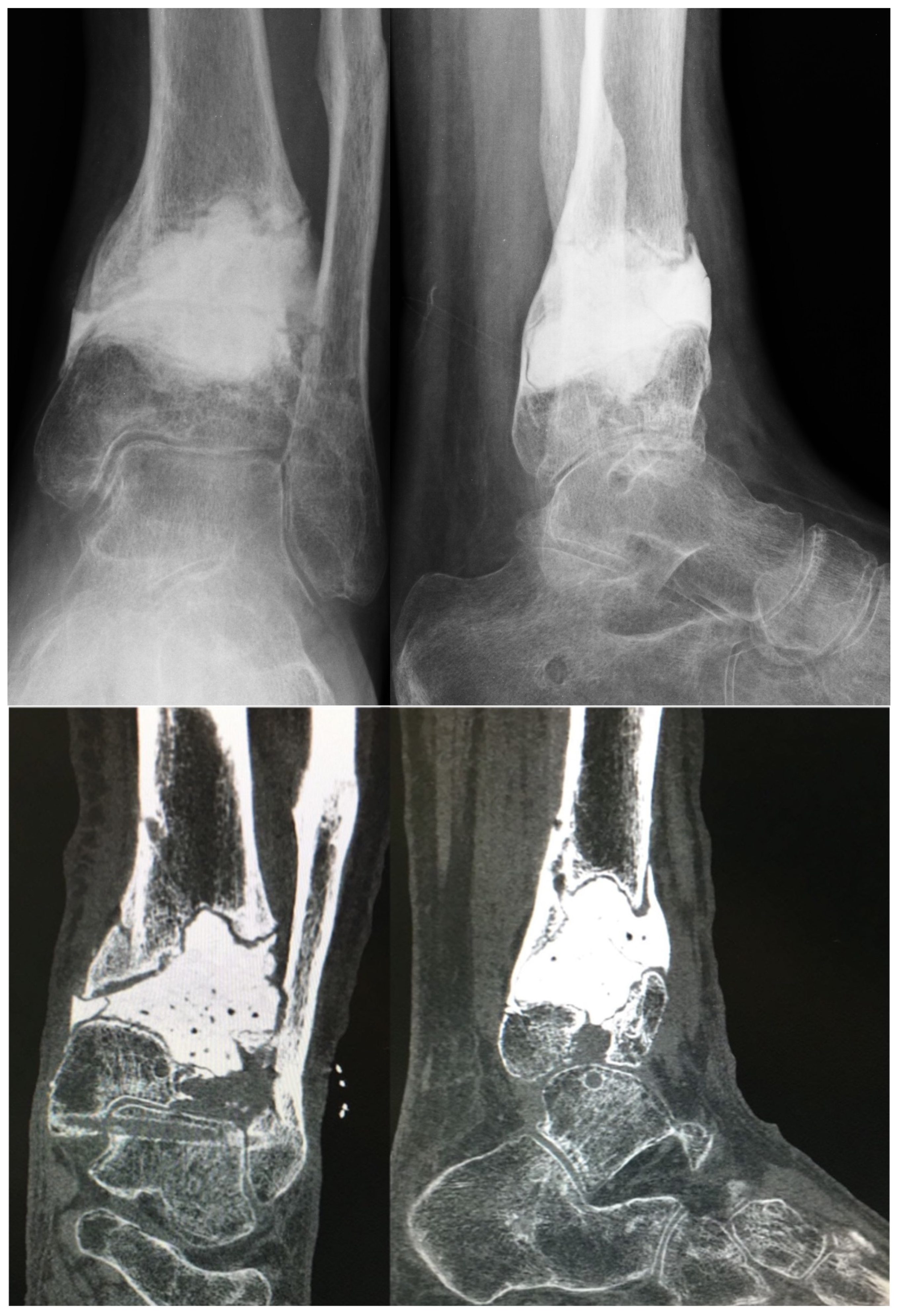
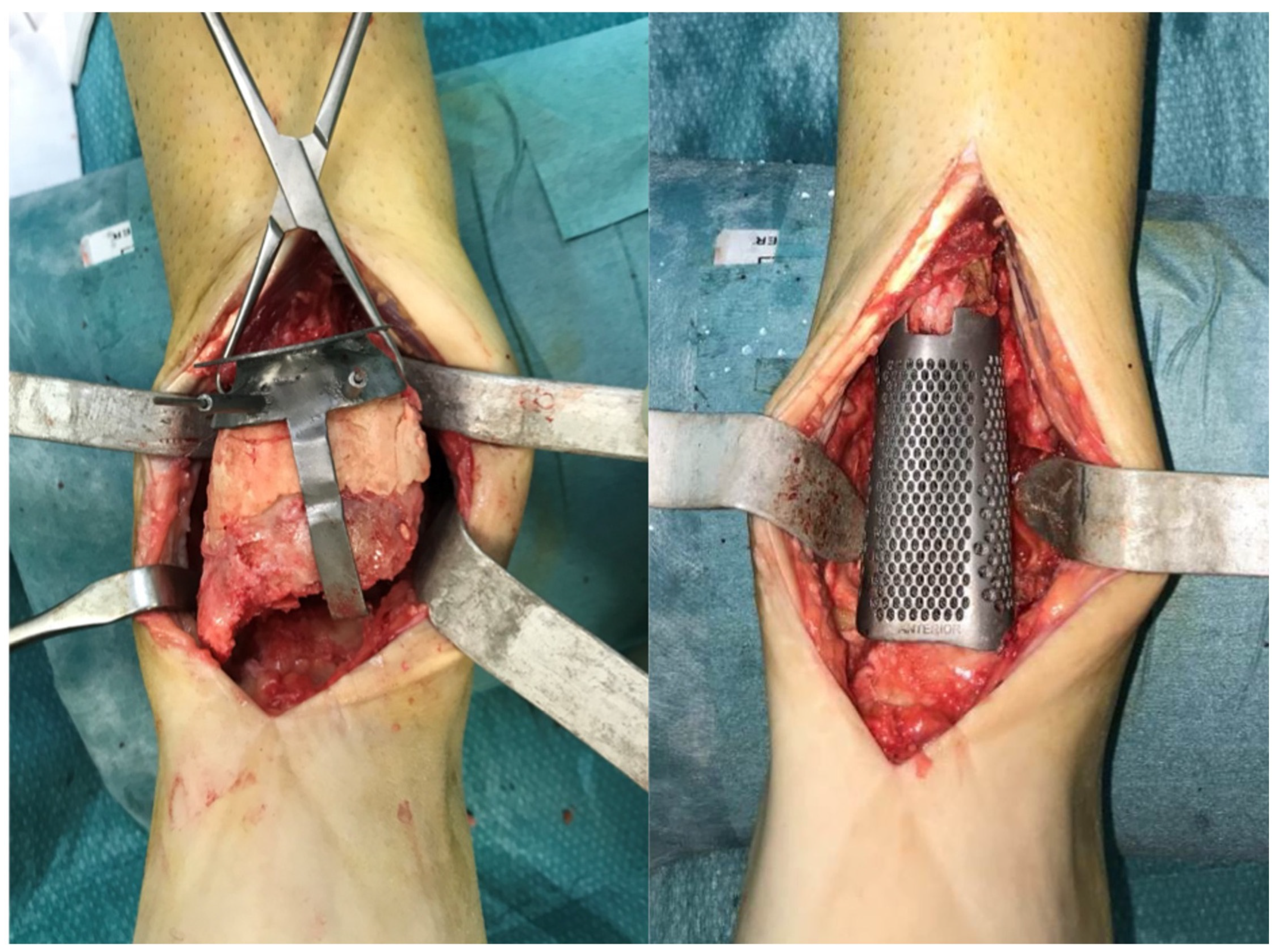
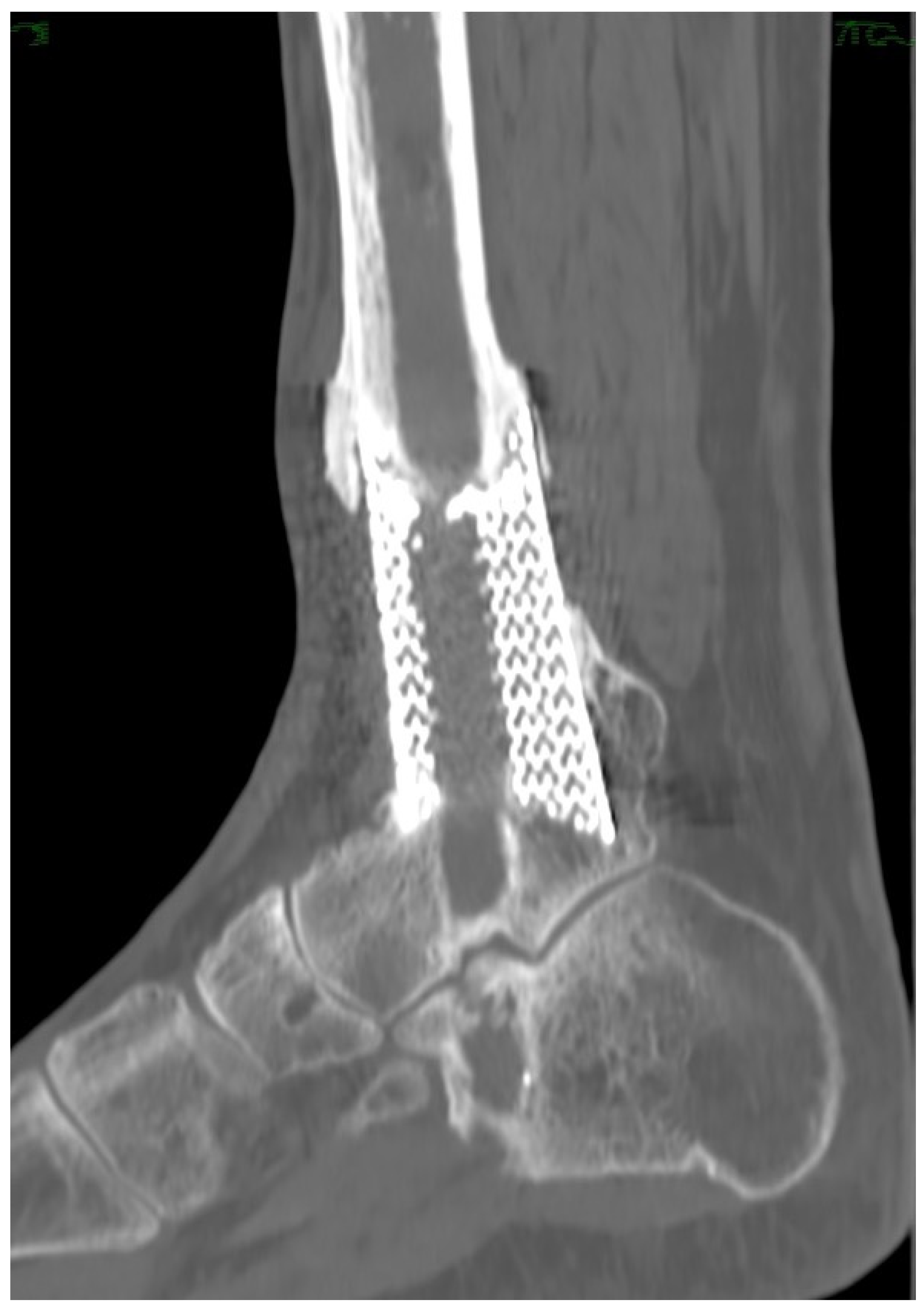
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Planning Procedures and 3D Technology
2.2. Study Population
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Court-Brown, C.M.; Bugler, K.E.; Clement, N.D.; Duckworth, A.D.; McQueen, M.M. The epidemiology of open fractures in adults. A 15-year review. Injury 2012, 43, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elniel, A.R.; Giannoudis, P.V. Open fractures of the lower extremity: Current management and clinical outcomes. EFORT Open Rev. 2018, 3, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauns, A.; Lammens, J. The challenge of the infected pilon tibial non-union: Treatment with radical resection, bone transport and ankle arthrodesis. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2020, 86, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biçici, V.; Bingöl, İ. Do different surgical techniques in tibia pilon fractures change the results of the midterm? Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, B.; Dean, E. Posttraumatic Reconstruction of the Foot and Ankle in the Face of Active Infection. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 48, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P. The treatment of infected tibial nonunion by bone transport using the Ilizarov external fixator and a systematic review of infected tibial nonunion treated by Ilizarov methods. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2014, 80, 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.K.; Chung, S. Ipsilateral island fibula transfer for segmental tibial defects: Antegrade and retrograde fashion. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 101, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierny, G., 3rd; Zorn, K.E. Segmental tibial defects. Comparing conventional and Ilizarov methodologies. