Prediction of Compartment Syndrome after Protobothrops mucrosquamatus Snakebite by Diastolic Retrograde Arterial Flow: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
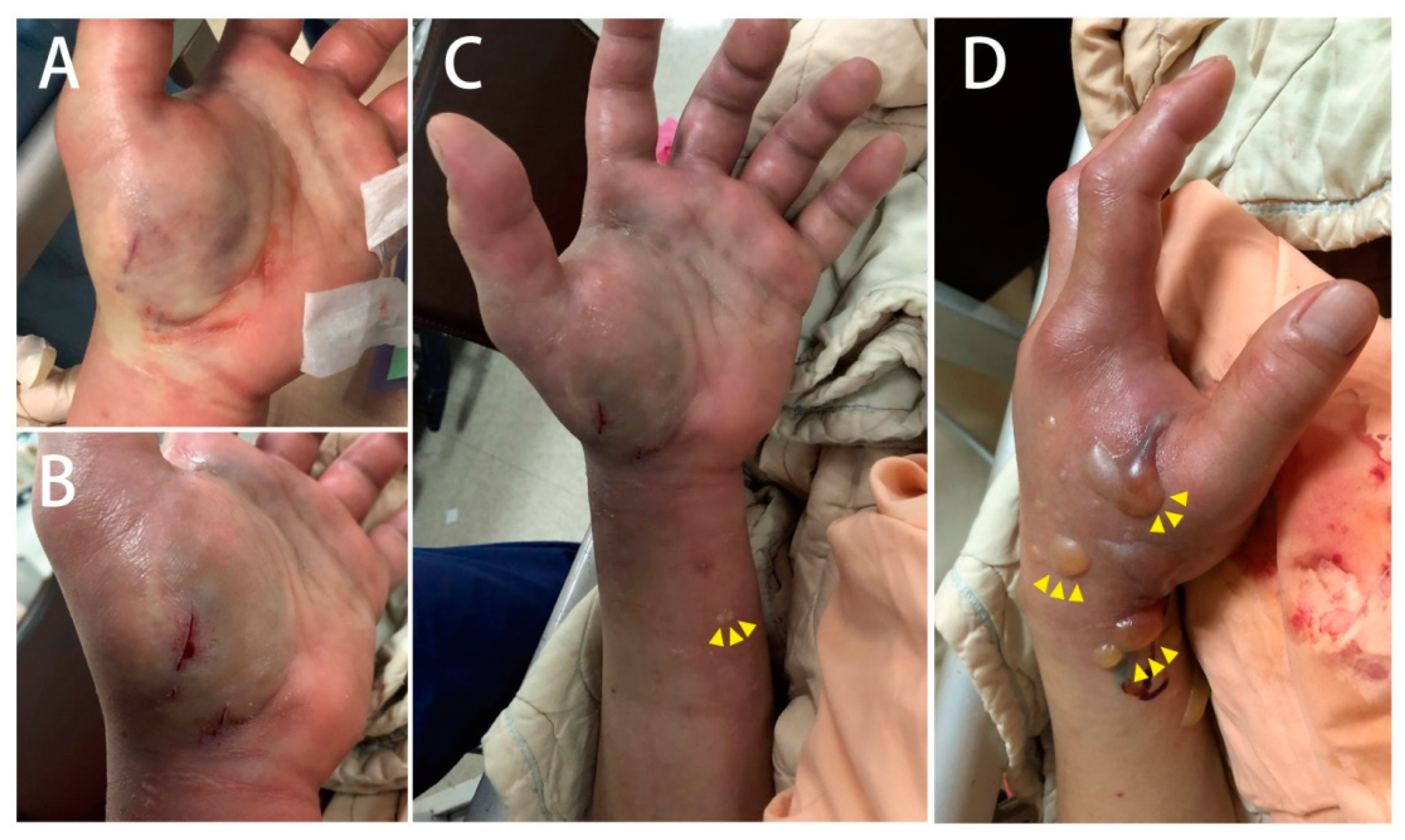
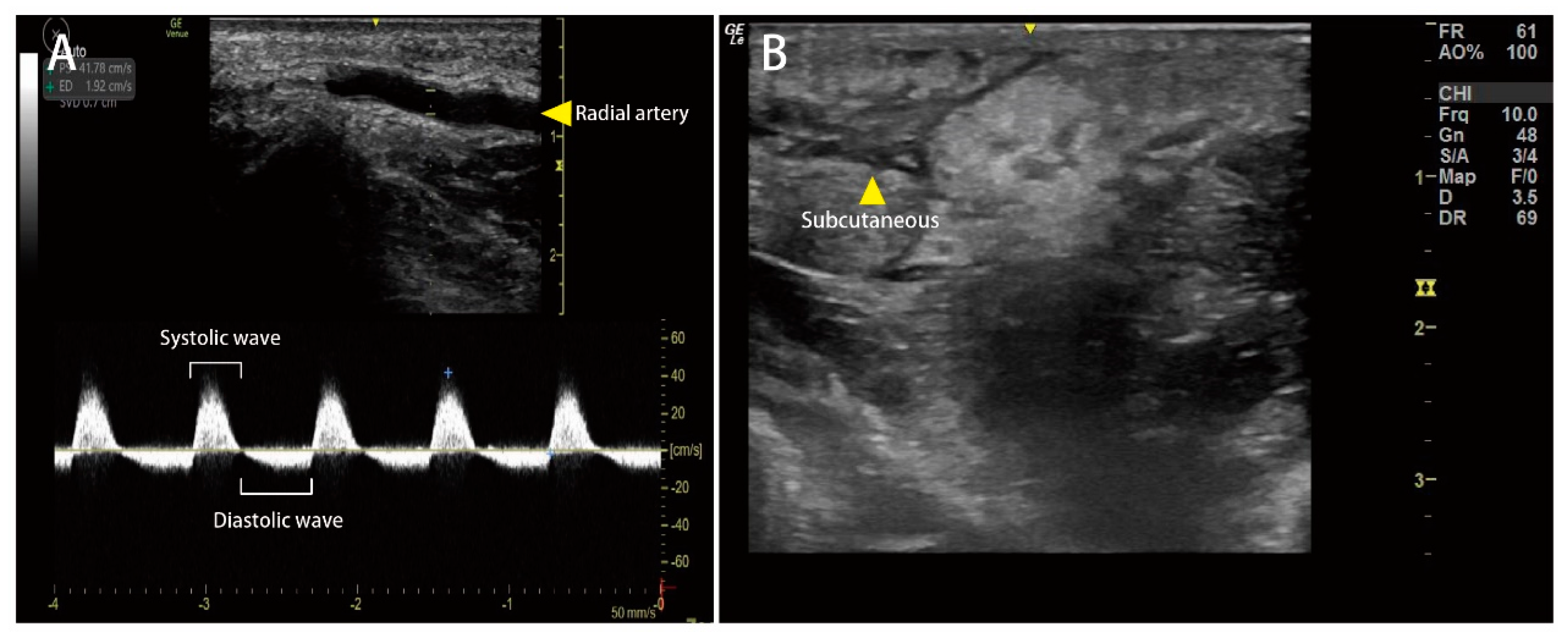
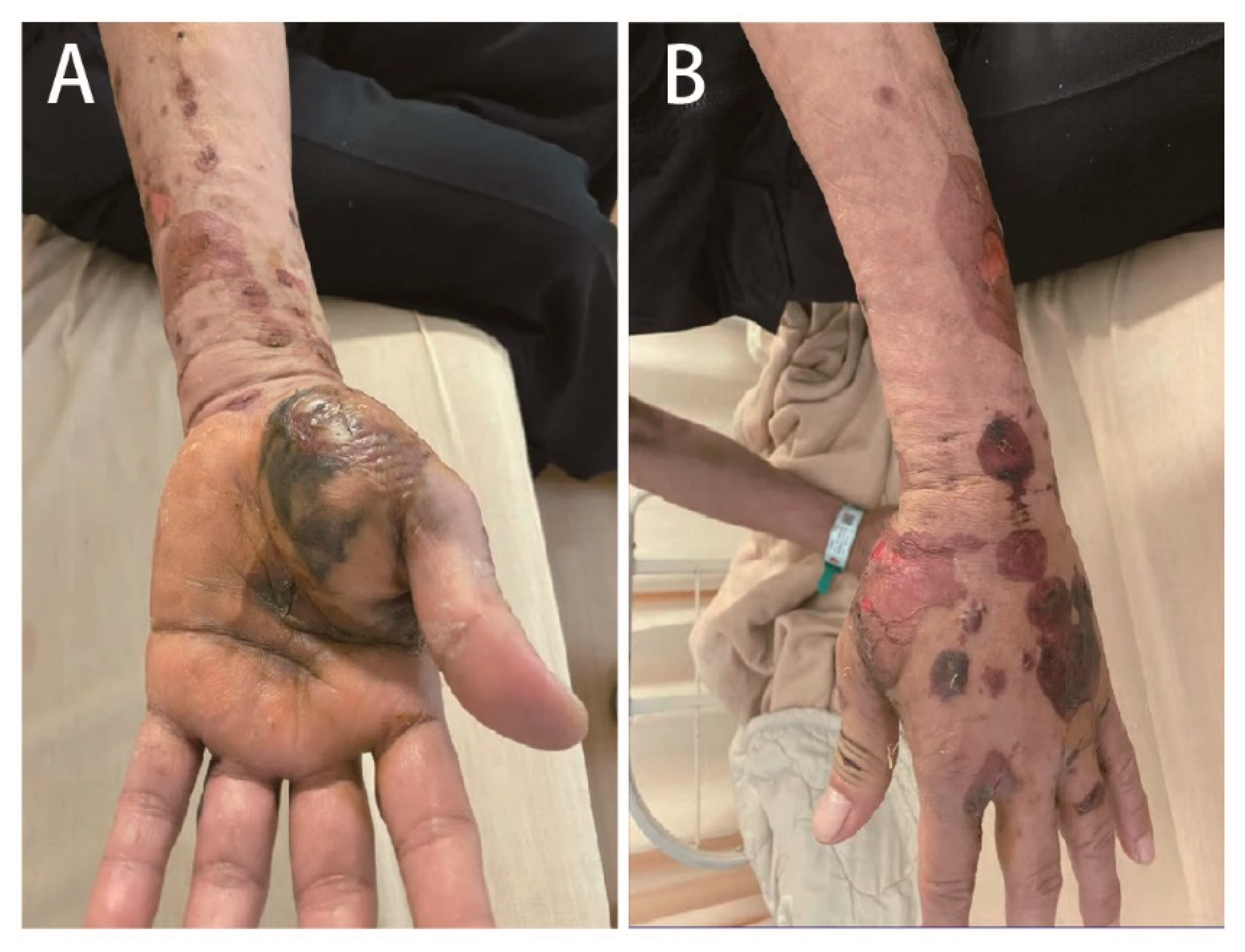
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, C.-H.; Mao, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-D.; Lin, C.-S.; Liu, S.-H.; Chiang, L.-C.; Hung, Y.; Tsai, S.-H. Descriptive study of snakebite patients in Northern Taiwan: 2009 to 2016. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 39, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-H.; Ismail, A.K.; Liu, S.-H.; Tzeng, Y.-S.; Li, L.-Y.; Pai, F.-C.; Hong, C.-W.; Mao, Y.-C.; Chiang, L.-C.; Lin, C.-S.; et al. The role of a point-of-care ultrasound protocol in facilitating clinical decisions for snakebite envenomation in Taiwan: A pilot study. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türkmen, A.; Temel, M. Algorithmic approach to the prevention of unnecessary fasciotomy in extremity snake bite. Injury 2016, 47, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfin, S.R.; Castilonia, R.R.; Mubarak, S.J.; Hargens, A.R.; Akeson, W.H.; Russell, F.E. Role of surgical decompression in treatment of rattlesnake bites. Surg. Forum 1979, 30, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, K.L. Is there a role for fasciotomy in Crotalinae envenomations in North America? Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkar, G.D.; Sundaram, M.S.; NaveenKumar, S.K.; Swethakumar, B.; Sharma, R.D.; Paul, M.; Vishalakshi, G.J.; Devaraja, S.; Girish, K.S.; Kemparaju, K. NETosis and lack of DNase activity are key factors in Echis carinatus venom-induced tissue