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 301, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- So, E.; Mandas, V.H.; Hlad, L. Large Osseous Defect Reconstruction Using a Custom ThreeDimensional Printed Titanium Truss Implant. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belvedere, C.; Siegler, S.; Fortunato, A.; Caravaggi, P.; Liverani, E.; Durante, S. New comprehensive procedure for custom-made total ankle replacements: Medical imaging, joint modeling, prosthesis design, and 3D printing. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K. 3D-printed patient-specific applications in orthopedics. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2016, 8, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosca, M.; Caravelli, S.; Fuiano, M.; Massimi, S.; Censoni, D.; Grassi, A.; Vocale, E.; Ceccarelli, F.; Zaffagnini, S. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis through retrograde nailing for the treatment of juxtaarticular distal tibia aseptic non-unions: A retrospective study at a minimum follow-up of 4 years. Injury 2020, 51, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigheb, M.; Janicka, P.; Andorno, S.; Marcuzzi, A.; Magnani, C.; Grassi, F. Italian translation, cultural adaptation and validation of the “American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society’s (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot scale”. Acta Biomed. 2016, 87, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Haglin, J.M.; Eltorai, A.E.M.; Gil, J.A.; Marcaccio, S.E.; Botero-Hincapie, J.; Daniels, A.H. Patient-Specific Orthopaedic Implants. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 8, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzel, A.P.; Lemonne, F.; Casoli, V. Tibial segmental bone defect reconstruction by Ilizarov type bone transport in an induced membrane. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2010, 96, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boone, D.W. Complications of iliac crest graft and bone grafting alternatives in foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Clin. 2003, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masquelet, A.C.; Fitoussi, F.; Begue, T.; Muller, G.P. Reconstruction of the long bones by the induced membrane and spongy auto-graft. Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthet. 2000, 45, 346–353. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- McGarvey, W.C.; Braly, W.G. Bone graft in hindfoot arthrodesis: Allograft vs autograft. Orthopedics 1996, 19, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.; Barker, L.G.; Claridge, R.J. Technique tip: Tantalum: A structural bone graft option for foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int. 2004, 25, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.F.; Wong, Y.S. Osteolysis of structural autograft after calcaneocuboid distraction arthrodesis for stage II posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Foot Ankle Int. 2002, 23, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, S.; Cadossi, M.; Mazzotti, A.; Ramponi, L.; Belvedere, C.; Leardini, A. Custom-Made Total Talonavicular Replacement in a Professional Rock Climber. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2016, 55, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, K.; Verheyen, C.C.; Gausepohl, T.; Pennig, D. Minimally invasive ankle arthrodesis with a retrograde locking nail after failed fusion. Strateg. Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2007, 2, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sex | Age | Smoker | Comorbidity | Exposure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | F | 55 | No | Allergy to Rifamycin | Yes |