destruction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, A.; Akdeniz, A.; Babus, S.B.; Göçmen, M.; Temel, G.O. The Usefulness of Platelet Distribution Width and Platelet Distribution Width to Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Severity and Outcomes in Patients with Snakebite. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2021, 32, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.P.; Chuang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.P.; Wang, S.Y.; Fu, C.Y.; Yuan, K.C.; Chen, C.H.; Kang, S.C.; Liao, C.H. Predictors of the development of post-snakebite compartment syndrome. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2015, 23, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petricevich, V.L. Cytokine and nitric oxide production following severe envenomation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2004, 3, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.B.; Luchette, F.A.; Papaconstantinou, H.T.; Lim, E.; Hurst, J.M.; Johannigman, J.A.; Davis, K. The effect of early versus late fasciotomy in the management of extremity trauma. Surgery 1997, 122, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, M.; Hadley, G.P. Raised compartmental pressure in children: A basis for management. Injury 1998, 29, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırat, C.; Erbatur, S.; Aytekin, A.H.; Kılınç, H. Effectiveness of early fasciotomy in the management of snakebites. Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2012, 18, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.S.; Khor, H.W.; Ahmad, R.; Rahman, N.H.N.A. A five-year retrospective review of snakebite patients admitted to a tertiary university hospital in Malaysia. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.T.; Corsi, J.M.; Boneti, C.; Jackson, R.J.; Smith, S.D.; Kokoska, E.R. Pediatric snakebites: Lessons learned from 114 cases. J. Pediatric Surg. 2008, 43, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.M.; Page, C.P.; Schwesinger, W.H.; McCarter, R.; Martinez, J.; Aust, J.B. Antivenin and fasciotomy/debridement in the treatment of the severe rattlesnake bite. Am. J. Surg. 1989, 158, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.; Sartorius, B.; Hift, R. Ultrasound findings in 42 patients with cytotoxic tissue damage following bites by South African snakes. Emerg. Med. J. 2016, 33, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockerse, P.; Mallin, M. Point of care ultrasound strikes again. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 909–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, R.; Rangan, C.; Bengiamin, R. Sonographic signs of snakebite. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Loughlin, M.J.; Mc Loughlin, S. Diastolic retrograde arterial flow and biphasic abdominal aortic Doppler wave pattern: An early sign of arterial wall deterioration? Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Loughlin, S.; Mc Loughlin, M.J.; Mateu, F. Pulsed Doppler in simulated compartment syndrome: A pilot study to record hemodynamic compromise. Ochsner J. 2013, 13, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Wu, C.-J.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Liu, K.-L.; Huang, G.-J.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Chen, C.-K.; Liaw, G.-W. Snake venom proteome of Protobothrops mucrosquamatus in Taiwan: Delaying venom-induced lethality in a rodent model by inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity with varespladib. J. Proteom. 