| P2 | M | 64 | No | Hypertension, depression | No |
| P3 | M | 57 | No | // | No |
| P4 | M | 61 | Yes | Hypertension | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caravelli, S.; Ambrosino, G.; Vocale, E.; Di Ponte, M.; Puccetti, G.; Perisano, C.; Greco, T.; Rinaldi, V.G.; Marcheggiani Muccioli, G.M.; Zaffagnini, S.; et al. Custom-Made Implants in Ankle Bone Loss: A Retrospective Assessment of Reconstruction/Arthrodesis in Sequelae of Septic Non-Union of the Tibial Pilon. Medicina 2022, 58, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111641
Caravelli S, Ambrosino G, Vocale E, Di Ponte M, Puccetti G, Perisano C, Greco T, Rinaldi VG, Marcheggiani Muccioli GM, Zaffagnini S, et al. Custom-Made Implants in Ankle Bone Loss: A Retrospective Assessment of Reconstruction/Arthrodesis in Sequelae of Septic Non-Union of the Tibial Pilon. Medicina. 2022; 58(11):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111641
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaravelli, Silvio, Giuseppe Ambrosino, Emanuele Vocale, Marco Di Ponte, Giulia Puccetti, Carlo Perisano, Tommaso Greco, Vito Gaetano Rinaldi, Giulio Maria Marcheggiani Muccioli, Stefano Zaffagnini, and et al. 2022. "Custom-Made Implants in Ankle Bone Loss: A Retrospective Assessment of Reconstruction/Arthrodesis in Sequelae of Septic Non-Union of the Tibial Pilon" Medicina 58, no. 11: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111641
APA StyleCaravelli, S., Ambrosino, G., Vocale, E., Di Ponte, M., Puccetti, G., Perisano, C., Greco, T., Rinaldi, V. G., Marcheggiani Muccioli, G. M., Zaffagnini, S., & Mosca, M. (2022). Custom-Made Implants in Ankle Bone Loss: A Retrospective Assessment of Reconstruction/Arthrodesis in Sequelae of Septic Non-Union of the Tibial Pilon. Medicina, 58(11), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111641