2021, 234, 104084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Hsu, C.; Chen, C.; Chang, H.; Xie, W. Application research of snake venom protein and anti-venom serum manufacturing technology. Taiwan Epidemiol. Bull. 2015, 31, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Hsu, W.H.; Huang, K.C.; Yu, P.A.; Chen, C.L.; Kuo, L.T. Necrotizing fasciitis following venomous snakebites in a tertiary hospital of southwest Taiwan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 63, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, M.H.; Wang, L.M.; Wu, J.J.; Huang, C.I.; Lee, C.H.; Yen, D.H.; Yang, C.C. Antivenom therapy for crotaline snakebites: Has the poison control center provided effective guidelines? J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2007, 106, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, C.C.; Chaou, C.H.; Tseng, C.Y. An investigation of snakebite antivenom usage in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.-W. Venomous snake bites in Taiwan. J. Assoc. Emerg. Intensive Care Med. Repub. China 2012, 23, 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Wang, P.J.; Liu, C.C. Venom concentrations in blisters and hemorrhagic bullae in a patient bitten by a Taiwan habu (Protobothrops mucrosquamatus). Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Normal Range | Patient Data | Variables | Normal Range | Patient Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day1 | Day4 | Day1 | Day4 | ||||
| White cell count | 3.9–10.6 × 109/L | 7.38 | 8.80 | Creatinine | 0.04–0.09 mmole/L | 0.82 | 0.83 |
| Band form Neu. | 0–3% | 0.0 | 0.0 | Sodium | 136–145 mmole/L | 137 | 138 |
| Segment form Neu. | 45–70% | 64.2 | 71.6 | Potassium | 3.5–5.1 mmole/L | 4.3 | 3.6 |
| Lymphocytes | 25–40% | 27.1 | 20.3 | CRP | <1.0 mg/dL | 0.3 | 1.34 |
| Eosinophils | 1–3% | 3.9 | 1.9 | Glucose | 3.9–5.6 mmole/L | 138 | --- |
| Monocytes | 2–8% | 4.5 | 6.0 | ALT | 16–63 U/L | 10 | 46 |
| Hemoglobin | 13.5–17.5 g/dL | 14.7 | 13.8 | AST | 15–37 U/L | 8 | 138 |
| Platelet counts | 150–400 × 109/L | 274 | 308 | BUN | 7–25 mg/dL | 14 | 13 |
| PT | 8.0–12.0 s | 10.3 | --- | ||||
| APTT | 23.9–35.5 s | 28.2 | --- | ||||
| FDP-Ddimer | 0–500 µg/L | 782.44 | 3102.06 | ||||
| INR | ---- | 0.99 | --- | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, Y.-T.; Chang, M.-C.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, P.-C.; Yiang, G.-T.; Wu, M.-Y. Prediction of Compartment Syndrome after Protobothrops mucrosquamatus Snakebite by Diastolic Retrograde Arterial Flow: A Case Report. Medicina 2022, 58, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080996
Hou Y-T, Chang M-C, Yang C, Chen Y-L, Lin P-C, Yiang G-T, Wu M-Y. Prediction of Compartment Syndrome after Protobothrops mucrosquamatus Snakebite by Diastolic Retrograde Arterial Flow: A Case Report. Medicina. 2022; 58(8):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080996
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Yueh-Tseng, Meing-Chung Chang, Ching Yang, Yu-Long Chen, Po-Chen Lin, Giou-Teng Yiang, and Meng-Yu Wu. 2022. "Prediction of Compartment Syndrome after Protobothrops mucrosquamatus Snakebite by Diastolic Retrograde Arterial Flow: A Case Report" Medicina 58, no. 8: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080996
APA StyleHou, Y.-T., Chang, M.-C., Yang, C., Chen, Y.-L., Lin, P.-C., Yiang, G.-T., & Wu, M.-Y. (2022). Prediction of Compartment Syndrome after Protobothrops mucrosquamatus Snakebite by Diastolic Retrograde Arterial Flow: A Case Report. Medicina, 58(8), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080996







